Unveiling the Microbiome Landscape: A Metagenomic Study of Bacterial Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Factors in the Sediments of the River Ganga, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequencing Summary
2.2. Bacterial Diversity Analysis
2.3. AMR Genes Abundance
2.4. Virulence Factor (VF) Abundance
2.5. KEGG Pathway Analysis
2.6. COG Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Genomic DNA Isolation, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
3.3. Bacterial Diversity Detection
3.4. Functional Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Tyagi, M.; Pandey, R. Influence of multidrug resistance bacteria in river Ganges in the stretch of Rishikesh to Haridwar. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Verma, D. Comparative bacteriome and antibiotic resistome analysis of water and sediment of the Ganga River of India. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Prasoodanan, P.K.V.; Dhakan, D.B.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, V.K. Metagenome of a polluted river reveals a reservoir of metabolic and antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Microbiome 2019, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Dubey, S.K. River Ganges water as reservoir of microbes with antibiotic and metal ion resistance genes: High throughput metagenomic approach. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Chakraborty, H.J.; Patra, B.; Rout, A.K.; Dehury, B.; Das, B.K.; Sarkar, D.J.; Parida, P.K.; Raman, R.K.; Rao, A.R. Metagenomic analysis reveals bacterial and fungal diversity and their bioremediation potential from sediments of river Ganga and Yamuna in India. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 556136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, B.K.; Patra, B.; Chakraborty, H.J.; Sahu, P.; Rout, A.K.; Sarkar, D.J.; Parida, P.K.; Raman, R.K.; Rao, A.R.; Rai, A. Metagenome analysis from the sediment of river Ganga and Yamuna: In search of beneficial microbiome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenni, P. Antimicrobial resistance in rivers: A review of the genes detected and new challenges. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Mathieu, J.; Stadler, L.; Senehi, N.; Sun, R.; Alvarez, P.J. Antibiotic resistance genes from livestock waste: Occurrence, dissemination, and treatment. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska, A.; Korzeniewska, E.; Harnisz, M.; Felis, E.; Bajkacz, S.; Jachimowicz, P.; Niestępski, S.; Konopka, I. Small-scale wastewater treatment plants as a source of the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in the aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 121221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, B.K.; Patra, B.; Chakraborty, H.J.; Rout, A.K.; Dixit, S.; Rai, A.; Das, B.K.; Mohapatra, T. Bacteriophages diversity in India’s major river Ganga: A repository to regulate pathogenic bacteria in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 34101–34114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, N.; Sahu, T.K.; Rao, A.R.; Rout, A.K.; Behera, B.K. An Improved Machine Learning-Based Approach to Assess the Microbial Diversity in Major North Indian River Ecosystems. Genes 2023, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Chaurasia, D.; Pandey, A.; Gupta, P. Co-occurrence of multidrug resistance, β-lactamase and plasmid mediated AmpC genes in bacteria isolated from river Ganga, northern India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, N.; Bisht, G. Detection and enumeration of coliforms in Ganga Water Collected from different ghats. J. Bioprocess Biotech. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.K.; Sahu, P.; Rout, A.K.; Parida, P.K.; Sarkar, D.J.; Kaushik, N.K.; Rao, A.R.; Rai, A.; Das, B.K.; Mohapatra, T. Exploring microbiome from sediments of River Ganga using a metagenomic approach. