Abstract
This study aimed to determine the global distribution and molecular characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. A total of 328 (11.1%, 328/2953) carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates from humans were obtained from public databases as of October 2019. Of which, the blaVIM and blaIMP genes were the most prevalent carbapenemases in the P. aeruginosa isolates. These carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates possessed 34 distinct sequence types (STs) and six predominated: ST357, ST823, ST308, ST233, ST175 and ST111. The ST357 and ST823 isolates were primarily found detected in Asia and all ST175 isolates were found in Europe. The ST308, ST233 and ST111 isolates were spread worldwide. Further, all ST823 isolates and the majority of ST111, ST233 and ST175 isolates carried blaVIM but ST357 isolates primarily carried blaIMP. ST308 isolates provide a key reservoir for the spread of blaVIM, blaIMP and blaNDM. WGS analysis revealed that ST111 carried a great diversity of ARG types (n = 23), followed by ST357 (n = 21), ST308 (n = 19), ST233 (n = 18), ST175 (n = 14) and ST823 (n = 10). The ST175 isolates carried a more diversity and frequent of aminoglycoside ARGs, and ST233 isolates harbored more tetracycline ARGs. Our findings revealed that different carbapenem resistance genes were distributed primarily in variant STs of P. aeruginosa isolates, these isolates also possessed an extensive geographical distribution that highlights the need for surveillance studies that detect carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates in humans.
1. Introduction
The antimicrobial-resistant ESKAPE pathogens (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter spp.) are a global threat to human health and include four Gram-negative bacteria [1]. In particular, K. pneumoniae ST307 isolates and Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198 from the USA and Egypt, respectively, have now worldwide dissemination [2,3]. A. baumannii ST195 isolates are distributed widely in eight countries and isolates recovered from different locations may present less genomic sequence similarity [4]. However, there is paucity of data regarding the global distribution of P. aeruginosa isolates.
Carbapenem antibiotics are generally considered last-line agents for the treatment of severe cases of P. aeruginosa infections [5]. However, the recent increases in the prevalence of carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa nosocomial isolates is great concern [5,6]. Evidence suggests that patients who are infected by carbapenem-resistant pathogens have an increased likelihood of morbidity and mortality compared with those infected by susceptible pathogens [7]. The clinical use of carbapenems is currently restricted as a result of the prevalence of carbapenem resistance genes. More seriously, mobile genetic elements have facilitated their rapid dissemination. So far, P. aeruginosa isolates producing blaIMP, blaVIM, blaNDM, or blaKPC have been detected in various countries [8]. These cases of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa are currently localized to a hospital or a country. Therefore, a large-scale survey to detect carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa worldwide needs to be further explored.
In this study, we employed genomic analysis to investigate the prevalence and global distribution characteristics of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates from human and we characterized their molecular characteristics, diversity, antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and virulence genotypes of these pathogens.
2. Results
2.1. Geographical Distribution of the Carbapenemase-Producing P. aeruginosa Identified from the Genome Database
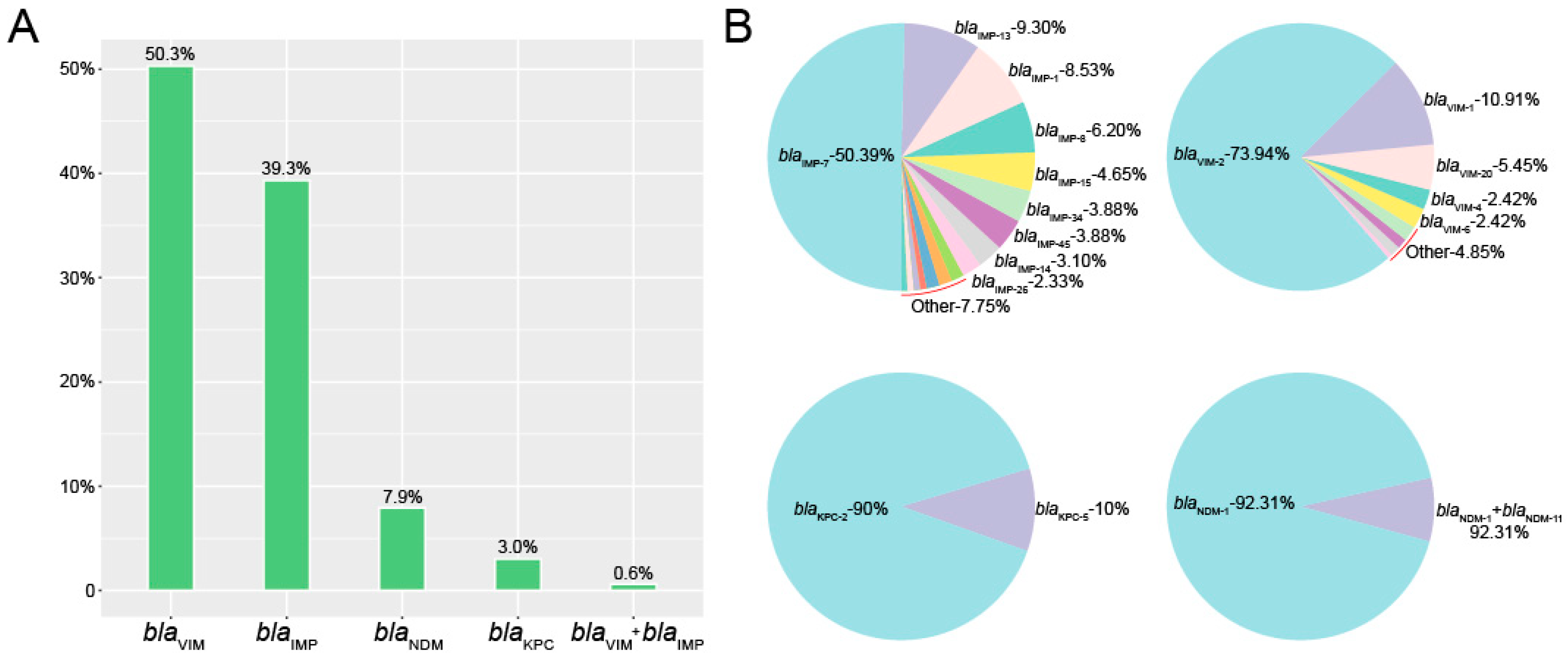
In this study, we first utilized a public database to evaluate the global distribution of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. We identified 2953 P. aeruginosa human isolates and 11.1% (328/2953) of the entries indicated the presence of carbapenem resistance genes. Among the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, the most prevalent were blaVIM (50.3%, 165/328), blaIMP (39.3%, 129/328), blaNDM (7.9%, 26/328) and blaKPC (3.0%, 10/328). There were no isolates positive for blaOXA-48-like. Interestingly, two P. aeruginosa isolates carried both blaVIM and blaIMP (Figure 1A).

Figure 1.
Identification of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. (A) The numbers of carbapenem resistance genes in P. aeruginosa isolates. (B) The rates and numbers of variants in carbapenem resistance genes.
