Quercetin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Choline Kinase of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hibiscus and Saint-John’s Wort Inhibit sChoK Activity and S. pneumoniae Cell Growth
2.2. Quercetin Is an Inhibitor of sChoK and Has Antimicrobial Activity against S. pneumoniae
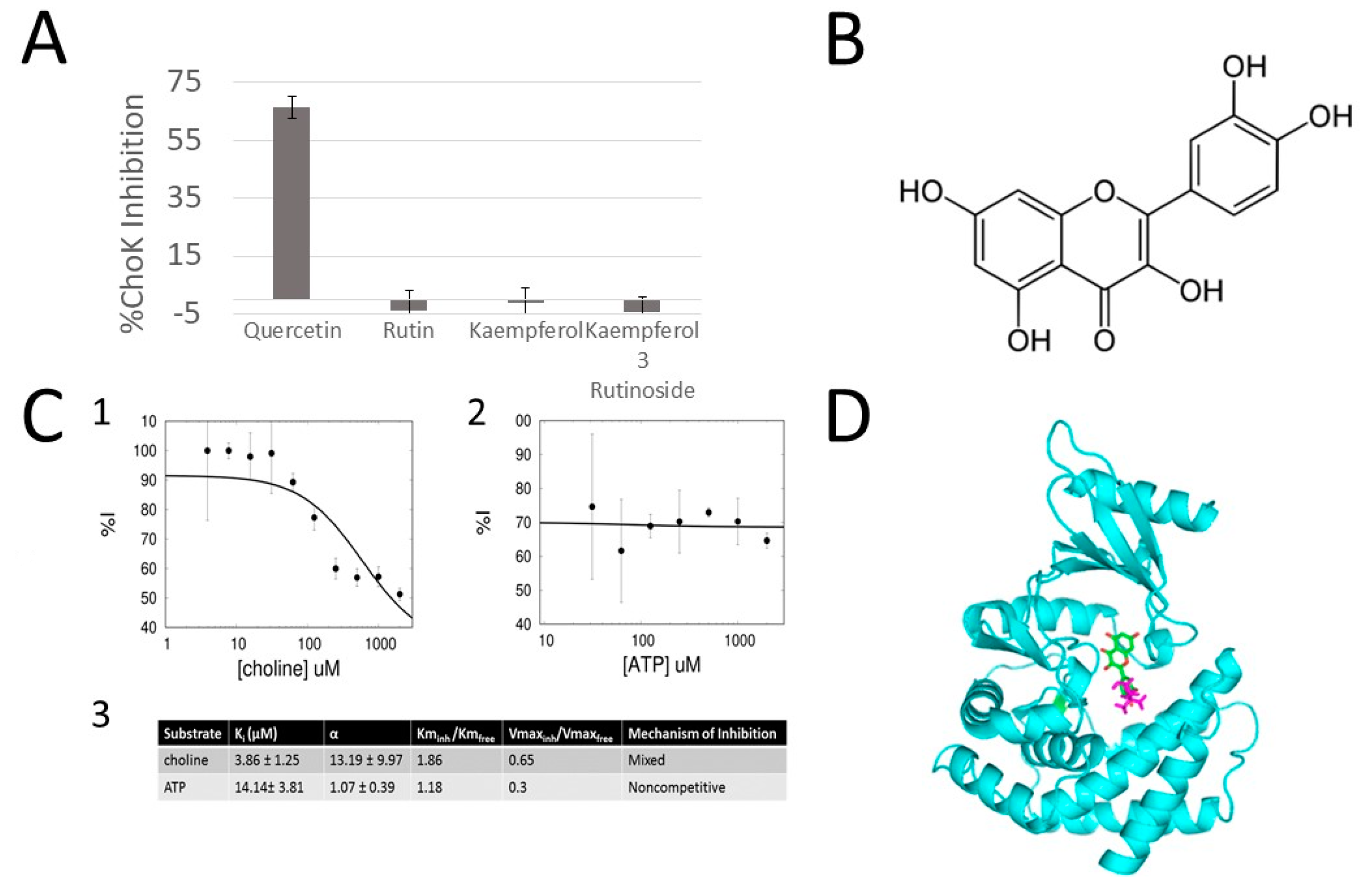
2.3. Quercetin Is a Competitive Inhibitor of sChoK
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Production of Tea Extracts
3.2. Determining IC50 Colorimetrically
3.3. Determining Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) by Broth Culture
3.4. Measuring Inhibitory Activity of Tea Extracts by Plating
3.5. Recombinant sChoK Expression and Purification
3.6. Colorimetric Method of Detection for Measuring IC50 of Plant Extracts
3.7. Determining Querecetin Competitivity by LDH/pK
3.8. Docking of Querecetin onto the Crystal Structure of sChoK
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmerman, T.; Lacal Sanjuan, J.C.; Ibrahim, S.A. Choline Kinase Emerges as a Promising Drug Target in Gram-Positive Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 6, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, B.M.; Kobosil, S.C.K.; Teichert, J.F. Catalytic hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid derivatives using copper(i)/N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2293–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, T.; Ibrahim, S. Choline Kinase, A Novel Drug Target for the Inhibition of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, T.; Chasten, V.; Lacal, J.C.; Ibrahim, S.A. Identification and validation of novel and more effective choline kinase inhibitors against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez-Braun, A.; Ravelo, A.G.; Pérez-Sacau, E.; Lacal, J.C. A new family of choline kinase inhibitors with antiproliferative and antitumor activity derived from natural products. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2015, 17, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aad, G.; Abbott, B.; Abdallah, J.; Abdinov, O.; Aben, R.; Abolins, M.; AbouZeid, O.S.; Abramowicz, H.; Abreu, H.; Abreu, R.; et al. Combined Measurement of the Higgs Boson Mass in pp Collisions at and 8 with the ATLAS and CMS Experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 191803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, G.C.; Gillespie, S.H. Incorporation of choline intoStreptococcus pneumoniaecell wall antigens: Evidence for choline kinase activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 138, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundling, A.; Schneewind, O. Synthesis of glycerol phosphate lipoteichoic acid in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8478–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N.M.; Foote, S.J.; Wakarchuk, W.W. Review of phosphocholine substituents on bacterial pathogen glycans: Synthesis, structures and interactions with host proteins. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 56, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, N.; Waldow, F.; Kohler, T.P.; Rohde, M.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Gomez-Mejia, A.; Hain, T.; Schwudke, D.; Vollmer, W.; Ham-merschmidt, S.; et al. Lipoteichoic acid deficiency permits normal growth but impairs virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsburg, I. Role of lipoteichoic acid in infection and inflammation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denapaite, D.; Brückner, R.; Hakenbeck, R.; Vollmer, W. Biosynthesis of Teichoic Acids in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Closely Related Species: Lessons from Genomes. Microb. Drug Resist. 2012, 18, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verónica María, G.R.; Cindy María Auxiliadora, G.S.; Daiva María, M.G.; Héctor David, N.; Francisco, F.; Griselda, F.; Liz, K.; Heriberto, N. Actividad antibacteriana in vitro de Maytenus ilicifolia Martius sobre Streptococcus mutans y Staphylococcus aureus. Investig. Estud.—UNA 2020, 11, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Shushni, M.A.M.; Belkheir, A. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Mentha piperita L. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimica-Dukic, N.; Bozin, B.; Sokovic, M.; Simin, N. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Melissa officinalis L. (Lami-aceae) Essential Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2485–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mármol, I.; Sánchez-De-Diego, C.; Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Ancín-Azpilicueta, C.; Rodríguez-Yoldi, M.J. Therapeutic Applications of Rose Hips from Different Rosa Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.J.; Hjelmqvist, D.; López-Alarcón, C.; Karamehmedovic, N.; Minehan, T.G.; Yepremyan, A.; Salehani, B.; Lissi, E.; Joubert, E.; Udekwu, K.I.; et al. Anti-Peroxyl Radical Quality and Antibacterial Properties of Rooibos Infusions and Their Pure Glycosylated Polyphenolic Constituents. Molecules 2013, 18, 11264–11280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, Y.W.; Chuah, L.O.; Ahmad, R.; Bhat, R. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.) and Cassia (Senna bicapsularis L.) flower extracts. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2013, 25, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avato, P.; Raffo, F.; Guglielmi, G.; Vitali, C.; Rosato, A. Extracts from St John’s wort and their antimicrobial activity. Phytotherapy Res. 2004, 18, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, X.; Ferchaud, V.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, H.; Tang, F.; Yue, Y.; Chin, K.L. Variations in chemical fingerprints and major flavonoid contents from the leaves of thirty-one accessions of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 30, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Chaudry, M.T.; Wang, M.; Xiao, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, W. Bacteriostatic Effect of Quercetin as an Antibiotic Alternative In Vivo and Its Antibacterial Mechanism In Vitro. J. Food Prot. 2017, 81, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, T.; Ibrahim, S.A. Parallel Colorimetric Quantification of Choline and Phosphocholine as a Method for Studying Choline Kinase Activity in Complex Mixtures. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, T.; Moneriz, C.; Diez, A.; Bautista, J.M.; Gómez del Pulgar, T.; Cebrián, A.; Lacal, J.C. Antiplasmodial Activity and Mechanism of Action of RSM-932A, a Promising Synergistic Inhibitor of Plasmodium falciparum Choline Kinase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5878–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pubchem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 2 January 2022).
- SMILES DATABASE. Available online: https://cactus.nci.nih.gov/translate/ (accessed on 2 January 2022).

| Tea Extract | Known Antimicrobial Activity | %Inhibition sChoK | MIC S. pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Espinheira Santa (ES) | S. mutans [11] S. aureus [11] | 17.5 | 40 mg/mL |
| Peppermint (PM) | S. aureus [12] S. pyogenes [12] K. pneumonia [12] | 23.2 | 42 mg/mL |
| Lemon Broth (LB) | Shigella sonei [13] | 27.6 | 25 mg/mL |
| Wormwood (W) | S. aureus [13] | 34 | 17.5 mg/mL |
| Rose Hips (RH) | S. aureus [14] | 35.5 | 60 mg/mL |
| Rooibos (RB) | S. aureus [12] S. epidermis [15] | 44.2 | 5 mg/mL |
| Hibiscus (HB) | S. aureus [16] | 54 | 4.5 mg/mL |
| Saint John’s Wort (SJ) | B. cereus [17] B. subtilis [18] | 100 | 3.5 mg/mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zimmerman, T.; Ibrahim, S.A. Quercetin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Choline Kinase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091272
Zimmerman T, Ibrahim SA. Quercetin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Choline Kinase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(9):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091272
Chicago/Turabian StyleZimmerman, Tahl, and Salam A. Ibrahim. 2022. "Quercetin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Choline Kinase of Streptococcus pneumoniae" Antibiotics 11, no. 9: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091272
APA StyleZimmerman, T., & Ibrahim, S. A. (2022). Quercetin Is a Novel Inhibitor of the Choline Kinase of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antibiotics, 11(9), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091272