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2021, 24, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, A.K.; Dehury, B.; Parida, P.K.; Sarkar, D.J.; Behera, B.; Das, B.K.; Rai, A.; Behera, B.K. Taxonomic profiling and functional gene annotation of microbial communities in sediment of river Ganga at Kanpur, India: Insights from whole-genome metagenomics study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 82309–82323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Verma, D. Ganga River sediments of India predominate with aerobic and chemo-heterotrophic bacteria majorly engaged in the degradation of xenobiotic compounds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 752–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Gupta, A.K.; Sudan, S.K.; Pal, D.; Randhawa, V.; Sahni, G.; Mayilraj, S.; Kumar, M. Abundance and diversity of phages, microbial taxa, and antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of the River Ganges through metagenomic approach. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 1336–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Tsementzi, D.; Hatt, J.K.; Bivins, A.; Khelurkar, N.; Brown, J.; Tripathi, S.N.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Intensive allochthonous inputs along the Ganges River and their effect on microbial community composition and dynamics. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Su, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, G. Antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community dynamics in the seawater environment of Dapeng Cove, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Balcázar, J.L. Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteriophages from diverse marine habitats. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkman, A.; Pärnänen, K.; Larsson, D.J. Fecal pollution can explain antibiotic resistance gene abundances in anthropogenically impacted environments. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare, A.; Eckert, E.M.; D’Urso, S.; Bertoni, R.; Gillan, D.C.; Wattiez, R.; Corno, G. Co-occurrence of integrase 1, antibiotic and heavy metal resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 94, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basili, M.; Techtmann, S.M.; Zaggia, L.; Luna, G.M.; Quero, G.M. Partitioning and sources of microbial pollution in the Venice Lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccheri, M.A.; Salvo, E.; Coci, M.; Quero, G.M.; Zoccarato, L.; Privitera, V.; Rappazzo, G. Investigating microbial indicators of anthropogenic marine pollution by 16S and 18S High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) library analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Zeng, W.; Huson, D.H. MeganServer: Facilitating interactive access to metagenomic data on a server. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Rincon, N.; Wood, D.E.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Pockrandt, C.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Steinegger, M. Metagenome analysis using the Kraken software suite. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 2815–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. KofamKOALA: KEGG Ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score threshold. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. EggNOG-mapper v2: Functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.J.; Julien, P.; Kuhn, M.; von Mering, C.; Muller, J.