Abstract
Since 2008, veterinary authorities in Greece have implemented national control programmes (NSCPs) targeting S. Enteritidis (SE) and S. Typhimurium (ST) in poultry. We assessed the effect of the programs on the reported number of human isolates. Using monthly data for 2006–2017, we defined two groups (SE, ST) and one control group with serotypes unrelated to poultry or eggs. For SE we also analysed data for 2006–2015 due to a multi-county SE outbreak in 2016. We performed an interrupted time series analysis and used a negative binominal regression model. For both SE and ST, there was no significant trend of the isolation rate before or after NSCPs’ introduction. After the NSCPs’ introduction there was an increasing rate (IRR: 1.005, 95% CI: 1.001–1.008) for control serotypes and a decreasing one for SE (IRR: 0.990, 95% CI: 0.986–0.995) (for 2009 to 2015 analysis). From 2006 to 2017, NSCPs had a statistically significant impact on the number of SE isolates that decreased by 49% (IRR:0.511, 95% CI: 0.353–0.739). No impact was shown on the number of ST (p-value = 0.741) and control isolates (p = 0.069). As a conclusion, NSCP’s implementation was associated with decreased SE isolates and overall burden of salmonellosis; however further measures aiming at human salmonellosis due to ST, should be considered.
1. Introduction
Non-typhoidal salmonellosis is caused by bacteria of genus Salmonella spp. which is one of the most frequently isolated foodborne pathogens, accounting for 93.8 million foodborne illnesses and 155,000 deaths per year [1]. To date, over 2600 Salmonella serotypes have been identified and more than half of them belong to Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica [2].
In the EU, over 90,000 salmonellosis cases are recorded every year making salmonellosis the second most frequently reported zoonotic disease after Campylobacter spp. infection [3]. It has been estimated that the overall annual economic burden of human salmonellosis in Europe is as high as three billion euros [3]. The three most commonly reported Salmonella serotypes, belonging to Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica, are Enteritidis, Typhimurium and the monophasic variant of Typhimurium with the antigenic formula 1,4,[5],12:i:- (referred as S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium and monophasic S. Typhimurium hereafter). The risk of infection is mostly associated with the consumption of contaminated eggs, pig and poultry meat [3].
To protect consumers from Salmonella spp., the EU has adopted an integrated approach to food safety from “farm to fork” that includes the annual monitoring of salmonellosis notification rate in humans, the control of the pathogen in specific animal species and the production of food free of Salmonella [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. The control of the pathogen mainly focuses at poultry meat and eggs. Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 sets targets for the reduction of targeted salmonella serotypes in flocks of breeding hens, laying hens, broilers, breeding turkeys and fattening turkeys [6,7,8,9,10]. The targets are set on two serotypes (S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium, including monophasic S. Typhimurium), except for breeding hens for which also S. Hadar, S. Virchow and S. Infantis are also targeted. In order to achieve the targets, Member States have introduced National Salmonella Control Programmes (NSCPs) in poultry populations. NSCPs include enhanced surveillance on the basis of specific sampling protocols according to EU legislation, vaccination against S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium in poultry, implementation of strict biosecurity measures, restriction of movements and destruction or heat treatment of infected birds and eggs, in the event of the detection of targeted Salmonella serotypes in a flock of poultry [7,8,9,10,12].
In Greece, 10,321 salmonellosis cases were reported from 2004 to 2019 with a mean annual notification rate of 5.9 cases per 100,000 population [13]. S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium and monophasic S. Typhimurium accounted for 80% of the total isolated serotypes in the country [13]. NSCPs were implemented for the first time in 2007 in breeders [14]. In 2008, their implementation expanded to layers, in 2009 to broilers and since 2010, the programmes have also been covering breeding and fattening turkeys [14].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of NSCPs in poultry breeding on human salmonellosis reported number of cases.
