Characterization of Resistance and Virulence of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Pet Cats in South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
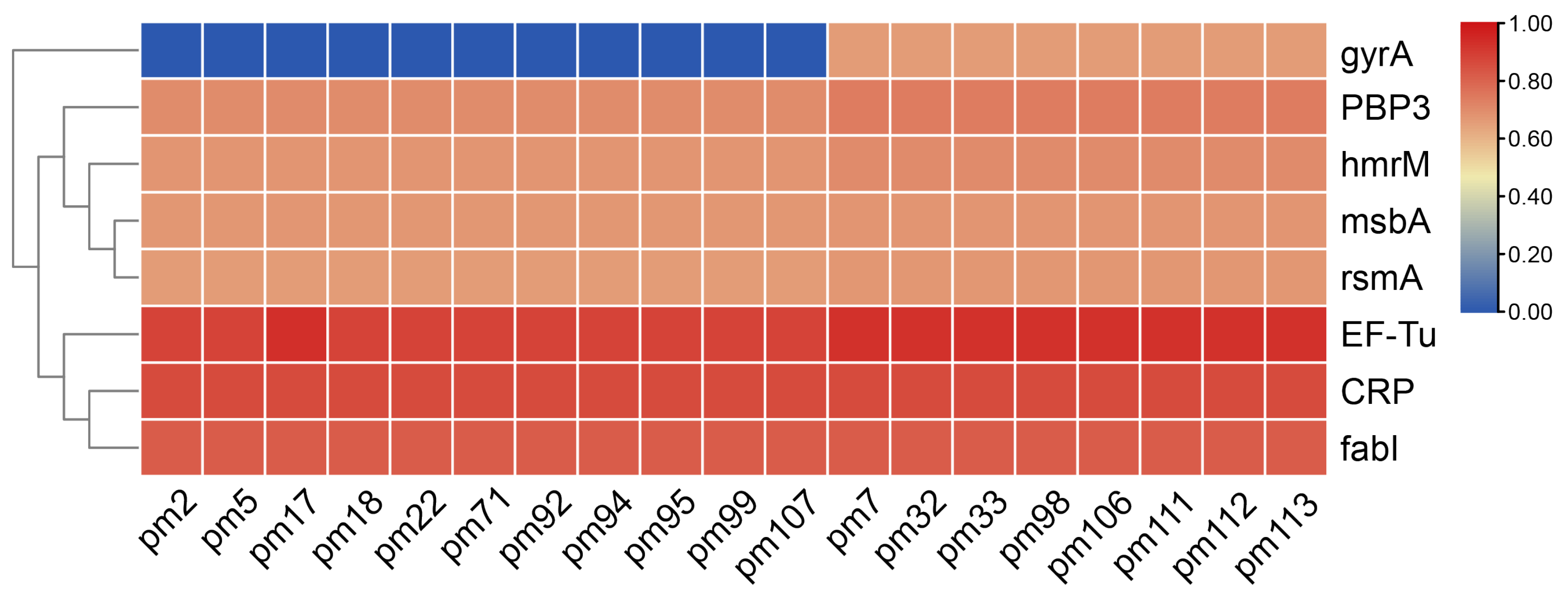
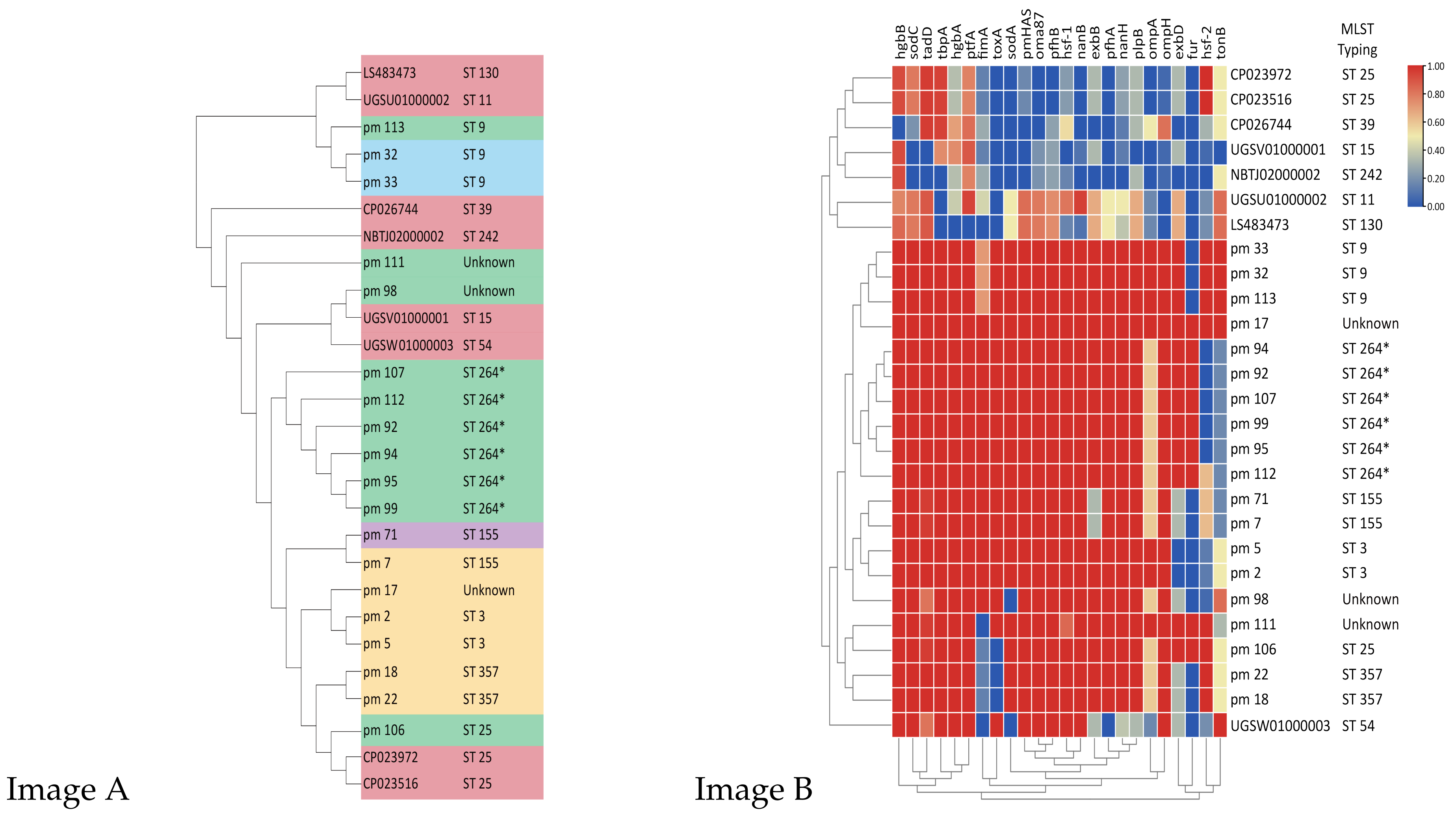
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolate Identification
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.4. Genomic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.; Miller, E.; Aguayo, J.M.; Figueroa, C.F.; Nezworski, J.; Studniski, M.; Wileman, B.; Johnson, T. Genomic diversity and molecular epidemiology of Pasteurella multocida. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzi, B.; Dalloul, R.A.; LeRoith, T.; Evans, N.P.; Pierson, F.W.; Inzana, T.J. Biofilm formation and avian immune response following experimental acute and chronic avian cholera due to Pasteurella multocida. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 222, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.C.; Lo, D.Y.; Chang, S.K.; Chou, C.C.; Kuo, H.C. Antimicrobial susceptibility, serotypes and genotypes of Pasteurella multocida isolates associated with swine pneumonia in Taiwan. Vet. Rec. 2017, 181, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Dong, W.L.; Jia, B.Y.; Gao, D.; Jiang, X.Y.; Ma, H.X. Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of Pasteurella multocida isolated from six provinces in China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.J.; Wolfson, J.S.; Swartz, M.N.; Hooper, D.C. Pasteurella multocida infections. Report of 34 cases and review of the literature. Medicine 1984, 63, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolieslager, S.M.; Riggio, M.P.; Lennon, A.; Lappin, D.F.; Johnston, N.; Taylor, D.; Bennett, D. Identification of bacteria associated with feline chronic gingivostomatitis using culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.S.P.; Felizardo, M.R.; Gobbi, D.D.S.D.; Moreno, M.; Moreno, A.M. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene profiles in P. multocida strains isolated from cats. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvári, B.; Weiczner, R.; Deim, Z.; Terhes, G.; Urbán, E.; Tóth, A.; Magyar, T. Characterization of Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from human infections. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 63, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, A.; Egberink, H.; Addie, D.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Hartmann, K.; Hosie, M.J.; Lutz, H.; et al. Pasteurella multocida infection in cats: ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Shimizu, M.; Iwata, M.; Tanahashi, J.; Ito, M. Pasteurella multocida septicemia caused by close contact with a domestic cat: Case report and literature review. J. Infect. Chemother. 