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. EggNOG: Automated construction and annotation of orthologous groups of genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 36, D250–D254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, T.; Cai, W.; Hua, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Changes of bacterial communities in response to prolonged hydrodynamic disturbances in the eutrophic water-sediment systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sen, B.; Zhou, S.; Xie, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G. Distinct seasonal patterns of bacterioplankton abundance and dominance of phyla α-Proteobacteria and cyanobacteria in Qinhuangdao coastal waters off the Bohai sea. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Qiu, X.; Wan, Y.; Lee, L. Structural Diversity of Bacterial Communities and Its Relation to Environmental Factors in the Surface Sediments from Main Stream of Qingshui River. Water 2022, 14, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.S.; Cheng, J.F.; Li, X.D.; Li, Y.H. Unique bacterial communities associated with components of an artificial aquarium ecosystem and their possible contributions to nutrient cycling in this microecosystem. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finster, K.; Liesack, W.; Tindall, B. Sulfurospirillum arcachonense sp. nov., a new microaerophilic sulfur-reducing bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1997, 47, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, A.; Coyne, S.; Berendonk, T.U. Origin and evolution of antibiotic resistance: The common mechanisms of emergence and spread in water bodies. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-García, F.; Sánchez, M.B.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Martínez, J.L. Evolutionary landscapes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa towards ribosome-targeting antibiotic resistance depend on selection strength. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, J.E.; Chaguza, C.; Harris, S.R.; Yalcin, F.; Senghore, M.; Kiran, A.M.; Govindpershad, S.; Ousmane, S.; Plessis, M.D.; Pluschke, G. Region-specific diversification of the highly virulent serotype 1 Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb. Genom. 2015, 1, e000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, J.; Verma, R.; Chatterjee, O.; Pachouri, P.K.; Upadhyay, P.; Singh, R.; Yadav, J.; Naaz, F.; Ravikumar, R.; Buggi, S. Whole genome sequencing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates from India reveals genetic heterogeneity and region-specific variations that might affect drug susceptibility. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, C.; Wentzel, J.F.; Du Plessis, L.H.; Gouws, C.; Hamman, J.H. Efflux as a mechanism of antimicrobial drug resistance in clinical relevant microorganisms: The role of efflux inhibitors. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, R.; Ahmad, S.; Raza, K. Comparative genomic assessment of members of genus Tenacibaculum: An exploratory study. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2023, 298, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenazy, R. Drug efflux pump inhibitors: A promising approach to counter multidrug resistance in Gram-negative pathogens by targeting AcrB protein from AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump from Escherichia coli. Biol. 2022, 11, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.; Vavra, M.; Greim, L.; Kern, W.V. Exploring the contribution of the AcrB homolog MdtF to drug resistance and dye efflux in a multidrug resistant E. coli isolate. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plattner, M.; Gysin, M.; Haldimann, K.; Becker, K.; Hobbie, S.N. Epidemiologic, phenotypic, and structural characterization of aminoglycoside-resistance gene aac (3)-IV. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Sami, M. Genetic Investigation of beta-lactam associated antibiotic resistance among Escherichia coli strains isolated from water sources. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Prenna, M.; Thaller, M.C.; Frère, J.