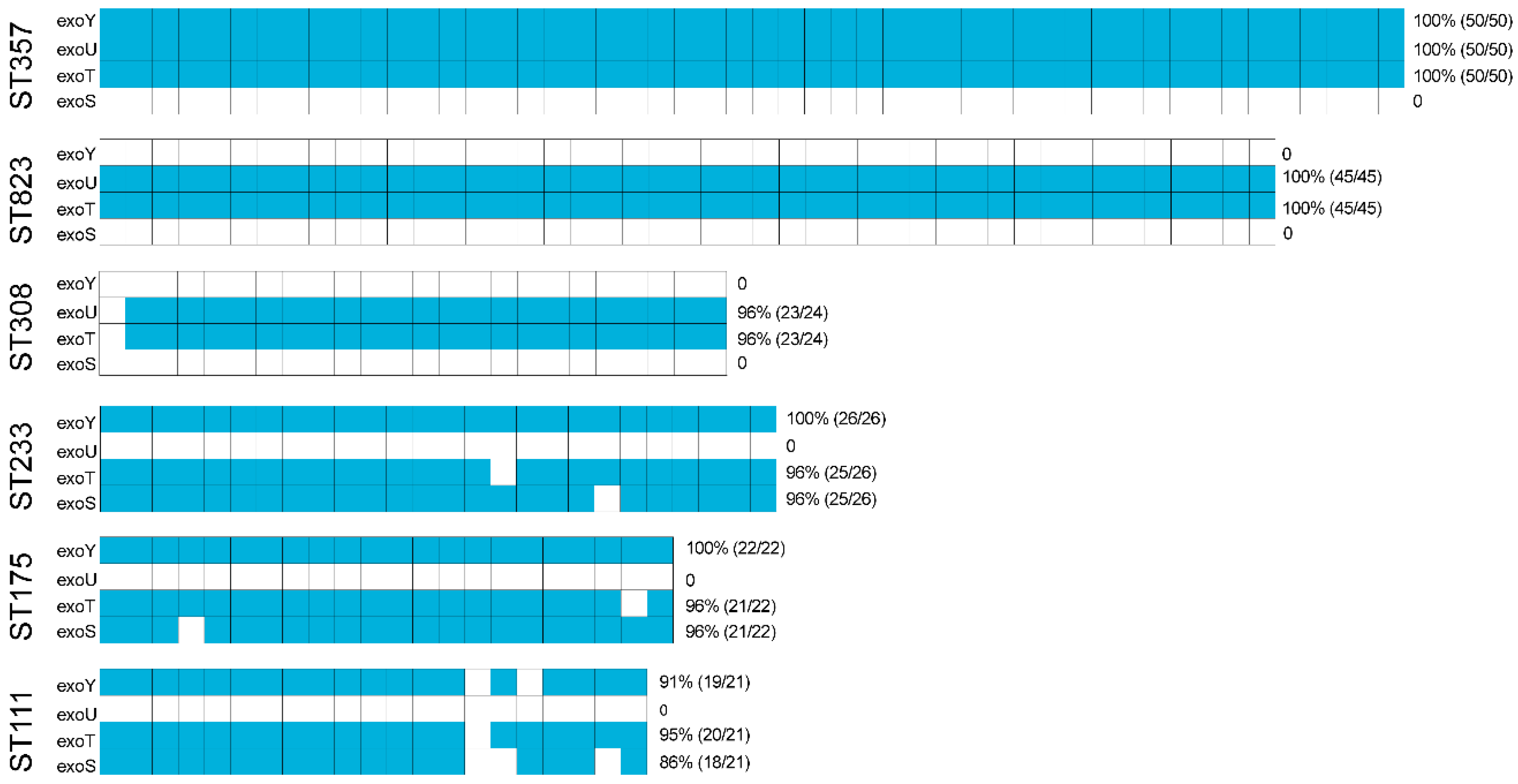
Within the group of 165 blaVIM-positive P. aeruginosa in this study, blaVIM-2 accounted for almost 75% of the total, from nine possible variants (73.94%, 122/165). Furthermore, within the 129 members of the blaIMP group, blaIMP-7 represented half of the total (50.39%, 65/129). The blaNDM-1 and blaKPC-2 were the most prevalent in blaNDM- and blaNDM- positive isolates respectively (Figure 1B).
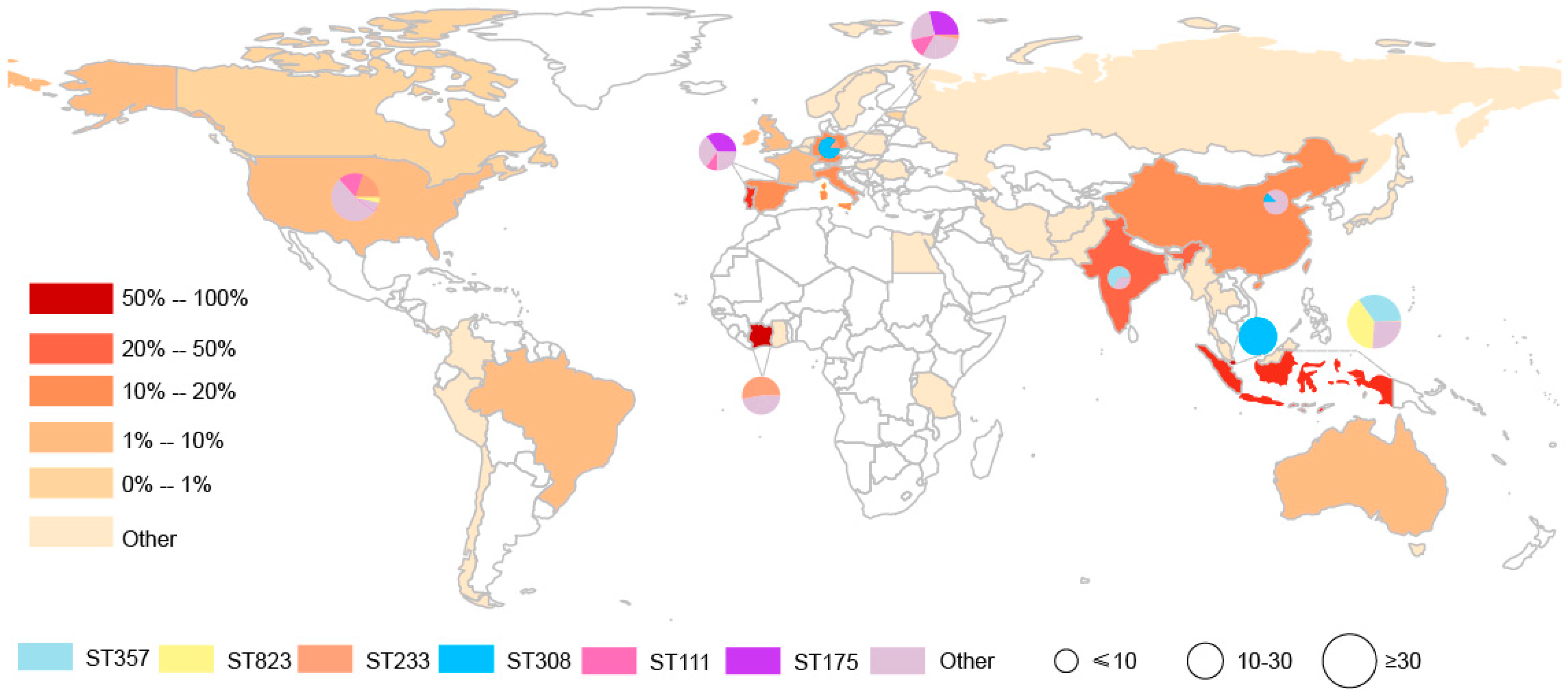
These carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates were distributed across 40 countries in Asia (n = 14), Europe (n = 14), Americas (n = 7), Africa (n = 4) and Australia (n = 1). The countries possessing the greatest numbers of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates were Indonesia (50.45%, 112/222), India (23.08%, 9/39), Italy (17.72%, 45/254), China (14.81%, 8/54), Germany (11.48%, 7/61), and Spain (11.30%, 20/177) (Table A1). These data demonstrate that Asia has been severely contaminated by carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. In the current data, we identified a high incidence of both blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa from Indonesia (blaVIM: 27.3%, 45/165; blaIMP: 51.9%, 67/129) and Italy (blaVIM: 18.8%, 31/165; blaIMP: 10.1%, 13/129) compared with other countries (Table A2). This suggested that Indonesia and Italy have been severely contaminated by carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates.
