Antibiofilm Effect of Nitric Acid-Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Based Surfaces against E. coli and S. aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
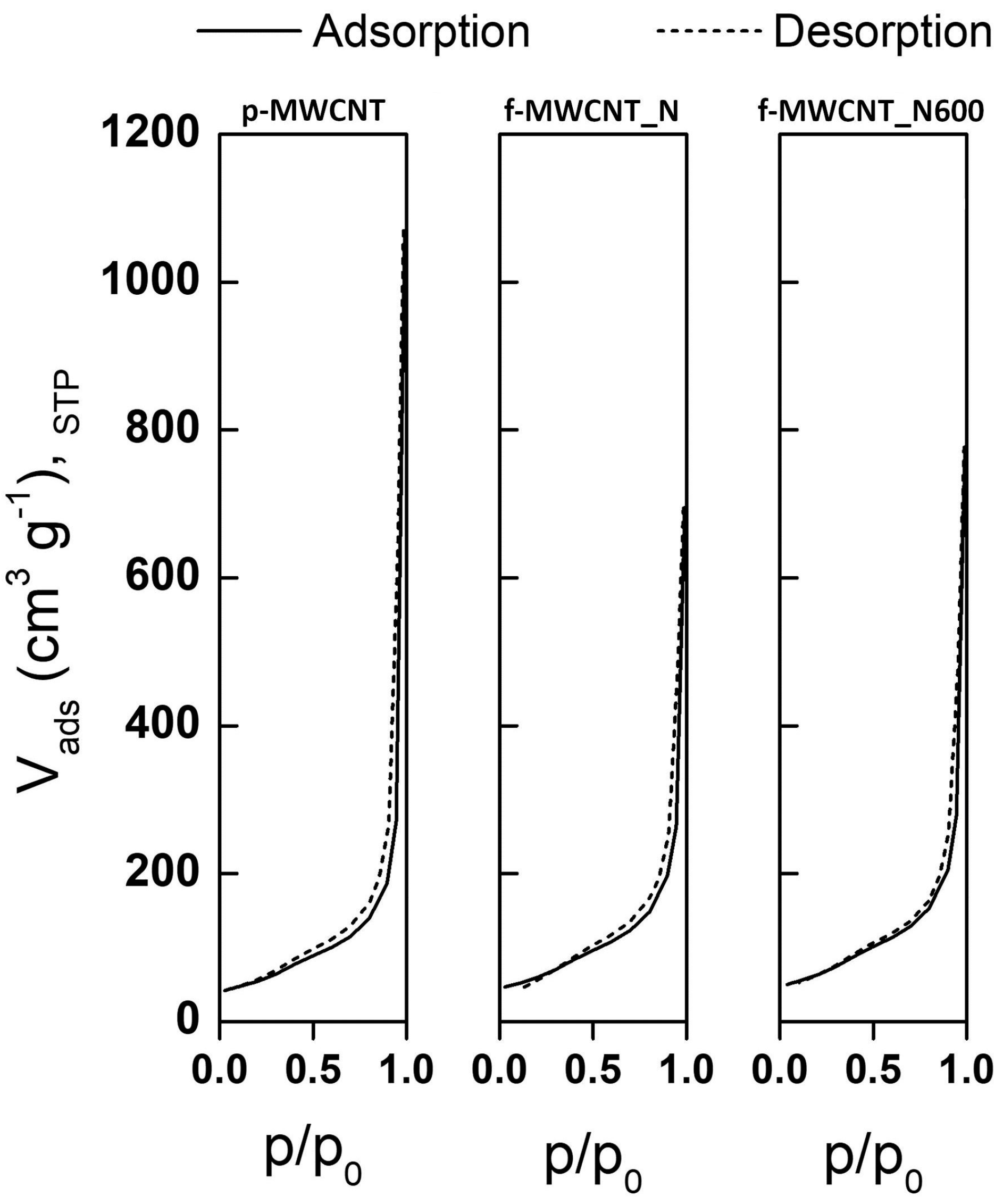
2.1. Characterization of MWCNTs
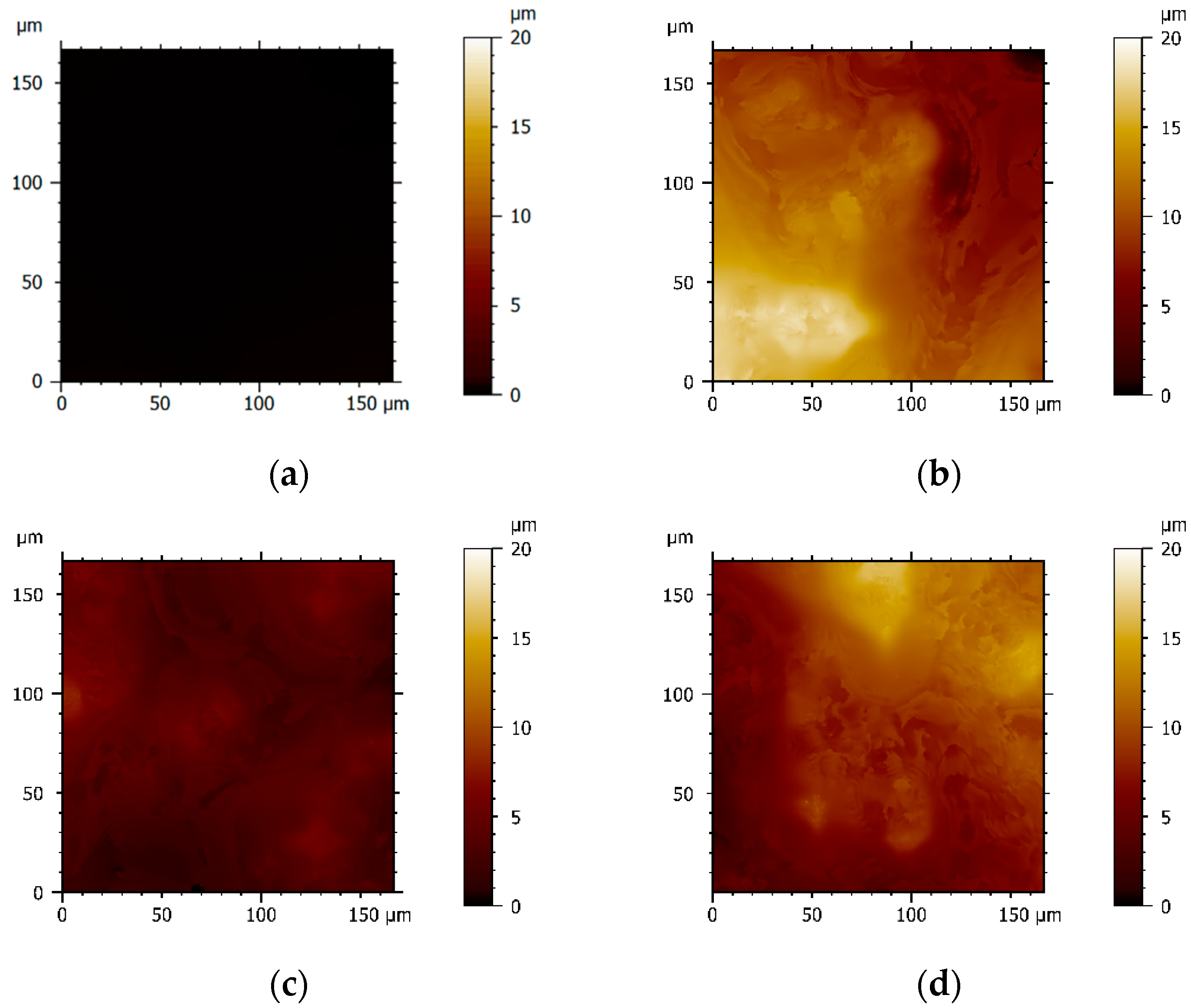
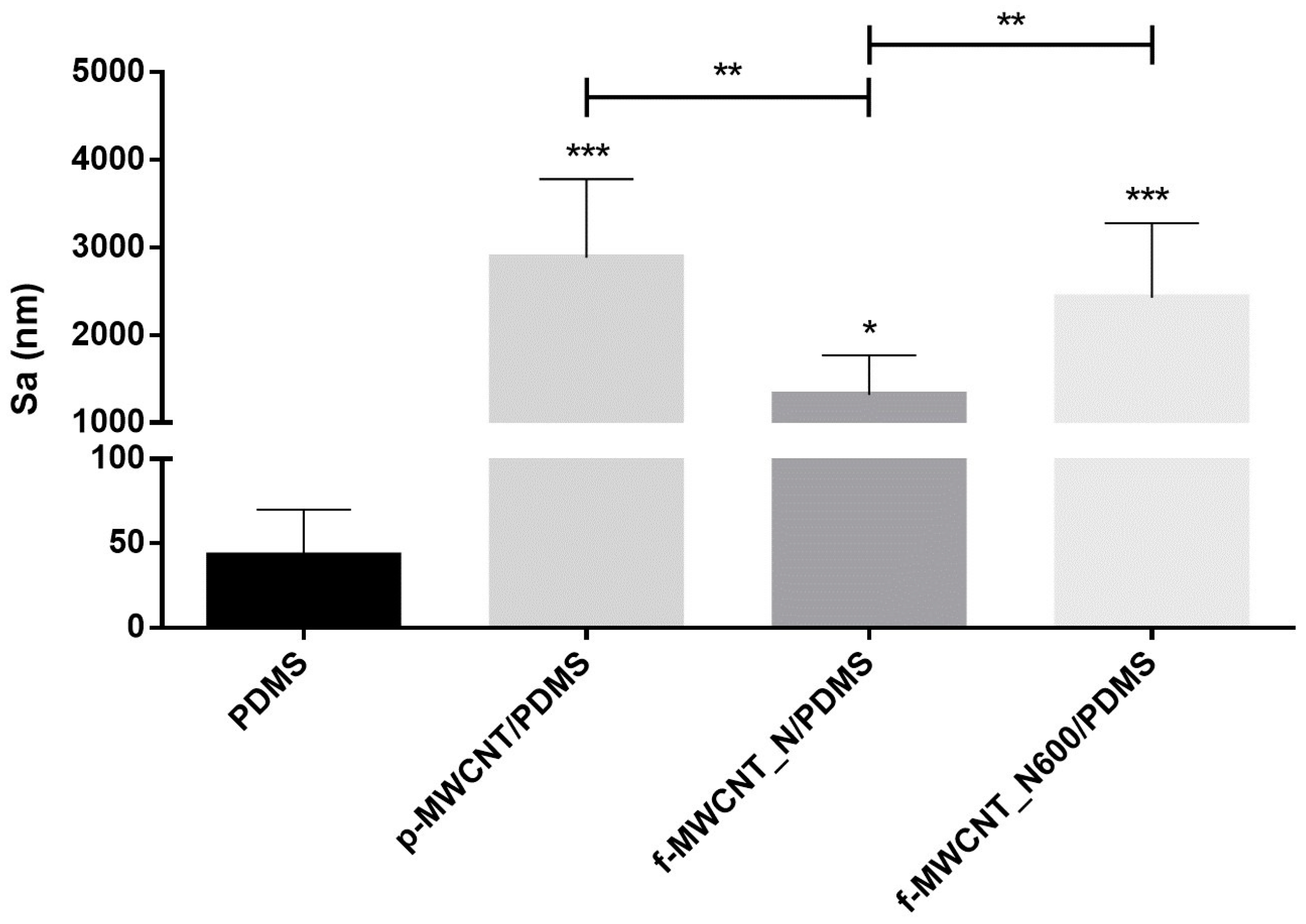
2.2. Characterization of MWCNT/PDMS Surfaces
2.3. Antibiofilm Analysis
2.4. MWCNT Antibacterial Mechanisms
2.5. Effect of MWCNT/PDMS on Human Cell Viability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Functionalization of Pristine MWCNTs
3.2. Synthesis of MWCNT/PDMS Surfaces
3.3. Textural Characterization of MWCNTs
3.4. Characterization of MWCNT/PDMS Surfaces
3.4.1. MWCNT/PDMS Surface Topography
3.4.2. MWCNT/PDMS Surface Morphology
3.5. Evaluation of MWCNT Leaching from PDMS Surfaces
3.6. Antibiofilm Activity of MWCNT/PDMS Surfaces
3.6.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
3.6.2. Biofilm Formation Assay
3.7. Characterization of MWCNT Antibacterial Mechanisms
3.8. Cytotoxicity Assessment of MWCNT/PDMS Composites
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pietrocola, G.; Campoccia, D.; Motta, C.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R.; Speziale, P. Colonization and Infection of Indwelling Medical Devices by Staphylococcus aureus with an Emphasis on Orthopedic Implants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Santos, R.; Lima, M.; Gomes, L.C.; Mergulhão, F.J. Antimicrobial coatings based on chitosan to prevent implant-associated infections: A systematic review. iScience 2021, 24, 103480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryers, J.D. Medical biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.-F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y. Novel Approaches to Combat Medical Device-Associated BioFilms. Coatings 2021, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouiche, R.O. Treatment of Infections Associated with Surgical Implants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, V.; Chittaranjan, S.; Kurian, V.M.; Doble, M. Characteristics of bacterial biofilm associated with implant material in clinical practice. Polym. J. 2013, 45, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Miele, M.C.; Al Ismail, D.; Di Timoteo, F.; De Angelis, M.; Rosa, L.; Cutone, A.; Venditti, M.; Mascellino, M.T.; Valenti, P.; et al. Challenges in the microbiological diagnosis of implant-associated infections: A summary of the current knowledge. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanEpps, J.S.; Younger, J.G. Implantable Device-Related Infection. Shock. 2016, 46, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.; Tak, V.; Gunjiyal, J.; Nair, S.A.; Lalwani, S.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, B.; Sinha, S.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, D.; et al. Device-associated infections at a level-1 trauma centre of a developing Nation: Impact of automated surveillance, training and feedbacks. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 33, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, R.A.; Darouiche, R.O. Device-Associated Infections: A Macroproblem that Starts with Microadherence. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Hetrick, E.M.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Reducing implant-related infections: Active release strategies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, L.G.; Richards, R.G. Staphylococci and implant surfaces: A review. Injury 2006, 37, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, G.M. The Role of Bacterial Biofilm in Antibiotic Resistance and Food Contamination. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1705814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandi, V.; Vadakedath, S. Implant-associated infections: A review of the safety of cardiac implants. Cureus 2020, 12, e12267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebach, E.; Kubatzky, K.F. Chronic implant-related bone infections-can immune modulation be a therapeutic strategy? Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F. Biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehl, R.; Brunetto Priscilla, S.; Woischnig, A.-K.; Varisco, M.; Rajacic, Z.; Vosbeck, J.; Terracciano, L.; Fromm Katharina, M.; Khanna, N. Preventing Implant-Associated Infections by Silver Coating. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.C.; Siedlecki, C.A. 9—Antibacterial Polyurethanes. In Advances in Polyurethane Biomaterials; Cooper, S.L., Guan, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 247–284. [Google Scholar]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. A review of the biomaterials technologies for infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8533–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Chandra, N.; Kumar, S. The Role of Biofilms in Medical Devices and Implants. In Biofilms