-M.; Docquier, J.-D.; Lopizzo, T.; Liberatori, S. Biochemical Characterization of the THIN-B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4778. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xue, B.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X. The occurrence and distribution pattern of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community in the ili river. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 840428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagui, G.S.; de Almeida, O.G.G.; Moreira, N.C.; Abichabki, N.; Machado, G.P.; De Martinis, E.C.P.; Darini, A.L.C.; Andrade, L.N.; Segura-Munoz, S.I. A set of antibiotic-resistance mechanisms and virulence factors in GES-16-producing Klebsiella quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae from hospital wastewater revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, P.J.; Vogel, J.P. Bacterial type IV secretion: Conjugation systems adapted to deliver effector molecules to host cells. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.E.; Lara-Tejero, M.; Marlovits, T.C.; Wagner, S. Bacterial type III secretion systems: Specialized nanomachines for protein delivery into target cells. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 415–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lou, H.; Wang, W. AlgU controls environmental stress adaptation, biofilm formation, motility, pyochelin synthesis and antagonism potential in Pseudomonas protegens SN15-2. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 272, 127396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, B.; Singh, D.; Sanyal, S. Attachment of non-culturable toxigenic Vibrio cholerae 01 and non-01 and Aeromonas spp. to the aquatic arthropod Gerris spinolae and plants in the River Ganga, Varanasi. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1995, 12, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watnick, P.I.; Fullner, K.J.; Kolter, R. A role for the mannose-sensitive hemagglutinin in biofilm formation by Vibrio cholerae El Tor. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 3606–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthurst, S.J. The Type VI secretion system—A widespread and versatile cell targeting system. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.T.; Dong, T.G.; Mekalanos, J.J. A view to a kill: The bacterial type VI secretion system. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Vahidi, M.F.; Bahram, M.; Han, J.-L.; Ding, X.-Z.; Salekdeh, G.H. Metagenomic analysis reveals a dynamic microbiome with diversified adaptive functions to utilize high lignocellulosic forages in the cattle rumen. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzymski, J.J.; Murray, A.E.; Campbell, B.J.; Kaplarevic, M.; Gao, G.R.; Lee, C.; Daniel, R.; Ghadiri, A.; Feldman, R.A.; Cary, S.C. Metagenome analysis of an extreme microbial symbiosis reveals eurythermal adaptation and metabolic flexibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17516–17521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, J.N.; Weisenhorn, P.; Conrad, N.; Xia, F.; Overbeek, R.; Stevens, R.L.; Henry, C.S. Modeling central metabolism and energy biosynthesis across microbial life. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yan, Y.; Feng, L.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z. Bisphenol A alters volatile fatty acids accumulation during sludge anaerobic fermentation by affecting amino acid metabolism, material transport and carbohydrate-active enzymes. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, C.O.; Lloyd, D.; Coogan, M.P.; Rumsey, J.; Cable, J. Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism of Spironucleus vortens. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 129, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.N.; Turkarslan, S.; Beer, K.D.; Yin Lo, F.; Baliga, N.S. Adaptation of cells to new environments. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 544–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.; Romano, G.H.; Groisman, B.; Yona, A.; Dekel, E.; Kupiec, M.; Dahan, O.; Pilpel, Y. Adaptive prediction of environmental changes by microorganisms. Nature 2009, 460, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torsvik, V.; Øvreås, L. Microbial Diversity, Life Strategies, and Adaptation to Life in Extreme Soils. In Microbiology of Extreme Soils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 15–43. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Ahmed, S.; Gu, Y.; Huang, J.; An, B.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G. The effects of natural products and environmental conditions on antimicrobial resistance. Molecules 2021, 26, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
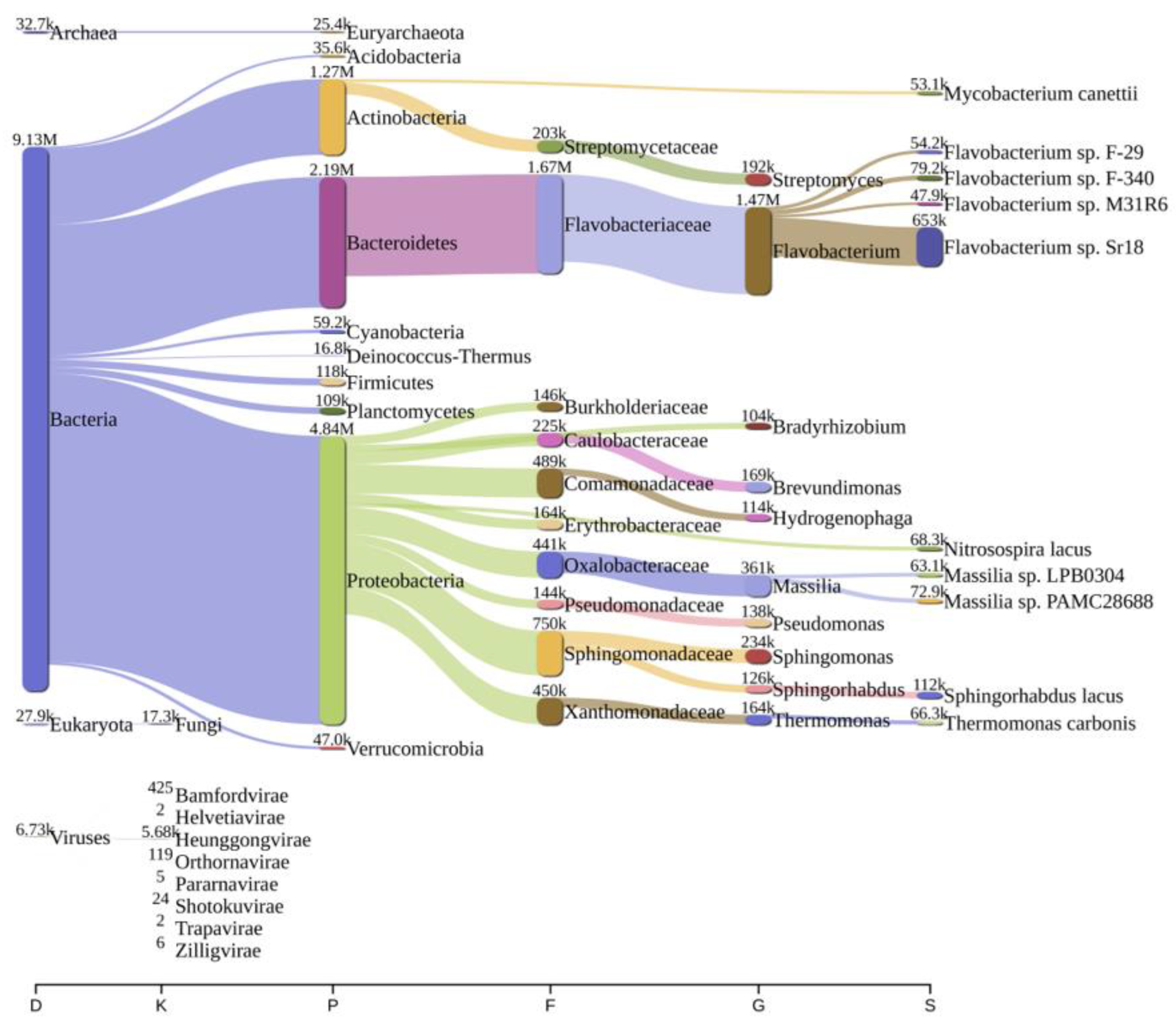
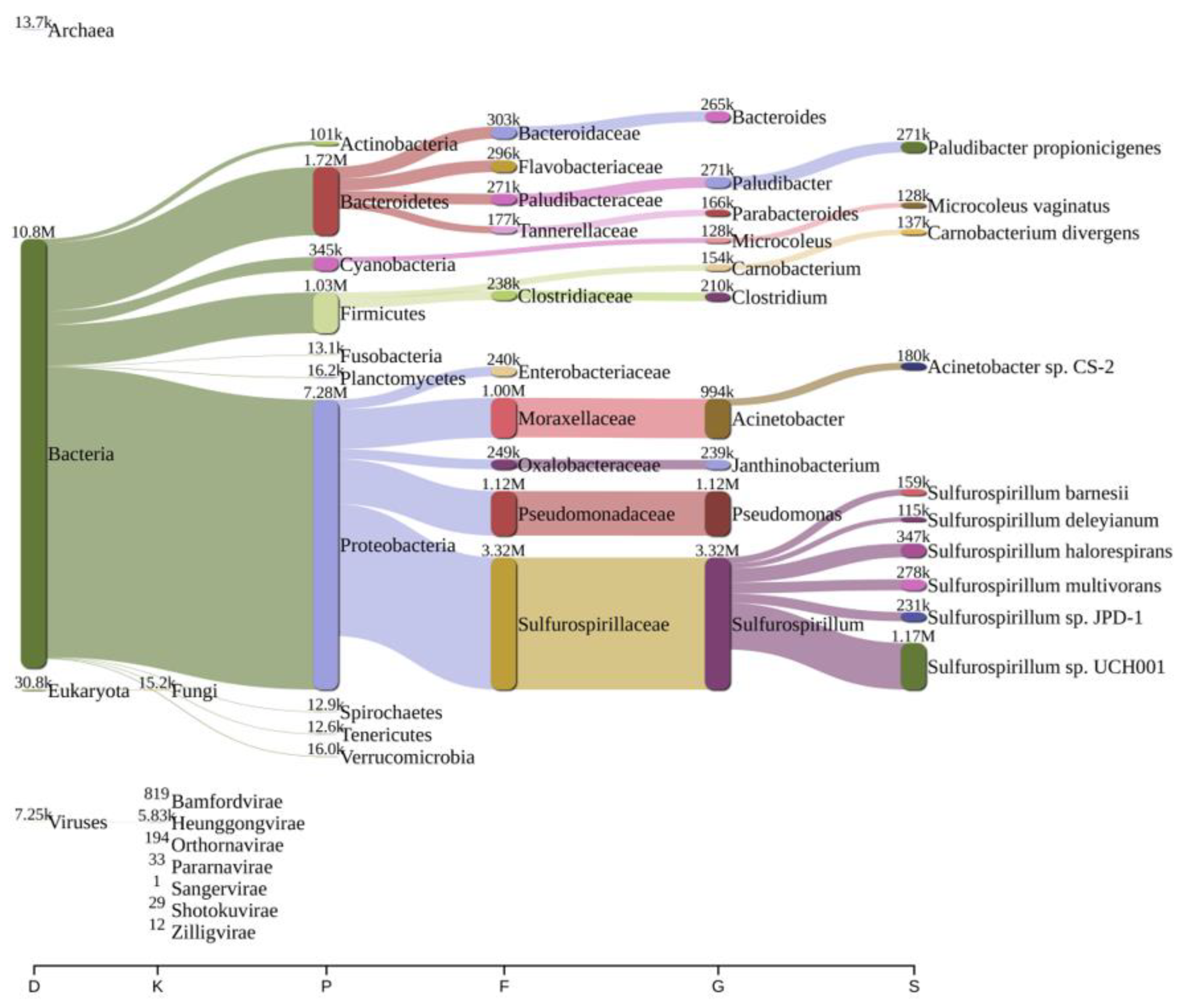



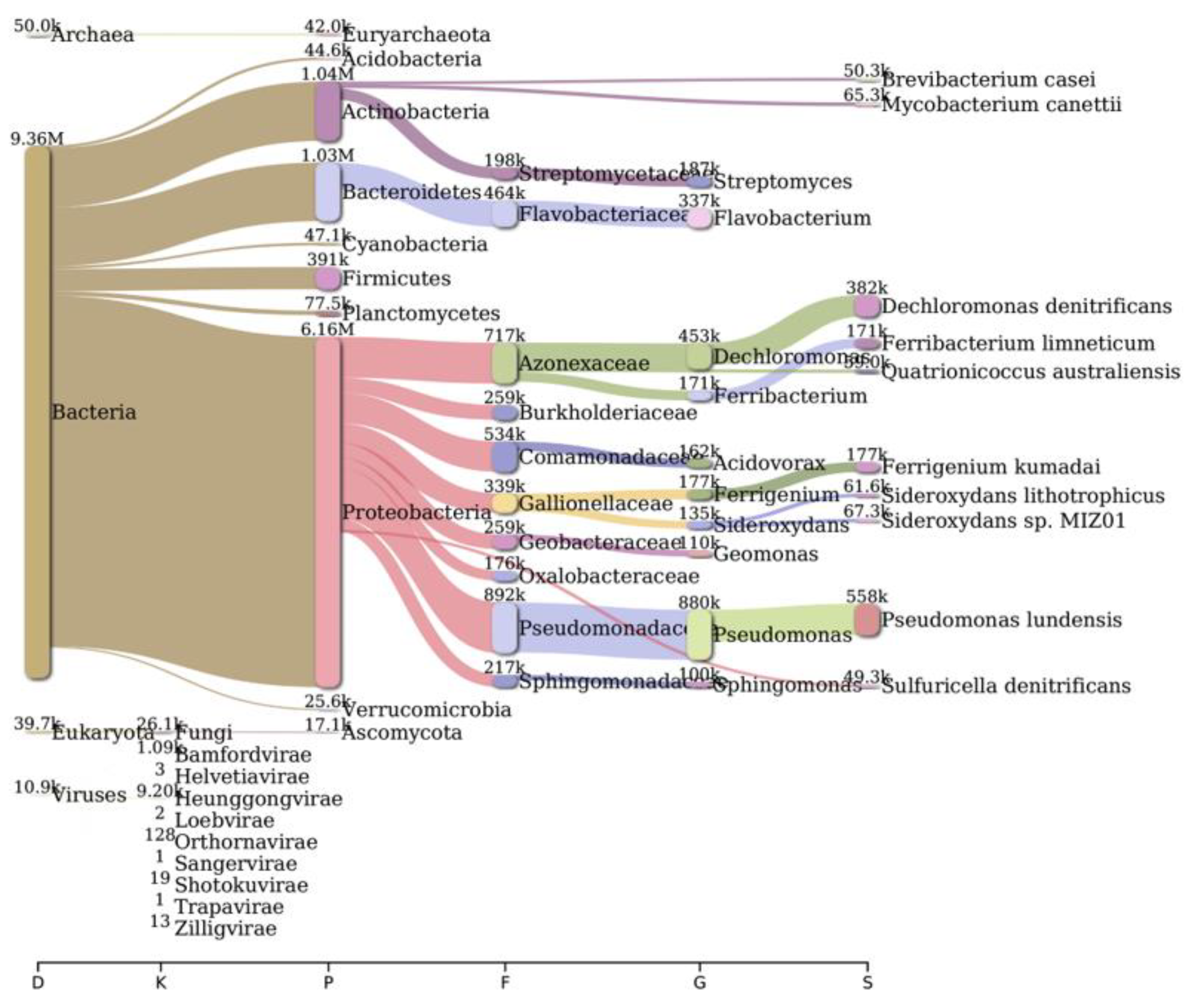
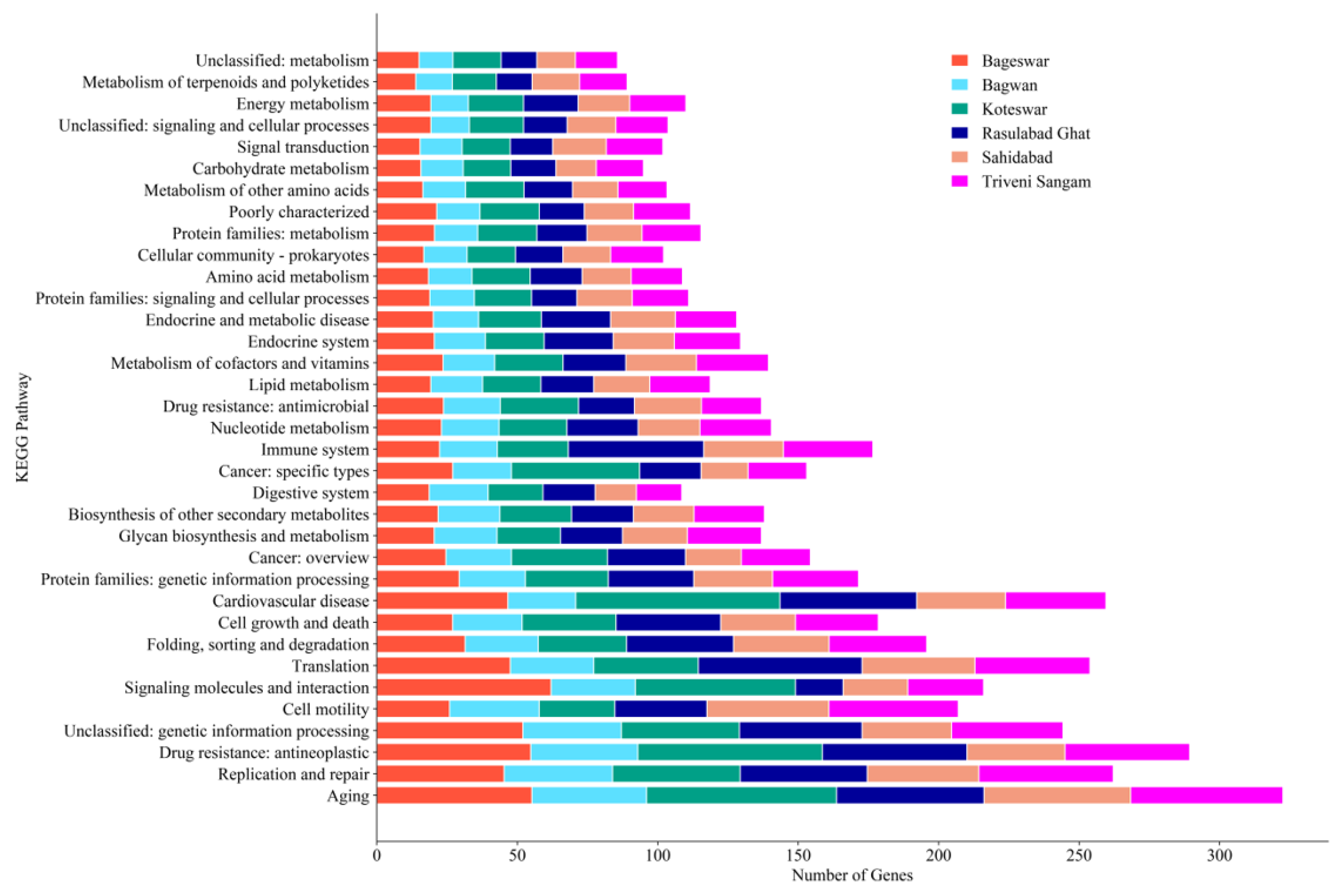
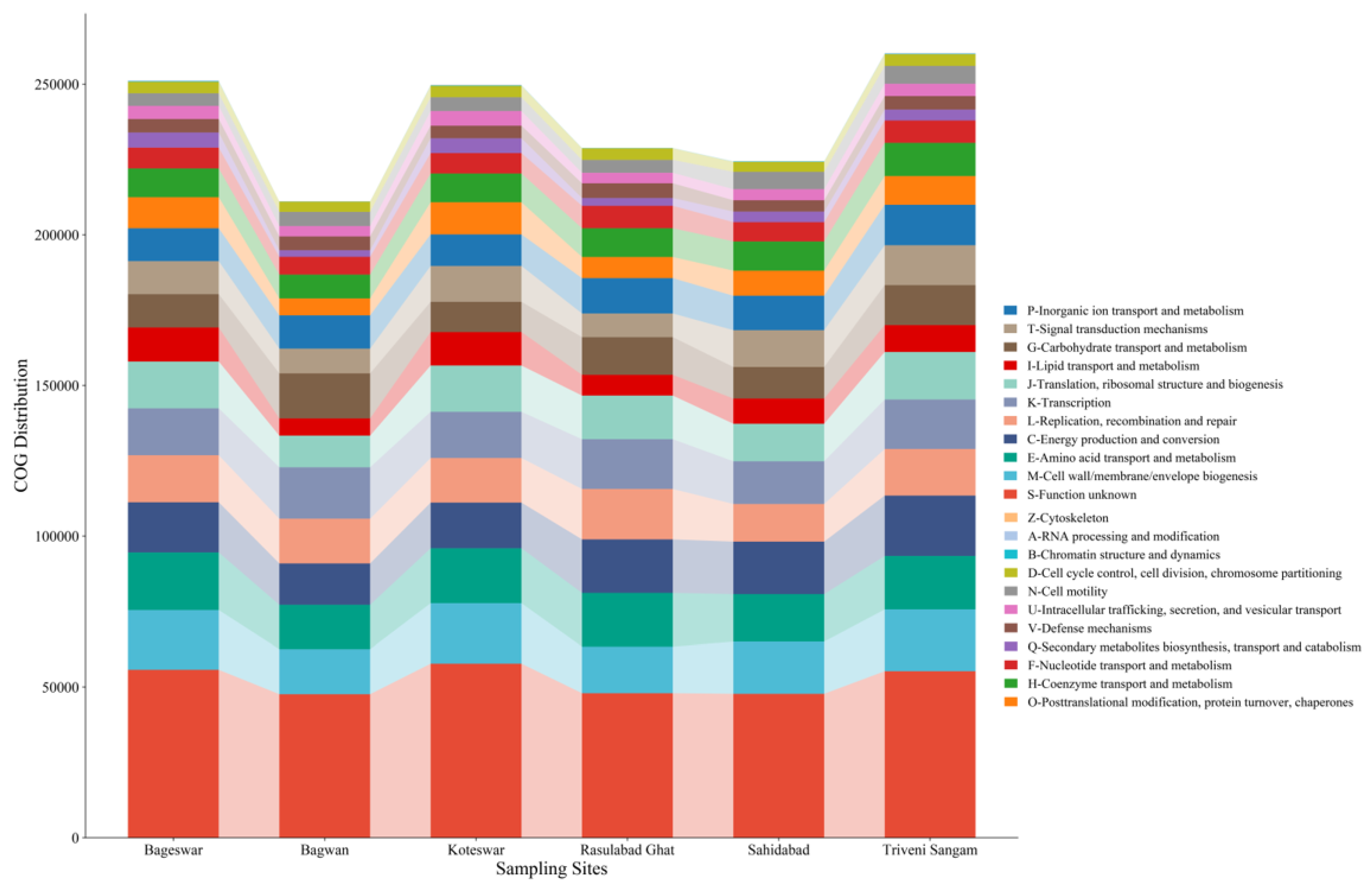
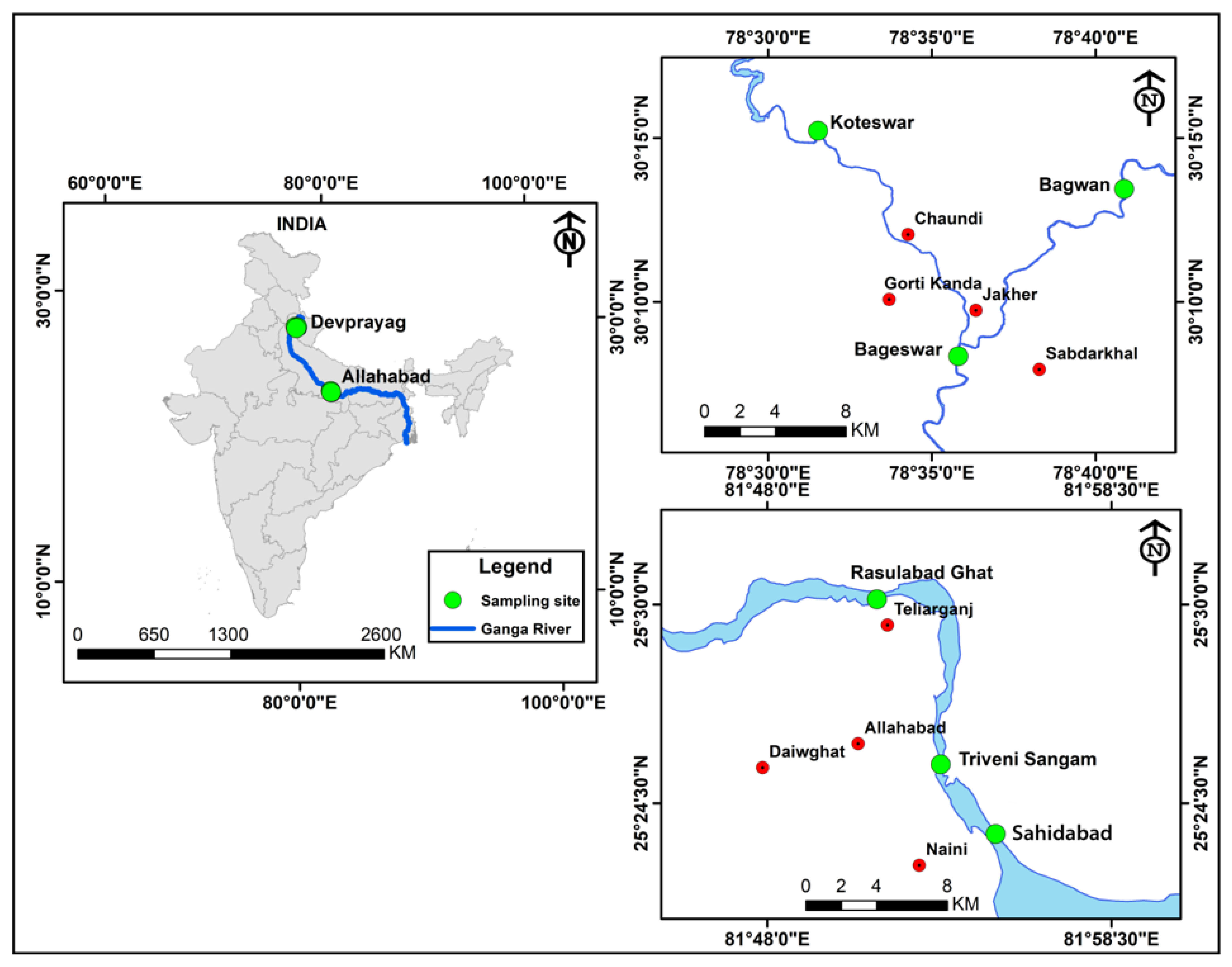

| Parameters | Bageswar | Bagwan | Koteswar | Rasulabad Ghat | Sahidabad | Triveni Sangam |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contigs (≤150 bp) | 460,537 | 71,161 | 87,682 | 40,754 | 43,771 | 58,237 |
| Contigs (≥150 bp) | 1,008,926 | 1,766,259 | 5,172,327 | 3,263,830 | 3,839,878 | 4,791,158 |
| Total contigs | 1,469,463 | 1,837,420 | 5,260,009 | 3,304,584 | 3,883,649 | 4,849,395 |
| Largest contig | 887,047 | 897,272 | 1,192,971 | 343,376 | 789,499 | 645,470 |
| Total length (in bp) | 468,274,061 | 340,847,742 | 444,765,440 | 366,965,171 | 374,775,947 | 433,423,693 |
| GC content (in %) | 52 | 40 | 52 | 46 | 50 | 47 |
| N50 | 1091 | 2615 | 1237 | 1517 | 1402 | 1471 |
| N90 | 558 | 619 | 561 | 578 | 573 | 575 |
| L50 | 91,382 | 21,741 | 66,190 | 41,780 | 48,856 | 55,263 |
| L90 | 346,262 | 148,883 | 298,653 | 215,191 | 232,472 | 263,312 |
| Ns per 100 kbp | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Resistance | Gene Name | Number of Reads | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bageswar | Bagwan | Rasulabad Ghat | Sahidabad | Triveni Sangam | ||
| Aminoglycoside | aac(6′)-Ib | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Streptomycin | aadA1 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Streptomycin | aadA5 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Streptomycin | aadA6 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | aadS | NF | F | F | NF | F |
| Cephalosporin; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Penam; Phenicol; Rifamycin; Tetracycline; Triclosan | acrB | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | acrD | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| Penam | AER-1 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | ANT(2″)-Ia | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | ANT(3″)-Ia | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | ANT(6)-Ia | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | aph(3″)-Ib | NF | NF | F | NF | F |
| Aminoglycoside | aph(6)-Id | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Peptide | arnA | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| Rifamycin | arr-2 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Peptide | bacA | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin; Aminoglycoside | baeR | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | bla-A | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaAER-1 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Carbapenem | blaGES-14 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Carbapenem | blaGES-5 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaMCA | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaOXA-119 | NF | NF | NF | NF | F |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaOXA-209 | F | NF | F | NF | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaOXA-296 | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaOXA-347 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Carbapenem; Cephalosporin; Penam | blaRm3 | NF | F | NF | F | NF |
