Metabolomic Profiling, In Vitro Antimalarial Investigation and In Silico Modeling of the Marine Actinobacterium Strain Rhodococcus sp. UR111 Associated with the Soft Coral Nephthea sp.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Soft Coral Collection
2.2. Strain Isolation
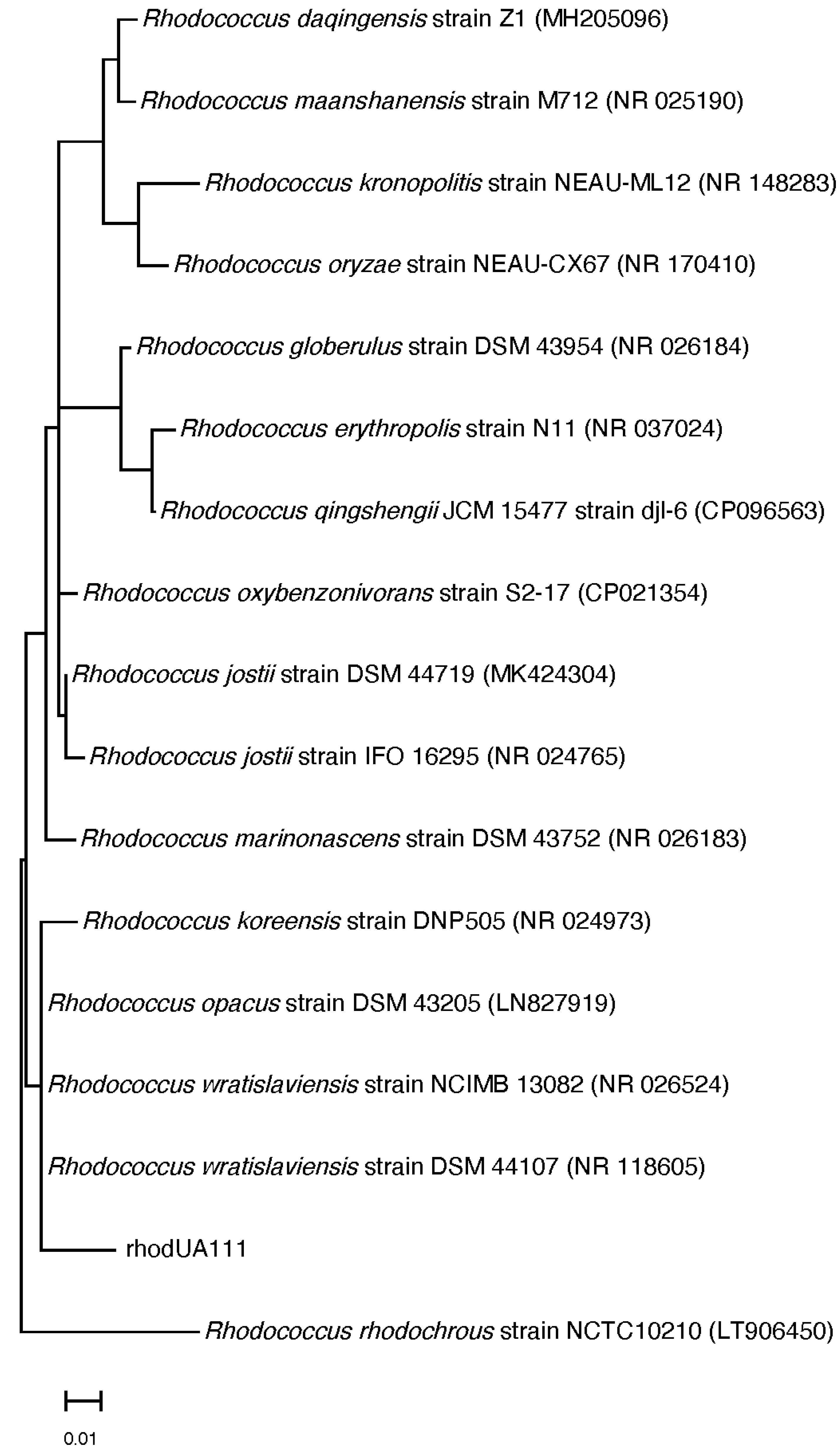
2.3. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Extract Preparation
2.5. Antimalarial Assay
2.6. LC-MS Profiling
2.7. In silico Molecular Docking Simulations
2.8. ADME Parameters and Drug-Likeness Computational Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of Red Sea Soft Coral Associated Actinobacteria
3.2. Antimalarial Assay
3.3. Metabolomic Analysis
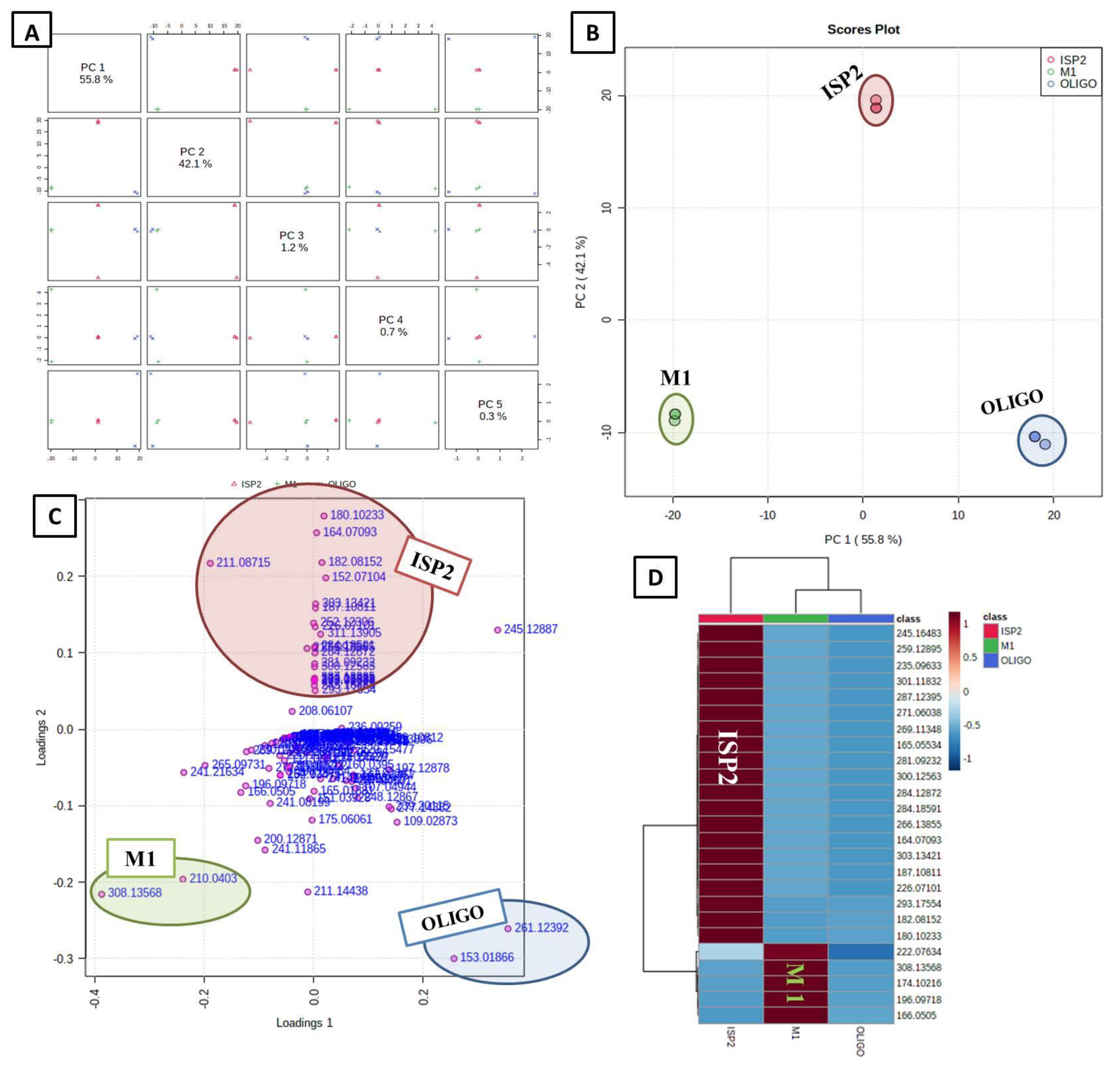
3.4. Multivariate Data Analysis
3.4.1. Unsupervised Analysis
3.4.2. Supervised Analysis
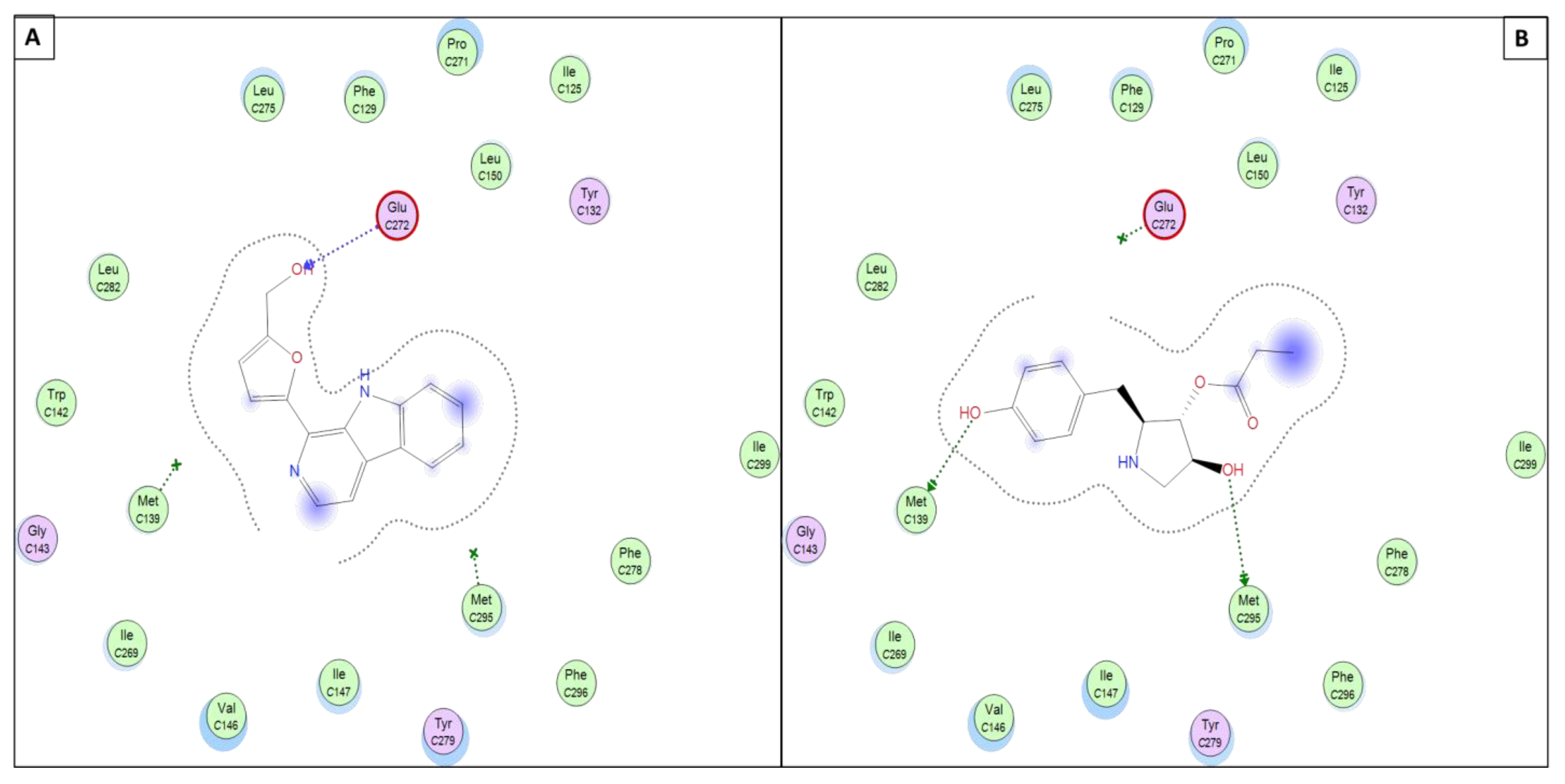
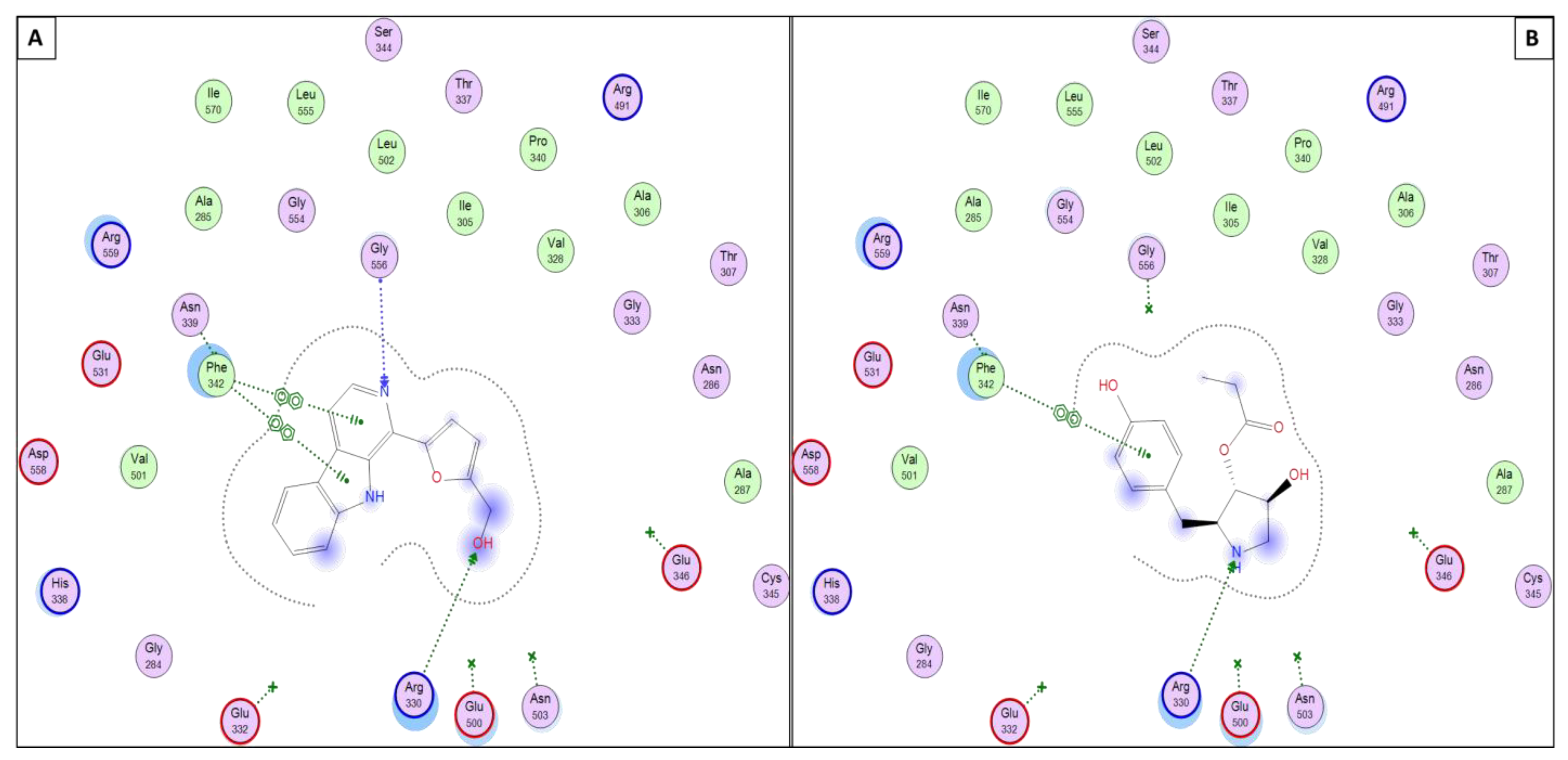
3.5. Molecular Docking Simulations
3.5.1. ADME Parameters and Drug-likeness Computational Analysis
3.5.2. Perlolyrine (11) and 3097-B2 (12)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsayed, Y.; Refaat, J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Othman, E.M.; Stopper, H.; Fouad, M.A. Metabolomic Profiling and Biological Investigation of the Marine Sponge-Derived Bacterium Rhodococcus sp. UA13. Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Yang, C.; Horn, H.; Hajjar, D.; Ravasi, T.; Hentschel, U. Actinomycetes from Red Sea Sponges: Sources for Chemical and Phylogenetic Diversity. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2771–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, Y.; Fahim, J.; Abdelmohsen, U.; Fouad, M. Chemical and Biological Investigation of the Marine Bacterium Rhodococcus Sp. UA13. J. Adv. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.S.; Philp, J.C.; Aw, D.W.J.; Christofi, N. A Review: The Genus Rhodococcus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 85, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, Y.; Refaat, J.; Yasmin Elsayed, C.