Phage Biocontrol of Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease on Welsh Onion Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
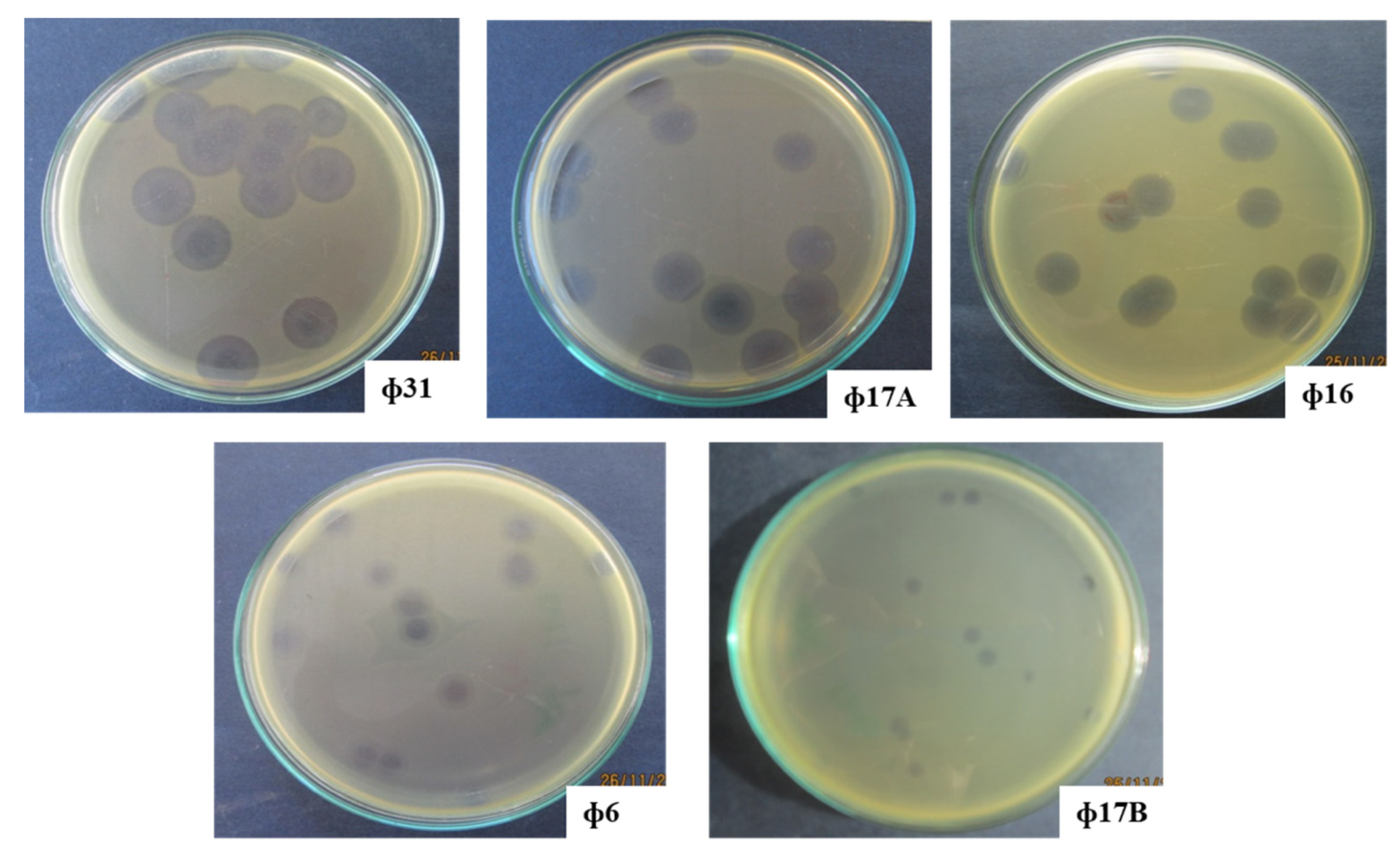
2.1. Isolation of Bacteriophages of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii, Causing Leaf Blight on Welsh Onion in the Mekong Delta in Vietnam
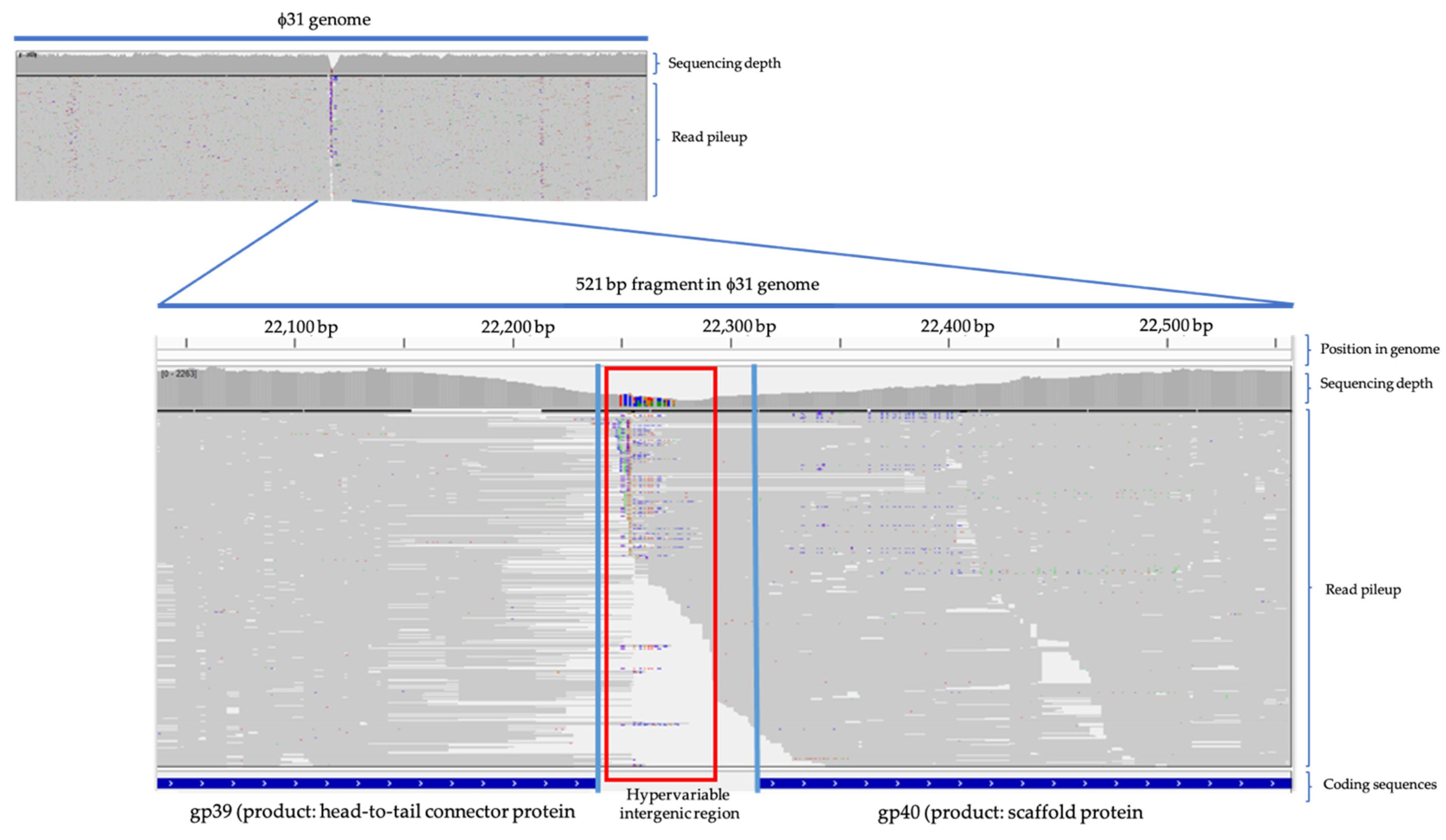
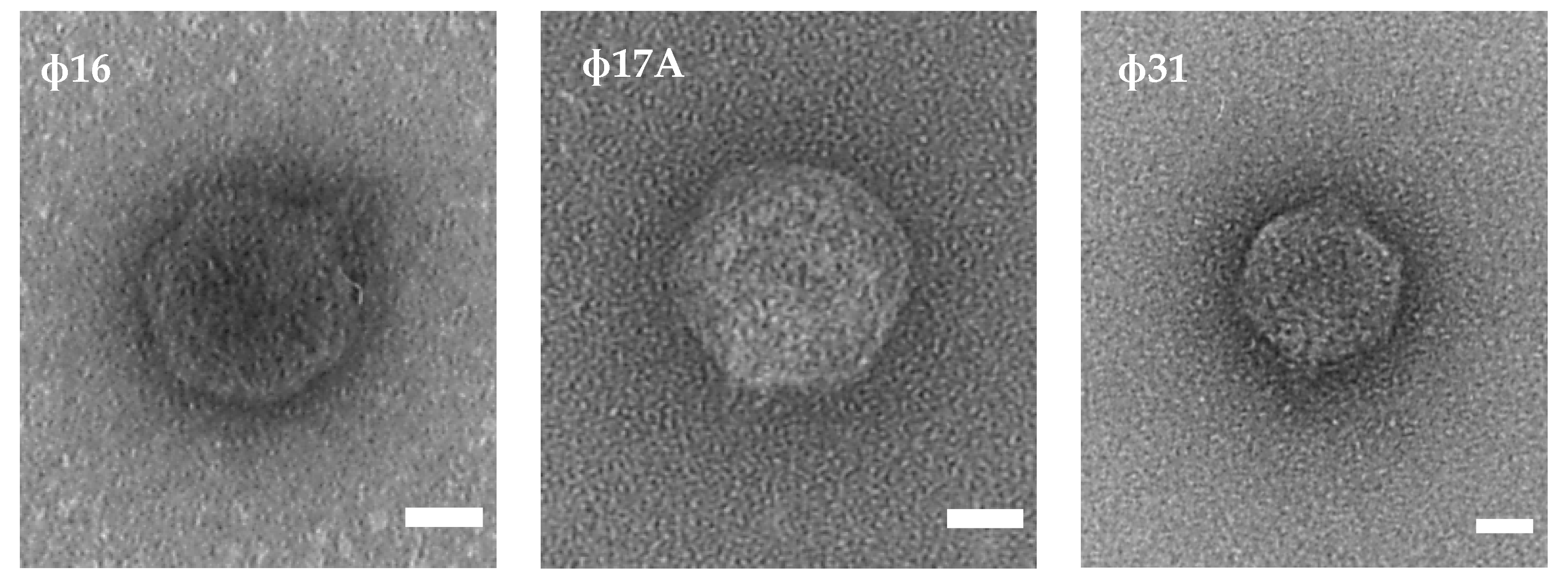
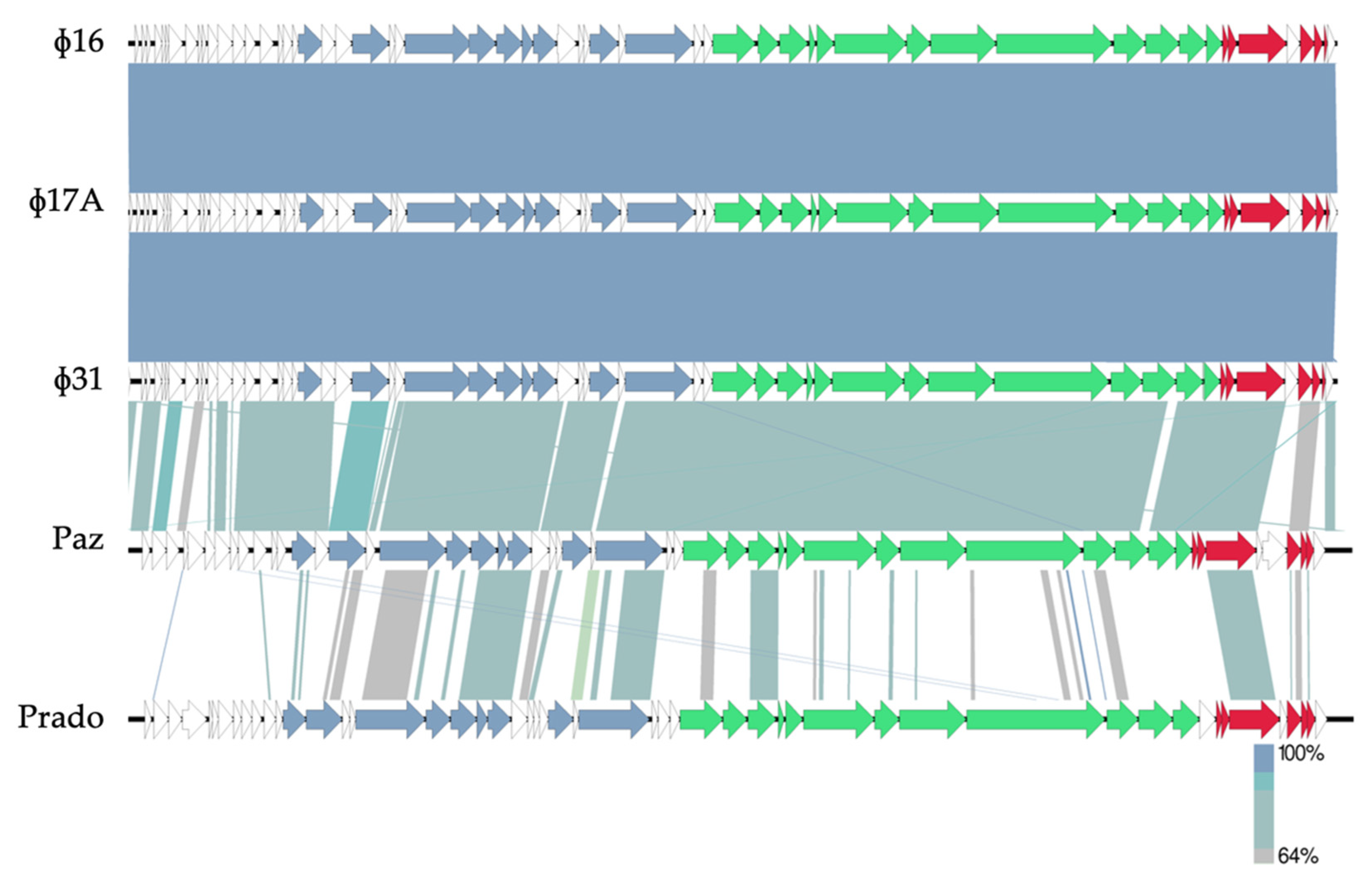
2.2. Phage Characterization by Transmission Electron Microscopy and Whole-Genome Sequencing
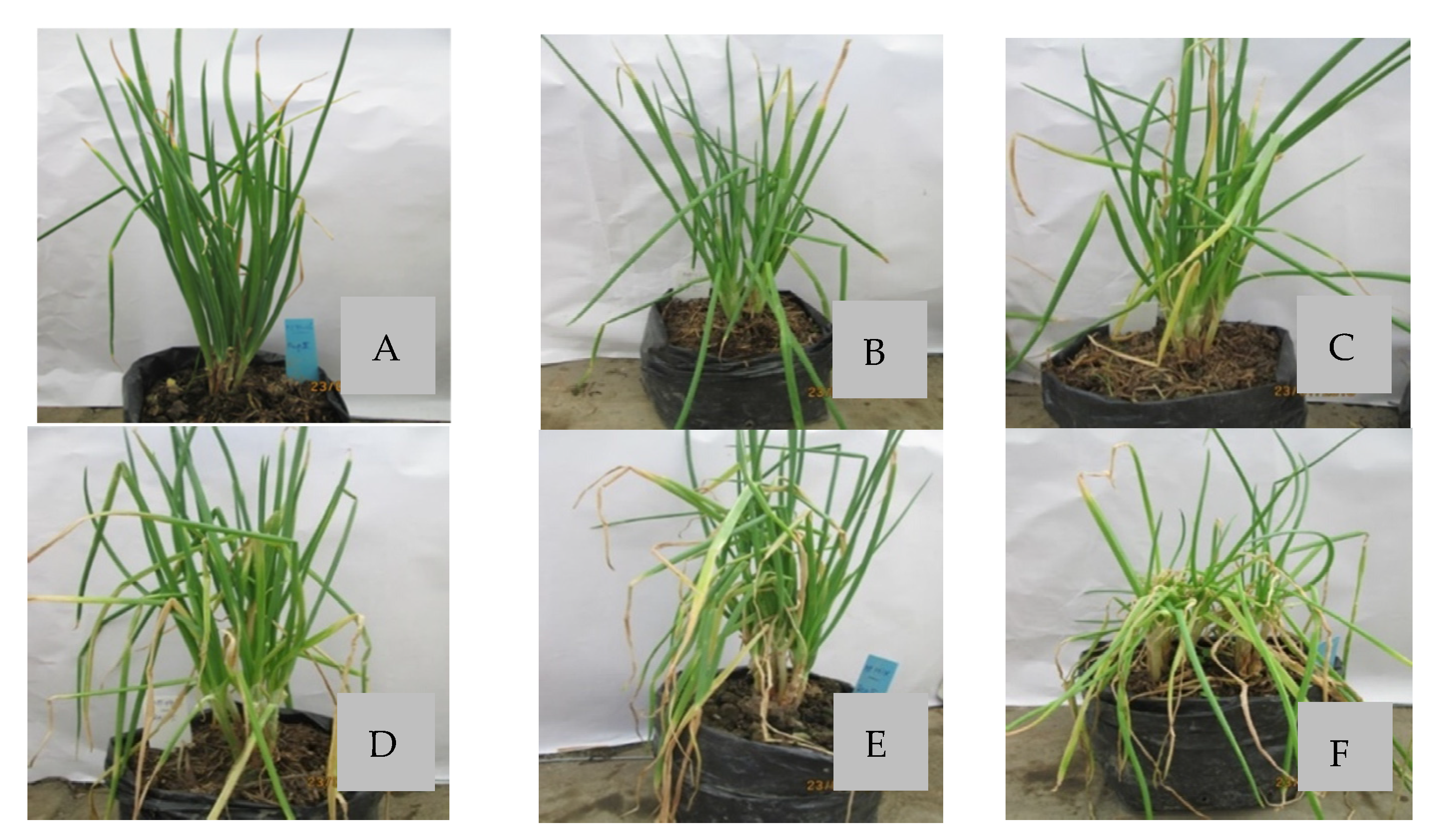
2.3. Efficacy of Phages against Bacterial Leaf Blight on Welsh Onion in Greenhouse Conditions
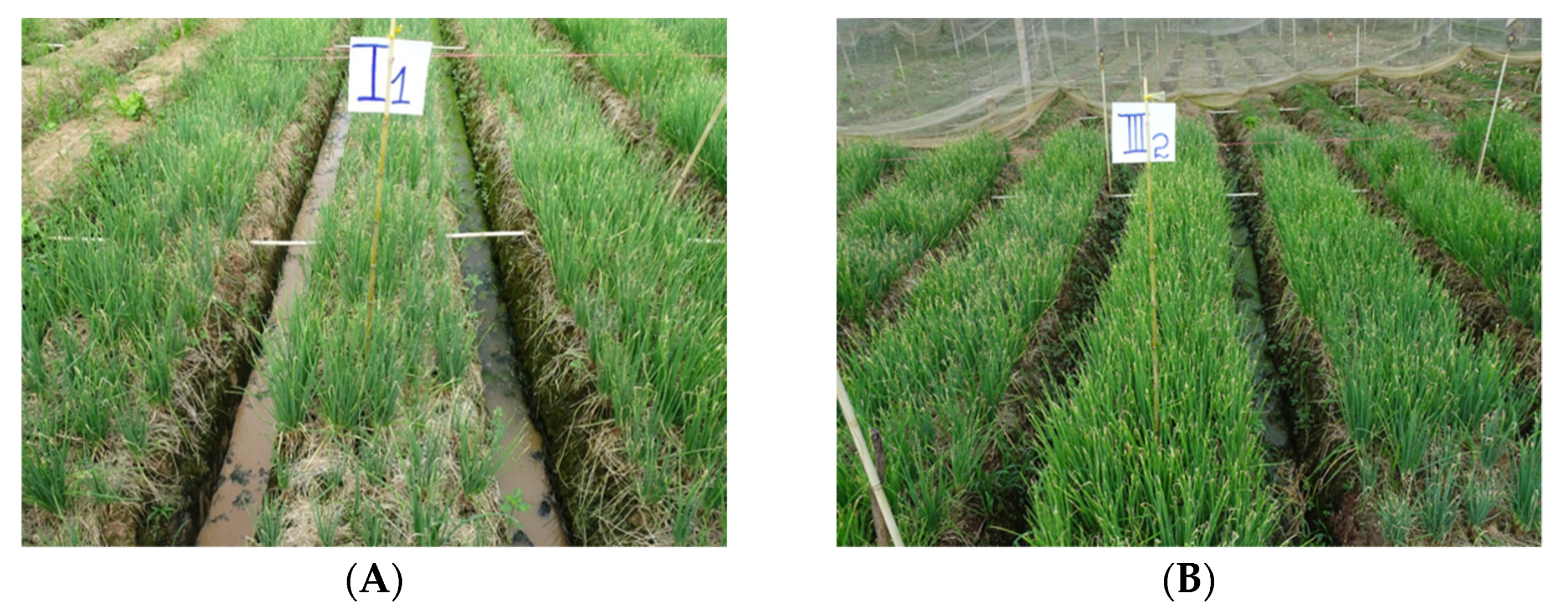
2.4. Efficacy of Bacteriophage in Controlling Bacterial Leaf Blight in Field Conditions
3. Discussion
3.1. Isolation of Promising Bacteriophages for Biocontrol of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii
3.2. Efficacy of Phages against Bacterial Leaf Blight on Welsh Onion in Greenhouse and Field Conditions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Host Bacterium Isolation and Phage Manipulations
4.2. Phage Characterization
4.3. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Phage Treatment in Greenhouse Conditions
4.4. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Phage Biocontrol in Field Conditions
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Picard, Y.; Roumagnac, P.; Legrand, D.; Humeau, L.; Robène-Soustrade, I.; Chiroleu, F.; Gagnevin, L.; Pruvost, O. Polyphasic characterization of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii associated with outbreaks of bacterial blight on three Allium species in the Mascarene archipelago. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.H.; Lang, J.M.; Bartolo, M.E.; Schwartz, H.F. Inoculum Sources and Survival of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii in Colorado. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Humeau, L.; Roumagnac, P.; Picard, Y.; Robène-Soustrade, I.; Chiroleu, F.; Gagnevin, L.; Pruvost, O. Quantitative and Molecular Epidemiology of Bacterial Blight of Onion in Seed Production Fields. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.; Conn, K.; Gabor, B.; Kao, J.; Lutton, J. Onion Disease Guide; Seminis Vegetable Seeds: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2012; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, H.F.; Otto, K. First Report of a Leaf Blight of Onion Caused by Xanthomonas campestris in Colorado. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, J.J.; Gilbertson, R.L.; Meng, X.; Davis, R.M. First Report of Xanthomonas Leaf Blight of Onion in California. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumagnac, P.; Pruvost, O.; Chiroleu, F.; Hughes, G. Spatial and Temporal Analyses of Bacterial Blight of Onion Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, P.A.; Khabbaz, S.E.; Weselowski, B.; Zhang, L. Occurrence of copper-resistant strains and a shift in Xanthomonas spp. causing tomato bacterial spot in Ontario. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooksey, D.A.; Azad, H.R.; Cha, J.S.; Lim, C.K. Copper resistance gene homologs in pathogenic and saprophytic bacterial species from tomato. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, G.W.; Wang, N. Antibiotic Resistance in Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Kuile, B.H.; Kraupner, N.; Brul, S. The risk of low concentrations of antibiotics in agriculture for resistance in human health care. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanner, S.; Drissner, D.; Walsh, F. Antimicrobial Resistance in Agriculture. MBio 2016, 7, e02227-e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Jackson, L.E.; Balogh, B.; Obradovic, A.; Iriarte, F.B.; Momol, M.T. Bacteriophages for plant disease control. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2007, 45, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtappels, D.; Fortuna, K.; Lavigne, R.; Wagemans, J. The future of phage biocontrol in integrated plant protection for sustainable crop production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 68, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, A.; Fujisawa, M.; Hamasaki, R.; Kawasaki, T.; Fujie, M.; Yamada, T. Biocontrol of Ralstonia solanacearum by treatment with lytic bacteriophages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4155–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Jousset, A.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Friman, V.-P. Phage combination therapies for bacterial wilt disease in tomato. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, B.; Canteros, B.I.; Stall, R.E.; Jones, J.B. Control of Citrus Canker and Citrus Bacterial Spot with Bacteriophages. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, J.-C.; Hung, N.B.; Yu, S.-M.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, Y.H. Diversity of bacteriophages infecting Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in paddy fields and its potential to control bacterial leaf blight of rice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.E.; Saleh, A.A.; Al-Saleh, M.A. Management of Asiatic Citrus Canker Under Field Conditions in Saudi Arabia Using Bacteriophages and Acibenzolar-S-Methyl. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.M.; Gent, D.H.; Schwartz, H.F. Management of Xanthomonas Leaf Blight of Onion with Bacteriophages and a Plant Activator. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, S.J.; Das, M.; Bhowmick, T.S.; Young, R.; Gonzalez, C.F. Characterization of novel virulent broad-host-range phages of Xylella fastidiosa and Xanthomonas. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaenssens, E.M.; Rodney Brister, J. How to Name and Classify Your Phage: An Informal Guide. Viruses 2017, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, B.D.; Ward, A.T.; Grose, J.H.; Hope, S. Software-based analysis of bacteriophage genomes, physical ends, and packaging strategies. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Suarez, S.; Jordan, B.; Heinemann, J.A. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages infecting Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis, the causal agent of walnut blight disease. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Xing, S.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.; Ruan, L.; Sun, M.; Tong, Y.; Peng, D. Isolation and characterization of a novel phage Xoo-sp2 that infects Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, A.; Ceyssens, P.-J.J.; T’Syen, J.; Van Praet, H.; Noben, J.-P.P.; Shaburova, O.V.; Krylov, V.N.; Volckaert, G.; Lavigne, R. The T7-Related Pseudomonas putida Phage phi15 Displays Virion-Associated Biofilm Degradation Properties. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, A.; Ceyssens, P.J.; Krylov, V.N.; Noben, J.P.; Volckaert, G.; Lavigne, R. Identification of EPS-degrading activity within the tail spikes of the novel Pseudomonas putida phage AF. Virology 2012, 434, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszak, T.; Shneider, M.M.; Latka, A.; Maciejewska, B.; Browning, C.; Sycheva, L.V.; Cornelissen, A.; Danis-Wlodarczyk, K.