Fitness Costs of Tigecycline Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and the Resistance Mechanism Revealed by a Transposon Mutation Library
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Selection of Tigecycline-Resistant or Tigecycline-Susceptible A. baumannii
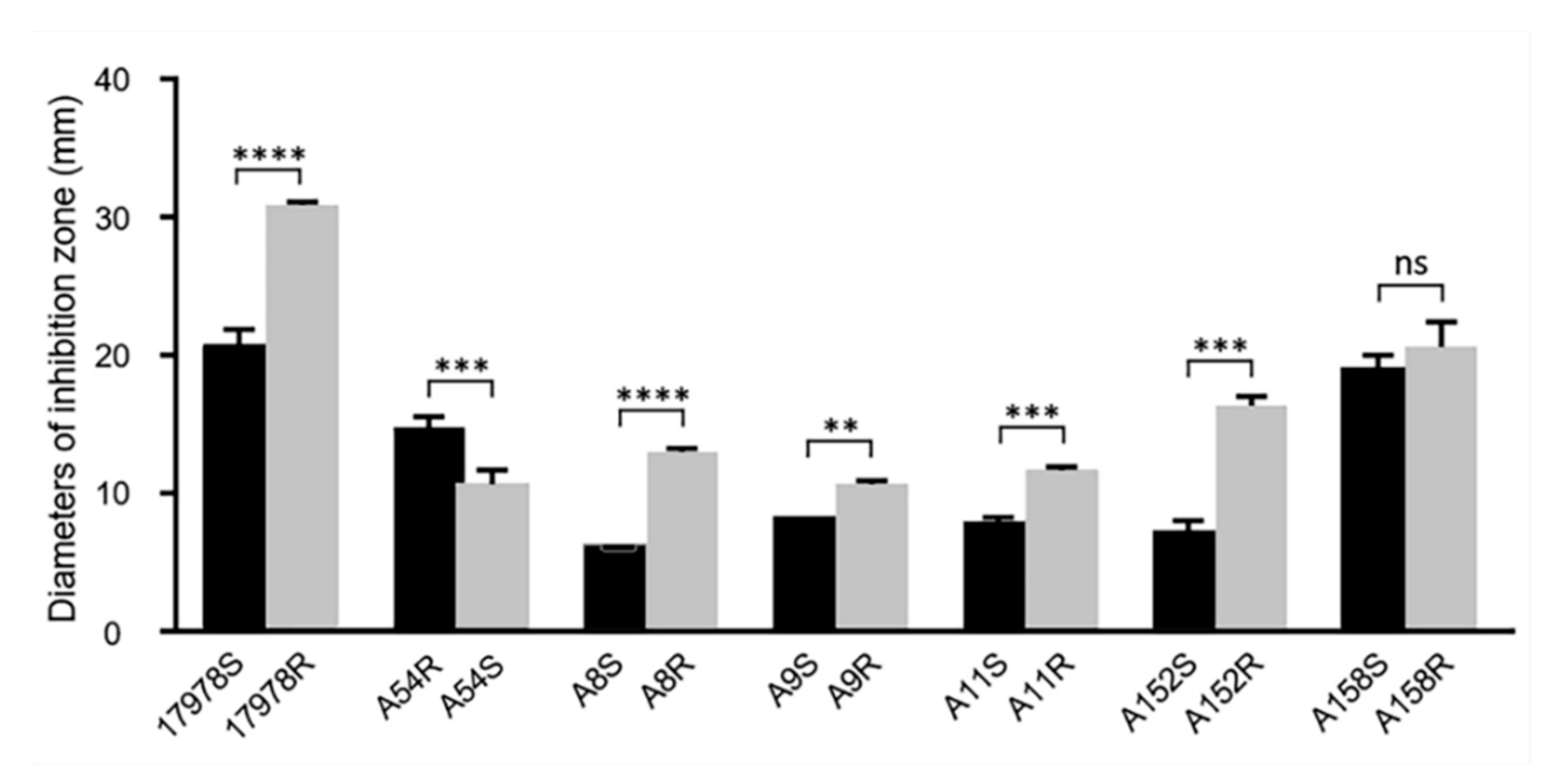
2.2. The Acquisition/Loss of Tigecycline Resistance Affected Susceptibility to Other Antibiotics
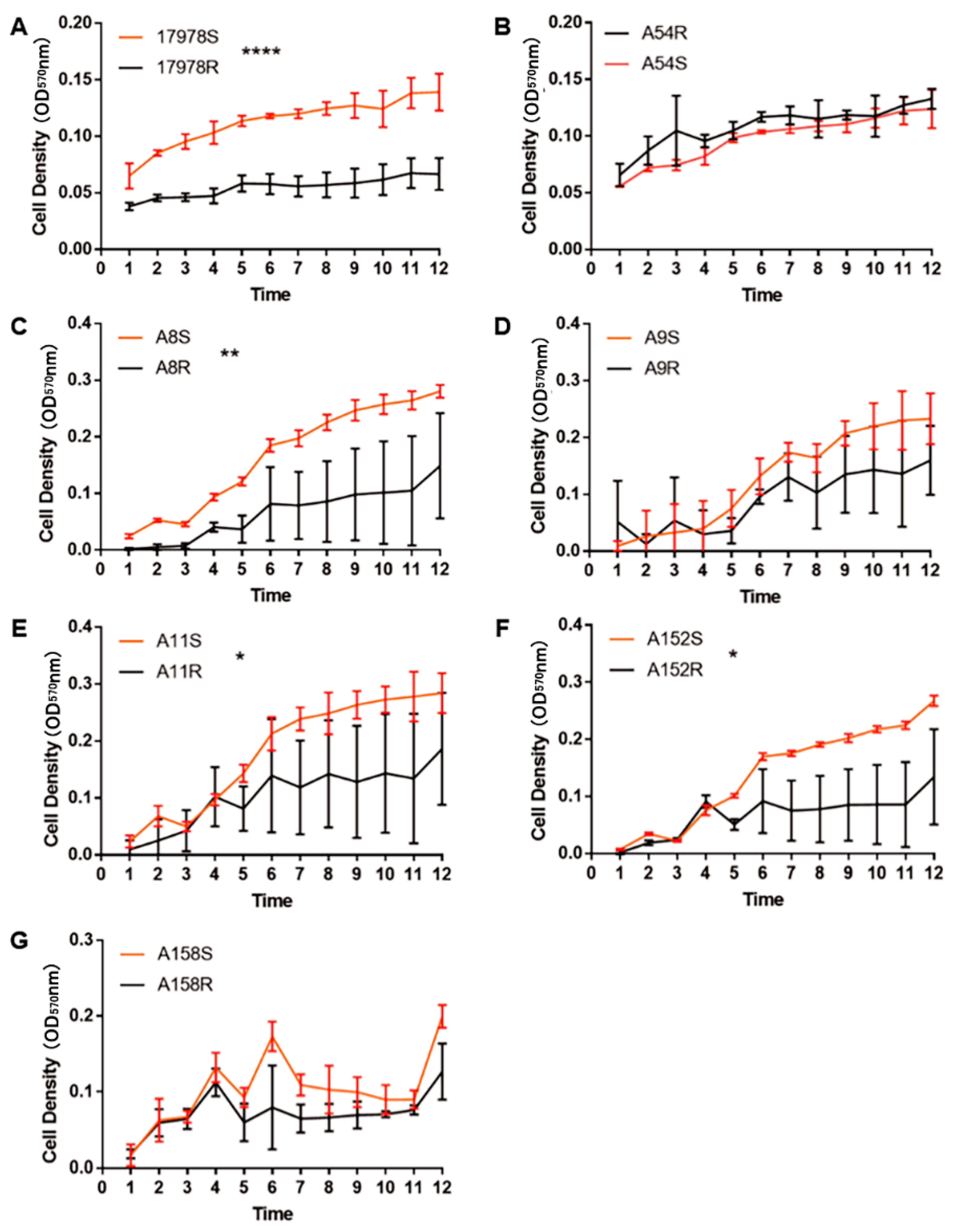
2.3. Acquisition of Tigecycline Resistance Elicited Fitness Costs in A. baumannii
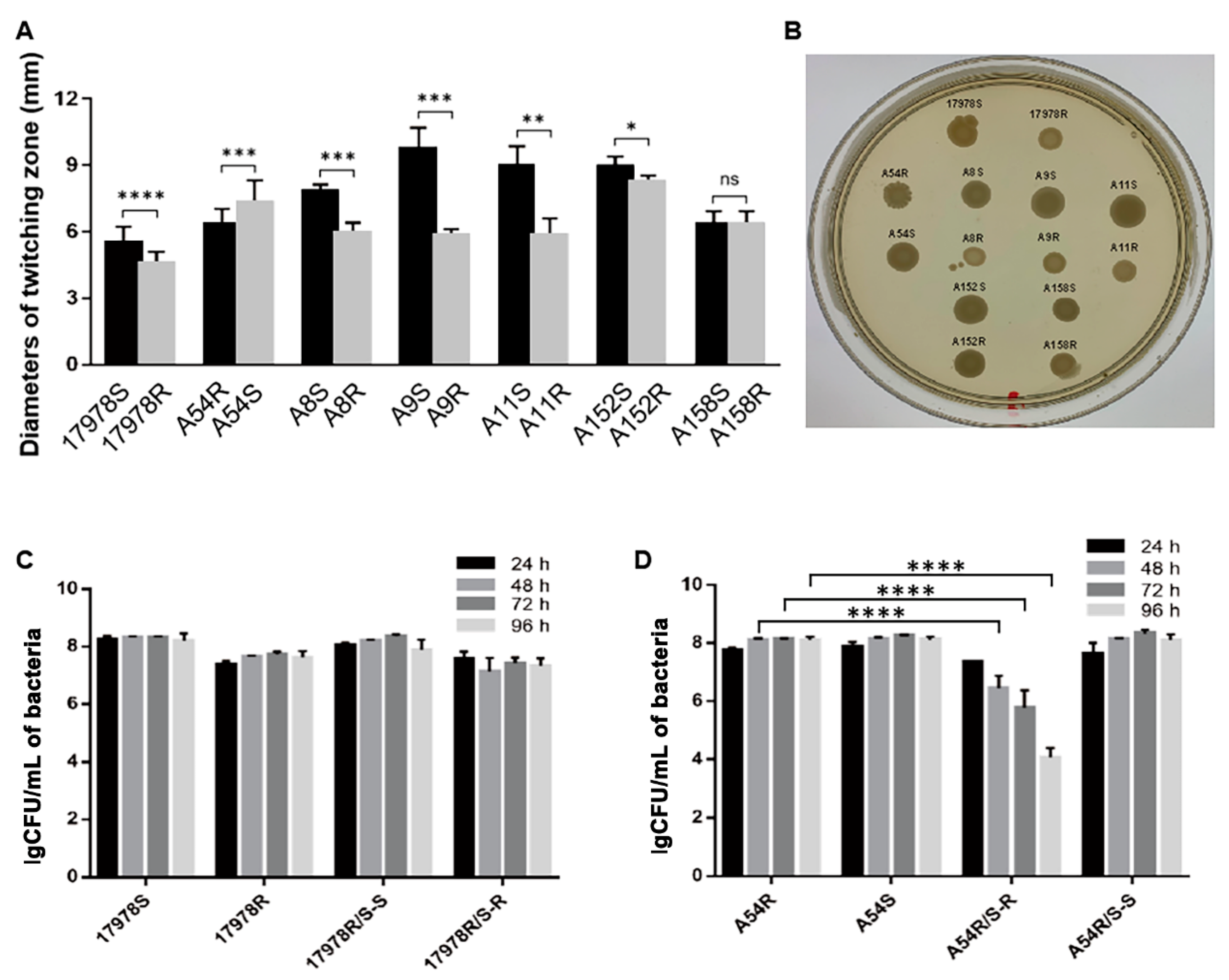
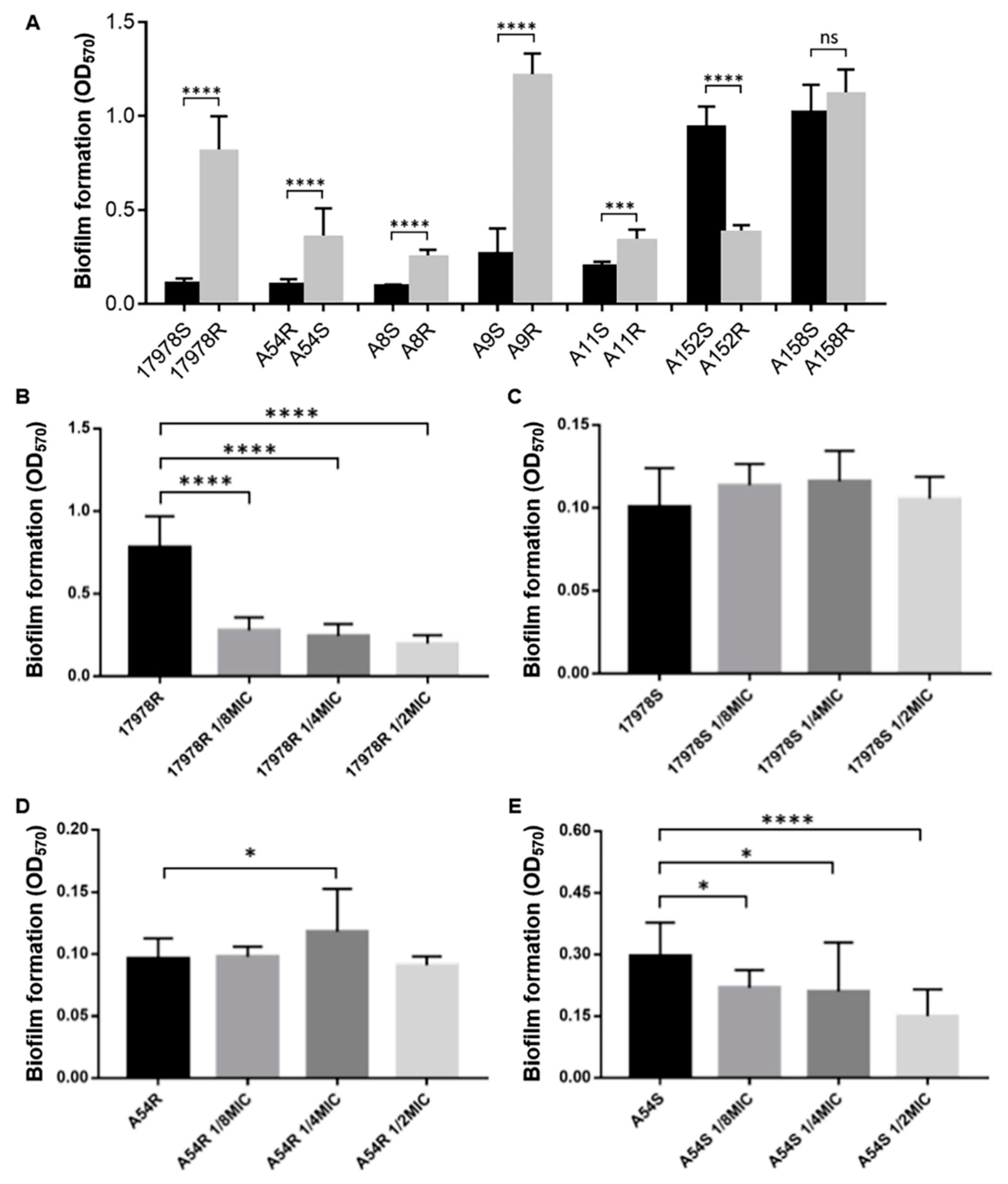
2.4. Biofilm Formation Ability Was Related to Tigecycline Resistance in A. baumannii
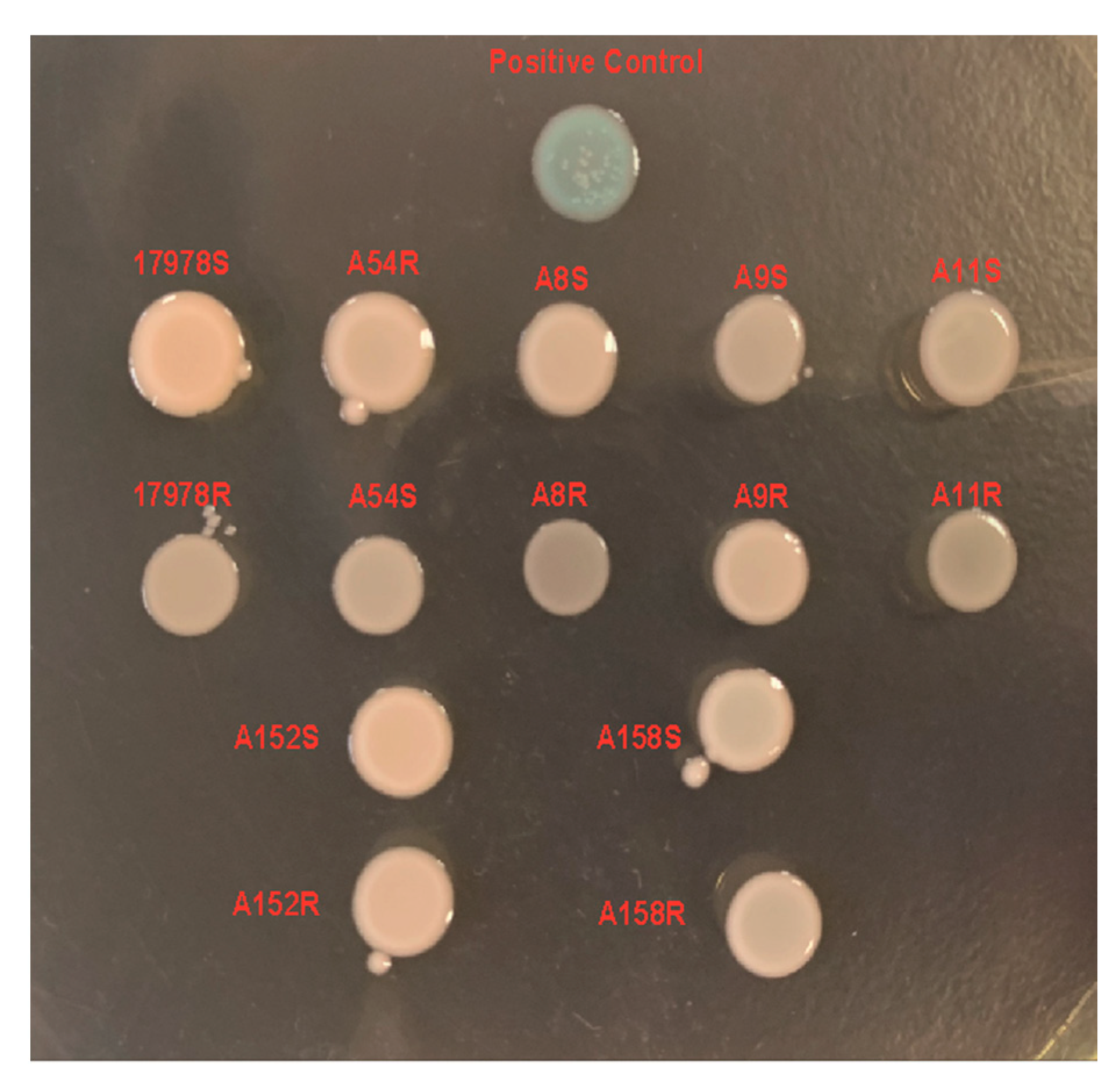
2.5. Tigecycline Resistance in A. baumannii Was Not Related to 16S rRNA Target Variation or Outer Membrane Integrity Alteration
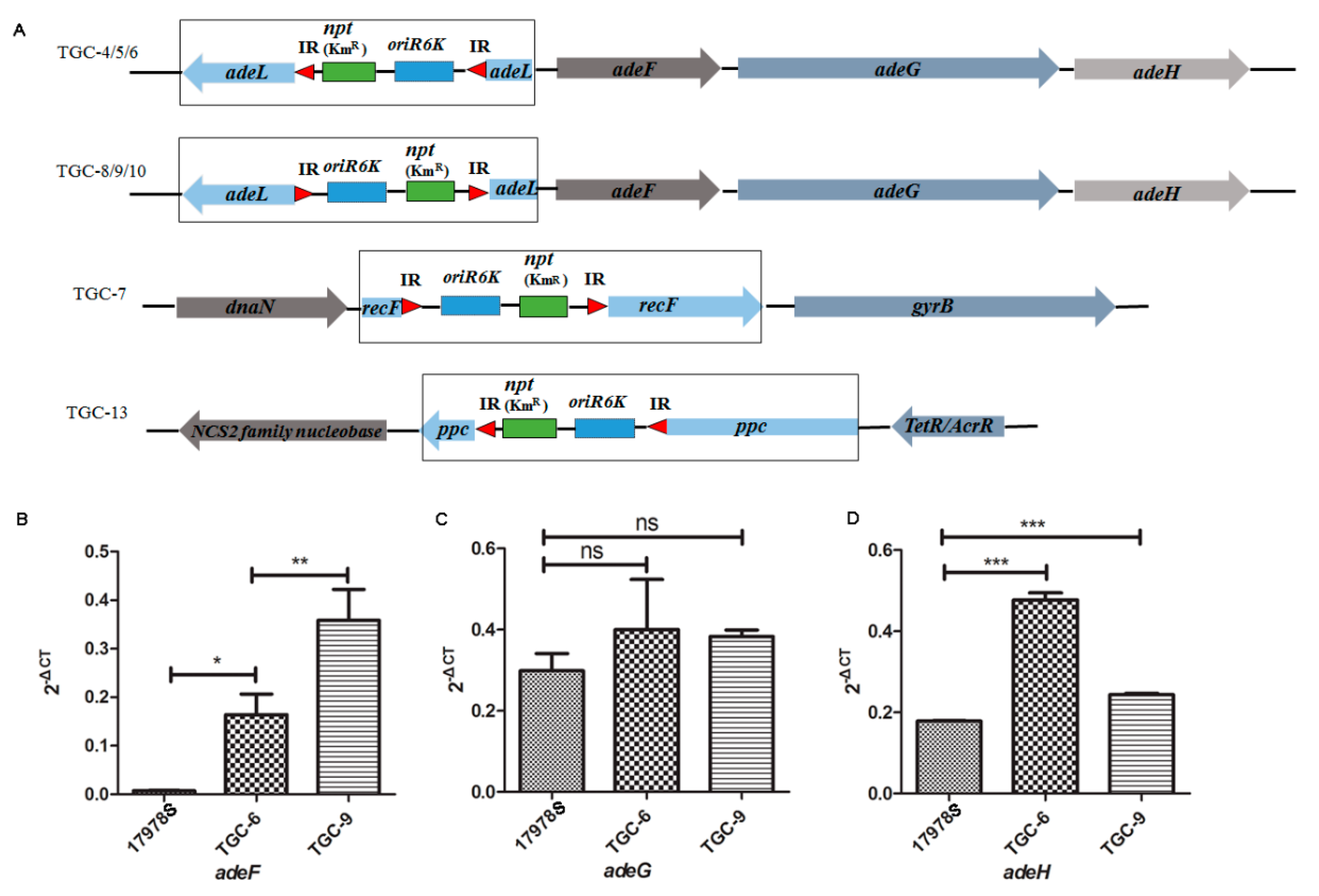
2.6. The Deprivation of adeL Triggered Tigecycline Resistance in A. baumannii
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Antibiotic Susceptibility Monitoring
4.2. Induction of Tigecycline-Susceptible and Tigecycline-Intermediate Strains into Tigecycline-Resistant Strains
4.3. Induction of Tigecycline-Resistant Strain into Tigecycline-Susceptible Strain
4.4. Examination of Stability for Tigecycline Resistance
4.5. Detection of the Fitness Cost of Tigecycline Resistance
4.6. Determination of Biofilm Formation
4.7. Investigation of Variability in 16S rRNA
4.8. Detection of Outer Membrane Integrity
4.9. Transposon-Insertion Sequencing
4.10. Construction of the adeL Complementation Strain
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Ortiz-Leyba, C.; Fernández-Hinojosa, E.; Aldabó-Pallás, T.; Cayuela, A.; Marquez-Vácaro, J.A.; Garcia-Curiel, A.; Jiménez-Jiménez, F.J. Acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-associated pneumonia: Epidemiological and clinical findings. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Weinstein, R.A. Acinetobacter Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.M.; Hennon, S.W.; Feldman, M.F. Uncovering the mechanisms of Acinetobacter baumannii virulence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.; Park, K.S.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Biology of Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms, and Prospective Treatment Options. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.R.; Fakhoury, J.N.; Monteith, A.J.; Pi, H.; Giedroc, D.P.; Skaar, E.P. Bacterial hydrophilins promote pathogen desiccation tolerance. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 975–987.