Discrepancies in Antimicrobial Susceptibility between the JP2 and the Non-JP2 Genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
Abstract
1. Introduction
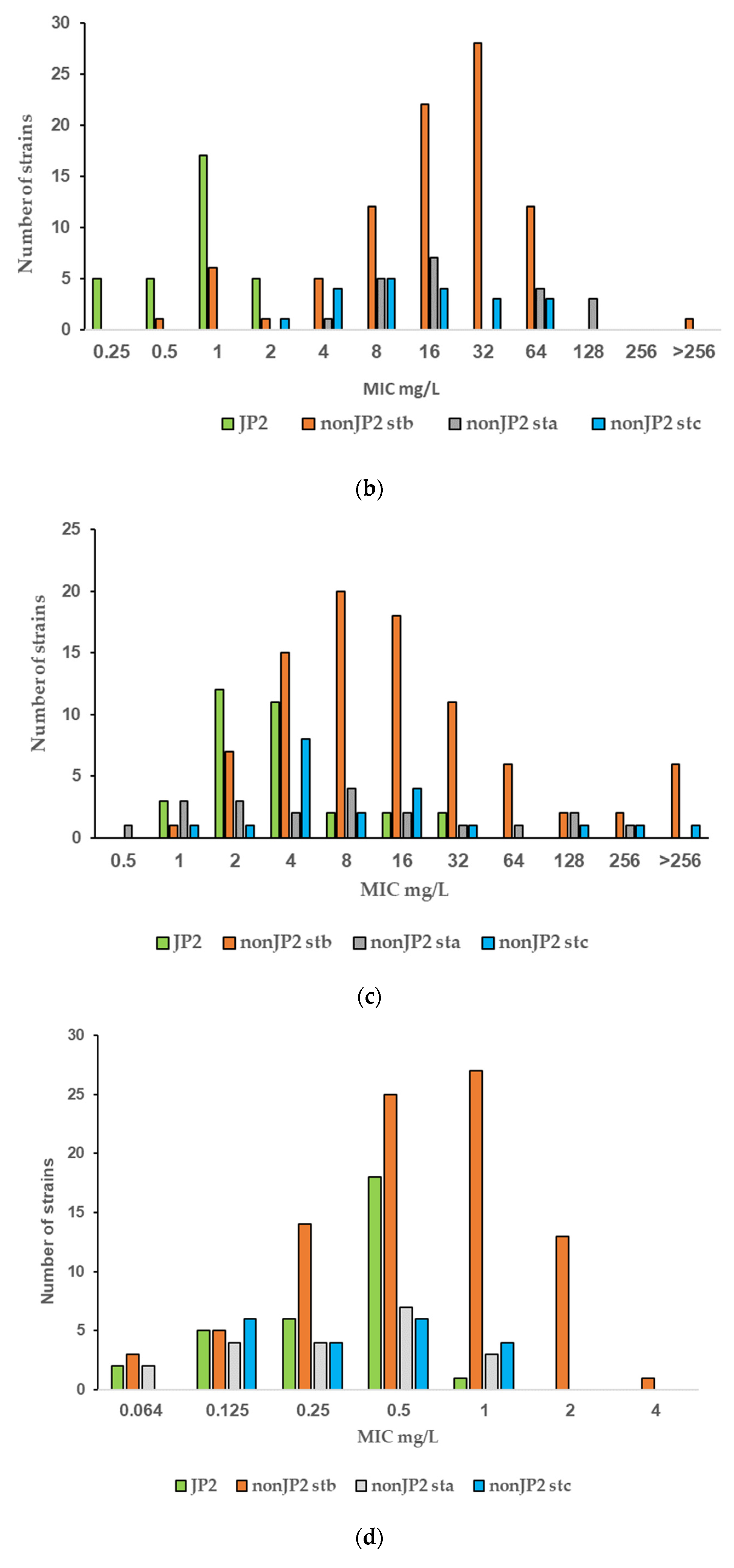
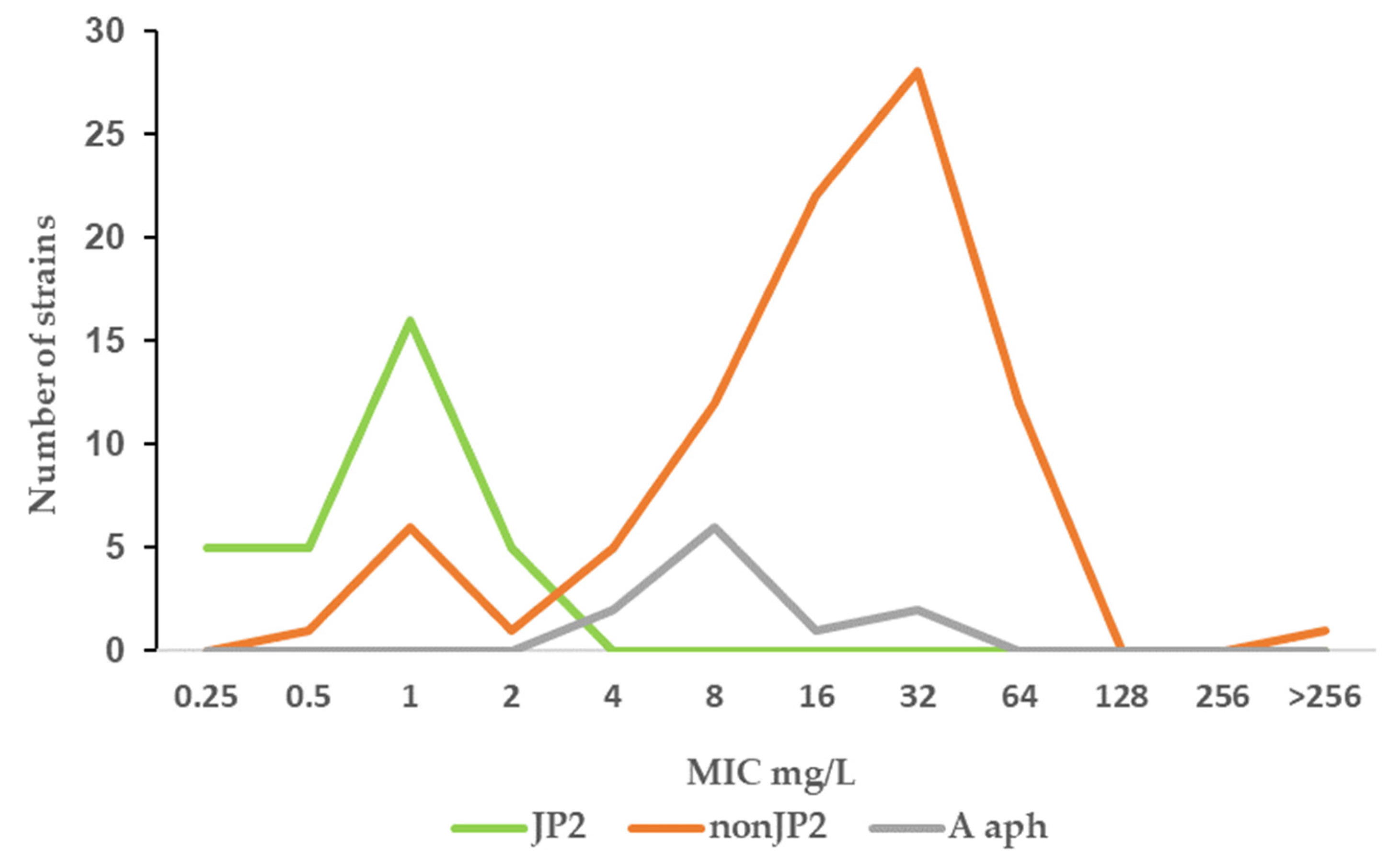
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Serotyping and JP2 Genotype Identification
4.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.4. Beta-Lactamase Production
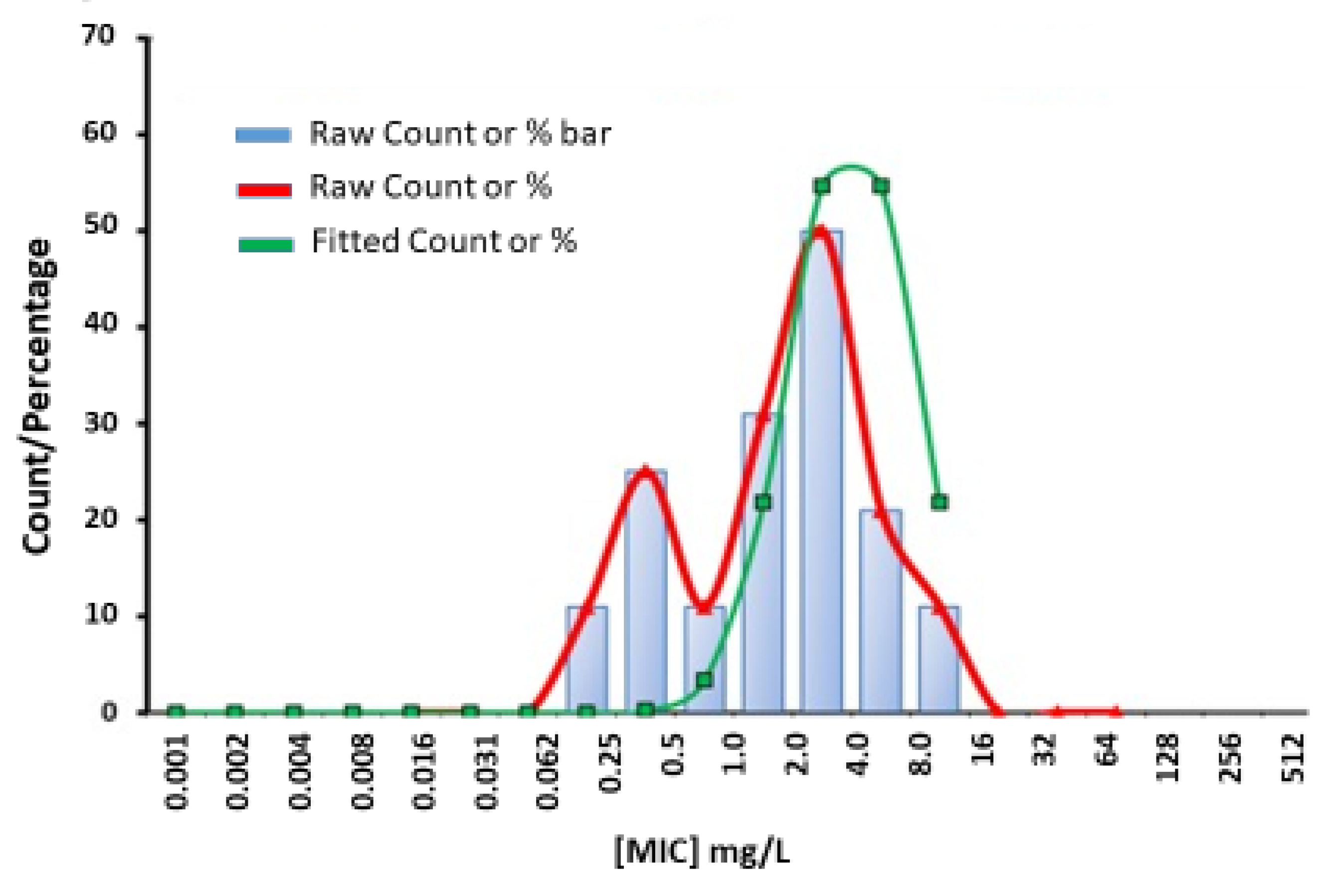
4.5. Determination of Epidemiological Cut-Off Value (ECOFF)
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Haemophilus and Aggregatibacter species with host specificity for humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 214–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, S.T.; Murdoch, D.; Morris, A.; Holland, D.; Pappas, P.; Almela, M.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Almirante, B.; Bouza, E.; Forno, D.; et al. International Collaboration on Endocarditis Prospective Cohort Study Investigators. HACEK infective endocarditis: Characteristics and outcomes from a large; multi-national cohort. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahamat-Langendoen, J.C.; van Vonderen, M.G.A.; Engström, L.J.; Manson, W.L.; van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Mooi-Kokenberg, E.A.N.M. Brain abscess associated with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: Case report and review of literature. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lützen, L.; Olesen, B.; Voldstedlund, M.; Christensen, J.J.; Moser, C.; Knudsen, J.D.; Fuursted, K.; Hartmeyer, G.N.; Chen, M.; Søndergaard, T.S.; et al. Incidence of HACEK bacteraemia in Denmark: A 6-year population-based study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, A.; Morenius, C.; Petropoulos, A.; Nilson, B.; Rasmussen, M. Epidemiology, bacteriology, and clinical characteristics of HACEK bacteremia and endocarditis: A population-based retrospective study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, J.J.; Slots, J.; Genco, R.J. Serology of oral Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and serotype distribution in human periodontal disease. Infect. Immun. 1983, 41, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitznagel, J., Jr.; Kraig, E.; Kolodrubetz, D. Regulation of leukotoxin in leukotoxic and nonleukotoxic strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, J.J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1985, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, D.H.; Patil, A.G.; Velusamy, S.K. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (Aa) Under the Radar: Myths and Misunderstandings of Aa and Its Role in Aggressive Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubek, D.