2. Results
2.1. Descriptive Data
From 2006 to 2017, 5,432 human Salmonella spp. isolates were serotyped; 42% (2260) were S. Enteritidis, 13% (681) S. Typhimurium, 5% (247) monophasic S. Typhimurium and 40% (2244) other Salmonella serotypes. The mean number of human Salmonella spp. isolates per year was 453 (min: 241, max: 630).
Figure 1 depicts the monthly distribution of Salmonella spp., S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, monophasic S. Typhimurium and “Control Salmonella serotypes” of human isolates for the period 2006 to 2017 and the annual trend of these serotypes using moving averages. According to the Figure 1, there was a decrease in the total number of Salmonella cases, S. Enteritidis cases, and cases due to “Control Salmonella serotypes” after the implementation of NSCPs in 2008. However, the number of Salmonella cases due to the above-mentioned serotypes started to increase again in different time periods for different serotypes. S. Enteritidis increased sharply in 2016 and decreased again in 2017.
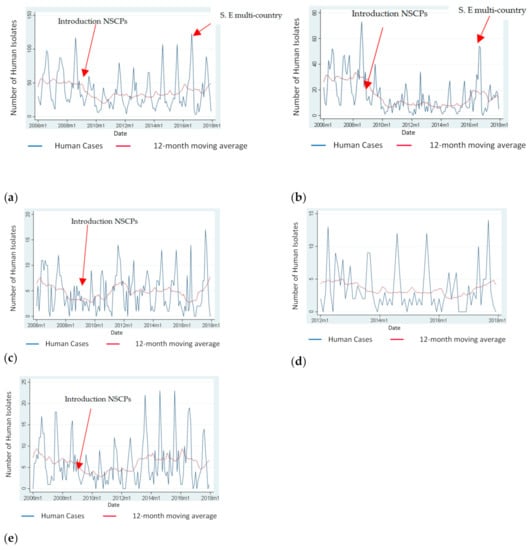
Figure 1.
Monthly number of Salmonella spp., S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, monophasic S. Typhimurium and “Control Salmonella serotypes” of human isolates and 12-month moving average.(a) Monthly cases attributed to Salmonella spp. and 12-month moving average, Greece, 2006–2017; (b) Monthly cases attributed to S. Enteritidis and 12-month moving average, Greece, 2006–2017; (c) Monthly cases attributed to S. Typhimurium and 12-month moving average, Greece, 2006–2017; (d) Monthly cases attributed to monophasic S. Typhimurium and 12-month moving average, Greece, 2012–2017 (Data on monophasic S. Typhimurium were only available since 2012 and the introduction of the NSCPs was much earlier in 2009, therefore there is no arrow in panel (d); (e) Monthly cases attributed to “Control Salmonella serotypes” (serotypes detected from human cases between 2004 and 2017 but were either not detected or rarely detected, maximum of two times each, in poultry) and 12-month moving average, Greece, 2006–2017.
From 2006 to 2017 the trend of the number of all Salmonella serotypes, and of S. Enteritidis isolates were statistically significantly decreasing while there was no significant trend for the number of S. Typhimurium, monophasic S. Typhimurium, and “Control Salmonella serotypes” (Table 1).

Table 1.
Trends of the number of Salmonella spp., S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium, monophasic S. Typhimurium and “Control Salmonella serotypes” of human isolates, Greece, 2006–2017.
2.2. Results of the Interrupted Time Series Analysis
During the study period 2006–2017, there was no evidence of significant trends in the number of S. Enteritidis isolates both, before, as well after, the introduction of the NSCPs. However, the programs had a statistically significant impact on the total number of S. Enteritidis human isolates and resulted in a statistically significant decrease of their total number by 49% (IRR: 0.511, 95% CI: 0.353–0.739).
When analysis for 2006–2015 was performed there was no trend of the number of S. Enteritidis isolates before the introduction of the intervention, however, afterwards there was a statistically significantly decreasing trend and the reported number of S. Enteritidis isolates decreased by 0.95% per month on average (IRR: 0.990, 95% CI: 0.986–0.995). The introduction of the NSCPs resulted in a statistically significant decrease by 47% (IRR: 0.526, 95% CI: 0.384–0.720) of the total number of S. Enteritidis isolates.