| BETA-LACTAM | blaRSD1-1 | NF | NF | NF | NF | F |
| Carbapenem | blaTHIN-B | NF | NF | NF | F | NF |
| Cephalosporin | blaVEB-9 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Phenicol | catQ | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside; Fluoroquinolone | ceoB | NF | NF | NF | F | F |
| Phenicol | cmlA5 | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin; Aminoglycoside | cpxA | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Fluoroquinolone; Macrolide; Penam | CRP | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Trimethoprim | dfrA3 | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| Trimethoprim | dfrG | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Fluoroquinolone | emrR | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Cephalosporin; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Penam; Phenicol; Rifamycin; Tetracycline; Triclosan | Enterobacter cloacaeacrA | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Macrolide | ere(D) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Chloramphenicol | EstDL136 | F | NF | NF | NF | NF |
| Fosfomycin | fos1 | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| Cephalosporin; Cephamycin; Fluoroquinolone; Macrolide; Penam; Tetracycline | H-NS | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside; Carbapenem; Cephalosporin; Fluoroquinolone; Macrolide; Penam; Peptide | Klebsiella pneumoniaeKpnH | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside; Carbapenem; Cephalosporin; Fluoroquinolone; Macrolide; Penem; Peptide | KpnG | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Lincosamide | lnu(D) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Carbapenem; Cephalosporin; Cephamycin; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Monobactam; Penem;phenicol; Rifamycin; Tetracycline; Triclosan | marA | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin | mdtB | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin | mdtC | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Macrolide | mefA | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Macrolide | mefB | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Macrolide | mefC | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Lincosamide; Macrolide; Oxazolidinone; Phenicol; Pleuromutilin; Streptogramin; Tetracycline | mel | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin; Aminoglycoside; Cephalosporin; diaminopyrimidine; Fluoroquinolone; Macrolide; penam; Phenicol; Tetracycline | MexD | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Diaminopyrimidine; Fluoroquinolone; Phenicol | MexF | NF | F | F | NF | F |
| Macrolide | mphE | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Macrolide | mphF | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Nitroimidazole | msbA | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Erythromycin; Azithromycin; Telithromycin; Quinupristin; Pristinamycin_IA; Virginiamycin_S | msr(D) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Macrolide | msr(E) | F | F | F | NF | NF |
