Microbial Photoinactivation by Visible Light Results in Limited Loss of Membrane Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
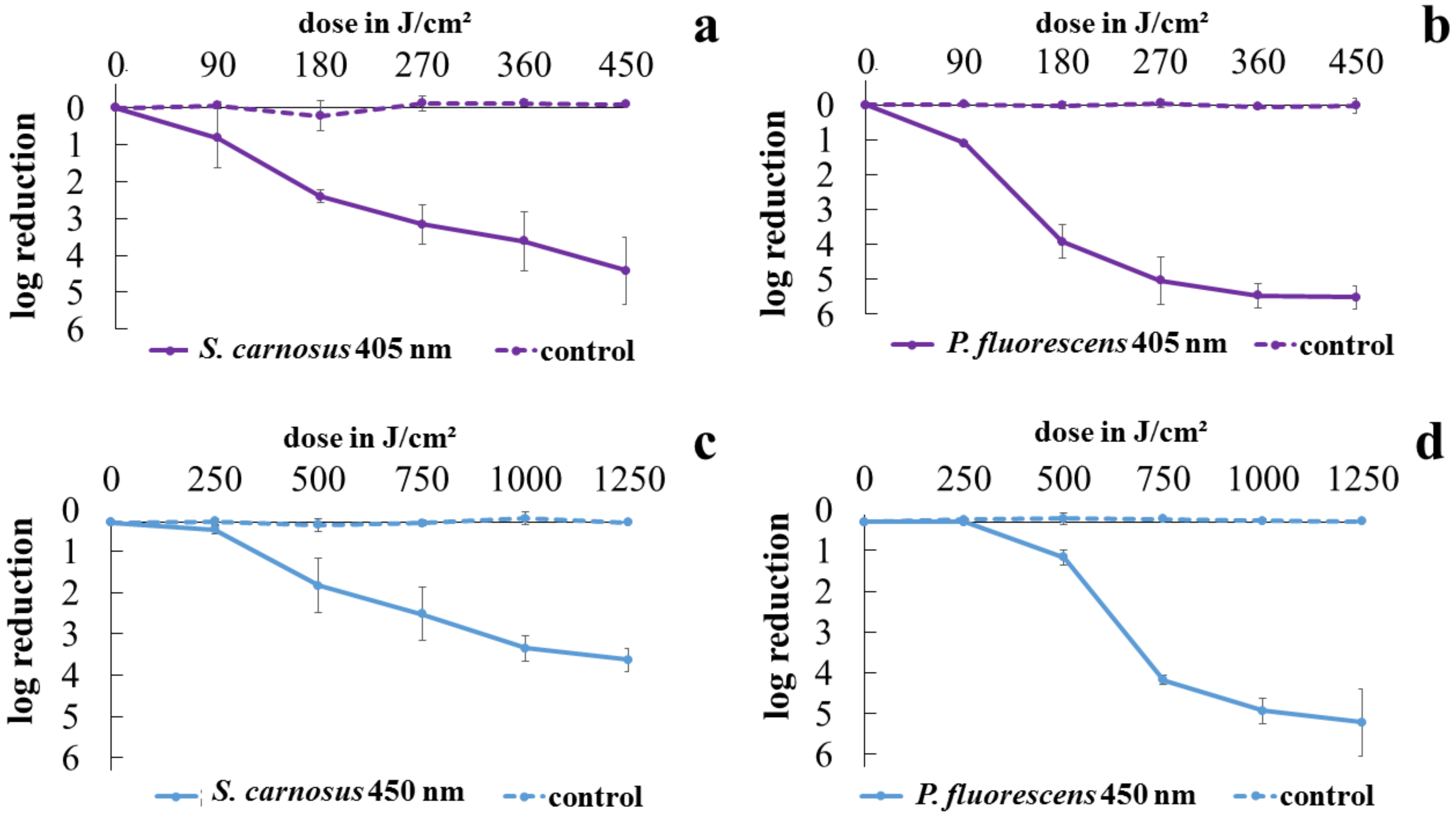
2.1. Viability Determination with Colony Forming Units
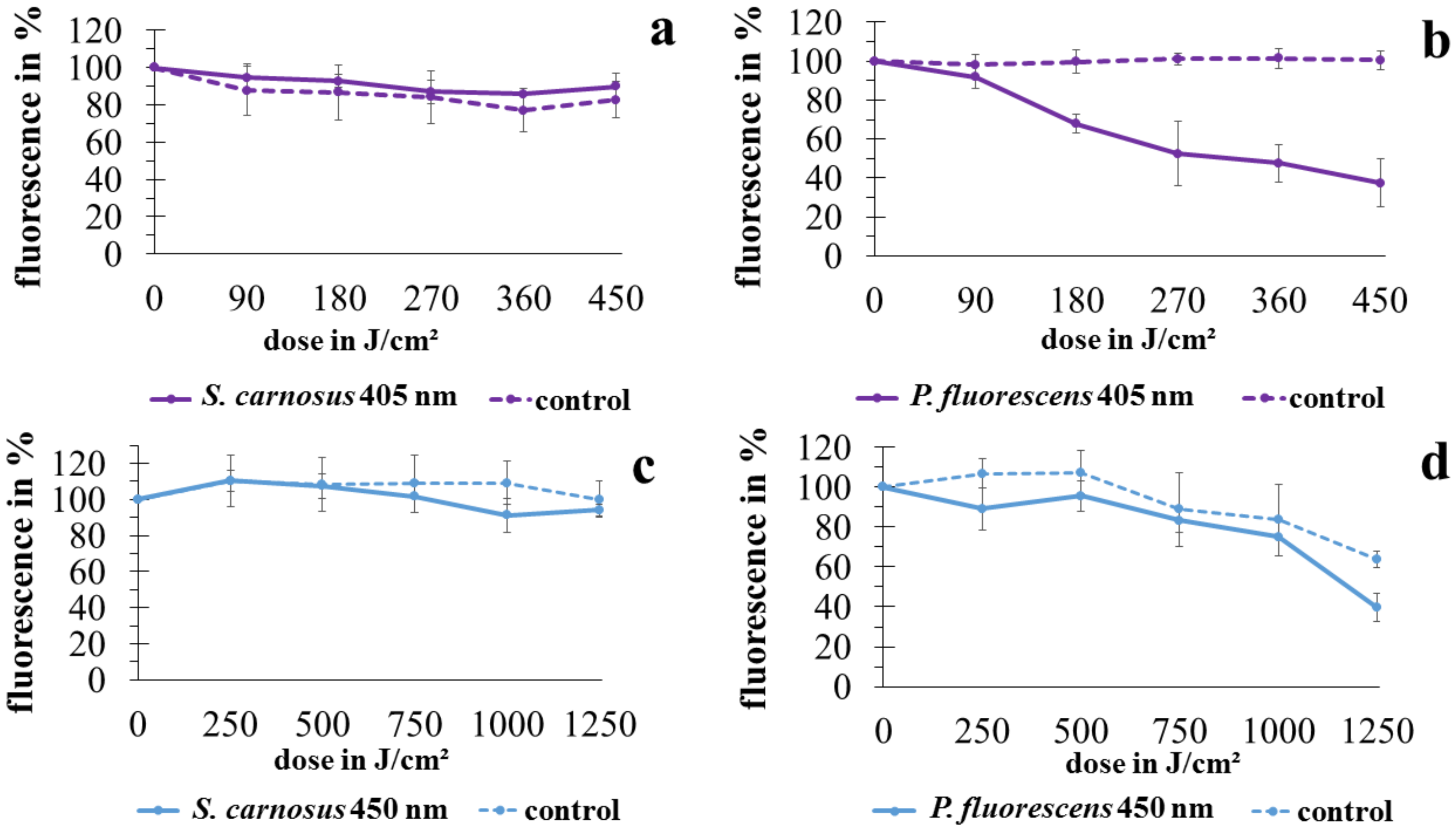
2.2. Vitality Determination with ATP Assay
2.3. Fluorescence Staining
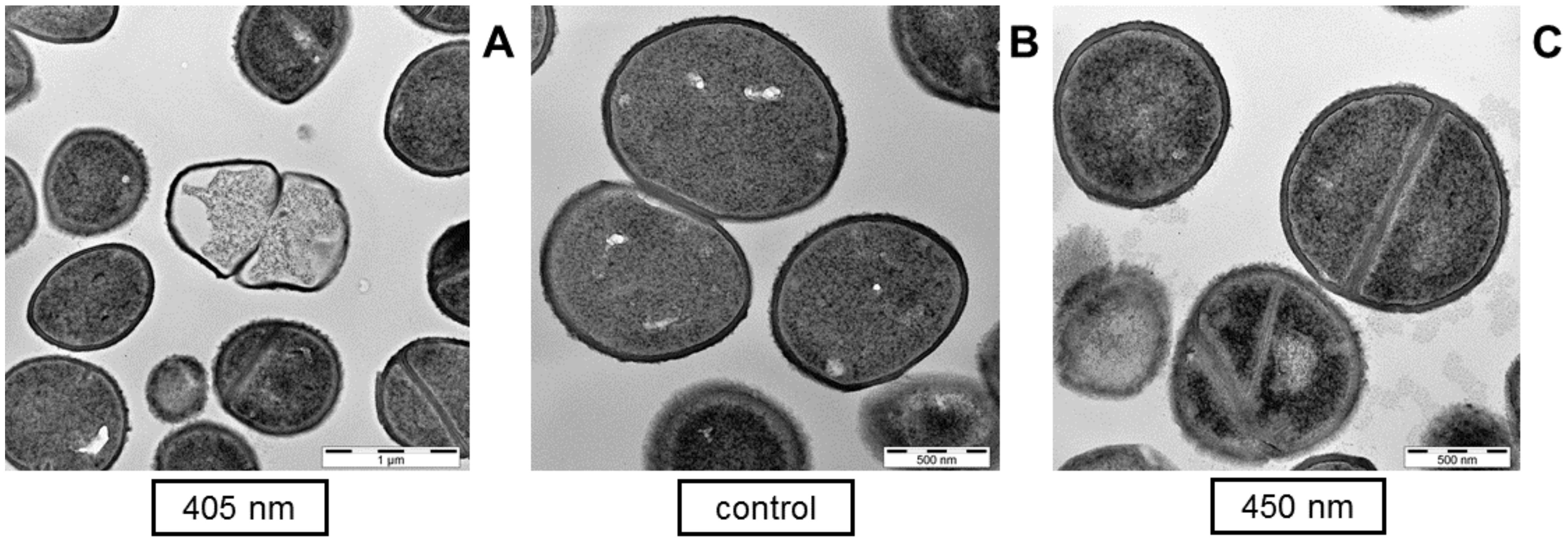
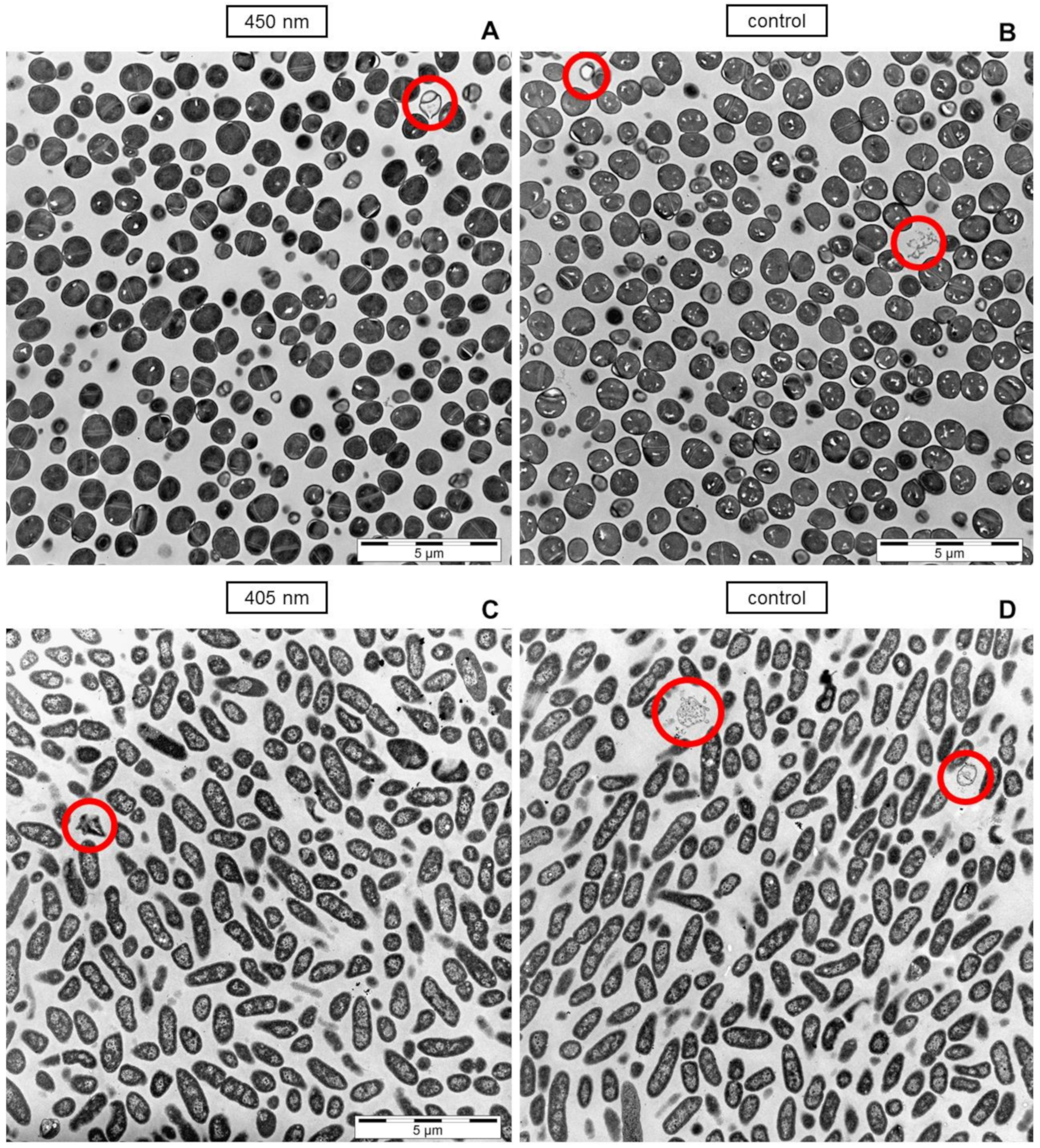
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Irradiation Setup
4.3. Viability Determination with Colony Forming Units
4.4. Vitality Determination with ATP Assay
4.5. Fluorescence Staining
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sicks, B.; Hönes, K.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Blue LEDs in Endotracheal Tubes May Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2020, 38, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehatou, C.; Logunov, S.L.; Dunman, P.M.; Haidaris, C.G.; Klubben, W.S. Characterizing the Antimicrobial Properties of 405 nm Light and the Corning® Light-Diffusing Fiber Delivery System. Lasers Surg. Med. 2019, 51, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, R.A.; Bs, J.V.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmadi, A.; Khalil, A.; Ms, M.J.T.; Nishioka, N.S.; Hamblin, M.R. Helicobacter pylori in patients can be killed by visible light. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 36, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, H.; Malik, Z.; Harth, Y.; Nitzan, Y. Eradication of Propionibacterium acnes by its endogenic porphyrins after illumination with high intensity blue light. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 35, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenes, K.; Wenzel, U.; Hessling, M. Realisation and assessment of a low-cost LED device for contact lens disinfection by visible violet light. Biomed. Tech. Eng. 2020, 65, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenes, K.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Enhancement of Contact Lens Disinfection by Combining Disinfectant with Visible Light Irradiation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, M.; Booth, M.; Anderson, J.; MacGregor, S.; Woolsey, G.; Coia, J.; Hamilton, K.; Gettinby, G. Continuous decontamination of an intensive care isolation room during patient occupancy using 405 nm light technology. J. Infect. Prev. 2013, 14, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, M.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G.; Woolsey, G. High-intensity narrow-spectrum light inactivation and wavelength sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endarko, E.; Maclean, M.; Timoshkin, I.V.