Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Slaughtered Pigs and Pork in the Central Region of Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prevalence of MRSA
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility
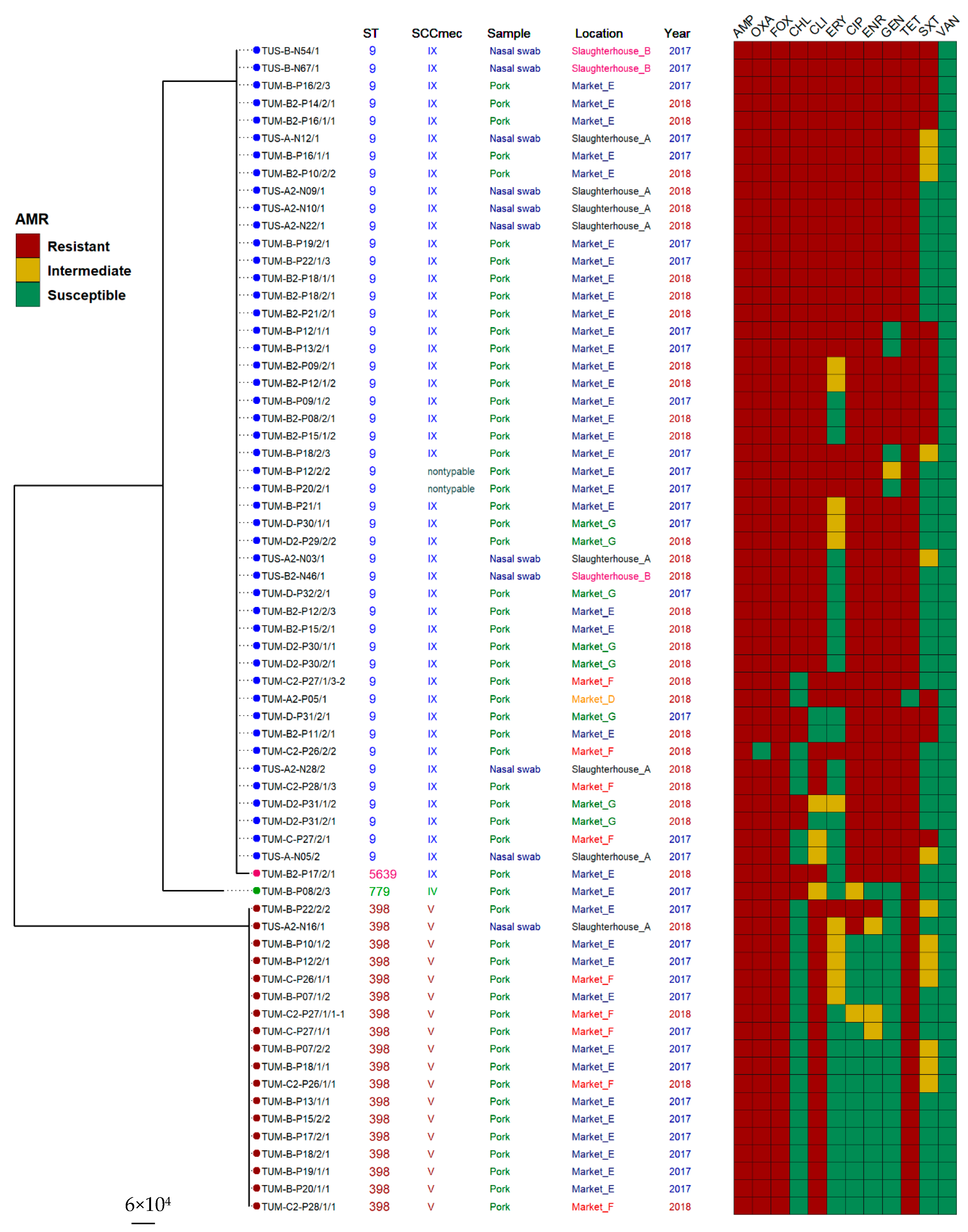
2.3. Molecular Characteristics (by Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) and SCCmec Typing) of MRSA Isolates
2.4. Association between Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Typing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
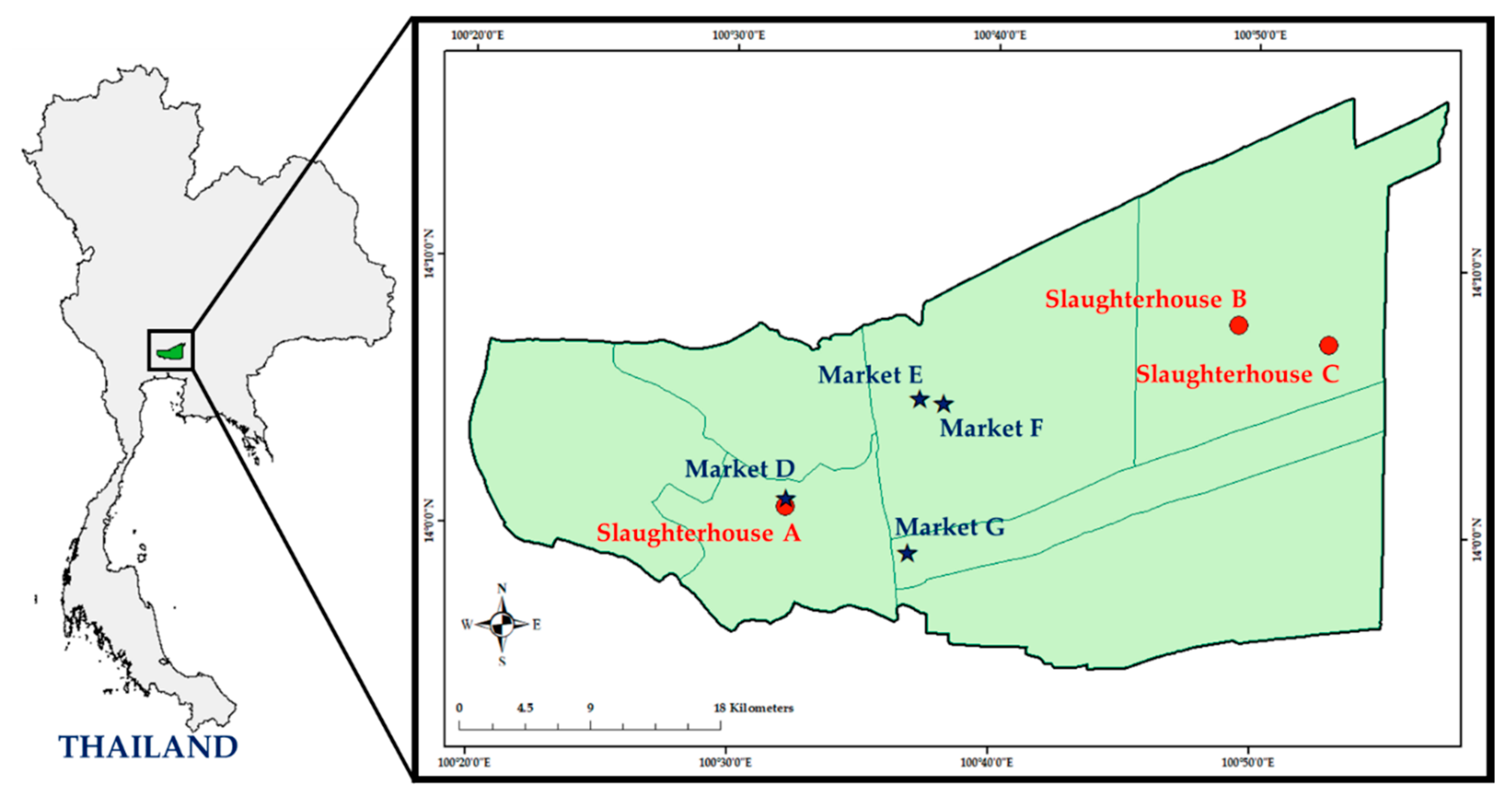
4.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
4.2. Isolation and Identification of MRSA
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.4. Molecular Typing of MRSA
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lencastre, H.; Oliveira, D.; Tomasz, A. Antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A paradigm of adaptive power. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, S.; Chung, D.R.; Lindsay, J.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Kearns, A.M.; Westh, H.; MacKenzie, F.M. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Global epidemiology and harmonisation of typing methods. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires-De-Sousa, M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among animals: Current overview. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 007, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombé, F.; Angeles Argudín, M.; Vanderhaeghen, W.; Hermans, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P. Transmission dynamics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, R.; Becker, K.; Cookson, B.; Van Gemert-Pijnen, J.E.; Harbarth, S.; Kluytmans, J.; Mielke, M.; Peters, G.; Skov, R.L.; Struelens, M.J.; et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): Burden of disease and control challenges in Europe. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C. Livestock-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Asia: An emerging issue? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butaye, P.; Argudín, M.A.; Smith, T.C. Livestock-associated MRSA and its current evolution. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 3, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.P.; Wan, M.T.; Chen, M.M.; Su, H.Y.; Lauderdale, T.L.; Chou, C.C. Molecular characterization and clonal genetic diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of pig origin in Taiwan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Li, J.; Hu, C.; Jin, S.; Li, F.; Guo, Y.; Ran, L.; Ma, Y. Isolation and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from swine and workers in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L.; O’Donoghue, M.; Moodley, A.; Ho, J.; Boost, M. Novel lineage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Hong Kong. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1998–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neela, V.K.; Zafrul, A.M.; Mariana, N.S.; Van Belkum, A.; Liew, Y.K.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E. Prevalence of ST9 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among pigs and pig handlers in Malaysia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 4138–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.; Imanishi, M.; Hinjoy, S.; Tharavichitkul, P.; Duangsong, K.; Davis, M.F.; Nelson, K.E.; Larsen, A.R.; Skov, R.L. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST9 in Pigs in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, H.C.; Mølbak, K.; Reese, C.