Effect of Farm Management Practices on Morbidity and Antibiotic Usage on Calf Rearing Farms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Statistics
2.2. Predictors Associated with a Calf’s Odds to Become Medicated
2.3. Predictors Associated with Calf’s Possibility to Become Repeatedly Medicated
3. Discussion
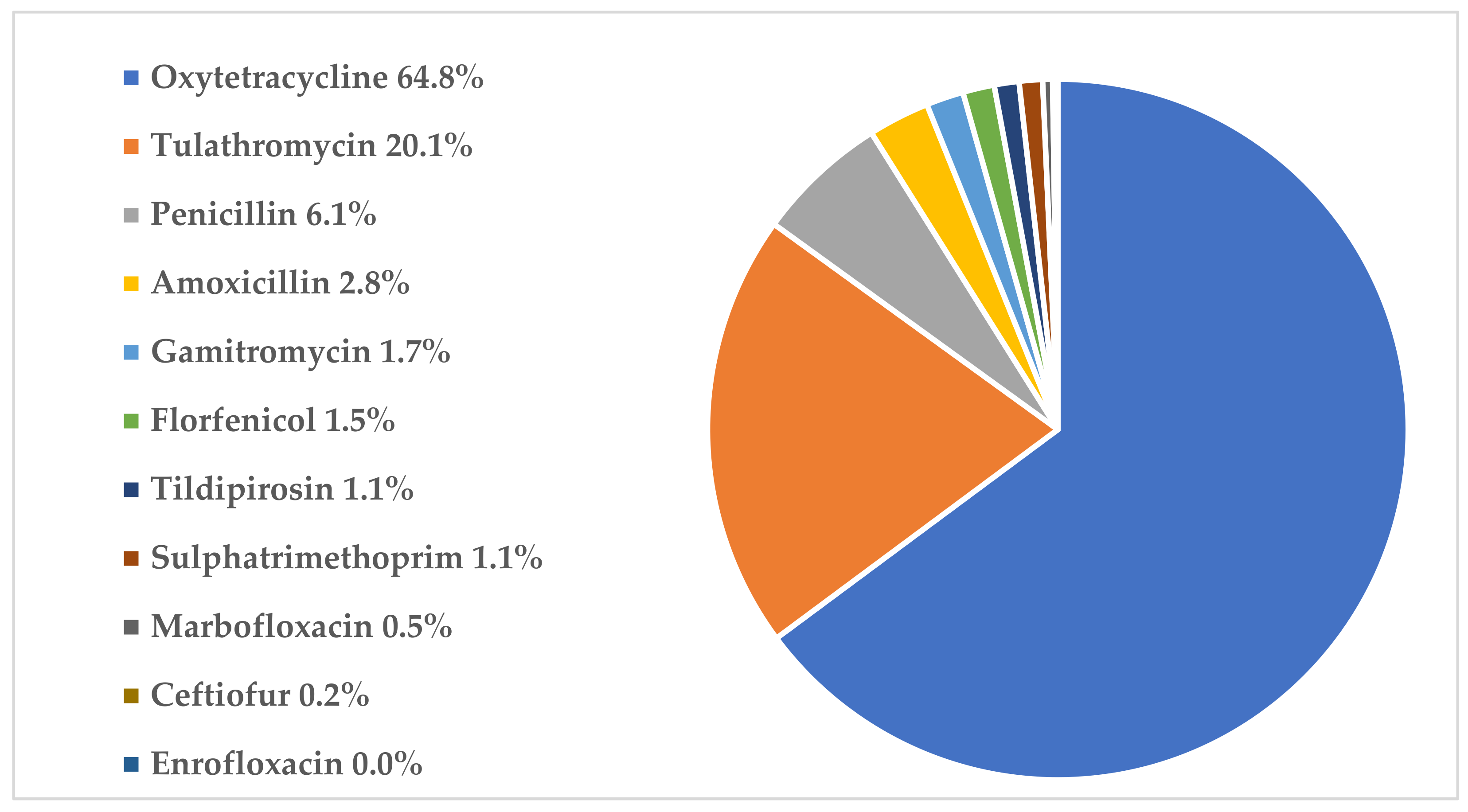
3.1. Use of Antibiotics on Calf Rearing Farms
3.2. Calf Level Factors Associated with Medication Incidence on Calf Rearing Farms
3.3. Farm Level Factors Associated with Medication Incidence on Calf Rearing Farms
3.4. Study Population
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Study Design
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarrige, N.; Cazeau, G.; Morignat, E.; Chanteperdrix, M.; Gay, E. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of antimicrobial usage in white veal calves in France. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 144, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppä-Lassila, L.; Oksanen, J.; Herva, T.; Dorbek-Kolin, E.; Kosunen, H.; Parviainen, L.; Soveri, T.; Orro, T. Associations between group sizes, serum protein levels, calf morbidity and growth in dairy-beef calves in a Finnish calf rearing unit. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 161, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bokma, J.; Boone, R.; Deprez, P.; Pardon, B. Risk factors for antimicrobial use in veal calves and the association with mortality. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salaheen, S.; Kim, S.W.; Cao, H.; Wolfgang, D.R.; Hovingh, E.; Karns, J.S.; Haley, B.J.; Van Kessel, J.A.S. Antimicrobial Resistance Among Escherichia coli Isolated from Veal Calf Operations in Pennsylvania. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönecker, L.; Schnyder, P.; Overesch, G.; Schüpbach-Regula, G.; Meylan, M. Associations between antimicrobial treatment modalities and antimicrobial susceptibility in Pasteurellaceae and E. coli isolated from veal calves under field conditions. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catry, B.; Dewulf, J.; Maes, D.; Pardon, B.; Callens, B.; Vanrobaeys, M.; Opsomer, G.; de Kruif, A.; Haesebrouck, F. Effect of Antimicrobial Consumption and Production Type on Antibacterial Resistance in the Bovine Respiratory and Digestive Tract. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuny, C.; Wieler, L.H.; Witte, W. Livestock-Associated MRSA: The Impact on Humans. Antibiotics 2015, 45, 21–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandelin, A.; Hälli, O.; Härtel, H.; Herva, T.; Seppä-Lassila, L.; Tuunainen, E.; Rautala, H.; Soveri, T.; Simojoki, H. Effect of farm and animal-level factors on youngstock mortality and growth on calf rearing farms. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 193, 105416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autio, T.; Pohjanvirta, T.; Holopainen, R.; Rikula, U.; Pentikäinen, J.; Huovilainen, A.; Rusanen, H.; Soveri, T.; Sihvonen, L.; Pelkonen, S. Etiology of respiratory disease in non-vaccinated, non-medicated calves in rearing herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 119, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, P.; De Fontguyon, G. Veal calf industry economics. Rev. Vet. Med. 2009, 160, 420. [Google Scholar]
