Aquatic Environments as Hotspots of Transferable Low-Level Quinolone Resistance and Their Potential Contribution to High-Level Quinolone Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Quinolone Residues in Aquatic Environments
3. Mechanisms of Quinolone Resistance
3.1. High-Level Resistance to Quinolones
3.2. Acquired Low-Level Resistance to Quinolones
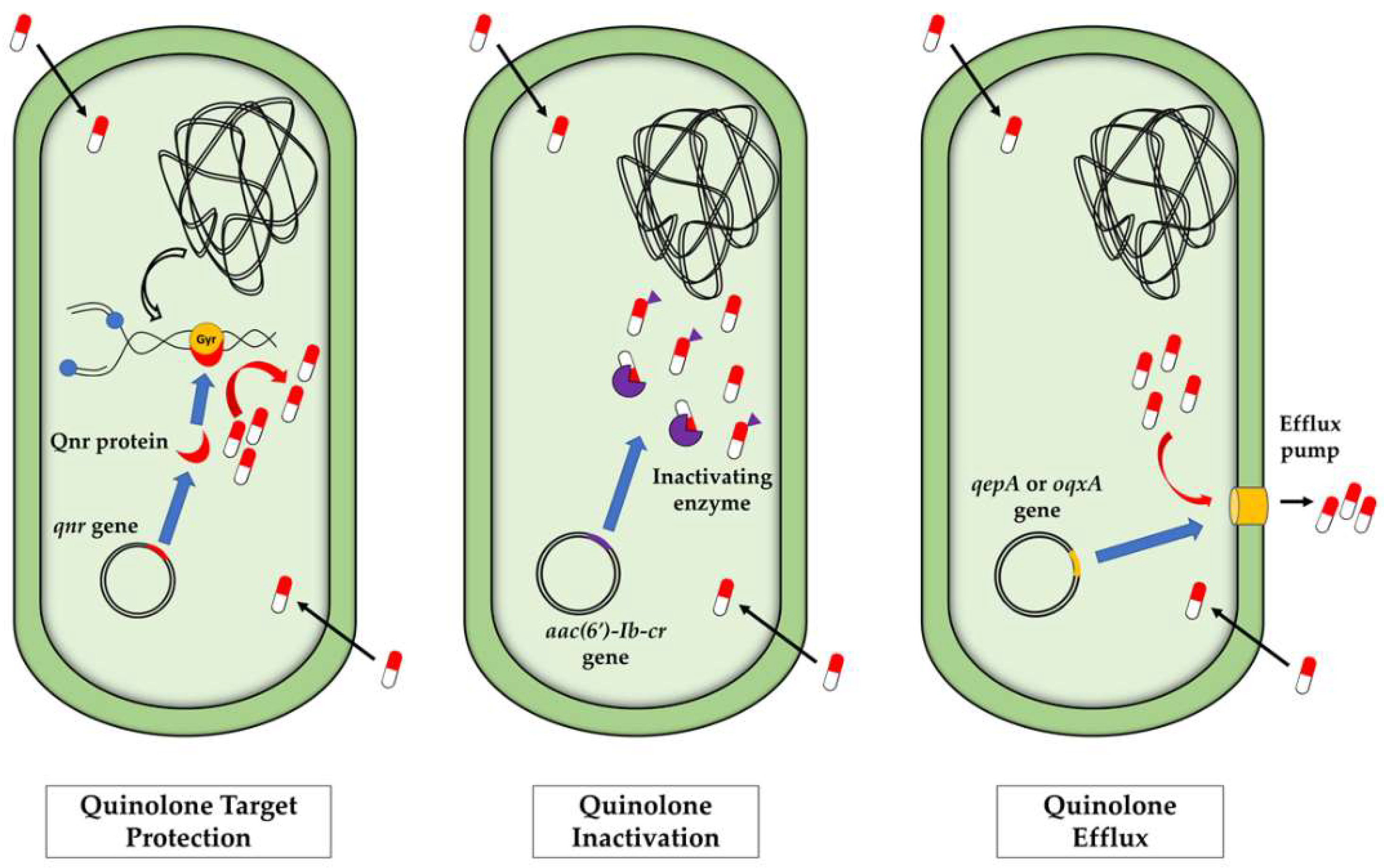
4. Quinolone Resistance Genes (qnr)
4.1. Origin and Structure of qnr Genes
4.2. Antimicrobial Activity of qnr Genes
| Gene | MIC (µg/mL) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIP | LVX | NFX | NAL | ||
| qnrA | 0.125 (0.002) | 0.5 (0.008) | 0.5 (0.015) | NT | [149] |
| 0.125 (0.002) | NT | 0.25 (0.015) | 8 (2) | [144] | |
| 0.125 (0.002) | 0.5 (0.008) | NT | NT | [121] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | 0.5 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [87] | |
| 0.125 (0.002) | 0.125 (0.004) | NT | NT | [163] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | 0.5 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [109] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | NT | NT | NT | [164] | |
| qnrB | 0.125 (0.002) | 0.125 (0.008) | 0.25 (0.015) | NT | [149] |
| 0.125 (0.002) | 0.125 (0.008) | NT | NT | [121] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | 0.5 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [87] | |
| 0.06 (0.002) | NT | NT | 8 (2) | [150] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | 0.5 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [109] | |
| qnrC | 0.25 (0.008) | 0.25 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [109] |
| qnrD | 0.06 (0.002) | NT | 0.06 (0.015) | 4 (2) | [144] |
| 0.06 (0.008) | NT | NT | 4 (4) | [109] | |
| qnrE | 0.125 (0.002) | 0.125 (0.004) | NT | 8 (1) | [148] |
| qnrS | 0.125 (0.002) | 0.5 (0.008) | 0.5 (0.015) | NT | [149] |
| 0.06 (0.002) | NT | 0.06 (0.015) | 4 (2) | [144] | |
| 0.125 (0.002) | 0.5 (0.008) | NT | NT | [121] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | 0.38 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [87] | |
| 0.25 (0.008) | 0.38 (0.015) | NT | 16 (4) | [109] | |
| 0.25 (<0.01) | NT | 1 (0.03) | 4 (1) | [165] | |
| qnrVC | 0.5 (0.0075) | NT | NT | 16 (0.12) | [166] |
| 0.5 (0.125) | NT | 4 (1) | 400 (50) | [156] | |
| 0.25 (0.125) | NT | 2 (1) | 200 (50) | [156] | |
| E. coli SBV | ≤1 | ≤2 | NT | ≤16 | [167] |
4.3. Occurrence of qnr Genes in Aquatic Environments
4.4. Prevalence and Spread of qnr Genes in Aquatic Environments
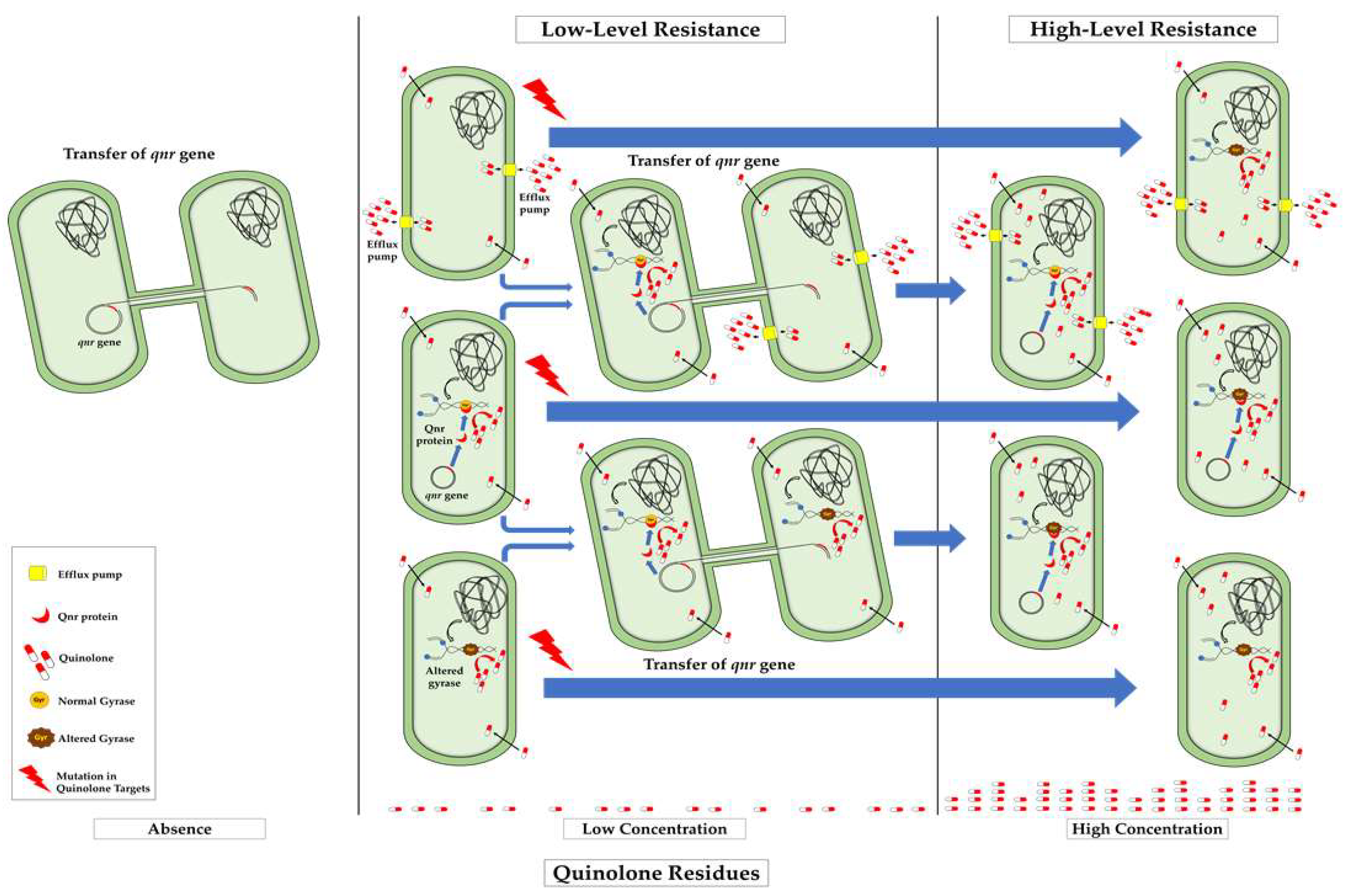
4.5. Role of qnr Genes in the Acquisition of High-Level Resistance
5. Conclusions
6. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hooper, D.C. Mechanisms of action and resistance of older and newer fluoroquinolones. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, S24–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkey, P.M. Mechanisms of quinolone action and microbial response. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldred, K.J.; Kerns, R.J.; Osheroff, N. Mechanism of quinolone action and resistance. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G.A.; Brink, A.J.; Feldman, C. Rational use of the fluoroquinolones. S. Afr. Med. J. 2019, 109, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appelbaum, P.C.; Hunter, P.A. The fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Past, present and future perspectives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 16, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiasa, H.; Shea, M.E. DNA gyrase-mediated wrapping of the DNA strand is required for the replication fork arrest by the DNA gyrase-quinolone-DNA ternary complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34780–34786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooper, D.C. Mechanisms of action of antimicrobials: Focus on fluoroquinolones. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drlica, K.; Malik, M.; Kerns, R.J.; Zhao, X. Quinolone-mediated bacterial death. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooper, D.C. Mechanism of quinolone resistance. In Quinolone Antimicrobial Agents, 3rd ed.; Hooper, D.C., Rubinstein, E., Eds.; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, G.A. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, S120–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L.; Cantón, R. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Ba, Y.; Niu, L.; Lou, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y. A comprehensive research on antibiotic resistance genes in microbiota of aquatic animals. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, L.A.; Desbois, A.P.; Garza, M.; Wieland, B.; Mohan, C.V.; Häsler, B.; Tam, C.C.; Le, P.N.T.; Phuong, N.T.; Van, P.T.; et al. Identifying hotspots for antibiotic resistance emergence and selection, and elucidating pathways to human exposure: Application of a systems-thinking approach to aquaculture systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, M.; Achmon, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Siame, B.A.; Leung, K.Y. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijbers, P.M.C.; Blaak, H.; de Jong, M.C.; Graat, E.A.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Role of the environment in the transmission of antimicrobial resistance to humans: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11993–12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, T.; Fang, H.H. Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, C.F.; Odume, O.N. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F. Low-level antibacterial resistance: A gateway to clinical resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2001, 4, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part II. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kümmerer, K.; Henninger, A. Promoting resistance by the emission of antibiotics from hospitals and households into effluent. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Chamorro, S.; Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Gros, M.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Borrego, C.M.; Barceló, D.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015, 69, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Y.; Fu, C.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Wong, M.H.; Zheng, C. Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, X.; Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: An emerging class of environmental micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500–501, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, J.; McNaughtan, M.; Hunter, C.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Helwig, K. Chemical Fate and Partitioning Behavior of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment—A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3275–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, M.E.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Rodríguez Castro, M.C.; Giorgie, A.; Barceló, D.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Amé, M.V. Distribution of antibiotics in water, sediments and biofilm in an urban river (Córdoba, Argentina, LA). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böger, B.; Surek, M.; Vilhena, R.d.O.; Fachi, M.M.; Junkert, A.M.; Santos, J.M.; Domingos, E.L.; Cobre, A.d.F.; Momade, D.R.; Pontarolo, R. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant bacteria in subtropical urban rivers in Brazil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chang, X.; Liu, Z. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of typical antibiotics in the surface water of Hunhe River. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 361–368. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in coastal water of the Bohai Bay, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.J.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Yang, J.F.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Liu, S. Trends in the occurrence of human and veterinary antibiotics in the sediments of the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.P.; Li, J.; Wang, C.M. Residual level and safety assessment of quinolone antibiotics in aquatic products in Suzhou. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. 2012, 22, 2417–2418. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, R.M.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, D.J.; Zou, T.; Tang, J.H.; Lü, J. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of antibiotic pollution in Xiaoqing River watershed. J. AgroEnviron. Sci. 2016, 35, 1384–1391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z. Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of antibiotics in the Huangpu River, Shanghai. China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, R.; Wang, J.G. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of antibiotics in surface water of the Gonghu Bay, Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 4596–4604. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.M.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X. Occurrence of antibiotics in typical aquaculture of the Pearl River Estuary. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 304–310. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Minh, T.B.; Leung, H.W.; Loi, I.H.; Chan, W.H.; So, M.K.; Mao, J.Q.; Choi, D.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zheng, G.; Martin, M.; et al. Antibiotics in the Hong Kong metropolitan area: Ubiquitous distribution and fate in Victoria Harbour. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Qiu, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, W. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and behavior of antibiotics in water and sediments from the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, S.; Wu, P.; Tsang, Y.F. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in a wastewater treatment plant and their biological effects on receiving waters in Guizhou. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Shen, Y.; Di, M.; Wang, J. Antibiotics in surface water and sediments from Hanjiang River, central China: Occurrence, behavior and risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.F.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Tao, R.; Su, H.C.; Liu, Y.S. Spatial and seasonal distribution of selected antibiotics in surface waters of the Pearl Rivers, China. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2011, 46, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Wang, Z.; Nie, X.; Yang, Y.; Pan, D.; Leung, A.O.W.