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M. Microevolution and patterns of dissemination of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3080–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, R.; Höglund-Åberg, C.; Haubek, D.; Johansson, A. Age-related prevalence and characteristics of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in periodontitis patients living in Sweden. J. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 9, 1334504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubek, D.; Ennibi, O.K.; Poulsen, K.; Vaeth, M.; Poulsen, S.; Kilian, M. Risk of aggressive periodontitis in adolescent carriers of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans in Morocco: A prospective longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2008, 371, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, C.; Kwamin, F.; Claesson, R.; Dahlén, G.; Johansson, A.; Haubek, D. Progression of attachment loss is strongly associated with presence of the JP2 genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: A prospective cohort study of a young adolescent population. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, J.M.; Lally, E.T.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M.; Demuth, D.R. Regulation of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin expression: Analysis of the promoter regions of leukotoxic and minimally leukotoxic strains. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubek, D.; Johansson, A. Pathogenicity of the highly leukotoxic JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and its geographic dissemination and role in aggressive periodontitis. J. Oral Microbiol. 2014, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelk, P.; Claesson, R.; Hänström, L.; Lerner, U.H.; Kalfas, S.; Johansson, A. Abundant secretion of bioactive interleukin-1beta by human macrophages induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittichotirat, W.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Asikainen, S.; Chen, C. Identification of the pangenome and its components in 14 distinct Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans strains by comparative genomic analysis. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e22420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Kittichotirat, W.; Mayer, M.P.; Hall, R.; Bumgarner, R.; Chen, C. Comparative genomic hybridization and transcriptome analysis with a pan-genome microarray reveal distinctions between JP2 and non-JP2 genotypes of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2013, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittichotirat, W.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Chen, C. Evolutionary Divergence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, S.; Kobel, C.M.; Nielsen, M.B.; Møller, R.T.; Jensen, A.B.