A Narrative Review on the Role of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Characteristics and Profile of Dalbavancin
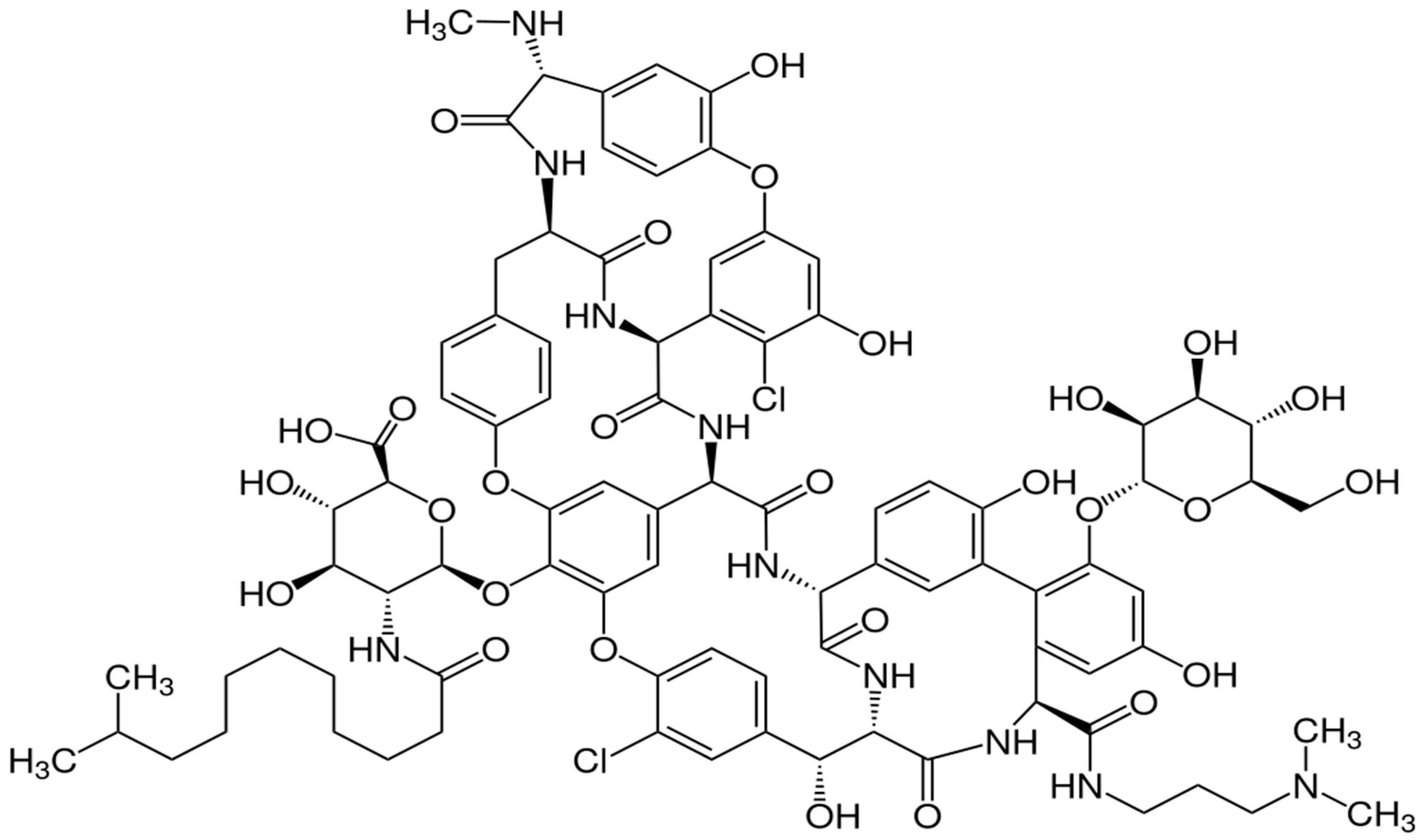
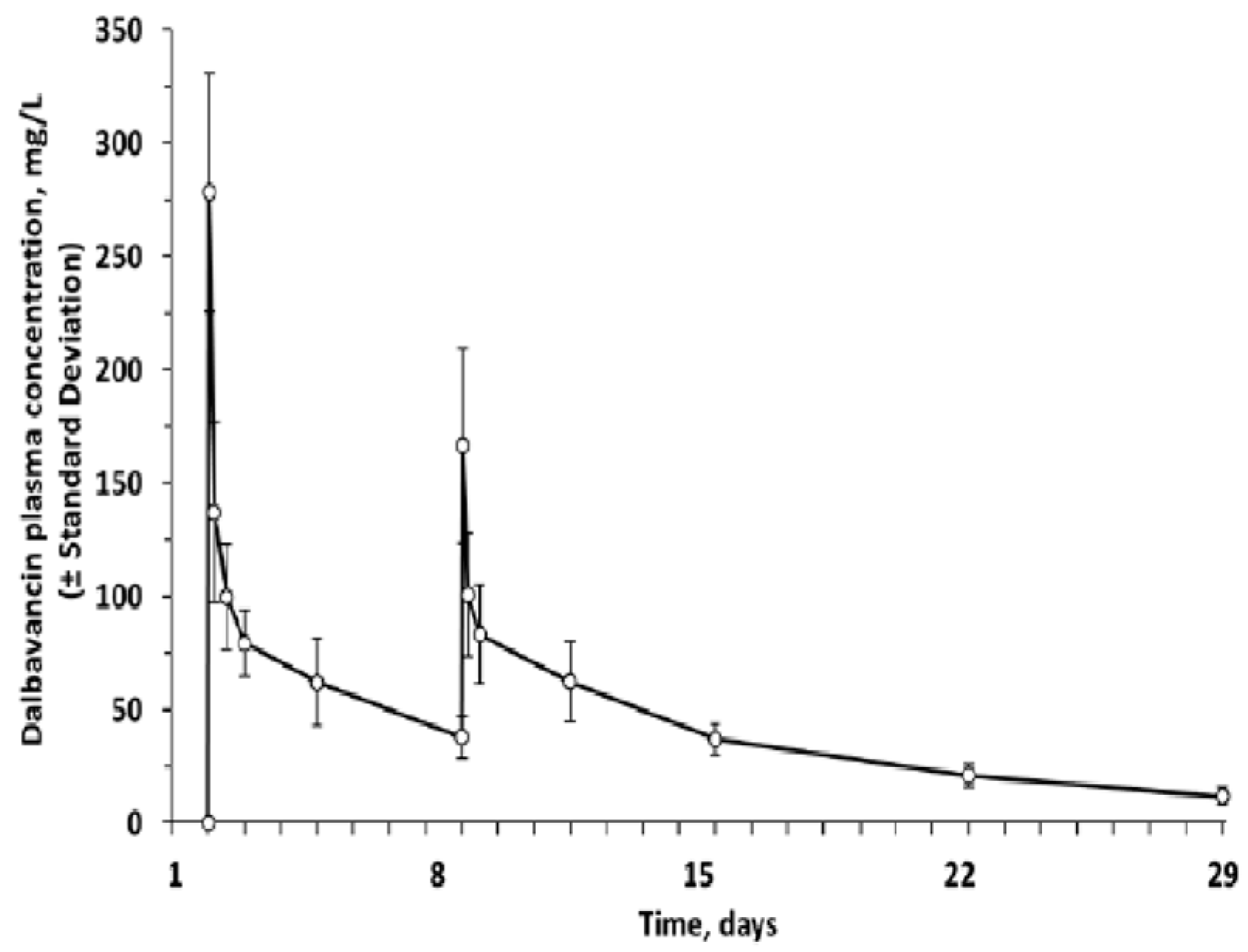
3.1. Pharmacological and Pharmacokinetic Characteristics
3.2. Antimicrobial Characteristics and Activity
3.3. Safety and Tolerability
3.4. Pharmacoeconomic Characteristics
4. Clinical Efficacy of Dalbavancin in BJI
4.1. Dalbavancin Treatment in Native BJI
4.1.1. Dalbavancin Treatment in Osteomyelitis
4.1.2. Dalbavancin Treatment in Septic Arthritis
4.1.3. Dalbavancin Treatment in Spondylodiscitis
4.1.4. Dalbavancin Treatment for Diabetic Foot Infections
4.2. Dalbavancin Treatment in PJI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lew, P.D.P.; Waldvogel, P.F.A. Osteomyelitis. Lancet 2004, 364, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colston, J.; Atkins, B. Bone and Joint Infection. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, C.J.; Holloway, A.M. Bone and Joint Infections. Medicine 2022, 50, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darton, T.; Townsend, R. Bone and Joint Infections. Surgery 2010, 28, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darley, E.S.R.; MacGowan, A.P. Antibiotic Treatment of Gram-Positive Bone and Joint Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, C.R.; Bradley, J.S.; Chatterjee, A.; Copley, L.A.; Robinson, J.; Kronman, M.P.; Arrieta, A.; Fowler, S.L.; Harrison, C.; Carrillo-Marquez, M.A.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2021 Guideline on Diagnosis and Management of Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis in Pediatrics. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 801–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, E.F.; Kanj, S.S.; Kowalski, T.J.; Darouiche, R.O.; Widmer, A.F.; Schmitt, S.K.; Hendershot, E.F.; Holtom, P.D.; Huddleston, P.M.; Petermann, G.W.; et al. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, e26–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bayer, A.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Daum, R.S.; Fridkin, S.K.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Kaplan, S.L.; Karchmer, A.W.; Levine, D.P.; Murray, B.E.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America for the Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in Adults and Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e18–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, L.; Arvieux, C.; Brunschweiler, B.; Touchais, S.; Ansart, S.; Bru, J.-P.; Oziol, E.; Boeri, C.; Gras, G.; Druon, J.; et al. Antibiotic Therapy for 6 or 12 Weeks for Prosthetic Joint Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodise, T.P.; McKinnon, P.S. Burden of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Focus on Clinical and Economic Outcomes. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styers, D.; Sheehan, D.J.; Hogan, P.; Sahm, D.F. Laboratory-Based Surveillance of Current Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns and Trends among Staphylococcus Aureus: 2005 Status in the United States. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2006, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, A.L.S.; Bonfanti, J.W.; Perez, L.R.R.; Pinto, C.C.F.; de Freitas, A.L.P.; Macedo, A.J.; Barth, A.L. High Vancomycin Resistance among Biofilms Produced by Staphylococcus Species Isolated from Central Venous Catheters. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbago, B.M.; Kallen, A.J.; Zhu, W.; Eggers, P.; McDougal, L.K.; Albrecht, V.S. Report of the 13th Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolate from the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, J.N.; Alder, J.; Thorne, G.M.; Tally, F.P. Daptomycin: A Lipopeptide Antibiotic for the Treatment of Serious Gram-Positive Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cave, K.; Gould, I. Daptomycin. Compr. Pharmacol. 2022, 7, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekema, D.J.; Jones, R.N. Oxazolidinone Antibiotics. Lancet 2001, 358, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Preuss, C.V. Linezolid; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Klinker, K.P.; Borgert, S.J. Beyond Vancomycin: The Tail of the Lipoglycopeptides. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 2619–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.C.; Stein, G.E.; Mitra, S.; Abubaker, A.; Havlichek, D.H. Long-Acting Lipoglycopeptides for the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections. Surg. Infect. 2021, 22, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; Bradley, J.S.; Blumer, J.; Yogev, R.; Watt, K.M.; James, L.P.; Palazzi, D.L.; Bhatt-Mehta, V.; Sullivan, J.E.; Zhang, L.; et al. Dalbavancin Pharmacokinetics and Safety in Children 3 Months to 11 Years of Age. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.W.; Puttagunta, S.; Giordano, P.; Krievins, D.; Zelasky, M.; Baldassarre, J. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Single-Dose Versus Weekly Dalbavancin for Treatment of Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.; Summers, K.M. Dalbavancin: A New Lipoglycopeptide Antibiotic. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.P.; Babu, R.J.; Srinivas, N.R. Review of the Pharmacokinetics of Dalbavancin, a Recently Approved Lipoglycopeptide Antibiotic. Infect. Dis. 2017, 49, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbury, T.; Dowell, J.A.; Seltzer, E.; Buckwalter, M. Pharmacokinetics of Dalbavancin in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 49, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andes, D.; Craig, W.A. In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Activity of the Glycopeptide Dalbavancin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, M.W.; Puttagunta, S.; Sprenger, C.R.; Rubino, C.; Van Wart, S.; Baldassarre, J. Extended-Duration Dosing and Distribution of Dalbavancin into Bone and Articular Tissue. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, S.; Krause, R.; Valentin, T.; Prattes, J.; Janata, O.; Lenger, A.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G.; Zollner-Schwetz, I. Multicenter Clinical Experience of Real Life Dalbavancin Use in Gram-Positive Infections. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 81, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappo, U.; Puttagunta, S.; Shevchenko, V.; Shevchenko, A.; Jandourek, A.; Gonzalez, P.L.; Suen, A.; Mas Casullo, V.; Melnick, D.; Miceli, R.; et al. Dalbavancin for the Treatment of Osteomyelitis in Adult Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial of Efficacy and Safety. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofy331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.S.; Puttagunta, S.; Rubino, C.M.; Blumer, J.L.; Dunne, M.; Sullivan, J.E. Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Single Dose Dalbavancin in Children 12–17 Years of Age. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Flamm, R.K.; Castanheira, M.; Sader, H.S.; Mendes, R.E. Dalbavancin In-Vitro Activity Obtained against Gram-Positive Clinical Isolates Causing Bone and Joint Infections in US and European Hospitals (2011–2016). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Mendes, R.E.; Duncan, L.R.; Flamm, R.K.; Sader, H.S. Activity of Dalbavancin and Comparator Agents against Gram-Positive Cocci from Clinical Infections in the USA and Europe 2015–2016. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2748–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Antão, H.S.; Guimarães, J.; Prada, J.; Pires, I.; Martins, Â.; Maltez, L.; Pereira, J.E.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G.; et al. Efficacy of Dalbavancin against MRSA Biofilms in a Rat Model of Orthopaedic Implant-Associated Infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2182–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Miranda, C.; Bezerra, M.; Antão, H.S.; Guimarães, J.; Prada, J.; Pires, I.; Maltez, L.; Pereira, J.E.; Capelo, J.L.; et al. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Dalbavancin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Human Bone Infection. J. Chemother. 2021, 33, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurdy, S.P.; Jones, R.N.; Mendes, R.E.; Puttagunta, S.; Dunne, M.W. In Vitro Activity of Dalbavancin against Drug-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from a Global Surveillance Program. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5007–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Boucher, H.W.; Wilcox, M.; Puttagunta, S. Safety of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Skin and Skin Structure Infections: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized, Comparative Studies. Drug Saf. 2016, 39, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Wilcox, M.; Talbot, G.H.; Puttagunta, S.; Das, A.F.; Dunne, M.W. Once-Weekly Dalbavancin versus Daily Conventional Therapy for Skin Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, L.; Cobo, J.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Guisado Vasco, P.; Ruano, E.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Sánchez Somolinos, M.; González Ruano, P.; Rico Nieto, A.; Arnaiz, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Prolonged Use of Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliseno, M.; Bavaro, D.F.; Brindicci, G.; Luzzi, G.; Carretta, D.M.; Spinarelli, A.; Messina, R.; Miolla, M.P.; Achille, T.I.; Dibartolomeo, M.R.; et al. Dalbavancin Efficacy and Impact on Hospital Length-of-Stay and Treatment Costs in Different Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosz, K.; Al-Hasan, M.N.; Lu, Z.K.; Tabor, B.; Justo, J.A.; Milgrom, A.; Kohn, J.; Bookstaver, P.B. Clinical Utility and Cost Effectiveness of Long-Acting Lipoglycopeptides Used in Deep-Seated Infections among Patients with Social and Economic Barriers to Care. Pharmacy 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Worf, K.; Preisendörfer, B.; Heinlein, W.; Kast, T.; Bodmann, K.