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Shashkov, A.S.; et al. The O-specific polysaccharide lyase from the phage LKA1 tailspike reduces Pseudomonas virulence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T. Filamentous phages of Ralstonia solanacearum: Double-edged swords for pathogenic bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevelige, P.E.; Fane, B.A. Building the Machines: Scaffolding Protein Functions During Bacteriophage Morphogenesis. In Viral Molecular Machines; Rossmann, M.G., Rao, V.B., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 325–350. ISBN 978-1-4614-0980-9. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, B.; Tu, Y.; Du, S.; Chen, X. Prophage LambdaSo uses replication interference to suppress reproduction of coexisting temperate phage MuSo2 in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2079–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refardt, D. Within-host competition determines reproductive success of temperate bacteriophages. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, B.; Nga, N.T.T.; Jones, J.B. Relative level of bacteriophage multiplication in vitro or in phyllosphere may not predict in planta efficacy for controlling bacterial leaf spot on tomato caused by Xanthomonas perforans. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Q.; He, X.; Baker, J.L.; Xiong, K.; Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; et al. Development of a Bacteriophage Cocktail to Constrain the Emergence of Phage-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kering, K.K.; Kibii, B.J.; Wei, H. Biocontrol of phytobacteria with bacteriophage cocktails. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0879695773. [Google Scholar]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattam, A.R.; Davis, J.J.; Assaf, R.; Boisvert, S.; Brettin, T.; Bun, C.; Conrad, N.; Dietrich, E.M.; Disz, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; et al. Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource center. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D535–D542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, T.; Harris, S.R.; Berriman, M.; Parkhill, J.; Mcquillan, J.A. Artemis: An integrated platform for visualization and analysis of high-throughput sequence-based experimental data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Gangavarapu, K.; Quick, J.; Matteson, N.L.; De Jesus, J.G.; Main, B.J.; Tan, A.L.; Paul, L.M.; Brackney, D.E.; Grewal, S.; et al. An amplicon-based sequencing framework for accurately measuring intrahost virus diversity using PrimalSeq and iVar. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Location (Mekong Delta, Vietnam) | Host Isolate | Bacteriophage Isolate |
|---|---|---|
| Binh Tan-Vinh Long | XaaVL02 | |
| Chau Phu-An Giang | XaaAG04 | |
| Binh Tan-Vinh Long | XaaVL05 | Φ5A, Φ5B |
| Binh Tan-Vinh Long | XaaVL06 | Φ6 |
| Binh Tan-Vinh Long | XaaVL07 | Φ7A, Φ7B |
| O Mon-Can Tho | XaaCT10 | |
| Hiep Thanh-Bac Lieu | XaaBL11 | |
| Vinh Trach Đong-Bac Lieu | XaaBL12 | |
| Hiep Thanh-Bac Lieu | XaaBL13 | Φ14 |
| Hiep Thanh-Bac Lieu | XaaBL14 | Φ16 |
| Vinh Trach Đong-Bac Lieu | XaaBL17 | Φ17A, Φ17B |
| Vinh Chau-Soc Trang | XaaST22 | Φ31 |
| Xaa Strain | Xaa Phage | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ5A | Φ5B | Φ6 | Φ7A | Φ7B | Φ14 | Φ16 | Φ17A | Φ17B | Φ31 | |
| XaaVL02 | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| XaaAG04 | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | + | − | + |
| XaaVL05 | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + |
| XaaVL06 | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| XaaVL07 | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| XaaCT10 | + | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| XaaBL11 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| XaaBL12 | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| XaaBL13 | + | + | + | − | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| XaaBL14 | + | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | − | + |
