Abstract
This study aimed to determine the global prevalence and molecular characterization of CTX-M-producing Salmonella Typhimurium isolates. A total of 330 (15.2%, 330/21779) blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium were obtained from the public databases in July 2021. Thirteen variants were found in the 330 members of the blaCTX-M group, and blaCTX-M-9 (26.4%, 88/330) was the most prevalent. The majority of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium were obtained from humans (59.7%, 197/330) and animals (31.5%, 104/330). The number of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium increased annually (p < 0.0001). These isolates were primarily found from China, the United Kingdom, Australia, the USA, and Germany. In addition, these isolates possessed 14 distinct sequence types (ST), and three predominated: ST34 (42.7%, 141/330), ST19 (37.0%, 122/330), and ST313 (10.3%, 34/330). The majority of ST34 S. Typhimurium isolates were distributed in China and mainly from swine. However, the majority of ST19 were distributed in the United Kingdom and Australia. Analysis of contigs showed that the major type of blaCTX-M-carrying plasmid was identified as IncI plasmid (52.9%, 27/51) and IncHI2 plasmid (17.6%, 9/51) in 51 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. In addition, WGS analysis further revealed that blaCTX-M co-existed with nine antibiotic-resistant genes with a detection rate over 50%, conferring resistance to five classes of antimicrobials. The 154 virulence genes were detected among these isolates, of which 107 virulence genes were highly common. This study revealed that China has been severely contaminated by blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates, these isolates possessed numerous ARGs and virulence genes, and highlighted that continued vigilance for blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium in animals and humans is urgently needed.
1. Introduction
Salmonella is an important foodborne pathogen that has a nearly ubiquitous distribution among humans, animals, and the open environment. According to the WHO, there over 90 million people are infected by Salmonella annually, and 150,000 people die from Salmonella infection [1]. Over 2600 Salmonella serotypes have been identified and can be referred to as typhoidal or non-typhoidal (NTS); the latter are present in different animal reservoirs and are responsible for self-limiting gastrointestinal syndromes [2]. S. Typhimurium can cause potential threat to human health through the consumption of contaminated food or water [3]. Through estimates of the global invasive non-typhoidal Salmonella disease, a study recently found that S. Typhimurium is emerging in several African countries [4]. After its oral acquisition, S. Typhimurium travels down the intestinal tract and reaches the large intestine, where most of its replication is thought to occur [5].
Treatment of invasive salmonellosis has been compromised due to the emergence of Salmonella isolates with single or multidrug resistance to a number of first-line agents. Consequently, the third generation cephalosporins, such as ceftriaxone, have become treatment modalities of choice for therapy against severe Salmonella infections [6]. However, the increasing prevalence of cephalosporin-resistant Salmonella is also an emerging problem in recent years [7]. Resistance to cephalosporins is mainly due to the acquisition of extended-spectrum β-lactamase genes (ESBLs), among which CTX-M-type enzymes are currently most common—usually located on transmissible plasmids— and can disseminate among the Enterobacteriaceae family [8]. The number of reported cases in various ESBL-producing Salmonella serotypes has been increasing worldwide in recent years, with the predominant CTX-M group that was recently detected in poultry and poultry products in different countries [9,10].
In general, Salmonella virulence factors have a crucial role in systemic infections [11]. Virulence genes are located on various locations of the genome, including Salmonella pathogenicity islands (SPIs) and several mobile genetic elements such as prophages and plasmids [12]. SPI-1 and SPI-2 encode for Type III secretion system (TTSS) and play an important role in delivering different effector proteins into the host that mediates pathogenesis [13]. SPI-1 encodes for genes such as invA, sipABD, and sopBD involved in the invasion of epithelial cells, whereas SPI-2 encodes the genes sifA and ssaR related to the survival and replication of Salmonella within phagocytic cells [14]. In addition, the virulence plasmids carrying virulence genes, such as the spv genes, play a role in Salmonella multiplication within its host cell, increasing the severity of enteritis [15].