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Selchau, M.; Sørum, M.; Skov, R.L. Pigs as source of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 infections in humans, Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.Z.; Daum, R.S. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 616–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petinaki, E.; Spiliopoulou, I. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among companion and food-chain animals: Impact of human contacts. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.; Petersen, A.; Sørum, M.; Stegger, M.; Van Alphen, L.; Valentiner-Branth, P.; Knudsen, L.K.; Larsen, L.S.; Feingold, B.; Price, L.B.; et al. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 is an increasing cause of disease in people with no livestock contact in Denmark, 1999 to -2011. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 30021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekkerkerk, W.; Van De Sande-Bruinsma, N.; Van Der Sande, M.; Tjon-A-Tsien, A.; Groenheide, A.; Haenen, A.; Timen, A.; Van Den Broek, P.; Van Wamel, W.; De Neeling, A.; et al. Emergence of MRSA of unknown origin in the Netherlands. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, J.; Sung, K.; Khan, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in food-producing and companion animals and food products. In Frontiers in Staphylococcus aureus; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Assessment of the Public Health significance of meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in animals and foods. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1–73. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.; Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Petersen, A.; Larsen, A.R.; Westh, H.; Agersø, Y.; Fetsch, A.; Kraushaar, B.; Käsbohrer, A.; et al. Evidence for human adaptation and foodborne transmission of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of Agriculture Economics. Report of Important Agricultural Goods and Trend in 2016; Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives: Bangkok, Thailand, 2015. Available online: http://www.oae.go.th/view/1/Home/EN-US (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- Charoensook, R.; Knorr, C.; Brenig, B.; Gatphayak, K. Thai pigs and cattle production, genetic diversity of livestock and strategies for preserving animal genetic resources. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchaithong, P.; Perreten, V.; Am-In, N.; Lugsomya, K.; Tummaruk, P.; Prapasarakul, N. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from pigs and swine workers in Central Thailand. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anukool, U.; O’Neill, C.E.; Butr-Indr, B.; Hawkey, P.M.; Gaze, W.H.; Wellington, E.M. Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pigs from Thailand. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Cavaco, L.M.; Sirichote, P.; Unahalekhakac, A.; Dangsakul, W.; Svendsen, C.A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Butaye, P.R.; Golding, G. SCCmec type IX element in methicillin resistant Staphylococcusaureusspa type t337 (CC9) isolated from pigs and pork in Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivbule, M.; Miklaševičs, E.; Čupāne, L.; Bērziņa, L.; Bālinš, A.; Valdovska, A. Presence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in slaughterhouse environment, pigs, carcasses, and workers. J. Vet.-Res. 2017, 61, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, X.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Dong, R.; Xue, C.; Grundmann, H.; Zhang, J. Staphylococcus aureus ST398 from slaughter pigs in northeast China. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassok, B.; Tenhagen, B.-A. From Pig to Pork: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the pork production chain. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.; Avery, B.; Reid-Smith, R. Detection and quantification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clones in retail meat products. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.; Dressler, A.; Harper, A.; Scheibel, R.; Wardyn, S.; Roberts, L.; Kroeger, J.; Smith, T. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) on retail meat in Iowa. J. Infect. Public Heal. 2011, 4, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-K.; Nam, H.-M.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Choi, M.-J.; Jung, S.-C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Song, S.-W.; Wee, S.-H. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in raw meat in Korea. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 775–778. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue, M.; Chan, M.; Ho, J.; Moodley, A.; Boost, M. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in meat from Hong Kong shops and markets. In Proceedings of the ASM Conference of Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic Bacteria and Foodborne Pathogens in Animals, Humans and the Environment, Toronto, ON, Canada, 8–11 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Detection and phylogeny of Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 398 in Taiwan. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Skov, R.L.; Han, X.; Larsen, A.R.; Larsen, J.; Sørum, M.; Wulf, M.; Voss, A.; Hiramatsu, K.; Ito, T. Novel types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec elements identified in Clonal Complex 398 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3046–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchanee, P.; Tadee, P.; Arjkumpa, O.; Love, D.; Chanachai, K.; Alter, T.; Hinjoy, S.; Tharavichitkul, P. Occurrence and characterization of livestock-associated methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureusin pig industries of northern Thailand. J. Vet.-Sci. 2014, 15, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, J.A.; Yue, H.; Pritchard, J.; Broekhuizen-Stins, M.; Huijsdens, X.; Mevius, D.J.; Bosch, T.; Van Duijkeren, E. Unexpected sequence types in livestock associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): MRSA ST9 and a single locus variant of ST9 in pig farming in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, G.; Pearson, J.; Christiansen, K.; Nimmo, G. Staphylococcus aureus Programme 2010 (SAP 2010). Community Survey. MRSA Epidemiology and Typing Report on Behalf of the Australian Group for Antimicrobial Resistance (AGAR). The Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance: Australia, 2011. Available online: https://agargroup.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/FED-REPORT-SAP210-MRSA-FINAL-shrink.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Monecke, S.; Coombs, G.; Shore, A.C.; Coleman, D.C.; Akpaka, P.; Borg, M.; Chow, H.; Ip, M.; Jatzwauk, L.; Jonas, D.; et al. A field guide to pandemic, epidemic and sporadic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnevey, P.M.; Shore, A.C.; Brennan, G.I.; Sullivan, D.J.