Abstract
This study was designed to evaluate the stability of chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin against antibiotic-sensitive Salmonella Typhimurium (ASST) and antibiotic-resistant S. Typhimurium (ARST) during the broth microdilution assay. The antimicrobial activity in association with antibiotic stability was measured by using antibiotic susceptibility, time-delayed inoculation, time-extended incubation, and inoculum effect assays. The loss of the antimicrobial activity of cephalothin against ASST exposed to 1 MIC was observed for the 10 h delayed inoculation. The antimicrobial activities of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin against ASST and ARST exposed to ½ MIC were significantly decreased after the 10 h delayed inoculation. All antibiotics used in this study, except for ciprofloxacin, showed the considerable losses of antimicrobial activities against ASST and ARST after 40 h of incubation at 37 °C when compared to the 20 h of incubation during AST. Compared to the standard inoculum level (6 log CFU/mL), the MIC0.1 values of bactericidal antibiotics, ciprofloxacin and tobramycin against ASST were increased by more than 4-fold at the high inoculum level of 9 log CFU/mL. This would provide practical information for better understanding the clinical efficacy of the currently used antibiotics by considering the antibiotic stability during incubation time at different inoculum levels.
1. Introduction
Antibiotics are mainly classified based on their target sites, including the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis, membrane function, and metabolic pathway [1,2]. These antibiotics act through different mechanisms of action against bacteria [2]; bacteriostatic antibiotics include clindamycin, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, and trimethoprim, whereas bactericidal antibiotics include gentamicin, kanamycin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin [3,4]. Antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) is widely used to select appropriate and effective treatment options that play an important role in making clinical decision to treat bacterial infections [5,6,7]. Although the antibiotic potential is commonly evaluated by using gold standard methods such as disc diffusion and broth microdilution, the quantitative and qualitative AST results do not provide sufficient information on the mechanisms of antibiotic action [6,8,9]. Furthermore, the modes of action of antibiotics against bacteria vary with growth medium, inoculum level, and incubation period [3,10,11]. Therefore, it is necessary to re-evaluate the in vitro antibiotic stability under different test conditions.
The accurate determination of the antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria remains a key factor for optimizing the antibiotic treatment regimen in association with pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) properties [12]. However, during the AST, the degradation of antibiotics may be attributed to the growth condition, bacterial inoculum, incubation time, temperature, and growth medium [3,5,11]. The evaluation of the clinical efficacy of antibiotics needs to take into consideration the antibiotic degradation [12]. The overestimation or underestimation of antibiotic efficacy leads to the misprescription of antibiotics and the accumulation of residual antibiotics, contributing to antibiotic resistance in bacteria [11,13]. However, little attention has been paid to the antibiotic stability during the AST. Therefore, the objective of this study was to assess the stability of bacteriostatic (chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and tetracycline) and bactericidal (cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, tobramycin) antibiotics against Salmonella Typhimurium under the conditions of time-delayed inoculation, time-extended incubation, and different inoculum levels.
2. Results
2.1. Stability of Antibiotics in the Media
The antibiotic susceptibility testing against ASST and ARST was conducted to evaluate the antibiotic stability in media at the 0 h and 10 h delayed inoculation (Figure 1). Cephalothin and ciprofloxacin showed a significant loss in activity against ASST exposed to ½ MIC at the 0 h inoculation compared to 1 MIC (Figure 1d,e). No significant difference in the antimicrobial activity of tobramycin was observed against ASST between exposures to ½ MIC and 1 MIC (Figure 1f). The cephalothin activity against ASST exposed to 1 MIC was decreased at the 10 h delayed inoculation compared to the 0 h inoculation (Figure 1d). The loss of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin activity against ASST exposed to ½ MIC was observed for the 10 h delayed inoculation compared to the 0 h inoculation (Figure 1c,e).
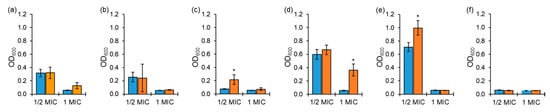
Figure 1.
Growths of antibiotic-sensitive Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 19585 (ASST) exposed to ½ and 1 MICs of chloramphenicol (a), erythromycin (b), tetracycline (c), cephalothin (d), ciprofloxacin (e), tobramycin (f) at 0 h (■) and 10 h (■) delayed inoculation. * indicates the significant difference within MIC at p < 0.05.