In this study, we first employed genomic analysis from a public database to conduct a global survey of epidemic characterization of CTX-M-producing S. Typhimurium. We then characterized the molecular characteristics, diversity, antibiotic-resistant genes, and virulence genotypes of these pathogens.
2. Results
2.1. Prevalence of Blactx-M-Producing S. Typhimurium Identified from the Genome Database
In this study, we identified 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium from 21,779 assembled genomes of S. Typhimurium from the NCBI database. Thirteen variants were found in the 330 members of the blaCTX-M group, of which, the most predominant variants of blaCTX-M were blaCTX-M-9 (26.4%, 88/330), followed by blaCTX-M-55 (68%, 204/330), blaCTX-M-14 (19.8%, 66/330), blaCTX-M-15 (16.5%, 55/330), blaCTX-M-65 (6.9%, 23/330), and blaCTX-M-1 (5.7%, 19/330) (Figure 1A). The majority of blaCTX-M -positive S. Typhimurium were obtained from humans (59.7%, 197/330) and animals (31.5%, 104/330). A noteworthy observation was that swine (18.5%, 61/330) were the primary animal host in (Figure 1B). In addition, the blaCTX-M-9, blaCTX-M-55, and blaCTX-M-14 positive Salmonella isolates were obtained from animals and humans, and the latter was more dominant (Figure S1). During this period, we noticed a shift in the quantity of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium. The percentage of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates increased from 2.1% (7/330) in 2014 and 10.3% (34/330) in 2015 to 14.2% (47/330) in 2019 and 37.0% (122/330) in 2020 (Figure 1C). The χ2 test revealed a significant linear trend among the ordered years from 2014 to 2020 (p < 0.0001). These blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates were distributed across 15 countries. China (34.5%, 114/330) has been severely contaminated by blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates, followed by the United Kingdom (28.2%, 93/330), Australia (13.0%, 43/330), USA (5.5%, 18/330), Germany (4.5%, 15/330), and other countries (7.6%, 25/330) (Figure 1D).
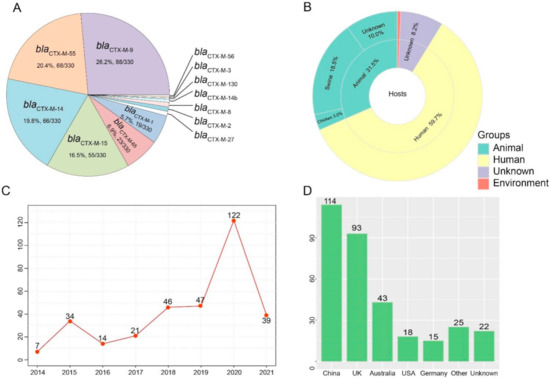
Figure 1.
Prevalence of blaCTX-M-positive Salmonella Typhimurium isolates. (A) The rate and number of variants in blaCTX-M genes. (B) The hosts of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. (C) The number of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates from 2014 to 2021. (D) The number of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates in different countries.
2.2. Molecular Characterization of Blactx-M-Producing S. Typhimurium
This group of 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates possessed 14 distinct ST. Three were predominant: ST34 (42.7%, 141/330), ST19 (37.0%, 122/330), and ST313 (10.3%, 34/330), but we could not find a matching ST for 13 of the database isolates (Table S1). It is worth mentioning that the majority of blaCTX-M-positive ST34 S. Typhimurium isolates were distributed in China (n = 94). However, the majority of ST19 were distributed in the United Kingdom (n = 63) and Australia (n = 34) (Figure 2A). In addition, swine were one of the most dominant hosts in the blaCTX-M-positive ST34 S. Typhimurium isolates (Figure 2B).
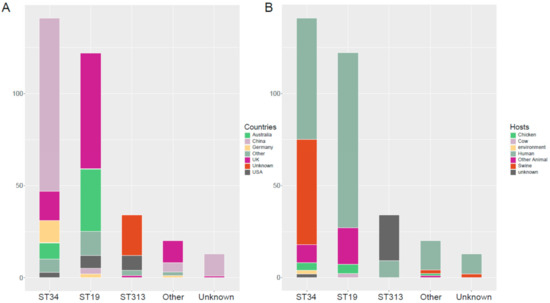
Figure 2.