For S. Typhimurium we did not find a significant trend both before as well after the introduction of the NSCPs. Additionally, there was no evidence that the implementation of the intervention had an impact on the total number of S. Typhimurium isolates.
Finally, regarding the “Control Salmonella serotypes”, before the introduction of the intervention there was no significant change in the reported monthly number of those isolates, while after the introduction of the intervention there was an increase by 0.45% on average per month (IRR: 1.004, 95%CI: 1.001–1.008).
Table 2 summarises the results of the interrupted time series analysis for the evaluation of the impact of the introduction of the NSCPs on the trend and the total number of S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium and “Control Salmonella serotypes” isolates.

Table 2.
Results of the evaluation of the impact of the introduction of the National Salmonella Control Programmes (NSCPs) on the trend and total number of S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium and “Control Salmonella serotypes” of human isolates.
Figure 2 illustrates the distribution of Salmonella isolates due to: (a) S. Enteritidis (2006–2017), (b) S. Enteritidis (2006–2015), (c) S. Typhimurium, (d) “Control Salmonella serotypes” over time and the predicted number of isolates based to the model used.
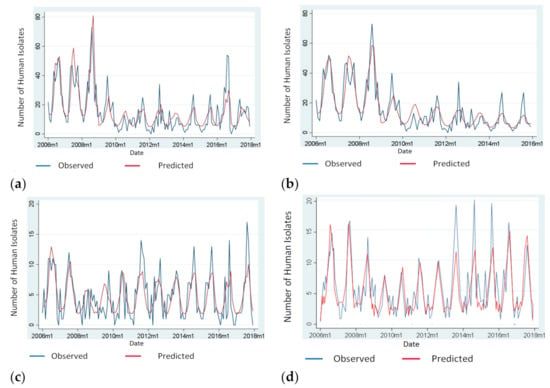
Figure 2.
Number of observed and predicted human Salmonella isolates, Greece, 2006–2017; (a) Number of observed and predicted human S. Enteritidis isolates according to the model used, Greece, 2006–2017; (b) Number of observed and predicted human S. Enteritidis isolates according to the model used, Greece, 2006–2015 (For S. Enteritidis, a sensitivity analysis was also performed for both periods 2006–2017 and 2006–2015. The reason was that in 2016 there was an excess in the number of S. Enteritidis cases in Greece probably attributed to the multi-country S. Enteritidis outbreak related to the consumption of infected Polish eggs); (c) Number of observed and predicted human S. Typhi-murium isolates according to the model used, Greece, 2006–2017; (d) Number of observed and predicted human isolates attributed to “Control Salmonella serotypes” (serotypes detected from human cases between 2004 and 2017, but were either not detected or rarely detected, the maximum of two times each, in poultry) according to the model used, Greece, 2006–2017.
3. Discussion
This is the first study in Greece evaluating the impact of NSCPs in poultry breeding on human salmonellosis reported number of cases.
Based on descriptive analysis, the number of human cases attributed to all serotypes, to S. Enteritidis, to S. Typhimurium and to “Control Salmonella serotypes” was decreased after the implementation of the NSCPs in 2008. However, after this initial decrease, the number of cases remained stable or increased for different time periods depending on the serotype.
Overall, the results of the interrupted time series analysis support that the implementation of the NSCPs was followed by a reduction of the number of the total S. Enteritidis isolates in humans. This decrease resulted in the reduction of the total number of Salmonella isolates in humans. Similarly, a reduction in the human salmonellosis cases was also reported between 2005 and 2013 in several EU countries following the coordinated approach implemented at EU level for the control of salmonella in poultry [14]. However, from 2014 to 2018, the trend in most of the member states became stable [14].
The aforementioned decrease was to be expected as according to EFSA, eggs and poultry meat are the main sources of transmission for S. Enteritidis and in Greece the NSCPs are only implemented in poultry populations [14]. Therefore, the implementation of control measures against this serotype in poultry populations is important. The positive impact of the implementation of NSCPs on human salmonellosis has also been demonstrated in other member states and at European level [14,15,16].
