Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Effects of Selected Chemokine and Antimicrobial Peptide on Cytokine Profile during Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Mouse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification of Css54 Peptide and MCP-1 Chemokine
2.2. Css54 Is Bactericidal against Salmonella Typhimurium
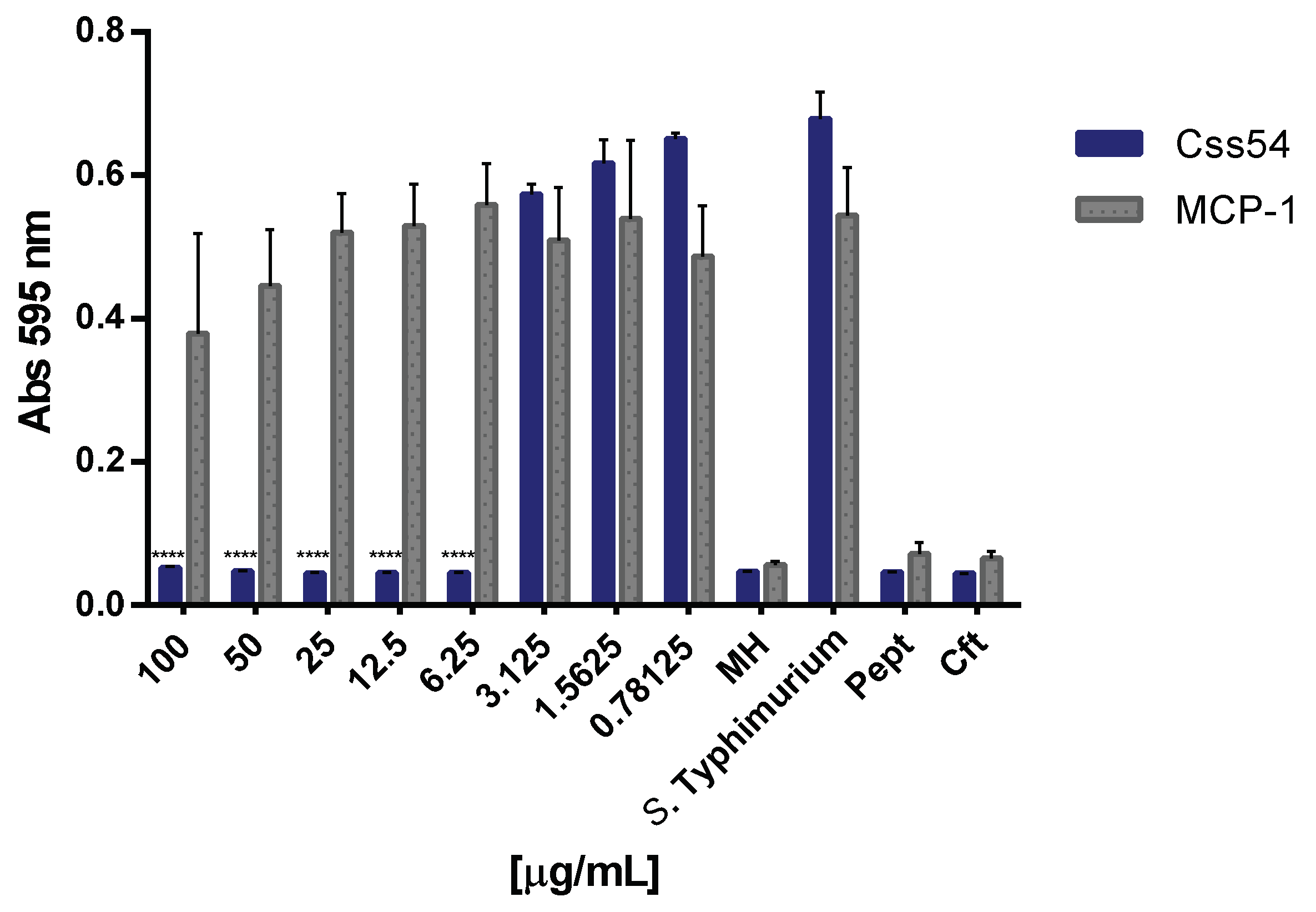
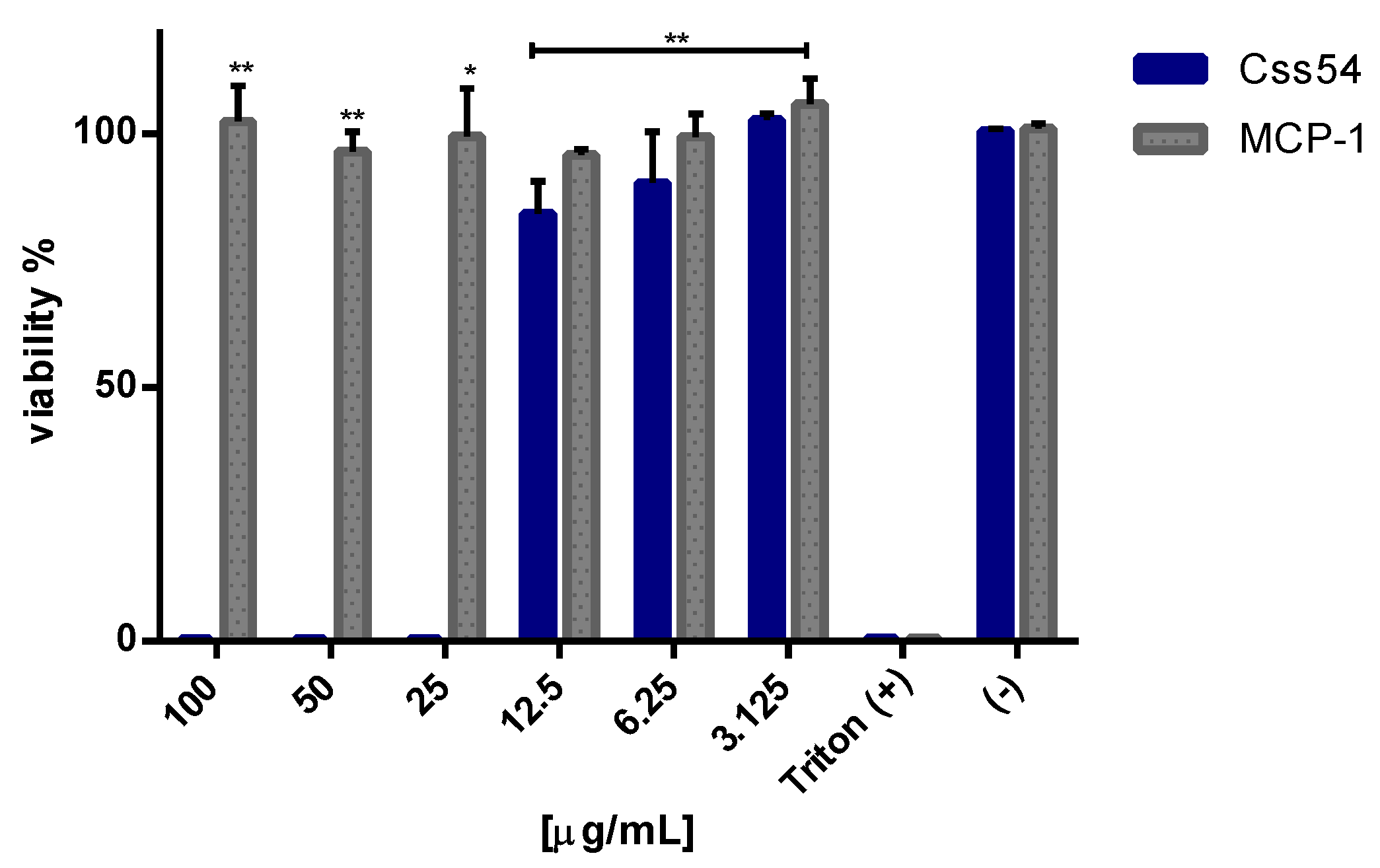
2.3. Css54 Is Cytotoxic against Macrophages
2.4. Css54 Promotes Phagocytic Activity of Macrophages
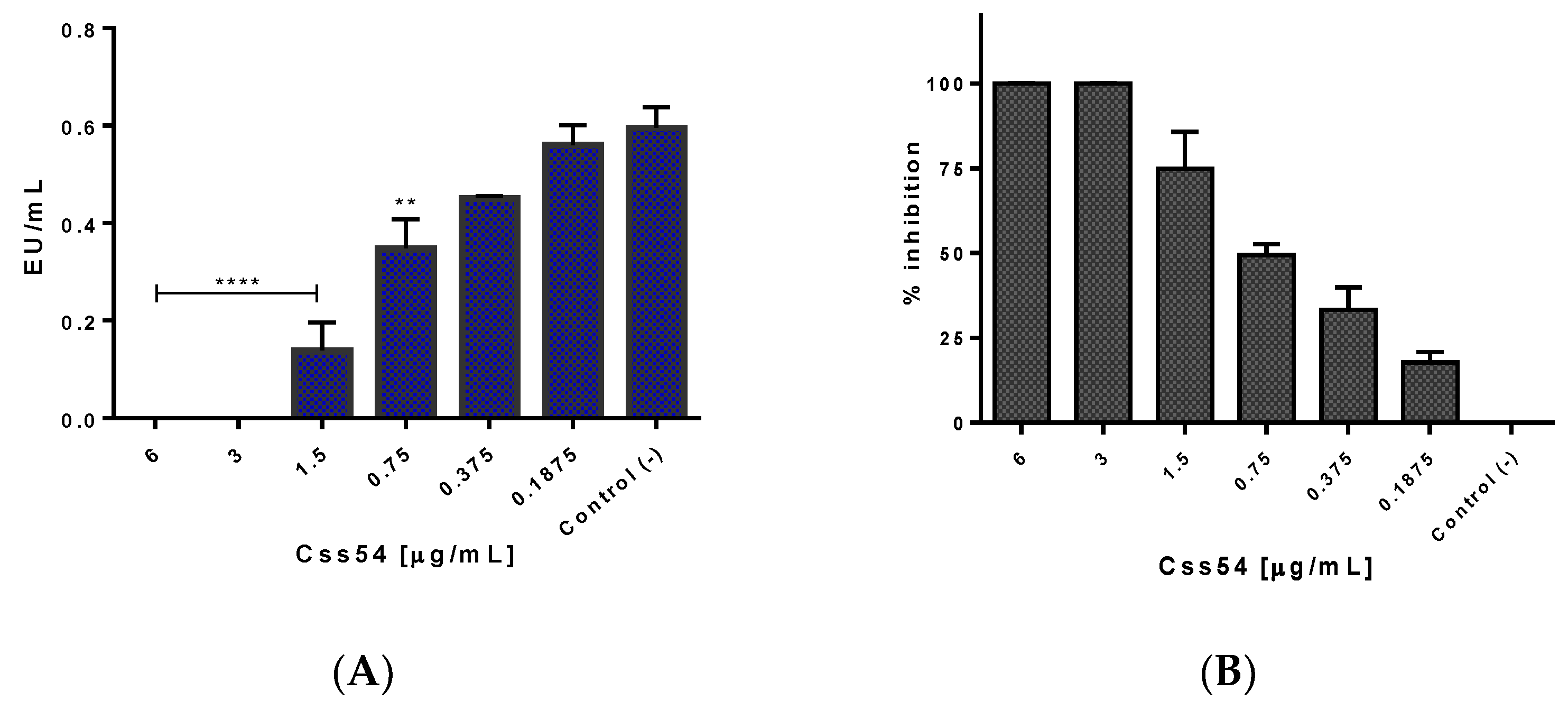
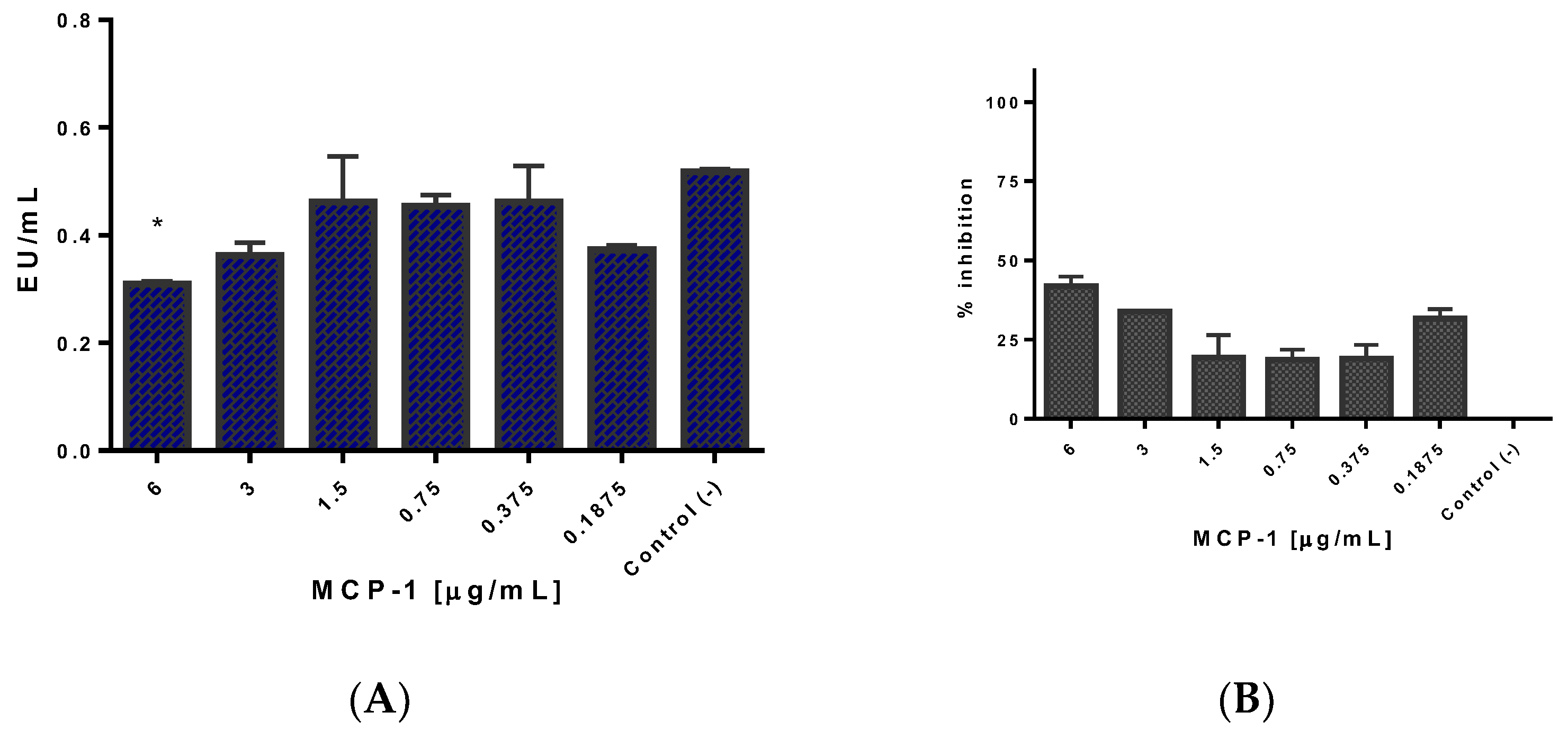
2.5. Css54 Binds to the Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide
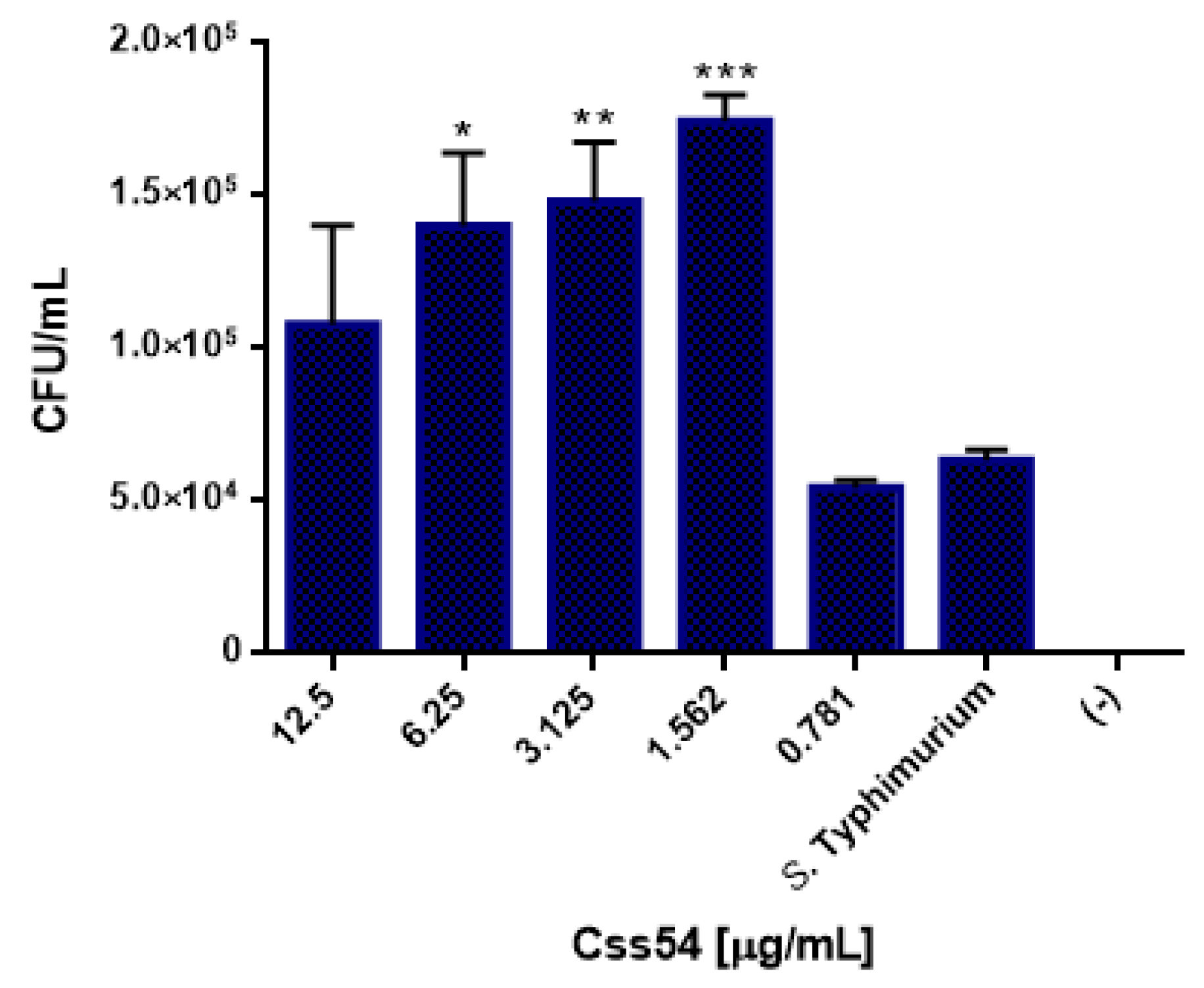
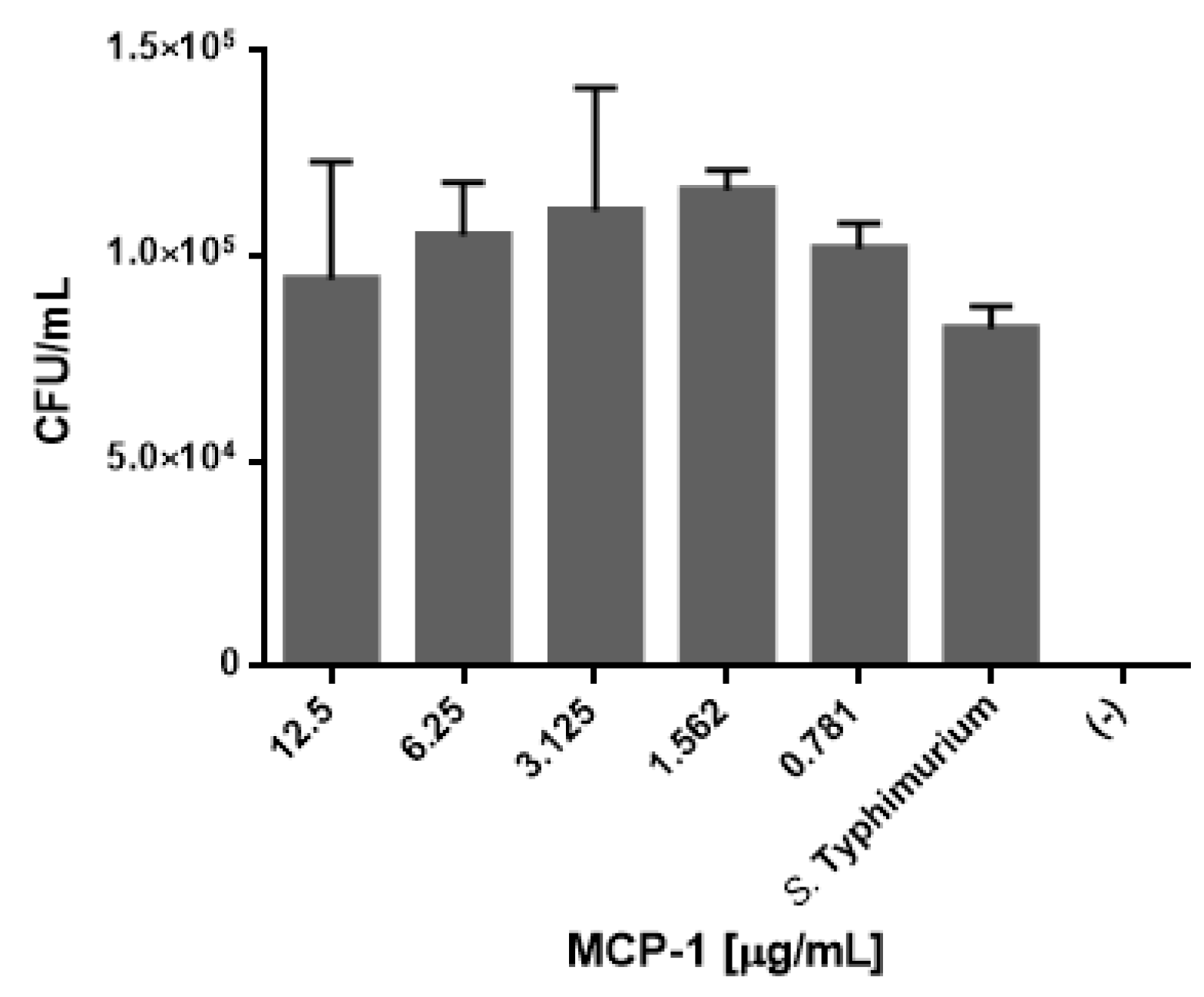
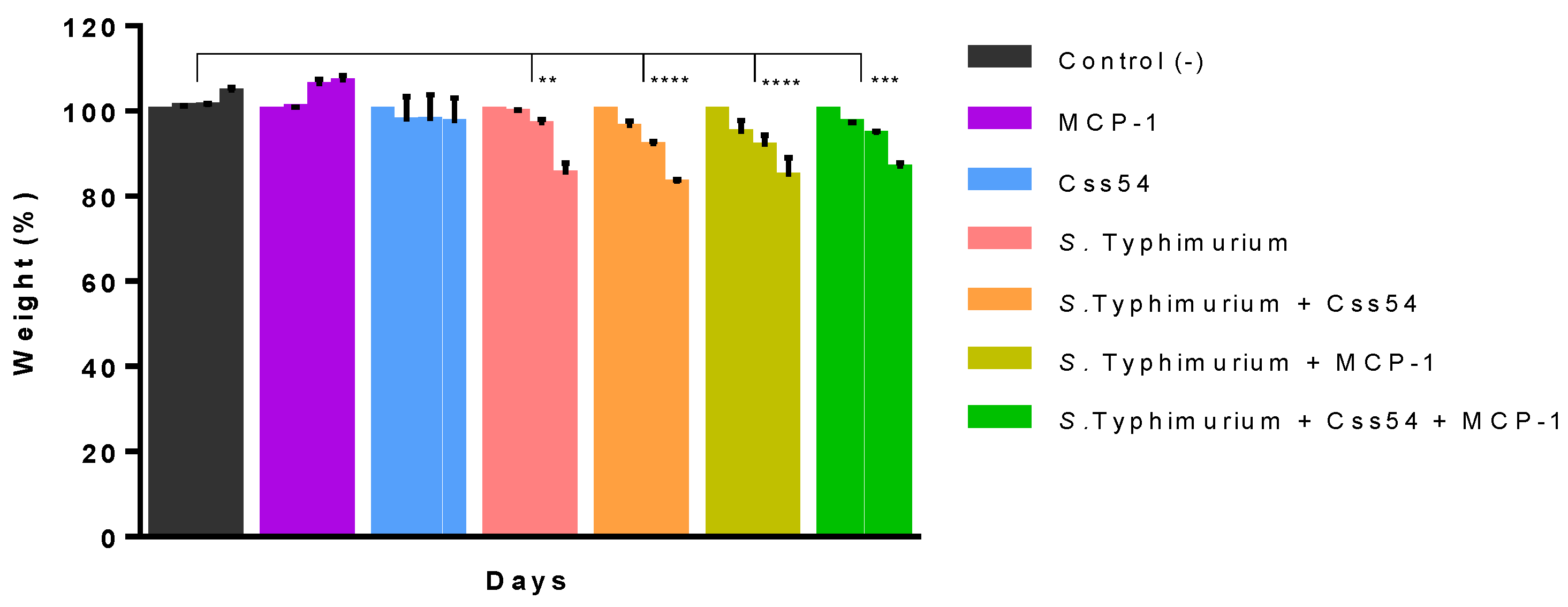