Geographic distribution and host diversity of the dominant ST blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. (A) Geographic distribution the dominant ST blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. (B) Host diversity of the dominant ST blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates.
2.3. Plasmid Analysis
The contigs carrying blaCTX-M were confirmed as numerous types of plasmids in 51 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. As shown in Figure 3, the major type of blaCTX-M-carrying plasmid was identified as IncI plasmid (52.9%, 27/51), followed by IncHI2 plasmid (17.6%, 9/51), IncA/C plasmid (7.8%, 4/51), and IncB//O/K/Z plasmid (7.8%, 4/51). Additionally, an analysis of WGS indicated that blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates in this study were carrying 17 types of Inc plasmids (Figure 4). IncHI2 (69.1%, 228/330) and IncHI2A (68.8%, 227/330) were the most prevalent type of plasmid, followed by IncFIB plasmid (33.9%, 112/330) and IncFII plasmid (30.9%, 102/330).
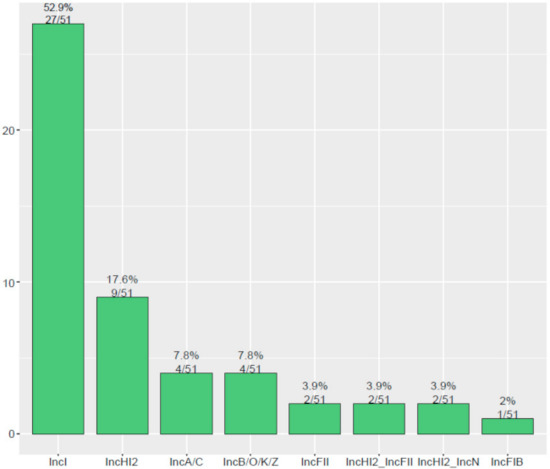
Figure 3.
The diversity of plasmid types carrying blaCTX-M among 51 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates.
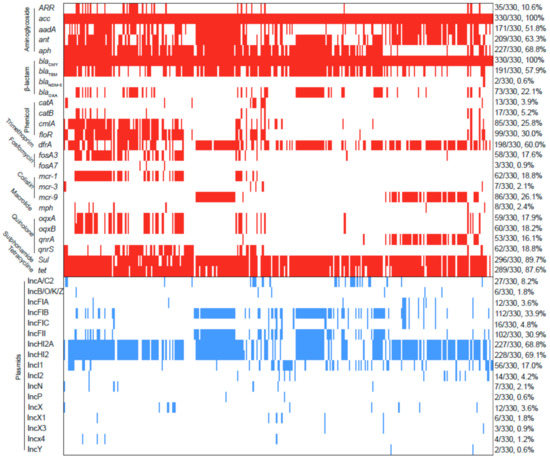
Figure 4.
Analysis of ARGs and plasmids among 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. The red and blue squares represent positivity for ARGs and plasmid Inc types, respectively.
2.4. Other ARGs
In addition to blaCTX-M, a total of 26 ARGs were identified among these S. Typhimurium isolates and conferred resistance to ten classes of antibiotics (Figure 4). Of these, nine ARGs were common with a detection rate of over 50%, including aminoglycoside-resistant genes acc (100%, 330/330), aadA (51.8%, 171/330), ant (63.3%, 209/330), aph (68.8%, 227/330); β-lactam-resistant genes blaCMY (100%, 330/330) and blaTEM (57.9%, 191/330); trimethoprim-resistant gene drfA (60.0%, 198/330); sulphonamide-resistant gene sul (89.7%, 296/330); and tetracycline-resistant gene tet (87.6%, 289/330). Notably, colistin-resistant genes mcr-1, mcr-3, and mcr-9 were detected in 62, 7, and 86 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates, respectively. Carbapenem-resistant gene blaNDM-5 was detected in two blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates.