- The Council of European Union. Council Directive 2008/119/EC of 18 December 2008 Laying Down Minimum Standards for the Protection of Calves (Codified Version). 2008. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/119/oj (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Pardon, B.; De Bleecker, K.; Hostens, M.; Callens, J.; Dewulf, J.; Deprez, P. Longitudinal study on morbidity and mortality in white veal calves in Belgium. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brscic, M.; Leruste, H.; Heutinck, L.F.M.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; Wolthuis-Fillerup, M.; Stockhofe, N.; Gottardo, F.; Lensink, B.J.; Cozzi, G.; Van Reenen, C.G. Prevalence of respiratory disorders in veal calves and potential risk factors. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 2753–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrington, G.M.; Parish, S.M. Bovine Neonatal Immunology. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2001, 17, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Fulton, R.W.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Step, D.L.; Confer, A.W. The epidemiology of bovine respiratory disease: What is the evidence for predisposing factors? Can. Vet. J. 2010, 51, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Earley, B.; Buckham Sporer, K.; Gupta, S. Invited review: Relationship between cattle transport, immunity and respiratory disease. Animal 2017, 11, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, C.; Cooper, V.; Schwartz, K.; Engelken, T.; Yoon, K. Case–control study of microbiological etiology associated with calf diarrhea. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.H.S.; Dall Agnol, A.M.; Fritzen, J.T.T.; Lorenzetti, E.; Alfieri, A.A.; Alfieri, A.F. Microbial diversity involved in the etiology of a bovine respiratory disease outbreak in a dairy calf rearing unit. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lava, M.; Schüpbach-Regula, G.; Steiner, A.; Meylan, M. Antimicrobial drug use and risk factors associated with treatment incidence and mortality in Swiss veal calves reared under improved welfare conditions. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 126, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnyder, P.; Schönecker, L.; Schüpbach-Regula, G.; Meylan, M. Effects of management practices, animal transport and barn climate on animal health and antimicrobial use in Swiss veal calf operations. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 167, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Kelton, D.F.; Duffield, T.F.; Renaud, D.L. Risk factors identified on arrival associated with morbidity and mortality at a grain-fed veal facility: A prospective single cohort study. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9224–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, H.M.; Kelton, D.F.; Costa, J.H.C.; Winder, C.B.; Renaud, D.L. Identification of biomarkers measured upon arrival associated with morbidity, mortality, and average daily gain in grain-fed veal calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lava, M.; Pardon, B.; Schüpbach-Regula, G.; Keckeis, K.; Deprez, P.; Steiner, A.; Meylan, M. Effect of calf purchase and other herd-level risk factors on mortality, unwanted early slaughter, and use of antimicrobial group treatments in Swiss veal calf operations. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 126, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertner, M.; Toft, N.; Martin, H.L.; Boklund, A. A register-based study of the antimicrobial usage in Danish veal calves and young bulls. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 131, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francoz, D.; Buczinski, S.; Apley, M. Evidence Related to the Use of Ancillary Drugs in Bovine Respiratory Disease (Anti-Inflammatory and Others): Are They Justified or Not? Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2012, 28, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.K.; Step, D.L.; Maxwell, C.L.; Wagner, J.J.; Richards, C.J.; Krehbiel, C.R. Evaluation of multiple ancillary therapies used in combination with an antimicrobial in newly received high-risk calves treated for bovine respiratory disease. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 3661–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koster, J.; Tena, J.K.; Stegemann, M.R. Treatment of bovine respiratory disease with a single administration of tulathromycin and ketoprofen. Vet. Rec. 2021, e834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnish Food Authority. Recommendations for the Use of Antimicrobials in the Treatment of the Most Significant Infectious and Contagious Diseases in Animals; Finnish Food Authority: Helsinki, Finland, 2018. Available online: https://www.ruokavirasto.fi/globalassets/viljelijat/elaintenpito/elainten-laakitseminen/hallittu_laakekekaytto/mikrobilaakekaytonperiaatteet/mikrobilaakkeiden_kayttosuositukset_en.pdf (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Carroll, J.A.; Forsberg, N.E. Influence of Stress and Nutrition on Cattle Immunity. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2007, 23, 105–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolums, A.R.; Berghaus, R.D.; Smith, D.R.; White, B.J.; Engelken, T.J.; Irsik, M.B.; Matlick, D.K.; Jones, A.L.; Ellis, R.W.; Smith, I.J.; et al. Producer survey of herd-level risk factors for nursing beef calf respiratory disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 243, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, M.W.; Dargatz, D.A.; Wagner, B.A. Risk factors for initial respiratory disease in United States’ feedlots based on producer-collected daily morbidity counts. Can. Vet. J. 2008, 49, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Gulliksen, S.M.; Lie, K.I.; Løken, T.; Østerås, O. Calf mortality in Norwegian dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2782–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Total n = 28,228 | Specialized Calf Rearing Farm n = 23,946 | Fattening Farm for Milk Calves n = 3746 | Fattening Farm for Weaned Calves n = 536 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n/%) | (n/%) | (n/%) | (n/%) | ||
| Number of calves medicated at least once during follow-up | Antibiotic | 17,180/60.9 | 15,820/66.1 | 1331/35.5 | 29/5.4 |
| Antibiotic, NSAID or both * | 17,435/61.8 | 16,010/66.9 | 1391/37.1 | 34/6.3 | |
| Number of medications when recurrent medications are taken into account | Antibiotic ** | 34,532/122.3 | 32,721/136.6 | 1780/47.5 | 31/5.8 |
| Antibiotic, NSAID or both *** | 33,403/118.3 | 31,526/131.7 | 1841/49.2 | 36/6.7 |
| Variable | Total Calves/Farms | % Calves/Farms | Medicated at Least Once (%) | Average Number of Medication Events per Calf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | p-Value | Missing | n | Average * | p-Value | Missing | |||
| Farm type | ||||||||||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | 23,946/45 | 84.8/51.7 | 23,946 | 66.9 | ref. | 0 | 16,010 | 1.956 | ref. | 7936 |
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 3746/28 | 13.3/32.2 | 3746 | 37.1 | 0.010 | 0 | 1391 | 1.324 | <0.001 | 2355 |
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 536/14 | 1.9/16.1 | 536 | 6.3 | <0.001 | 0 | 34 | 1.059 | 0.004 | 502 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Contract meat company | ||||||||||
| Company A | 18,304/40 | 64.8/46.0 | 18,304 | 66.7 | ref. | 0 | 12,033 | 1.848 | ref. | 6271 |
| Company B | 7819/39 | 27.7/44.8 | 7819 | 46.3 | 0.148 | 0 | 3622 | 2.089 | <0.001 | 4197 |