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G. High-Intensity 405 nm Light Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenes, K.; Wenzel, U.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Photoinactivation Sensitivity of Staphylococcus carnosus to Visible-light Irradiation as a Function of Wavelength. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 96, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavskii, V.; Mikulich, A.; Tretyakova, A.; Leusenka, I.; Plavskaya, L.; Kazyuchits, O.; Dobysh, I.; Krasnenkova, T. Porphyrins and flavins as endogenous acceptors of optical radiation of blue spectral region determining photoinactivation of microbial cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 183, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Viveiros, J.; Yang, C.; Ahmadi, A.; Ganz, R.A.; Tolkoff, M.J. Helicobacter pylori Accumulates Photoactive Porphyrins and Is Killed by Visible Light. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, M.; MacGregor, S.; Anderson, J.; Woolsey, G. The role of oxygen in the visible-light inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2008, 92, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Abrahamse, H. Oxygen-Independent Antimicrobial Photoinactivation: Type III Photochemical Mechanism? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, K.; Maclean, M.; Grant, M.H.; Ramakrishnan, P.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G. The effects of 405 nm light on bacterial membrane integrity determined by salt and bile tolerance assays, leakage of UV-absorbing material and SYTOX green labelling. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Gupta, A.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Sherwood, M.E.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Kielian, T.; Hamblin, M.R. Blue Light Eliminates Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Infected Mouse Skin Abrasions. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2013, 31, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biener, G.; Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Bumah, V.V.; Hussey, G.; Stoneman, M.R.; Enwemeka, C.S.; Raicu, V. Blue/violet laser inactivates methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by altering its transmembrane potential. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 170, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Mikš-Krajnik, M.; Kumar, A.; Ghate, V.; Yuk, H.