| Diaminopyrimidine; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Nitrofuran; Tetracycline | oqxA | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Diaminopyrimidine; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Nitrofuran; Tetracycline | oqxB | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin; Aminoglycoside; Carbapenem;cephalosporin; Cephamycin; Diaminopyrimidine; Fluoroquinolone; Macrolide; Monobactam; Penem; Peptide; Phenicol; Sulfonamide; Tetracycline | Pseudomonas aeruginosaCpxR | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Fluoroquinolone | qnrD2 | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| Carbapenem; Cephalosporin; Cephamycin; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Monobactam; Penam; Phenicol; Rifamycin; Tetracycline; Triclosan | ramA | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Rifamycin | rphB | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminoglycoside | spw | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Sulfonamide | sul1 | NF | NF | F | NF | F |
| Sulfonamide | sul2 | NF | NF | F | NF | F |
| Sulfonamide | sul4 | NF | NF | F | F | NF |
| Tetracycline | tet(36) | NF | F | F | NF | NF |
| Tetracycline | tet(39) | F | F | F | NF | NF |
| Tetracycline | tet(A) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Tetracycline | tet(G) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Doxycycline; Tetracycline; Minocycline | tet(M) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Doxycycline; Tetracycline; Minocycline | tet(O) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Doxycycline; Tetracycline; Minocycline | tet(Q) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Doxycycline; Tetracycline; Minocycline | tet(X) | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Tetracycline | tetC | NF | NF | F | NF | NF |
| Aminocoumarin; Aminoglycoside; Carbapenem; Cephalosporin; Cephamycin; Fluoroquinolone; Glycylcycline; Macrolide; Penam; Peptide; Phenicol; Rifamycin; Tetracycline; Triclosan | tolC | NF | F | NF | NF | NF |
| Contig Id | Location | NCBI Accession No. | Virulence Gene | Virulence Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| contigs_2469; contigs_1; contigs_240 | Bagwan; Triveni Sangam; Rasulabad Ghat | NP_249769 | flgC | Flagella (VF0273) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_45; contigs_11691; contigs_19; contigs_3945 | Rasulabad Ghat; sahidabad; Triveni Sangam; Bagwan | NP_249773 | flgG | |
| contigs_45 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_250143 | flhA | |
| contigs_45; contigs_641; contigs_19 | Rasulabad Ghat; Bagwan; Triveni Sangam | NP_250137 | fliP | |
| contigs_45 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_250138 | fliQ | |
| contigs_11691; contigs_19; contigs_3945 | Sahidabad; Triveni Sangam; Bagwan | NP_249774 | flgH | |
| contigs_45; contigs_641; contig_19; contigs_366 | Rasulabad Ghat; Bagwan; Triveni Sangam; Bagwan | NP_250134 | fliM | |
| contigs_45; contigs_641; contig_19; contigs_366 | Rasulabad Ghat; Bagwan; Triveni Sangam; Bagwan | NP_249793 | fliG | |
| contigs_45; contigs_11691; contigs_19; contigs_3945 | Rasulabad Ghat; sahidabad; Triveni Sangam; Bagwan | NP_249775 | flgI | |
| contigs_45; contigs_641; contig_19; contigs_366 | Rasulabad Ghat; Bagwan; Triveni Sangam; Bagwan | NP_250145 | fleN | |
| contigs_45; contigs_641; contigs_19 | Rasulabad Ghat; Bagwan; Triveni Sangam | NP_249795 | fliI | |
| contigs_45; contigs_641 | Rasulabad Ghat; Bagwan | NP_249788 | fleQ | |
| contigs_4 | Triveni Sangam | NP_250394 | pcrD | Type III TTSS (VF0083) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_4 | Triveni Sangam | NP_250384 | pscR | |
| contigs_4 | Triveni Sangam | NP_250398 | pcrH | |
| contigs_68665 | Sahidabad | NP_249453 | algU | Alginate (VF0091) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_5362; contigs_1 | Bagwan; Triveni Sangam | NP_252238 | algI | |
| contigs_1 | Triveni Sangam | NP_252231 | alg8 | |
| contigs_42942 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_273273 | katA | |
| contigs_41 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_460110 | csgG | |