The antimicrobial activities of chloramphenicol and erythromycin against ARST exposed to ½ MIC were significantly decreased at the 0 h inoculation after 20 h of incubation at 37 °C compared to 1 MIC (Figure 2a,b), while those of tetracycline, cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin against ARST showed no significant difference between exposures to ½ MIC and 1 MIC at the 0 h inoculation (Figure 2c,f). No significant losses in antimicrobial activities against ARST exposed to 1 MIC of all antibiotics were observed between the 0 h inoculation and the 10 h delayed inoculation, while the antimicrobial activities of tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin against ARST exposed to ½ MIC were significantly lost at the 10 h delayed inoculation compared to the 0 h inoculation (Figure 2c,e,f).
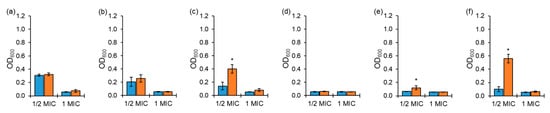
Figure 2.
Growths of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium CCARM 8009 (ARST) exposed to ½ and 1 MICs of chloramphenicol (a), erythromycin (b), tetracycline (c), cephalothin (d), ciprofloxacin (e), tobramycin (f) at 0 h (■) and 10 h (■) delayed inoculation. * indicates the significant difference within MIC at p < 0.05.
2.2. Sustainability of Antimicrobial Activity
The antibiotic susceptibilities against ASST and ARST were evaluated after 20 h and 40 h of incubation as shown in the dose–response curves (Figure 3 and Figure 4). All antibiotics used in this study showed significant losses of antimicrobial activity against both ASST (Figure 3) and ARST (Figure 4) after 40 h of incubation with the exception of ciprofloxacin. The MIC values of tetracycline (>32 µg/mL) and tobramycin (>8 µg/mL) against ASST (Figure 3c,f), and those of cephalothin (>64 µg/mL) and tobramycin (>32 µg/mL) against ARST (Figure 4d,f), were increased after 40 h of incubation at 37 °C.
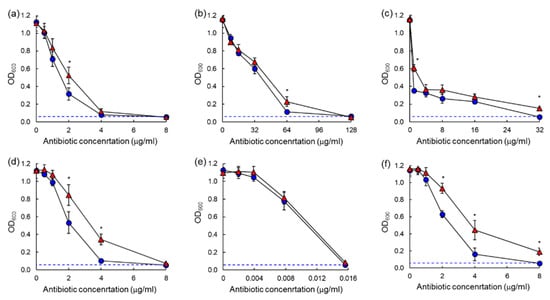
Figure 3.
Dose–response curves of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 19585 (ASST) exposed to different concentrations of chloramphenicol (a), erythromycin (b), tetracycline (c), cephalothin (d), ciprofloxacin (e), tobramycin (f) after 20 h (●) and 40 h (▲) of incubation. * indicates the significant difference within MIC at p < 0.05.
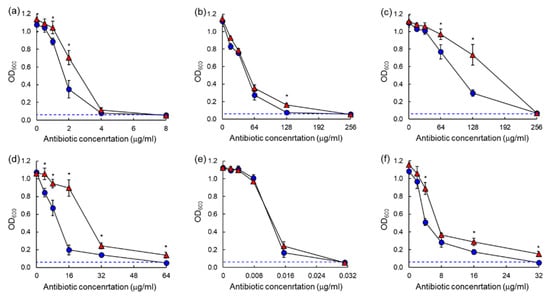
Figure 4.
Dose–response curves of antibiotic-sensitive Salmonella Typhimurium CCARM 8009 (ARST) exposed to different concentrations of chloramphenicol (a), erythromycin (b), tetracycline (c), cephalothin (d), ciprofloxacin (e), tobramycin (f) after 20 h (●) and 40 h (▲) of incubation. * indicates the significant difference within MIC at p < 0.05.
