Development of IgY-Based Indirect Competitive ELISA for the Detection of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
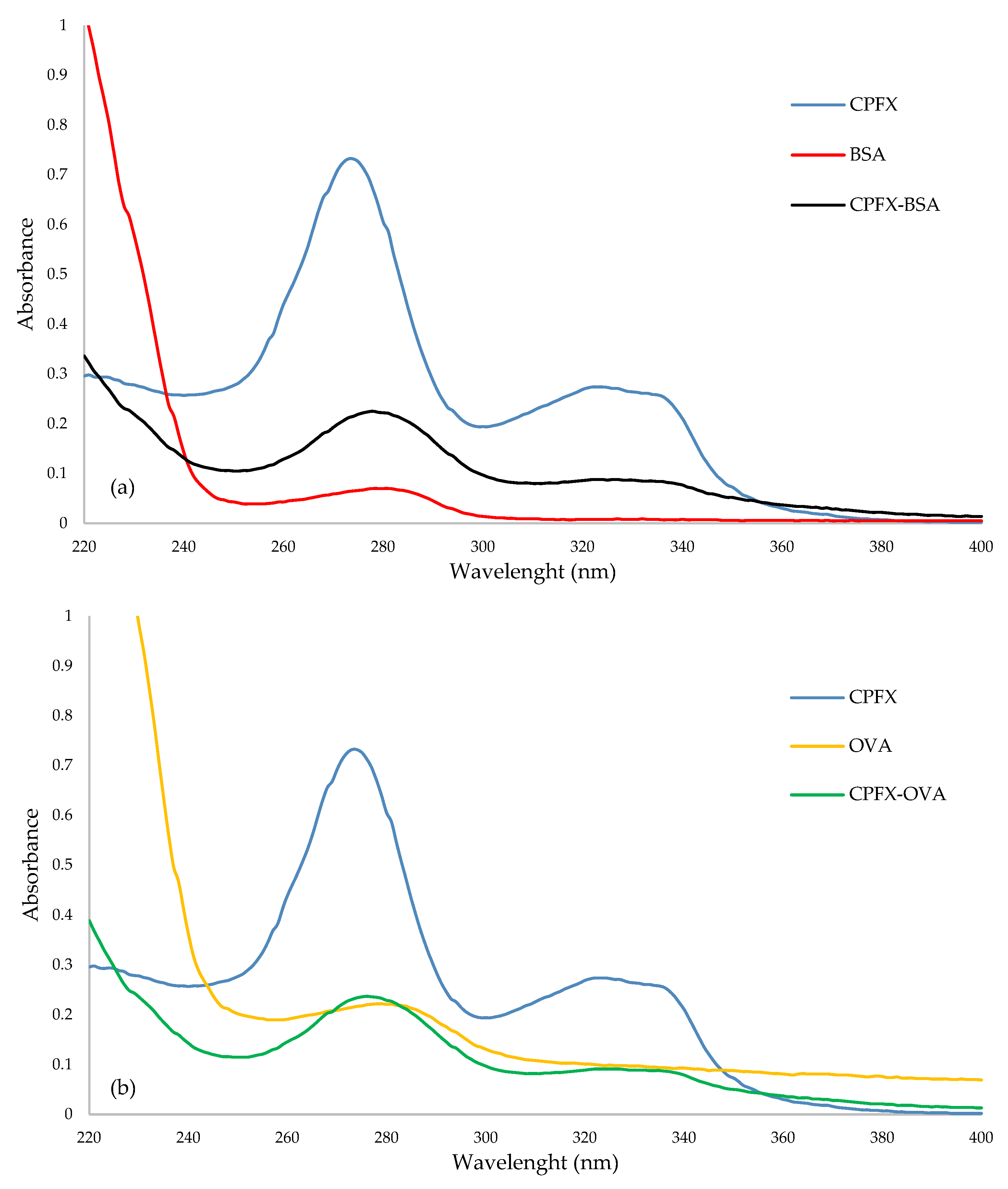
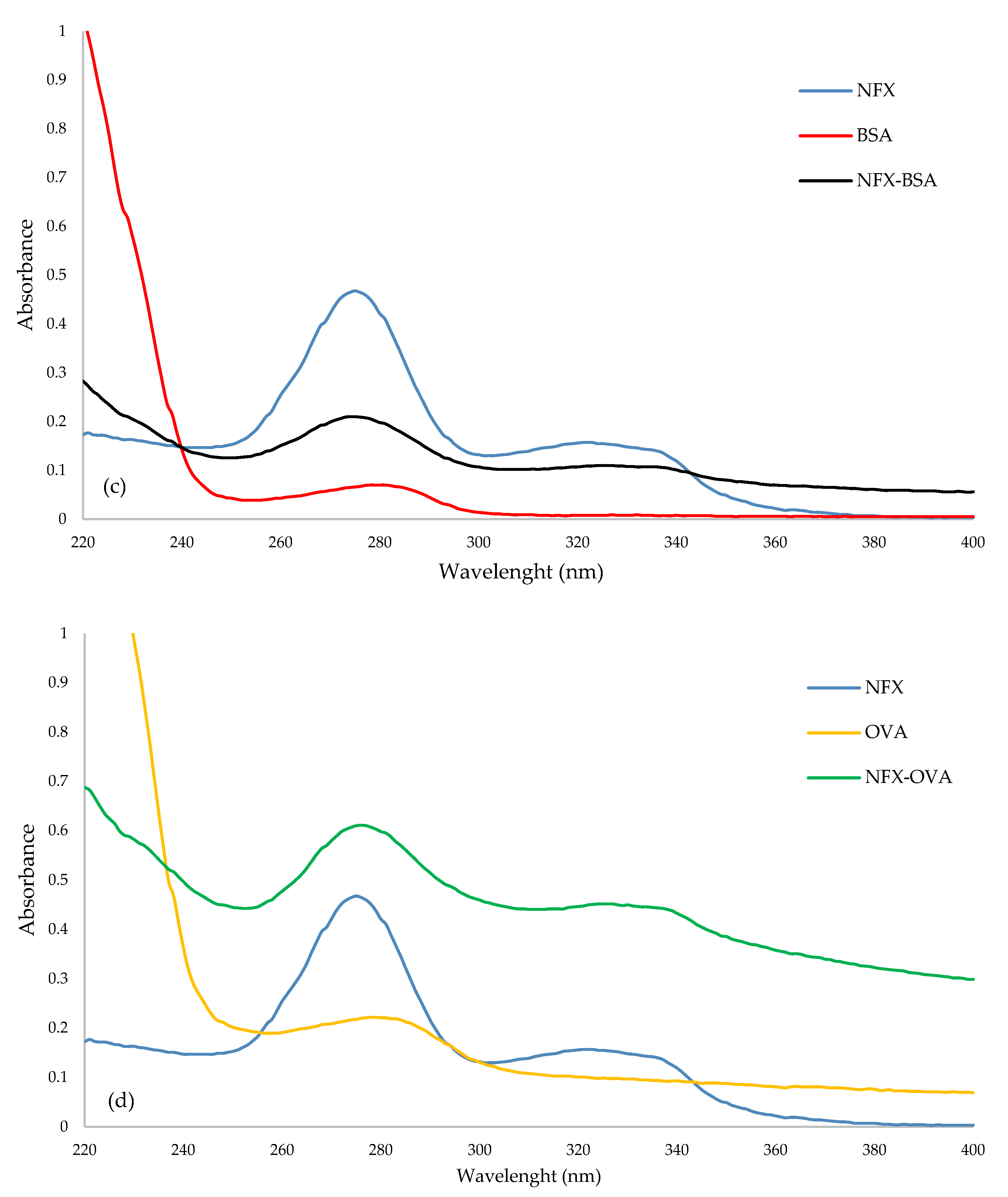
2.1. Immunogen and Coating Antigen Characterization
2.2. Production of Antibody to Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics
2.2.1. The Immunoglobulin G Response in Chicken Hen Serum after Immunization
2.2.2. Preparation of Immunoglobulin Y from Egg Yolk and the Characterization of Sensitivity and Specificity
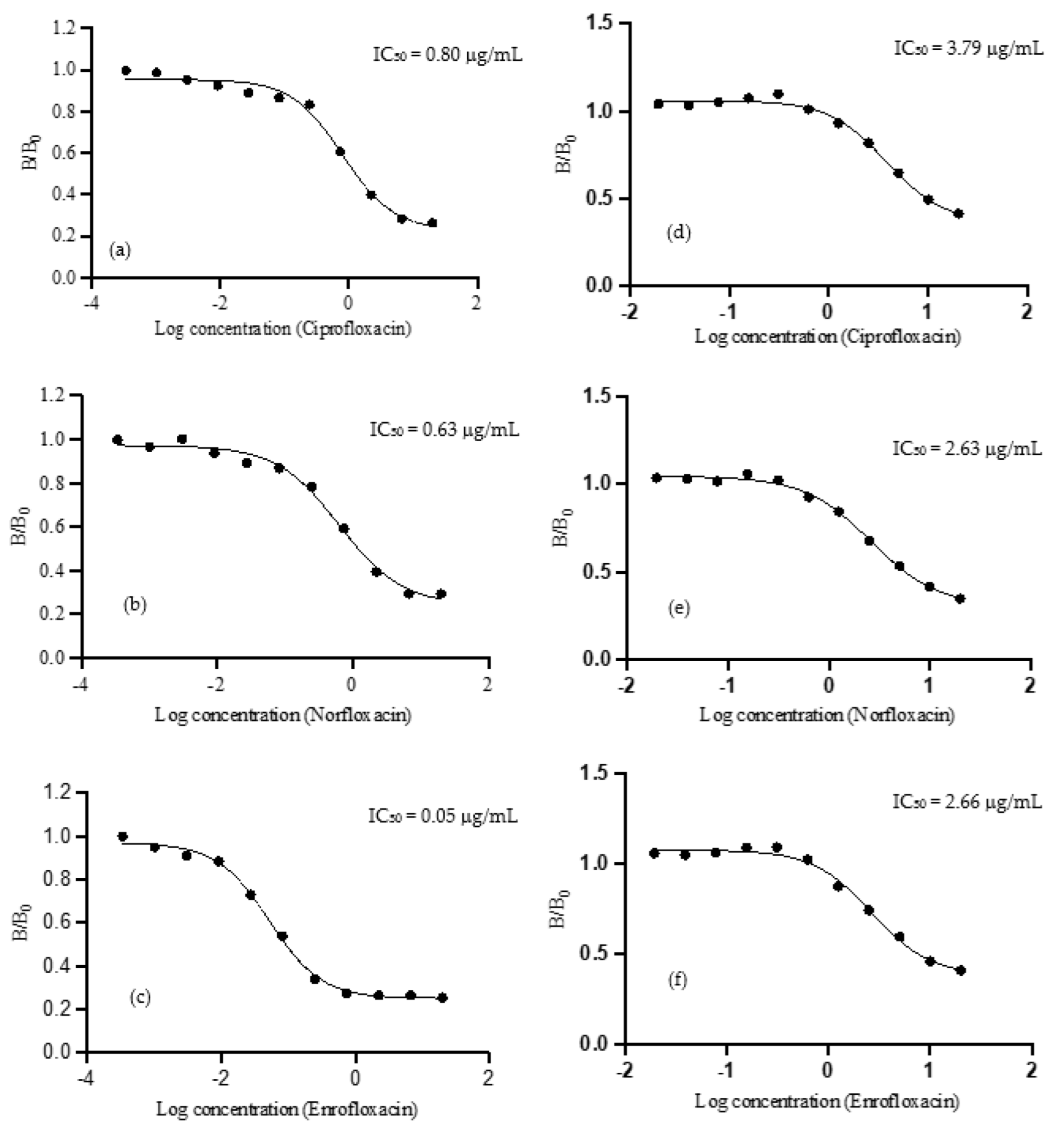
2.2.3. The Characteristic of IgY Antibody by Using Indirect Competitive ELISA
2.2.4. Antibody Specificity
2.3. The Validation of Heterologous ELISA for Detecting Enrofloxacin in Chicken and Pork Meat Samples
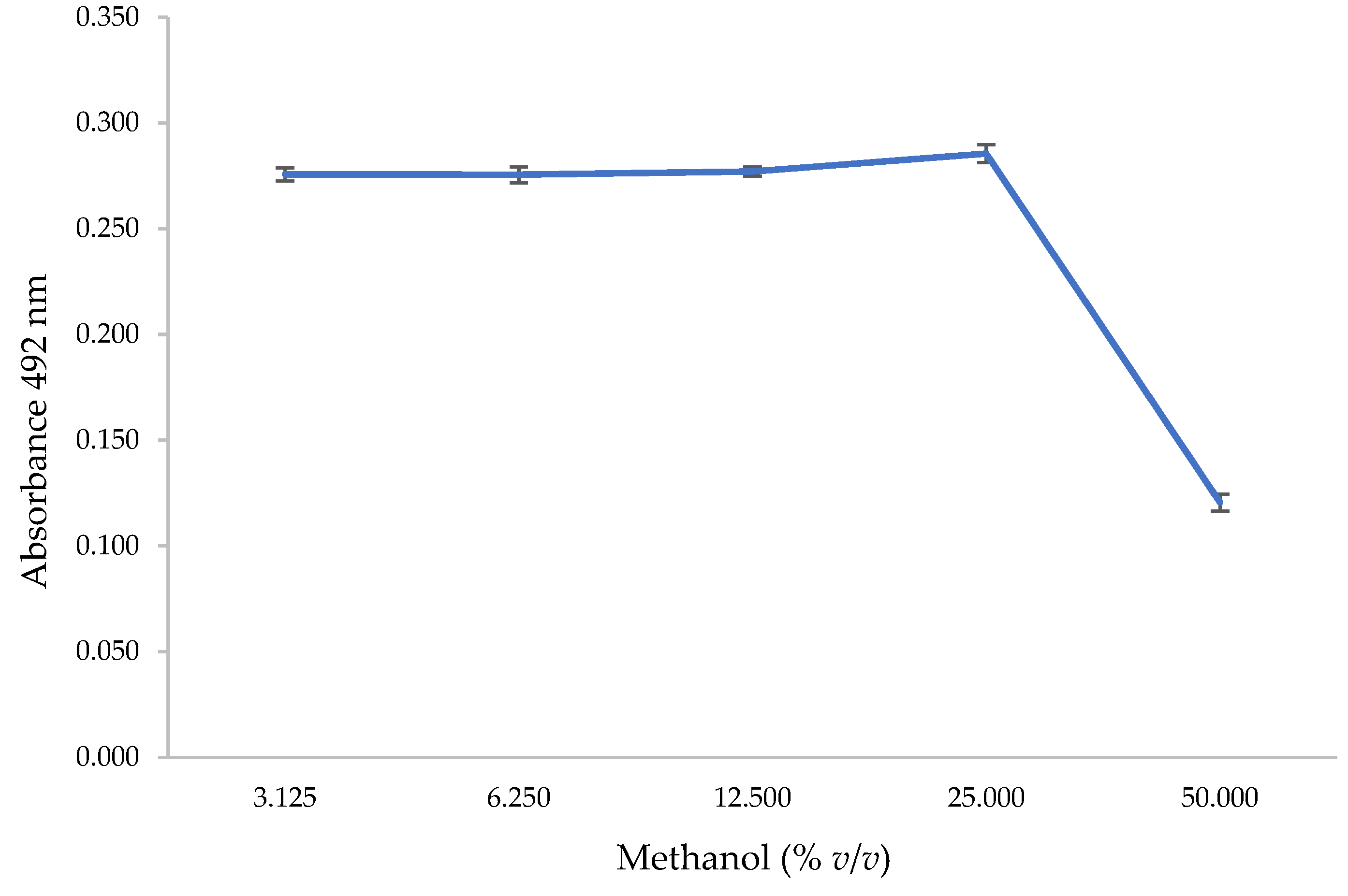
2.3.1. Methanol Effect on Antibody
2.3.2. Recovery Study for ELISA in Matrix
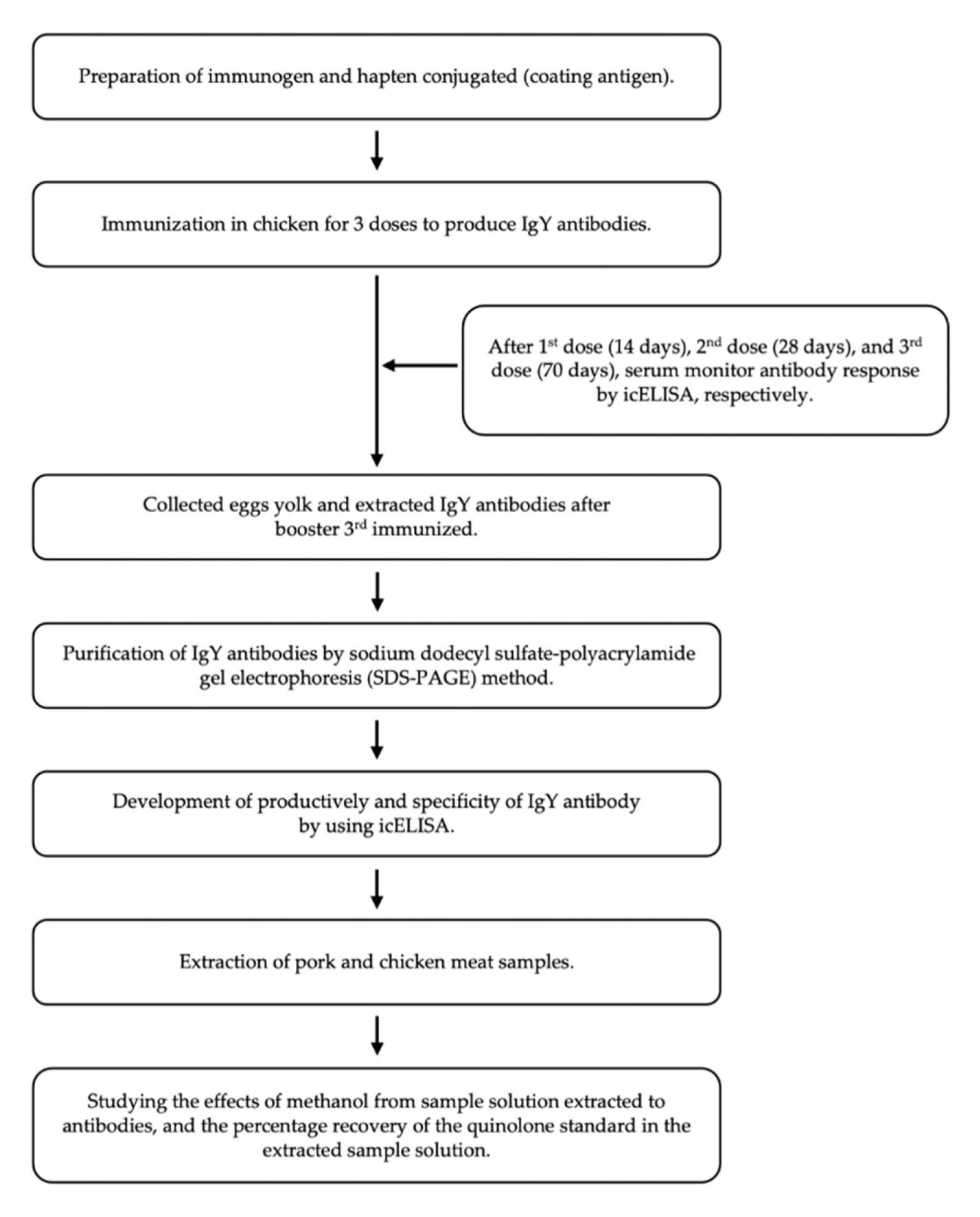
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Solutions and Buffers
3.3. Preparation of Immunogen for Immunization and Coating Antigen for Immunoassay Development
3.4. Antibody Production and Characterization
3.5. Indirect Competitive ELISA Development
3.6. Specificity Determination
3.7. Preparation of Chicken and Pork Meat Samples Extract
3.8. Statistical Analysis and Curve Fitting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Y.; Yang, H.; Wen, K.; Ke, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Current advances in immunoassays for quinolones in food and environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.C.; Jain, A.; Jain, S.; Pahwa, R.; Yar, M.S. Ciprofloxacin: Review on developments in synthetic, analytical, and medicinal aspects. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010, 25, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R. Norfloxacin-a review of pharmacology and tissue penetration. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1984, 13, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chierentin, L.; Salgado, H.R.N. Review of Properties and Analytical Methods for the Determination of Norfloxacin. Critical Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.J. Norfloxacin, a Fluoroquinolone Antibacterial Agent Classification, Mechanism of Action, and in Vitro Activity. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Chen, L.; Lu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Toxic effects of enrofloxacin on Scenedesmus obliquus. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2012, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, B.; Onurdağ, F.K.; Demirhan, B.; Özgacar, S.Ö.; Öktem, A.B.; Abbasoğlu, U. Screening of quinolone antibiotic residues in chicken meat and beef sold in the markets of Ankara, Turkey. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Jia, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Tu, X.; Zhang, J. Multi-class confirmatory method for analyzing trace levels of tetracycline and quinolone antibiotics in pig tissues by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 3487–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, W.E.; Evans, M.E. Guide to Selection of Fluoroquinolones in Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. Drugs 2005, 65, 949–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siltrakool, B.; Berrou, I.; Griffiths, D.; Alghamdi, S. Antibiotics’ Use in Thailand: Community Pharmacists’ Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antibiotic Use in Food Animals: Thailand Overview. Available online: https://www.reactgroup.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Antibiotic_Use_in_Food_Animals_Thailand_Overview_LIGHT_2018_web.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Wongsuvan, G.