2004, 10, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, F.; Rodrïguez-Lucas, C.; Rodicio, M.R.; Vela, A.I.; Fernändez-Garayzäbal, J.F.; Leiva, P.S.; Cuesta, F.; Cid, D.; Fernändez, J. Human Pasteurella multocida infection with likely zoonotic transmission from a pet dog, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcantonio, Y.C.; Kulkarni, P.A.; Sachs, S.; Ting, K.; Lee, J.; Mendoza, D. Disseminated Pasteurella multocida infection: Cellulitis, osteomyelitis, and myositis. IDCases 2017, 10, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MJ, U.B.; Aspichueta, C.; Díaz de Tuesta, J. Septic shock and empyema induced by Pasteurella multocida. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. Publ. Off. Soc. Esp. Quimioter. 2021, 34, 506–508. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, W.; Rong, S. Pet-related Pasteurella multocida induced peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: A case report and review of the literatures. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieber, S.; Mehrotra, R. Peritoneal dialysis access associated infections. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, R.V.; Rostand, S.G. Cat-bite peritonitis: Pasteurella multocida peritonitis following feline contamination of peritoneal dialysis tubing. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1987, 10, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria, 3rd ed.; Clsi Guideline M45; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aski, H.S.; Tabatabaei, M. Occurrence of virulence-associated genes in Pasteurella multocida isolates obtained from different hosts. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 96, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, B.; Bulach, D.; Chung, J.; Doughty, S.; Hunt, M.; Rajakumar, K.; Serrano, M.; Van Zanden, A.; Zhang, Y.; Ruffolo, C. Candidate vaccine antigens and genes in Pasteurella multocida. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 73, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, C.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Bethe, A.; Kießling, S.; Filter, M.; Wieler, H.L. Virulence genotype of Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from different hosts with various disease status. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 114, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, T.E.; Kennedy, M.J.; Lowery, D.E. Identification of Pasteurella multocida virulence genes in a septicemic mouse model using signature-tagged mutagenesis. Microb. Pathog. 2000, 29, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.L.; Adler, B.; Townsend, K.M. The molecular biology of Pasteurella multocida. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 72, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasfi Marandi, M.; Mittal, K. Role of outer membrane protein H (OmpH)-and OmpA-specific monoclonal antibodies from hybridoma tumors in protection of mice against Pasteurella multocida. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 4502–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.D.; Berliner, Y.; Carr, D. Deadly case of Pasteurella multocida aortitis and mycotic aneurysm following a cat bite. World J. Clin. Cases 2016, 4, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlsson, A.; Friberg, Ö.; Källman, J. An angry cat causing Pasteurella multocida endocarditis and aortic valve replacement—A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2016, 24, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Freshwater, A. Why your housecat’s trite little bite could cause you quite a fright: A study of domestic felines on the occurrence and antibiotic susceptibility of Pasteurella multocida. Zoonoses Public Health 2008, 55, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamesipour, F.; Momtaz, H.; Azhdary Mamoreh, M. Occurrence of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance in Pasteurella multocida strains isolated from slaughter cattle in Iran. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beceiro, A.; Tomás, M.; Bou, G. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence: A successful or deleterious association in the bacterial world? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarangi, L.N.; Thomas, P.; Gupta, S.; Priyadarshini, A.; Kumar, S.; Nagaleekar, V.K.; Kumar, A.; Singh, V.P. Virulence gene profiling and antibiotic resistance pattern of Indian isolates of Pasteurella multocida of small ruminant origin. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 38, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, C.; Conroy, M.; Carpentier, A.; Lozniewski, A. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Pasteurella strains isolated from humans. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 27, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Oh, J.; Park, S.; Sum, S.; Song, W.; Chae, J.; Park, H. Antimicrobial resistance and novel mutations detected in the gyrA and parC genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from companion dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushibara, N.; Suzaki, K.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Aung, M.S.; Shinagawa, M.; Takahashi, S.; Kobayashi, N. Contribution of type II topoisomerase mutations to fluoroquinolone resistance in Enterococcus faecium from Japanese clinical setting. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.J.; Su, X.Z.; Morita, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the HmrM multidrug efflux pump from Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 47, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Horiyama, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Nishino, K.; Yan, A. The multidrug efflux pump MdtEF protects against nitrosative damage during the anaerobic respiration in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 