2.3. Inoculum Effect
The fold changes in the MIC0.1 values of chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin were compared to evaluate the inoculum effect (Figure 5). The high inoculum levels (6.5 and 9 log CFU/mL) showed a noticeable increase in the MIC0.1 values of all antibiotics against both ASST and ARST compared to the low inoculum levels (4.5 and 5 log CFU/mL). The highest fold change in the MIC0.1 of ciprofloxacin was observed at the inoculum of 9 log CFU/mL of ASST, showing a more than 4-fold increase, followed by tobramycin (>3-fold) (Figure 5a). The MIC0.1 values of all antibiotics against ARST were increased up to 2-fold at the inoculum of 9 log CFU/mL (Figure 5b).
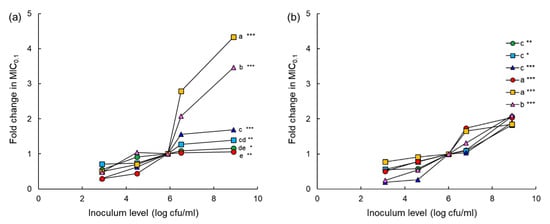
Figure 5.
Inoculum effect of chloramphenicol (CHL; ●), erythromycin (ERY; ■), tetracycline (TET; ▲), cephalothin (CEP; ●), ciprofloxacin (CIP; ■), tobramycin (TOB; ▲) against different levels of antibiotic-sensitive Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 19585 (ASST; (a)) antibiotic-resistant S. Typhimurium CCARM 8009 (ARST; (b)). Markers with different letters within an inoculum level (a–e) are significantly different among antibiotics at p < 0.05. *, **, and *** indicate significant difference between high (>6 log CFU/mL) and low (<5 log CFU/mL) inoculum levels at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively.
3. Discussion
The antimicrobial activity is directly associated with the antibiotic stability during the AST. For instance, the incubation and inoculation conditions can affect the degradation of antibiotics during the broth microdilution assay, ultimately resulting in inaccurate AST results. Therefore, the AST results might not provide sufficient information on the antibiotic stability over the incubation period [14]. Cephalothin and ciprofloxacin showed the concentration-dependent activity against ASST (Figure 1). The concentration-dependent antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth proportionally with increasing concentrations of antibiotics, such as aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones, while the time-dependent antibiotics increase the activity against bacteria up to MICs of antibiotics such as β-lactams and oxazolidinones [3]. The significant losses in tetracycline and cephalothin activities were observed at ½ MIC and 1 MIC, respectively, against ASST (Figure 1c,d). These antibiotics were unstable in aqueous solution, leading to a reduced half-life [15,16]. As shown in Figure 2, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin were unstable to media at ½ MIC against ARST. Factors influencing the stability of antibiotics include light, media, pH, and temperature [11,17]. These losses of antimicrobial activity at the 10 h delayed inoculation indicates that the antibiotics were susceptible to the exposed conditions, such as media and incubation temperature [18]. This is in good agreement with the previous result that β-lactam antibiotics were degraded during the AST [5]. The growth media containing metals contributed to the degradation of the β-lactam antibiotics [5]. In addition, a previous study reported that the stability of tetracycline in fresh media was reduced after incubation in aged media. The loss in antimicrobial activities was due to the dissolved oxygen during incubation [19]. Therefore, the instability of antibiotics may cause sublethal effects, resulting in the development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria [20,21,22]. However, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and tobramycin were stable to retain the antimicrobial activity against ASST exposed to both ½ MIC and 1 MIC during the AST (Figure 1), and the antimicrobial activities of chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and cephalothin remained unchanged during the AST (Figure 2). The results suggest that the stability of antibiotics under AST depends on the classes of antibiotics, concentrations of antibiotics, and degree of antibiotic resistance.
The dose–response curves for chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, cephalothin, and tobramycin showed a significant decrease in antimicrobial activity against both ASST and ARST after 40 h of incubation when compared to 20 h (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The results suggest that ASST and ARST developed the ability to survive prolonged periods of exposure to antibiotics. This observation is in good agreement with the previous report that the development of resistance was noticeable when bacteria were exposed to sublethal concentrations of antibiotics [23]. The MIC values of tetracycline and tobramycin were increased against ASST after an extended incubation time of 40 h, while those of cephalothin and tobramycin were increased against ARST (Figure 3 and Figure 4). On the other side, these results indicate the loss of antibiotic activity throughout the incubation period [11]. This observation is in good agreement with the previous report that the antibiotic concentration was decreased over long-term incubation, leading to the increase in MIC [24]. A similar dose–response curve of ciprofloxacin against ASST and ARST was observed after 20 h and 40 h of incubation. This confirms that ciprofloxacin was relatively stable when compared to other classes of antibiotics [25]. The degradation of the antibiotics result from nutrient media, temperature, and test bacteria during the incubation period can cause a misreading of AST results [26]. This suggests that proper interpretations of the MIC results are essential to estimate the clinical efficacy of antibiotics. Therefore, the underestimation of antibiotic activity can cause substantial economic loss and public health risk [11].