The sample types for our group of 328 carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates included throat swabs (12.8%, n = 42), urine (11.9%, n = 39), rectal swabs (11.6%, n = 38), blood (11.0%, n = 36), bronchial aspirates (9.8%, n = 32), sputum (8.2%, n = 27) and other sites (10.8%, n = 26), such as wounds, abscesses, cornea, groin and so on, but the source information of the remaining was missing (26.8%, n = 88) (Table A3).
2.2. Molecular Characterization of the Carbapenemase-Producing P. aeruginosa
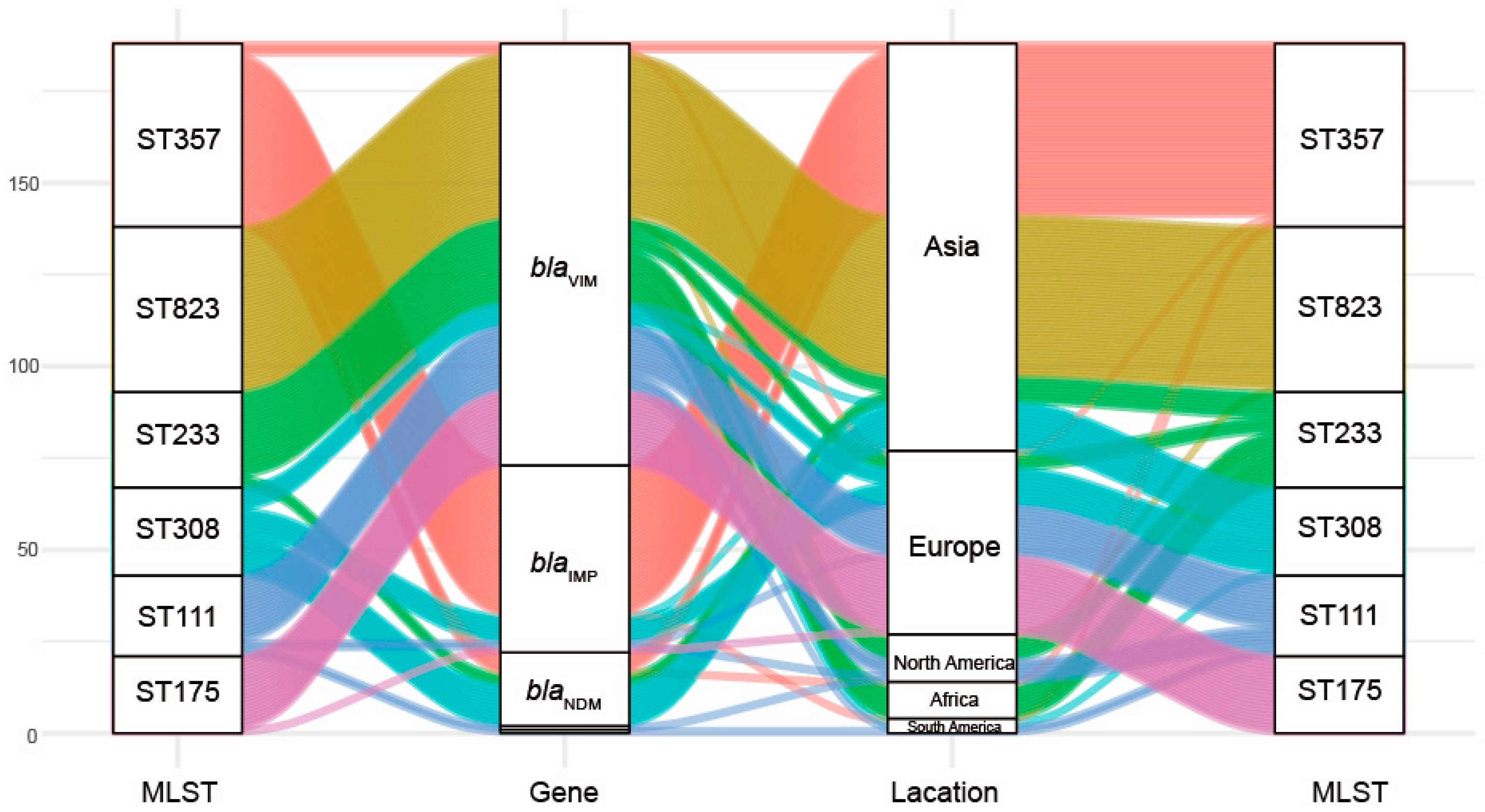
This group of 328 carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates possessed 34 distinct ST and six predominated: ST357 (15.24%, n = 50), ST823 (13.72% n = 45), ST233 (7.93%, n = 26), ST308 (7.32%, n = 24), ST111 (6.71%, n = 22) and ST175 (6.40%, n = 21). Interestingly we could not find a matching ST for 66 of the database isolates (Table A4). Minimum-spanning trees were constructed using 34 distinct STs of 262 carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, and the results showed that ST111 might be an ancestral isolate and differentiated into a large number of STs among carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates (see Appendix A Figure A1). We further explored the clonal relatedness of these isolates in which 10 countries possessed carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa > 5. The ST types were highly diverse such as for the eleven unique STs in USA, nine for Italy and six for China and Spain, respectively. In contrast, Germany (n = 2), India (n = 1) and Singapore (n = 1) possessed a low level of diverse (Figure 2). More significantly, we identified for the first time that different carbapenem resistance genes were distinctly distributed among the variant STs (Figure 3). All ST823 isolates and the majority of ST111, ST233 and ST175 isolates carried blaVIM while the majority of ST357 isolates carried blaIMP. Furthermore, ST308 isolates provided a reservoir for the spread of blaVIM, blaIMP and blaNDM (Figure 3). In addition, there were distinctive geographical distributions for these variant STs. For instance, ST357 and ST823 isolates were primarily from Asia and all ST175 isolates were from Europe. However, ST308, ST233 and ST111 isolates were globally distributed (Figure 3).