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Hinjoy, S.; Day, N.P.J.; Limmathurotsakul, D. Antibiotic use in poultry: A survey of eight farms in Thailand. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ying, G.G.; Deng, W.J. Antibiotic Residues in Food: Extraction, Analysis, and Human Health Concerns. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7569–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amro, W.A.; Al-Qaisi, W.; Al-Razem, F. Production and purification of IgY antibodies from chicken egg yolk. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, W.; Xi, R. Preparation of anti-pefloxacin antibody and development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of pefloxacin residue in chicken liver. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6995–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Jiang, J.Q. Monoclonal antibody-based solvent tolerable indirect competitive ELISA for monitoring ciprofloxacin residue in poultry samples. Food Agric. Immunol. 2013, 24, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.B.; Alving, C.R.; Matyas, G.R. Synthesis of hapten-protein conjugate vaccines with reproducible hapten densities. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1403, 695–710. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, F.B.M.B.; Riedstra, S.; Ferreira, J.P.M. Development of an immunoassay for ciprofloxacin based on phage-displayed antibody fragments. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 358, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KATAGiRi, M.; Kadoya, T.; Miyake, K.; Ishibashi, F.; Ohkawa, H. Effects of methanol and temperature on enzyme immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies specific to the insecticide etofenprox. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 1988–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Fan, M.T. Synthesis of three haptens for the class-specific immunoassay of O,O-dimethyl organophosphorus pesticides and effect of hapten heterology on immunoassay sensitivity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 615, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yuan, Z. Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for ciprofloxacin residues in food animal edible tissues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee For Veterinary Medicinal Products—Enrofloxacin (Extension to all food producing species). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/mrl-report/enrofloxacin-extension-all-food-producing-species-summary-report-5-committee-veterinary-medicinal_en.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Lei, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, L.; Xu, C. Immunochromatographic assays for ultrasensitive and high specific determination of enrofloxacin in milk, eggs, honey, and chicken meat. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochi, B.N.; Khaemba, G.; Isanga, J.; Mukunzi, D.; Liu, L.; Peng, J.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Monoclonal antibody for the development of specific immunoassays to detect Enrofloxacin in foods of animal origin. Food Agric. Immunol. 2016, 27, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, F.; Jiang, H.; Hou, Y.; Rao, Q.; Guo, P.; Ding, S. A novel quantum dot-based fluoroimmunoassay method for detection of Enrofloxacin residue in chicken muscle tissue. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1197–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X.; Mi, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. Determination of Enrofloxacin in Bovine Milk by a Novel Single-Stranded DNA Aptamer Chemiluminescent Enzyme Immunoassay. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 2844–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ni, H.