| Company C | 2105/8 | 7.5/9.2 | 2105 | 84.6 | 0.002 | 0 | 1780 | 1.903 | 0.182 | 325 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Farm receives additional older animals ** | ||||||||||
| No | 10,569/50 | 37.4/57.5 | 10,569 | 52.0 | ref. | 0 | 5501 | 2.012 | ref. | 5068 |
| Yes | 17,659/37 | 62.6/42.5 | 17,659 | 67.6 | 0.333 | 0 | 11,934 | 1.854 | <0.001 | 5725 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Calf mortality on origin dairy farm | ||||||||||
| 0–2% | 4463/- | 15.8/- | 4463 | 59.1 | ref. | 0 | 2639 | 1.868 | ref. | 1824 |
| 2.1–5.9% | 8617/- | 30.5/- | 8617 | 60.4 | 0.612 | 0 | 5204 | 1.900 | 0.632 | 3413 |
| 6–9.9% | 7435/- | 26.3/- | 7435 | 61.4 | 0.998 | 0 | 4567 | 1.896 | 0.207 | 2868 |
| 10% or more | 7713/- | 27.4/- | 7713 | 65.1 | 0.017 | 0 | 5025 | 1.934 | 0.218 | 2688 |
| Sum: | 28,228/- | 100/- | 28,228 | 17,435 | 10,793 | |||||
| Missing: | 0/- | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | 0.004 | 0.487 | ||||||||
| Sex | ||||||||||
| Bull | 25,018/- | 88.6/- | 25,018 | 61.6 | ref. | 0 | 15,403 | 1.919 | ref. | 9615 |
| Heifer | 3210/- | 11.4/- | 3210 | 63.3 | <0.001 | 0 | 2032 | 1.787 | 0.398 | 1178 |
| Sum: | 28,228/- | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | |||||
| Missing: | 0/- | |||||||||
| Calf breed | ||||||||||
| Finnish Ayrshire | 10,818/- | 38.3/- | 10,818 | 62.2 | ref. | 0 | 6733 | 1.967 | ref. | 4085 |
| Holstein | 11,405/- | 40.4/- | 11,405 | 61.9 | <0.001 | 0 | 7060 | 1.907 | <0.001 | 4345 |
| Aberdeen Angus | 1111/- | 3.9/- | 1111 | 57.2 | 0.202 | 0 | 635 | 1.865 | 0.126 | 476 |
| Limousine | 1331/- | 4.7/- | 1331 | 61.4 | <0.001 | 0 | 817 | 1.846 | 0.435 | 514 |
| Blonde d’aquitaine | 2563/- | 9.1/- | 2563 | 61.6 | <0.001 | 0 | 1579 | 1.764 | <0.001 | 984 |
| Other breeds | 1000/- | 3.5/- | 1000 | 61.1 | <0.001 | 0 | 611 | 1.653 | <0.001 | 389 |
| Sum: | 28,228/- | 100/- | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/- | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Variable | Total Calves/Farms | % Calves/Farms | Medicated at Least Once (%) | Average Number of Medication Events per Calf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | p-Value | Missing | n | Average * | p-Value | Missing | |||
| Number of calves in one milk-feeding compartment | ||||||||||
| 1–20 calves | 1014/11 | 3.6/15.1 | 1014 | 25.2 | ref. | 0 | 256 | 1.316 | ref. | 758 |
| 21–40 calves | 6272/28 | 22.7/38.3 | 6272 | 37.3 | 0.177 | 0 | 2367 | 1.500 | 0.006 | 3905 |
| 41–80 calves | 17,098/27 | 61.7/37.0 | 17,098 | 75.9 | <0.001 | 0 | 12,972 | 2.072 | <0.001 | 4126 |
| 81–100 calves | 3308/7 | 12.0/9.6 | 3308 | 54.6 | 0.046 | 0 | 1806 | 1.327 | 0.266 | 1502 |
| Sum: | 27,692/73 | 100/100 | 27,692 | 0 | 17,401 | 10,291 | ||||
| Missing: | 536/14 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Sizes of the calf groups in milk-feeding compartments | ||||||||||
| 1–10 calves | 516/4 | 1.9/5.5 | 516 | 24.2 | ref. | 0 | 125 | 0.332 | ref. | 391 |
| 11–20 caves | 4437/25 | 16.0/34.2 | 4437 | 46.3 | 0.661 | 0 | 2054 | 0.566 | 0.193 | 2383 |
| 21–30 calves | 9660/21 | 34.9/28.8 | 9660 | 73.6 | 0.123 | 0 | 7111 | 1.584 | 0.012 | 2549 |
| More than 30 calves | 13,079/23 | 47.2/31.5 | 13,079 | 62.0 | 0.140 | 0 | 8111 | 0.724 | 0.018 | 4968 |
| Sum: | 27,692/73 | 100/100 | 27,692 | 0 | 17,401 | 10,291 | ||||
| Missing: | 536/14 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | 0.068 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Milk-feeding compartments operated as all in/all out | ||||||||||
| Yes | 26,145/63 | 94.4/86.3 | 26,145 | 64.0 | ref. | 0 | 16,741 | 1.925 | ref. | 9404 |
| No | 1547/10 | 5.6/13.7 | 1547 | 42.7 | 0.677 | 0 | 660 | 1.403 | 0.011 | 887 |