Figure 2.
Geographic distribution and MLST diversity of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The presence of the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates is indicated by brown; the pie chart represents MLST diversity.

Figure 3.
Associations of MLST with antibiotic resistance and geographic locations for the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates.
2.3. Other ARGs
We also identified the presence of other ARGs from the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. Almost all isolates carried aph, blaOXA, blaPAO, cat and fosA4 that conferred resistance to aminoglycosides, β-lactams, chloramphenicol and fosfomycin. Interestingly, drfB that confers resistance to sulfonamides was detected in blaVIM-positive P. aeruginosa at a higher prevalence than in blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa (Appendix A Figure A2). Generally, the ARGs types among the different STs varied greatly. In particular, the largest numbers of ARGs types were present in ST111 (n = 23), ST357 (n = 21), ST308 (n = 19), ST233(n = 18), ST175 (n = 14) and ST823 (n = 10) (Appendix A Figure A3). The diversity and frequency of aminoglycoside resistance genes carried by ST175 were significantly higher than for the other STs and tetracycline resistance genes carried by ST233 were more numerous than for the other STs (Appendix A Figure A3). These data indicate that the six predominant STs for our group of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates possessed shared ARGs and at the same time carried unique ARGs.
2.4. Virulence Factor
In our group of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, we detected the presence of exoY, exoU and exoT that coexisted in ST357 isolates, while exoU and exoT were found together in ST823 and ST308 isolates (Appendix A Figure A4). Interestingly, ST233 isolates possessed the same complement of virulence factors as the ST111 and ST175 isolates (Appendix A Figure A3). These results revealed that the distribution of these cytotoxin genes was not uniform among carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, none of the isolates possessed all the cytotoxin genes.
3. Discussion
Carbapenems are the most effective antimicrobial agents against serious infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli [9]. However, carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa are emerging worldwide with increasing reports of carbapenemase-producing isolates, such as China, Singapore, Canada, Germany, Spain, US and so on [8,10,11,12,13,14]. In this study, 328 carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates were collected from public database, and distributed across from 40 countries. Of which, the countries possessing the greatest numbers of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates were Indonesia, India, Italy, China, Germany and Spain, further demonstrate that Asia has been severely contaminated by carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates.
Among the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, the most prevalent were blaVIM, blaIMP, blaNDM and blaKPC. The VIM family contains the most important carbapenemases among P. aeruginosa strains, while blaNDM and blaKPC are the most prevalent for E. coli and K. pneumoniae, respectively [15,16,17]. There is a distinct species preference associated with possession of particular carbapenemase variants. In addition, the high incidence of both blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa from Indonesia and Italy compared with other countries. This is consistent with previous research; Indonesia and Italy have been severely contaminated by carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates [18,19]. Within the group of 165 blaVIM-positive P. aeruginosa in this study, blaVIM-2 accounted for almost 75% of the total from nine possible variants. Furthermore, within the 129 members of the blaIMP group, blaIMP-7 represented half of the total. Consistent with previous studies, blaIMP-7 and blaVIM-2 were the dominant variants in carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates from the Czech Republic and Spain, respectively [6,20].
This group of 328 carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates possessed 34 distinct ST and six predominated: ST357, ST823, ST233, ST308, ST111 and ST175. Core-genome analysis showed that ST111 might be an ancestral isolate and differentiated into a large number of STs among carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. This is consistent with previous studies, the international high-risk clone ST111 is the founder of a subgroup from which an important number of STs derive [21]. Interestingly, we identified for the first time that different carbapenem resistance genes were distinctly distributed among the variant STs. All ST823 isolates and the majority of ST111, ST233 and ST175 isolates carried blaVIM while the majority of ST357 isolates carried blaIMP. Furthermore, ST308 isolates provided a reservoir for the spread of blaVIM, blaIMP and blaNDM. In addition, there were distinctive geographical distributions for these variant STs. For instance, ST357 and ST823 isolates were primarily from Asia and all ST175 isolates were from Europe. However, ST308, ST233 and ST111 isolates were globally distributed. Consistent with these results, ST823 isolates that harbored blaVIM-2 have been identified in multiple Asian countries [18,22]. ST233 is an internationally recognized high-risk clone and frequently associated with carbapenemase production as well as exhibiting resistance to all antimicrobial drugs, and is present in at least 12 countries [21,23]. Additionally, 90% of multidrug resistant isolates belonged to only three clones and classified as the major international MDR/XDR high-risk clones: ST175, ST111 and ST235 [24]. In particular, the ST111 high-risk clonal isolates have also been found associated with blaVIM globally distribution and blaVIM-positive ST175 isolates have been detected in Germany and Spain. ST357 is also frequently but not exclusively associated with possession of the carbapenemase IMP gene in Asia [6,23]. The blaNDM, blaVIM and blaIMP positive ST308 isolates have previously identified in Asian countries [25], we found blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive ST308 P. aeruginosa isolates in Europe.
We also identified the presence of other ARGs from the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. Almost all isolates carried aph, blaOXA, blaPAO, cat and fosA4 that conferred resistance to aminoglycosides, β-lactams, chloramphenicol and fosfomycin [23,26]. It is similar to carbapenemase-producing E. coli isolates: carbapenem resistance genes often co-existed with other antibiotic resistance genes, conferring resistance to multiple antimicrobials [27,28].
The possession of specific virulence genes by a pathogen including P. aeruginosa, is a relevant independent marker of potential disease-causing potential [29]. P. aeruginosa possesses numerous virulence factors and one of the most important is its possession of a type III secretion system (TTSS). This system functions to inject effector cytotoxins encoded by exoS, exoT, exoU and exoY into host cells [24]. In our group of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, we detected the presence of exoY, exoU and exoT that co-existed in ST357 isolates, while exoU and exoT were found together in ST823 and ST308 isolates. The exoU genotype has been associated with increased early mortality and is a potential prognostic biomarker in P. aeruginosa infections as an indicator of predicated disease severity [24]. In agreement with this, we found that the ST111 and ST175 high-risk clones possessed exoY, exoT and exoS [6]. Interestingly, ST233 isolates possessed the same complement of virulence factors as the ST111 and ST175 isolates. These results revealed that the distribution of these cytotoxin genes was not uniform among carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, none of the isolates possessed all the cytotoxin genes and possession of exoS and exoU appeared to be mutually exclusive. Our findings are therefore in agreement with previous studies showing that exoT and exoY were present in the vast majority of strains but exoS and exoU were nearly mutually exclusive among our P. aeruginosa clinical isolates [29].
We acknowledge that our study mainly has two limitations. Firstly, the isolates collection was only dependent on the public repository that could not harbor all the P. aeruginosa in the world. Secondly, we could not obtain strains for further research. For instance, the levels of antimicrobial susceptibility and evaluated the transfer of carbapenem resistance genes.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
A total of 5208 assembled genomes and information of P. aeruginosa isolates were downloaded from the NCBI database as of October 2019. Human-derived isolates (n = 2953) were filtered according to detailed information from the P. aeruginosa database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens, accessed on 19 October 2019).