-F. Potential Savings through Single-Dose Intravenous Dalbavancin in Long-Term MRSA Infection Treatment—A Health Economic Analysis Using German DRG Data. GMS Infect. Dis. 2019, 7, Doc03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobudic, S.; Forstner, C.; Burgmann, H.; Lagler, H.; Steininger, C.; Traby, L.; Vossen, M.G.; Winkler, S.; Thalhammer, F. Real-World Experience with Dalbavancin Therapy in Gram-Positive Skin and Soft Tissue Infection, Bone and Joint Infection. Infection 2019, 47, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescini, L.; Della Martera, F.; Morroni, G.; Mazzanti, S.; Di Pietrantonio, M.; Mantini, P.; Candelaresi, B.; Pallotta, F.; Olivieri, S.; Iencinella, V.; et al. Use of Dalbavancin in Skin, Bone and Joint Infections: A Real-Life Experience in an Italian Center. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Perry, G.K.; Alhifany, A.A. Dalbavancin versus Standard of Care for the Treatment of Osteomyelitis in Adults: A Retrospective Matched Cohort Study. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Aldieri, C.; Cattelan, A.M.; Raumer, F.; Di Meco, E.; Moioli, M.C.; Tordato, F.; Morelli, P.; Borghi, F.; Rizzi, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSIs) and Other Infections in a Real-Life Setting: Data from an Italian Observational Multicentric Study (DALBITA Study). Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.; Williamson, J.; Luther, V.; Stone, T.; Johnson, J.; Gruss, Z.; Russ-Friedman, C.; Ohl, C.; Beardsley, J. Evaluating the Use of Dalbavancin for Off-Label Indications. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouza, E.; Valerio, M.; Soriano, A.; Morata, L.; Carus, E.G.; Rodríguez-González, C.; Hidalgo-Tenorio, M.C.; Plata, A.; Muñoz, P.; Vena, A.; et al. Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Different Gram-Positive Infections: A Real-Life Experience. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, A.R.; Bremmer, D.N.; Carr, D.R.; Buchanan, C.; Jacobs, M.; Walsh, T.L.; Moffa, M.A.; Shively, N.R.; Trienski, T.L. Effectiveness of Dalbavancin Compared With Standard of Care for the Treatment of Osteomyelitis: A Real-World Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofab589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangour, T.A.; Perry, G.K.; Terriff, C.M.; Alhifany, A.A.; Kaye, K.S. Dalbavancin for the Management of Gram-Positive Osteomyelitis: Effectiveness and Potential Utility. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrisette, T.; Miller, M.A.; Montague, B.T.; Barber, G.R.; Brett McQueen, R.; Krsak, M. On- And off-Label Utilization of Dalbavancin and Oritavancin for Gram-Positive Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez Deida, A.A.; Shihadeh, K.C.; Preslaski, C.R.; Young, H.L.; Wyles, D.L.; Jenkins, T.C. Use of a Standardized Dalbavancin Approach to Facilitate Earlier Hospital Discharge for Vulnerable Patients Receiving Prolonged Inpatient Antibiotic Therapy. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Núñez, M.; Casas-Hidalgo, I.; García-Fumero, R.; Vallejo-Rodríguez, I.; Anguita-Santos, F.; Hernández-Quero, J.; Cabeza-Barrera, J.; Ruiz-Sancho, A. Dalbavancin Is a Novel Antimicrobial against Gram-Positive Pathogens: Clinical Experience beyond Labelled Indications. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2020, 27, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, A.; Duran, C.; Pavese, P.; Khatchatourian, L.; Monnin, B.; Bleibtreu, A.; Denis, E.; Etienne, C.; Rouanes, N.; Mahieu, R.; et al. French National Cohort of First Use of Dalbavancin: A High Proportion of off-Label Use. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bork, J.T.; Heil, E.L.; Berry, S.; Lopes, E.; Davé, R.; Gilliam, B.L.; Amoroso, A. Dalbavancin Use in Vulnerable Patients Receiving Outpatient Parenteral Antibiotic Therapy for Invasive Gram-Positive Infections. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2019, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoletti, M.; Mikus, E.; Pascale, R.; Giannella, M.; Tedeschi, S.; Calvi, S.; Tenti, E.; Tumietto, F.; Viale, P. Clinical Experience with Dalbavancin for the Treatment of Deep Sternal Wound Infection. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryson-Cahn, C.; Beieler, A.M.; Chan, J.D.; Harrington, R.D.; Dhanireddy, S. Dalbavancin as Secondary Therapy for Serious Staphylococcus Aureus Infections in a Vulnerable Patient Population. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jame, W.; Basgut, B.; Abdi, A. Efficacy and Safety of Novel Glycopeptides versus Vancomycin for the Treatment of Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections Including Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgobiani, M.; Burroughs, M.H.; Antadze, T.; Carrothers, T.J.; Riccobene, T.A.; Patel, R.; Lin, T.; Stefanova, P. The Safety and Efficacy of Dalbavancin and Active Comparator in Pediatric Patients With Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, L.; Mantero, M.; Esposito, S. Update on the Management of Pediatric Acute Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovatti, S.; Tiecco, G.; Mulé, A.; Rossi, L.; Sforza, A.; Salvi, M.; Signorini, L.; Castelli, F.; Quiros-Roldan, E. Dalbavancin in Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.M.; Preslaski, C.R.; Shihadeh, K.C.; Hawkins, K.L.; Jenkins, T.C. Multiple-Dose Dalbavancin Regimens as the Predominant Treatment of Deep-Seated or Endovascular Infections: A Scoping Review. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, M.; Bassetti, M.; Corrao, S.; De Rosa, F.G.; Esposito, V.; Falcone, M.; Grossi, P.; Pea, F.; Petrosillo, N.; Tascini, C.; et al. The Role of Dalbavancin for Gram Positive Infections in the COVID-19 Era: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Expert. Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, M.S.; Gallo, R.; Lugarà, M.; Gambardella, M.; Oliva, G.; Bertolino, L.; Andini, R.; Coppola, N.; Zampino, R.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Dalbavancin Treatment for Spondylodiscitis: Multi-Center Clinical Experience and Literature Review. J. Chemother. 2022, 34, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veve, M.P.; Patel, N.; Smith, Z.A.; Yeager, S.D.; Wright, L.R.; Shorman, M.A. Comparison of Dalbavancin to Standard-of-Care for Outpatient Treatment of Invasive Gram-Positive Infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almangour, T.A.; Fletcher, V.; Alessa, M.; Alhifany, A.A.; Tabb, D. Multiple Weekly Dalbavancin Dosing for the Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis Caused by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pitocco, D.; Spanu, T.; Di Leo, M.; Vitiello, R.; Rizzi, A.; Tartaglione, L.; Fiori, B.; Caputo, S.; Tinelli, G.; Zaccardi, F.; et al. Diabetic Foot Infections: A Comprehensive Overview. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, A.; Nachar, O.; Boudet, A.; Loubet, P.; Schuldiner, S.; Cellier, N.; Sotto, A.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Lavigne, J.P. In Vitro Activity of Dalbavancin against Gram-Positive Bacteria Isolated from Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Jiménez, G.; Fuentes-Santos, C.; Moreno-Núñez, L.; Alfayate-García, J.; Campelo-Gutierrez, C.; Sanz-Márquez, S.; Pérez-Fernández, E.; Velasco-Arribas, M.; Hervás-Gómez, R.; Martín-Segarra, O.; et al. Experience in the Use of Dalbavancin in Diabetic Foot Infection. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2022, 40, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupa, C.V.; Lykoudi, E.; Meimeti, E.; Moisoglou, I.; Voyatzoglou, E.D.; Kalantzi, S.; Konsta, E. Successful Treatment of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis with Dalbavancin. Med. Arch. 2020, 74, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Frank, B.J.H.; Hartmann, S.; Hinterhuber, L.; Reitsamer, M.; Aichmair, A.; Dominkus, M.; Söderquist, B.; Hofstaetter, J.G. Dalbavancin in Gram-Positive Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2274–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzón Martín, L.; Mora Fernández, M.; Perales Ruiz, J.M.; Ortega Lafont, M.; Álvarez Paredes, L.; Morán Rodríguez, M.A.; Fernández Regueras, M.; Machín Morón, M.A.; Mejías Lobón, G. Dalbavancin for Treating Prosthetic Joint Infections Caused by Gram-Positive Bacteria: A Proposal for a Low Dose Strategy. A Retrospective Cohort Study. Rev. Esp. Quim. 2019, 32, 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Matt, M.; Duran, C.; Courjon, J.; Lotte, R.; Moing, V.L.; Monnin, B.; Pavese, P.; Chavanet, P.; Khatchatourian, L.; Tattevin, P.; et al. Dalbavancin Treatment for Prosthetic Joint Infections in Real-Life: A National Cohort Study and Literature Review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Sancho, A.; Núñez-Núñez, M.; Castelo-Corral, L.; Martínez-Marcos, F.J.; Lois-Martínez, N.; Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Vinuesa-García, D. Dalbavancin as Suppressive Antibiotic Therapy in Patients with Prosthetic Infections: Efficacy and Safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1185602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldoni, D.; Furustrand Tafin, U.; Aeppli, S.; Angevaare, E.; Oliva, A.; Haschke, M.; Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A. Activity of Dalbavancin, Alone and in Combination with Rifampicin, against Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in a Foreign-Body Infection Model. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knafl, D.; Tobudic, S.; Cheng, S.C.; Bellamy, D.R.; Thalhammer, F. Dalbavancin Reduces Biofilms of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Epidermidis (MRSE). Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žiemytė, M.