Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human and Veterinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Colistin Resistance in K. pneumoniae Veterinary Isolates
2.2. Molecular Mechanisms of COL Resistance in K. pneumoniae Isolates
2.3. Genetic Relatedness of COL-Resistant K. pneumoniae from Human and Animal Origin
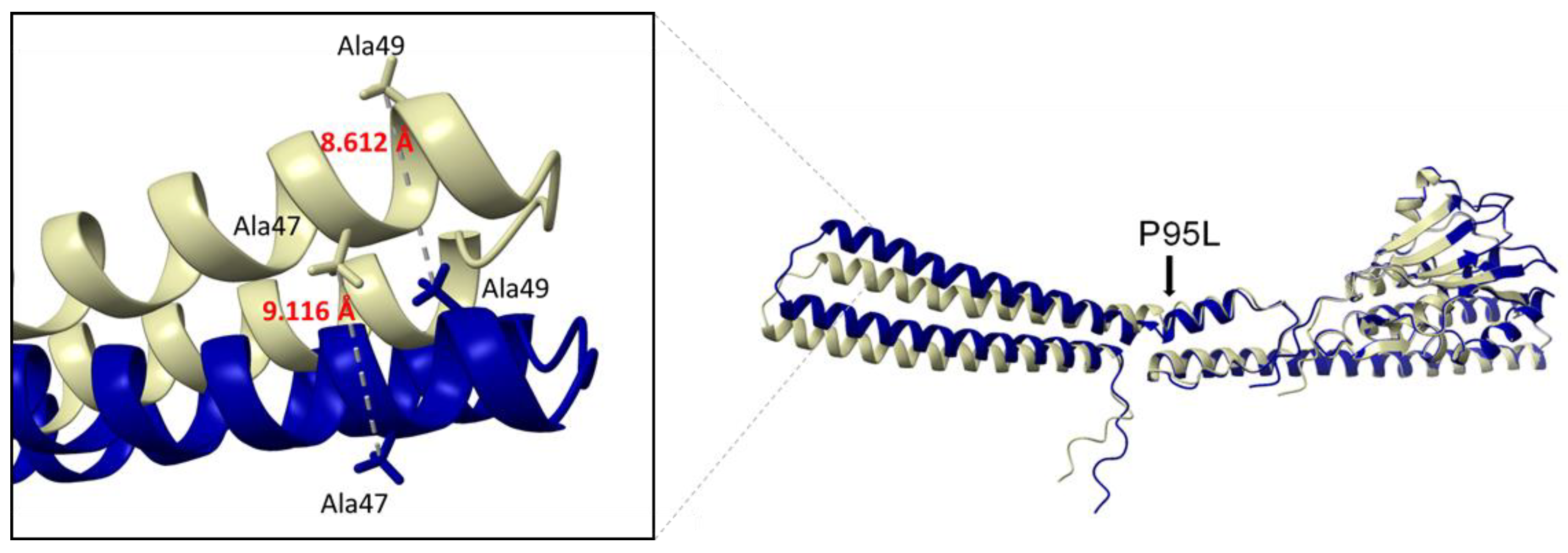
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Detection and Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants
4.4. Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Genetic Relatedness
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Key Pathogen Set for Global Nosocomial Dominance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5873–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Milne, R.W.; Coulthard, K.; Rayner, C.R.; Paterson, D.L. Colistin: The re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, H.; Chen, B.-H.; Kuca, K.; Nepovimova, E.; Kaushal, A.; Nagraik, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; et al. Understanding of Colistin Usage in Food Animals and Available Detection Techniques: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA updates its advice on the use of colistin in animals. Vet. Rec. 2016, 179, 131–132. [CrossRef]
- Velkov, T.; Thompson, P.E.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Structure—Activity relationships of polymyxin antibiotics. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1898–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Maier, E.; Benz, R.; Hancock, R.E. Mechanism of interaction of different classes of cationic antimicrobial peptides with planar bilayers and with the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7235–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Chapple, D.S. Peptide antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clausell, A.; Rabanal, F.; Garcia-Subirats, M.; Asunción Alsina, M.; Cajal, Y. Membrane association and contact formation by a synthetic analogue of polymyxin B and its fluorescent derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4465–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajal, Y.; Rogers, J.; Berg, O.G.; Jain, M.K. Intermembrane molecular contacts by polymyxin B mediate exchange of phospholipids. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, M.E.; Elliott, A.G.; Cao, M.D.; Ganesamoorthy, D.; Karaiskos, I.; Giamarellou, H.; Abboud, C.S.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Cooper, M.A.; Coin, L.J.M. Multifactorial chromosomal variants regulate polymyxin resistance in extensively drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Ko, K.S. Mutations and expression of PmrAB and PhoPQ related with colistin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.K.; Brannon, M.K.; Stevens, L.; Johansen, H.K.; Selgrade, S.E.; Miller, S.I.; Høiby, N.; Moskowitz, S.M. PhoQ mutations promote lipid A modification and polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa found in colistin-treated cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5761–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannatelli, A.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Giani, T.; Di Pilato, V.; Arena, F.; Ambretti, S.; Gaibani, P.; Rossolini, G.M. In vivo emergence of colistin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae producing KPC-type carbapenemases mediated by insertional inactivation of the PhoQ/PhoP mgrB regulator. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5521–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietgen, M.; Semmler, T.; Riedel-Christ, S.; Kempf, V.A.J.; Molinaro, A.; Ewers, C.; Göttig, S. Impact of the colistin resistance gene mcr-1 on bacterial fitness. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Fedorov, B.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Klimke, W. Curation of the AMRFinderPlus databases: Applications, functionality and impact. Microb. Genomics 2022, 8, mgen000832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovich, T.; Adams-Haduch, J.M.; Tian, G.-B.; Nguyen, M.H.; Kwak, E.J.; Muto, C.A.; Doi, Y. Colistin-resistant, Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae belonging to the international epidemic clone ST258. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catry, B.; Cavaleri, M.; Baptiste, K.; Grave, K.; Grein, K.; Holm, A.; Jukes, H.; Liebana, E.; Lopez Navas, A.; Mackay, D.; et al. Use of colistin-containing products within the European Union and European Economic Area (EU/EEA): Development of resistance in animals and possible impact on human and animal health. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2015, 46, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, N.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P.; Madec, J.-Y.; Haenni, M. Emergence of colistin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae from veterinary medicine. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1265–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Wang, R.; Jin, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. Molecular epidemiology of colistin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in inpatient and avian isolates from China: High prevalence of mcr-negative Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngbede, E.O.; Adekanmbi, F.; Poudel, A.; Kalalah, A.; Kelly, P.; Yang, Y.; Adamu, A.M.; Daniel, S.T.; Adikwu, A.A.; Akwuobu, C.A.; et al. Concurrent Resistance to Carbapenem and Colistin among Enterobacteriaceae Recovered from Human and Animal Sources in Nigeria Is Associated with Multiple Genetic Mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 740348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishnian, Z.; Haeili, M.; Feizi, A. Prevalence and molecular determinants of colistin resistance among commensal Enterobacteriaceae isolated from poultry in northwest of Iran. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savin, M.; Bierbaum, G.; Blau, K.; Parcina, M.; Sib, E.; Smalla, K.; Schmithausen, R.; Heinemann, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Kreyenschmidt, J. Colistin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Process Waters and Wastewater from German Poultry and Pig Slaughterhouses. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN web server: A tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyres, K.L.; Hawkey, J.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Fostervold, A.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Hamidian, M.; Howden, B.P.; Löhr, I.H.; Holt, K.E. Emergence and rapid global dissemination of CTX-M-15-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ST307. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arana, D.M.; Saez, D.; García-Hierro, P.; Bautista, V.; Fernández-Romero, S.; La Ángel de Cal, M.; Alós, J.I.; Oteo, J. Concurrent interspecies and clonal dissemination of OXA-48 carbapenemase. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 148.e1–148.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damjanova, I.; Tóth, A.; Pászti, J.; Hajbel-Vékony, G.; Jakab, M.; Berta, J.; Milch, H.; Füzi, M. Expansion and countrywide dissemination of ST11, ST15 and ST147 ciprofloxacin-resistant CTX-M-15-type β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae epidemic clones in Hungary in 2005—The new ‘MRSAs’? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewers, C.; Stamm, I.; Pfeifer, Y.; Wieler, L.H.; Kopp, P.A.; Schønning, K.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Scheufen, S.; Stolle, I.; Günther, S.; et al. Clonal spread of highly successful ST15-CTX-M-15 Klebsiella pneumoniae in companion animals and horses. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2676–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenni, M.; Ponsin, C.; Métayer, V.; Médaille, C.; Madec, J.-Y. Veterinary hospital-acquired infections in pets with a ciprofloxacin-resistant CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15 clone. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 770–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Diene, S.M.; Kempf, M.; Berrazeg, M.; Bakour, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Thongmalayvong, B.; Akkhavong, K.; Somphavong, S.; Paboriboune, P.; et al. Worldwide emergence of colistin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae from healthy humans and patients in Lao PDR, Thailand, Israel, Nigeria and France owing to inactivation of the PhoP/PhoQ regulator mgrB: An epidemiological and molecular study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamame, A.; Davoust, B.; Cherak, Z.; Rolain, J.