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J. Development of a highly sensitive and specific immunoassay for enrofloxacin based on heterologous coating haptens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 820, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.F.; Feng, T.T.; Yao, Y.; Gao, L.H.; Jiang, G.B. Time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay as an advantageous analytical method for assessing the total concentration and environmental risk of fluoroquinolones in surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, E.O.; Rosa, A.M.; Amaral, M.S.; Sversut, R.A.; Baroni, A.C.M.; Oliveira, L.C.S.; Kassab, N.M. Stability-indicating HPLC-DAD method for the simultaneous determination of fluoroquinolone in combination with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug in pharmaceutical formulation. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 56, e17758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.M.; Suhagia, B.N.; Singhvi, I. Analytical Method Development and Validation for Enrofloxacin in Bulk and Formulation by RP-HPLC Method. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2018, 8, 2249–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonserm, P.; Puthong, S.; Noitang, S.; Wichai, T.; Khunrae, P.; Komolpis, K.; Sooksai, S. Kinetics of Binding Interaction between Norfloxacin and Monoclonal Antibody Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Int. J. Pharma Med. Biol. Sci. 2020, 9, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, J.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, E.; Li, X. Preparation of a Chicken scFv to Analyze Gentamicin Residue in Animal Derived Food Products. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4092–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrsen, J.; Wemmer, S.; Wyngaardt, W.V. Construction of chicken antibody libraries. In Phage Display; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1701, pp. 