| XaaBL17 | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| XaaST22 | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + |
| Total | 5 | 5 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 12 |
| Phage Isolate | Location of Isolation | Halo Diameter (mm) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | ||
| Φ6 | Binh Tan-Vinh Long | 4.9 b | 5.9 c | 8.7 b |
| Φ16 | Vinh Trach Dong-Bac Lieu | 5.9 a | 11.2 a | 12.7 a |
| Φ17A | Hiep Thanh-Bac Lieu | 5.2 b | 7.2 b | 10.3 b |
| Φ17B | Hiep Thanh-Bac Lieu | 3.9 c | 6.0 c | 6.6 c |
| Φ31 | Vinh Chau-Soc Trang | 6.5 a | 11.5 a | 12.3 a |
| Treatment | Percentage of Infected Leaf Area (%) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 dai 2 | 7 dai 2 | 9 dai 2 | |
| Φ16 | 20.2 b | 33.2 b | 37.2 b |
| Φ17A | 22.6 b | 38.9 b | 39.8 b |
| Φ31 | 11.4 c | 22.4 c | 26.6 c |
| Three-phage cocktail | 26.3 ab | 40.3 b | 43.3 b |
| Starner | 7.7 c | 15.7 c | 18.3 d |
| Bacteria only | 30.5 a | 51.2 a | 67.5 a |
| Treatment | Density of Bacteriophage on Leaf Surface (pfu/g leaf) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 hai 2 | 48 hai 2 | 72 hai 2 | |
| Φ16 | 3.53 b | 8.55 a | 7.35 bc |
| Φ17A | 4.04 ab | 8.42 a | 7.89 b |
| Φ31 | 3.97 b | 8.73 a | 9.03 a |
| Three-phage cocktail | 4.15 a | 7.60 b | 6.97 c |
| Treatments | Percentage of Leaf Area Infection (%) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 dai 2 | 6 dai 2 | 8 dai 2 | |
| 105 pfu/mL | 8.2 b | 21.4 b | 43.1 b |
| 106 pfu/mL | 6.1 bc | 16.6 bc | 34.8 c |
| 107 pfu/mL | 3.3 cd | 9.4 cd | 20.3 d |
| 108 pfu/mL | 0.6 d | 4.9 d | 18.4 d |
| Control | 15.9 a | 34.1 a | 60.0 a |
| Treatments | Disease Index 1 | AUDPC 3 | Actual Yield (kg/25 m2) | Commercial Yield (kg/25 m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 dai 2 | 9 dai 2 | 15 dai 2 | ||||