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Fouad, M.A. The Genus Rhodococcus as a Source of Novel Bioactive Substances: A Review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Uwimana, A.; Legrand, E.; Stokes, B.H.; Ndikumana, J.L.M.; Warsame, M.; Umulisa, N.; Ngamije, D.; Munyaneza, T.; Mazarati, J.B.; Munguti, K.; et al. Emergence and Clonal Expansion of in Vitro Artemisinin-Resistant Plasmodium Falciparum Kelch13 R561H Mutant Parasites in Rwanda. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotie, J. Quinones and Malaria. Antiinfect. Agents Med. Chem. 2006, 5, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.; Specht, S.; Sarite, S.R.; Saeftel, M.; Hoerauf, A.; Schulz, B.; Krohn, K. A New Class of Phenazines with Activity against a Chloroquine Resistant Plasmodium falciparum Strain and Antimicrobial Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4913–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Mohammed, R.; Bahr, H.S.; Attia, E.Z.; El-Katatny, M.H.; Abelyan, N.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; Moawad, A.S.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Soybean-Associated Endophytic Fungi as Potential Source for Anti-COVID-19 Metabolites Supported by Docking Analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 1193–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, C.J. Biological Production of Optically Active Muconolactones by Rhodococcus Rhodochrous. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, N.M.; Gomaa, A.A.-R.; Mostafa, Y.A.; Hajjar, D.; Makki, A.A.; Alaaeldin, E.; Refaat, H.; Bringmann, G.; Zayed, A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Diterpenoids Profile of the Marine Sponge Chelonaplysilla erecta and Candidacy as Potential Antitumor Drugs Investigated by Molecular Docking and Pharmacokinetic Studies. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaka, T.; Matsui, T.; Maruhashi, K. Metabolite Detection in Rhodococcus benzothiophene Desulfurization Using Reversed-Phase Solid-Phase Extraction and a Derivatization Technique. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereliaeva, E.V.; Dmitrieva, M.E.; Morgunova, M.M.; Belyshenko, A.Y.; Imidoeva, N.A.; Ostyak, A.S.; Axenov-Gribanov, D.V. The Use of Baikal Psychrophilic Actinobacteria for Synthesis of Biologically Active Natural Products from Sawdust Waste. Fermentation 2022, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, C.J.; Lee, J.C.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Indole-3-Acetaldehyde from Rhodococcus sp. BFI 332 Inhibits Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Biofilm Formation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhadrami, H.A.; Thissera, B.; Hassan, M.H.A.; Behery, F.A.; Ngwa, C.J.; Hassan, H.M.; Pradel, G.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Rateb, M.E. Bio-Guided Isolation of Antimalarial Metabolites from the Coculture of Two Red Sea Sponge-Derived Actinokineospora and Rhodococcus spp. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, Y.; Asano, Y. Biosynthetic Pathway for the Cyanide-Free Production of Phenylacetonitrile in Escherichia Coli by Utilizing Plant Cytochrome P450 79A2 and Bacterial Aldoxime Dehydratase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6828–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; Frese, M.; Wibberg, D.; El-Haddad, A.F.; Ibrahim, T.M.A.; Kalinowski, J.; Sewald, N.; Shaaban, M. New Oxaphenalene Derivative from Marine-Derived Streptomyces Griseorubens sp. ASMR4. Zeitschrift fur Naturforsch.—Sect. B J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 72, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, A.; Prabhakar, P.; Vijayalakshmi, M.; Venkateswarlu, Y. Purification and Biological Evaluation of the Metabolites Produced by Streptomyces sp. TK-VL_333. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.A. Ent-Homoabyssomicins A and B, Two New Spirotetronates, Khatmiamycin, a Zoosporicidal Naphthoquinone, and Further New Biologically Active Secondary Metabolites; Cuvillier Verlag: Göttingen, Germany, 2010; ISBN 3736935013. [Google Scholar]