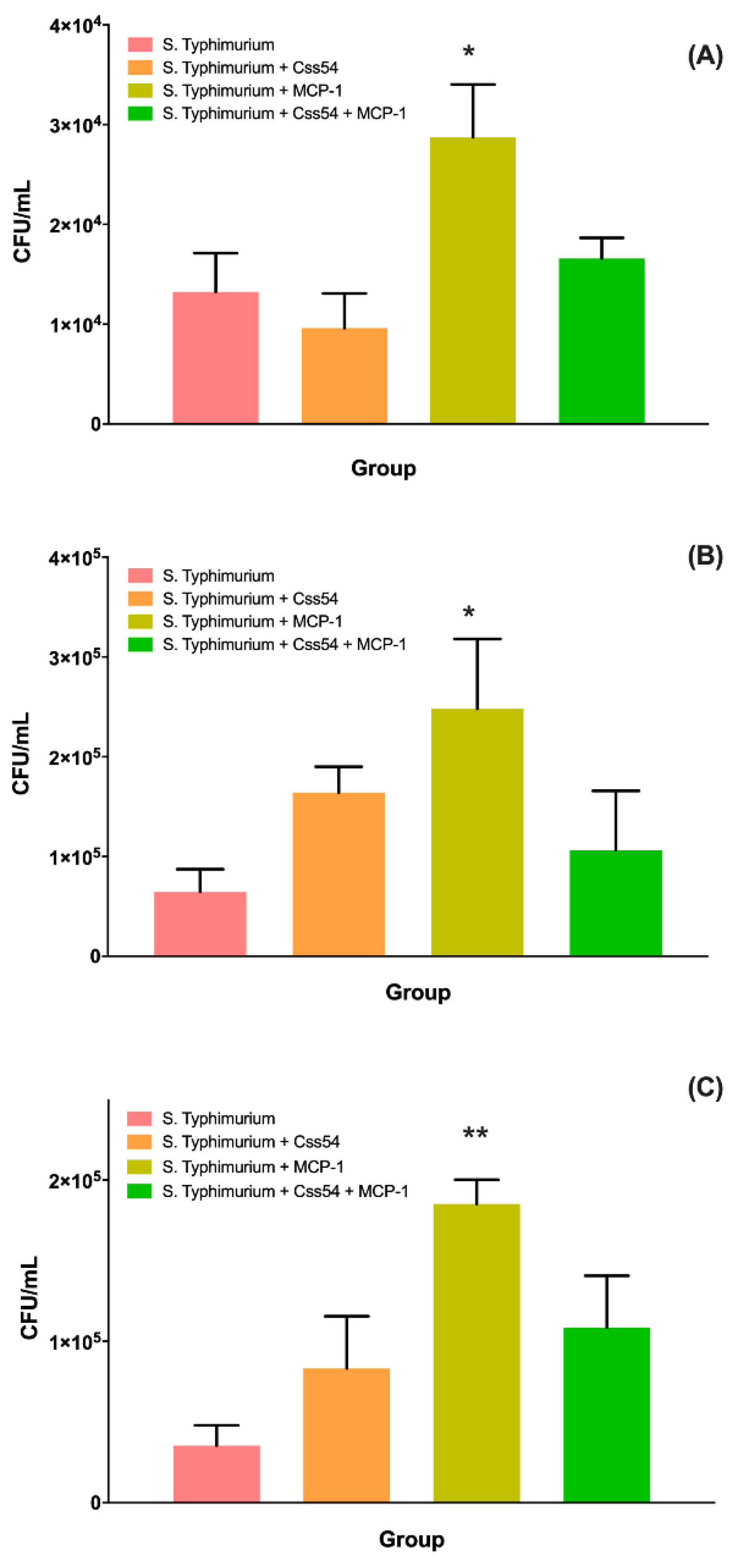
2.6. Css54 Increases Bacterial Load in the Murine Model of Sepsis
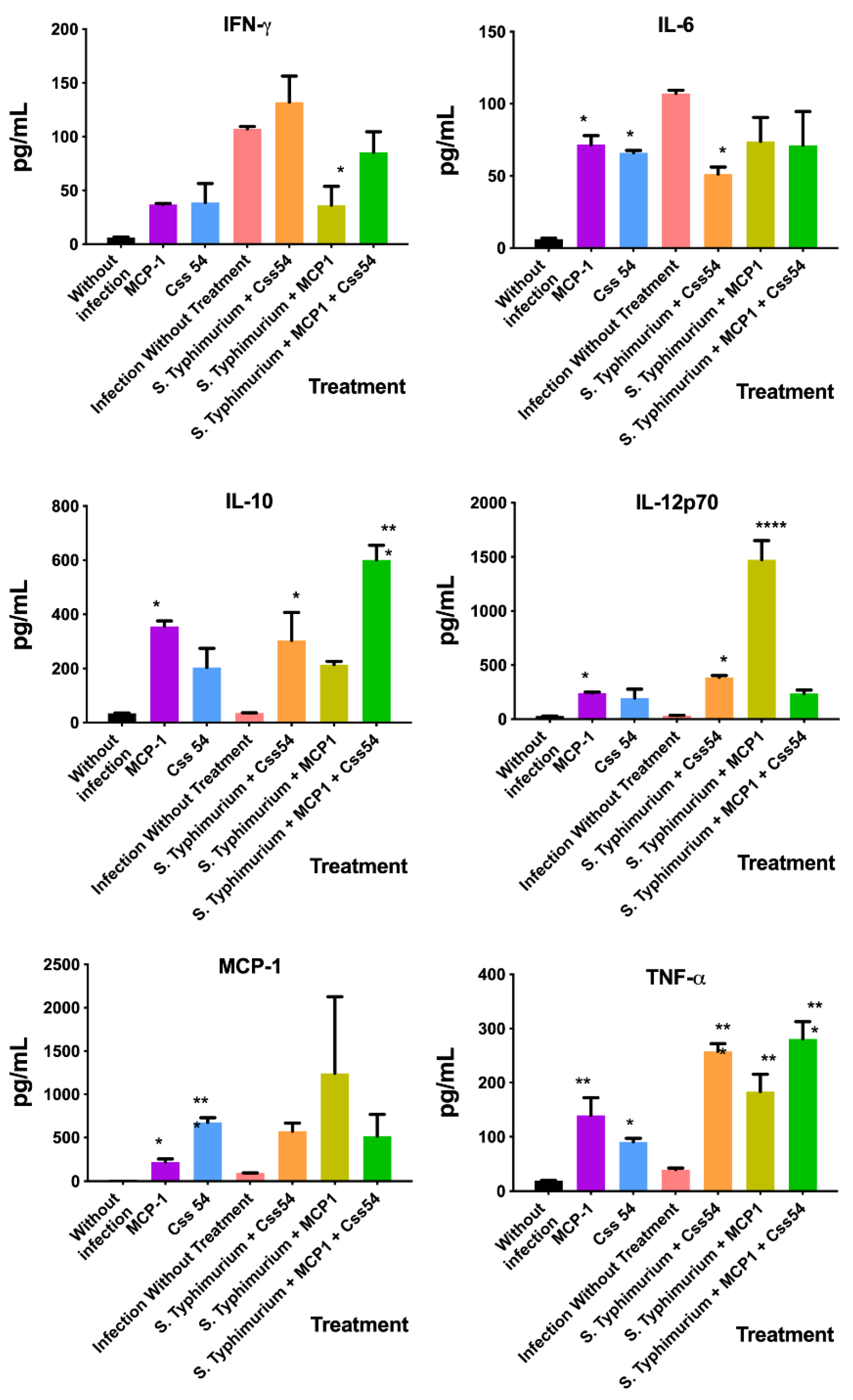
2.7. Cytokine Expression Analysis in Murine Sepsis Model
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Bacterial Strains and Cell Line
5.2. Purification of Peptide Css54 and Expression of MCP-1
5.3. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
5.4. Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
5.5. Cytotoxicity
5.6. Phagocytosis Stimulation
5.7. Neutralization of LPS of S. Typhimurium
5.8. Sepsis Induction in Mice
5.9. Bacterial Load Count
5.10. Cytokine Analysis by Flow Cytometry
5.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayalon, I.; Shen, H.; Williamson, L.; Stringer, K.; Zingarelli, B.; Kaplan, J.M. Sepsis induces