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, K. Residues of fluoroquinolones in marine aquaculture environment of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2012, 34, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Rad, S.; Song, X.; Zeng, H.; Bashir, S.; Kang, B.; Chen, Z. Occurrence, distribution, and health risk assessment of quinolone antibiotics in water, sediment, and fish species of Qingshitan reservoir, South China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar. Occurrence of High Levels of Fluoroquinolones in Aquatic Environment due to Effluent Discharges from Bulk Drug Manufacturers. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2017, 21, 5016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, D.; Hanna, N.; Purohit, M.; Chandran, S.; Riggi, E.; Parashar, V.; Tamhankar, A.J.; Lundborg, C.S. Seasonal Variations in Water-Quality, Antibiotic Residues, Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of Escherichia coli Isolates from Water and Sediments of the Kshipra River in Central India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei, R.; Yunesian, M.; Nasseri, S.; Gholami, M.; Jalilzadeh, E.; Shoeibi, S.; Mesdaghinia, A. Occurrence and fate of most prescribed antibiotics in different water environments of Tehran, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Melis, M.; Fanelli, R. Source, occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Italian aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, F.; Zuccato, E.; Davoli, E.; Fattore, E.; Castiglioni, S. Risk assessment of a mixture of emerging contaminants in surface water in a highly urbanized area in Italy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, F.; Yamamoto, A.; Takakura, K.-I.; Kawahara, R. Occurrence of fluoroquinolones and fluoroquinolone-resistance genes in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairigo, P.; Ngumba, E.; Sundberg, L.R.; Gachanja, A.; Tuhkanen, T. Occurrence of antibiotics and risk of antibiotic resistance evolution in selected Kenyan wastewaters, surface waters and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.J.; Paíga, P.; Silva, A.; Llaguno, C.P.; Carvalho, M.; Vázquez, F.M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Antibiotics and antidepressants occurrence in surface waters and sediments collected in the north of Portugal. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilca, F.Z.; Galarza, N.C.; Tejedo, J.R.; Zamalloa Cuba, W.A.; Campos Quiróz, C.N.; Tornisielo, V.L. Occurrence of residues of veterinary antibiotics in water, sediment and trout tissue (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the southern area of Lake Titicaca, Peru. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, A.L.; Bruce, I.B.; Aga, D.S. Evaluating the vulnerability of surface waters to antibiotic contamination from varying wastewater treatment plant discharges. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, D.L.; Liu, N. Investigation on the typical quinolone antibiotics in the surface sediments of Jiaozhou bay China. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 655–661. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, Z. Research on pollution characteristics of antibiotics in Qinghe River in Beijing. Ecol. Sci. 2014, 33, 83–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Labadie, P.; Alliot, F.; Teil, M.J.; Blanchard, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence of antibiotics in rural catchments. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansson, E.; Fick, J.; Janzon, A.; Grabic, R.; Rutgersson, C.; Weijdegård, B.; Söderström, H.; Larsson, D.G.J. Pyrosequencing of antibiotic-contaminated river sediments reveals high levels of resistance and gene transfer elements. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Söderström, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G.J. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golet, E.M.; Strehler, A.; Alder, A.C.; Giger, W. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents in sewage sludge and sludge-treated soil using accelerated solvent extraction followed by solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5455–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibs, J.; Heckathorn, H.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Klapinski, F.R.; Alebus, M.; Lippincott, R.L. Occurrence and partitioning of antibiotic compounds found in the water column and bottom sediments from a stream receiving two wastewater treatment plant effluents in Northern New Jersey, 2008. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.R.; Fang, X.; Cai, J.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Z. Residues characteristics of fluoroquinolones (FQs) in the river sediments and fish tissues in a drinking water protection area of Guangdong Province. Acta Sci. Circum. 2016, 36, 760–766. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Xue, Y.L.; Xu, H.; Luo, M. Residual levels of fluoroquinolones in freshwater fish from aquatic products markets in Guiyang. J. Environ. Health 2017, 34, 139–141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Q.; Sun, T. Antibiotic residues in aquatic products of Hongze lake investigation and research. Guangdong Chem. 2011, 38, 151–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.T.; Luan, L.J. Residues and health risk assessment of Quinolones in fishes from the markets in Jining City. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 141–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sukul, P.; Spiteller, M. Fluoroquinolones antibiotics in the environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 191, 131–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzstein, H.-G.; Schmeer, N.; Karl, W. Degradation of fluoroquinolone enrofloxacin by the brown rot fungus Gloeophyllum striatum: Identification of metabolites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4272–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutgersson, C.; Fick, J.; Marathe, N.; Kristiansson, E.; Janzon, A.; Angelin, M.; Johansson, A.; Shouche, Y.; Flach, C.F.; Larsson, D.G.J. Fluoroquinolones and qnr Genes in Sediment, Water, Soil, and Human Fecal Flora in an Environment Polluted by Manufacturing Discharges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7825–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Steele, J.C.; Meng, X. Usage, residue, and human health risk of antibiotics in Chinese aquaculture: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Spiegelman, G.B.; Yim, G. The world of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Variatza, E.; Balcazar, J.L. The role of aquatic ecosystems as reservoirs of antibiotic resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminov, R.I. The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2970–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, L.; Waldron, L.; Gillings, M.R. Potential impacts of aquatic pollutants: Sub-clinical antibiotic concentrations induce genome changes and promote antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garric, J.; Ferrari, B. Pharmaceuticals in aquatic ecosystems. Levels of exposure and biological effects: A review. Rev. Sci. l’Eau/J. Water Sci. 2005, 18, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löffler, D.; Römbke, J.; Meller, M.; Ternes, T.A. Environmental fate of pharmaceuticals in water/sediment systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5209–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojemaye, C.Y.; Petrik, L. Pharmaceuticals in the marine environment: A review. Environ. Rev. 2019, 27, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.-S.; Zhang, T.; Gillings, M.R.; Su, J.-Q. Continental-scale pollution of estuaries with antibiotic resistance genes. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in natural environmental. Science 2008, 321, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones: Target alterations, decreased accumulation and DNA gyrase protection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, J.; Pons, M.J.; Gomes, C. Transferable mechanisms of quinolone resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redgrave, L.S.; Sutton, S.B.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J.V. Fluoroquinolone resistance: Mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fàbrega, A.; Madurga, S.; Giralt, E.; Vila, J. Mechanism of action of and resistance to quinolones. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Gómez, J.M.; Blázquez, J.; Espinosa De Los Monteros, L.E.; Baquero, M.R.; Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.L. In vitro plasmid-encoded resistance to quinolones. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 154, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M. Mechanisms of plasmid-mediated resistance to quinolones. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2005, 23, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 475–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Machuca, J.; Cano, M.E.; Calvo, J.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: Two decades on. Drug Resist. Updates 2016, 29, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: Quinolone resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Topoisomerase inhibitors: Fluoroquinolone mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, M.M.; Varela, M.F. Modulation of bacterial resistance efflux pumps of the major facilitator superfamily. Int. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 204141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floyd, J.L.; Smith, K.P.; Kumar, S.H.; Floyd, J.T.; Varela, M.F. LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5406–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boncoeur, E.; Durmort, C.; Bernay, B.; Ebel, C.; Di Guilmi, A.M.; Croize, J.; Vernet, T.; Jault, J.M. PatA and PatB form a functional heterodimeric ABC multidrug efflux transporter responsible for the resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae to fluoroquinolones. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 7755–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, M.D. Multidrug efflux pumps of Gram-positive bacteria. Drug Resist. Updates 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips-Jones, M.K.; Harding, S.E. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) nanomachines—Mechanisms for fluoroquinolone and glycopeptide recognition, efflux and/or deactivation. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weigel, L.M.; Steward, C.D.; Tenover, F.D. gyrA mutations associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in eight species of Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akasaka, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Sato, K. Type II topoisomerase mutations in fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated in 1998 and 1999: Role of target enzyme in mechanism of fluoroquinolone resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heisig, P. Genetic evidence for a role of parC mutations in development of high-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Lee, M.