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Liang, X.; Li, J. Efficient production of human norovirus-specific igy in egg yolks by vaccination of hens with a recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus expressing VP1 protein. Viruses 2019, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.R.; Ferreira, F.; Domingues, P.; Coutinho, J.A.; Freire, M.G. Towards the purification of IgY from egg yolk by centrifugal partition chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Liang, D.; Ye, H.; Cai, Z.; Ma, M.; Geng, F. Effects of high-intensity ultrasonic (HIU) treatment on the functional properties and assemblage structure of egg yolk. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 60, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Shen, C.; Dong, S.; Hu, X.; Lin, M.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhong, J.; Xie, Y.; et al. Construction and characterization of a class-specific single-chain variable fragment against pyrethroid metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7345–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanbaş, E. Determination of Some Antibiotic Residues by HPLC Method in Chicken Meats Prepared for Consumption. Erciyes Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2018, 15, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
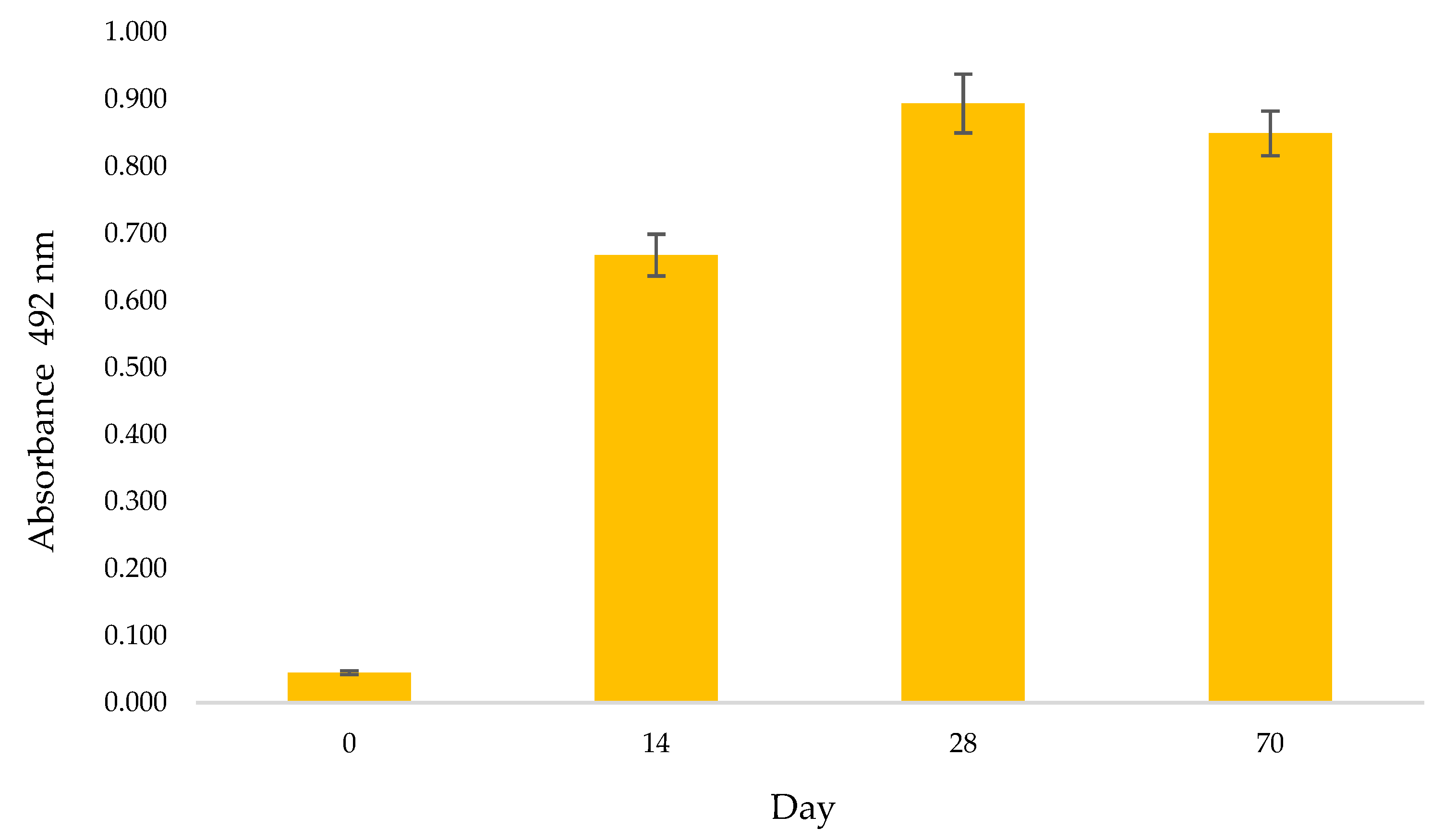


| No. | Sample 1 | Hapten Density (Number of Amines/Protein) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Immunogens | BSA-Ciprofloxacin | 0.0030 ± 0.0016 |
| 2 | BSA-Norfloxacin | 0.0107 ± 0.0030 | |
| 3 | Coating antigen | OVA-Ciprofloxacin | 0.0021 ± 0.0006 |
| 4 | OVA-Norfloxacin | 0.0226 ± 0.0043 |