2.5. Virulence Factor
Among the 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates, we detected 154 virulence genes (Table S1). Of these, 107 virulence genes were highly common, with a detection rate over 79%. In contrast, the detection rate of 38 virulence genes were low (<10%). Of note was the detection rate of some virulence genes that ranged from 26.4% to 31.8%, including grvA, spvB, spvC, spvR, pefA, pefB, pefC, pefD, and rck (Figure 5A). The majority of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates carried 107 virulence genes (34.8%, 115/330), followed by 106 (18.5%, 61/330), 114 (8.8%, 29/330), 115 (8.5%, 28/330), 108 (7.6%, 25/330), and 116 (7.3%, 24/330) (Figure 5B).
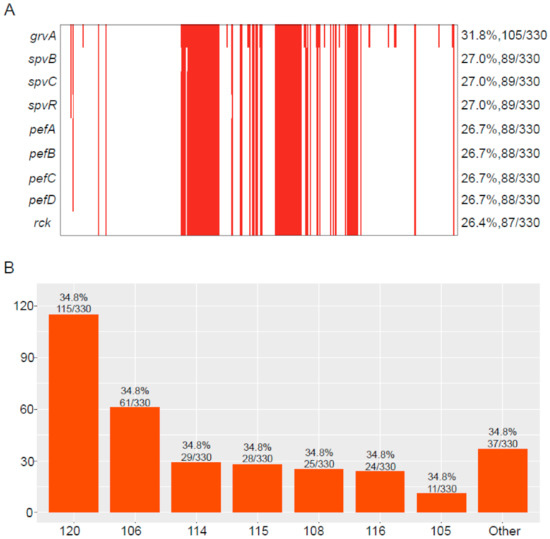
Figure 5.
Virulence genes were identified in blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. (A) The detection rate of virulence genes in blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates; the red represents positive for virulence genes. (B) The number of isolates carrying different numbers of virulence genes.
3. Discussion
At present, it is concerning that the increasing incidence of infections is caused by ESBL-producing organisms, especially Salmonella spp., because they are resistant to most of the β-lactam antimicrobials and other antimicrobial classes [16,17]. During the last decade, the most encountered ESBL genes were the CTX-M enzyme family, primarily carried by transferable plasmids and transposons [18]. In this study, all 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium were collected from humans and animals, especially swine. These isolates were distributed across 15 countries. The countries possessing the greatest amount of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates were China, UK, Australia, USA, and Germany [19,20,21,22,23]. In addition, we noticed an increase in quantity of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates from 2014 to 2020. This may be related to the increased rate of Salmonella after 2009 in food animals [24].
This group of 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates possessed 14 distinct ST, with three predominant: ST34, ST19, and ST313. Previous studies have shown that ST19, ST34, and ST313 are commonly found STs of S. Typhimurium. Recently, one of the most prevalent S. Typhimurium, ST34, was widely reported in Europe, North America, Asia, and Australia [25]. In addition, ST34 S. Typhimurium isolates have acquired strong biofilm-forming ability and were often reportedly carrying the colistin-resistant genes (mcr-1, mcr-3, mcr-5, and mcr-9) and even the blaNDM gene [25,26,27]. ST19 and ST34 were the most common STs in Asia. However, ST19 isolates were resistant to fewer antibiotic classes than ST34 isolates [27]. Thus far, ST19 has been reported from humans, reptiles, ovine, swine, poultry, food, and bovine from France, Mexico, China, Germany, Scotland, Portugal, Qatar, Korea, Ireland, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Denmark, according to Enterobase [28]. ST313 is a relatively newly emerged sequence type and closely related to the ST19 group of S. Typhimurium, which has caused a devastating epidemic of bloodstream infections across sub-Saharan Africa [29].