-F.; Peng, C.-F. Mutations in the quinolone resistance-determining regions associated with ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Southern Taiwan. Biomark. Genom. Med. 2014, 6, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oethinger, M.; Kern, W.V.; Jellen-Ritter, A.S.; McMurry, L.M.; Levy, S.B. Ineffectiveness of topoisomerase mutations in mediating clinically significant fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli in the absence of the AcrAB efflux pump. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, S.; Dey, K.; Ramamurthy, T.; Nair, G.B.; Kundu, M. Role of Active Efflux in Association with Target Gene Mutations in Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2676–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baucheron, S.; Imberechts, H.; Chaslus-Dancla, E.; Cloeckaert, A. The AcrB multidrug transporter plays a major role in high-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium phage type DT204. Microb. Drug Resist. 2002, 8, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, V.M.; McGrann, K.M.; Hughes, D.W.; Wright, G.D. Sampling the antibiotic resistome. Science 2006, 311, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistome. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.; Wright, G. The antibiotic resistance “mobilome”: Searching for the link between environment and clinic. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Research progress on distribution, migration, transformation of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in aquatic environment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Wang, Q.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Donner, E.; Yin, H.; Nghiem, L.D. Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment: Current strategies and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skandalis, N.; Maeusli, M.; Papafotis, D.; Miller, S.; Lee, B.; Theologidis, I.; Luna, B. Environmental Spread of Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: A multifaceted threat. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 664–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Eliecer, M.; Velasco, C.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: An update. J. Infect. Chemother. 2011, 17, 149–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.H.; Johannesen, E.; Burmølle, M.; Sørensen, A.H.; Sørensen, S.J. Plasmid-encoded multidrug efflux pump conferring resistance to olaquindox in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3332–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, L.H.; Jensen, L.B.; Jørgensen, H.S.; Sørensen, S.J. Substrate specificity of the OqxAB multidrug resistance pump in Escherichia coli and selected enteric bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perichon, B.; Courvalin, P.; Galimand, M. Transferable resistance to aminoglycosides by methylation of G1405 in 16S rRNA and to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones by QepA-mediated efflux in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2464–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamane, K.; Wachino, J.; Suzuki, S.; Kimura, K.; Shibata, N.; Kato, H.; Shibayama, K.; Konda, T.; Arakawa, Y. New plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone efflux pump, QepA, found in an Escherichia coli clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3354–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poirel, L.; Cattoir, V.; Nordmann, P. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance; interactions between human, animal, and environmental ecologies. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Macielag, M.; Abbanat, D.; Park, C.H.; Bush, K.; Hooper, D.C. Fluoroquinolone modifying enzyme: A new adaptation of a common aminoglycoside acetyltransferase. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Sánchez, M.B.; Martínez, J.L. Quinolone resistance: Much more than predicted. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bearden, D.T.; Danziger, L.H. Mechanism of Action of and Resistance to Quinolones. Pharmacotherapy 2001, 21, 2245–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drlica, K.; Hiasa, H.; Kerns, R.; Malik, M.; Mustaev, A.; Zhao, X. Quinolones: Action and resistance updated. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kwon, H.H.; Lee, S.R.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, M.N.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Effects of a plasmid-encoded qnrA1 determinant in Escherichia coli strains carrying chromosomal mutations in the acrAB efflux pump genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 60, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Herrera, J.; Velasco, C.; Docobo-Pérez, F.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; López-Rojas, R.; Briales, A.; Pichardo, C.; Díaz de Alba, P.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Pascual, A.; et al. Impact of qnrA1, qnrB1 and qnrS1 on the efficacy of ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin in an experimental pneumonia model caused by Escherichia coli with or without the GyrA mutation Ser83Leu. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotb, D.N.; Mahdy, W.K.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Khairy, R. Impact of co-existence of PMQR genes and QRDR mutations on fluoroquinolones resistance in Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated from community and hospital acquired UTIs. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, A.Y.; Nohut, O.K.; Çaycı, Y.T.; Bayramoğlu, G.; Pirinççiler, M.; Cetinkaya, E.; Cihan, C.C.; Bozdoğan, B.; Durupınar, B. Investigation of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants in Enterobacteriaceae: A multicenter study. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2012, 46, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doma, A.O.; Popescu, R.; Mitulețu, M.; Muntean, D.; Dégi, J.; Boldea, M.V.; Radulov, I.; Dumitrescu, E.; Muselin, F.; Puvača, N.; et al. Comparative evaluation of qnrA, qnrB, and qnrS Genes in Enterobacteriaceae ciprofloxacin-resistant cases, in swine units and a hospital from Western Romania. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.D.; Godoy, F.A.; Lee, M.R. Current Status of the Use of Antibiotics and the Antimicrobial Resistance in the Chilean Salmon Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, S.M.; Chen, L.-Q.; Zhang, M.-L.; Du, Z.-Y. A global analysis on the systemic effects of antibiotics in cultured fish and their potential human health risk: A review. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORM/NORM-VET, 2020. Usage of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Norway. Tromsø/Oslo. Available online: www.vetinst.no (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Buschmann, A.; Tomova, A.; López, A.; Maldonado, M.; Henríquez, L.; Ivanova, L.; Moy, F.; Godfrey, H.; Tomova, A.; López, A.; et al. Salmon aquaculture and antimicrobial resistance in the marine environment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, B.; Tucca, F.; Srain, B.M.; Mejanelle, L.; Aranda, M.; Fernandez, C.; Pantoja-Gutierrez, S. Antibiotics florfenicol and flumequine in the water column and sediments of Puyuhuapi Fjord, Chilean Patagonia. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarska, K.; Wołkowicz, T.; Zacharczuk, K.; Rzeczkowska, M.; Chróst, A.; Bareja, E.; Olak, M.; Gierczynski, R. Co-existence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants and mutations in gyrA and parC among fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical Enterobacteriaceae isolated in a tertiary hospital in Warsaw, Poland. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamber, S.W.; Kolek, K.; Brookshire, W.D.; Bonner, D.P.; Fung-Tomc, J. Activity of quinolones in the Ames Salmonella TA102 mutagenicity test and other bacterial genotoxicity assays. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizenman, E.; Engelberg-Kulka, H.; Glaser, G. An Escherichia coli chromosomal ‘addiction module’ regulated by guanosine 3′, 5′-bispyrophosphate: A model for programmed bacterial cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6059–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ching, C.; Orubu, E.S.F.; Wirtz, V.J.; Zaman, M.H. Bacterial antibiotic resistance development and mutagenesis following exposure to subminimal inhibitory concentrations of fluoroquinolones in vitro: A systematic literature review protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e030747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, J.H.; Jacoby, G.A. Mechanism of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5638–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aminov, R.I.; Mackie, R.I. Evolution and ecology of antibiotic resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 271, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, C.; Mateu, G.; Rodríguez, R.; Takiff, H. Intrinsic resistance of Mycobacterium smegmatis to fluoroquinolones may be influenced by new pentapeptide protein MfpA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hegde, S.S.; Vetting, M.W.; Roderick, S.L.; Mitchenall, L.A.; Maxwell, A.; Takiff, H.E.; Blanchard, J.S. A fluoroquinolone resistance protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis that mimics DNA. Science 2005, 308, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, X.; Bromley, E.H.; Oelschlaeger, P.; Woolfson, D.N.; Spencer, J. Structural insights into quinolone antibiotic resistance mediated by pentapeptide repeat proteins: Conserved surface loops direct the activity of a Qnr protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3917–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetting, M.W.; Hegde, S.S.; Wang, M.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C.; Blanchard, J.S. Structure of QnrB1, a plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25265–25273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Corcoran, M.A.; Mills, D.M.; Griffin, C.M.; Hooper, D.C. Mutational analysis of quinolone resistance protein QnrB1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5733–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A.; Jacoby, G.A. Quinolone resistance from a transferable plasmid. Lancet 1998, 351, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, M.; Suzuki, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Takahashi, M.; Sato, K.; Ibe, S.; Sakae, K. Cloning of a novel gene for quinolone resistance from a transferable plasmid in Shigella flexneri 2b. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Walsh, K.E.; Mills, D.M.; Walker, V.J.; Oh, H.; Robicsek, A.; Hooper, D.C. qnrB, another plasmid mediated gene for quinolone resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavaco, L.M.; Hasman, H.; Xia, S.; Aarestrup, F.M. qnrD, a novel gene conferring transferable quinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar kentucky and bovismorbificans strains of human origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Wu, S.; Hooper, D.C.; Wang, M. New plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance gene, qnrC, found in a clinical isolate of Proteus mirabilis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, E.L.; Vicente, A.C. Epidemiology of qnrVC alleles and emergence out of the Vibrionaceae family. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1628–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavio, M.M.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. QnrS1 structure–activity relationships. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albornoz, E.; Tijet, N.; De Belder, D.; Gomez, S.; Martino, F.; Corso, A.; Melano, R.G.; Petroni, A. qnrE1, a Member of a New Family of Plasmid-Located Quinolone Resistance Genes, Originated from the Chromosome of Enterobacter Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02555-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briales, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Velasco, C.; Díaz de Alba, P.; Domínguez-Herrera, J.; Pachón, J.; Pascual, A. In vitro effect of qnrA1, qnrB1, and qnrS1 genes on fluoroquinolone activity against isogenic Escherichia coli isolates with mutations in gyrA and parC. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Friederichs, S.; Schwarz, S.; De Jong, A. A novel variant of the qnrB gene, qnrB12, in Citrobacter werkmanii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 52, 1206–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Concha, C.; Miranda, C.D.; Rojas, R.; Godoy, F.A.; Romero, J. Characterization of a novel variant of the quinolone-resistance gene qnrB (qnrB89) carried by a multi-drug resistant Citrobacter gillenii strain isolated from farmed salmon in Chile. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J. Transferable mechanisms of quinolone resistance from 1998 onward. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00007-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Liard, A.; Rodriguez-Martinez, J.M.; Nordmann, P. Vibrionaceae as a possible source of Qnr-like quinolone resistance determinants. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Rodriguez-Martinez, J.M.; Mammeri, H.; Liard, A.; Nordmann, P. Origin of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinant QnrA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3523–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cattoir, V.; Poirel, L.; Mazel, D.; Soussy, C.J.; Nordmann, P. Vibrio splendidus as the source of plasmid-mediated QnrS-like quinolone resistance determinants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2650–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinothkumar, K.; Kumar, G.N.; Bhardwaj, A.K. Characterization of Vibrio fluvialis qnrVC5 Gene in Native and Heterologous Hosts: Synergy of qnrVC5 with other Determinants in Conferring Quinolone Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, S.; Paradela, A.; Velez, J.; Ramalheira, E.; Walsh, T.R.; Mendo, S. Carriage of qnrA1 and qnrB2, blaCTX-M15, and complex class 1 integron in a clinical multiresistant Citrobacter freundii isolate. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 67, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, G.; Kwong, W.; Davies, J.; Miao, V. Complex integrons containing qnrB4-ampC (bla(DHA-1)) in plasmids of multidrug-resistant Citrobacter freundii from wastewater. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicsek, A.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. The worldwide emergence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, G.; Pazhani, G.P.; Nair, G.B.; Ghosh, A.; Ramamurthy, T. Transferable plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in association with extended-spectrum β-lactamases and fluoroquinolone-acetylating aminoglycoside-6’-N-acetyltransferase in clinical isolates of Vibrio fluvialis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, S.A.; Omar, H.H.; Hassan, W.H. Characterization of plasmid-mediated qnrA and qnrB genes among Enterobacteriaceae strains: Quinolone resistance and ESBL production in Ismailia, Egypt. Egypt J. Med. Human Genet. 2019, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sahm, D.F.; Jacoby, G.A.; Zhang, Y.; Hooper, D.C. Activities of Newer Quinolones against Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Containing the Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance Determinant qnr. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1400–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Velasco, C.; García, L.; Cano, M.E.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A. Mutant prevention concentrations of fluoroquinolones for Enterobacteriaceae expressing the plasmid-carried quinolone resistance determinant qnrA1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2236–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Tran, J.H.; Jacoby, G.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Escherichia coli from Shanghai, China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Picao, R.C.; Poirel, L.; Demarta, A.; Silva, C.S.; Corvaglia, A.R.; Petrini, O.; Nordmann, P. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in Aeromonas allosaccharophila recovered from a Swiss lake. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chan, E.W.; Dong, N.; Xia, X.; Chen, S. Molecular characterization of qnrVC genes and their novel alleles in Vibrio spp. isolated from food products in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00529-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A.; García, I.; Tran, J.; Jacoby, G.A. Interaction of plasmid and host quinolone resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hu, C.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, H.; Cui, S. Joint effects of topoisomerase alterations and plasmid-mediated quinolone-resistant determinants in Salmonella enterica Typhimurium. Microb. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z. Quinolone resistance in bacteria: Emphasis on plasmid-mediated mechanisms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Bettoni, R.R.; Lascols, C.; Merens, A.; Soussy, C.J.; Cambau, E. Low selection of topoisomerase mutants from strains of Escherichia coli harbouring plasmid-borne qnr genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Shoma, S.; Bari, S.M.N.; Ginn, A.N.; Wiklendt, A.M.; Partridge, S.R.; Faruque, S.M.; Iredell, J.R. Genetic diversity and antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli from environmental surface water in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 76, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, L.; Anzil, A.; Subirats, J.; Borrego, C.; Farrè, M.; Llorca, M.; Balcázar, J.L.; Servais, P. Antibiotic resistance along an urban river impacted by treated wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, D.; Palmeiro, J.K.; da Silva, K.; de Lima, T.M.R.; Cardoso, M.A.; Pontarolo, R.; Degaut, F.L.; Dalla-Costa, L.M. Characterization of CTX-M enzymes, quinolone resistance determinants, and antimicrobial residues from hospital sewage, wastewater treatment plant, and river water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, J.P.R.; Rodrigues dos Santos, L.D.; Silva Moretto, J.A.; Santana Ramos, M.; Lage Gallo, I.F.; Dias Alves, G.; Paulelli, A.C.; de Souza Rocha, C.C.; Cesila, C.A.; Gallimberti, M.; et al. Occurrence and abundance of clinically relevant antimicrobial resistance genes in environmental samples after the Brumadinho dam disaster, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neudorf, K.D.; Huang, Y.N.; Ragush, C.M.; Yost, C.K.; Jamieson, R.C.; Truelstrup, L. Antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment system and receiving water in Artic Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awan, F.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. Comparative genome analysis provides deep insights into Aeromonas hydrophila taxonomy and virulence-related factors. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.-X.; Tang, D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Xu, L.; Hawkey, P.M. Prevalence and characteristics of β-lactamase and plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolated from farmed fish in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2350–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, J.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Han, Y.; Di, Z.; Ling, B.; Ahmad, A.; Yang, N.; Fan, L.; et al. Prevalence, virulence-related genes and antimicrobial resistance of Aeromonas spp. from loach Misgurnus anguillicaudatus with skin ulcer and healthy controls in Southern China. Aquaculture 2022, 552, 738040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Jia, J.; Yue, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z. River contamination shapes the microbiome and antibiotic resistance in sharpbelly (Hemiculter leucisculus). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hao, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, N.; Ye, B. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes of wastewater and surface water in livestock farms of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13950–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zeng, Z. Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes, and Bacterial Community Composition in Fresh Water Aquaculture Environment in China. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Guan, Y.; Cheng, M.; Chen, H.; He, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in Ba River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Zou, Y.; Liao, X.; Liang, J.B.; Wu, Y. Occurrence and contamination profiles of antibiotic resistance genes from swine manure to receiving environments in Guangdong Province southern China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.; Du, P.-P.; Zeng, L.-J.; Mo, C.-H.; Li, Y.-W.; Lü, H.; Cai, Q.-Y. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes in water and sediments of urban rivers with black-odor water in Guangzhou, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Pu, X.; Zheng, W.; Hu, G. High prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance and IncQ plasmids carrying qnrS2 gene in bacteria from rivers near hospitals and aquaculture in China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, M.; Zhang, X.; Cai, P.; Dai, Y.; Song, T.