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapartegui-González, I.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Bravo, Z.; Navas, J.; Icardo, J.M.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Acinetobacter baumannii maintains its virulence after long-time starvation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.; Barnett, P.; Perlmutter, J.; Dunman, P.M. Identification of Acinetobacter baumannii serum-associated antibiotic efflux pump inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6360–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulens, S.; Yi, S.; Walters, M.; Jacob, J.; Bower, C.; Reno, J.; Wilson, L.; Vaeth, E.; Bamberg, W.; Janelle, S.; et al. Carbapenem-Nonsusceptible Acinetobacter baumannii, 8 US Metropolitan Areas, 2012–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 24, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisplinghoff, H.; Paulus, T.; Lugenheim, M.; Stefanik, D.; Higgins, P.G.; Edmond, M.B.; Wenzel, R.P.; Seifert, H. Nosocomial bloodstream infections due to Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter pittii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis in the United States. J. Infect. 2012, 64, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchai, J.; Pothirat, C.; Bumroongkit, C.; Limsukon, A.; Khositsakulchai, W.; Liwsrisakun, C. Prognostic factors associated with mortality of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-associated pneumonia. J. Intensive Care 2015, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Koletsi, P.K.; Bliziotis, I.A. The diversity of definitions of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and pandrug-resistant (PDR) Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lob, S.H.; Hoban, D.J.; Sahm, D.F.; Badal, R.E. Regional differences and trends in antimicrobial susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giammanco, A.; Calà, C.; Fasciana, T.; Dowzicky Michael, J.; Bradford Patricia, A. Global Assessment of the Activity of Tigecycline against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens between 2004 and 2014 as Part of the Tigecycline Evaluation and Surveillance Trial. mSphere 2017, 2, e00310-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.; Al Atrouni, A.; Rafei, R.; Dabboussi, F.; Hamze, M.; Osman, M. Molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii, with a special focus on its epidemiology in Lebanon. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, G.J. Domingues, S. Insights on the Horizontal Gene Transfer of Carbapenemase Determinants in the Opportunistic Pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnejad, R.; Heidary, M.; Bahramian, A.; Goudarzi, M.; Pournajaf, A. Evaluation of Polymyxin B Susceptibility Profile and Detection of Drug Resistance Genes among Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates in Tehran, Iran during 2015–2016. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 10, e2018044. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, B.A.; Hamouda, A.; Amyes, S.G. The rise of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakonstantis, S. A systematic review of implications, mechanisms, and stability of in vivo emergent resistance to colistin and tigecycline in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Chemother. 2021, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Dai, H. Risk factors for nephrotoxicity associated with polymyxin B therapy in Chinese patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2021, 43, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-López, R.; Solano-Gálvez, S.G.; Juárez Vignon-Whaley, J.J.; Abello Vaamonde, J.A.; Padró Alonzo, L.A.; Rivera Reséndiz, A.; Muleiro Álvarez, M.; Vega López, E.N.; Franyuti-Kelly, G.; Álvarez-Hernández, D.A.; et al. Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance: A Real Challenge for Clinicians. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, N.; Liang, B.; Wang, R. The emergence of clinical resistance to tigecycline. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Duan, X.; Jiang, Z. In Vitro Activity of Various Antibiotics in Combination with Tigecycline Against Acinetobacter baumannii: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, I.F.; Hughes, D.W.; Wright, G.D. Tigecycline Is Modified by the Flavin-Dependent Monooxygenase TetX. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11829–11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, C.; Cui, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.-H.; Ma, X.-Y.; Feng, Y.; Fang, L.-X.; Lian, X.-L.; et al. Plasmid-encoded tet(X) genes that confer high-level tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, W.E.; Wilhelm, J.; Tam, H.-K.; Pos, K.M. Tigecycline efflux in Acinetobacter baumannii is mediated by TetA in synergy with RND-type efflux transporters. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hua, X.; Yu, Y. Decreased susceptibility to tigecycline in Acinetobacter baumannii mediated by a mutation in trm encoding SAM-dependent methyltransferase. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebosc, V.; Gartenmann, S.; Royet, K.; Manfredi, P.; Tötzl, M.; Schellhorn, B.; Pieren, M.; Tigges, M.; Lociuro, S.; Sennhenn Peter, C.; et al. A Novel Genome-Editing Platform for Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Reveals an AdeR-Unrelated Tigecycline Resistance Mechanism. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7263–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Antibiotic resistance and its cost: Is it possible to reverse resistance? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride Mark, J. Shining a Light on an Opportunistic Pathogen. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 6325–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Barrenechea, V.; Vargas-Reyes, M.; Quiliano, M.; Milón, P. A Complementary Mechanism of Bacterial mRNA Translation Inhibition by Tetracyclines. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 682682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Feudi, C.; Fortini, D.; García-Fernández, A.; Carattoli, A. Genomics of KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 512 Clone Highlights the Role of RamR and Ribosomal S10 Protein Mutations in Conferring Tigecycline Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi, S.; Zekiy, A.O.; Krutova, M.; Gholami, M.; Kouhsari, E.; Sholeh, M.; Ghafouri, Z.; Maleki, F. Tigecycline antibacterial activity, clinical effectiveness, and mechanisms and epidemiology of resistance: Narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Quan, J.; Yang, Y.; Ji, J.; Liu, L.; Fu, Y.; Hua, X.; Chen, Y.; Pi, B.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Abrp, a new gene, confers reduced susceptibility to tetracycline, glycylcine, chloramphenicol and fosfomycin classes in Acinetobacter baumannii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalewitz, A.P.; Miller, S.I. Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Chloramphenicol Resistance Requires an Inner Membrane Permease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00513-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, J.J.; Davis, J.J.; Panichella, M.; Zwolak, A. Isolation of predation-deficient mutants of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus by using transposon mutagenesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5436–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Ghalavand, Z.; Yadegar, A.; Eslami, G. Characteristics and diversity of mutations in regulatory genes of resistance-nodulation-cell division efflux pumps in association with drug-resistant clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Overexpression of ppc or deletion of mdh for improving production of γ-aminobutyric acid in recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga-Castillo, J.; Romero, D.; Martínez-Salazar, J.M. The recombination genes addAB are not restricted to gram-positive bacteria: Genetic analysis of the recombination initiation enzymes RecF and AddAB in Rhizobium etli. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7905–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boral, B.; Unaldi, Ö.; Ergin, A.; Durmaz, R.; Eser, Ö.K.; Zarakolu, P.; Ersöz, G.; Kaya, A.; Haciseyitoglu, D.; Ak, Ö.; et al. A prospective multicenter study on the evaluation of antimicrobial resistance and molecular epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections in intensive care units with clinical and environmental features. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, L.R.R.; Carniel, E.; Dalpiaz, G.; Vetter, M.; Narvaez, G.A.; Dias, C.G. A four-year follow-up survey of antimicrobial resistance among Acinetobacter baumannii complex from inpatients in Southern Brazil. Am. J. Infect. Control 2021, 49, 1503–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Dong, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, S. Epidemiological Analysis of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in a Tertiary Hospital Over a 12-Year Period in China. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Venanzio, G.; Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Calix, J.J.; Haurat, M.F.; Scott, N.E.; Palmer, L.D.; Potter, R.F.; Hibbing, M.E.; Friedman, L.; Wang, B.; et al. Urinary tract colonization is enhanced by a plasmid that regulates uropathogenic Acinetobacter baumannii chromosomal genes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminov, R.I. The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2970–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, S.W.; Barnett, M.L.; MacFadden, D.R.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Grad, Y.H. The distribution of antibiotic use and its association with antibiotic resistance. eLife 2018, 7, e39435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buul, L.W.; van der Steen, J.T.; Veenhuizen, R.B.; Achterberg, W.P.; Schellevis, F.G.; Essink, R.T.G.M.; van Benthem, B.H.B.; Natsch, S.; Hertogh, C.M.P.M. Antibiotic Use and Resistance in Long Term Care Facilities. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 568.e1–568.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, M.; Enke, T.; Chubukov, V.; Ricci, V.; Piddock, L.; Sauer, U. Metabolic constraints on the evolution of antibiotic resistance. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 917. [Google Scholar]