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Whole Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cultured from Blood Stream Infections Reveals Three Major Phylogenetic Groups Including a Novel Lineage Expressing Serotype a Membrane O Polysaccharide. Pathogens 2019, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madiner, I.M.; Fosse, T.B.; Hitzig, C.; Charbit, Y.; Hannoun, L.R. Resistance profile survey of 50 periodontal strains of Actinobacillus actinomyectomcomitans. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mínguez, M.; Ennibi, O.K.; Perdiguero, P.; Lakhdar, L.; Abdellaoui, L.; Sánchez, M.C.; Sanz, M.; Herrera, D. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis strains from periodontitis patients in Morocco. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.P.; Holderrieth, S.; Burkhardt, U.; Höffler, U. In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of oral strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans to seven antibiotics. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2002, 29, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paju, S.; Carlson, P.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Asikainen, S. Heterogeneity of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans strains in various human infections and relationships between serotype, genotype, and antimicrobial susceptibility. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, E.M.; Lenkeit, K.; Chenaux, S.; Meyer, J. Antimicrobial susceptibility of periodontopathogenic bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K.G.; Khot, P.; Patil, S.; Pattar, G.; Majukar, S. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of oral isolates of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2019, 23, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.B.; Haubek, D.; Claesson, R.; Johansson, A.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Comprehensive antimicrobial susceptibility testing of a large collection of clinical strains of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans does not identify resistance to amoxicillin. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnidge, J.; Paterson, D.L. Setting and revising antibacterial susceptibility breakpoints. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlmeter, G. Defining antibiotic resistance-towards international harmonization. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 2022. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Mouton, J.; Brown, D.; Apfalter, P.; Cantón, R.; Giske, C.; Ivanova, M.; MacGowan, A.; Rodloff, A.; Soussy, C.-J.; Steinbakk, M.; et al. The role of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics in setting clinical MIC breakpoints: The EUCAST approach. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E37–E45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapun, A.; Contreras-Martel, C.; Vernet, T. Penicillin-binding proteins and beta-lactam resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, E.; Kerff, F.; Terrak, M.; Ayala, J.A.; Charlier, P. The penicillin-binding proteins: Structure and role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, D.J.; Castanheira, M.; Chopra, I. Characterization of global patterns and the genetics of fusidic acid resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcour, A.H. Outer Membrane Permeability and Antibiotic Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, K.; Theilade, E.; Lally, E.T.; Demuth, D.R.; Kilian, M. Population structure of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: A framework for studies of disease-associated properties. Microbiology 1994, 140, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaplan, J.B.; Schreiner, H.C.; Furgang, D.; Fine, D.H. Population structure and genetic diversity of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans strains isolated from localized juvenile periodontitis patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubek, D. The highly leukotoxic JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans: Evolutionary aspects, epidemiology and etiological role in aggressive periodontitis. APMIS Suppl. 2010, 130, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørskov-Lauritsen, N.; Kilian, M. Reclassification of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans.; Haemophilus aphrophilus.; Haemophilus paraphrophilus and Haemophilus segnis as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans gen. nov. comb. nov., Aggregatibacter aphrophilus comb. nov., and Aggregatibacter segnis comb. nov., and emended description of Aggregatibacter aphrophilus to include V factor-dependent and V factor-independent isolates. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturel, L.; Casalta, J.P.; Habib, G.; Nezri, M.; Raoult, D. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans endocarditis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höglund-Åberg, C.; Haubek, D.; Kwamin, F.; Johansson, A.; Claesson, R. Leukotoxic activity of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and periodontal attachment loss. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khureif, A.A.; Mohamed, B.A.; Siddiqui, A.Z.; Khan, A.A.; Divakar, D.D. Repeated application of photodynamic and antibiotic therapy as an adjunct to root surface debridement in patients with grade C and stage III or IV aggressive periodontitis. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020, 29, 101610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teughels, W.; Dhondt, R.; Dekeyser, C.; Quirynen, M. Treatment of aggressive periodontitis. Periodontol 2000 2014, 65, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Rodenburg, J.P.; Goené, R.J.; Abbas, F.; Winkel, E.G.; de Graaff, J. Metronidazole plus amoxycillin in the treatment of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans associated periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1989, 16, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandbergen, D.; Slot, D.E.; Niederman, R.; Van der Weijden, F.A. The