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H.; Qiao, M. Functional Identification and evolutionary analysis of two novel plasmids mediating quinolone resistance in Proteus vulgaris. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Korheina, D.K.A.; Fu, H.; Ge, X. Chronic exposure to dietary antibiotics affects intestinal health and antibiotic resistance gene abundance in oriental river prawn (Macrobrachium nipponense), and provokes human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Zhao, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, S.; Huang, Z.; Yin, D. Characteristics of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in Qingcaosha Reservoir in Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, C.; Wei, B.; Wang, J. Antibiotic resistance genes in lakes from middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China: Effect of land use and sediment characteristics. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Cao, X.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Antibiotic resistance genes in surface water of eutrophic urban lakes are related to heavy metals, antibiotics, lake morphology and anthropic impact. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, M.; Xu, H. Bacterial plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in aquatic environments in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Ren, Y.; Xu, H. Identification of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria from hospital wastewaters and receiving waters in the Jinan area, China. Microb. Drug Res. 2013, 19, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Wu, X.; Yan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X. Incidence of antimicrobial-resistance genes and integrons in antibiotic-resistant bacteria isolated from eels and aquaculture ponds. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 120, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Q.; Xu, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhang, D. Overview of the development of quinolone resistance in Salmonella species in China, 2005–2016. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, L.; Li, L.; Ashbolt, N.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhua, X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Arctic antibiotic resistance gene contamination, a result of anthropogenic activities and natural origin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Nie, H.; Wang, J. Tetracyclines, sulfonamides and quinolones and their corresponding resistance genes in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W. Profiles of antibiotic resistance genes in an inland salt-lake Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, China: The relationship with antibiotics, environmental factors, and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, G.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y. Occurrence and temporal variation of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in shrimp aquaculture: ARGs dissemination from farming source to reared organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Lv, X.; Han, B.; Gu, X.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; He, Z. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates in surface water of Taihu Lake Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11412–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Cui, J.; Li, D.; Huang, L. Membrane combined with artificial floating ecosystems for the removal of antibiotics and antibiotic-resistance genes from urban rivers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.-Y.; He, L.-Y.; Gao, F.-Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Wu, D.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; He, L.-X.; Bai, H.; Ying, G.-G. Antibiotic resistance genes in surface water and groundwater from mining affected environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, G.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, C.; Duan, L.; Wang, W. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in groundwater, surface water, and sediment in Xiong’an New Area, China, and their relationship with antibiotic resistance genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Effect of the selective pressure of sub-lethal level of heavy metals on the fate and distribution of ARGs in the catchment scale. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Ezzat, M.; Alfifi, K.J.; Esawy, A.M.; Elmasry, N.; El-Tarabili, R.M. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance (AMR) pattern, virulence determinant and AMR genes of emerging multi-drug resistant Edwardsiella tarda in Nile tilapia and African catfish. Aquaculture 2022, 548, 737643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoir, V.; Poirel, L.; Aubert, C.; Soussy, C.J.; Nordmann, P. Unexpected occurrence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants in environmental Aeromonas spp. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 231–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, T.; Das, B.; Bhadra, R.K.; Dam, B.; Mazumder, S. Complete nucleotide sequence of a quinolone resistance gene (qnrS2) carrying plasmid of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from fish. Plasmid 2011, 66, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, N.P.; Pal, C.; Gaikwad, S.S.; Jonsson, V.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Untreated urban waste contaminates Indian river sediments with resistance genes to last resort antibiotics. Water Res. 2017, 124, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, I.; Ali, A.; Gogry, F.A.; Rather, I.A.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Haq, Q.M.R. Bacterial isolates harboring antibiotics and heavy-metal resistance genes co-existing with mobile genetic elements in natural aquatic water bodies. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2660–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, V.; Purohit, M.; Chandran, S.; Parashar, V.; Shah, H.; Mahadik, V.K.; Lundborg, C.S.; Tamhankar, A.J.A. Three-Year Follow-Up Study of Antibiotic and Metal Residues, Antibiotic Resistance and Resistance Genes, Focusing on Kshipra—A River Associated with Holy Religious Mass-Bathing in India: Protocol Paper. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Sulfikar; Chaminda, T.; Patel, A.K.; Sewwandi, H.; Mazumder, P.; Joshi, M.; Honda, R. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in the tropical rivers of Sri Lanka and India. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Tavanania, S.; Sabokbar, A.; Khamesipour, F. Prevalence and characterization of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes among Escherichia coli strains isolated from different water sources in Alborz province, Iran. Indones. Biomed. J. 2019, 11, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rafyai, H.M.; Alwash, M.S.; Al-Khafaji, N.S. Quinolone resistance (qnrA) gene in isolates of Escherichia coli collected from the Al-Hillah river in Babylon province, Iraq. Pharmacia 2021, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Comorera, L.; Nolan, T.M.; Reynolds, L.J.; Venkatesh, A.; Cheung, L.; Martin, N.A.; Stephens, J.H.; Gitto, A.; O’Hare, G.M.P.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; et al. Bacterial and bacteriophage antibiotic resistance in marine bathing waters in relation to rivers and urban streams. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 718234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantanella, F.; Lekunberri, I.; Gagliardi, A.; Venuto, G.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Fabiani, M.; Balcázar, J.L.; Schipa, S.; De Giusti, M.; Borrego, C.; et al. Effect of urban wastewater discharge on the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in two italian rivers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucato, A.; Vecchioni, L.; Savoca, D.; Presentato, A.; Arculeo, M.; Alduina, R. A Comparative analysis of aquatic and polyethylene associated antibiotic-resistant microbiota in the Mediterranean sea. Biology 2021, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corno, G.; Yang, Y.; Eckert, E.M.; Fontaneto, D.; Fiorentino, A.; Galafassi, S.; Zhang, T.; Di Cesare, A. Effluents of wastewater treatment plants promote the rapid stabilization of the antibiotic resistome in receiving freshwater bodies. Water Res. 2019, 158, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Eckert, E.M.; Rogora, M.; Corno, G. Rainfall increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes within a riverine microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Kim, J.H.; Cheresca, C.J.; Shin, S.P.; Jun, J.W.; Chai, J.Y.; Han, S.Y.; Park, S.C. First description of the qnrS-like (qnrS5) gene and analysis of quinolone resistance determining regions in motile Aeromonas spp. from diseased fish and water. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botts, R.T.; Apffel, B.A.; Walters, C.J.; Davidson, K.E.; Echols, R.S.; Geiger, M.R.; Guzman, V.L.; Haase, V.S.; Montana, M.A.; La Chat, C.A.; et al. Characterization of four multidrug resistance plasmids captured from the sediments of an urban coastal wetland. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummings, D.E.; Archer, K.F.; Arriola, D.J.; Baker, P.A.; Faucett, K.G.; Laroya, J.B.; Pfeil, K.L.; Ryan, C.R.; Ryan, K.R.U.; Zuill, D.E. Broad dissemination of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in sediments of two urban coastal wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osinska, A.; Harnisz, M.; Korzeniewska, E. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated multidrug resistance determinants in fluoroquinolone-resistant bacteria isolated from sewage and Surface water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10818–10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, N.; Ramalho, J.; Vieira, P.; Da Silva, G.J. Association of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance and virulence markers in Escherichia coli isolated from water. J. Water Health 2012, 10, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocha, J.; Manaia, C.M. Cell-based internal standard for qPCR determinations of antibiotic resistance indicators in environmental water simples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Nunes, M.; Barreto, M.T.; Silva, A.F. The environmental contribution to the dissemination of carbapenem and (fluoro)quinolone resistance genes by discharged and reused wastewater effluents: The role of cellular and extracellular DNA. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacão, M.; Moura, A.; Correia, A.; Henriques, I. Co-resistance to different classes of antibiotics among ESBL-producers from aquatic systems. Water Res. 2014, 48, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, E.; Huerta, B.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D.; Jofre, J.; Balcázar, J.L. Characterization of ciprofloxacin-resistant isolates from a wastewater treatment plant and its receiving river. Water Res. 2014, 61, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proia, L.; von Schiller, D.; Sánchez-Melsió, A.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C.M.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Balcázar, J.L. Occurrence and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in river biofilms after wastewater inputs in small rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Jofre, J.; Balcazar, J.L. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in a river influenced by a wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Balcázar, J.L. Real-time PCR assays for quantification of qnr genes in environmental water samples and chicken feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1743–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piedra-Carrasco, N.; Fábrega, A.; Calero-Cáceres, W.; Cornejo-Sánchez, T.; Brown-Jaque, M.; Mir-Cros, A.; Muniesa, M.; González-López, J.J. Carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae recovered from a Spanish river ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lekunberri, I.; Villagrasa, M.; Balcázar, J.L.; Borrego, C.M. Contribution of bacteriophage and plasmid DNA to the mobilization of antibiotic resistance genes in a river receiving treated wastewater discharges. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer-Lluch, M.; Jofre, J.; Muniesa, M. Quinolone resistance genes (qnrA and qnrS) in bacteriophage particles from wastewater samples and the effect of inducing agents on packaged antibiotic resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subirats, J.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Mandaric, L.; Acuña, V.; Balcázar, J.L.; Sabater, S.; Borrego, C.M. Wastewater pollution differently affects the antibiotic resistance gene pool and biofilm bacterial communities across streambed compartments. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5567–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Méndez, J.; Martín-Díaz, J.; Muniesa, M. The occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in a Mediterranean river and their persistence in the riverbed sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenia, H.Y. Prevalence and characterization of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from South African freshwater fish. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 231, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurfluh, K.; Abgottspon, H.; Hächler, H.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Stephan, R. Quinolone resistance mechanisms among extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Escherichia coli isolated from rivers and lakes in Switzerland. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rortana, C.; Wajjwalku, W.; Boonyawiwat, V.; Hrianpreechab, C.; Thongratsakul, S.; Amavisit, P. Antimicrobial resistance and pirAB-like profiles of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Pacific white shrimp. Agricult. Nat. Res. 2018, 52, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, H.; Suzuki, S.; Reungsang, A.; Viet, P.H. Fluoroquinolone (FQ) contamination does not correlate with occurrence of FQ-resistant bacteria in aquatic environments of Vietnam and Thailand. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castrignanò, E.; Kannan, A.M.; Proctor, K.; Petrie, B.; Hodgen, S.; Feil, E.J.; Lewis, S.E.; Lopardo, L.; Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Rice, J.; et al. (Fluoro)quinolones and quinolone resistance genes in the aquatic environment: A river catchment perspective. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, F.C.T.; Proctor, K.; Barden, R.; Gaze, W.H.; Snape, J.; Feil, E.J.; Kasprzyk-Hordern. Spatiotemporal profiling of antibiotics and resistance genes in a river catchment: Human population as the main driver of antibiotic and antibiotic resistance gene presence in the environment. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, K.; Boopathy, R.; Nathaniel, R.; LaFleur, G. Water pollution and observation of acquired antibiotic resistance in Bayou Lafourche, a major drinking water source in Southeast Louisiana, USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34220–34232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, G.; Wang, C.; Gao, H.; Li, R.; Jin, S.; Zhang, W.; Zong, H. The occurrence of sulfonamide and quinolone resistance genes at the Fildes Peninsula in Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, R.L.; Labbate, M.; Siboni, N.; Tagg, K.A.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Seymour, J.R. Urban beaches are environmental hotspots for antibiotic resistance following rainfall. Water Res. 2019, 167, 115081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, J.P.R.; Ramos, M.S.; Dos Santos, L.D.R.; Gallo, I.F.L.; Lopes, R.; Stehling, E.G. Appearance of mcr-9, blaKPC, cfr and other clinically relevant antimicrobial resistance genes in recreation waters and sands from urban beaches, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Buschmann, A.H.; Rioseco, M.L.; Kalsi, R.K.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Antimicrobial resistance genes in marine bacteria and human uropathogenic Escherichia coli from a region of intensive aquaculture. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Buschmann, A.H.; Godfrey, H.P.; Cabello, F.C. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance (PMQR) Genes and Class 1 Integrons in Quinolone-Resistant Marine Bacteria and Clinical Isolates of Escherichia coli from an Aquacultural Area. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Shu, C.; Liu, L.; Geng, J.; Hu, S.; Feng, J. Marine Sediment Bacteria Harbor Antibiotic Resistance Genes Highly Similar to Those Found in Human Pathogens. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Hong Lu, H.; Yan, B.; Chen, S. Nutrients, heavy metals and microbial communities co-driven distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in adjacent environment of mariculture. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H. Propagation of antibiotic resistance genes in an industrial recirculating aquaculture system located at northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Tetracyclines, sulfonamides and quinolones and their corresponding resistance genes in coastal areas of Beibu Gulf, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Li, A.; Chen, J.; Huang, B.; Mu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wen, D. Wastewater discharge drives ARGs spread in the coastal area: A case study in Hangzhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dang, H. Coastal seawater bacteria harbor a large reservoir of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance determinants in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Na, G.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Gao, H.; Li, R.; Jin, S. Effects of corresponding and non-corresponding contaminants on the fate of sulfonamide and quinolone resistance genes in the Laizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Ahmed, A.M.; Mahfouz, N.B.; Kimura, T.; El-Khodery, S.A.; Moawad, A.A.; Shimamoto, T. Molecular análisis of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria isolated from fish farms in Egypt. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zago, V.; Vaschetti, L.; Patuzzo, C.; Malerba, G.; Lleo, M.M. Resistome, mobilome and virulome analysis of Shewanella algae and Vibrio spp. strain isolated in italian aquaculture centers. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salgueiro, V.; Manageiro, V.; Bandarra, N.; Reis, L.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M. Bacterial diversity and antibiotic susceptibility of Sparus aurata from aquaculture. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro, V.; Reis, L.; Ferreira, E.; Botelho, M.J.; Manageiro, V.; Caniça, M. Assessing the bacterial community composition of bivalve mollusks collected in aquaculture farms and respective susceptibility to antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Chen, H.; Go, S.G.; Haller, L.; Wu, Z.; Charles, F.R.; Trottet, A.; Gin, K. Microbial water quality and the detection of multidrug resistant E. coli and antibiotic resistance genes in aquaculture sites of Singapore. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Raza, S.; Farooq, A.; Kim, J.; Unno, T. Fish farm effluents as a source of antibiotic resistance gene dissemination on Jeju Island, South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.; Shin, S.G.; Unno, T.; Kim, Y.M. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes from effluent of coastal aquaculture, South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saticioglu, I.B.; Duman, M.; Altun, S. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characterization of Pantoea agglomerans isolated from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 119, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, N.A.; Nazaret, S.; Barkay, T. Whole genome sequences to assess the link between antibiotic and metal resistance in three coastal marine bacteria isolated from the mummichog gastrointestinal tract. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amos, G.C.A.; Zhang, L.; Hawkey, P.M.; Gaze, W.H.; Wellington, E.M. Functional metagenomic analysis reveals rivers are a reservoir for diverse antibiotic resistance genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.-G.; Huang, Q.; Yin, X.; Zhang, T. Source tracking of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment—Challenges, progress, and prospects. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Sahm, D.F.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. qnr prevalence in ceftazidime-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2872–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanat, B.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Touati, A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: A systematic review with a focus on Mediterranean countries. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Griffin, C.M.; Hooper, D.C. Citrobacter spp. as a source of qnrB alleles. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4979–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, T.G.; Novais, Â.; Branquinho, R.; Machado, E.; Peixe, L. Phylogeny and comparative genomics unveil independent diversification trajectories of qnrB and genetic platforms within particular Citrobacter species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5951–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toleman, M.A.; Bennett, P.M.; Walsh, T.R. ISCR elements: Novel gene-capturing systems of the 21st century? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2006, 70, 296–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.J.; Kim, M.-N.; Park, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Karim, A.M.; Park, M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Complex Class 1 Integron Carrying qnrB62 and blaVIM-2 in a Citrobacter freundii Clinical Isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6937–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quiroga, M.P.; Andres, P.; Petroni, A.; Bistué, A.J.C.S.; Guerriero, L.; Vargas, L.J.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tokumoto, M.; Quiroga, C.; Tolmasky, M.E.; et al. Complex Class 1 Integrons with Diverse Variable Regions, Including aac(60)-Ib-cr, and a Novel Allele, qnrB10, Associated with ISCR1 in Clinical Enterobacterial Isolates from Argentina. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4466–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Wintersdorff, C.J.H.; Penders, J.; van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkoul, P.H.M.; Wolffs, P.F.G. Dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in microbial ecosystems through horizontal gene transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domingues, S.; DaSilva, G.J.; Nielsen, K.M. Integrons: Vehicles and pathways for horizontal dissemination in bacteria. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2012, 2, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, L.; Breidenstein, E.; Hancock, R. Importance of adaptive and stepwise changes in the rise and spread of antimicrobial resistance. In Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment; Keen, P.L., Montforts, M.H.M.M., Eds.; Wiley—Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanes, C.; Köhler, T.; Patry, I.; Dehecq, B.; van Delden, C.; Plésiat, P. Role of the MexEF-OprN efflux system in low-level resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5676–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alekshun, M.N.; Levy, S.B. Molecular Mechanisms of Antibacterial Multidrug Resistance. Cell 2007, 128, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correia, S.; Poeta, P.; Hébraud, M.; Capelo, J.L.; Igrejas, G. Mechanisms of quinolone action and resistance: Where do we stand? J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, N.G.; Diez-Santos, I.; Abbott, L.R.; Maxwell, A. Quinolones: Mechanism, Lethality and Their Contributions to Antibiotic Resistance. Molecules 2020, 25, 5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkou, A.; Hedge, J.; Kapel, N.; Young, B.; MacLean, R.C. Efflux pump activity potentiates the evolution of antibiotic resistance across Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bambeke, F.; Balzi, E.; Tulkens, P.M. Antibiotic efflux pumps. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, N.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, A.; Verma, G.; Sharma, M. Enhanced resistance to fluoroquinolones in laboratory-grown mutants and clinical isolates of Shigella due to synergism between efflux pump expression and mutations in quinolone resistance determining region. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 141, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, C.; Miranda, C.D.; Hurtado, L.; Romero, J. Characterization of Mechanisms Lowering Susceptibility to Flumequine among Bacteria Isolated from Chilean Salmonid Farms. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Evolution of antibiotic resistance at non-lethal drug concentrations. Drug Resist. Updates 2012, 15, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureti, L.; Matic, I.; Gutierrez, A. Bacterial responses and genome instability induced by subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. Antibiotics 2013, 2, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jørgensen, K.M.; Wassermann, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Hengzuang, W.; Molin, S.; Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O. Sublethal ciprofloxacin treatment leads to rapid development of high-level ciprofloxacin resistance during long-term experimental evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poole, K. Multidrug efflux pumps and antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related organisms. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 3, 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Aeschlimann, J.R. The role of multidrug efflux pumps in the antibiotic resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other gram-negative bacteria. Insights from the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy 2003, 23, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charvalos, E.; Tselentis, Y.; Hamzehpour, M.M.; Köhler, T.; Pechére, J.C. Evidence for an efflux pump in multidrug-resistant Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Source | Mean or Range of Quinolones (ng/L or µg/kg) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFX | NFX | CIP | ENR | |||
| Water | Suquía River, Argentina | nd–69 | nd–80 | nd–78 | NT | [26] |
| Southeast Queensland, Australia | NT | 1,150 | 300 | 1300 | [27] | |
| Belém River, Brazil | NT | 110 | <20 | NT | [28] | |
| Barigui River, Brazil | NT | <20–130 | 70 | NT | [28] | |
| Hunhe River, China | nd–280 | nd–1380 | nd–65 | nd–17 | [29] | |
| Bohai Sea, China | 3–5100 | 32–6800 | 4.9–390 | NT | [30] | |
| Haihe River, China | 180 | NT | 130 | NT | [31] | |
| Baiyangdian Lake, China | 0.38–32.6 | nd–156 | nd–60.3 | nd–4.42 | [32] | |
| Laizhou Bay, China | nd–45.5 | nd–572 | nd–346 | nd–24.6 | [33] | |
| Xiaoqing River, China | 9.5–1605 | nd | nd–56.6 | nd | [34] | |
| Huangpu River, China | nd–6.5 | nd–2.6 | nd–2.7 | nd | [35] | |
| Tai Lake, China | 14–474 | 59–271 | 18–269 | 19–229 | [36] | |
| Pearl River, China | 7.1 | 67.5 | NT | nd | [37] | |
| Victoria Harbor, China | 660–6840 | 14–2290 | NT | NT | [38] | |
| River, Beijing, China | 663.9–2722 | NT | NT | NT | [39] | |
| Huangpu River, China | nd–28.5 | nd–0.2 | nd–34.2 | nd–14.6 | [40] | |
| Yangjie River, China | 0.14–4.49 | 0.11–2.37 | 0.77–4.32 | 0.53 5.56 | [41] | |
| Danjiangkou Reservoir, China | 2.0–2.9 | 0.55–0.61 | 0.87–1.1 | 0.81 1.2 | [42] | |
| Liuxi River, China | NT | 7.06 | NT | NT | [43] | |
| Zhujiang River, China | NT | 4.85 | NT | NT | [43] | |
| Shijing River, China | NT | 70.4 | NT | NT | [43] | |
| Pearl River Delta, China | NT | 4.14–6.62 | NT | NT | [44] | |
| Qingshitan Reservoir, China | 50.0–660.13 | 3.70–3.49 | 3.49–6.22 | 4.59–6.06 | [45] | |
| Musi River, India | 1553.0–542,452.0 | 16,148.0–251,137.0 | 7447.0–5015.7 | 2262.0–181,609.0 | [46] | |
| Kshipra River, India | 640–1460 | nd–980 | nd | NT | [47] | |
| Kan River, Iran | NT | NT | 9.87 | NT | [48] | |
| Firozabad Ditch, Iran | NT | NT | 212.83 | NT | [48] | |
| Po River, Italy | 0.65–18.06 | NT | 1.32–16 | NT | [49] | |
| Arno River, Italy | <1.4–10.88 | NT | <1.8–37.5 | NT | [49] | |
| Lambro River, Italy | 306 | NT | 26,200 | NT | [50] | |
| River and Estuaries, Osaka, Japan | nd–510 | nd–33 | 2.6–37 | nd–4.4 | [51] | |
| Mitheu River, Kenya | NT | 600–2200 | 500–1300 | NT | [52] | |
| Sagana River, Kenya | NT | nd | 200 | NT | [52] | |
| Chania River, Kenya | NT | 100–2600 | nd | NT | [52] | |
| Mwania River, Kenya | NT | 110 | 500 | NT | [52] | |
| Kanyuru River, Kenya | NT | nd | 200 | NT | [52] | |
| Douro River, Portugal | nd | NT | nd | NT | [53] | |
| Leça River, Portugal | 120 | NT | 339 | NT | [53] | |
| Titicaca Lake, Perú | NT | NT | 85.5–652.7 | 56.2–63.0 | [54] | |
| East Aurora, USA | NT | NT | nd–360 | NT | [55] | |
| Sediment | Suquía River, Argentina | nd–39 | nd | NT | NT | [26] |
| Jiaozhou Bay, China | nd–33.83 | NT | nd–11.52 | nd–1.92 | [56] | |
| Yellow River, China | 3.07 | 8.34 | 32.8 | nd | [31] | |
| Haihe River, China | 10.3 | 32 | 16 | nd | [31] | |
| Liaohe River, China | 3.56 | 3.32 | Nd | nd | [31] | |
| Qinghe River, China | 5.9 | 49.1 | 28.3 | 2.2 | [57] | |
| Huangpu River, China | nd–12.4 | NT | nd–3.2 | NT | [40] | |
| Danjiangkou Reservoir, China | 1.2–1.9 | 1.7–2 | 0.98–1.1 | 1.2–1.3 | [42] | |
| Pearl River Estuary, China | nd–2.08 | 50.24–153.06 | NT | nd–25.62 | [37] | |
| Pearl River Delta, China | NT | 1.88–11.20 | 0.76–2.42 | NT | [44] | |
| Qingshitan Reservoir, China | 1.03–118.11 | 20.17–722.18 | 17.48–557.18 | 4.70–331.82 | [45] | |
| Charmoise River, France | 4.9–603 | 1.6–225 | 2.9–569 | 6.6–11 | [58] | |
| Patancheru River, India | nd–3545 * | nd | 449–914,044 * | 374–102,865 * | [59] | |
| Musi River, India | 890.0–444,916.0 | nd–232,918.0 | nd–3316.5 | 4471.0–721,491.0 | [46] | |
| Nakkavagu River, India | 0.63 | 0.14 | 10 | 0.064 | [60] | |
| Isakavagu River, India | 0.91 | 0.68 | 12 | nd | [60] | |
| Mitheu River, Kenya | NT | nd | 29.3 | NT | [52] | |
| Sagana River, Kenya | NT | nd | nd | NT | [52] | |
| Chania River, Kenya | NT | 26.6 | nd | NT | [52] | |
| Kanyuru River, Kenya | NT | nd | 47.4 | NT | [52] | |
| Titicaca Lake, Perú | NT | NT | 950–3010 | 150–3740 | [54] | |
| Grifn Lake, Switzerland | NT | 2.4 | 2.52 | NT | [61] | |
| Northwest River, USA | <21 | NT | <10 | NT | [62] | |
| Fish | Guangdong, China | NT | 46.64–106.85 | 27.07–165.15 | 1.0–34.20 | [63] |
| Guiyang, China | nd–385.73 | nd | nd–16.37 | 0.30–312.00 | [64] | |
| Hongze Lake, China | NT | NT | 15.0–24.0 | NT | [65] | |
| Jining, China | NT | NT | 2.08–33.8 | nd–3.25 | [66] | |
| Suzhou, China | nd–4.35 | NT | nd–33.7 | 3.7–90.6 | [33] | |
| Pearl River Delta, China | NT | 1.95–43.51 | 1.03–2.16 | 0.65–1.71 | [44] | |
| Qingshitan Reservoir, China | 58.59–968.66 | 9.15–33.27 | 12.15–80.26 | 6.73–102.87 | [45] | |
| Titicaca Lake, Perú | NT | NT | 3.4–3.9 | 3.8–4.8 | [54] | |
| Gene | Percentage of Nuleotide/Amino Acid Similarity (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qnrA | qnrB | qnrC | qnrD | qnrE | qnrS | qnrVC | |
| qnrA | 100/100 | 46.33/41.59 | 59.36/64.22 | 47.91/46.26 | 48.99/42.06 | 58.75/59.63 | 60.43/61.93 |
| qnrB | 100/100 | 48.78/42.99 | 62.79/64.49 | 75.81/85.98 | 48.32/39.72 | 50/42.99 | |
| qnrC | 100/100 | 49.77/44.39 | 46.98/42.52 | 60.73/60.09 | 68.65/73.85 | ||
| qnrD | 100/100 | 63.10/65.89 | 46.51/39.25 | 50.70/43.93 | |||
| qnrE | 100/100 | 48.37/35.98 | 49.61/42.06 | ||||
| qnrS | 100/100 | 63.93/64.68 | |||||