4.2. Methods
All the P. aeruginosa isolates were applied to a filter for the presence of at least one of the five major acquired carbapenem resistance genes (blaKPC, blaNDM, blaIMP, blaOXA-48-like and blaVIM) using ABRicate (https://github.com/tseemann/abricate, accessed on 7 January 2020) The blaKPC, blaNDM, blaIMP, blaOXA-48-like and blaVIM were the most broadly spread carbapenemases [30]. Multilocus sequence types (MLST) were identified using Github (https://github.com/tseemann/mlst, accessed on 7 January 2020). P. aeruginosa isolates virulence factors were identified using the Virulence Factor Database (http://www.mgc.ac.cn/VFs/main.htm, accessed on 7 January 2020). Epidemic ST clones (The STs with the higher detection and distributed in the world) for the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates selections were used to analyze associations between STs, geographic location and carbapenem resistance genes. The map was generated using R 3.6.0 using the rworidmap package (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rworldmap/, accessed on 19 July 2020). Minimum-spanning tree of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates based on a core-genome MLST was constructed using PHYLOViZ software of BIGSdb [31,32].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we identified 328 carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa human clinical isolates from public databases and the carbapenem resistance genes blaVIM and blaIMP were the most prevalent and present in ~50 and 39% of the isolates, respectively. These strains possessed diverse ST types in most countries and eleven unique STs were identified in the USA, nine in Italy and six in China and Spain, respectively. In contrast, Germany (n = 2), India (n = 1) and Singapore (n = 1) possessed a low level of diverse. We found six prevalent STs and comprised distinct groups. For instance, all ST823 isolates and the majority of ST111, ST233 and ST175 isolates carried blaVIM, while the majority of ST357 isolates carried blaIMP. The ST308 isolates provided a reservoir for the spread of blaVIM, blaIMP and blaNDM. The distribution of the genes encoding these cytotoxins was not uniform among carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates, none possessed all cytotoxins, and some of them, particularly exoS and exoU, appeared to be mutually exclusive. These results suggest that surveillance studies for carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates in humans are urgently needed.
Author Contributions
Methodology, M.-G.W.; software, R.-Y.S.; validation, R.-B.L.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, L.-X.F.; resources, Z.-Y.L.; data curation, L.-X.F.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-G.W. and X.-P.L.; writing—review and editing, R.-M.Z. and Z.-Y.L.; project administration, R.-M.Z.; funding acquisition, J.S., Y.-H.L. and R.-M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31802243, 31730097, and 31772793), the Program for Innovative Research Team in the University of Ministry of Education of China (IRT_17R39), the Guangdong Special Support Program Innovation Team (2019BT02N054).
Data Availability Statement
The data for this manuscript is available from correspondence author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Distribution of carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa in various countries.
Table A1.
Distribution of carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa in various countries.
| Continents | Countries | Carbapenemase-Positive P. aeruginosa | Total of P. aeruginosa | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia (162) | Indonesia | 112 | 222 | 50.45% |
| China | 8 | 54 | 14.81% | |
| Iran | 1 | 1 | ||
| Japan | 3 | 6 | ||
| Afghanistan | 2 | 3 | ||
| India | 9 | 39 | 23.08% | |
| Bangladesh | 1 | 1 | ||
| Myanmar | 1 | 1 | ||
| Turkey | 2 | 2 | ||
| Singapore | 11 | 11 | ||
| Malaysia | 4 | 16 | ||
| Lebanon | 4 | 8 | ||
| Thailand | 3 | 25 | ||
| Pakistan | 1 | 1 | ||
| Europe (101) | Russia | 2 | 9 | |
| Netherlands | 2 | 6 | ||
| Italy | 45 | 254 | 17.72% | |
| Portugal | 9 | 16 | ||
| Germany | 7 | 61 | 11.48% | |
| Norway | 2 | 2 | ||
| Estonia | 1 | 148 | 0.68% | |
| France | 5 | 65 | 7.69% | |
| Hungary | 1 | 1 | ||
| United Kingdom | 3 | 181 | 1.66% | |
| Belgium | 1 | 9 | ||
| Poland | 1 | 2 | ||
| Spain | 20 | 177 | 11.30% | |
| Sweden | 2 | 6 | ||
| America (40) | Brazil | 4 | 87 | 4.60% |
| Colombia | 1 | 3 | ||
| Peru | 2 | 2 | ||
| Chile | 1 | 2 | ||
| Panama | 1 | 1 | ||
| USA | 30 | 767 | 3.91% | |
| Canada | 1 | 497 | 0.20% | |
| Africa (23) | Ghana | 4 | 5 | |
| Cote d’Ivoire | 17 | 18 | ||
| Egypt | 1 | 1 | ||
| Tanzania | 1 | 16 | ||
| Oceania (2) | Australia | 2 | 117 | 1.71% |

Table A2.
Distribution of VIM- and IMP-positive P. aeruginosa in various countries.
Table A2.
Distribution of VIM- and IMP-positive P. aeruginosa in various countries.
| VIM | IMP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Countries | Numbers | Rate | Countries | Numbers | Rate |
| Indonesia | 45 | 27.3% | Indonesia | 67 | 51.9% |
| Italy | 31 | 18.8% | Italy | 13 | 10.1% |
| USA | 19 | 11.5% | China | 7 | 5.4% |
| Spain | 16 | 9.7% | cote | 6 | 4.7% |
| cote | 11 | 6.7% | Germany | 6 | 4.7% |
| Portugal | 11 | 6.7% | Ghana | 4 | 3.1% |
| India | 5 | 3.0% | Malaysia | 4 | 3.1% |
| Lebanon | 4 | 2.4% | Spain | 4 | 3.1% |
| United Kingdom | 3 | 1.8% | USA | 4 | 3.1% |
| Afghanistan | 2 | 1.2% | France | 3 | 2.3% |
| Netherlands | 2 | 1.2% | Australia | 2 | 1.6% |
| Norway | 2 | 1.2% | Peru | 2 | 1.6% |
| Russia | 2 | 1.2% | Thailand | 2 | 1.6% |
| Brazil | 1 | 0.6% | Iran | 1 | 0.8% |
| Chile | 1 | 0.6% | Sweden | 1 | 0.8% |
| China | 1 | 0.6% | Tokyo | 1 | 0.8% |
| Colombia | 1 | 0.6% | Turkey | 1 | 0.8% |
| Egypt | 1 | 0.6% | Belgium | 1 | 0.8% |
| France | 1 | 0.6% | |||
| Germany | 1 | 0.6% | |||
| Panama | 1 | 0.6% | |||
| Peru | 1 | 0.6% | |||
| Sweden | 1 | 0.6% | |||
| Turkey | 1 | 0.6% | |||
| Bangladesh | 1 | 0.6% | |||

Table A3.
The origin of the carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa isolates.
Table A3.