in Human Diseases: Treatment and Control; Kumar, S., Chandra, N., Singh, L., Hashmi, M.Z., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira-Santos, R.; Gomes, M.; Gomes, L.C.; Mergulhão, F.J. Antimicrobial and anti-adhesive properties of carbon nanotube-based surfaces for medical applications: A systematic review. iScience 2021, 24, 102001–102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleemi, M.A.; Kong, Y.L.; Yong, P.V.C.; Wong, E.H. An Overview of Antimicrobial Properties of Carbon Nanotubes-Based Nanocomposites. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 12, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Herzberg, M.; Rodrigues, D.F.; Elimelech, M. Antibacterial effects of carbon nanotubes: Size does matter! Langmuir 2008, 24, 6409–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagos, M.R.; Gomes, M.; Moreira, J.M.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Mergulhão, F.J. Carbon Nanotube/Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Composite Materials to Reduce Bacterial Adhesion. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagos, M.R.; Moreira, J.M.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Mergulhao, F.J. Incorporation of Carbon Nanotubes in Polydimethylsiloxane to Control Escherichia coli Adhesion. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelgund, G.M.; Oki, A. Deposition of silver nanoparticles on dendrimer functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3621–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, E.; Vimala, G. Effective functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotube with amphiphilic poly(propyleneimine) dendrimer carrying silver nanoparticles for better dispersability and antimicrobial activity. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelgund, G.M.; Oki, A.; Luo, Z. Antimicrobial activity of CdS and Ag2S quantum dots immobilized on poly(amidoamine) grafted carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 100, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Gao, D.; Guan, M.; Zheng, L.; Ouyang, H.; Chai, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, W. Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Activity of Carbon Nanotubes to Human Gut Bacteria. Small 2013, 9, 2735–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bose, S.; Chatterjee, K. Amine-functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes impart osteoinductive and bactericidal properties in poly(ε-caprolactone) composites. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 19086–19098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Razmjou, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Jannesar, R. Nanoporous solid-state membranes modified with multi-wall carbon nanotubes with anti-biofouling property. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, L.R.; Yang, L. Inactivation of Bacterial Pathogens by Carbon Nanotubes in Suspensions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3003–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, L.M.; Goodwin, D.G.; Taylor, A.D.; Pfefferle, L.; Zimmerman, J.B. Toward Tailored Functional Design of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWNTs): Electrochemical and Antimicrobial Activity Enhancement via Oxidation and Selective Reduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5938–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, L.M.; Sekol, R.C.; Taylor, A.D.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Zimmerman, J.B. Realizing comparable oxidative and cytotoxic potential of single- and multiwalled carbon nanotubes through annealing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8775–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1982, 54, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.G.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Influence of the surface chemistry of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on their activity as ozonation catalysts. Carbon 2010, 48, 4369–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Voitko, K.V.; Bakalinska, O.; Prykhod’ko, G.P.; Bertóti, I.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D.; Gun’ko, V.M.; László, K. Morphology and adsorption properties of chemically modified MWCNT probed by nitrogen, n-propane and water vapor. Carbon 2012, 50, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinjari, S.; Bera, T.; Kapur, G.S.; Kjeang, E. The mechanism and sorption kinetic analysis of hydrogen storage at room temperature using acid functionalized carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 1930–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.P.; Silva, A.M.T.; Romero, S.M.