The blaCTX-M genes were mainly located on IncI plasmid in the S. Typhimurium isolates, followed by IncHI2 and IncA/C plasmids. Additionally, 17 types of Inc plasmids were identified among the blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates. IncHI2 and IncHI2A were the most prevalent type of plasmid, followed by IncFIB and IncFII plasmids. IncI plasmids were closely associated with the spread of several ESBL genes. The blaCTX-M gene was located on IncI1 plasmids in all of the isolates, which were obtained from slaughterhouses located in seven districts in France [30]. A previous study has shown that IncA/C and IncHI2 were the most common types of plasmids among ESBL-producing Salmonella, and they often carried multiple antibiotic-resistant genes, including strB, qnrS, tet(A), sul, and dfrA14 [31]. Additionally, the numerous types of plasmids may serve as important vehicles for the spread of ARGs [32].
In addition to blaCTX-M, a total of 26 ARGs were identified among the S. Typhimurium isolates and conferred resistance to ten classes of antibiotics, including quinolone, aminoglycoside, β-lactam, sulphonamide, trimethoprim, tetracycline, phenicol, macrolide, fosfomycin, and colistin. Consistent with a previous study, most of the blaCTX-M-positive isolates carried acquired-resistance determinants associated with three or more drug classes [33]. Notably, a few blaCTX-M genes co-existed with mcr-1, mcr-3, mcr-9, and blaNDM-5, conferring resistance to colistin and carbapenem, which were considered as the last-resort antibiotics used for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria [34].
An important trait of Salmonella is that they can invade, survive, and multiply in a host cell in the presence of genetic determinants for virulence. Virulence genes have been extensively studied in Salmonella [35]. In this study, a total of 154 virulence genes were identified in the 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates, and most of the isolates carried 107 virulence genes. Of these, the detection rate of some virulence genes ranged from 26.4% to 31.8%, including grvA, spvB, spvC, spvR, pefA, pefB, pefC, pefD, and rck. The gene grvA (for Gifsy-2-related virulence) is located on the prophage Gifsy-2; grvA null mutant showed an increase in the virulence of serovar Typhimurium in mice [36]. SpvB facilitated Salmonella survive and replicate within macrophages via perturbing cellular iron metabolism [37]. The protein encoded by the spvC gene has a phosphorylated threonine lyase activity that inhibits MAP phosphokinase. The pathogenicity of Salmonella strains greatly increases when both spvB and spvC genes co-exist in the bacteria [38]. The spvR encodes a positive activator for the following four genes, spvABCD [39]. Plasmid-encoded fimbriae (Pef) of Salmonella are among the fimbriae whose expression have been observed in animals. Pef fimbriae biogenesis depends on the pef operon, located on the virulence plasmid of S. Typhimurium. This operon encodes the major Pef fimbriae subunit pefA, the usher protein pefC, required for the assembly of the fimbriae, and the pefD periplasmic chaperone for pefA [40]. Recent research has shown that rck protein is able to induce the Salmonella entry mechanism. rck mimics natural host cell ligands and triggers engulfment of the bacterium by interacting with the epidermal growth factor receptor [41].
There are several limitations of this study. First, the increase in genomes in the pubic repository may be related to the development of sequencing technology rather than an actual increase. Second, not all genomes of isolates will upload to the database. Finally, the phenotypes of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes and the transfer of resistance genes were not evaluated in this study.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
A total of 21,779 assembled genomes of Salmonella Typhimurium were downloaded from the NCBI database in 8 July 2021 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly. The detailed information (collected year, hosts, and location) was obtained from the pathogens database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens, accessed on 8 July 2021).