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.C.; Ventero, M.P.; Mira, A.; Ferrer, M.D. Effect of Dalbavancin on Staphylococcal Biofilms When Administered Alone or in Combination With Biofilm-Detaching Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea, Y.; Lerner, A.; Aizic, A.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Rachi, E.; Dunne, M.W.; Puttagunta, S.; Carmeli, Y. Efficacy of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of MRSA Rat Sternal Osteomyelitis with Mediastinitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pilato, V.; Ceccherini, F.; Sennati, S.; D’Agostino, F.; Arena, F.; D’Atanasio, N.; Di Giorgio, F.P.; Tongiani, S.; Pallecchi, L.; Rossolini, G.M. In Vitro Time-Kill Kinetics of Dalbavancin against Staphylococcus Spp. Biofilms over Prolonged Exposure Times. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouiche, R.O.; Mansouri, M.D. Dalbavancin Compared with Vancomycin for Prevention of Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization of Devices in Vivo. J. Infect. 2005, 50, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Díaz-Navarro, M.; Benjumea, A.; Tormo, M.; Matas, J.; Vaquero, J.; Muñoz, P.; Sanz-Ruíz, P.; Guembe, M. Determination of the Elution Capacity of Dalbavancin in Bone Cements: New Alternative for the Treatment of Biofilm-Related Peri-Prosthetic Joint Infections Based on an In Vitro Study. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
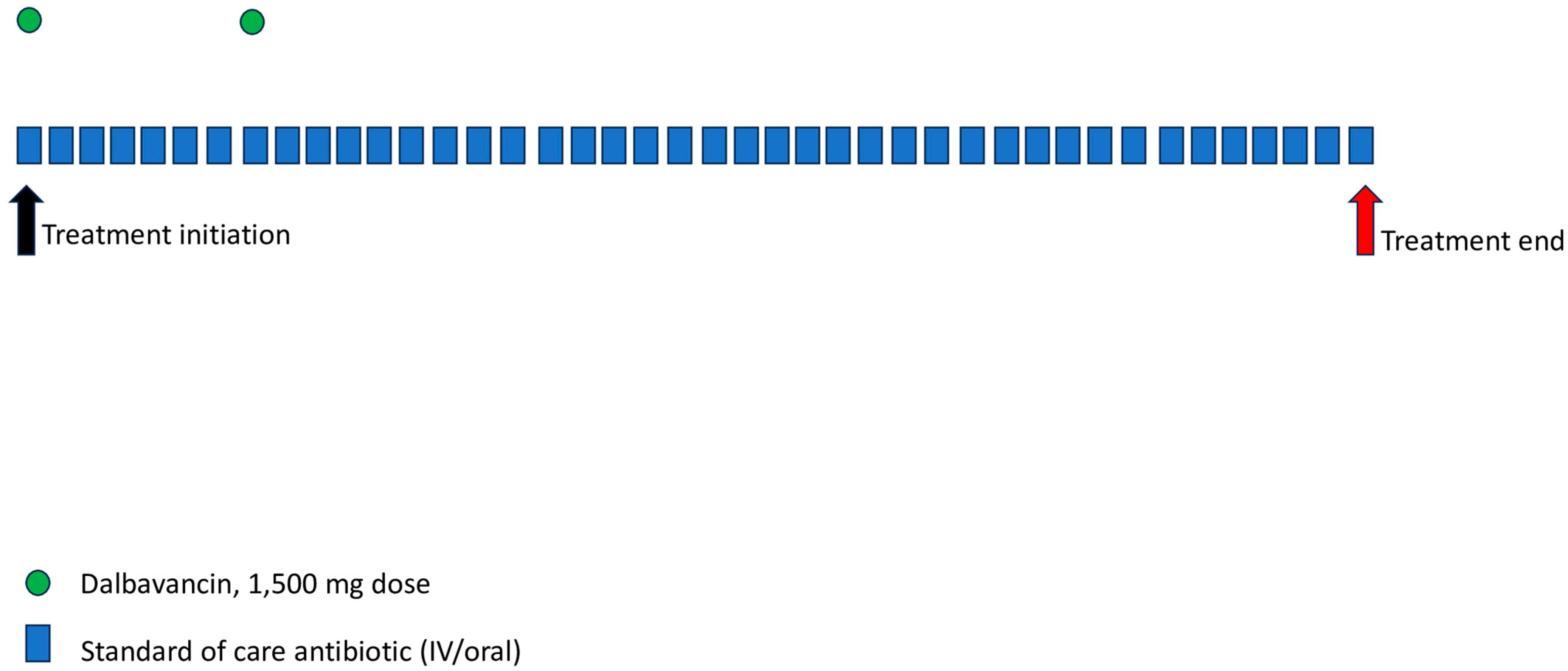
| Dose Regimens of Dalbavancin in BJI | |
|---|---|
| Adults |
|
| |
| Children |
|
| |
| |
| |
| Nausea Vomiting Abdominal pain Headache Rash Pruritus Urinary tract infections Constipation Diarrhea |
| Authors (Year) [Ref] | Design | Sample Size | Dalbavancin Regimen | Follow-Up | Clinical Outcome | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bouza et al. (2018) [39] | Retrospective | 12 | 2 doses of 1500 mg 1 week apart, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly Median duration: 3 weeks (range 1–24) | ≥1 month | Clinical success: 92% | AE in 13% of the patients |
| Nunez-Nunez et al. (2018) [44] | Prospective observational | 6 | 2 doses of 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 smg weekly | 3 months | Clinical success: 100% | Mild AE in 4.5% of the patients |
| Rappo et al. (2019) [20] | Prospective, RCT | 80 Dalbavancin: 70 vs. SOC: 10 | 2 doses of 1500 mg 1 week apart | 12 months | Clinical cure: 94% at day 21, 97% at day 42 and 96% at 6 months and 1 year | Treatment-emergent AE in 10 (14.3%) patients |
| Tobudic et al. (2019) [19] | Retrospective | 20 | Various regimens: 1500 mg × 1, followed by 1000 mg every 2 weeks, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly, or 2 doses of 1500 mg 1 week apart Median duration: 8 weeks (range 4–32) | 6 months | Clinical cure: 60% | Mild AE, such as exanthema, nausea, and hyperglycaemia, in 5% of the patients |
| Wunsch et al. (2019) [19] | Retrospective | 30 | Various regimens: 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly Median doses: 3 (range 1–32) | 3 months | Clinical success: 89% | Mild AE in 3% of the patients |
| Almangour et al. (2019) [41] | Retrospective | 31 | Various regimens: 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly Median doses: 3 (range 1–14) | 3 months | Clinical cure: 90% | None |