The origin of the carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa isolates.
| Body Site | Number of Isolates | Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Throat | 42 | 17.50% |
| Urine | 39 | 16.25% |
| Rectal | 38 | 15.83% |
| Blood | 36 | 15.00% |
| Bronchial | 32 | 13.33% |
| Sputum | 27 | 11.25% |
| Wound | 11 | 4.58% |
| Abscess | 4 | 1.67% |
| Cornea | 2 | 0.83% |
| Feces | 2 | 0.83% |
| Lung | 2 | 0.83% |
| Eye | 1 | 0.42% |
| Groin | 1 | 0.42% |
| Peritoneal fluid | 1 | 0.42% |
| Pleural fluid | 1 | 0.42% |
| Knee | 1 | 0.42% |
| Unknown | 88 | 26.83% |

Table A4.
The number of carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa of various MLST types.
Table A4.
The number of carbapenemase-positive P. aeruginosa of various MLST types.
| MLST | Number of Carbapenemase-Positive P. aeruginosa |
|---|---|
| Unknown | 66 |
| ST357 | 50 |
| ST823 | 45 |
| ST233 | 26 |
| ST308 | 24 |
| ST111 | 22 |
| ST175 | 21 |
| ST621 | 12 |
| ST244 | 9 |
| ST234 | 5 |
| ST316 | 5 |
| ST179 | 4 |
| ST260 | 3 |
| ST309 | 3 |
| ST532 | 3 |
| ST664 | 3 |
| ST773 | 3 |
| ST155 | 2 |
| ST253 | 2 |
| ST282 | 2 |
| ST654 | 2 |
| ST1207 | 2 |
| ST1006 | 2 |
| ST17 | 1 |
| ST235 | 1 |
| ST277 | 1 |
| ST298 | 1 |
| ST313 | 1 |
| ST381 | 1 |
| ST389 | 1 |
| ST446 | 1 |
| ST549 | 1 |
| ST1420 | 1 |
| ST1816 | 1 |
| ST2584 | 1 |

Figure A1.
Minimum-spanning tree of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates based on a core-genome MLST (cgMLST). Each node within the tree represents a cgMLST type, with diameters scaled to the number of isolates belonging to that type.
Figure A1.
Minimum-spanning tree of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates based on a core-genome MLST (cgMLST). Each node within the tree represents a cgMLST type, with diameters scaled to the number of isolates belonging to that type.
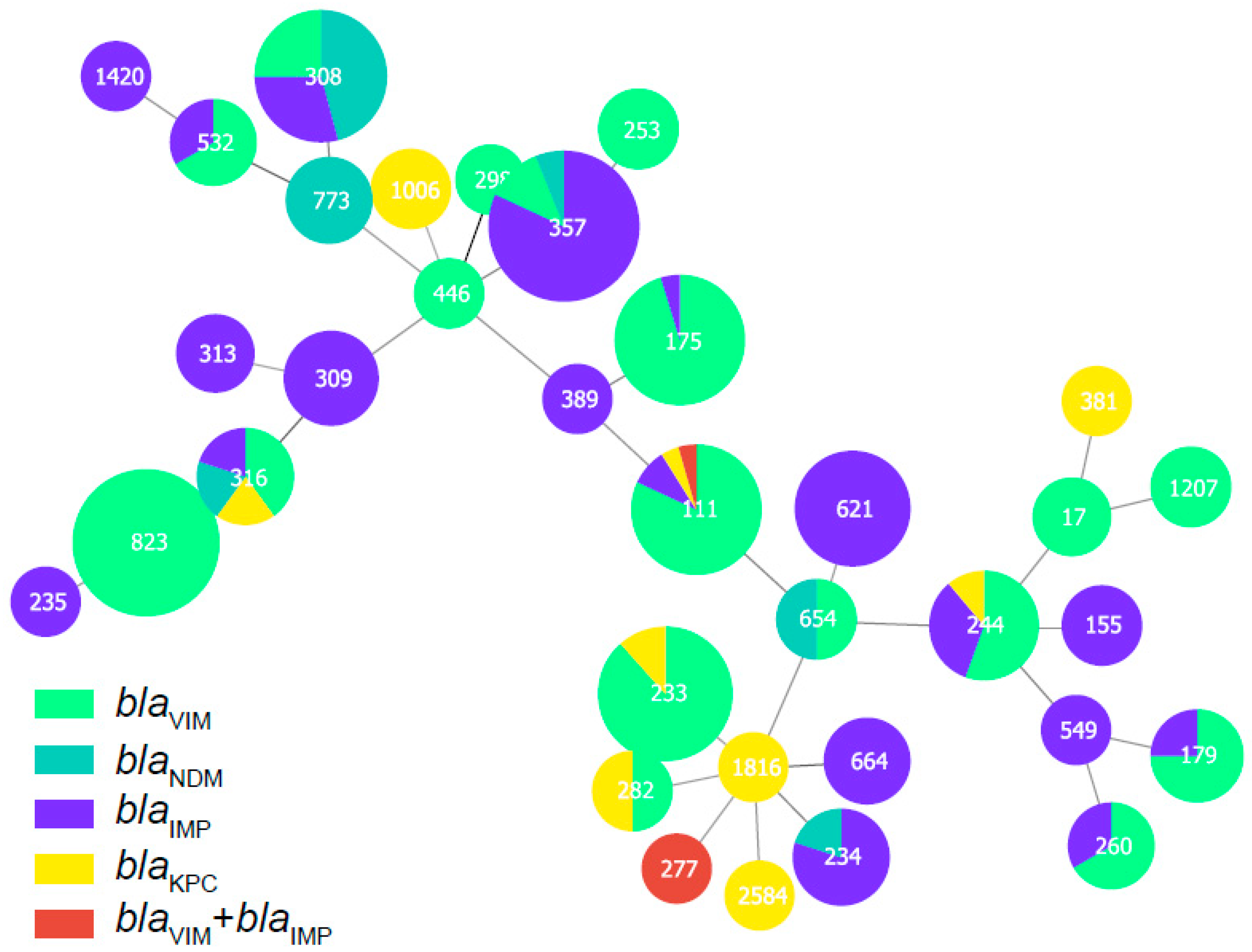

Figure A2.
ARGs present among the blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa isolates found in this study. The blue represents positive for ARGs in the blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa isolates. The red dotted line represents a special value of worth noting
Figure A2.
