What Is the Most Reliable Concordance Rate of Preoperative Synovial Fluid Aspiration and Intraoperative Biopsy to Detect Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Knee, Hip and Shoulder Arthroplasty?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patients
4.2. Diagnostic Tests
4.3. Outcome Measures
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sangaletti, R.; Zanna, L.; Akkaya, M.; Sandiford, N.; Ekhtiari, S.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. Periprosthetic joint infection in patients with multiple arthroplasties. Bone Joint J. 2023, 105-B, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Fassihi, S.C.; Enayatollahi, M.A. Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop. Clin. North. Am. 2016, 47, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, A.; Tan, T.L.; Chen, A.F.; Maltenfort, M.G.; Parvizi, J. In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 948–952.e941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Parvizi, J.; Hansen, E.N.; Culvern, C.N.; Segreti, J.C.; Tan, T.; Hartman, C.W.; Sporer, S.M.; Della Valle, C.J.; Knee Society Research Group. 2020 Mark Coventry Award: Microorganism-directed oral antibiotics reduce the rate of failure due to further infection after two-stage revision hip or knee arthroplasty for chronic infection: A multicentre randomized controlled trial at a minimum of two years. Bone Joint J. 2020, 102-B, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, P.; Dlaska, C.E.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A.; Renz, N. Preoperative synovial fluid culture poorly predicts the pathogen causing periprosthetic joint infection. Infection 2021, 49, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Morawietz, L.; Hasart, O.; Strube, P.; Perka, C.; Tohtz, S. Diagnosis of periprosthetic infection following total hip arthroplasty--evaluation of the diagnostic values of pre- and intraoperative parameters and the associated strategy to preoperatively select patients with a high probability of joint infection. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2008, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schaik, T.J.A.; de Jong, L.D.; van Meer, M.P.A.; Goosen, J.H.M.; Somford, M.P. The concordance between preoperative synovial fluid culture and intraoperative tissue cultures in periprosthetic joint infection: A systematic review. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2022, 7, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Sebillotte, M.; Lomas, J.; Taylor, A.; Palomares, E.B.; Murillo, O.; Parvizi, J.; Shohat, N.; Reinoso, J.C.; Sanchez, R.E.; et al. Clinical outcome and risk factors for failure in late acute prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and implant retention. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, F.; Martinez-Pastor, J.C.; Garcia-Ramiro, S.; Bori, G.; Macule, F.; Sierra, J.; Font, L.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. Outcome and predictors of treatment failure in early post-surgical prosthetic joint infections due to Staphylococcus aureus treated with debridement. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, I.G.; Vles, G.; Busch, S.M.; Frommelt, L.; Gehrke, T.; Salber, J.; Citak, M. Septic Failure After One-Stage Exchange for Prosthetic Joint Infection of the Hip: Microbiological Implications. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, G.; Zhou, S. Comparable clinical outcomes of culture-negative and culture-positive periprosthetic joint infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holleyman, R.J.; Deehan, D.J.; Charlett, A.; Gould, K.; Baker, P.N. Does pre-operative sampling predict intra-operative cultures and antibiotic sensitivities in knee replacements revised for infection?: A study using the NJR dataset. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 3056–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter-Parrat, V.; Ronde-Oustau, C.; Boeri, C.; Gaudias, J.; Jenny, J.Y. Agreement between pre-operative and intra-operative bacteriological samples in 85 chronic peri-prosthetic infections. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, P.; Neyt, J.; Depypere, M.; Goris, S.; Van Wijngaerden, E.; Verhaegen, J.; Wauters, J.; Spriet, I. Preoperative joint aspiration culture results and causative pathogens in total hip and knee prosthesis infections: Mind the gap. Acta Clin. Belg. 2020, 75, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, K.K.; Kapadia, M.; Chiu, Y.F.; Khilnani, T.; Miller, A.O.; Henry, M.W.; Lyman, S.; Carli, A.V. The James A. Rand Young Investigator’s Award: Are Intraoperative Cultures Necessary If the Aspiration Culture Is Positive? A Concordance Study in Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.; Tang, A.; Rozell, J.C.; Babb, J.S.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Lin, D. Factors predicting hip joint aspiration yield or “dry taps” in patients with total hip arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottinger, P.; Butler-Wu, S.; Neradilek, M.B.; Merritt, A.; Bertelsen, A.; Jette, J.L.; Warme, W.J.; Matsen, F.A., 3rd. Prognostic factors for bacterial cultures positive for Propionibacterium acnes and other organisms in a large series of revision shoulder arthroplasties performed for stiffness, pain, or loosening. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangehl, M.J.; Masri, B.A.; O’Connell, J.X.; Duncan, C.P. Prospective analysis of preoperative and intraoperative investigations for the diagnosis of infection at the sites of two hundred and two revision total hip arthroplasties. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1999, 81, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerst, M.; Fink, B.; Ruther, W. The value of preoperative knee aspiration and arthroscopic biopsy in revision total knee arthroplasty. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 2005, 143, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Arco, A.; Bertrand, M.L. The diagnosis of periprosthetic infection. Open Orthop. J. 2013, 7, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tande, A.J.; Patel, R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 302–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trampuz, A.; Hanssen, A.D.; Osmon, D.R.; Mandrekar, J.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Synovial fluid leukocyte count and differential for the diagnosis of prosthetic knee infection. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, R.; Berendt, A.R.; Athanasou, N.A.; The OSIRIS Collaborative Study Group. Histological and microbiological findings in non-infected and infected revision arthroplasty tissues. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2000, 120, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xu, C.; Hao, L.; Chai, W.; Jun, F.; Chen, J. The concordance between preoperative aspiration and intraoperative synovial fluid culture results: Intraoperative synovial fluid re-cultures are necessary whether the preoperative aspiration culture is positive or not. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiddema, J.S. Periprosthetic joint infection: A South African perspective. South Afr. Med. J. 2023, 113, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huotari, K.; Vuorinen, M.; Vasara, A. Debridement, antimicrobials, and implant retention in the treatment of late acute and early acute Staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infections. Infect. Dis. 2023, 55, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiovine, C.; Pellegrino, L.; Bulgarelli, A.; Lauta, F.C.; Di Claudio, A.; Ciceri, R.; Cancellara, A.; Calcaterra, F.; Mavilio, D.; Grappiolo, G.; et al. Interaction of Bacteria, Immune Cells, and Surface Topography in Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, T.; Jiang, K.; Lv, J.; Huang, J. Pathogenic bacteria characteristics and drug resistance in acute, delayed, and chronic periprosthetic joint infection: A retrospective analysis of 202 patients. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, M.; Vles, G.; Sangaletti, R.; Zanna, L.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. What is the Safe Distance Between Hip and Knee Implants to Reduce the Risk of Ipsilateral Metachronous Periprosthetic Joint Infection? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2023, 481, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.S.; Olszewski, A.M.; Bedi, A. A Microcurrent Dressing Reduces Cutibacterium Acnes Colonization in Patients Undergoing Shoulder Arthroplasty or Arthroscopy: A Prospective Case Series. HSS J. 2023, 19, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.E.; Vaughan, A.K.; Cox, R.M.; Alfonsi, S.; Belden, K.A.; Namdari, S. Shoulder periprosthetic joint infection is associated with increased mortality. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2023, 32, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanna, L.; Sangaletti, R.; Akkaya, M.; Shen, T.; Abuljadail, S.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. What is the concordance rate of preoperative synovial fluid aspiration and intraoperative biopsy in detecting periprosthetic joint infection of the shoulder? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2023, 32, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unter Ecker, N.; Suero, E.M.; Gehrke, T.; Haasper, C.; Zahar, A.; Lausmann, C.; Hawi, N.; Citak, M. Serum C-reactive protein relationship in high- versus low-virulence pathogens in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T.; International Consensus Group on Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Definition of periprosthetic joint infection. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, V.T.; Liebisch, M.; Kolbel, B.; Renz, N.; Gehrke, T.; Huber, M.; Krukemeyer, M.G.; Trampuz, A.; Resch, H.; Krenn, V. CD15 focus score: Infection diagnosis and stratification into low-virulence and high-virulence microbial pathogens in periprosthetic joint infection. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W.; Moser, C. Pathogenesis and treatment concepts of orthopaedic biofilm infections. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, T.; Trampuz, A.; Hardt, S.; Janz, V.; Kleber, C.; Perka, C. Periprosthetic infection after hip arthroplasty. Orthopade 2014, 43, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, D.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A.; Renz, N. Outcome of hip and knee periprosthetic joint infections caused by pathogens resistant to biofilm-active antibiotics: Results from a prospective cohort study. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2018, 138, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, P.; Fink, B.; Sandow, D.; Margull, A.; Berger, I.; Frommelt, L. Prolonged bacterial culture to identify late periprosthetic joint infection: A promising strategy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Piper, K.E.; Jacobson, M.J.; Hanssen, A.D.; Unni, K.K.; Osmon, D.R.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Cockerill, F.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Greenleaf, J.F.; et al. Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