On the other hand, NSCPs did not have an impact on the number of S. Typhimurium isolates, although Greece has achieved the EU targets in both layers and broilers and the prevalence of S. Typhimurium in both poultry species is very low [17,18]. Therefore, we can assume that NSCPs did not affect the trend and the number of S. Typhimurium isolates and that identified cases were probably attributed to other sources of infection, such as swine animals and their products [14]. This is the reason why other countries have extended control programs to other susceptible animal species based on the results of a cost benefit analysis conducted at a national level [16,18,19].
According to our analysis, the number of reported monophasic S. Typhimurium 1,4 [5],12: i: - isolates remained at about the same levels between 2012–2016 and increased in 2017. Although this serotype has been detected from fattening turkeys in Greece [17,18], turkeys cannot be considered an important source of human monophasic S. Typhimurium infection due to the small size of the turkeys’ population in the country [17]. Taking also into account reports on the investigation of S. Typhimurium outbreaks, we can consider that pork meat and its products are important sources of monophasic S. Typhimurium infection in Greece [13].
Finally, the increasing trend of the number of “Control Salmonella serotypes” after the programmes’ implementation and the fact that programs did not have an impact on the number of “Control Salmonella serotypes” further supports our previous conclusions as we can assume that the reduction in the number of S. Enteritidis cases was not affected by a factor that had influenced Salmonella infection overall. On the other hand, the increased number of cases might suggest that other potential sources of infectivity exist and demonstrates the need for health education of the public regarding the prevention of salmonellosis infection, good hygiene and cooking practices [20]. There is no doubt that educating the public will further enhance the positive impact of the NSCPs on the protection of public health from the targeted Salmonella serotypes. Finally, it is possible that the eradication of S.Enteritidis may leave a niche for other serotypes to fill [21].
A primary limitation of our study was that the absence of MLVA and WGS data in Greece did not allow us to differentiate outbreak-related cases from sporadic ones. We considered this limitation especially important during the European S. Enteritidis multi-country outbreak in 2016 and 2017, the largest ever documented S. Enteritidis outbreak in Europe, which was attributed to Polish-eggs originating from infected flocks [13]. This is why sensitivity analysis was also performed for S. Enteritidis excluding 2016–2017 [22].
Another limitation regards the use of laboratory data on serotypes as proxy of the number of salmonellosis cases in humans, although we consider that this had a small impact on our results as the system was overall stable [23].
In conclusion, data support that the implementation of the NSCPs in poultry populations was followed by a decreased number of human salmonellosis cases. Programmes should continue, in order to keep meeting the EU targets, but for an effective public health program, the implementation of measures is needed in other animal species, as well as in all steps of food production (from farm to fork).
4. Materials and Methods
We extracted data from the National Reference Laboratory for Salmonella and Shigella (NRLSS) database in Greece for the period 2006–2017. The 2018–2019 data were excluded from the analysis as non-comparable with previous years due to changes in the operation of the reference laboratory. The NRLSS receives human Salmonella strains from the collaborating hospital laboratories across the country for serotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. This system is universal but not mandatory and specimens sent at NRLSS are a proxy of the number of diagnosed salmonellosis cases at medical services of the country [23].
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
Outbreak-related cases were excluded from the analyses. Reported cases were classified as outbreak-related when the results of investigation indicated an epidemiological link to other reported salmonellosis cases with the same serotype. Time-series were plotted by month and summary statistics of the number of isolates per month and year were calculated to describe the distributions on possible outliers and missing data. Proportions of the different targeted Salmonella serotypes were also calculated and the distribution of the different serotypes over time (month and year) was plotted. Moreover, data were assessed for stationarity by checking for constant mean using a linear regression model and constant variance using a mean versus variance plot and autocorrelation (autocorrelation and partial autocorrelation). Normality was assessed using a Shapiro-Wilk normality test. To describe the trend and seasonality of the time series we used moving averages. Windows size 6 and 12 were used to highlight seasonality, and annual trend, respectively. Additional cyclical patterns were also assessed using spectral analysis.