- Fotso, S.; Maskey, R.P.; Schröder, D.; Ferrer, A.S.; Grün-Wollny, I.; Laatsch, H. Furan Oligomers and β-Carbolines from Terrestrial Streptomycetes. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bondkly, A.; Abd-Alla, H.; Shaaban, M.; Shaaban, K. The Electrospray Ionization—Mass Spectra of Erythromycin A Obtained from a Marine Streptomyces sp. Mutant. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, Y.; Kameyama, T.; Naganawa, H.; Okami, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Anisomycin and new congeners active against human tumor cell lines. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1993, 46, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Raheem, D.J.; Tawfike, A.F.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; Fitzsimmons-Thoss, V. Application of Metabolomics and Molecular Networking in Investigating the Chemical Profile and Antitrypanosomal Activity of British Bluebells (Hyacinthoides Non-Scripta). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfike, A.F.; Romli, M.; Clements, C.; Abbott, G.; Young, L.; Schumacher, M.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Diederich, M.; Farag, M.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Isolation of Anticancer and Anti-Trypanosome Secondary Metabolites from the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus Flocculus via Bioactivity Guided Isolation and MS Based Metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1106, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.B.; Ye, W.W.; Han, Y.; Deng, Z.X.; Hong, K. Natural Products from Mangrove Actinomycetes. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2590–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnavas, A.; Lassiani, L.; Valenta, V.; Berti, F.; Mennuni, L.; Makovec, F. Anthranilic Acid Derivatives: A New Class of Non-Peptide CCK1 Receptor Antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, J.T.; Tenney, K.; Compton, J.; Crews, P. Chemical Investigations of a Deep Water Marine-Derived Fungus: Simple Amino Acid Derivatives from an Arthrinium sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2007, 2, 1934578X0700200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, H.S.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.M. Streptokordin, a New Cytotoxic Compound of the Methylpyridine Class from a Marine-Derived Streptomyces Sp. KORDI-3238. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2006, 59, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Wei, M.Y.; Pan, J.H.; Deng, D.S.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Penicinoline, a New Pyrrolyl 4-Quinolinone Alkaloid with an Unprecedented Ring System from an Endophytic Fungus Penicillium sp. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3284–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Isolation and Identification of Antibiotic T0007B_1 and T0007B_2. Zhongguo Kangshengsu Zazhi 1990, 15, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-Check: Validation of Diagnostic Statistics for PLS-DA Models in Metabolomics Studies. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, H.; Pierdet, M.; Thomas, O.P.; Zubia, M. Insights into the Metabolome of the Cyanobacterium Leibleinia Gracilis from the Lagoon of Tahiti and First Inspection of Its Variability. Metabolites 2020, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like Properties and the Causes of Poor Solubility and Poor Permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Y.C. A Bioavailability Score. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3164–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, J.A.D. The Alkaloids of Perennial Rye-Grass (Lolium perenne L.). Part 1V.l Isolation of a New Base, Perlolyrine; the Crystal Structure of Its Hydro-Bromide Dihydrate, and the Synthesis of the Base. J. Chem. Soc. 1970, 8, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Liang, W.; Tu, G. Perlolyrine: A β-Carboline Alkaloid from Codonopsis Pilosula. Planta Med. 1988, 54, 472–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.R.; Khadayat, K.; Aryal, N.; Aryal, B.; Lamichhane, U.; Bhattarai, K.; Rana, N.; Regmi, B.P.; Adhikari, A.; Thapa, S.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomics of Streptomyces Species Isolated from Soils of Nepal. Processes 2022, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| # | Cpd ID | Isolated Molecules | 1V0P a | 4PD4 b | 6AGT c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S g | RMSD h | S | RMSD | S | RMSD | |||