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. The role of O- and S-containing surface groups on carbon nanotubes for the elimination of organic pollutants by catalytic wet air oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 147, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likodimos, V.; Steriotis, T.A.; Papageorgiou, S.K.; Romanos, G.E.; Marques, R.R.N.; Rocha, R.P.; Faria, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T.; et al. Controlled surface functionalization of multiwall carbon nanotubes by HNO3 hydrothermal oxidation. Carbon 2014, 69, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessonnier, J.-P.; Rosenthal, D.; Hansen, T.W.; Hess, C.; Schuster, M.E.; Blume, R.; Girgsdies, F.; Pfänder, N.; Timpe, O.; Su, D.S.; et al. Analysis of the structure and chemical properties of some commercial carbon nanostructures. Carbon 2009, 47, 1779–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monthioux, M.; Smith, B.W.; Burteaux, B.; Claye, A.; Fischer, J.E.; Luzzi, D.E. Sensitivity of single-wall carbon nanotubes to chemical processing: An electron microscopy investigation. Carbon 2001, 39, 1251–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgrzebnicki, M.; Krauze, N.; Gęsikiewicz-Puchalska, A.; Kapica-Kozar, J.; Piróg, E.; Jędrzejewska, A.; Michalkiewicz, B.; Narkiewicz, U.; Morawski, A.W.; Wrobel, R.J. Impact on CO2 Uptake of MWCNT after Acid Treatment Study. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.P.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Different methodologies for synthesis of nitrogen doped carbon nanotubes and their use in catalytic wet air oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 2017, 548, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka, K.; Kądzioła, K.; Felczak, A.; Wrońska, N.; Piwoński, I.; Kisielewska, A.; Lisowska, K. Surface area or diameter–which factor really determines the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles grown on TiO2 coatings? New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3275–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zuber, F.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Brugger, J.; Ren, Q. Nanostructured surface topographies have an effect on bactericidal activity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, C.; Nolle, F.; Mischo, J.; Faidt, T.; Grandthyll, S.; Thewes, N.; Koch, M.; Muller, F.; Bischoff, M.; Klatt, M.A.; et al. Strength of bacterial adhesion on nanostructured surfaces quantified by substrate morphometry. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19713–19722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Abdullah, B.M.; Rowley-Neale, S.J.; Wylie, S.; Slate, A.J.; Banks, C.E.; Whitehead, K.A. Diamine Oxidase-Conjugated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes to Facilitate Electrode Surface Homogeneity. Sensors 2022, 22, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.; Gomes, L.C.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Mergulhão, F.J. Optimizing CNT loading in antimicrobial composites for urinary tract application. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.H.; Park, Y.-B.; Yoon, K.H. Rheological and mechanical properties of surface modified multi-walled carbon nanotube-filled PET composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 3434–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyayula, V.K.K.; Gadhamshetty, V. Appreciating the role of carbon nanotube composites in preventing biofouling and promoting biofilms on material surfaces in environmental engineering: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Madaeni, S.S.; Moradian, R.; Zinadini, S.; Astinchap, B. Fabrication and characterization of novel antifouling nanofiltration membrane prepared from oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube/polyethersulfone nanocomposite. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral, B.; Martín Gullón, I.; Navarro, R.; Galao, O.; Baeza, F.J.; Zornoza, E.; Calderón, B.; Rodríguez, I.; Arnaiz, N.; Romero Sánchez, M.D.; et al. The Effect of Different Oxygen Surface Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes on the Electrical Resistivity and Strain Sensing Function of Cement Pastes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenburg, B.J.; Rodrigues, E.D.; Wessling, M.; Stamatialis, D. Insights into the role of material surface topography and wettability on cell-material interactions. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4377–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Mauter, M.S.; Elimelech, M. Physicochemical determinants of multiwalled carbon nanotube bacterial cytotoxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7528–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Zodrow, K.R.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M. Electronic-structure-dependent bacterial cytotoxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5471–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwibbert, K.; Menzel, F.; Epperlein, N.; Bonse, J.; Krüger, J. Bacterial Adhesion on Femtosecond Laser-Modified Polyethylene. Materials 2019, 12, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Bawazir, M.; Dhall, A.; Kim, H.E.; He, L.; Heo, J.; Hwang, G. Implication of Surface Properties, Bacterial Motility, and Hydrodynamic Conditions on Bacterial Surface Sensing and Their Initial Adhesion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 643722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimova, Y.; Zorina, A.; Nesterova, L. Oxidative Stress Response and E. coli Biofilm Formation under the Effect of Pristine and Modified Carbon Nanotubes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.I.; Salama, N.R. The gram-negative bacterial periplasm: Size matters. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.P.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Characterisation of the surface chemistry of carbon materials by temperature-programmed desorption: An assessment. Catal. Today 2023, 418, 114136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankova, N.E.; Atanasov, P.A.; Nedyalkov, N.N.; Kolev, K.; Valova, E.; Armyanov, S. Chapter 15—Laser processing of biopolymers for development of medical and high-tech devices. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering; Holban, A.-M., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 487–526. [Google Scholar]
- Slate, A.J.; Wickens, D.J.; El Mohtadi, M.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.; West, G.; Banks, C.E.; Whitehead, K.A. Antimicrobial activity of Ti-ZrN/Ag coatings for use in biomaterial applications. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olborska, A.; Janas-Naze, A.; Kaczmarek, Ł.; Warga, T.; Halin, D.S.C. Antibacterial Effect of Graphene and Graphene Oxide as a Potential Material for Fiber Finishes. Autex Res. J. 2020, 20, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Santos, R.; Gomes, L.C.; Vieira, R.; Sousa-Cardoso, F.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Mergulhão, F.J. Exploring Nitrogen-Functionalized Graphene Composites for Urinary Catheter Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

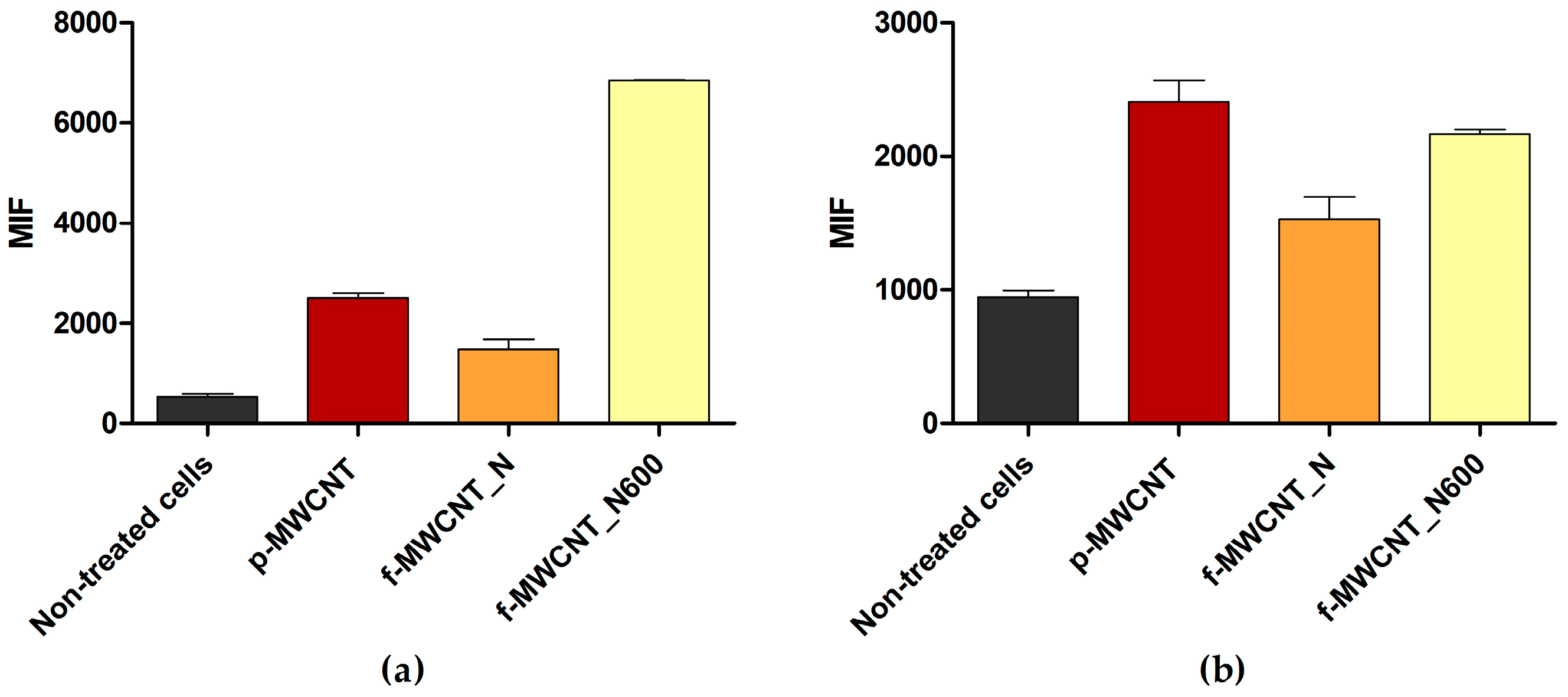
 ), p-MWCNT/PDMS (
), p-MWCNT/PDMS ( ), and f-MWCNT_N-based surfaces (
), and f-MWCNT_N-based surfaces ( ) against (a) E. coli and (b) S. aureus. The means ± standard error for at least three independent experiments are represented. Significant differences are indicated as * (p < 0.05) and ** (p < 0.01).