| qnrVC | 100/100 | ||||||
| Environment | Country | Source | Species Carrying a qnr Gene | Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freshwater | Bangladesh | Water | qnrB, qnrS: Eschericia coli | ND | [172] |
| Belgium | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [173] | |
| Brazil | Water | qnrB, qnrS: Klebsiella pneumonia | ND | [174] | |
| Brazil | River Water/Sediment | qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [175] | |
| Canada | Wastewater/River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [176] | |
| Canada, China, Sri Lanka, South Korea, USA | Fish | qnrA: Aeromonas hydrophila | ND | [177] | |
| Chile | Reared fish | qnrB: Citrobacter gillenii | ND | [151] | |
| China | Fish | qnrB, qnrD, qnrS: Escherichia coli | Pl (qnrS), ND | [178] | |
| China | Fish | qnrA, qnrS: Aeromonas spp. | ND | [179] | |
| China | Fish/River Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [180] | |
| China | Water | qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [181] | |
| China | Water/Sediment | qnrS: ND | ND | [182] | |
| China | River Water/Sediment | qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [183] | |
| Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [184] | ||
| China | River Water/Sediment | qnrA, qnrS: ND | ND | [185] | |
| China | Water | qnrB: Klebsiella pneumoniae, Raoultella omithinolytica.; qnrS: Aeromonas caviae, Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas allosaccharophila, Aeromonas veronii, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter hormaechei, Leclercia adecarboxylata, Enterococcus faecalis | Pl (qnrS), ND | [186] | |
| China | Fish/Shrimp | qnrA, qnrD: ND | ND | [13] | |
| China | Shrimp | qnrD: ND | Pl | [187] | |
| China | Shrimp | qnrA: ND | ND | [188] | |
| China | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [189] | |
| China | Lake Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [190] | |
| China | Lake Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [191] | |
| China | Wastewater/River Water | qnrA: Enterobacter sp., Proteus sp., Citrobacter sp.; qnrB: Klebsiella sp., Enterobacter sp., Proteus sp., Shigella sp., Citrobacter sp. qnrS: Klebsiella sp., Escherichia coli, Enterobacter sp.; | Pl, Cr | [192] | |
| China | Wastewater/River Water | qnrC, qnrD: ND | Pl | [39] | |
| China | Wastewater/River Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [193] | |
| China | Eel, Pond Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [194] | |
| China | Water | qnrB: Salmonella typhi, Salmonella enteriditis, Salmonella typhimurium | ND | [195] | |
| China | River Water/Sediment | qnrA, qnrB, qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [196] | |
| China | River Water | qnrD: ND | ND | [197] | |
| China | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [198] | |
| China | Water | qnrA, qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [199] | |
| China | Water | qnrB, qnrS: Escherichia coli | Pl | [200] | |
| China | Water | qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [201] | |
| China | River Water | qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [202] | |
| China | River Water/Sediment | qnrA: ND | ND | [203] | |
| China | Water/Sediment | qnrA, qnrB, qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [204] | |
| Egypt | Fish | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: Edwarsiella tarda | ND | [205] | |
| France | Water | qnrS: Aeromonas punctata, Aeromonas media | Pl | [206] | |
| India | Fish | qnrS: Aeromonas hydrophila | Pl | [207] | |
| India | Sediment | qnrB, qnrD, qnrS, qnrVC: ND | ND | [69] | |
| India | River Sediment | qnrS: ND | ND | [208] | |
| India | River Water | qnrD, qnrS, qnrVC: ND | ND | [59] | |
| India | Water | qnrS: Acinetobacter sp., Pseudomonas sp., Aeromonas sp., Brevibacterium frigoritolerans | Pl | [209] | |
| India | Water/Sediment | qnrA, qnrB: ND | ND | [210] | |
| India, Sri Lanka | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [211] | |
| Iran | Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: Escherichia coli | ND | [212] | |
| Iraq | Water | qnrA: Escherichia coli | ND | [213] | |
| Ireland | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [214] | |
| Italy | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [215] | |
| Italy | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [216] | |
| Italy | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [217] | |
| Italy | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [218] | |
| Japan | River Water | qnrS: Escherichia coli | Pl | [51] | |
| Korea | Fish | qnrS: Aeromonas sp. | Pl | [219] | |
| Mexico | Sediment | qnrB: ND | Pl | [220] | |
| Mexico, USA | Sediment | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [221] | |
| Poland | Water | qnrD: Eschericia coli, Acinetobacter sp., Acinetobacter johnsonii, Acinetobacter guillouiae, Aeromonas sp., Bacillus sp., Pseudomonas sp., Cronobacter sp., Acidovorax sp., Hydrogenophaga sp., Kurthia sp., Providencia sp., Psychrobacter sp., Shigella sp., Vibrio sp. qnrS: Sphingobacterium sp., Pedobacter sp., Eschericia coli, Acinetobacter sp., Acinetobacter johnsonii, Aeromonas sp., Bacillus sp, Kurthia sp., Shigella sp. | Pl | [222] | |
| Portugal | Water | qnrA: Escherichia coli | ND | [223] | |
| Portugal | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [224] | |
| Portugal | Water | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [225] | |
| Portugal | Water | qnrVC: Aeromonas hydrophila, Pseudomonas sp., Escherichia coli, Aeromonas sp. | ND | [226] | |
| Spain | Biofilm | qnrB: Klebsiella oxytoca; qnrS: Aeromonas sp. | Pl | [227] | |
| Spain | Biofilm | qnrS: ND | ND | [228] | |
| Spain | Sediment | qnrB: Citrobacter freundii; qnrS: Aeromonas sp., Raoutella terrígena | Pl | [227] | |
| Spain | Sediment | qnrS: ND | ND | [229] | |
| Spain | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [230] | |
| Spain | Sediment | qnrB: Escherichia coli, Raoultella ornithinolytica, Enterobacter cloacae | Pl | [231] | |
| Spain | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [22] | |
| Spain | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [232] | |
| Spain | Water | qnrA, qnrS: ND | ND | [233] | |
| Spain | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [234] | |
| Spain | Water/Sediment | qnrA, qnrS: ND | ND | [235] | |
| South Africa | Fish | qnrB: Aeromonas veronii, Aeromonas caviae, Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas jandaei qnrS: Aeromonas veronii, Aeromonas hydrophila, Aeromonas jandaei | ND | [236] | |
| Switzerland | Lake Water | qnrS: Aeromonas allosaccharophila | Pl | [164] | |
| Switzerland | Water | qnrS: Escherichia coli | Pl | [237] | |
| Thailand | Shrimp/Pond Water | qnrVC: Vibrio parahaemolyticus | ND | [238] | |
| Thailand and Vietnam | Water | qnrB: Brevundimonas diminuta, Blastobacter aggregatus, Janibacter anophelis; qnrS: Escherichia coli | ND | [239] | |
| United Kingdom | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [240] | |
| United Kingdom | River Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [241] | |
| United States | River Water | qnrA: ND | ND | [242] | |
| Seawater | Antarctica | Sediment | qnrS: ND | ND | [243] |
| Australia | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [244] | |
| Brazil | Water/Sand | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | ND | [245] | |
| Chile | Water/Sediment | qnrA: Alcanivorax sp., Arcobacter sp., Arthrobacter sp., Kytococcus sp., Marinobacter sp., Microbacterium sp., Pseudomonas sp., Rhodococcus sp.; qnrB: Kytococcus sp., Marinobacter sp., Rhodococcus sp., Actinobacterium sp., Cellulophaga sp., Flavobacteriaceae, Erythrobacter sp., Tsukamurella sp.; Rhodococcus sp.; Marinobacter sp.; Kylococcus sp.; qnrS: Arcobacter sp., Arthrobacter sp., Marinobacter sp., Pseudomonas sp., Rhodococcus sp., Cellulophaga sp., Erythrobacter sp., Dietzia sp., Microbacter sp. | Pl, Cr | [246,247] | |
| China | Fish | qnrA, qnrC: ND | ND | [178] | |
| China | Sediment | qnrA: Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Providencia stuartii, Klebsiella pneumoniae | Pl, ND | [248] | |
| China | Sediment | qnrS: ND | ND | [249] | |
| China | Fish | qnrA, qnrB, qnrD, qnrS: ND | ND | [250] | |
| China | Sediment | qnrA,qnrB,qnrD,qnrS: ND | ND | [251] | |
| China | Water/Sediment | qnrB,qnrS: ND | ND | [252] | |
| China | Water | qnrA: Shewanella algae; qnrB: Citrobacter freundii; qnrD: Proteus vulgaris; qnrS: Enterobacter sp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudoalteromonas sp., Pseudomonas sp. | Pl, Cr | [253] | |
| China | Water/Sediment | qnrS: ND | ND | [254] | |
| Egypt | Water | qnrA: Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Citrobacter koseri, Proteus mirabilis, Shewanella putrefaciens; qnrB: Klebsiella pneumoniae, Citrobacter koseri, qnrS: Klebsiella pneumoniae, Aeromonas hydrophila, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Citrobacter sp., Pasteurella sp. | ND | [255] | |
| Italy | Water | qnrS: ND | ND | [216] | |
| Italy | Water/Sediment | qnrA: Shewanella algae; qnrVC: Vibrio anguillarum | Pl | [256] | |
| Portugal | Fish | qnrB: Leclercia adecarboxylata | ND | [257] | |
| Portugal | Clams/Oysters | qnrA, qnrB, qnrS: ND | Pl | [258] | |
| Singapore | Water/Sediment | qnrA: ND | ND | [259] | |
| South Korea | Fish Farm Effluent | qnrS: ND | Pl | [260] | |
| South Korea | Fish Farm Effluent | qnrD: Psychrosphaera; qnrS: ND | ND | [261] | |
| Turkey | Fish | qnrS: Pantoea agglomerans | ND | [262] | |
| United States | Fish | qnrS: Vibrio sp. | ND | [263] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, C.D.; Concha, C.; Godoy, F.A.; Lee, M.R. Aquatic Environments as Hotspots of Transferable Low-Level Quinolone Resistance and Their Potential Contribution to High-Level Quinolone Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111487
Miranda CD, Concha C, Godoy FA, Lee MR. Aquatic Environments as Hotspots of Transferable Low-Level Quinolone Resistance and Their Potential Contribution to High-Level Quinolone Resistance. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111487
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Claudio D., Christopher Concha, Félix A. Godoy, and Matthew R. Lee. 2022. "Aquatic Environments as Hotspots of Transferable Low-Level Quinolone Resistance and Their Potential Contribution to High-Level Quinolone Resistance" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111487
APA StyleMiranda, C. D., Concha, C., Godoy, F. A., & Lee, M. R. (2022). Aquatic Environments as Hotspots of Transferable Low-Level Quinolone Resistance and Their Potential Contribution to High-Level Quinolone Resistance. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111487