| Sum: | 27,692/73 | 100/100 | 27,692 | 6.3 | 0 | 17,401 | 10,291 | |||
| Missing: | 536/14 | |||||||||
| Arriving calves are grouped to the pens according to | ||||||||||
| Body weight | 4545/12 | 17.7/16.9 | 4545 | 46.0 | ref. | 0 | 2092 | 1.461 | ref. | 2453 |
| Health status | 639/2 | 2.5/2.8 | 639 | 41.5 | 0.877 | 0 | 265 | 1.381 | 0.669 | 374 |
| Age | 1411/4 | 5.5/5.7 | 1411 | 36.7 | 0.647 | 0 | 518 | 1.241 | 0.237 | 893 |
| Calves kept in same groups as during transportation | 564/2 | 2.2/2.8 | 564 | 73.4 | 0.051 | 0 | 414 | 1.019 | 0.412 | 150 |
| Random | 18,107/48 | 70.6/67.6 | 18,107 | 66.4 | 0.696 | 0 | 12,022 | 1.915 | <0.001 | 6085 |
| Some other criteria | 398/3 | 1.5/4.2 | 398 | 39.5 | 0.657 | 0 | 157 | 1.573 | 0.588 | 241 |
| Sum: | 25,664/71 | 100/100 | 25,664 | 0 | ||||||
| Missing: | 2564/16 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | 0.425 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Filling of compartments for arriving milk calves | ||||||||||
| All compartments filled simultaneously | 10,203/46 | 37.5/66.7 | 10,203 | 50.6 | ref. | 0 | 5160 | 1.828 | ref. | 5043 |
| All compartments filled independently | 17,015/23 | 62.5/33.3 | 17,015 | 71.2 | 0.004 | 0 | 12,108 | 1.944 | <0.001 | 4907 |
| Sum: | 27,218/69 | 100/100 | 27,218 | 0 | 17,268 | 9950 | ||||
| Missing: | 1010/18 | |||||||||
| Washing and disinfection of milk-feeding compartments between calf batches | ||||||||||
| Washing and disinfection | 17,093/40 | 61.7/54.8 | 17,093 | 65.8 | ref. | 0 | 11,247 | 2.058 | ref. | 5846 |
| Only washing | 9402/25 | 34.0/34.2 | 9402 | 60.1 | 0.848 | 0 | 5647 | 1.642 | 0.107 | 3755 |
| Only mechanical cleaning | 1161/7 | 4.2/9.6 | 1161 | 43.4 | 0.626 | 0 | 504 | 1.470 | 0.021 | 657 |
| Only occasional cleaning | 36/1 | 0.1/1.4 | 36 | 8.3 | 0.284 | 0 | 3 | 1.333 | 0.544 | 33 |
| Sum: | 27,692/73 | 100/100 | 27,692 | 17,401 | 10,291 | |||||
| Missing: | 536/14 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | 0.721 | <0.044 | ||||||||
| Air connection between compartments | ||||||||||
| Milk-feeding compartment has own air space | 10,630/43 | 38.9/59.7 | 10,630 | 37.4 | ref. | 0 | 3978 | 1.320 | ref. | 6652 |
| Air connection between milk-feeding and other compartments | 16,700/29 | 61.1/40.3 | 16,700 | 78.2 | 0.001 | 0 | 13,062 | 2.109 | <0.001 | 3638 |
| Sum: | 27,330/72 | 100/100 | 27,330 | 0 | 17,040 | 10,290 | ||||
| Missing: | 898/15 | |||||||||
| Handling of calves after weaning | ||||||||||
| Calves relocated to new compartment | 19,647/54 | 78.5/79.4 | 19,647 | 58.5 | ref. | 0 | 11,503 | 1.848 | ref. | 8144 |
| Calves stay in the same compartment | 6679/14 | 21.5/20.6 | 6679 | 74.3 | 0.007 | 0 | 4965 | 2.040 | <0.001 | 1714 |
| Sum: | 26,326/68 | 100/100 | 26,326 | 50.8 | 0 | 16,468 | 8144 | |||
| Missing: | 1902/19 | |||||||||
| Air ventilation in compartments for weaned calves | ||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 22,768/66 | 81.8/76.7 | 22,768 | 68.2 | ref. | 0 | 15,522 | 1.936 | ref. | 7246 |
| Natural ventilation | 4401/17 | 15.8/19.8 | 4401 | 29.3 | 0.057 | 0 | 1288 | 1.392 | 0.002 | 3113 |
| Combination of mechanical and natural ventilation | 657/3 | 2.4/3.5 | 657 | 37.4 | 0.824 | 0 | 246 | 1.398 | 0.155 | 411 |
| Sum: | 27,826/86 | 100/100 | 27,826 | 17,056 | 10,770 | |||||
| Missing: | 402/1 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | 0.151 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| Air ventilation in compartments for weaned calves | ||||||||||
| Mechanical ventilation | 22,768/66 | 81.8/76.7 | 22,768 | 68.2 | ref. | 0 | 15,522 | 1.936 | ref. | 7246 |