The antimicrobial activity varies with the classes of antibiotics [10]. Tetracycline reversibly targeting the 30S ribosomal subunit can inhibit the binding of aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome [27]. Chloramphenicol targeting the 50S ribosomal subunit can prevent the formation of peptides. In contrast, the ribosome-targeting aminoglycosides, such as streptomycin and kanamycin, can irreversibly bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit, leading to the inhibition of initiation and the induction of mistranslation [27]. The reversible antibiotics are effective against fast-growing bacteria, whereas the irreversible antibiotics are effective against slow-growing bacteria [28]. Bacteriostatic antibiotics are effective against bacterial persister cells by inhibiting protein synthesis [3]. The terms, bactericidal and bacteriostatic antibiotics, can be defined at the in vitro test, depending on the antibiotic classes and test strains [3]. The bacteriostatic antibiotics exhibit bactericidal activity at high concentrations, while the bactericidal antibiotics show bacteriostatic activity at low concentrations [3].
The susceptibilities of ASST and ARST to chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin varied among inoculum levels (Figure 5). The fold changes in the MIC0.1 values of all antibiotics tested in this study were significantly increased as the inoculum levels of ASST and ARST increased, known as inoculum effect [29]. This is in good agreement with previous studies that bacteria showed antibiotic susceptibility at the standard inoculums (105 to 106 CFU/mL) but antibiotic resistance at high inoculum levels [28,29]. The inoculum effect is responsible for the reduction in antimicrobial activity and the enhanced antibiotic resistance [30]. Accordingly, the inoculum effect is a major consideration to evaluate the antimicrobial activity during the AST [31]. The inoculum effect of ciprofloxacin was considerably increased against ASST, showing more than 4-fold change in MIC0.1 value (Figure 5a). This observation might be due to the active efflux pump that can be specific for ciprofloxacin as substrate or the relatively low MIC0.1 values against ASST. This is in good agreement with the efflux-mediated resistance to fluoroquinolones in many bacterial populations [29,32]. Cephalothin showed a comparably high inoculum effect against ARST (Figure 5b). The result implies that the inoculum level of ARST was less susceptible to β-lactam antibiotics because of the elevated production of β-lactamases [31]. The emergence of resistant mutants is more likely to be increased within large bacterial populations [31]. Therefore, the antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria depends on the level of bacterial load and the degree of antibiotic resistance [33,34].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
Strains of antibiotic-sensitive Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 19585 (ASST) and antibiotic-resistant S. Typhimurium CCARM 8009 (ARST) were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) and Culture Collection of Antibiotic Resistant Microbes (CCARM, Seoul, Korea), respectively. The strains were sub-cultured at 37 °C for 20 h in trypticase soy broth (TSB) (BD, Becton, Dickinson and Co., Sparks, MD, USA). The activated cells were collected at the late exponential phase by centrifugation at 5000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The harvested cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2) and adjusted to 108 CFU/mL.
4.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Assay
The susceptibility of ASST and ARST to chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin (Table 1) was evaluated by broth microdilution assay [35]. The antibiotic stock solutions were prepared at a final concentration of 1024 mg/mL by dissolving in ethanol (chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and tetracycline), water (cephalothin and tobramycin), and acetic acid (ciprofloxacin). Each antibiotic stock was serially (1:2) diluted ranging from 1024 µg/mL with TSB in 96-well microtiter plates (BD Falcon, San Jose, CA, USA) and inoculated with 106 CFU/mL of ASST and ARST. The plates were incubated for 20 h at 37 °C to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of each antibiotic.

Table 1.
Characteristics of antibiotics used in this study.