| 1 | 3 | 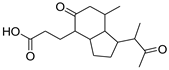 Indene propanoic acid derivative | −5.74 | 1.67 | −5.55 | 1.97 | −5.88 | 0.92 |
| 2 | 4 | 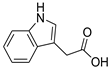 Indole-3-acetic acid | −4.45 | 1.40 | −5.16 | 1.77 | −5.15 | 1.10 |
| 3 | 5 | 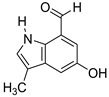 Rhodinodohyde | −5.01 | 0.96 | −4.85 | 0.81 | −5.37 | 1.53 |
| 4 | 6 |  Mitomycin-K | −5.39 | 1.68 | −5.37 | 0.73 | −6.09 | 1.16 |
| 5 | 11 | 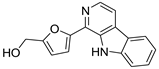 Perlolyrine | −5.98 | 1.04 | −5.84 | 1.69 | −6.91 | 1.12 |
| 6 | 12 | 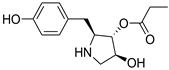 3097-B2 | −5.89 | 1.99 | −6.50 | 1.56 | −7.11 | 1.97 |
| Co-crystallized Ligand | −7.32 d | 1.21 | −6.45 e | 1.64 | −7.98 f | 0.63 | ||
| Molecule ID | 1V0P a | 4PD4 b | 6AGT c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | a.a. Residue | Distance e | Type | a.a. Residue | Distance | Type | a.a. Residue | Distance | |
| 11 | H-acceptor | THR14 | 3.20 | H-acceptor | GLU272 | 3.49 | H-acceptor | GLY556 | 3.46 |
| H-acceptor | ARG330 | 3.15 | |||||||
| Pi-H | VAL18 | 4.21 | Pi-Pi | PHE342 | 3.81 | ||||
| Pi-Pi | PHE342 | 3.83 | |||||||
| 12 | H-donor | LEU82 | 2.90 | H-donor | MET295 | 3.33 | H-acceptor | ARG330 | 3.15 |
| H-acceptor | THR14 | 2.86 | H-donor | MET139 | 3.83 | Pi-Pi | PHE342 | 3.90 | |
| Pi-H | ILE10 | 3.90 | |||||||
| Co-crystallized Ligands d | H-donor | GLU80 | 3.17 | Pi-H | ILE 125 | 4.15 | H-acceptor | ASN339 | 3.05 |
| H-donor | LEU82 | 2.76 | |||||||
| H-acceptor | LEU82 | 3.01 | Pi-Pi | PHE342 | 3.58 | ||||
| Ionic | LYS88 | 3.91 | |||||||
| Pi-H | VAL18 | 4.01 | |||||||
| ID | M.F. a | M.W. b | Nrotb c | HBA d | HBD e | MR f | TPSA g | iLogP h | Water Solubility | HIA% i | BBB Permeant j | Pgp Substrate k | F l | PAINS m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | C17H26O4 | 294.39 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 81.78 | 71.44 | 2.16 | Soluble | High | Yes | No | 0.85 | 0 |
| 4 | C10H9NO2 | 175.18 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 49.84 | 53.09 | 1.01 | Soluble | High | Yes | No | 0.85 | 0 |