- Mattick, J.S. Type IV Pili and Twitching Motility. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamiri, M.M.; Zhang, S.; Mi, P.; Liu, Y.; Xun, M.; Yang, E.; Ai, L.; Han, L.; Chen, Y. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Acinetobacter baumannii enrolled in the relationship among antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation and motility. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkevicius, M.; Sandegren, L.; Andersson, D.I. Mechanisms and fitness costs of tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2809–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Van Tyne, D. Genomic and Phenotypic Evolution of Tigecycline-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Critically Ill Patients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01593-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, K.J.; Jordan, J.A.; Lenski, R.E. Idiosyncratic variation in the fitness costs of tetracycline-resistance mutations in Escherichia coli. Evolution 2021, 75, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, G. Comparative efficacy and safety of combination therapy with high-dose sulbactam or colistin with additional antibacterial agents for multiple drug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 24, 136–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, G.C.; Hanes, S.D.; Croce, M.A.; Fabian, T.C.; Boucher, B.A. Comparison of ampicillin-sulbactam and imipenem-cilastatin for the treatment of acinetobacter ventilator-associated pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolyakov, R.; Borer, A.; Riesenberg, K.; Schlaeffer, F.; Alkan, M.; Porath, A.; Rimar, D.; Almog, Y.; Gilad, J. Nosocomial multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infection: Risk factors and outcome with ampicillin-sulbactam treatment. J. Hosp. Infect. 2003, 54, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temocin, F.; Erdinc, F.S.; Tulek, N.; Demirelli, M.; Ertem, G.; Kinikli, S.; Koksal, E. Synergistic effects of sulbactam in multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Karamouzos, V.; Lefkaditi, A.; Sklavou, C.; Kolonitsiou, F.; Christofidou, M.; Fligou, F.; Gogos, C.; Marangos, M. Triple combination therapy with high-dose ampicillin/sulbactam, high-dose tigecycline and colistin in the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by pan-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A case series study. Infez. Med. 2019, 27, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Scheetz, M.H.; Qi, C.; Warren, J.R.; Postelnick, M.J.; Zembower, T.; Obias, A.; Noskin, G.A. In vitro activities of various antimicrobials alone and in combination with tigecycline against carbapenem-intermediate or -resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, S.K.; Chowdhury, I.; Singh, R. Understanding the Mechanism of Bacterial Biofilms Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navidifar, T.; Amin, M.; Rashno, M. Effects of sub-inhibitory concentrations of meropenem and tigecycline on the expression of genes regulating pili, efflux pumps and virulence factors involved in biofilm formation by Acinetobacter baumannii. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Cheong, H.J.; Noh, J.Y.; Kim, W.J. In vitro Comparison of Anti-Biofilm Effects against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Imipenem, Colistin, Tigecycline, Rifampicin and Combinations. Infect. Chemother. 2015, 47, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lan, C.Y. Characterization of biofilm production in different strains of Acinetobacter baumannii and the effects of chemical compounds on biofilm formation. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, L.; Connell, S.R.; Taylor, D.E. 16S rRNA mutations that confer tetracycline resistance in Helicobacter pylori decrease drug binding in Escherichia coli ribosomes. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3708–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks, S.E.; Oyston, P.C.F. Structure and function of the LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) family proteins. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3609–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, S.; Rosenfeld, N.; Lambert, T.; Courvalin, P.; Périchon, B. Overexpression of Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Pump AdeFGH Confers Multidrug Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, S.; Nowak, J.; Zander, E.; Ertel, J.; Wen, Y.; Krut, O.; Seifert, H.; Higgins, P.G. Diversity of mutations in regulatory genes of resistance-nodulation-cell division efflux pumps in association with tigecycline resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Liu, Y.; He, P.; Ke, R.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Jing, R.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Geng, Y.; et al. iTRAQ-Based Differential Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Pathways Associated with Tigecycline Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Lv, R.; Xiao, L.; Wang, M.; Du, Z.; Tan, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, R.; et al. A1S_2811, a CheA/Y-like hybrid two-component regulator from Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC17978, is involved in surface motility and biofilm formation in this bacterium. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibiotics | 17978 | A8 | A9 | A11 | A152 | A158 | A54 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | R | S | |
| PIP | R | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| CAZ | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | R |