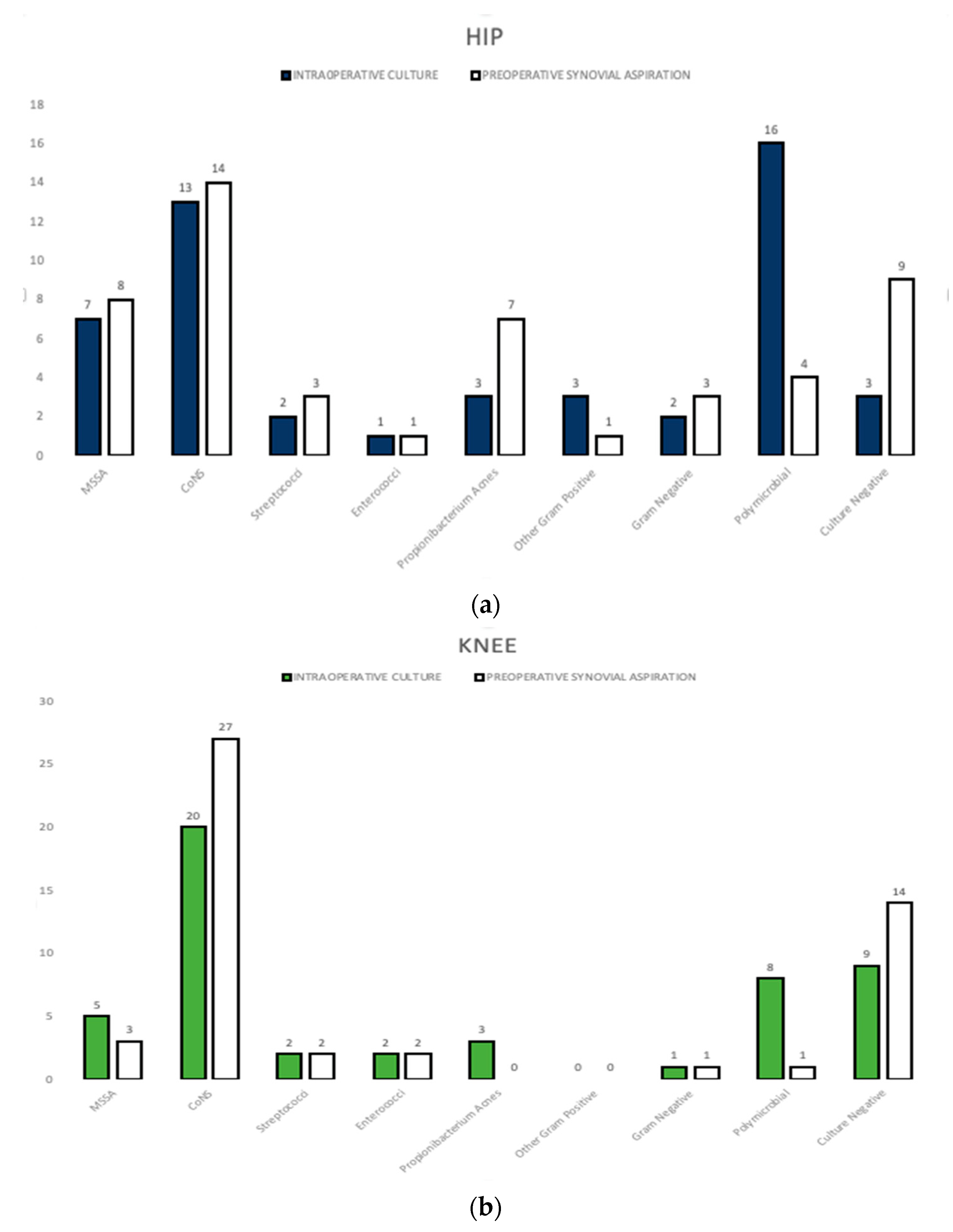

| Demographic Information and Organism Profile | Total | Concordant 1 | Discordant 2 | p1&2 Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 150 | 85 (56.7%) | 65 (43.3%) | |
| Age (years) | 69.21 ± 11.71 | 67.31 ± 11.65 | 71.69 ± 11.40 | 0.011 * |
| BMI | 30.6 ± 12.98 | 31.78 ± 16.63 | 29.08 ± 5.04 | 0.317 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 80 (53.3%) | 43 (50.6%) | 37 (56.9%) | |
| Female | 70 (46.7%) | 42 (49.4%) | 28 (43.1%) | 0.441 |
| Side | ||||
| Right | 80 (53.3%) | 46 | 34 | |
| Left | 70 (46.7%) | 39 | 31 | 0.826 |
| Organism | ||||
| Staphylococci | 52 | 42 | 10 | 0.0001 * |
| MRSA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MSSA | 13 | 9 | 4 | 0.394 |
| CoNS | 39 | 33 | 6 | 0.0004 * |
| Enterococcus | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Streptococcus | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0.133 |
| Propionibacterium acnes | 31 | 21 | 10 | 0.162 |
| Other Gram positive | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0.079 |
| Gram negative | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0.019 * |
| Polymicrobial | 36 | 2 | 34 | <0.0001 * |
| Culture negative | 14 | 7 | 7 | 0.597 |
| Hip 1 | Knee 2 | Shoulder 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median (Min.–Max.) | Mean ± SD | Median (Min.–Max.) | Mean ± SD | Median (Min.–Max.) | p1&2 | p1&3 | p2&3 | |
| Age at time of operation (years) | 70.5 ± 11.9 | 72.6 (40–92.7) | 69.7 ± 11.6 | 69.9 (43–88.4) | 67.5 ± 11.7 | 69.2 (44.3–89.3) | 0.909 | 0.391 | 0.611 |
| Height (cm) | 169.3 ± 14.4 | 170 (100–196) | 172.7 ± 9.1 | 171 (151–190) | 171.4 ± 9.1 | 170 (151–188) | 0.290 | 0.641 | 0.838 |
| Weight (kg) | 90.7 ± 23.4 | 85 (48–173) | 87.3 ± 19.3 | 83 (54–139) | 87.0 ± 19.9 | 82 (55–139) | 0.700 | 0.659 | 0.998 |
| BMI | 30.1 ± 5.9 | 30.3 (17.3–44.9) | 29.2 ± 5.6 | 29.0 (19.0–41.5) | 29.4 ± 5.5 | 29.9 (19.0–41.5) | 0.669 | 0.809 | 0.970 |
| Sex | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Male | 27 | 54.0 | 27 | 54.0 | 26 | 52.0 | |||
| Female | 23 | 46.0 | 23 | 56.0 | 24 | 48.0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Side | |||||||||
| Right | 32 | 64.0 | 25 | 50.0 | 24 | 48.0 | |||
| Left | 18 | 36.0 | 25 | 50.0 | 26 | 52.0 | 0.225 | 0.158 | 1.00 |
| Correct identification of bacteria with aspiration | |||||||||
| No | 23 | 46.0 | 20 | 40.0 | 22 | 44.0 | |||
| Yes | 27 | 54.0 | 30 | 60.0 | 28 | 56.0 | 0.544 | 0.841 | 0.685 |
| Hip 1 | Knee 2 | Shoulder 3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | p | p1&2 | p1&3 | p2&3 | |
| Intraoperative | ||||||||||
| Virulence | ||||||||||
| Low virulence | 28 | 56.0 | 30 | 60.0 | 44 | 88.0 | 0.0004 | 0.074 | 0.0011 | 0.056 |
| High virulence | 19 | 38.0 | 11 | 22.0 | 4 | 8.0 | ||||
| Culture negative | 3 | 6.0 | 9 | 18.0 | 2 | 4.0 | ||||
| Gram | ||||||||||
| Gram− | 2 | 4.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 4 | 8.0 | 0.088 | 0.104 | 0.662 | 0.070 |
| Gram+ | 29 | 58.0 | 32 | 64.0 | 32 | 64.0 | ||||
| Polymicrobial | 16 | 32.0 | 8 | 16.0 | 12 | 24.0 | ||||
| Culture negative | 3 | 6.0 | 9 | 18.0 | 2 | 4.0 | ||||
| Difficult to treat | ||||||||||
| No | 39 | 78.0 | 36 | 72.0 | 47 | 94.0 | 0.030 | 0.148 | 0.040 | 0.013 |
| Yes | 8 | 16.0 | 5 | 10.0 | 1 | 2.0 | ||||
| Culture negative | 3 | 6.0 | 9 | 18.0 | 2 | 4.0 | ||||
| Preoperative | ||||||||||
| Virulence | ||||||||||
| Low virulence | 24 | 48.0 | 30 | 60.0 | 38 | 76.0 | 0.002 | 0.029 | 0.003 | 0.225 |
| High virulence | 17 | 34.0 | 6 | 12.0 | 4 | 8.0 | ||||
| Culture negative | 9 | 18.0 | 14 | 28.0 | 8 | 16.0 | ||||
| Gram | ||||||||||