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Slickers, P.; Coleman, D.C. Emergence of sequence type 779 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus harboring a novel pseudo staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec(SCCmec)-SCC-SCCCRISPR composite element in Irish hospitals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnevey, P.M.; Shore, A.C.; Brennan, G.I.; Sullivan, D.J.; Ehricht, R.; Monecke, S.; Coleman, D.C. Extensive genetic diversity identified among sporadic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered in Irish hospitals between 2000 and 2012. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.C.; Joshi, P.R.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Müller, E.; Gawlik, D.; Paudel, S.; Acharya, M.; Bhattarai, S.; Pokharel, S.; et al. MRSA strains in Nepalese Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta) and their environment. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boost, M.V.; Wong, A.; Ho, J.; O’Donoghue, M. Isolation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from retail meats in Hong Kong. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendlandt, S.; Schwarz, S.; Silley, P. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A food-borne pathogen? Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, L.B.; Stegger, M.; Hasman, H.; Aziz, M.; Larsen, J.; Skytt Andersen, P.; Pearson, T.; Waters, A.E.; Foster, J.T.; Schupp, J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus CC398: Host adaptation and emergence of methicillin resistance in livestock. mBio 2012, 3, e00305-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, A.; Caruso, M.; Normanno, G.; Latorre, L.; Miccolupo, A.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Intini, F.; Manginelli, T.; Santagada, G. MRSA in swine, farmers and abattoir workers in Southern Italy. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchaithong, P.; Perreten, V.; Schwendener, S.; Tribuddharat, C.; Chongthaleong, A.; Niyomtham, W.; Prapasarakul, N. Strain typing and antimicrobial susceptibility of methicillin-resistant coagulase-positive staphylococcal species in dogs and people associated with dogs in Thailand. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulitanond, A.; Ito, T.; Li, S.; Han, X.; Ma, X.X.; Engchanil, C.; Chanawong, A.; Wilailuckana, C.; Jiwakanon, N.; Hiramatsu, K. ST9 MRSA strains carrying a variant of type IX SCCmec identified in the Thai community. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinlapasorn, S.; Lulitanond, A.; Angkititrakul, S.; Chanawong, A.; Wilailuckana, C.; Tavichakorntrakool, R.; Chindawong, K.; Seelaget, C.; Krasaesom, M.; Chartchai, S.; et al. SCCmec IX in meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and meticillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from pigs and workers at pig farms in Khon Kaen, Thailand. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilan, B.A.; Jacobs, D.; Del Dot, T.; Blackall, L.L.; Hawkins, P.R.; Cox, P.T.; Goodman, A.E. rRNA sequences and evolutionary relationships among toxic and nontoxic cyanobacteria of the genus microcystis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997, 47, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Minamide, W.; Wada, K.; Nakamura, E.; Teraoka, H.; Watanabe, S. Identification of methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococci by polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI standard VET01; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, Y.; Ito, T.; Ma, X.X.; Watanabe, S.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Etienne, J.; Hiramatsu, K. Combination of multiplex PCRs for staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type assignment: Rapid identification system for mec, ccr, and major differences in Junkyard Regions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 51, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.J.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Window 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids. Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample/Place | No. of MRSA-Positive Samples/Total No. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | Total | |