concomitant administration of systemic amoxicillin and metronidazole compared to scaling and root planing alone in treating periodontitis: =a systematic review=. BMC Oral Health 2016, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rams, T.E.; Degener, J.E.; Winkelhoff, A.J. Prevalence of β-lactamase-producing bacteria in human periodontitis. Periodontal Res. 2013, 48, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund-Åberg, C.; Kwamin, F.; Claesson, R.; Johansson, A.; Haubek, D. Presence of JP2 and Non-JP2 Genotypes of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and attachment loss in adolescents in Ghana. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, R.; Gudmundson, J.; Åberg, C.H.; Haubek, D.; Johansson, A. Detection of a 640-bp deletion in the Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin promoter region in isolates from an adolescent of Ethiopian origin. J. Oral Microbiol. 2015, 13, 26974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, W. Occurrence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans serotypes in subgingival plaque from United States subjects. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2010, 25, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnidge, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kronvall, G. Statistical characterisation of bacterial wild-type MIC value distributions and the determination of epidemiological cut-off values. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antimicrobial | MIC Range (mg/L) | MIC50 (mg/L) | MIC90 (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzylpenicillin | 0.125–8 | 1 | 4 |
| Amoxicillin | 0.25–2 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Cefotaxime | <0.016–0.25 | 0.064 | 0.064 |
| Meropenem | 0.064–0.25 | 0.125 | 0.125 |
| Azithromycin | 0.064–4 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Fusidic acid | 0.25–>256 | 16 | 64 |
| Gentamicin | 0.25–4 | 1 | 2 |
| Levofloxacin | <0.002–0.16 | 0.004 | 0.008 |
| Metronidazole | 0.5–>256 | 4 | 128 |
| Tetracycline | 0.125–1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Trimethoprim–Sulfamethoxazole | <0.002–0.064 | 0.008 | 0.032 |
| Antimicrobial | MIC-Range (mg/L) | MIC50 (mg/L) | MIC90 (mg/L) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole | ||||
| JP2 | 1–32 | 4 | 16 | <0.001 |
| non-JP2 | 0.5–>256 | 8 | 128 | |
| Benzylpenicillin | ||||
| JP2 | 0.125–0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 | <0.001 |
| non-JP2 | 0.25–8 | 2 | 4 | |
| Azithromycin | ||||
| JP2 | 0.064–1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | <0.01 |
| non-JP2 | 0.064–4 | 0.5 | 2 | |
| Fusidic acid | ||||
| JP2 | 0.25–2 | 1 | 2 | <0.001 |
| non-JP2 | 0.5–>256 | 32 | 64 |
| BP MIC mg/L | Fusidic Acid, MIC mg/L | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | ≥256 | |
| 8 |  |  |  | ||||||||
