One Health Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance: Challenges and Successes of Implementing Surveillance Programs in Sri Lanka
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overview of AMU and AMR in Non-Human Sectors
2.2. Antimicrobial Use in Farms
2.2.1. By Wholesale
2.2.2. By Retail
2.2.3. By Use/Consumption
2.2.4. By Prescription
2.3. Antimicrobial Resistance in Humans and Animals
2.3.1. AMR in the Human Sector
2.3.2. AMR in the Non-Human Sector
3. Discussion
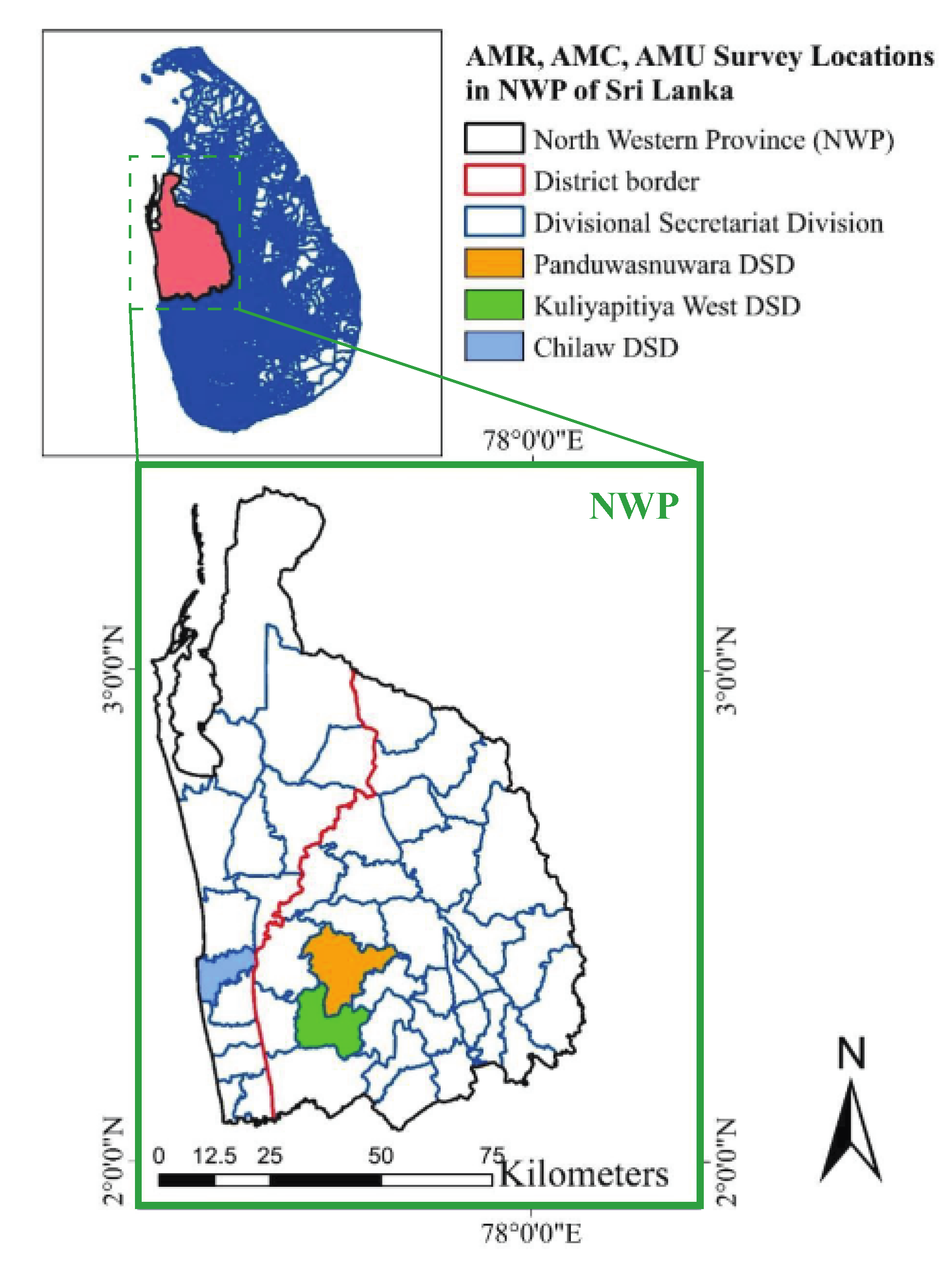
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. AMR Investigation in Human and Non-Human Samples
Isolates from Poultry
Isolates from Aquaculture
Genomics Analysis
ESBL and CTX-M Gene Identification
4.2.2. AMU Investigation in the Non-Human Sector
AMU in Poultry Farms
AMU in Aquaculture Farms
4.3. Database
4.3.1. AMR Data
4.3.2. AMC/U DATA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abo-Amer, A.E.; Shobrak, M.; Altalhi, A. Isolation and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from farm chickens in Taif, Saudi Arabia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, M.; Ranucci, E.; Romagnoli, P.; Giaccone, V. Antimicrobial resistance: A global emerging threat to public health systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, K.-H.; Byun, J.-W.; Lee, W.-K. Antimicrobial Resistance, Adhesin and Toxin Genes of Porcine Pathogenic Escherichia coli Following the Ban on Antibiotics as the Growth Promoters in Feed. Pak. Vet. J. 2021, 41, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Christaki, E.; Marcou, M.; Tofarides, A. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: Mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J. Mol. Evol. 2020, 88, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial resistance: Implications and costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Urbón, J.M.; Gil-Navarro, M.V.; Moreno-Ramos, F.; Núñez-Núñez, M.; Paño-Pardo, J.R.; Periáñez-Párraga, L. Indicators of the hospital use of antimicrobial agents based on consumption. Farm. Hosp. 2019, 43, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, F.; Nawaz, M.; Anjum, A.A.; Firyal, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Irfan, S.; Ahmed, F.; Bhatti, A.A. Molecular Characterization of Antibiotic Resistance in Poultry Gut Origin Enterococci and Horizontal Gene Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance to Staphylococcus aureus. Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, M.E.; Alders, R.; Unger, F.; Nguyen-Viet, H.; Le, T.T.H.; Toribio, J.-A. The challenges of investigating antimicrobial resistance in Vietnam-what benefits does a One Health approach offer the animal and human health sectors? BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth-Brockman, M.; Saxinger, L.M.; Miazga-Rodriguez, M.; Wierzbowski, A.; Otto, S.J. One Health evaluation of antimicrobial use and resistance surveillance: A novel tool for evaluating integrated, One Health antimicrobial resistance and antimicrobial use surveillance programs. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 693703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, T.; Wijayaratne, G.B.; Dabrera, T.M.; Drew, R.J.; Nagahawatte, A.; Bodinayake, C.K.; Kurukulasooriya, R.; Østbye, T.; Nagaro, K.J.; De Silva, C. Point-prevalence study of antimicrobial use in public hospitals in southern Sri Lanka identifies opportunities for improving prescribing practices. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawahir, S.; Lekamwasam, S.; Halvorsen, K.H.; Rose, G.; Aslani, P. Self-medication Behavior with antibiotics: A national cross-sectional survey in Sri Lanka. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambraki, I.; Chadag, V.; Cousins, M.; Graells, T.; Léger, A.; Henriksson, P.; Troell, M.; Harbarth, S.; Wernli, D.; Jørgensen, P.S. Factors Impacting Antimicrobial Resistance in the South East Asian Food System and Potential Places to Intervene: A Participatory, one Health Study. PLoS ONE 2023, 17, e0263914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, K.