4.3. Time-Delayed Inoculation Assay
The antibiotic stability was evaluated in bacterial culture media by using a delay-time assay [5]. ASST or ARST was inoculated at the level of 106 CFU/mL in 0 h incubated and 10 h delay incubated 96-well microtiter plates containing ½ MIC and 1 MIC of antibiotics. The growth of each test strain was measured after 20 h of incubation at 600 nm using a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Norwood, MA, USA).
4.4. Time-Extended Incubation Assay
The degradation of the antibiotics used in this study was evaluated by broth microdilution assay [35] with a slight modification. Each antibiotic stock was serially (1:2) diluted from 1024 µg/mL with TSB in 96-well microtiter plates (BD Falcon, San Jose, CA, USA), and ASST and ARST were inoculated at 105 CFU/mL. After 20 h and 40 h of incubation at 37 °C, the dose–response curves of ASST and ARST were generated to evaluate the changes in antibiotic susceptibility.
4.5. Estimation of Inoculum Effect
The inoculum effect on antibiotic activity was evaluated by comparing MICs determined at different inoculum levels of ASST and ARST [31]. The test strains were diluted with fresh TSB to obtain different inoculum levels ranging from 8.2 × 102 to 8.2 × 109 CFU/mL and inoculated in each well of 96-well microtiter plates containing antibiotics serially (1:2) diluted from 1024 to 0 µg/mL. MIC0.1 values were determined at the lowest concentrations of antibiotics at which the optical density (OD) at 600 nm reached 0.1 after 20 h of incubation at 37 °C. The fold change was determined by the ratio of the MIC0.1 of each antibiotic at different inoculum levels to the standard inoculum level (106 CFU/mL).
4.6. Statistical Analysis
The experiments were carried out in duplicate for three replicates. All data were analyzed by general linear model (GLM) and Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD) to determine significant differences at 5%, 1%, and 0.1% significance levels. The nonlinear curve fitting function of Microcal Origin® (Microcal Software Inc., Northampton, MA, USA) was used to determine the MIC0.1 values of the antibiotics.
5. Conclusions
This study describes the effects of incubation time and inoculum level on antibiotic stability. AST is the first step to evaluate the antimicrobial potential and then determine the effective antibiotic treatment of bacterial infection. The most significant findings in this study were that the stabilities of chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline, cephalothin, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin during the AST were highly influenced by incubation time, which might be a key factor in determining antimicrobial sustainability and antibiotic concentration; in addition, the antibiotic susceptibility of ASST and ARST was decreased at a high inoculum level when compared to standard inoculum, showing the noticeable inoculum effect of ciprofloxacin against ASST and cephalothin against ARST. Antibiotic stability is considered as an important factor for successful chemotherapeutic use. Thus, the AST might not provide sufficient information about the efficacy of antibiotics in association with the antibiotic stability under the incubation and inoculation conditions. The misinterpretation of the results obtained from the AST ultimately results in the underestimation or overestimation of antibiotic efficacy in clinical practice. Therefore, the current antibiotic susceptibility assays need to be re-evaluated by taking all test conditions (incubation time and inoculation level) into account in providing clinical guidelines and recommendations for chemotherapy and accurately predicting pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in vivo.