ARGs present among the blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa isolates found in this study. The blue represents positive for ARGs in the blaVIM- and blaIMP-positive P. aeruginosa isolates. The red dotted line represents a special value of worth noting
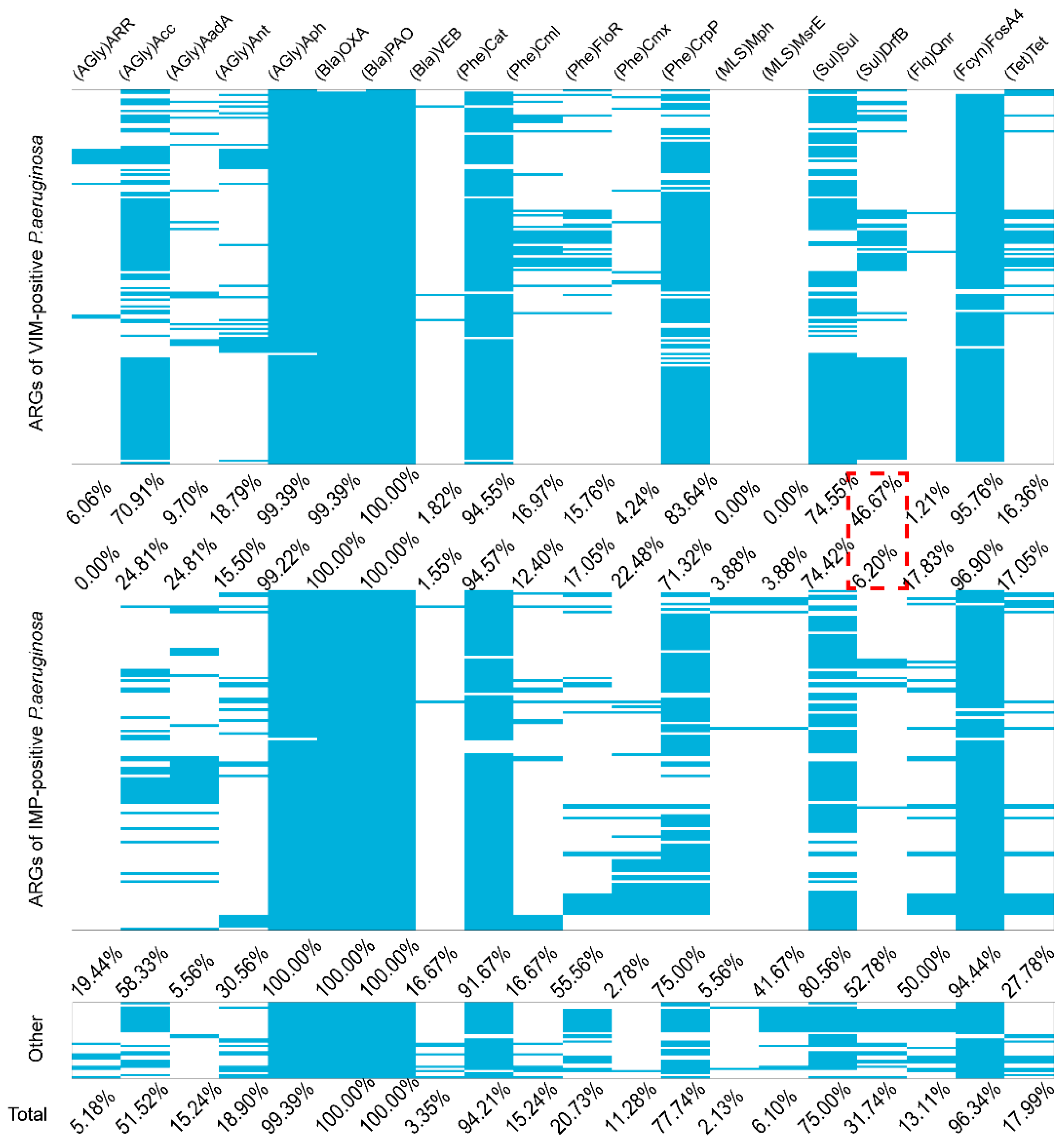

Figure A3.
ARGs present among the six most prevalent STs in carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The blue represents positive for ARGs in the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The red dotted line represents a special value of worth noting
Figure A3.
ARGs present among the six most prevalent STs in carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The blue represents positive for ARGs in the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The red dotted line represents a special value of worth noting
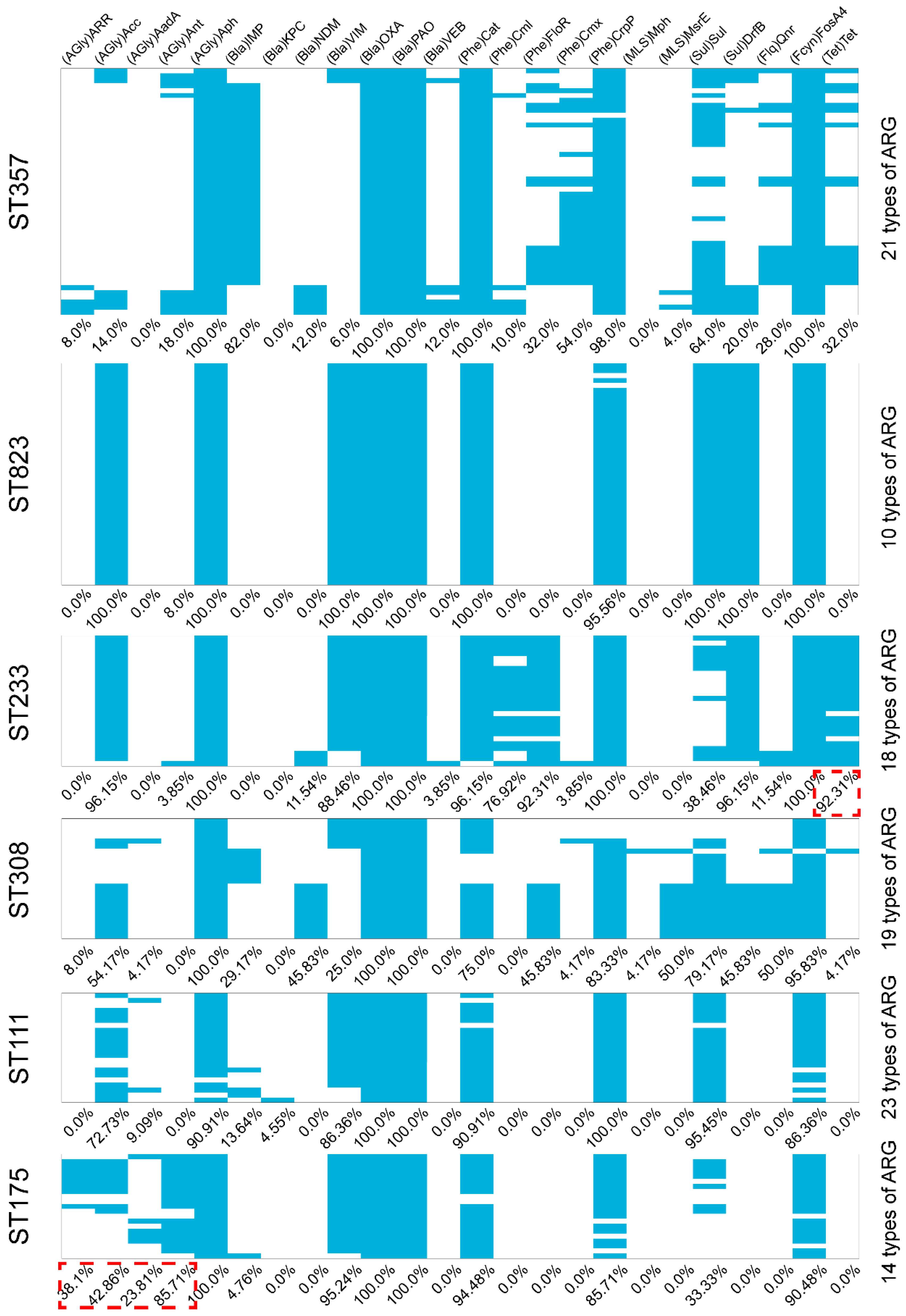

Figure A4.