26576–26584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colclough, A.L.; Alav, I.; Whittle, E.E.; Pugh, H.L.; Darby, E.M.; Legood, S.W.; McNeil, H.E.; Blair, J.M. RND efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria; regulation, structure and role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Hua, L.; Chen, H.; Wilson, B.A.; Wang, J.; et al. Development of an Online Tool for Pasteurella multocida Genotyping and Genotypes of Pasteurella multocida From Different Hosts. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 771157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the problem of comparing whole bacterial genomes across different sequencing platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Nielsen, E.M.; Kaas, R.S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. Evaluation of whole genome sequencing for outbreak detection of Salmonella enterica. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for routine typing, surveillance, and outbreak detection of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobial Agent | Disk Content | Number of Susceptible Strains (Susceptible Rate %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillins and -lactam/-lactamase inhibitor combinations | Amoxicillin-clavulanate | 20/10 μg | 44 (97.78) |
| Ampicillin | 10 μg | 44 (97.78) | |
| Penicillin | 10 units | 45 (100.00) | |
| Cephems | Ceftriaxone | 30 μg | 36 (80.00) |
| Fluoroquinolones | Moxifloxacin | 5 μg | 28 (62.22) |
| Levofloxacin | 5 μg | 28 (62.22) | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 30 μg | 45 (100.00) |
| Doxycycline | 30 μg | 45 (100.00) | |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | 15 μg | 0 (0.00) |
| Azithromycin | 15 μg | 42 (93.33) | |
| Others | Chloramphenicol | 30 μg | 45 (100.00) |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 1.25/23.75 μg | 40 (88.88) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, W.; Xu, Q. Characterization of Resistance and Virulence of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Pet Cats in South China. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101387
Lin H, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Lu W, Xu Q. Characterization of Resistance and Virulence of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Pet Cats in South China. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101387
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Haoyi, Zhihui Liu, Yingchun Zhou, Weiguo Lu, and Qian Xu. 2022. "Characterization of Resistance and Virulence of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Pet Cats in South China" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101387
APA StyleLin, H., Liu, Z., Zhou, Y., Lu, W., & Xu, Q. (2022). Characterization of Resistance and Virulence of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Pet Cats in South China. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101387