| 5 | C10H9NO2 | 175.18 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 50.68 | 53.09 | 1.08 | Soluble | High | Yes | No | 0.55 | 0 |
| 6 | C16H18N2O4 | 302.33 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 85.38 | 58.85 | 2.82 | Very soluble | High | No | No | 0.55 | 1 |
| 11 | C16H12N2O2 | 264.28 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 77.43 | 62.05 | 2.36 | Soluble | High | Yes | Yes | 0.55 | 0 |
| 12 | C14H19NO4 | 265.3 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 74.13 | 78.79 | 2.11 | Soluble | High | No | No | 0.55 | 0 |
| RO5 | ≤500 | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤5 | ≤130 | ≤140 | ≤5 | |||||||
| Sample | IC50 (µg/mL) |
|---|---|
| M1 | 24.7 |
| ISP2 | 8.5 |
| Oligo | >50 |
| Chloroquine | 0.022 |
| # | Ionization | m/z | Rt | Name | Formula | Key Fragments | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N | 135.0442 | 3.0118 | 2-(2′-Hydroxyphenyl) ethen-1-ol | C8H8O2 | Rhodococcus benzothiophene | [12] | |
| 2 | N | 155.0237 | 2.580592 | 2,5-Dihydro-3-methyl-5-oxo-2-furanacetic acid (S-form) | C7H8O4 | Rhodococcus rhodochrous | [10] | |
| 3 | N | 293.1755 | 4.668813 | Octahydro-7a-methyl-1-(1-methyl-2-oxo-propyl)-5-oxo-1H-indene-4-propanoic acid | C17H26O4 | 221.13 | Rhodococcus corallinus | [13] |
| 4 | N | 174.1022 | 2.6807 | Indole-3-acetic acid | C10H9NO2 | Rhodococcus sp. BFI 332 | [14] | |
| 5 | P | 176.0712 | 4.105067 | Rhodinodohyde | C10H9NO2 | 72.07 | Rhodococcus sp. UA13 | [3] |
| 6 | P | 303.1342 | 2.684719 | Mitomycin-K | C16H18N2O4 | 257.06 | Rhodococcus sp. UR59 | [15] |
| 7 | N | 116.0497 | 3.077592 2.708363 | 2-Phenylacetonitrile | C8H7N | marine Streptomyces sp. GWS-BW-H5 | [16] | |
| 8 | N | 131.0707 | 4.603822 | 3,4-Dihydroxy-3-methylpentan-2-one | C6H12O3 | 87.04 | Streptomyces griseorubens sp. ASMR4 | [17] |
| 9 | N | 160.0395 | 3.081942 | Indole-3-carboxylic acid | C9H7NO2 | Streptomyces sp. TK-VL_333 | [18] | |
| 10 | N | 166.0503 | 2.304583 | 2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzamide | C8H9NO3 | marine Streptomyces | [19] | |