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Herman, V.; Sallam, K.I.; Cristina, R.T.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Morar, D.; Popa, S.A.; Imre, M.; Morar, A. Occurrence, Pathogenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Raw Milk Cheese Commercialized in Banat Region, Romania. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, I.I.; Nasser, N.A.; Salibi, J. Prevalence and loads of fecal pollution indicators and the antibiotic resistance phenotypes of Escherichia coli in raw minced beef in Lebanon. Foods 2020, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.; Nahashon, S.N.; Pokharel, B.; Mafiz, A.I.; Nzomo, M. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant foodborne pathogens and indicator bacteria from edible offal and muscle meats in Nashville, Tennessee. Foods 2020, 9, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Bager, F.; Jensen, N.; Madsen, M.; Meyling, A.; Wegener, H.C. Resistance to antimicrobial agents used for animal therapy in pathogenic-, zoonotic-and indicator bacteria isolated from different food animals in Denmark: A baseline study for the Danish Integrated Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring Programme (DANMAP). Apmis 1998, 106, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoba, D.O.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Essack, S.Y. Transmission of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli from chicken litter to agricultural soil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.d.L.E.; Caniça, M.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Escherichia coli as commensal and pathogenic bacteria among food-producing animals: Health implications of extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) production. Animals 2020, 10, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umair, M.; Tahir, M.F.; Ullah, R.W.; Ali, J.; Siddique, N.; Rasheed, A.; Akram, M.; Zaheer, M.U.; Mohsin, M. Quantification and trends of antimicrobial use in commercial broiler chicken production in Pakistan. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, R.; Bobenchik, A.M.; Hindler, J.A.; Schuetz, A.N. Overview of changes to the clinical and laboratory standards institute performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, M100. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e00213–e00221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiambi, S.; Mwanza, R.; Sirma, A.; Czerniak, C.; Kimani, T.; Kabali, E.; Dorado-Garcia, A.; Eckford, S.; Price, C.; Gikonyo, S. Understanding antimicrobial use contexts in the poultry sector: Challenges for small-scale layer farms in Kenya. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaik, S.; Embrandiri, A.; Ravindran, B.; Hossain, K.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arasu, M.V.; Ignacimuthu, S.; Ismail, N. Veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and manure laden soil: Scenario and challenges in Asian countries. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, K.; Gräslund, S.; Wahlström, A.; Poungshompoo, S.; Bengtsson, B.E.; Kautsky, N. Antibiotic use in shrimp farming and implications for environmental impacts and human health. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, L.C.; Jarvis, W.R. Linking antimicrobial use to nosocomial infections: The role of a combined laboratory-epidemiology approach. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.-L.; Wai, H.K.-F.; Wu, P.; Lai, S.-W.; Chan, O.S.-K.; Tun, H.M. A Universal LC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Detection of Antibiotic Residues in Animal and Environmental Samples. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, S.; Shrestha, P.; Adhikari, B. Antimicrobial use in food animals and human health: Time to implement ‘One Health’approach. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Ranganathan, S.; Wanigatunge, C.; Senadheera, G.; Beneragama, B. A national survey of antibacterial consumption in Sri Lanka. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharshana, U.; Piyasiri, L.B.; Wijesinghe, C. Prevalence, antibiotic sensitivity pattern and genetic analysis of extended spectrum beta lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp among patients with community acquired urinary tract infection in Galle district, Sri Lanka. Ceylon Med. J. 2019, 64, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, G.; Sri Ranganathan, S.; Patabendige, G.; Fernando, G.; Gamage, D.; Maneke, R.; Fernandopulle, B. Resistance and Utilisation Pattern of Antibacterial Agents in Outpatient Settings in Two Teaching Hospitals in Colombo. Ceylon Med. J. 2016, 61, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyantha, M.; De Alwis, P.; Fernando, P. Determination of Carbapenem and Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamases in E. coli from Commercial Broilers, Sri Lanka. Asian J. Res. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bevan, E.R.; Jones, A.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: Temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, B.S.; O’Brien, C.L.; Gordon, D.M. Diversity and distribution of Klebsiella capsules in Escherichia coli. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munasinghe, T.; Vidanapathirana, G.; Kuthubdeen, S.; Ekanayake, A.; Angulmaduwa, S.; De Silva, K.; Subhasinghe, S.; Kalupahana, R.; Liyanapathirana, V.; Ip, M. Colonization with selected antibiotic resistant bacteria among a cohort of Sri Lankan university students. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumudunie, W.G.M.; Wijesooriya, L.I.; Namalie, K.D.; Sunil-Chandra, N.P.; Wijayasinghe, Y.S. Epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Sri Lanka: First evidence of blaKPC harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahin, K.; Bao, H.; Zhu, S.; Soleimani-Delfan, A.; He, T.; Mansoorianfar, M.; Wang, R. Bio-control of O157: H7, and colistin-resistant MCR-1-positive Escherichia coli using a new designed broad host range phage cocktail. LWT 2022, 154, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasabova, S.; Hartmann, M.; Freise, F.; Hommerich, K.; Fischer, S.; Wilms-Schulze-Kump, A.; Rohn, K.; Käsbohrer, A.; Kreienbrock, L. Antibiotic Usage Pattern in Broiler Chicken Flocks in Germany. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 673809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Human (Total n = 200) | Poultry (Total n = 401) | Aquaculture (Total n = 153) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial Classes | Antimicrobials | Number of Resistant E. coli | Resistant % | Number of Resistant E. coli | Resistant % | Number of Resistant E. coli | Resistant % |
| Aminopenicillin | Ampicillin | 133 | 66.5 | 379 | 94.5 | 62 | 40.5 |
| Aminopenicillin-Beta-lactamase inhibitor | Amoxycillin-clavulanic acid | 84 | 42 | 11 | 2.7 | 6 | 3.9 |
| Cephalosporin | Ceftazidim | 71 | 35.5 | 6 | 1.5 | NT * | NT * |
| Cephalosporin | Cefotaxmine | 71 | 35.5 | 30 | 7.5 | NT * | NT * |
| Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | 70 | 35 | 103 *** | 73.6 | NT * | NT * |
| Chloramphenicol | Chloramphenicol | 7 | 3.5 | 139 | 34.7 | 14 | 9.2 |
| Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones | Enrofloxacin | NT * | NT * | 137 ** | 68.5 | NT * | NT * |
| Macrolide | Erythromycin | NT * | NT | 393 | 98 | 138 | 90.2 |
| Aminoglycoside | Gentamicin | 25 | 12.5 | 97 | 27.2 | 69 | 45.1 |
| Carbapenems | Imipenem | 7 | 3.5 | NT * | NT * | NT * | NT * |
| Carbapenems | Meropenem | 8 | 4 | 5 | 1.3 | 19 | 12.4 |
| Quinolones and Fluoroquinolones | Nalidixic acid | 84 | 42 | 339 | 84.5 | 22 | 14.4 |
| Tetracycline | Tetracycline | 61 | 30.5 | 388 | 96.8 | 31 | 20.3 |
| Sulfonamides | Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 50 | 25 | 308 | 76.8 | 26 | 17 |