| Natural ventilation | 4401/17 | 15.8/19.8 | 4401 | 29.3 | 0.057 | 0 | 1288 | 1.392 | 0.002 | 3113 |
| Combination of mechanical and natural ventilation | 657/3 | 2.4/3.5 | 657 | 37.4 | 0.824 | 0 | 246 | 1.398 | 0.155 | 411 |
| Sum: | 27,826/86 | 100/100 | 27,826 | 17,056 | 10,770 | |||||
| Missing: | 402/1 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | 0.151 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| Compartmentation of weaned calves | ||||||||||
| Weaned calves in own air space | 8351/32 | 30.2/37.7 | 8351 | 39.8 | ref. | 0 | 3327 | 1.283 | ref. | 5024 |
| Weaned calves in same compartment and air space with older cattle | 6126/42 | 22.1/49.4 | 6126 | 35.0 | 0.239 | 0 | 2143 | 1.380 | <0.001 | 3983 |
| Weaned calves in own compartment but same air space with older cattle | 13,206/11 | 47.7/12.9 | 13,206 | 87.7 | <0.001 | 0 | 11,579 | 2.156 | <0.001 | 1627 |
| Sum: | 27,683/85 | 100/100 | 27,683 | 0 | 17,049 | 10,634 | ||||
| Missing: | 545/3 | |||||||||
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Variable | Total Calves/Farms | % Calves/Farms | Medicated at Least Once (%) | Average Number of Medication Events per Calf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | p-Value | Missing | n | Average * | p-Value | Missing | |||
| Temperature measured to detect sick calves | ||||||||||
| Yes | 20,416/54 | 73.4/62.1 | 20,416 | 68.9 | ref. | 0 | 14,058 | 2.038 | ref. | 6358 |
| No | 7812/33 | 26.6/37.9 | 7812 | 43.2 | 0.008 | 0 | 3377 | 1.348 | <0.001 | 4435 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Temperature measured systemically from all calves in the same group if at risk of illness | ||||||||||
| Yes | 3151/11 | 11.2/12.6 | 3151 | 66.6 | ref. | 0 | 2097 | 1.923 | ref. | 1054 |
| No | 25,077/76 | 88.8/87.4 | 25,077 | 61.2 | 0.193 | 0 | 15,339 | 1.901 | <.0.001 | 9738 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,436 | 10,792 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Medicines stored at farm for future use | ||||||||||
| Yes | 26,850/66 | 95.1/75.9 | 26,850 | 64.1 | ref. | 0 | 17,215 | 1.914 | ref. | 9635 |
| No | 1378/21 | 4.9/24.1 | 1378 | 16.0 | <0.001 | 0 | 220 | 1.127 | <0.001 | 1158 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Medication policy on farm | ||||||||||
| Only sick animals medicated | 19,676/64 | 69.7/73.6 | 19,676 | 60.2 | ref. | 0 | 11,809 | 1.756 | ref. | 7867 |
| Metaphylactic group treatments used if needed | 8552/23 | 30.3/26.4 | 8552 | 65.8 | 0.001 | 0 | 5626 | 1.974 | <0.001 | 2926 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| Use of vaccination against BRD ** | ||||||||||
| Yes | 1293/4 | 4.6/4.6 | 1293 | 56.1 | ref. | 0 | 726 | 1.332 | ref. | 567 |
| No | 26,935/83 | 95.4/95.4 | 26,935 | 62.0 | 0.990 | 0 | 16,709 | 1.929 | 0.371 | 10,226 |
| Sum: | 28,228/87 | 100/100 | 28,228 | 0 | 17,435 | 10,793 | ||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | |||||||||
| n Calves/Farms | Average Calf/Farm level | SD Calf/Farm level | Medicated 0/1 | Number of Medication Events per Calf | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | OR | p-Value | Missing | n | IRR | p-Value | Missing | ||||
| Herd size | 28,228/87 | 628/289 | 446/296 | 28,228 | 1.004 | <0.001 | 0 | 17,435 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 10,793 |
| Missing: | -/- | ||||||||||
| Herd size of the origin dairy farm | 28,226/87 | 122/117 | 104/- | 28,226 | 1.001 | <0.001 | 0 | 17,434 | 1.000 | 0.550 | 10,794 |
| Missing: | 2/- | ||||||||||
| Number of calves transported to farm | 28,228/ | 956/324 | 722/455 | 28,228 | 1.002 | <0.001 | 0 | 17,435 | 1.030 | <0.001 | 10,793 |
| Missing: | 0 /0 | ||||||||||
