Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenicity of Aliarcobacter butzleri Isolated from Poultry Meat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
4.2. Determination of MIC Values
4.3. Patogenicity In Vitro Tests
4.3.1. Biofilm
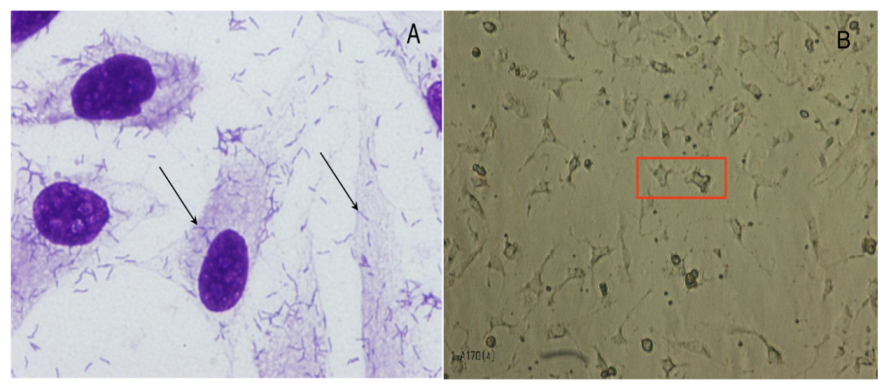
4.3.2. Bacterial Adherence and Toxicity
4.4. Patogenicity In Vivo Tests
4.4.1. Experimental Inoculation of Chickens
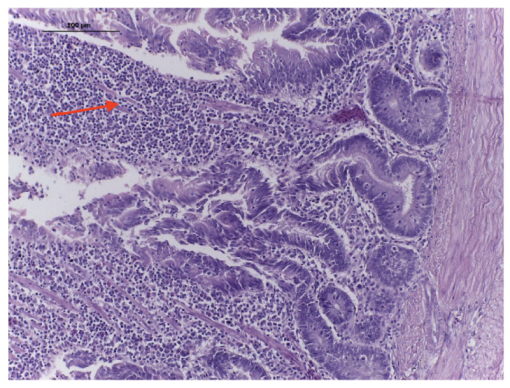
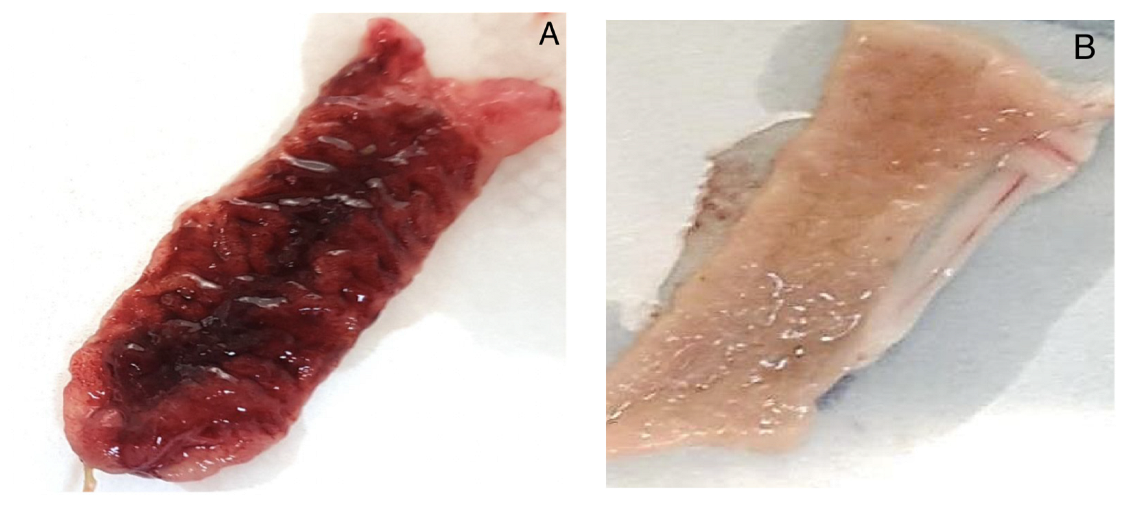
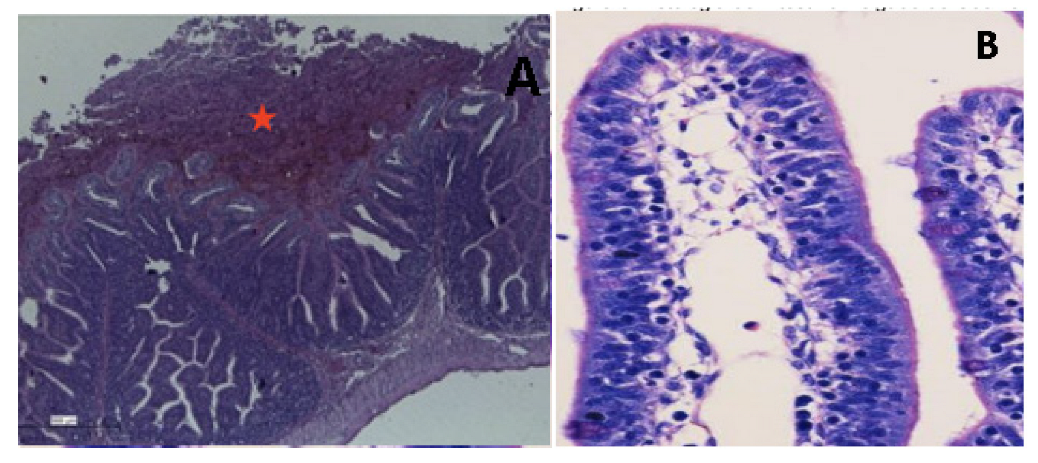
4.4.2. Rabbit Ileal Loop
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chieffi, D.; Fonelli, F.; Fusco, U. Arcobacter butzleri: Up-to-date taxonomy, ecology and pathogenicity of an emerging pathogen. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2071–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouzet-Mauléon, V.; Labardi, L.; Bouges, N.; Ménard, A.; Mégraud, F. Arcobacter butzleri: Underestimated enteropathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertas, N.; Dogruer, Y.; Gonulalan, Z.; Guner, A.; Ulger, I. Prevalence of Arcobacter species in drinking water, spring water, and raw milk as determined by multiplex PCR. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 2099–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieva-Echevarria, B.; Martinez-Malaxetxebarria, I.; Girbau, C.; Alonso, R.; Fernandez-Astorga, A. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Arcobacter in food products in the north of Spain. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1447–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobb, D.D.S.; Spindola, M.G.; Moreno, L.Z.; Matajira, C.E.C.; Oliveira, M.G.X.; Paixão, R.; Ferreira, T.S.P.; Moreno, A.M. Isolation and molecular characterization of Arcobacter butzleri and Arcobacter cryaerophilus from pork production chain in Brazil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.G.X.; Gomes, V.T.D.M.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Moreno, L.Z.; Moreno, A.M.; Knöbl, T. Genotypic Characterization of Arcobacter spp. Isolated from Chicken Meat in Brazil. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Martins, S.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C.; Ferreira, S. Arcobacter spp. at retail food from Portugal: Prevalence, genotyping and antibiotics resistance. Food Control 2018, 85, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado-Bravo, M.L.M.; Barancelli, G.V.; Dini Andreote, A.P.; Saldana, E.; Vidal-Veuthey, B.; Collado, L.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J. Occurrence of Arcobacter spp. in Brazilian Minas frescal cheese and raw cow milk and its association with microbiological and physicochemical parameters. Food Control 2020, 109, 106904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro, J.; Ferreira, S.; Pinto, M.; Domingues, F.; Oleastro, M.; Gomes, J.; Borges, V. Virulence and antibiotic resistance plasticity of Arcobacter butzleri: Insights on the genomic diversity of an emerging human pathogen. Infection. Genet. Evol. 2020, 80, 104213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shange, N.; Gouws, P.; Hoffman, L.C. Campylobacter and Arcobacter species in food-producing animals: Prevalence at primary production and during slaughter. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Queiroz, J.A.; Oleastro, M.; Domingues, F.C. Insights in the pathogenesis and resistance of Arcobacter: A review. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Guerra, G.; Casanovas MorenoTorres, I.; Moldovan, T.D.; Navarro-Marí, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, J. Arcobacter butzleri and intestinal colonization. Rev. Espanõla De Quimioter. 2020, 33, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, H.; Villanueva, M.P.; Mansilla, I.; Gonzalez, M.; Latif, F. Arcobacter butzleri and A. cryaerophilus in human, animals and food sources, in southern Chile. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, I.; Englen, M.D.; Berrang, M.E.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Harrison, M.A. Antimicrobial resistance of Arcobacter and Campylobacter from broiler carcasses. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2007, 29, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesenberg, A.; Fromke, C.; Stingl, K.; Fesler, A.T.; Golz, G.; Glocker, E.O.; Kreienbrock, L.; Klarmann, D.; Werckenthin, C.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Arcobacter butzleri: Development and application of a new protocol for broth microdilution. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2769–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, C.; Pinar, O.; Sipari, N. The prevalence of Alicobacter species in the fecal microbiota of farm animals and potential effective agents for their treatment: A review of past decades. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houf, K.; Tutenel, A.; De Zutter, L.; Van Hoof, J.; Vandamme, P. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the simultaneous detection and identification of Arcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus and Arcobacter skirrowii. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 193, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabay, H.I.; Aydin, F. Susceptibility of Arcobacter butzleri isolates to 23 antimicrobial agents. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 33, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houf, K.; Devriese, L.A.; Van Hoof, J.; Vandamme, P. Susceptibility of Arcobacter butzleri, Arcobacter cryaerophilus, and Arcobacter skirrowii to antimicrobial agents used in selective media. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fera, M.T.; Maugeri, T.L.; Giannone, M.; Gugliandolo, C.; La Camera, E.; Blandino, G.; Carbone, M. In vitro susceptibility of Arcobacter butzleri and Arcobacter cryaerophilus to different antimicrobial agents. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 21, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, H.; Maruyama, S.; Morita, Y.; Ohsuga, T.; Ozawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Abe, M.; Katsube, Y.; Mikami, T. Prevalence of Arcobacter species in retail meats and antimicrobial susceptibility of the isolates in Japan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 90, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debruyne, L.; Gevers, D.; Vandamme, P. Taxonomy of the family Campylobacteraceae. In Campylobacter, 3rd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; American Society of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 3-25-121. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System for Enteric Bacteria (NARMS): Human Isolates Final Report. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/narms/faq.html (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- Van den Abeele, A.M.; Vogelaers, D.; Vanlaere, E.; Houf, K. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Arcobacter butzleri and Arcobacter cryaerophilus strains isolated from Belgian patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.H.; Saleha, A.A.; Zunita, Z.; Murugaiyah, M. Arcobacter–An emerging threat to animals and animal origin food products? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boven, M.; Veldman, K.T.; de Jong, M.C.; Mevius, D.J. Rapid selection of quinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni but not in Escherichia coli in individually housed broilers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, C.M.; Danzeisen, G.T.; Sherwood, J.S.; Thorsness, J.L.; Mercier, B.M.; Axtman, J.E. Repeated therapeutic dosing selects macrolide-resistant Campylobacter spp. in a turkey facility. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acheson, D.; Allos, B.M. Campylobacter jejuni infections: Update on emerging issues and trends. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J.; Engberg, J. Clinical aspects of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli infections. In Campylobacter, 3rd ed.; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C.M., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; American Society of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Douidah, L.; De Zutter, L.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Deforce, D.; Ingmer, H.; Vandenberg, O.; Vanden Abeele, A.M.; Houf, K. Presence and analysis of plasmids in human and animal associated arcobacter species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbaqi, K.; Buissonniere, A.; Prouzet-Mauleon, V.; Gresser, J.; Wesley, I.; Mégraud, F.; Ménard, A. Development of a real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer PCR to detect Arcobacter species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3015–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.; Vazquez-Valverde, D.; Fernández-Jaramillo, H.; Arias-Echandi, M.L. The ability of Aliarcobacter butzleri strains isolates from foods of animal origin in Costa Rica to form biofilm. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2021, 10, 9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, R.C.; Neal-Mckinney, J.M.; Dhillon, A.S.; Miller, W.G.; Konkel, M.E. Examination of Campylobacter jejuni putative adhesins leads to the identification of a new protein, designated FlpA, required for chicken colonization. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzanca, D.; Botta, C.; Cocolin, l.S.; Alessandria, V.; Rantsiou, K. Exploring the Virulence Gene Expression of Arcobacter butzleri during Simulated Infection of Human Gut Models. IAFP’s European Symposium on Food Safety: Nantes, France, 2019; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Karadas, G.; Alutis, M.; Fischer, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Breithaupt, A.; Göbel, U.B.; Alter, T.; Bereswill, S.; Gölz, G. Survey of small intestinal and systemic immune responses following murine Arcobacter butzleri infection. Gut Pathog. 2015, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.T.K.; Lipman, L.J.A.; Gaastra, W. The Introduction of Arcobacter Spp. in Poultry Slaughterhouses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Açik, M.N.; Yüksel, H.; Ulucan, A.; Çetinkaya, B. The first experimental research on the pathogenicity of Arcobacter butzleri in zebrafish. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 189, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, O.; Dediste, A.; Houf, K.; Ibekwem, S.; Souayah, H.; Cadranel, S.; Douat, N.; Zissis, G.; Butzler, J.-P.; Vandamme, P. Arcobacter species in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.G.; Murano, E.A. Development of a new medium for the isolation of Arcobacter spp. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastyns, K.; Chapelle, S.; Vandamme, P.; Goossens, H.; De Wachter, R. Species-specific detection of campylobacters important in veterinary medicine by PCR amplification of 23S rDNA areas. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1995, 17, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douidah, L.; De Zutter, L.; Vandamme, P.; Houf, K. Identification of five human and mammal associated Arcobacter species by a novel multiplex-PCR assay. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 80, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douidah, L.; De Zutter, L.; Baré, J.; De Vos, P.; Vandamme, P.; Vandenberg, O.; Van Den Abeele, A.M.; Houf, K. Occurrence of putative virulence genes in Arcobacter species isolated from humans and animals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 13th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Silley, P.; Simjee, S.; Woodford, N.; van Duijkeren, E.; Johnson, A.P.; Gaastra, W. Assessing the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria obtained from animals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbath, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Lijequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclennan, M.K.; Ringoir, D.D.; Frirdich, E.; Svensson, S.L.; Wells, D.H.; Jarrel, H.; Szymanski, C.M.; Gaynor, E.C. Campylobacter jejuni biofilms up-regulated in the absence of the stringent response utilize a calcofluor white-reactive polysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naves, P.; Del Prado, G.; Huelves, L.; Gracia, M.; Ruiz, V.; Blanco, J.; Rodríguez-Cerrato, V.; Ponte, M.C.; Soriano, F. Measurement of biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Escherichia coli is method-dependent. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.A.M.; Andrade, J.R.C.; Trabulsi, L.R.; Rosa, A.C.P.; Dias, A.M.G.; Ramos, S.R.T.S.; Frankel, G.; Gomes, T.A.T. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characteristics of Escherichia coli strains of non-Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) Serogroups that carry eae and lack the EPEC adherence factor and Shiga Toxin DNA probe sequences. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.H.; Guth, B.E.C.; Piazza, R.M.; Leão, S.C.; Ludovico, A.; Ludovico, M.S.; Dahbi, G.; Marzoa, J.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; et al. Diversity of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in sheep flocks of Paraná State, southern Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia-Di Chiacchio, R.M.; Cunha, M.P.V.; de Sá, L.R.M.; Davies, Y.M.; Pereira, C.B.P.; Martins, F.H.; Munhoz, D.D.; Abe, C.M.; Franzolin, M.R.; Dos Santos, L.F.; et al. Novel Hybrid of Typical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Shiga-Toxin-Producing E. coli (tEPEC/STEC) Emerging from Pet Birds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Resistant Profiles | Number of Strains | |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | Susceptible strains | 5 |
| R2 | CLIN | 2 |
| R3 | NAL/CIP | 1 |
| R4 | NAL/CIP/CLIN | 1 |
| R5 | FLOR/CLIN | 3 |
| R6 | NAL/FLOR/CLIN | 11 |
| R7 | TET/NAL/FLOR/CLIN | 1 |
| R8 | NAL/AZI/CLIN | 1 |
| R9 | NAL/AZI/FLOR/CLIN | 1 |
| R10 | AZI/ERI/TELI/FLOR/CLIN | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, M.G.X.d.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Moreno, L.Z.; Saidenberg, A.B.S.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Moreno, A.M.; Knöbl, T. Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenicity of Aliarcobacter butzleri Isolated from Poultry Meat. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020282
Oliveira MGXd, Cunha MPV, Moreno LZ, Saidenberg ABS, Vieira MAM, Gomes TAT, Moreno AM, Knöbl T. Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenicity of Aliarcobacter butzleri Isolated from Poultry Meat. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(2):282. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020282
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Maria Gabriela Xavier de, Marcos Paulo Vieira Cunha, Luisa Zanolli Moreno, André Becker Simões Saidenberg, Mônica Aparecida Midolli Vieira, Tânia Aparecida Tardelli Gomes, Andrea Micke Moreno, and Terezinha Knöbl. 2023. "Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenicity of Aliarcobacter butzleri Isolated from Poultry Meat" Antibiotics 12, no. 2: 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020282
APA StyleOliveira, M. G. X. d., Cunha, M. P. V., Moreno, L. Z., Saidenberg, A. B. S., Vieira, M. A. M., Gomes, T. A. T., Moreno, A. M., & Knöbl, T. (2023). Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenicity of Aliarcobacter butzleri Isolated from Poultry Meat. Antibiotics, 12(2), 282. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020282