) against (a) E. coli and (b) S. aureus. The means ± standard error for at least three independent experiments are represented. Significant differences are indicated as * (p < 0.05) and ** (p < 0.01).
 ), p-MWCNT/PDMS (
), p-MWCNT/PDMS ( ), and f-MWCNT_N-based surfaces (
), and f-MWCNT_N-based surfaces ( ) against (a) E. coli and (b) S. aureus. The means ± standard error for at least three independent experiments are represented. Significant differences are indicated as * (p < 0.05) and ** (p < 0.01).
) against (a) E. coli and (b) S. aureus. The means ± standard error for at least three independent experiments are represented. Significant differences are indicated as * (p < 0.05) and ** (p < 0.01).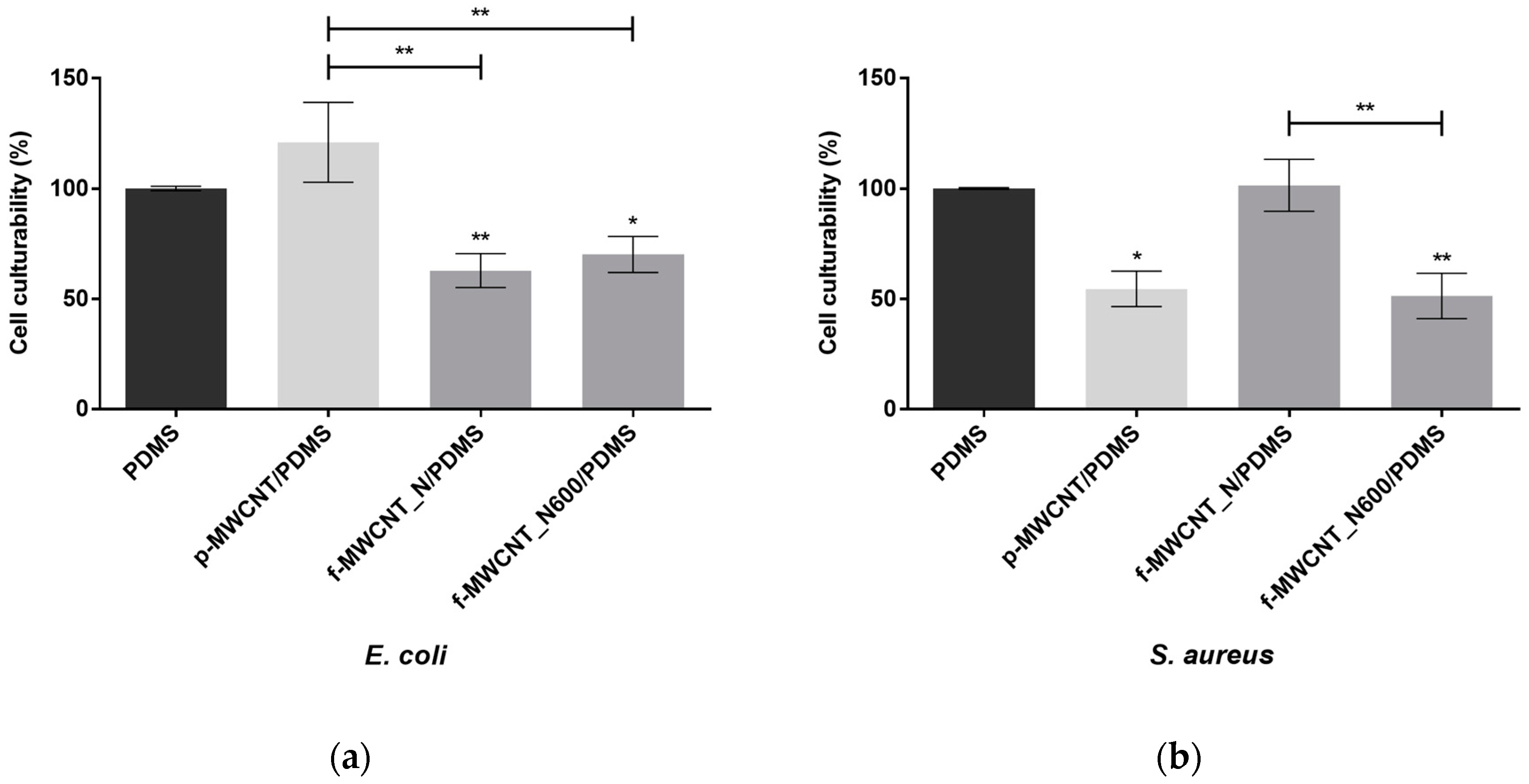


| Sample | SBET (m2 g−1) | Vp P/P0=0.95 (cm3 g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| p-MWCNT | 196 | 0.419 |
| f-MWCNT_N | 210 | 0.408 |
| f-MWCNT_N600 | 223 | 0.432 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, M.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Gomes, L.C.; Sousa-Cardoso, F.; Carvalho, F.M.; Tomé, A.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Whitehead, K.A.; Mergulhão, F.J. Antibiofilm Effect of Nitric Acid-Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Based Surfaces against E. coli and S. aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111620
Gomes M, Teixeira-Santos R, Gomes LC, Sousa-Cardoso F, Carvalho FM, Tomé AR, Soares OSGP, Whitehead KA, Mergulhão FJ. Antibiofilm Effect of Nitric Acid-Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Based Surfaces against E. coli and S. aureus. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(11):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111620
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Marisa, Rita Teixeira-Santos, Luciana C. Gomes, Francisca Sousa-Cardoso, Fábio M. Carvalho, Andreia R. Tomé, Olívia S. G. P. Soares, Kathryn A. Whitehead, and Filipe J. Mergulhão. 2023. "Antibiofilm Effect of Nitric Acid-Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Based Surfaces against E. coli and S. aureus" Antibiotics 12, no. 11: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111620
APA StyleGomes, M., Teixeira-Santos, R., Gomes, L. C., Sousa-Cardoso, F., Carvalho, F. M., Tomé, A. R., Soares, O. S. G. P., Whitehead, K. A., & Mergulhão, F. J. (2023). Antibiofilm Effect of Nitric Acid-Functionalized Carbon Nanotube-Based Surfaces against E. coli and S. aureus. Antibiotics, 12(11), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12111620