| 4 |  |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| 2 |  | 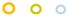 |  |  |  |  | 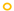 | ||||
| 1 |  | 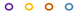 |  | 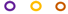 | 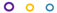 | 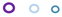 | |||||
| 0.5 |  |  |  | 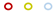 | 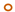 |  | |||||
| 0.25 | 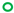 |  |  | 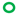 | |||||||
| 0.125 | 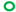 |  |  | ||||||||
 JP2 genotype strains (n = 32);
JP2 genotype strains (n = 32);  serotype b strains (Ghana, n = 41);
serotype b strains (Ghana, n = 41); 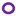 serotype b strains (Sweden no. 47);
serotype b strains (Sweden no. 47);  serotype a strains (Ghana, n = 10);
serotype a strains (Ghana, n = 10); 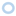 serotype a strains (Sweden, n = 10);
serotype a strains (Sweden, n = 10); 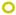 serotype c strains (Ghana, no. 10);
serotype c strains (Ghana, no. 10);  serotype c strains (Sweden, n = 10). The size of the circle in relation to number of strains: 1:
serotype c strains (Sweden, n = 10). The size of the circle in relation to number of strains: 1: 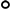 ; 2:
; 2:  ; 3:
; 3:  ; 4:
; 4:  ; 5:
; 5:  ; 6:
; 6:  ; 7:
; 7:  ; 8:
; 8:  ; 9:
; 9:  ; 10:
; 10:  ; 11:
; 11:  ; 12:
; 12:  .
.| Origin and Serotype | Number | MIC ≥ 64 mg/L (Number) | Highly Resistant Strains (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweden, b | 47 | 10 | 15.2 |
| Sweden, a + c | 20 | 0 | |
| Ghana, b | 41 | 6 | 21.3 |
| Ghana, a + c | 20 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Granlund, M.; Åberg, C.H.; Johansson, A.; Claesson, R. Discrepancies in Antimicrobial Susceptibility between the JP2 and the Non-JP2 Genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11030317
Granlund M, Åberg CH, Johansson A, Claesson R. Discrepancies in Antimicrobial Susceptibility between the JP2 and the Non-JP2 Genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(3):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11030317
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranlund, Margareta, Carola Höglund Åberg, Anders Johansson, and Rolf Claesson. 2022. "Discrepancies in Antimicrobial Susceptibility between the JP2 and the Non-JP2 Genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans" Antibiotics 11, no. 3: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11030317
APA StyleGranlund, M., Åberg, C. H., Johansson, A., & Claesson, R. (2022). Discrepancies in Antimicrobial Susceptibility between the JP2 and the Non-JP2 Genotype of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Antibiotics, 11(3), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11030317