4.2. Methods
All the genomes of S. Typhimurium were applied to a filter for the presence of blaCTX-M and other antibiotic-resistant genes using ResFinder (https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/ResFinder/ accessed on 29 July 2021). The contigs carrying blaCTX-M genes were extracted for the identification of plasmid types by PlasmidFinder software. Multilocus sequence types (MLST) and replicating type of plasmid were identified using MLST and PlasmidFinder (https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services accessed on 29 July 2021). Virulence factors were identified using the Virulence Factor Database (http://www.mgc.ac.cn/VFs/main.htm accessed on 13 September 2021). The heatmaps were visualized with the “pheatmap” package. The histogram, stack bar diagram, pie diagram, and line chart were plotted with “ggplot2” and colour was used with the “RColourBrewer” package. The χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test were used to perform the statistical analysis. For all models, we considered p < 0.01 statistically significant and then performed 2-sided probability on those results by using SPSS version 23.0.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we identified 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates from the public database. Thirteen variants were found in the 330 members of the blaCTX-M group, and blaCTX-M-9 was the most prevalent. The majority of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium were obtained from humans and animals. The number of blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium increased annually. These isolates were primarily detected in China, the United Kingdom, Australia, the USA and Germany. In addition, these isolates possessed 14 distinct ST, and three were predominant: ST34, ST19, and ST313. The majority of ST34 S. Typhimurium isolates were distributed in China and were mainly from swine. However, the majority of ST19 were distributed in the United Kingdom and Australia. The major types of blaCTX-M-carrying plasmid were identified as IncI plasmid and IncHI2 plasmid. In addition, blaCTX-M co-existed with nine antibiotic-resistant genes with a detection rate of over 50%, conferring resistance to five classes of antimicrobials. The 154 virulence genes were detected among these isolates, of which 107 virulence genes were highly common. This study provides new insights into clinical antibiotic therapy for Salmonella infection and provides a foundation for further scientific research.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics10111417/s1, Figure S1: The analysis of hosts carrying the most common CTX-M allelic variants; Table S1: The detection rate of 154 virulence genes in 330 blaCTX-M-positive S. Typhimurium isolates.
Author Contributions
Methodology, software, data curation, and writing, L.G.; review and editing, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the PhD Fund of Qingdao Agricultural University (663-1119017), Shandong Provincial College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project (S202010435088), and Shandong Provincial Development of new raw materials and preparations for Animal Respiratory Disease Control under Grant (662-2321018).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviation
The lists of abbreviation used in this study.
| MLST | Multilocus sequence types |
| WGS | Whole genome sequencing |
| Inc | Incompatible |
| ARGs | Antibiotic resistance genes |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum β-lactamase |
| SPI | Salmonella pathogenicity island |
| TTSS | Type III secretion system |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
References
- Xu, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Zhou, C.; Liang, J.; Gu, G.; Wei, P. The emergence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Salmonella London isolates from human patients, retail meats and chickens in southern China and the evaluation of the potential risk factors of Salmonella London. Food Control 2021, 128, 108187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrorilli, E.; Petrin, S.; Orsini, M.; Longo, A.; Cozza, D.; Luzzi, I.; Ricci, A.; Barco, L.; LoSasso, C. Comparative genomic analysis reveals high intra-serovar plasticity within Salmonella Napoli isolated in 2005–2017. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohl, M.E.; Miller, S.I. Salmonella: A Model for Bacterial Pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2001, 52, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselbeck, A.H.; Panzner, U.; Im, J.; Baker, S.; Meyer, C.G.; Marks, F. Current perspectives on invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella disease. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.E. Salmonella Typhimurium and inflammation: A pathogen-centric affair. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 19, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollister, B.; Kotter, C.V.; Frank, D.N.; Washburn, T.; Jobling, M.G. Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies In Vivo Acquisition of a bla CTX-M-27 -Carrying IncFII Transmissible Plasmid as the Cause of Ceftriaxone Treatment Failure for an Invasive Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7224–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Lin, X.-Y.; Xu, L.; Gu, X.-X.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Ren, S.-Q.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Jiang, H.-X. CTX-M-27 Producing Salmonella enterica Serotypes Typhimurium and Indiana Are Prevalent among Food-Producing Animals in China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, J.; Gan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Emergence and Diversity of Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolates with Concurrent Resistance to Ciprofloxacin and Cefotaxime from Patients and Food-Producing Animals in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Ghilardi-Rodrigues, Â.C.; Adams-Haduch, J.M.; Tavechio, A.T.; Doi, Y. CTX-M-2–Producing Salmonella Typhimurium Isolated from Pediatric Patients and Poultry in Brazil. Microb. Drug Resist. 2009, 15, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozyreva, V.K.; Ilina, E.; Malakhova, M.V.; Carattoli, A.; Azizov, I.; Tapalski, D.; Kozlov, R.S.; Edelstein, M.V. Long-Term Dissemination of CTX-M-5-Producing Hypermutable Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Sequence Type 328 Strains in Russia, Belarus, and Kazakhstan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5202–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thung, T.Y.; Radu, S.; Mahyudin, N.A.; Rukayadi, Y.; Zakaria, Z.; Mazlan, N.; Tan, B.H.; Lee, E.; Yeoh, S.L.; Chin, Y.Z.; et al. Prevalence, Virulence Genes and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Salmonella Serovars from Retail Beef in Selangor, Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Hassena, A.; Haendiges, J.; Zormati, S.; Guermazi, S.; Gdoura, R.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Siala, M. Virulence and resistance genes profiles and clonal relationships of non-typhoidal food-borne Salmonella strains isolated in Tunisia by whole genome sequencing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 337, 108941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ray, S.; Ryan, D.; Sahu, B.; Suar, M. Identification of a novel gene in ROD9 island of Salmonella Enteritidis involved in the alteration of virulence-associated genes expression. Virulence 2018, 9, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dantas, S.T.A.; Camargo, C.H.; Tiba-Casas, M.R.; Vivian, R.C.; Pinto, J.P.; Pantoja, J.C.; Hernandes, R.T.; Júnior, A.F.; Rall, V.L. Environmental persistence and virulence of Salmonella spp. Isolated from a poultry slaughterhouse. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, W.; Rjeibi, M.R.; Mhadhbi, M.; Jbeli, M.; Zrelli, S.; Ettriqui, A. Prevalence, virulence and antibiotic susceptibility of Salmonella spp. strains, isolated from beef in Greater Tunis (Tunisia). Meat Sci. 2016, 119, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Xu, X.; Yan, M.; Chang, H.; Li, Y.; Kan, B.; Zeng, M. Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis Infections in Sporadic Diarrhea in Children: Source Tracing and Resistance to Third-Generation Cephalosporins and Ciprofloxacin. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Feltrin, F.; Alba, P.; Cordaro, G.; Iurescia, M.; Tolli, R.; D’Incau, M.; Staffolani, M.; Di Giannatale, E.; et al. Emergence of a Clonal Lineage of Multidrug-Resistant ESBL-Producing Salmonella Infantis Transmitted from Broilers and Broiler Meat to Humans in Italy between 2011 and 2014. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantón, R.; González-Alba, J.M.; Galán, J.C. CTX-M Enzymes: Origin and Diffusion. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.-Z.; Ding, X.-M.; Lin, X.-L.; Sun, R.-Y.; Lu, Y.-W.; Cai, R.-M.; Webber, M.; Ding, H.-Z.; Jiang, H.-X. The Emergence of Chromosomally Located blaCTX-M-55 in Salmonella from Foodborne Animals in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, G.S.; Day, M.R.; Murthy, S.; Chattaway, M.; Nair, S. First Report of CTX-M-15 Salmonella Typhi from England. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1976–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparham, S.J.; Kwong, J.C.; Valcanis, M.; Easton, M.; Trott, D.J.; Seemann, T.; Stinear, T.P.; Howden, B.P. Emergence of multidrug resistance in locally-acquired human infections with Salmonella Typhimurium in Australia owing to a new clade harbouring bla CTX-M-9. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittum, T.E.; Mollenkopf, D.F.; Erdman, M.M. Detection of Salmonella enterica Isolates Producing CTX-M Cephalosporinase in U.S. Livestock Populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7487–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, J.; Rodríguez, I.; Baumann, B.; Guiral, E.; Beutin, L.; Schroeter, A.; Kaesbohrer, A.; Pfeifer, Y.; Helmuth, R.; Guerra, B. bla CTX-M-15-carrying Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolates from livestock and food in Germany. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2951–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, C.; Gu, G.; Liang, J.; Hou, X.; Wang, M.; Wei, P. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of retail-meat-borne Salmonella in southern China during the years 2009–2016: The diversity of contamination and the resistance evolution of multidrug-resistant isolates. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Li, Y.; Elbediwi, M.; Yue, M. Emergence and Dissemination of mcr-Carrying Clinically Relevant Salmonella Typhimurium Monophasic Clone ST34. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Hao, R.; Li, P. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ST34 co-expressing blaNDM-5 and blaCTX-M-55 isolated in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Jiang, M.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, L.; et al. Clonal Expansion of Biofilm-Forming Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 with Multidrug-Resistance Phenotype in the Southern Coastal Region of China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seribelli, A.A.; da Silva, P.; da Cruz, M.F.; de Almeida, F.; Frazão, M.R.; Medeiros, M.I.C.; Rodrigues, D.D.P.; Kich, J.D.; Benevides, L.D.J.; Soares, S.D.C.; et al. Insights about the epidemiology of Salmonella Typhimurium isolates from different sources in Brazil using comparative genomics. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarlöf, D.L.; Kröger, C.; Owen, S.V.; Canals, R.; Lacharme-Lora, L.; Wenner, N.; Schager, A.E.; Wells, T.J.; Henderson, I.R.; Wigley, P.; et al. Role of a single noncoding nucleotide in the evolution of an epidemic African clade of Salmonella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 115, E2614–E2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carattoli, A. Resistance Plasmid Families in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadimpalli, M.; Fabre, L.; Yith, V.; Sem, N.; Gouali, M.; Delarocque-Astagneau, E.; Sreng, N.; Le Hello, S.; Raheliarivao, B.T.; Randrianirina, F.; et al. CTX-M-55-type ESBL-producing Salmonella enterica are emerging among retail meats in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 74, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-G.; Zhang, R.-M.; Wang, L.-L.; Sun, R.-Y.; Bai, S.-C.; Han, L.; Fang, L.-X.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liao, X.-P. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli from duck farms in south-east coastal China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Hawkey, J.; Hetland, M.A.K.; Fostervold, A.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.; Hamidian, M.; Howden, B.; Löhr, I.H.; Holt, K. Emergence and rapid global dissemination of CTX-M-15-associated Klebsiella pneumoniae strain ST307. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Shen, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y. Emergence of a novel mobile colistin resistance gene, mcr-8, in NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, D.; Hussain, S.; Pathak, A.; Shukla, M.; Kumar, V.P.; Anisha, P.; Rautela, R.; Upadhyay, A.; Singh, S. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes characterization of nontyphoidal Salmonella isolated from retail chicken meat shops in Northern India. Food Control 2019, 102, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Slauch, J.M. Characterization of grvA, an Antivirulence Gene on the Gifsy-2 Phage in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Dong, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, R. Salmonella effector SpvB aggravates dysregulation of systemic iron metabolism via modulating the hepcidin−ferroportin axis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1849996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Du, Y.; Guo, W.; Bellefleur, M.; Wang, S.; Shi, H. Serotype distribution, antimicrobial susceptibility, antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence genes of Salmonella isolated from a pig slaughterhouse in Yangzhou, China. AMB Express 2019, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulig, P.A.; Danbara, H.; Guiney, D.G.; Lax, A.J.; Norel, F.; Rhen, M. Molecular analysis of spv virulence genes of the salmonella virulence plasmids. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 7, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Escobar, G.A.; Grépinet, O.; Raymond, P.; Abed, N.; Velge, P.; Virlogeux-Payant, I. H-NS is the major repressor of Salmonella Typhimurium Pef fimbriae expression. Virulence 2019, 10, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambu, J.; Virlogeux-Payant, I.; Holbert, S.; Grépinet, O.; Velge, P.; Wiedemann, A. An Updated View on the Rck Invasin of Salmonella: Still Much to Discover. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).