-M.; Diene, S.M. Mobile Colistin Resistance (mcr) Genes in Cats and Dogs and Their Zoonotic Transmission Risks. Pathogens 2022, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Chan, E.W.-c.; Zhou, H.; Chen, S. Dissemination of the mcr-1 colistin resistance gene. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dierikx, C.M.; Meijs, A.P.; Hengeveld, P.D.; van der Klis, F.R.M.; van Vliet, J.; Gijsbers, E.F.; Rozwandowicz, M.; van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Hordijk, J.; et al. Colistin-resistant Enterobacterales among veterinary healthcare workers and in the Dutch population. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 4, dlac041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Qiu, L.; Guo, Z.; Huang, J.; Qiu, J.; et al. Colistin-resistance mcr genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae from companion animals. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, S.M.; Brannon, M.K.; Dasgupta, N.; Pier, M.; Sgambati, N.; Miller, A.K.; Selgrade, S.E.; Miller, S.I.; Denton, M.; Conway, S.P.; et al. PmrB mutations promote polymyxin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from colistin-treated cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, S.M.; Ernst, R.K.; Miller, S.I. PmrAB, a two-component regulatory system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that modulates resistance to cationic antimicrobial peptides and addition of aminoarabinose to lipid A. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlesinger, J.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Chmelnitsky, I.; Hammer-Münz, O.; Leavitt, A.; Gold, H.S.; Schwaber, M.J.; Carmeli, Y. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases among Enterobacter isolates obtained in Tel Aviv, Israel. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallenne, C.; Da Costa, A.; Decré, D.; Favier, C.; Arlet, G. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ries, J.I.; Heß, M.; Nouri, N.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Göttig, S.; Falcone, F.H.; Kraiczy, P. CipA mediates complement resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii by formation of a factor I-dependent quadripartite assemblage. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 942482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jünemann, S.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Prior, K.; Albersmeier, A.; John, U.; Kalinowski, J.; Mellmann, A.; Goesmann, A.; von Haeseler, A.; Stoye, J.; et al. Updating benchtop sequencing performance comparison. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain | Year | Disease | Animal | Specimen | Colistin Treatment | Sequence Type (ST) |
| IHIT27665 | 2012 | Unknown | Swine | Faeces | - | 15 |
| IHIT27662 | 2012 | Mastitis | Dairy cattle | Milk | - | 976 |
| IHIT27663 | 2011 | Mastitis | Dairy cattle | Milk | - | 1864 |
| IHIT27664 | 2007 | Mastitis | Dairy cattle | Milk | - | 163 |
| IHIT32358 | 2016 | Otitis | Dog | Ear swab | unknown | 15 |
| IHIT33535 | 2017 | Cystitis | Dog | Urine | unknown | 307 |
| Strain | Year | Disease | Detection Site/Specimen | Colistin Treatment | Sequence Type (ST) | |
| KP_03 | 2011 | Heart surgery | BAL | - | 48 | |
| KP_53 | 2010 | Kidney transplantation | Abdominal swab | Yes | 16 | |
| KP_54 | 2007 | Liver cirrhosis | Wound swab | - | 11 | |
| KP_1153 | 2011 | ARDS | Bronchial secretion | - | 11 | |
| KP_1200 | 2011 | Renal insufficiency | Peritoneal fluid | - | 1583 | |
| KP_1377 | 2011 | Sarcoma | Urine | - | 258 | |
| KP_1585 | 2013 | AML | Blood | Yes | 437 | |
| KP_1710 | 2013 | Ileus | Tracheal secretion | - | 395 | |
| KP_1954 | 2014 | Pancreatitis | Bronchial secretion | Yes | 258 | |
| KP_2442 | 2015 | ALL | Blood | - | 2299 | |
| KP_3405 | 2016 | Liver cirrhosis | Rectal swab | - | 15 | |
| KP_3996 | 2017 | Cardiomyopathy | Blood | - | 101 | |
| MIC (mg/L) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Veterinary Isolates | Human Isolates | |||||||||||||||||
| Antibiotic Agent | IHIT27662 | IHIT27663 | IHIT27664 | IHIT27665 | IHIT32358 | IHIT33535 | KP_03 | KP_53 | KP_54 | KP_1153 | KP_1200 | KP_1377 | KP_1585 | KP_1710 | KP_1954 | KP_2442 | KP_3405 | KP_3996 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam | 2 | 2 | 1 | 64 | 16 | 8 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 32 | >256 | >256 |
