Comprehensive Genome and Plasmidome Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent of Tokyo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
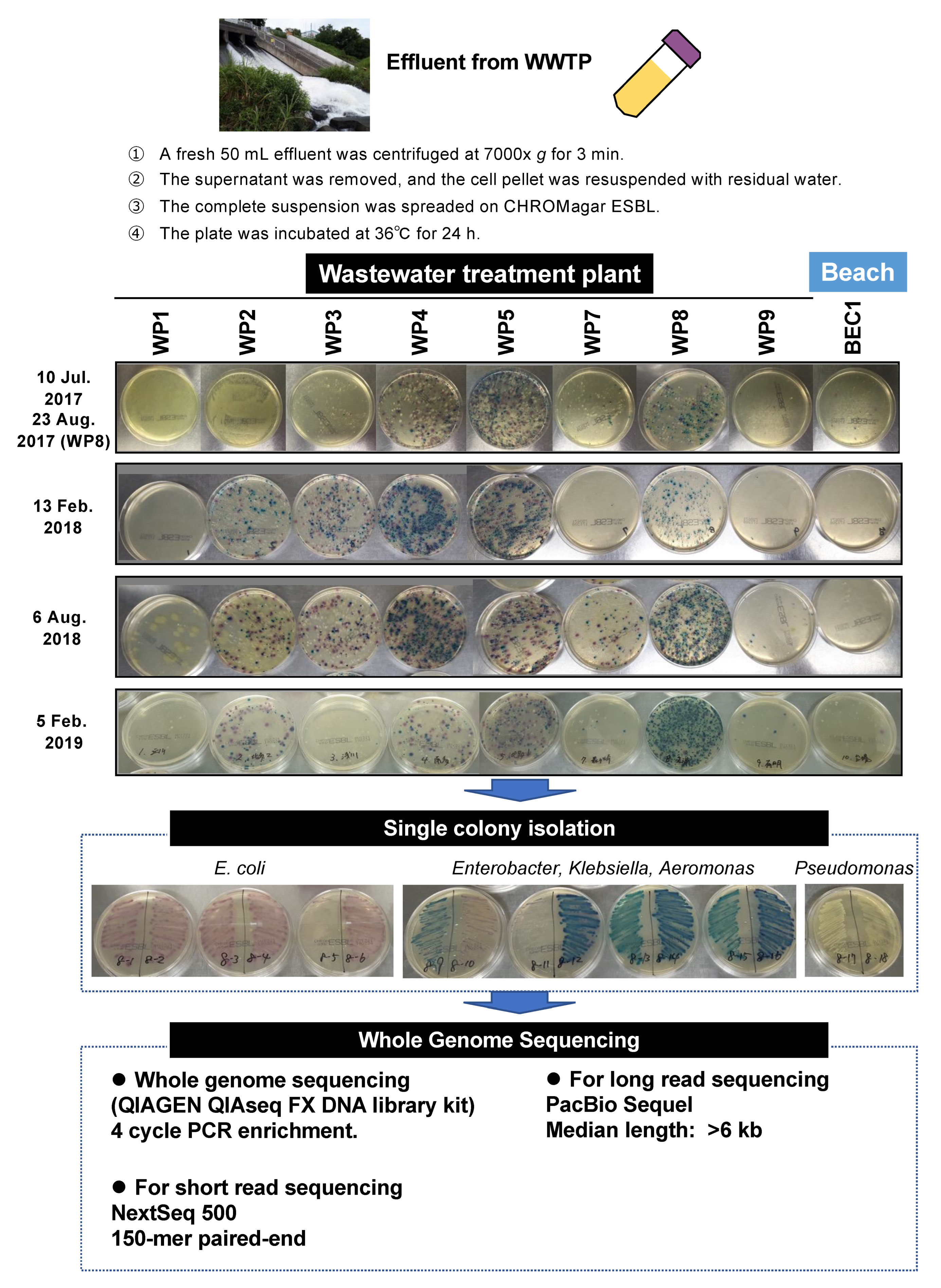
2.1. Bacterial Proportion in WWTP Effluents Genome Analysis of ESBL/Carbapenemase-Producing Bacteria (EPB and CPB) Isolated from WWTP Effluents and Environment
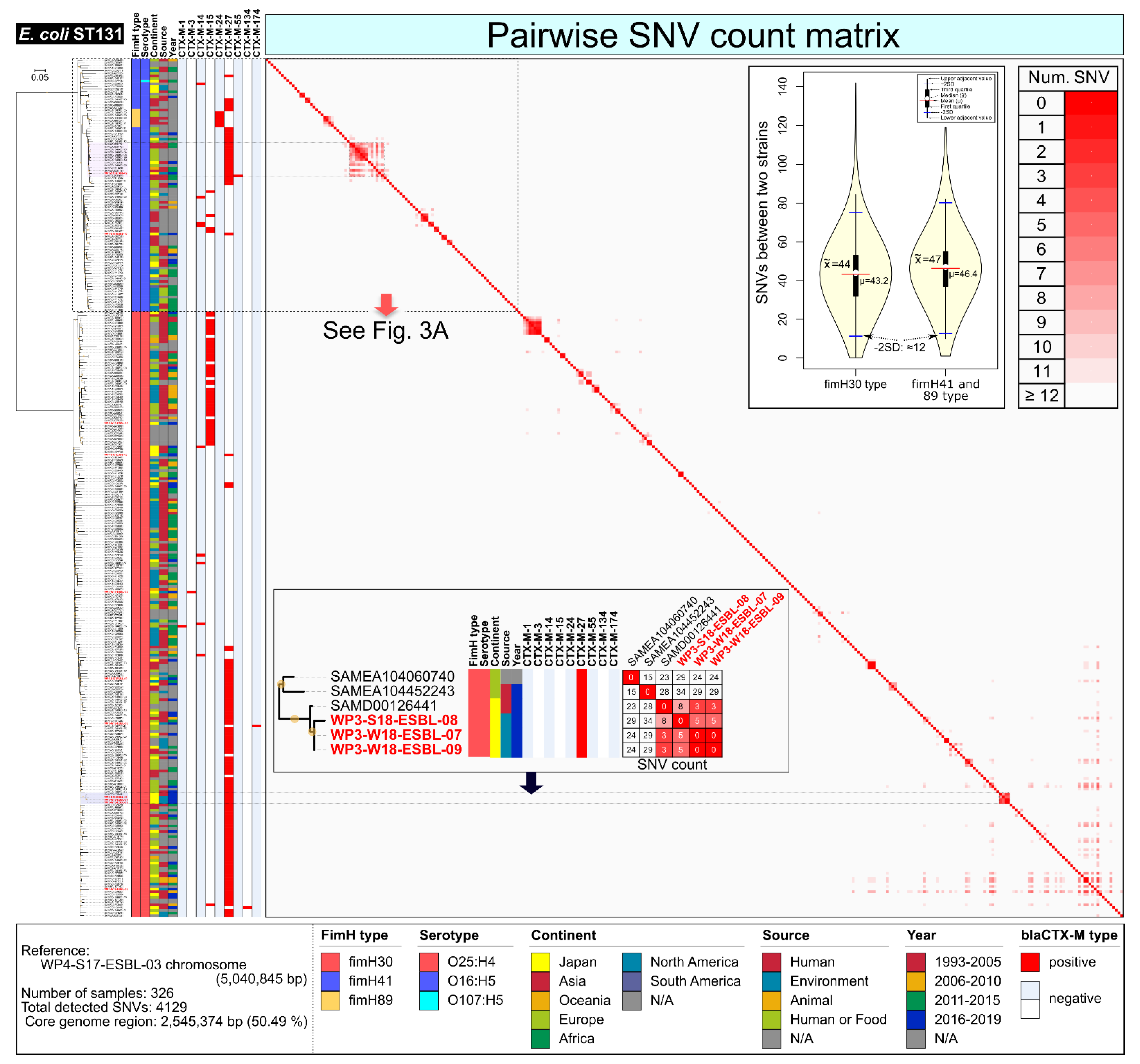
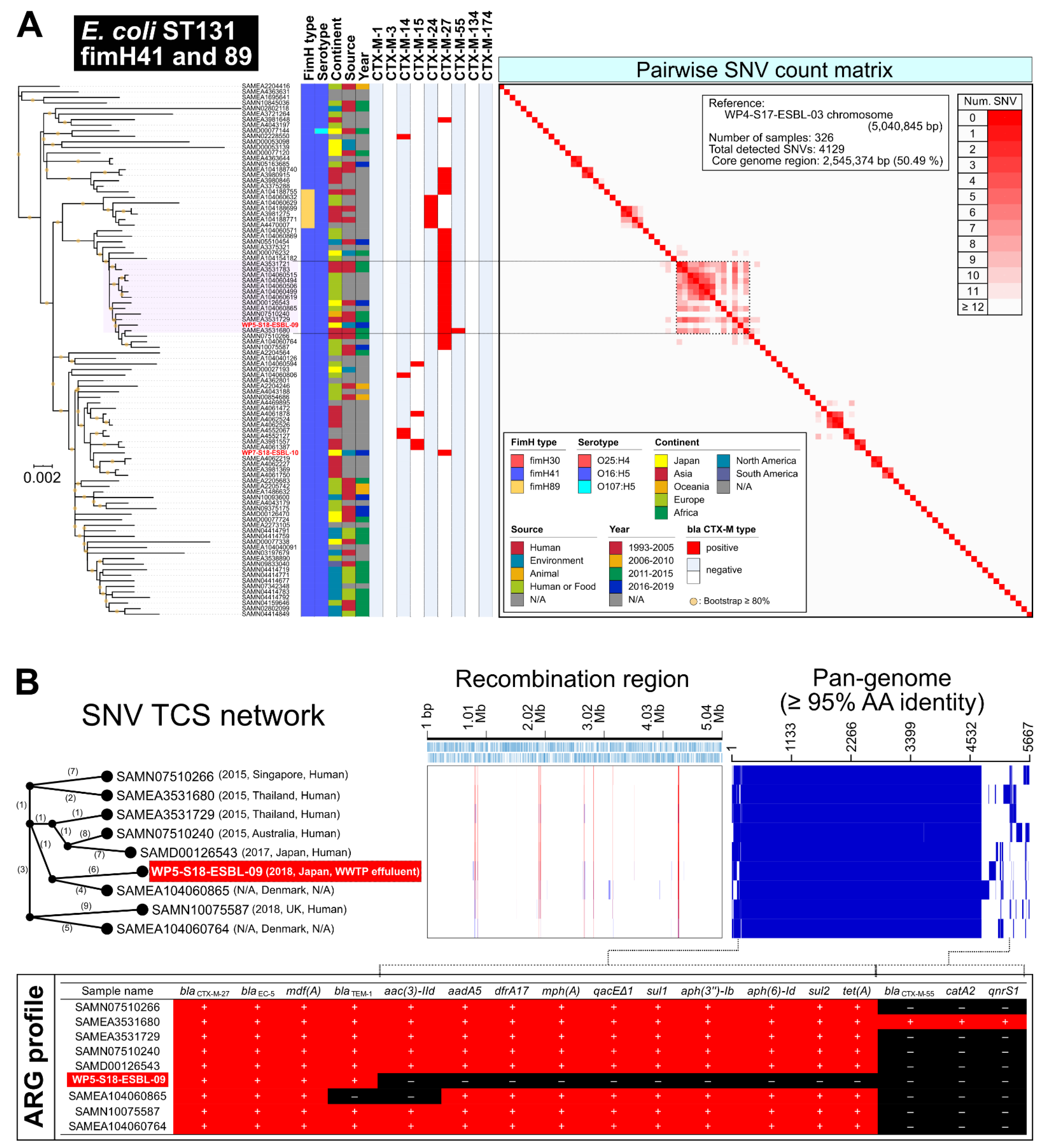
2.2. E. coli ST131
2.3. Other E. coli ST Isolates
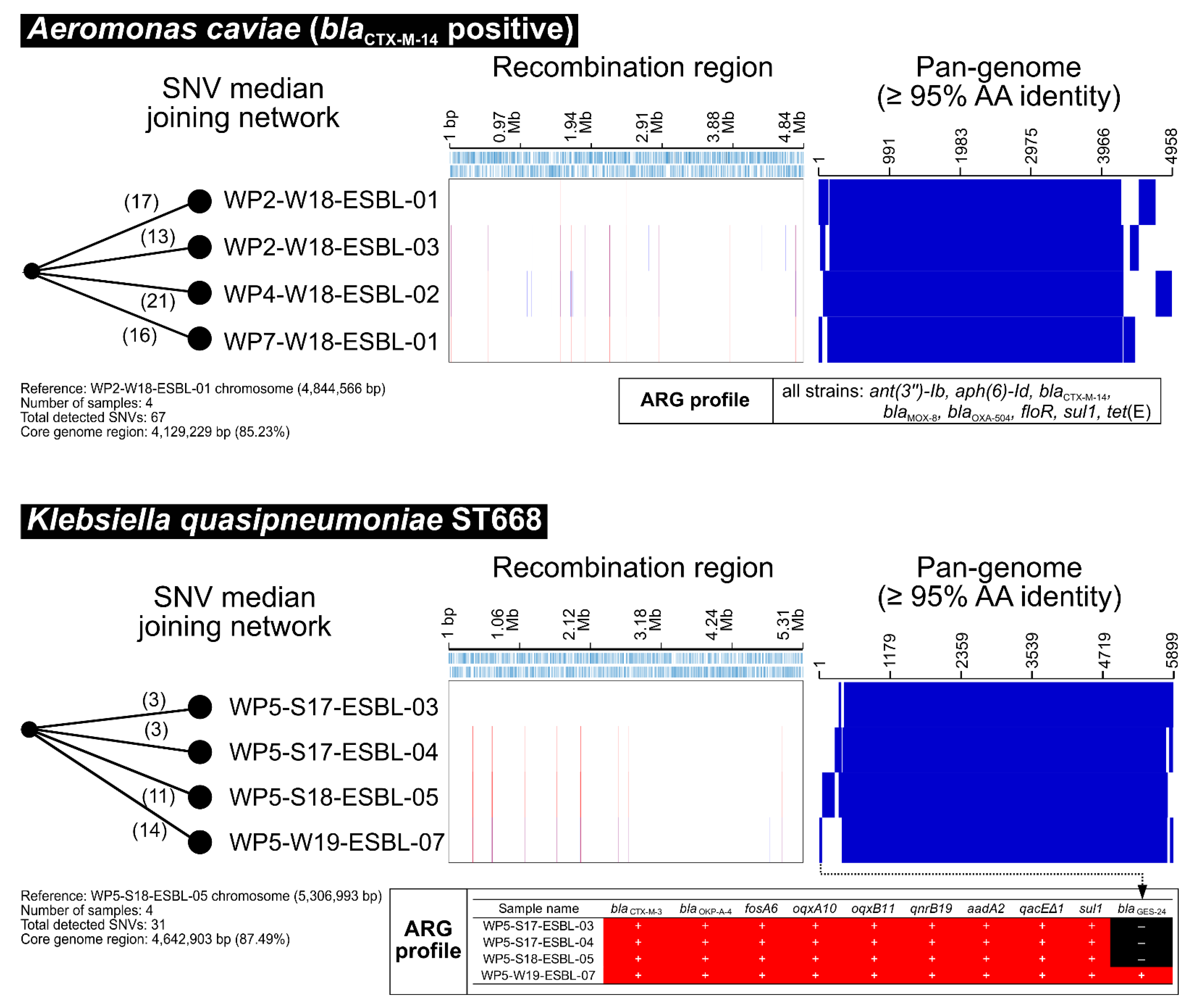
2.4. Other CTX-M Positive Bacteria
2.5. Plasmidome Analysis of EPB and CPB Isolated from WWTP Effluents and Environment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Bacterial Isolates
4.3. SNV Phylogenetic Analysis and Pan-Genome Analysis
4.4. Plasmidome Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System: Manual for Early Implementation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–4.
- Fijalkowski, K.; Rorat, A.; Grobelak, A.; Kacprzak, M.J. The presence of contaminations in sewage sludge—The current situation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, G.C.; Hawkey, P.M.; Gaze, W.H.; Wellington, E.M. Waste water effluent contributes to the dissemination of CTX-M-15 in the natural environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, E.; Jofre, J.; Balcazar, J.L. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in a river influenced by a wastewater treatment plant. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Brinda, K.; Hanage, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T. High-resolution genomic surveillance elucidates a multilayered hierarchical transfer of resistance between WWTP- and human/animal-associated bacteria. Microbiome 2022, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, fux053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osinska, A.; Harnisz, M.; Korzeniewska, E. Prevalence of plasmid-mediated multidrug resistance determinants in fluoroquinolone-resistant bacteria isolated from sewage and surface water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 10818–10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Sabatino, R.; Yang, Y.; Brambilla, D.; Li, P.; Fontaneto, D.; Eckert, E.M.; Corno, G. Contribution of plasmidome, metal resistome and integrases to the persistence of the antibiotic resistome in aquatic environments. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwanzala, M.D.; Dewar, J.B.; Momba, M.N.B. Environmental resistome risks of wastewaters and aquatic environments deciphered by shotgun metagenomic assembly. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, M.; Kuroda, M.; Sekizuka, T.; Nakada, N.; Ito, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kusachi, S. Comprehensive Genomic Survey of Antimicrobial-Resistance Bacteria in the Sewage Tank Replacement with Hospital Relocation. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 5563–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Salvo, S.; Fernandez-Lopez, R.; Ruiz, R.; Vielva, L.; de Toro, M.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Garcillan-Barcia, M.P.; de la Cruz, F. Pathways for horizontal gene transfer in bacteria revealed by a global map of their plasmids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirstahler, P.; Teudt, F.; Otani, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Pamp, S.J. A Peek into the Plasmidome of Global Sewage. mSystems 2021, 6, e0028321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizuka, T.; Itokawa, K.; Tanaka, R.; Hashino, M.; Yatsu, K.; Kuroda, M. Metagenomic analysis of urban wastewater treatment plant effluents in Tokyo. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 4763–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizuka, T.; Yatsu, K.; Inamine, Y.; Segawa, T.; Nishio, M.; Kishi, N.; Kuroda, M. Complete Genome Sequence of a blaKPC-2-Positive Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain Isolated from the Effluent of an Urban Sewage Treatment Plant in Japan. mSphere 2018, 3, e00314-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizuka, T.; Inamine, Y.; Segawa, T.; Hashino, M.; Yatsu, K.; Kuroda, M. Potential KPC-2 carbapenemase reservoir of environmental Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas caviae isolates from the effluent of an urban wastewater treatment plant in Japan. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 11, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizuka, T.; Inamine, Y.; Segawa, T.; Kuroda, M. Characterization of NDM-5- and CTX-M-55-coproducing Escherichia coli GSH8M-2 isolated from the effluent of a wastewater treatment plant in Tokyo Bay. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Pitout, J.D.; Gomi, R.; Matsuda, T.; Noguchi, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Peirano, G.; DeVinney, R.; Bradford, P.A.; Motyl, M.R.; et al. Global Escherichia coli Sequence Type 131 Clade with blaCTX-M-27 Gene. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Katagiri, M.; Sekizuka, T.; Kuroda, M.; Watanabe, M. Inactivation of Bacteria and Residual Antimicrobials in Hospital Wastewater by Ozone Treatment. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Usui, M.; Hayashi, T. Inactivation of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater by Ozone-Based Advanced Water Treatment Processes. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.M.; Liu, W.E.; Liang, X.H.; Li, Y.M.; Jian, Z.J.; Hawkey, P.M. Emergence and spread of O16-ST131 and O25b-ST131 clones among faecal CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli in healthy individuals in Hunan Province, China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgy, A.; Levy, C.; Bidet, P.; Thollot, F.; Derkx, V.; Bechet, S.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Cohen, R.; Bonacorsi, S. ESBL-producing Escherichia coli ST131 versus non-ST131: Evolution and risk factors of carriage among French children in the community between 2010 and 2015. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2949–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.A.; Ingram, P.R.; Runnegar, N.; Pitman, M.C.; Freeman, J.T.; Athan, E.; Havers, S.; Sidjabat, H.E.; Gunning, E.; De Almeida, M.; et al. Sequence type 131 fimH30 and fimH41 subclones amongst Escherichia coli isolates in Australia and New Zealand. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, H.; Yano, H.; Hirakata, Y.; Arai, K.; Endo, S.; Kanamori, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Ichimura, S.; Ogawa, M.; Shimojima, M.; et al. Molecular characteristics of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Japan: Emergence of CTX-M-15-producing E. coli ST131. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, E.R.; Jones, A.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Global epidemiology of CTX-M beta-lactamases: Temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, R.A.; Burd, E.M.; Conly, J.; Limbago, B.M.; Poirel, L.; Segre, J.A.; Westblade, L.F. Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms: A Global Scourge. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Peirano, G.; Motyl, M.R.; Adams, M.D.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.; DeVinney, R.; Pitout, J.D. Global Molecular Epidemiology of IMP-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02729-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayama, S.; Shigemoto, N.; Kuwahara, R.; Oshima, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Hisatsune, J.; Jove, T.; Nishio, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Wada, Y.; et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of the IncN plasmid encoding IMP-6 and CTX-M-2 from emerging carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, R.; Akeda, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Takeuchi, D.; Matsumoto, Y.; Motooka, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Kawahara, R.; Tomono, K.; Fujino, Y.; et al. Characterization of the Plasmidome Encoding Carbapenemase and Mechanisms for Dissemination of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. mSystems 2020, 5, e00759-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA, Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Antimicrobial-consumption-EU-EEA.pdf2018 (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- Higa, S.; Sarassari, R.; Hamamoto, K.; Yakabi, Y.; Higa, K.; Koja, Y.; Hirai, I. Characterization of CTX-M type ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae isolated from asymptomatic healthy individuals who live in a community of the Okinawa prefecture, Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, K.; Kawamura, K.; Goto, K.; Arakawa, Y. Long-Term Colonization by bla(CTX-M)-Harboring Escherichia coli in Healthy Japanese People Engaged in Food Handling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manaia, C.M. Assessing the Risk of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission from the Environment to Humans: Non-Direct Proportionality between Abundance and Risk. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Moreira, I.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Bacterial diversity and antibiotic resistance in water habitats: Searching the links with the human microbiome. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 761–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Minimap and miniasm: Fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaser, R.; Sovic, I.; Nagarajan, N.; Sikic, M. Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.; Silva, N.D.; Otto, T.D.; Parkhill, J.; Keane, J.A.; Harris, S.R. Circlator: Automated circularization of genome assemblies using long sequencing reads. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizawa, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y. DFAST: A flexible prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline for faster genome publication. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2012 update: Toward the genetic diversity and molecular evolution of bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D641–D645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souvorov, A.; Agarwala, R.; Lipman, D.J. SKESA: Strategic k-mer extension for scrupulous assemblies. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, N.T.; Irber, L.; Reiter, T.; Brooks, P.; Brown, C.T. Large-scale sequence comparisons with sourmash. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Phillippy, A.; Delcher, A.L.; Smoot, M.; Shumway, M.; Antonescu, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Cunha, J.L.; Bartholomeu, D.C.; Manson, A.L.; Earl, A.M.; Cerqueira, G.C. ProphET, prophage estimation tool: A stand-alone prophage sequence prediction tool with self-updating reference database. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Chen, K.; Wylie, T.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Mardis, E.R.; Weinstock, G.M.; Wilson, R.K.; Ding, L. VarScan: Variant detection in massively parallel sequencing of individual and pooled samples. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croucher, N.J.; Page, A.J.; Connor, T.R.; Delaney, A.J.; Keane, J.A.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; Harris, S.R. Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2--approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Croucher, N.J.; Goater, R.J.; Abudahab, K.; Aanensen, D.M.; Harris, S.R. Phandango: An interactive viewer for bacterial population genomics. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 292–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, M.; Yaser, N.H.; Naz, S.; Fatima, M.; Ahmad, I. Emergence of ciprofloxacin-resistant extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing enteric bacteria in hospital wastewater and clinical sources. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 5, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Summer, 2017 | Winter, 2018 | Summer, 2018 | Winter, 2019 | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total isolates | 98 | 93 | 109 | 104 | 404 | |
| EPB/CPB | ||||||
| E. coli | 18 | 19 | 18 | 16 | 71 | |
| Klebsiella spp. | 8 | 12 | 18 | 10 | 48 | |
| Enterobacter spp. | 5 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 23 | |
| Acinetobacter spp. | 10 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 26 | |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 24 | 12 | 20 | 25 | 81 | |
| Aeromonas spp. | 17 | 25 | 25 | 21 | 88 | |
| Others | 16 | 12 | 12 | 27 | 67 | |
| β-lactamase type | ||||||
| CTX-M | 29 | 35 | 32 | 30 | 126 | |
| IMP | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | |
| KPC-2 | 0 | 0 | 5 a | 3 | 8 | |
| NDM | 0 | 0 | 1 b | 1 | 2 | |
| GES | 1 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 16 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sekizuka, T.; Tanaka, R.; Hashino, M.; Yatsu, K.; Kuroda, M. Comprehensive Genome and Plasmidome Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent of Tokyo. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101283
Sekizuka T, Tanaka R, Hashino M, Yatsu K, Kuroda M. Comprehensive Genome and Plasmidome Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent of Tokyo. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101283
Chicago/Turabian StyleSekizuka, Tsuyoshi, Rina Tanaka, Masanori Hashino, Koji Yatsu, and Makoto Kuroda. 2022. "Comprehensive Genome and Plasmidome Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent of Tokyo" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101283
APA StyleSekizuka, T., Tanaka, R., Hashino, M., Yatsu, K., & Kuroda, M. (2022). Comprehensive Genome and Plasmidome Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent of Tokyo. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101283