| contigs_45 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_251103 | pvdH | |
| contigs_45; contigs_53 | Rasulabad Ghat; Triveni Sangam | NP_251116 | pvdS | |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252911 | fptA | |
| contigs_76423 | Bagwan | BAA94855 | astA | |
| contigs_2 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_253699 | waaF | |
| contigs_45; contigs_269352 | Rasulabad Ghat; Sahidabad | NP_251102 | mbtH-like | |
| contigs_627 | Bagwan | AAF37887 | ompA | |
| contigs_5362 | Bagwan | NP_252241 | algA | |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252918 | pchD | Pyochelin (VF0095) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252919 | pchC | |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252914 | pchG | |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252915 | pchF | |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252920 | pchB | |
| contigs_665 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_252917 | pchR | |
| contigs_4; contigs_24665; contigs_67305; contigs_39 | Triveni Sangam; Bagwan; sahidabad; Bagwan | NP_249099 | pilG | Type IV pili (VF0082) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_24665; contigs_67305; contigs_39 | Bagwan; Sahidabad; Bagwan | NP_249100 | pilH | |
| contigs_39 | Bagwan | NP_249086 | pilT | |
| contigs_622 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_248780 | clpV1 | Type VI HSI-I (VF0334) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_622 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_248778 | hsiG1 | |
| contigs_622 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_248768 | dotU1 | |
| contigs_622 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_248775 | hcp1 | |
| contigs_622 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_248773 | hsiB1/vipA | |
| contigs_622 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_248774 | hsiC1/vipB | |
| contigs_239842 | Bageswar | NP_540392 | acpXL | LPS (CVF383) (Brucella) |
| contigs_240 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_249768 | flgB | Deoxyhexose linking sugar 209 Da capping structure (AI138) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
| contigs_641 | Bagwan | NP_250146 | fliA | |
| contigs_204 | Rasulabad Ghat | NP_254009 | algC | Alginate biosynthesis (CVF522) (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rout, A.K.; Tripathy, P.S.; Dixit, S.; Behera, D.U.; Behera, B.; Das, B.K.; Behera, B.K. Unveiling the Microbiome Landscape: A Metagenomic Study of Bacterial Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Factors in the Sediments of the River Ganga, India. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121735
Rout AK, Tripathy PS, Dixit S, Behera DU, Behera B, Das BK, Behera BK. Unveiling the Microbiome Landscape: A Metagenomic Study of Bacterial Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Factors in the Sediments of the River Ganga, India. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(12):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121735
Chicago/Turabian StyleRout, Ajaya Kumar, Partha Sarathi Tripathy, Sangita Dixit, Dibyajyoti Uttameswar Behera, Bhaskar Behera, Basanta Kumar Das, and Bijay Kumar Behera. 2023. "Unveiling the Microbiome Landscape: A Metagenomic Study of Bacterial Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Factors in the Sediments of the River Ganga, India" Antibiotics 12, no. 12: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121735
APA StyleRout, A. K., Tripathy, P. S., Dixit, S., Behera, D. U., Behera, B., Das, B. K., & Behera, B. K. (2023). Unveiling the Microbiome Landscape: A Metagenomic Study of Bacterial Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence Factors in the Sediments of the River Ganga, India. Antibiotics, 12(12), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12121735