| Morata et al. (2019) [30] | Retrospective | 19 | Various regimens: 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg weekly Median doses: 2 (IQR 2–4) | Median: 164 days (IQR:93–262.5) | Clinical success: 89.5% | Mild AE in 7 patients |
| Morrisette et al. (2019) [42] | Retrospective | 15 | NA | Median: 6.1 months (IQR: 3.7–11.8) | Clinical success: 92% | Mild AE in 11% of the patients |
| Bryson-Cahn et al. (2019) [48] | Retrospective | 7 | Various regimens: 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg weekly Median doses: 1 (IQR 1–5) | 1–12 months | Clinical cure: 71.4% | None |
| Bork et al. (2019) [46] | Retrospective | 13 | NA Median doses: 3 (IQR 4.5) | 3 months | Clinical success: 46% at 30 days | 1 patient with generalized pruritus and rash and 1 patient with acute kidney injury |
| Dinh et al. (2019) [45] | Retrospective | 48 | Various regimens: 2 doses of 1500 mg weekly, or 1500 mg every 2 weeks, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly/every 2 weeks Median duration: 14 days (IQR: 14–19.25) | Mean: 87.8 ± 86.9 days | Clinical cure: 76.1% | Mild AE in 5 patients |
| Bartoletti et al. (2019) [47] | Retrospective | 15 | 2 doses of 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly Median doses: 4 | 6 months | Clinical cure: 93% at 6 months | None |
| Bai et al. (2020) [37] | Retrospective | 29 | 1500 mg weekly Maximum 7 doses | 1–3 months | Clinical cure: 89.7% | Mild AE in 5.4% of the patients |
| Almangour et al. (2020) [36] | Retrospective Matched cohort study | 21 Dalbavancin:11 vs. SOC:10 | Various regimens: 1500 mg weekly, or 1000 mg × 1, followed by 500 mg weekly Median duration: 42 days (IQR 5) | 3 months | Clinical cure: 100% | None |
| Vazquez Deida et al. (2020) [43] | Retrospective | 5 | 1500 mg × 1 | 3 months | Clinical cure: 80% | Mild AE in 7% of the patients |
| Brescini et al. (2021) [35] | Retrospective | 8 | Various regimens: 2 doses of 1500 mg weekly, or 1500 mg every 2 weeks Median doses: 1 (IQR: 1–9) | 1–3 months | Clinical success: 100% | Rash in 1 patient |
| Cain et al. (2021) [40] | Retrospective | 132 Dalbavancin: 42 vs. SOC: 90 | 2 doses of 1500 mg weekly | 12 months | Clinical cure: 78.6% | Mild AE in 21.4% of the patients |
| Taylor et al. (2022) [38] | 26 | 1500 mg weekly Range: 1–4 doses | 3 months | Clinical success: 87% | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimopoulou, D.; Mantadakis, E.; Koutserimpas, C.; Samonis, G. A Narrative Review on the Role of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101492
Dimopoulou D, Mantadakis E, Koutserimpas C, Samonis G. A Narrative Review on the Role of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(10):1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101492
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimopoulou, Dimitra, Elpis Mantadakis, Christos Koutserimpas, and George Samonis. 2023. "A Narrative Review on the Role of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections" Antibiotics 12, no. 10: 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101492
APA StyleDimopoulou, D., Mantadakis, E., Koutserimpas, C., & Samonis, G. (2023). A Narrative Review on the Role of Dalbavancin in the Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections. Antibiotics, 12(10), 1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101492