| Cefotaxime | 0.064 | 0.064 | 0.064 | 64 | 0.064 | 128 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 128 | >256 | >256 |
| Ceftazidime | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 8 | 1 | 16 | 48 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >64 | >256 | >64 | 64 | >256 | 32 | >64 | >256 |
| Imipenem | 0.032 | 0.25 | 0.064 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.25 | >32 | >32 | 2 | 1 | 32 | 2 | 0.25 | >32 | 0.125 | 1 | >32 |
| Meropenem | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.125 | 1 | 0.032 | 0.064 | 0.064 | >32 | >32 | 16 | 4 | 32 | 4 | 0.125 | >32 | 0.032 | 8 | >32 |
| Tobramycin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 8 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 16 | 8 | >256 |
| Amikacin | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 16 | 16 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 8 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 2 | >256 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.016 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 1 | >32 | 32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 |
| TMP-SMX | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 2 | 2 | >16 | >32 | >32 | 1.5 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | 8 | 0.19 |
| Polymyxin B | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Colistin a | 64 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 64 | 128 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 8 | 32 | 32 |
| Isolate | MgrB a | IS | PmrA | PmrB b | PmrC | PmrE | PmrH | KdtA | PhoQ | LpxB | LpxH | LpxK | Mcr-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IHIT27665 | Q30Stop | - | - | T112P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| IHIT27662 | Insertion (Pos +69) | IS903B (1057 bp) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | E234- | L218H | - |
| IHIT27663 | K2E | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| IHIT27664 | Deletion (1253 bp) | - | - | - | - | P89L | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| IHIT32358 | Q30Stop | - | G53S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| IHIT33535 | Q33Stop | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_03 | - | - | - | P95L | - | - | P264S | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_53 | Insertion (Pos +60) | IS1R (767 bp) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_54 | Deletion (10,934 bp) | - | - | R256G | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_1153 | Insertion (Pos +75) | ISEcp1 (1656 bp) | - | R256G | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_1200 | Deletion (3481 bp) | - | - | - | I83T | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_1377 | Insertion (Pos +133) | ISKpn25 (8154 bp) | - | R256G | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_1585 | Deletion (6378 bp) | - | - | R256G | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_1710 | Deletion (1300 bp) | - | - | R256G | - | - | - | A180T | - | A152T | - | - | - |
| KP_1954 | Insertion (Pos +74) | ISKpn26 (1195 bp) | - | R256G | - | - | - | - | N253P | - | - | - | - |
| KP_2442 | - | - | - | - | S257L | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| KP_3405 | Deletion (12,160 bp) | - | - | - | S257L | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KP_3996 | Insertion (Pos +6) | kdgR (1147 bp) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tietgen, M.; Sedlaczek, L.; Higgins, P.G.; Kaspar, H.; Ewers, C.; Göttig, S. Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human and Veterinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111672
Tietgen M, Sedlaczek L, Higgins PG, Kaspar H, Ewers C, Göttig S. Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human and Veterinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111672
Chicago/Turabian StyleTietgen, Manuela, Lisa Sedlaczek, Paul G. Higgins, Heike Kaspar, Christa Ewers, and Stephan Göttig. 2022. "Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human and Veterinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111672
APA StyleTietgen, M., Sedlaczek, L., Higgins, P. G., Kaspar, H., Ewers, C., & Göttig, S. (2022). Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Human and Veterinary Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111672