-G. Antibacterial effect and mechanism of high-intensity 405 ± 5 nm light emitting diode on Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus under refrigerated condition. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 153, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Mikš-Krajnik, M.; Kumar, A.; Yuk, H.-G. Inactivation by 405 ± 5 nm light emitting diode on Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, and Shigella sonnei under refrigerated condition might be due to the loss of membrane integrity. Food Control 2016, 59, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouiai, B.; Thwaite, J.E.; Laws, T.R.; Commichau, F.M.; Setlow, B.; Setlow, P.; Moeller, R. Role of DNA Repair and Protective Components in Bacillus subtilis Spore Resistance to Inactivation by 400-nm-Wavelength Blue Light. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Yuk, H.-G. Antibacterial Mechanism of 405-Nanometer Light-Emitting Diode against Salmonella at Refrigeration Temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 83, 02582-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Bang, W.S.; Yuk, H.-G. 405 ± 5 nm light emitting diode illumination causes photodynamic inactivation of Salmonella spp. on fresh-cut papaya without deterioration. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grangeteau, C.; Lepinois, F.; Winckler, P.; Perrier-Cornet, J.-M.; Dupont, S.; Beney, L. Cell Death Mechanisms Induced by Photo-Oxidation Studied at the Cell Scale in the Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumah, V.V.; Aboualizadeh, E.; Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Eells, J.T.; Enwemeka, C.S.; Hirschmugl, C.J. Spectrally resolved infrared microscopy and chemometric tools to reveal the interaction between blue light (470 nm) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 167, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, T.L.; Drum, B.E. RNA-Seq reveals changes in the Staphylococcus aureus transcriptome following blue light illumination. Genomics Data 2016, 9, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.; Yao, Y.; Fu, X.; Yu, W.; Cai, R.; Yao, M. 460 nm visible light irradiation eradicates MRSA via inducing prophage activation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 166, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gupta, A.; Huang, Y.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Sherwood, M.E.; Baer, D.G.; Hamblin, M.R.