| Sulfonamides | Trimethoprim | NT * | NT * | 317 | 79.1 | NT * | NT * |
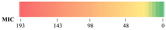
| Antimicrobials | 0.094 | 0.125 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 24 | 32 | 48 | 64 | 96 | 128 | 256 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ampicillin | 3 | 56 | 3 | 3 | 131 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Amoxicillin/Clavulonic acid | 1 | 4 | 77 | 29 | 5 | 81 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ceftazidime | 98 | 31 | 58 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cefotaxmin | 125 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 70 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cefoxitin | 1 | 170 | 7 | 20 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Imipenem | 193 | 0 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Meropenem | 193 | 0 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gentamicin | 9 | 81 | 77 | 4 | 3 | 25 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | 11 | 115 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 66 | |||||||||||||||||
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 31 | 111 | 4 | 2 | 52 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chloramphenicol | 1 | 4 | 148 | 37 | 3 | 6 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tetracycline | 44 | 69 | 23 | 58 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Poultry | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ampicillin | 14 | 1 | 125 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Piperacillin | 19 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 25 | 51 | |||||||||||||||||
| amoxicillin/Clavulonic acid | 19 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 25 | 51 | |||||||||||||||||
| Ceftazidime | 1 | 15 | 38 | 61 | 24 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cefotaxmin | 24 | 115 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cefepime | 112 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cefoxitin | 136 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Azetronam | 114 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Imipenem | 112 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Meropenem | 136 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Amikacin | 115 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gentamicin | 24 | 102 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | 37 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 97 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 55 | 1 | 4 | 72 | 6 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| chloramphenicol | 94 | 23 | 3 | 20 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Tetracycline | 3 | 7 | 122 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Aquaculture | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ampicillin | 44 | 1 | 1 | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Piperacillin | 46 | 1 | 1 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Amoxicillin/Clavulonic acid | 2 | 1 | 18 | 33 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ceftazidime | 55 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cefotaxmin | 3 | 0 | 51 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cefepime | 54 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cefoxitin | 55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aztreonam | 54 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Imipenem | 55 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Meropenem | 55 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Amikacin | 55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gentamicin | 1 | 2 | 52 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | 54 | 0 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 47 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chloramphenicol | 39 | 14 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Tetracycline | 3 | 49 | 3 |
 .