| CRO | I | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| CTX | I | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | I | R | R |
| FEP | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | R |
| IPN | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | R | R |
| AMS | S | S | R | I | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | R |
| PIT | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R |
| GM | I | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | I | R | R | R |
| TM | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| MNO | S | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | I |
| LVF | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | S | R | R |
| CIP | I | I | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | I | R | R |
| SXT | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | S | S | S | R | R |
| PMB | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Strains | AMP (μg/mL) | Sulbactam (μg/mL) | AMS (2:1) (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17978S | 32 | 2 | 2/1 |
| 17978R | 32 | 2 | 2/1 |
| A8S | >1024 | 1024 | 256/128 |
| A8R | >1024 | 512 | 16/8 |
| A9S | >1024 | 64 | 128/64 |
| A9R | >1024 | 32 | 64/32 |
| A11S | >1024 | 128 | 128/64 |
| A11R | >1024 | 8 | 16/8 |
| A152S | >1024 | 16 | 32/16 |
| A152R | >1024 | 4 | 8/4 |
| A158S | 32 | 8 | 2/1 |
| A158R | 32 | 4 | 2/1 |
| A54R | >1024 | 32 | 16/8 |
| A54S | >1024 | 32 | 32/16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Feng, C.; Lu, Q.; Zou, Q. Fitness Costs of Tigecycline Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and the Resistance Mechanism Revealed by a Transposon Mutation Library. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101379
Wang P, Wang H, Liu C, Feng C, Lu Q, Zou Q. Fitness Costs of Tigecycline Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and the Resistance Mechanism Revealed by a Transposon Mutation Library. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101379
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ping, Hongou Wang, Cunwei Liu, Chengjie Feng, Qinghui Lu, and Qinghua Zou. 2022. "Fitness Costs of Tigecycline Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and the Resistance Mechanism Revealed by a Transposon Mutation Library" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101379
APA StyleWang, P., Wang, H., Liu, C., Feng, C., Lu, Q., & Zou, Q. (2022). Fitness Costs of Tigecycline Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and the Resistance Mechanism Revealed by a Transposon Mutation Library. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101379