| Gram− | 3 | 6.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 3 | 6.0 | 0.214 | 0.246 | 0.246 | 0.364 |
| Gram+ | 32 | 64.0 | 34 | 68.0 | 38 | 76.0 | ||||
| Polymicrobial | 6 | 12.0 | 2 | 2.0 | 1 | 2.0 | ||||
| Culture negative | 9 | 18.0 | 14 | 28.0 | 8 | 16.0 | ||||
| Difficult to treat | ||||||||||
| No | 36 | 72.0 | 33 | 66.0 | 41 | 82.0 | 0.234 | 0.423 | 0.217 | 0.173 |
| Yes | 5 | 10.0 | 3 | 6.0 | 1 | 2.0 | ||||
| Culture negative | 9 | 18.0 | 14 | 28.0 | 8 | 16.0 | ||||
| Intraoperative | Preoperative | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Hip | |||||
| Virulence | |||||
| Low virulence | 28 | 56.0 | 24 | 48.0 | 0.181 |
| High virulence | 19 | 38.0 | 17 | 34.0 | |
| Culture negative | 3 | 6.0 | 9 | 18.0 | |
| Gram | |||||
| Gram− | 2 | 4.0 | 3 | 6.0 | 0.048 |
| Gram+ | 29 | 58.0 | 32 | 64.0 | |
| Polymicrobial | 16 | 32.0 | 6 | 12.0 | |
| Culture negative | 3 | 6.0 | 9 | 18.0 | |
| Difficult to treat | |||||
| No | 39 | 78.0 | 36 | 72.0 | 0.148 |
| Yes | 8 | 16.0 | 5 | 10.0 | |
| Culture negative | 3 | 6.0 | 9 | 18.0 | |
| Knee | |||||
| Virulence | |||||
| Low virulence | 30 | 60.0 | 30 | 60.0 | 0.278 |
| High virulence | 11 | 22.0 | 6 | 12.0 | |
| Culture negative | 9 | 18.0 | 14 | 28.0 | |
| Gram | |||||
| Gram− | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 2.0 | 0.086 |
| Gram+ | 32 | 64.0 | 34 | 68.0 | |
| Polymicrobial | 8 | 16.0 | 1 | 2.0 | |
| Culture negative | 9 | 18.0 | 14 | 28.0 | |
| Difficult to treat | |||||
| No | 36 | 72.0 | 33 | 66.0 | 0.423 |
| Yes | 5 | 10.0 | 3 | 6.0 | |
| Culture negative | 9 | 18.0 | 14 | 28.0 | |
| Shoulder | |||||
| Virulence | |||||
| Low virulence | 44 | 88.0 | 38 | 76.0 | 0.132 |
| High virulence | 4 | 8.0 | 4 | 8.0 | |
| Culture negative | 2 | 4.0 | 8 | 16.0 | |
| Gram | |||||
| Gram− | 4 | 8.0 | 3 | 6.0 | 0.003 |
| Gram+ | 32 | 64.0 | 38 | 76.0 | |
| Polymicrobial | 12 | 24.0 | 1 | 2.0 | |
| Culture negative | 2 | 4.0 | 8 | 16.0 | |
| Difficult to treat | |||||
| No | 47 | 94.0 | 41 | 82.0 | 0.134 |
| Yes | 1 | 2.0 | 1 | 2.0 | |
| Culture negative | 2 | 4.0 | 8 | 16.0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akkaya, M.; Zanna, L.; Sangaletti, R.; Bokhari, A.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. What Is the Most Reliable Concordance Rate of Preoperative Synovial Fluid Aspiration and Intraoperative Biopsy to Detect Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Knee, Hip and Shoulder Arthroplasty? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101482
Akkaya M, Zanna L, Sangaletti R, Bokhari A, Gehrke T, Citak M. What Is the Most Reliable Concordance Rate of Preoperative Synovial Fluid Aspiration and Intraoperative Biopsy to Detect Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Knee, Hip and Shoulder Arthroplasty? Antibiotics. 2023; 12(10):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101482
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkkaya, Mustafa, Luigi Zanna, Rudy Sangaletti, Ali Bokhari, Thorsten Gehrke, and Mustafa Citak. 2023. "What Is the Most Reliable Concordance Rate of Preoperative Synovial Fluid Aspiration and Intraoperative Biopsy to Detect Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Knee, Hip and Shoulder Arthroplasty?" Antibiotics 12, no. 10: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101482
APA StyleAkkaya, M., Zanna, L., Sangaletti, R., Bokhari, A., Gehrke, T., & Citak, M. (2023). What Is the Most Reliable Concordance Rate of Preoperative Synovial Fluid Aspiration and Intraoperative Biopsy to Detect Periprosthetic Joint Infection in Knee, Hip and Shoulder Arthroplasty? Antibiotics, 12(10), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101482