adipose tissue browning in nonobese mice but not in obese mice. Shock 2018, 50, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Report on the Epidemiology and Burden of Sepsis: Current Evidence, Identifying Gaps and Future Directions. 2020, p. 56. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/334216/9789240010789-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Askar, B.; Higgins, J.; Barrow, P.; Foster, N. Immunomodulation by vasoactive intestinal peptide is associated with increased survival and growth of Salmonella Typhimurium in mice. Cytokine 2019, 125, 154787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darkwah, S.; Nago, N.; Appiah, M.G.; Myint, P.K.; Kawamoto, E.; Shimaoka, M.; Park, E.J. Differential Roles of Dendritic Cells in Expanding CD4 T Cells in Sepsis. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Bobillo, F.; Iglesias, V.; Almansa, R.; Rico, L.; Gandía, F.; Resino, S.; Tamayo, E.; de Lejarazu, R.O.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F. A combined score of pro- and anti-inflammatory interleukins improves mortality prediction in severe sepsis. Cytokine 2012, 57, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angurana, S.K.; Bansal, A.; Muralidharan, J.; Aggarwal, R.; Singhi, S. Cytokine Levels in Critically Ill Children with Severe Sepsis and Their Relation With the Severity of Illness and Mortality. J. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 36, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.D.; Ghori, N.; Falkow, S. Salmonella typhlrnurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the peyer’s patches. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fàbrega, A.; Vila, J. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Skills to Succeed in the Host: Virulence and Regulation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 308–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero-fresno, A.; Olsen, J.E. Salmonella Typhimurium metabolism affects virulence in the host—A mini-review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 71, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Van Meegern, A.; Doemming, S.; Schuerholz, T. Antimicrobial Peptides in Human Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hancock, R.E.W.; Sahl, H.-G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnaud, S.; Spiller, C.; Moriarty, L.C.; Patel, A.; Gant, V.; Odell, E.W.; Evans, R.W. Interactions of lactoferricin-derived peptides with LPS and antimicrobial activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 233, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, F.; Villegas, E.; Espino-Solis, G.P.; Rodriguez, A.J.; Paniagua-Solis, J.F.; Sandoval-Lopez, G.; Possani, L.D.; Corzo, G. Antimicrobial peptides from arachnid venoms and their microbicidal activity in the presence of commercial antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 2012, 66, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Tseng, S.; Horner, R.M.; Tam, C.; Loda, M.; Rollins, B.J. Control of T(H) 2 polarization by the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Nature 2000, 404, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundumani-Sridharan, V.; Singh, N.K.; Kumar, S.; Gadepalli, R.; Rao, G.N. Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells c1 Mediates p21-activated Kinase 1 Activation in the Modulation of Chemokine-induced Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cell F-actin Stress Fiber Formation, Migration, and Proliferation and Injury-induced Vascular Wall Remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 22150–22162. [Google Scholar]
- Matsukawa, A.; Hogaboam, C.M.; Lukacs, N.W.; Lincoln, P.M.; Strieter, R.M.; Kunkel, S.L. Endogenous monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) protects mice in a model of acute septic peritonitis: Cross-talk between MCP-1 and leukotriene B4. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6148–6154. Available online: https://www.jimmunol.org/content/163/11/6148.long (accessed on 22 October 2019).