Author Contributions
N.N.L. conducted all experiments and also wrote the manuscript. J.D. and J.A. designed the experiment and contributed to the data analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2016R1D1A3B01008304).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kapoor, G.; Saigal, S.; Elongavan, A. Action and resistance mechanisms of antibiotics: A guide for clinicians. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Levin, B.R. Proximate and ultimate causes of the bactericidal action of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankey, G.A.; Sabath, L.D. Clinical relevance of bacteriostatic versus bactericidal mechanisms of action in the treatment of Gram-positive bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbings, W.J.; Bostock, J.M.; Ingham, E.; Chopra, I. Assessment of a microplate method for determining the post-antibiotic effect in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, R.; Vass, H.; Dawson, A.; Squires, T.; Tavaddod, S.; Allen, R.J. Stability of β-lactam antibiotics in bacterial growth media. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmerman, R.; Goethals, K.; Garmyn, A.; Vanantwerpen, G.; Vanrobaeys, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Antonissen, G.; Devreese, M. Agreement of quantitative and qualitative antimicrobial susceptibility testing methodologies: The case of enrofloxacin and avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.A.; Spence, D.M. A rapid method for post-antibiotic bacterial susceptibility testing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharmaceut. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.A. Does the dose matter? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, S233–S237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallemand, E.A.; Lacroix, M.Z.; Toutain, P.-L.; Boullier, S.; Ferran, A.A.; Bousquet-Melou, A. In vitro degradation of antimicrobials during use of broth microdilution method can increase the measured minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonev, B.; Hooper, J.; Parisot, J. Principles of assessing bacterial susceptibility to antibiotics using the agar diffusion method. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levison, M.E.; Levison, J.H. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antibacterial agents. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 791–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaho, E.; Nakayama, H. An innovative classification of, and a new structure-activity-relationship approach to degradation kinetics of cephalosporins: An attempt to enhance the therapeutic activity. J. Antibiot. 2003, 56, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sah, H. Degradation patterns of tetracycline antibiotics in reverse micelles and water. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdiyeva, S.; Yardım, Y.; Şentürk, Z. Electrooxidation of tetracycline antibiotic demeclocycline at unmodified boron-doped diamond electrode and its enhancement determination in surfactant-containing media. Talanta 2021, 223, 121695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, W.E. Influence of antibiotic stability on the results of in vitro testing procedures. J. Bacteriol. 1964, 87, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, R.; Warner, M.; Mushtaq, S.; Ward, M.E.; Parsons, T.; Livermore, D.M. Effect of medium type, age and aeration on the MICs of tigecycline and classical tetracyclines. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F. Low-level antibacterial resistance: A gateway to clinical resistance. Drug. Resist. Updat. 2001, 4, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Suo, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, F.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Effect of sublethal concentrations of ceftriaxone on antibiotic susceptibility of multiple antibiotic-resistant Salmonella strains. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fny283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broussou, D.C.; Toutain, P.-L.; Woehrlé, F.; El Garch, F.; Bousquet-Melou, A.; Ferran, A.A. Comparison of in vitro static and dynamic assays to evaluate the efficacy of an antimicrobial drug combination against Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.L.; Kays, M.B.; Friedrich, L.V.; Brown, E.W.; Koonce, J.R. Pseudoresistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa resulting from degradation of imipenem in an automated susceptibility testing system with predried panels. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okerman, L.; Van Hende, J.; De Zutter, L. Stability of frozen stock solutions of beta-lactam antibiotics, cephalosporins, tetracyclines and quinolones used in antibiotic residue screening and antibiotic susceptibility testing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 586, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voumard, R.; Van Neyghem, N.; Cochet, C.; Gardiol, C.; Decosterd, L.; Buclin, T.; de Valliere, S. Antibiotic stability related to temperature variations in elastomeric pumps used for outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy (OPAT). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1462–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, P.; Scott, M.; Evans, M.R.; Allen, R.J. Growth-dependent bacterial susceptibility to ribosome-targeting antibiotics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, R.H.; Padberg, F.T.; Smith, S.M.; Tan, E.N.; Cherubin, C.E. Bactericidal effects of antibiotics on slowly growing and nongrowing bacteria. Antimicrob. Agent. Chemother. 1991, 35, 1824–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, S.; Ahmed, S.; Wang, F.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chai, X.; Wu, Y.; Cai, J.; Cheng, G. Antimicrobial activity and resistance: Influencing factors. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferran, A.A.; Toutain, P.L.; Bousquet-Melou, A. Comparison of the reduction in the antibacterial potency of a fluoroquinolone conferred by a single mutation in the quinolone resistance-determining region or by the inoculum size effect. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbrun, M.V.; Rossler, E.; Olivero, C.R.; Soto, L.P.; Zimmermann, J.A.; Frizzo, L.S.; Signorini, M.L. Possible reservoirs of thermotolerant Campylobacter at the farm between rearing periods and after the use of enrofloxacin as a therapeutic treatment. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 340, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Langevin, A.M.; Dunlop, M.J. Antibiotic export by efflux pumps affects growth of neighboring bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, N.; Dover, R.S.; Titon, E.; Shai, Y.; Rom-Kedar, V. Bistable bacterial growth dynamics in the presence of antimicrobial agents. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.P.; Kirby, J.E. The inoculum effect in the era of multidrug resistance: Minor differences in inoculum have dramatic effect on MIC determination. Antimicrob. Agent. Chemother. 2018, 62, e00433-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Approved Method of Analysis of CLSI 10th ed. M07-A10. In Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).