Analysis was conducted separately for (a) Salmonella spp. serotypes, (b) S. Enteritidis, (c) S. Typhimurium, (d) monophasic S. Typhimurium, (e) “control Salmonella serotypes”.
“Control Salmonella serotypes” were those detected from human cases between 2004 and 2017, but were, either not detected or rarely detected (maximum of two times each) in poultry based on the data of the surveillance system for animal salmonellosis of the Greek Ministry of Rural Development and Food for 2011–2017 [17].
4.2. Interrupted Time Series Analysis
To assess the impact of the intervention (introduction of NSCPs) on the reported number of human salmonellosis cases, we used interrupted time series analysis and looked for changes after the intervention in important parameters of the model; intercept, slope and cyclical patterns. We defined intervention (S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium) and control series.
Monophasic S. Typhimurium isolates were excluded as they have started to be recorded separately from S. Typhimurium only since 2012, after NSCPs had been launched.
Control group (“Control Salmonella serotypes”) was used to test if the results for the targeted Salmonella serotypes had been affected by factors other than NSCPs’ implementation. This group was used as a “baseline” of the trend of the reported number of human salmonellosis cases in Greece.
The study period for the interrupted time series analysis was 2006 to 2017. However, for S. Enteritidis, a sensitivity analysis was also performed for both periods 2006–2017 and 2006–2015. The reason was that in 2016 there was an excess in the number of S. Enteritidis cases in Greece probably attributed to the multi-country S. Enteritidis outbreak related to the consumption of infected Polish eggs [14].
Analysis was conducted separately for each series. We set the time of introduction of the intervention in January 2009, despite the fact that the implementation of the NSCPs in breeders, layers started in 2007, and 2008 respectively, as it takes some time for the NSCPs to produce results, namely reduction of the prevalence of the targeted Salmonella serotypes, in poultry species producing animal products for human consumption.
Poisson and negative binomial regression models were used to study the impact of the intervention on the number and trend of the recorded isolates. The selection of the final model for the evaluation of the intervention’s impact was based on the residual analysis performed for these two models and was a negative binominal regression model which included trend and a sine wave with a 12-month period to adjust estimates for secular and cyclical trends, the intervention (a binominal variable), the interaction between trend and intervention and one lag to count for autocorrelation.
IRR values and the respective CIs were calculated. In all cases, p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Residuals of each model were plotted against the model and checked for stationarity, autocorrelation and normality. Additionally, residuals were tested with Portmanteau test to check if they were statistically significantly similar to white noise.
Analysis was performed in Stata v16.1. [24].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.T. and K.M.; data curation, M.T.; formal analysis, M.T.; investigation, M.T.; methodology, M.T., J.G.D. and K.M.; project administration, M.T.; supervision, K.M.; validation, K.M.; Visualization, M.T.; writing–original draft, M.T.; writing–review and editing, G.M., J.G.D., T.S., A.C. and K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
“The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The data are publicly available at the official website of the National Reference Laboratory for Salmonella, Shigella and other enteropathogens at http://www.mednet.gr/whonet/, but only until 2016. Further approval was not requested as only aggregated data on the number of Salmonella isolates were used.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable” as only aggregated data on Salmonella isolates were used.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are publicly available at the official website of the National Reference Laboratory for Salmonella, Shigella and other enteropathogens at http://www.mednet.gr/whonet/, but only until 2016.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the contribution of all personnel who collected data used in this study. Special thanks to Frantiska Hruba, EPIET Scientific Coordinator of European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, Solna (ECDC) for her mentoring and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, S.K.; Pusparajah, P.; Mutalib, N.S.A.; Ser, H.L.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Salmonella. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/salmonella (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU law. Commission Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 28 January 2002 Laying Down the General Principles and Requirements of Food Law, Establishing the European Food Safety Authority and Laying Down Procedures in Matters of Food Safety. Official Journal L 1–24. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32002R0178 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU law. Directive 2003/99/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 November 2003 on the Monitoring of Zoonoses and Zoonotic Agents, Amending Council Decision 90/424/EEC and Repealing Council Directive 92/117/EEC. Official Journal L 325, 12/12/2003 P. 0031–0040. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32003L0099&from=EN (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU Law. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 November 2003 on the Control of Salmonella and Other Specified Food-Borne Zoonotic Agents. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32003R2160 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU Law. Commission Regulation (EU) No 200/2010 of 10 March 2010 Implementing Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards a Union Target for the Reduction of the Prevalence of Salmonella Serotypes in Adult Breeding Flocks of Gallus gallus. Official Journal of the European Union 1–9. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32010R0200 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU law. Commission Regulation (EU) No 517/2011 of 25 May 2011 implementing Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards a Union Target for the Reduction of the Prevalence of Certain Salmonella Serotypes in Laying Hens of Gallus Gallus and Amending Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 and Commission Regulation (EU) No 200/2010. Official Journal of the European Union 45–51. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32011R0517 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU Law. Commission Regulation (EU) No 200/2012 of 8 March 2012 Concerning a Union Target for the Reduction of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium in Flocks of Broilers, as Provided for in Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Official Journal of the European Union 31–36. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32012R0200 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU Law. Commission Regulation (EU) No 1190/2012 of 12 December 2012 Concerning a Union Target for the Reduction of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium in Flocks of Turkeys, as Provided for in Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2012/1190/oj (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU Law. Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32005R2073 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EUR-Lex: EU Law. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1177/2006 of 1 August 2006 Implementing Regulation (EC) No 2160/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Requirements for the Use of Specific Control Methods in the Framework of the National Programmes for the Control of Salmonella in Poultry. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/1177/oj (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Hellenic National Public Health Organisation (EODY): Epidemiological Data for Salmonellosis (Non-Typhoid/Paratyphoid) in Greece, 2004–2019. Available online: https://eody.gov.gr/en/epidemiological-statistical-data/annual-epidemiological-data/#heading-13 (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union One Health 2018 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, E.; Watier, L.; Espie, E.; Weill, F.X.; De Valk, H.; Desenclos, J.C. Evaluation of the impact on human salmonellosis of control measures targeted to Salmonella Enteritidis and Typhimurium in poultry breeding using time-series analysis and intervention models in France. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, H.C.; Hald, T.; Lo Fo Wong, D.; Madsen, M.; Korsgaard, H.; Bager, F.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Mølbak, K. Salmonella control programs in Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenic Ministry of Rural Development and Food. Reports of the Multiannual Control Programmes. Available online: http://www.minagric.gr/index.php/el/the-ministry-2/poese (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authoritiy). National Zoonoses Country Reports. Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/biological-hazards-data/reports (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Maijala, R.; Ranta, J.; Seuna, E.; Peltola, J. The efficiency of the Finnish Salmonella Control Programme. Food Control 2005, 16, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Velsen, L.; Beaujean, D.J.; van Gemert-Pijnen, J.E.; van Steenbergen, J.E.; Timen, A. Public knowledge and preventive behavior during a large-scale Salmonella outbreak: Results from an online survey in the Netherlands. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, T.A.; Humphrey, T.J. The rise and fall of Salmonella enteritidis in the UK. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 114S–119S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijnacker, R.; Dallman, T.J.; Tijsma, A.S.L.; Hawkins, G.; Larkin, L.; Kotila, S.M.; Amore, G.; Amato, E.; Suzuki, P.M.; Denayer, S.; et al. International Outbreak Investigation Team. An international outbreak of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis linked to eggs from Poland: A microbiological and epidemiological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellou, K.; Sideroglou, T.; Kallimani, A.; Potamiti-Komi, M.; Pervanidou, D.; Lillakou, E.; Georgakopoulou, T.; Mandilara, G.; Lambiri, M.; Vatopoulos, A.; et al. Evaluation of underreporting of salmonellosis and shigellosis hospitalised cases in Greece, 2011: Results of a capture-recapture study and a hospital registry review. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 16; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).