| Arrival age of the calf/days | 28,228 | 0.979 | <0.001 | 0 | 17,435 | 0.996 | <0.001 | 10,793 | |||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | 23,946/45 | 23/22.3 | 9.2/3.7 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 37,46/28 | 21.5/21.0 | 8.7/3.6 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 536/14 | 97.4/97.6 | 33.2/23.8 | ||||||||
| Total: | 28,228/87 | 24.2/34.0 | 14.4/29.7 | ||||||||
| Missing: | -/- | ||||||||||
| Arrival weight of the calf/kg | 27,724 | 0.985 | <0.001 | 504 | 17,221 | 0.998 | 0.001 | 10,503 | |||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | 23,536/45 | 58.5/58.6 | 10.1/2.6 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 3659/28 | 57.5/57.3 | 9.4/2.9 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 529 (14) | 117.4/117.9 | 39.4/21.3 | ||||||||
| Total: | 27,724/87 | 59.5/67.7 | 14.1/23.9 | ||||||||
| Missing: | 504/0 | ||||||||||
| Average arrival age of calves in the same batch | 28,228 | 0.955 | <0.001 | 0 | 17,435 | <1.000 | 0.874 | 10,793 | |||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | 23,946/45 | 23.0/22.3 | 5.3/3.7 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 3746/28 | 21.5/21.0 | 5.1/3.6 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 536/14 | 97.4/97.6 | 24.0/23.8 | ||||||||
| Total: | 28,228/87 | 24.2/34.0 | 11.9/29.7 | ||||||||
| Missing: | 0/0 | ||||||||||
| Age variation in arrival batch (SD) | 28,226 | 0.986 | 0.608 | 2 | 17,434 | 1.004 | 0.401 | 10,793 | |||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | 23,946/45 | 7.4/7.2 | 1.8/1.7 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 37,46/28 | 6.7/6.6 | 2.4/2.1 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 534/14 | 22.4/21.8 | 9.1/7.0 | ||||||||
| Total: | 28,224/87 | 7.6/9.3 | 3.1/6.3 | ||||||||
| Missing: | 4/0 | ||||||||||
| Number of caretakers/100 calves | 28,228 | 1.541 | <0.001 | 0 | 17,435 | 0.725 | <0.001 | 10,793 | |||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | 23,946/45 | 0.6/1.0 | 0.4/0.6 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 3746/28 | 0.7/0.8 | 0.4/0.5 | ||||||||
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 536/14 | 1.6/1.6 | 0.6/0.6 | ||||||||
| Total: | 28,228/87 | 0.6/1.00 | 0.4/0.6 | ||||||||
| Missing: | 0 | ||||||||||
| Predictor Variable | Odds Ratio | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of calves transported to the farm/100 * | 1.141 | 0.002 | 1.049–1.240 | |
| Age of calf on arrival | 0.981 | <0.001 | 0.977–0.985 | |
| Arrival age variation in calf batch (standard deviation) | 1.090 | 0.007 | 1.024–1.160 | |
| Number of caretakers/100 calves | 0.294 | <0.001 | 0.149–0.580 | |
| Farm type | ||||
| Specialized calf rearing farm | ref. | ref. | ||
| Fattening farm for milk calves | 0.569 | 0.179 | 0.250–1.296 | |
| Fattening farm for weaned calves | 0.212 | 0.123 | 0.029–1.524 | |
| Wald-test: | 0.181 | |||
| Contract meat company | ||||
| Meat company A | ref. | ref. | ||
| Meat company B | 0.876 | 0.717 | 0.427–1.796 | |
| Meat company C | 15.208 | <0.001 | 4.749–48.700 | |
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | |||
| Sex | ||||
| Bull | ref. | ref. | ||
| Heifer | 0.723 | <0.001 | 0.642–0.814 | |
| Breed | ||||
| Ayrshire | ref. | ref. | ||
| Holstein | 0.807 | <0.001 | 0.747–0.873 | |
| Crossbred Aberdeen Angus | 0.628 | <0.001 | 0.526–0.750 | |
| Crossbred Limousine | 0.797 | 0.007 | 0.675–0.940 | |
| Crossbred Blonde d’aquitaine | 0.746 | <0.001 | 0.654–0.851 | |
| Other breeds ** | 0.951 | 0.593 | 0.790–1.145 | |
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | |||
| Type of ventilation for weaned calves | ||||