Virulence factors present in carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The blue represents positive for virulence factor in the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates.
Figure A4.
Virulence factors present in carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates. The blue represents positive for virulence factor in the carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa isolates.
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, J.; Le Hello, S.; Doublet, B.; Granier, S.A.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Fricke, W.F.; Ceyssens, P.-J.; Gomart, C.; Billman-Jacobe, H.; Holt, K.E.; et al. Global phylogenomics of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Hawkey, J.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Fostervold, A.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Hamidian, M.; Howden, B.P.; Löhr, I.H.; Holt, K.E. Emergence and rapid global dissemination of CTX-M-15-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ST307. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Ruan, Z. Emerging challenges of whole-genome-sequencing-powered epidemiological surveillance of globally distributed clonal groups of bacterial infections, giving Acinetobacter baumannii ST195 as an example. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 309, 151339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Huang, A.-W.; Liu, S.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Zhang, N.; Lu, X.-Z. Mortality attributable to carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2016, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Medvecky, M.; Chudejova, K.; Skalova, A.; Rotova, V.; Spanelova, P.; Jakubu, V.; Zemlickova, H.; Hrabak, J. Molecular Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa of Czech Origin and Evidence for Clonal Spread of Extensively Resistant Sequence Type 357 Expressing IMP-7 Metallo-β-Lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01811-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrice, N.; Poirel, L. Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Carbapenem Resistance in Gram-negative Bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, S521–S528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, M.G.; Adam, H.J.; Blondeau, J.M.; Walkty, A.J.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Hoban, D.J.; Zhanel, G.G.; Mulvey, M.R.; Baxter, M.R.; Nichol, K.A.; et al. Characterization of carbapenem-resistant and XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Canada: Results of the CANWARD 2007–16 study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, iv32–iv38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Cao, J.-M.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S.; Lv, H.-Y.; Zhou, H.-W.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R. Risk Factors for Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Zhejiang Province, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, J.W.P.; La, M.-V.; Jureen, R. Emergence of a New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase-1-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Singapore. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2015, 4, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkty, A.; Alexander, D.C.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Nichol, K.; Embil, J. Report of a KPC-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate in Canada. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1748–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, J.B.; Pfennigwerth, N.; Gatermann, S.G.; Von Baum, H.; Essig, A. KPC-2 carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa reaching Germany. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1812–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Barrio-Tofiño, E.; López-Causapé, C.; Cabot, G.; Rivera, A.; Benito, N.; Segura, C.; Montero, M.M.; Sorlí, L.; Tubau, F.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S.; et al. Genomics and Susceptibility Profiles of Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Spain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, 01589-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, M.S.; Grass, J.E.; Bulens, S.N.; Hancock, E.B.; Phipps, E.C.; Muleta, D.; Mounsey, J.; Kainer, M.A.; Concannon, C.; Dumyati, G.; et al. Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa at US Emerging Infections Program Sites, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarca, J.A.; Salles, M.J.C.; Seas, C.; Guzmán-Blanco, M. Carbapenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumanniiin the nosocomial setting in Latin America. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Feng, Y.; Tang, G.; Qiao, F.; McNally, A.; Zong, Z. NDM Metallo-β-Lactamases and Their Bacterial Producers in Health Care Settings. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00115-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dong, N.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Carbapenem Resistance-Encoding and Virulence-Encoding Conjugative Plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharman, Y.R.; Pelegrin, A.C.; Karuniawati, A.; Sedono, R.; Aditianingsih, D.; Goessens, W.H.; Klaassen, C.H.; Van Belkum, A.; Mirande, C.; Verbrugh, H.A.; et al. Epidemiology and characterisation of carbapenem-non-susceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a large intensive care unit in Jakarta, Indonesia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Riccio, M.L.; Cornaglia, G.; Pagani, L.; Lagatolla, C.; Selan, L.; Fontana, R. Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Acquired blavim Metallo-β-Lactamase Determinants, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viedma, E.; Juan, C.; Villa, J.; Barrado, L.; Orellana, M.; Sanz, F.; Otero, J.R.; Oliver, A.; Chaves, F. VIM-2–producing Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST175 Clone, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Mulet, X.; López-Causapé, C.; Juan, C. The increasing threat of Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. Drug Resist. Updat. 2015, 21–22, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrin, A.C.; Saharman, Y.R.; Griffon, A.; Palmieri, M.; Mirande, C.; Karuniawati, A.; Sedono, R.; Aditianingsih, D.; Goessens, W.H.F.; Van Belkum, A.; et al. High-Risk International Clones of Carbapenem-Nonsusceptible Pseudomonas aeruginosa Endemic to Indonesian Intensive Care Units: Impact of a Multifaceted Infection Control Intervention Analyzed at the Genomic Level. MBio 2019, 10, 02384-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimoin, A.W.; Kisalu, N.; Kebela-Ilunga, B.; Mukaba, T.; Wright, L.L.; Formenty, P.; Wolfe, N.D.; Shongo, R.L.; Tshioko, F.; Okitolonda, E.; et al. Endemic Human Monkeypox, Democratic Republic of Congo, 2001–2004. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Montero, M.; Oliver, A.; Sorlí, L.; Luque, S.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S.; Benito, N.; Grau, S. Epidemiology and Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 00031-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.L.; Octavia, S.; Ng, O.T.; Marimuthu, K.; Venkatachalam, I.; Cheng, B.; Lin, R.T.P.; Teo, J.W.P. Challenge of drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Clonal spread of NDM-1-positive ST-308 within a tertiary hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falgenhauer, L.; Schwengers, O.; Schmiedel, J.; Baars, C.; Lambrecht, O.; Heß, S.; Berendonk, T.U.; Falgenhauer, J.; Chakraborty, T.; Imirzalioglu, C. Multidrug-Resistant and Clinically Relevant Gram-Negative Bacteria Are Present in German Surface Waters. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Fu, B.; Shi, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shen, Z.; Walsh, T.R.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Contaminated in-house environment contributes to the persistence and transmission of NDM-producing bacteria in a Chinese poultry farm. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, D.-J.; Sun, R.-Y.; Mai, J.-L.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Wang, D.; Guo, W.-Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.-F.; Zhang, R.-M.; et al. Occurrence and Transmission of blaNDM-Carrying Enterobacteriaceae from Geese and the Surrounding Environment on a Commercial Goose Farm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, 00087-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, C.; Cabot, G.; Gómez-Zorrilla, S.; Zamorano, L.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.; Murillas, J.; Almirante, B.; Pomar, V.; Aguilar, M.; Granados, A.; et al. Influence of Virulence Genotype and Resistance Profile in the Mortality of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bloodstream Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusignani, L.S.; Presterl, E.; Zatorska, B.; Nest, M.V.D.; Diab-Elschahawi, M. Infection control and risk factors for acquisition of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae. A 5 year (2011–2016) case-control study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.; Sousa, A.; Ramirez, M.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Vaz, C. PHYLOViZ 2.0: Providing scalable data integration and visualization for multiple phylogenetic inference methods. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).