.| Antimicrobials | E. coli from Shrimp (n = 60) | E. coli from Shrimp Pond Water (n = 93) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R% | I% | S% | R% | I% | S% | |
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid | 1.67 | 16.67 | 81.66 | 5.38 | 22.58 | 72.04 |
| Ampicillin | 28.33 | 10 | 61.67 | 48.39 | 9.68 | 41.94 |
| Amoxicillin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Chloramphenicol | 1.67 | 8.33 | 90 | 13.98 | 6.45 | 79.57 |
| Erythromycin | 81.67 | 18.33 | 0 | 95.7 | 4.3 | 0 |
| Gentamicin | 45 | 26.67 | 28.33 | 54.16 | 36.56 | 18.28 |
| Meropenem | 10 | 20 | 70 | 13.98 | 35.48 | 50.54 |
| Nalidixic acid | 16.67 | 30 | 53.33 | 12.9 | 45.16 | 41.94 |
| Neomycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oxytetracycline | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 16.67 | 1.67 | 81.66 | 22.58 | 4.3 | 73.12 |
| Tetracycline | 11.67 | 0 | 88.33 | 20.43 | 2.15 | 77.42 |
| Resistant Gene | Number of Positive Isolates | % |
|---|---|---|
| Carbapenem | 6 | 3 |
| AmpC | 20 | 10 |
| ESBL | 71 | 35.5 |
| CTX-15 | 51 | 25.5 |
| CTX-14 | 7 | 3.5 |
| OXA-48 | 1 | 0.5 |
| CTX-M and OXA-48 | 134 | 67 |
| MHT/Modified Hodge test positive | 8 | 4 |
| MCIM/ Carbapenem inactivation method | 6 | 3 |
| Total isolates | 304 | 152 |
| Sites | Sectors | Study Focus | Type of Sample | Sample Number and Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kuliyapitiya and Chillaw | Human | AMR | Urine | 200 individuals |
| Paduwasnuwara, Kuliyapitiya | Poultry | AMR | Cloaca | 401 broilers |
| Chillaw | Aquaculture | AMR | Shrimp & pond water | 153 shrimps |
| Paduwasnuwara, Kuliyapitiya | Poultry | AMC/AMU | Data | 18 veterinary Pharmaceutical product distributors |
| Paduwasnuwara, Kuliyapitiya | Poultry | AMC/AMU | Data | 56 poultry farms |
| Paduwasnuwara, Kuliyapitiya | Poultry | AMC/AMU | Data | 3 government veterinary surgeons |
| Paduwasnuwara, Kuliyapitiya | Poultry | AMC/AMU | Data | 6 feed manufacturers |
| Chilaw | Aquaculture | AMC/AMU | Data | 68 shrimp farms |
| Chilaw | Aquaculture | AMC/AMU | Data | 17 shrimp hatcheries |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ariyawansa, S.; Gunawardana, K.N.; Hapudeniya, M.M.; Manelgamage, N.J.; Karunarathne, C.R.; Madalagama, R.P.; Ubeyratne, K.H.; Wickramasinghe, D.; Tun, H.M.; Wu, P.; et al. One Health Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance: Challenges and Successes of Implementing Surveillance Programs in Sri Lanka. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030446
Ariyawansa S, Gunawardana KN, Hapudeniya MM, Manelgamage NJ, Karunarathne CR, Madalagama RP, Ubeyratne KH, Wickramasinghe D, Tun HM, Wu P, et al. One Health Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance: Challenges and Successes of Implementing Surveillance Programs in Sri Lanka. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030446
Chicago/Turabian StyleAriyawansa, Sujeewa, Kuruwitage N. Gunawardana, Muditha M. Hapudeniya, Nimal J. Manelgamage, Chinthana R. Karunarathne, Roshan P. Madalagama, Kamalika H. Ubeyratne, Darshana Wickramasinghe, Hein M. Tun, Peng Wu, and et al. 2023. "One Health Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance: Challenges and Successes of Implementing Surveillance Programs in Sri Lanka" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030446
APA StyleAriyawansa, S., Gunawardana, K. N., Hapudeniya, M. M., Manelgamage, N. J., Karunarathne, C. R., Madalagama, R. P., Ubeyratne, K. H., Wickramasinghe, D., Tun, H. M., Wu, P., Lam, T. T. Y., & Chan, O. S. K. (2023). One Health Surveillance of Antimicrobial Use and Resistance: Challenges and Successes of Implementing Surveillance Programs in Sri Lanka. Antibiotics, 12(3), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030446