| Mechanical ventilation | ref. | ref. | ||
| Natural ventilation | 0.393 | 0.028 | 0.171–0.905 | |
| Partly mechanical and natural ventilation | 0.918 | 0.919 | 0.176–4.780 | |
| Wald-test: | 0.088 | |||
| Medicines stored at farm for future use | ||||
| Yes | ref. | ref. | ||
| No | 0.131 | <0.001 | 0.045–0.387 | |
| Medication policy on farm | ||||
| Metaphylactic group treatments used if needed | ref. | ref. | ||
| Only sick animals medicated | 0.307 | 0.001 | 0.152–0.620 | |
| Temperature measured to detect sick calves | ||||
| Yes | ref. | ref. | ||
| No | 0.534 | 0.031 | 0.268–1.067 | |
| Total | % | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Calves | Proportion of All Calves | Average at Farm Level | |
| Medicated at least once during follow-up | |||
| Yes | 17,435 | 61.8 | 36.6 |
| No | 10,793 | 38.2 | 63.4 |
| Total: | 28,228 | 100 | 100 |
| Missing: | 0 | ||
| Number of medication events during follow-up | |||
| Zero | 10,793 | 38.2 | |
| One | 8158 | 28.9 | |
| Two | 5036 | 17.9 | |
| Three | 2565 | 9.1 | |
| Four | 1110 | 3.9 | |
| Five or more | 566 | 2.0 | |
| Total: | 28,228 | 100.0 | |
| Missing: | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| Predictor Variable | IRR | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of calves transported to the farm/100 * | 1.023 | <0.001 | 1.020–1.026 |
| Age of calf on arrival | 0.997 | <0.001 | 0.995–0.998 |
| Age variation in arrival batch (standard deviation) | 1.010 | 0.091 | 0.998–1.021 |
| Contract meat company | |||
| Meat company A | ref. | ref. | |
| Meat company B | 0.971 | 0.684 | 0.850–1.121 |
| Meat company C | 1.320 | 0.007 | 1.080–1.615 |
| Wald-test: | 0.008 | ||
| Breed | |||
| Ayrshire | ref. | ref. | |
| Holstein | 0.949 | <0.001 | 0.926–0.973 |
| Crossbred Aberdeen Angus | 0.954 | 0.129 | 0.897–1.014 |
| Crossbred Limousine | 0.984 | 0.572 | 0.931–1.040 |
| Crossbred Blonde d’Aquitaine | 0.900 | <0.001 | 0.863–0.939 |
| Other breeds ** | 0.876 | <0.001 | 0.820–0.937 |
| Wald-test: | <0.001 | ||
| Filling of compartments for arriving milk calves | |||
| All compartments filled simultaneously | ref. | ref. | |
| All compartments filled independently | 1.221 | 0.002 | 1.073–1.388 |
| Handling of calves after weaning | |||
| Calves relocated to new compartment | ref. | ref. | |
| Calves stay in the same compartment | 1.094 | <0.001 | 1.052–1.136 |
| Temperature measured to detect sick calves | |||
| Yes | ref. | ref. | |
| No | 0.779 | < 0.001 | 0.743–0.817 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandelin, A.; Hälli, O.; Härtel, H.; Herva, T.; Kaartinen, L.; Tuunainen, E.; Rautala, H.; Soveri, T.; Simojoki, H. Effect of Farm Management Practices on Morbidity and Antibiotic Usage on Calf Rearing Farms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020270
Sandelin A, Hälli O, Härtel H, Herva T, Kaartinen L, Tuunainen E, Rautala H, Soveri T, Simojoki H. Effect of Farm Management Practices on Morbidity and Antibiotic Usage on Calf Rearing Farms. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandelin, Atte, Outi Hälli, Heidi Härtel, Tuomas Herva, Liisa Kaartinen, Erja Tuunainen, Helena Rautala, Timo Soveri, and Heli Simojoki. 2022. "Effect of Farm Management Practices on Morbidity and Antibiotic Usage on Calf Rearing Farms" Antibiotics 11, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020270
APA StyleSandelin, A., Hälli, O., Härtel, H., Herva, T., Kaartinen, L., Tuunainen, E., Rautala, H., Soveri, T., & Simojoki, H. (2022). Effect of Farm Management Practices on Morbidity and Antibiotic Usage on Calf Rearing Farms. Antibiotics, 11(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11020270