- Serbina, N.V.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte emigration from bone marrow during bacterial infection requires signals mediated by chemokine receptor CCR2. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.; Jayaraman, V.; Huelsmann, E.J.; Bonish, B.; Burgad, D.; Sivaramakrishnan, G.; Qin, S.; DiPietro, L.A.; Zloza, A.; Zhang, C.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory Chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) Promotes Healing in Diabetic Wounds by Restoring the Macrophage Response. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, R.N.; Figueiredo, R.T.; Bozza, F.A.; Pacheco, P.; Amâncio, R.T.; Laranjeira, A.P.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Bozza, P.T.; Bozza, M.T. Increased susceptibility to septic and endotoxic shock in monocyte chemoattractant protein 1/CC chemokine ligand 2-deficient mice correlates with reduced interleukin 10 and enhanced macrophage migration inhibitory factor production. Shock 2006, 26, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, D.; Cardoso-Arenas, S.; Corrales-García, L.-L.; Clement, H.; Arenas, I.; Montero-Dominguez, P.A.; Olamendi-Portugal, T.; Zamudio, F.; Csoti, A.; Borrego, J.; et al. A Novel Insecticidal Spider Peptide that Affects the Mammalian Voltage-Gated Ion Channel hKv1.5. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 563858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, G.L. Bactericidal agents in the treatment of MRSA infections—The potential role of daptomycin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Yount, N.Y. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Peptide Action and Resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Q.; Hoover, D.M.; Staley, P.; Tucker, K.D.; Lubkowski, J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Many chemokines including CCL20/MIP-3α display antimicrobial activity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söbirk, S.K.; Mörgelin, M.; Egesten, A.; Bates, P.; Shannon, O.; Collin, M. Human Chemokines as Antimicrobial Peptides with Direct Parasiticidal Effect on Leishmania mexicana In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, M.; van der Does, A.M.; Tang, X.; Lindbom, L.; Agerberth, B.; Haeggström, J.Z. Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 promotes bacterial phagocytosis by human macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 95, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ye, Q.; Wang, K.; Zeng, X.; Huang, S.; Yu, H.; Ge, Q.; Qi, D.; Qiao, S. Enhancement of Macrophage Function by the Antimicrobial Peptide Sublancin Protects Mice from Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 3979352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Liao, C.; Xiao, J.; Fang, K.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, W.; Lu, W. Human Enteric Defensin 5 Promotes Shigella Infection of Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2019, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, F. CYTL1 Promotes the Activation of Neutrophils in a Sepsis Model. Inflammation 2020, 43, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, A.; Olin, A.I.; Ljunggren, L. LPS interactions with immobilized and soluble antimicrobial peptides. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2010, 70, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Willcox, M.D.P. Comparative mode of action of antimicrobial peptide melimine and its derivative Mel4 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 9, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, Y.; Lev, N.; Shai, Y. Effect of the Hydrophobicity to Net Positive Charge Ratio on Antibacterial and Anti-Endotoxin Activities of Structurally Similar Antimicrobial Peptides. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jacob, B.; Jang, M.; Kwak, C.; Lee, Y.; Son, K.; Lee, S.; Jung, I.D.; Jeong, M.S.; Kwon, S.-H.; et al. Development of a novel short 12-meric papiliocin-derived peptide that is effective against Gram-negative sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.A.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Lee, W.H.; Zhang, Y. Naturally occurring antimicrobial peptide OH-CATH30 selectively regulates the innate immune response to protect against sepsis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9136–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, P.; Ohlson, M.B.; Monack, D.M. Innate immune response to Salmonella typhimurium, a model enteric pathogen. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Bang, J.; Kim, Y. Antiseptic Effect of Ps-K18: Mechanism of Its Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaoka, I.; Tamura, H.; Reich, J. Therapeutic Potential of Cathelicidin Peptide LL-37, an Antimicrobial Agent, in a Murine Sepsis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Mereuta, L.; Luchian, T.; Park, Y. Antimicrobial peptide HPA3NT3-A2 effectively inhibits biofilm formation in mice infected with drug-resistant bacteria. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 5068–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso Júnior, P.H.H.; Simon, K.S.; de Castro, R.J.A.; Coelho, L.C.; Erazo, F.A.H.; de Souza, A.C.B.; das Neves, R.C.; Lozano, V.F.; Schwartz, E.F.; Tavares, A.H.; et al. Peptides ToAP3 and ToAP4 decrease release of inflammatory cytokines through TLR-4 blocking. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, O.N.; de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Haney, E.F.; Fensterseifer, I.C.M.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Porto, W.F.; Brown, P.; Faria-Junior, C.; Rezende, T.M.B.; Moreno, S.E.; et al. An anti-infective synthetic peptide with dual antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuxpan-Pérez, A.; Ibarra-Valencia, M.A.; Estrada, B.E.; Clement, H.; Corrales-García, L.L.; Espino-Solis, G.P.; Corzo, G. Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Effects of Selected Chemokine and Antimicrobial Peptide on Cytokine Profile during Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Mouse. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050607
Tuxpan-Pérez A, Ibarra-Valencia MA, Estrada BE, Clement H, Corrales-García LL, Espino-Solis GP, Corzo G. Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Effects of Selected Chemokine and Antimicrobial Peptide on Cytokine Profile during Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Mouse. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(5):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050607
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuxpan-Pérez, Astrid, Marco Antonio Ibarra-Valencia, Blanca Elisa Estrada, Herlinda Clement, Ligia Luz Corrales-García, Gerardo Pavel Espino-Solis, and Gerardo Corzo. 2022. "Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Effects of Selected Chemokine and Antimicrobial Peptide on Cytokine Profile during Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Mouse" Antibiotics 11, no. 5: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050607
APA StyleTuxpan-Pérez, A., Ibarra-Valencia, M. A., Estrada, B. E., Clement, H., Corrales-García, L. L., Espino-Solis, G. P., & Corzo, G. (2022). Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Effects of Selected Chemokine and Antimicrobial Peptide on Cytokine Profile during Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Mouse. Antibiotics, 11(5), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050607