| Control | 18.3 a | 23.2 a | 28.2 a | 288.8 a | 31.4 b | 26.3 b |
| Φ31 | 11.5 b | 13.1 c | 18.2 bc | 178.8 b | 34.0 ab | 30.9 a |
| Three-phage cocktail | 13.1 b | 17.8 b | 22.1 b | 216.6 b | 33.9 ab | 29.0 ab |
| Starner | 13.9 b | 14.6 bc | 15.9 c | 189.2 b | 34.8 a | 31.3 a |
| p-value 4 | 0.0087 | 0.0030 | 0.0013 | 0.0001 | 0.0238 | 0.0027 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nga, N.T.T.; Tran, T.N.; Holtappels, D.; Kim Ngan, N.L.; Hao, N.P.; Vallino, M.; Tien, D.T.K.; Khanh-Pham, N.H.; Lavigne, R.; Kamei, K.; et al. Phage Biocontrol of Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease on Welsh Onion Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050517
Nga NTT, Tran TN, Holtappels D, Kim Ngan NL, Hao NP, Vallino M, Tien DTK, Khanh-Pham NH, Lavigne R, Kamei K, et al. Phage Biocontrol of Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease on Welsh Onion Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(5):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050517
Chicago/Turabian StyleNga, Nguyen Thi Thu, Tran Ngoc Tran, Dominique Holtappels, Nguyen Le Kim Ngan, Nguyen Phuoc Hao, Marta Vallino, Doan Thi Kieu Tien, Nguyen Huan Khanh-Pham, Rob Lavigne, Kaeko Kamei, and et al. 2021. "Phage Biocontrol of Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease on Welsh Onion Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii" Antibiotics 10, no. 5: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050517
APA StyleNga, N. T. T., Tran, T. N., Holtappels, D., Kim Ngan, N. L., Hao, N. P., Vallino, M., Tien, D. T. K., Khanh-Pham, N. H., Lavigne, R., Kamei, K., Wagemans, J., & Jones, J. B. (2021). Phage Biocontrol of Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease on Welsh Onion Caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. allii. Antibiotics, 10(5), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050517