| Nasal swab | |||
| Slaughterhouse A | 2/34 (5.9) | 6/34 (17.6) | 8/68 (11.8) |
| Slaughterhouse B | 2/34 (5.9) | 1/34 (2.9) | 3/68 (4.4) |
| Slaughterhouse C | 0/34 | 0/34 | 0/68 |
| Total (n) | 4/102 (3.9) | 7/102 (6.9) | 11/204 (5.4) |
| Pork | |||
| Market D | 0/6 | 1/7 (14.3) | 1/13 (7.7) |
| Market E | 22/37 (59.5) a | 14/38 (36.8) | 36/75 (48.0) |
| Market F | 3/6 (50.0) | 4/6 (66.7) a | 7/12 (58.3) |
| Market G | 3/8 (37.5) | 5/8 (62.5) | 8/16 (50.0) |
| Total (n) | 28/57 (49.1) | 24/59 (40.7) | 52/116(44.8) |
| Typing Profiles | Slaughterhouse | Market | Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 2017 | 2018 | |||||||||||||
| SCCmec Typing | ST | A | B | C | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | D | E | F | G | |
| IX | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 13 | 3 | 5 | 45 |
| V | 398 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 28 |
| NT | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| IV | 779 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| IX | 5639 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Genotype Profiles | Antimicrobial Agents (No. of Isolates) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMP | OXA | FOX | CHL | CLI | ERY | CIP | ENR | GEN | TET | SXT | VAN | ||
| ST9-SCCmec IX | (n = 45) | 45 | 44 | 45 | 38 * | 39 | 22 * | 45 * | 45 * | 42 * | 44 | 16 * | 0 |
| ST398-SCCmec V | (n = 18) | 18 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 18 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 18 | 0 | 0 |
| ST9-SCCmec NT | (n = 2) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| ST779-SCCmec IV | (n = 1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| ST5639-SCCmec IX | (n = 1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanomsridachchai, W.; Changkaew, K.; Changkwanyeun, R.; Prapasawat, W.; Intarapuk, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Yamasamit, N.; Flav Kapalamula, T.; Nakajima, C.; Suthienkul, O.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Slaughtered Pigs and Pork in the Central Region of Thailand. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020206
Tanomsridachchai W, Changkaew K, Changkwanyeun R, Prapasawat W, Intarapuk A, Fukushima Y, Yamasamit N, Flav Kapalamula T, Nakajima C, Suthienkul O, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Slaughtered Pigs and Pork in the Central Region of Thailand. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanomsridachchai, Wimonrat, Kanjana Changkaew, Ruchirada Changkwanyeun, Watsawan Prapasawat, Apiradee Intarapuk, Yukari Fukushima, Nattapong Yamasamit, Thoko Flav Kapalamula, Chie Nakajima, Orasa Suthienkul, and et al. 2021. "Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Slaughtered Pigs and Pork in the Central Region of Thailand" Antibiotics 10, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020206
APA StyleTanomsridachchai, W., Changkaew, K., Changkwanyeun, R., Prapasawat, W., Intarapuk, A., Fukushima, Y., Yamasamit, N., Flav Kapalamula, T., Nakajima, C., Suthienkul, O., & Suzuki, Y. (2021). Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Slaughtered Pigs and Pork in the Central Region of Thailand. Antibiotics, 10(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020206