| Compounds | Structures | Coating Antigen | IC50 (μg/mL) | Cross-Reactivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin | 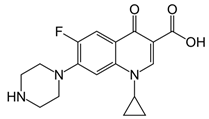 | CPFX-OVA | 0.80 | 100.00 |
| NFX-OVA | 3.79 | 63.39 | ||
| Norfloxacin |  | CPFX-OVA | 0.63 | 126.98 |
| NFX-OVA | 2.63 | 100.00 | ||
| Enrofloxacin | 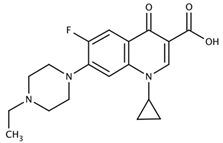 | CPFX-OVA | 0.05 | 1531.34 |
| NFX-OVA | 2.66 | 98.87 | ||
| Ofloxacin * | CPFX-OVA | >20.00 | - | |
| Levofloxacin * | CPFX-OVA | >20.00 | - |
| Analyte | Spiked Conc. (μg/mL) | Matrix (n = 2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken | Pork | Blank * | |||||
| (%R) | (%CV) | (%R) | (%CV) | (%R) | (%CV) | ||
| Enrofloxacin | 1.00 | 111.81–112.71 | 0.57 | 109.90–117.22 | 4.55 | 103.34–119.59 | 10.31 |
| 0.10 | 96.69–103.62 | 4.89 | 98.45–103.00 | 3.19 | 99.22–103.64 | 3.08 | |
| 0.01 | 86.65–95.01 | 6.51 | 84.24–87.90 | 3.00 | 83.20–87.27 | 3.38 | |
| Method | Immunogen | Antibody | IC50 | Author (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunochromatographic assays | ENFX-1-BSA | mAb (mouse) | 0.03 ng/mL | Xianlu Lei et al. (2022) [23] |
| Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) | ENFX-BSA | mAb (mouse) | 0.15 ng/mL | Bitange Nipa Tochi et al. (2016) [24] |
| Indirect competitive fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (cFLISA) | ENFX-BSA | mAb | 8.30 ng/mL | Junxia Chen et al. (2009) [25] |
| Chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassays (CLEIAs) | - | Aptamer (in vitro) | 24.27 ng/mL | Hengjia Ni et al. (2014) [26] |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | ENFX-BSA | pAb (rabbit) | 70.00 ng/mL | Zhanhui Wang et al. (2014) [27] |
| Time-resolved fluoro-immunoassay (TRFIA) | ENFX-BSA | mAb (mouse) | 1.83 μg/L | Zhen Zhang et al. (2013) [28] |
| Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA) | CPFX-BSA + NFX-BSA | pAb (chicken) | 0.05 μg/L | This work |
| Ultraperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC/MS/MS method) | - | - | 0.05 μg/kg (LOD) | Bing Shao et al. (2007) [8] |
| High performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection (HPLC-DAD) | - | - | 0.096 μg/mL (LOD) | Elaine de Oliveira Araujo et al. (2020) [29] |
| Reversed phase–high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) | - | - | 1.00 μg/mL (LOD) | Kandarp M. Patel et al. (2018) [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadoung, S.; Ishimatsu, R.; Xu, Z.-L.; Sringarm, K.; Pata, S.; Thongkham, M.; Chantara, S.; Pattarawarapan, M.; Hongsibsong, S. Development of IgY-Based Indirect Competitive ELISA for the Detection of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork Samples. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111512
Yadoung S, Ishimatsu R, Xu Z-L, Sringarm K, Pata S, Thongkham M, Chantara S, Pattarawarapan M, Hongsibsong S. Development of IgY-Based Indirect Competitive ELISA for the Detection of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork Samples. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111512
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadoung, Sumed, Ryoichi Ishimatsu, Zhen-Lin Xu, Korawan Sringarm, Supansa Pata, Marninphan Thongkham, Somporn Chantara, Mookda Pattarawarapan, and Surat Hongsibsong. 2022. "Development of IgY-Based Indirect Competitive ELISA for the Detection of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork Samples" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111512
APA StyleYadoung, S., Ishimatsu, R., Xu, Z.-L., Sringarm, K., Pata, S., Thongkham, M., Chantara, S., Pattarawarapan, M., & Hongsibsong, S. (2022). Development of IgY-Based Indirect Competitive ELISA for the Detection of Fluoroquinolone Residues in Chicken and Pork Samples. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111512