| 11 | P | 265.0973 | 3.675722 | Perlolyrin | C16H12N2O2 | 264.87, 165.64 | Streptomyces sp. isolate GW11/1695 | [20] |
| Marine streptomyces | [21] | |||||||
| 12 | N | 264.1238 | 2.991953 | 3097-B | C14H19NO4 | marine Streptomyces | [22] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamaleldin, N.M.; Bahr, H.S.; Mostafa, Y.A.; McAllister, B.F.; El Zawily, A.; Ngwa, C.J.; Pradel, G.; Hassan, H.M.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Alkhalifah, D.H.M.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling, In Vitro Antimalarial Investigation and In Silico Modeling of the Marine Actinobacterium Strain Rhodococcus sp. UR111 Associated with the Soft Coral Nephthea sp. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111631
Gamaleldin NM, Bahr HS, Mostafa YA, McAllister BF, El Zawily A, Ngwa CJ, Pradel G, Hassan HM, Abdelmohsen UR, Alkhalifah DHM, et al. Metabolomic Profiling, In Vitro Antimalarial Investigation and In Silico Modeling of the Marine Actinobacterium Strain Rhodococcus sp. UR111 Associated with the Soft Coral Nephthea sp. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111631
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamaleldin, Noha M., Hebatallah S. Bahr, Yaser A. Mostafa, Bryant F. McAllister, Amr El Zawily, Che J. Ngwa, Gabriele Pradel, Hossam M. Hassan, Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen, Dalal Hussien M. Alkhalifah, and et al. 2022. "Metabolomic Profiling, In Vitro Antimalarial Investigation and In Silico Modeling of the Marine Actinobacterium Strain Rhodococcus sp. UR111 Associated with the Soft Coral Nephthea sp." Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111631
APA StyleGamaleldin, N. M., Bahr, H. S., Mostafa, Y. A., McAllister, B. F., El Zawily, A., Ngwa, C. J., Pradel, G., Hassan, H. M., Abdelmohsen, U. R., Alkhalifah, D. H. M., & Hozzein, W. N. (2022). Metabolomic Profiling, In Vitro Antimalarial Investigation and In Silico Modeling of the Marine Actinobacterium Strain Rhodococcus sp. UR111 Associated with the Soft Coral Nephthea sp. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111631