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Therapy for Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection in a Mouse Burn Model: Implications for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Combat-related Wound Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 209, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sherwood, M.E.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Hooper, D.C.; Hamblin, M.R.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial blue light inactivation of Candida albicans: In vitro and in vivo studies. Virulence 2016, 7, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.-E.; Lee, S.-Y. Antibacterial effect and mechanisms of action of 460–470 nm light-emitting diode against Listeria monocytogenes and Pseudomonas fluorescens on the surface of packaged sliced cheese. Food Microbiol. 2020, 86, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Gupta, A.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Yin, R.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Sherwood, M.E.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Blue Light Rescues Mice from Potentially Fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Burn Infection: Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanism of Action. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 57, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Chu, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, T.; Hu, X. Changes of Intracellular Porphyrin, Reactive Oxygen Species, and Fatty Acids Profiles During Inactivation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Antimicrobial Blue Light. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomb, R.M.; MacLean, M.; Coia, J.E.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G. Assessment of the potential for resistance to antimicrobial violet-blue light in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.M.; Bhayana, B.; Hamblin, M.R.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial blue light inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by photo-excitation of endogenous porphyrins: In vitro and in vivo studies. Lasers Surg. Med. 2016, 48, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacka-Zdonczyk, A.; Wozniak, A.; Pieranski, M.; Woziwodzka, A.; Bielawski, K.P.; Grinholc, M. Development of Staphylococcus aureus tolerance to antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation and antimicrobial blue light upon sub-lethal treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guffey, J.S.; Payne, W.; Jones, T.; Martin, K. Evidence of Resistance Development by Staphylococcus aureus to an In Vitro, Multiple Stage Application of 405 nm Light from a Supraluminous Diode Array. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2013, 31, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenes, K.; Hess, M.; Vatter, P.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. 405 nm and 450 nm photoinactivation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 8, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, S.; Nunes, C.S.M.; Endringer, D.C.; De Andrade, T.U.; Tarnok, A.; Lenz, D. Trypan blue as an affordable marker for automated live-dead cell analysis in image cytometry. Scanning 2016, 38, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strober, W. Trypan Blue Exclusion Test of Cell Viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2001, 21, A.3B.1–A.3B.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwolek-Mirek, M.; Zadrag-Tecza, R. Comparison of methods used for assessing the viability and vitality of yeast cells. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, M.; MacGregor, S.J.; Anderson, J.G.; Woolsey, G. Inactivation of Bacterial Pathogens following Exposure to Light from a 405-Nanometer Light-Emitting Diode Array. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, F.D.; Thwaite, J.E.; Burt, R.; Laws, T.R.; Raguse, M.; Moeller, R.; Webber, M.A.; Oppenheim, B.A. Antibacterial Activity of Blue Light against Nosocomial Wound Pathogens Growing Planktonically and as Mature Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4006–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dong, J.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G. Blue light therapy to treat Candida vaginitis with comparisons of three wavelengths: An in vitro study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ghate, V.; Kim, M.; Zhou, W.; Khoo, G.H.; Yuk, H. Antibacterial efficacy of 405, 460 and 520 nm light emitting diodes on Lactobacillus plantarum, Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enwemeka, C.S.; Williams, D.; Enwemeka, S.K.; Hollosi, S.; Yens, D. Blue 470-nm Light Kills Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in Vitro. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2009, 27, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braissant, O.; Astasov-Frauenhoffer, M.; Waltimo, T.; Bonkat, G. A Review of Methods to Determine Viability, Vitality, and Metabolic Rates in Microbiology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 547458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomb, R.M.; White, T.A.; Coia, J.E.; Anderson, J.G.; MacGregor, S.J.; MacLean, M. Review of the Comparative Susceptibility of Microbial Species to Photoinactivation Using 380–480 nm Violet-Blue Light. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessling, M.; Spellerberg, B.; Hoenes, K. Photoinactivation of bacteria by endogenous photosensitizers and exposure to visible light of different wavelengths—A review on existing data. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 364, fnw270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenes, K.; Bauer, R.; Meurle, T.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Inactivation Effect of Violet and Blue Light on ESKAPE Pathogens and Closely Related Non-pathogenic Bacterial Species—A Promising Tool Against Antibiotic-Sensitive and Antibiotic-Resistant Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 3429. [Google Scholar]
- Sassoubre, L.M.; Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B. Mechanisms for Photoinactivation of Enterococcus faecalis in Seawater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7776–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berney, M.; Weilenmann, H.-U.; Egli, T. Flow-cytometric study of vital cellular functions in Escherichia coli during solar disinfection (SODIS). Microbiology 2006, 152, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, F.; Berney, M.; Scheifele, M.; Weilenmann, H.-U.; Egli, T. Solar disinfection (SODIS) and subsequent dark storage of Salmonella typhimurium and Shigella flexneri monitored by flow cytometry. Microbiology 2009, 155, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, B.; Wunderlich, J.; Muranyi, P. Pulsed light induced damages in Listeria innocua and Escherichia coli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Sasaki, H.; Toyama, T.; Araki, M.; Fujioka, J.; Tsukiyama, K.; Hamada, N.; Yoshino, F. Antimicrobial effect of blue light using Porphyromonas gingivalis pigment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Dai, T.; Wang, X. Inactivation of Cronobacter sakazakii by blue light illumination and the resulting oxidative damage to fatty acids. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, E.; Faustino, M.A.; Neves, M.G.; Cunha, A.; Tome, J.; Almeida, A. An insight on bacterial cellular targets of photodynamic inactivation. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitzan, Y.; Kauffman, M. Endogenous Porphyrin Production in Bacteria by δ-Aminolaevulinic Acid and Subsequent Bacterial Photoeradication. Lasers Med. Sci. 1999, 14, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morici, P.; Battisti, A.; Tortora, G.; Menciassi, A.; Checcucci, G.; Ghetti, F.; Sgarbossa, A. The in vitro Photoinactivation of Helicobacter pylori by a Novel LED-Based Device. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.B.; Brown, M.S. Sensitivity of Strains of Escherichia coli Differing in Repair Capability to Far UV, Near UV and Visible Radiations. Photochem. Photobiol. 1976, 24, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, C.; Cypionka, H. Propidium ion enters viable cells with high membrane potential during live-dead staining. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 142, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.L.; Poot, M.; Yue, S.T.; Millard, P.J. Bacterial viability and antibiotic susceptibility testing with SYTOX green nucleic acid stain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipovsky, A.; Nitzan, Y.; Friedmann, H.; Lubart, R. Sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus Strains to Broadband Visible Light. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yao, M.; Dong, J. Application of 460 nm visible light for the elimination of Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocks, S.M. Mechanism and use of the commercially available viability stain, BacLight. Cytometry 2003, 61, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Probes. LIVE/DEAD(R) BacLight (TM) Bacterial Viability Kits. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/document-connect/document-connect.html?url=https%3A%2F%2Fassets.thermofisher.com%2FTFS-Assets%2FLSG%2Fmanuals%2Fmp07007.pdf&title=TElWRSYjNDc7REVBRCAmbHQ7aSZndDtCYWMmbHQ7L2kmZ3Q7TGlnaHQgQmFjdGVyaWFsIFZpYWJpbGl0eSBLaXRz (accessed on 22 September 2020).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoenes, K.; Bauer, R.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Microbial Photoinactivation by Visible Light Results in Limited Loss of Membrane Integrity. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030341
Hoenes K, Bauer R, Spellerberg B, Hessling M. Microbial Photoinactivation by Visible Light Results in Limited Loss of Membrane Integrity. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(3):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030341
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoenes, Katharina, Richard Bauer, Barbara Spellerberg, and Martin Hessling. 2021. "Microbial Photoinactivation by Visible Light Results in Limited Loss of Membrane Integrity" Antibiotics 10, no. 3: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030341
APA StyleHoenes, K., Bauer, R., Spellerberg, B., & Hessling, M. (2021). Microbial Photoinactivation by Visible Light Results in Limited Loss of Membrane Integrity. Antibiotics, 10(3), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030341






