Identified Seaweed Compound Diphenylmethane Serves as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. DPM Modulates the Activities of Macrolides and Fluoroquinolones against Drug-Resistant E. coli
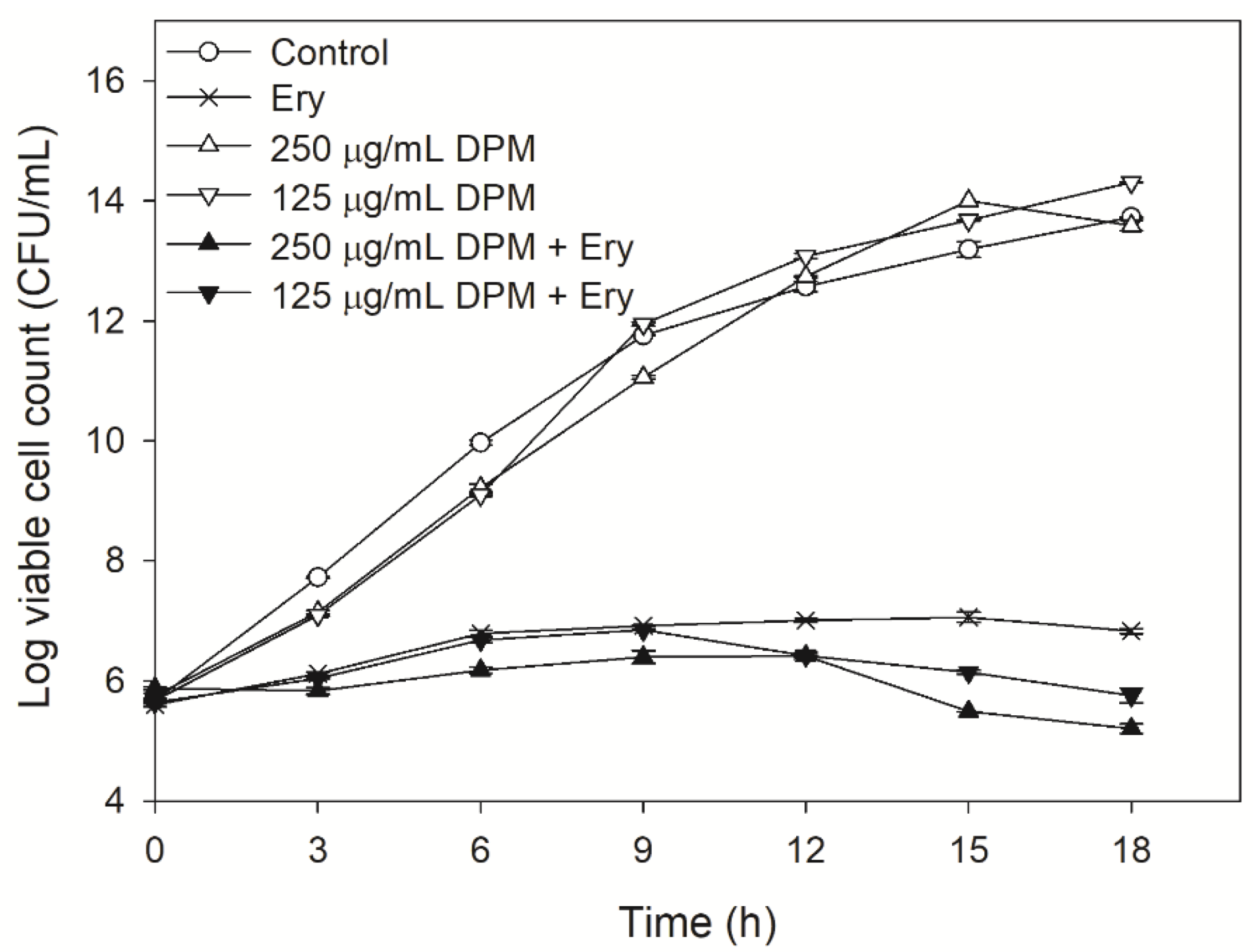
2.2. Effect of DPM on Time-Kill Curves
2.3. DPM Reduced Dye Accumulation in E. coli Kam3-AcrB
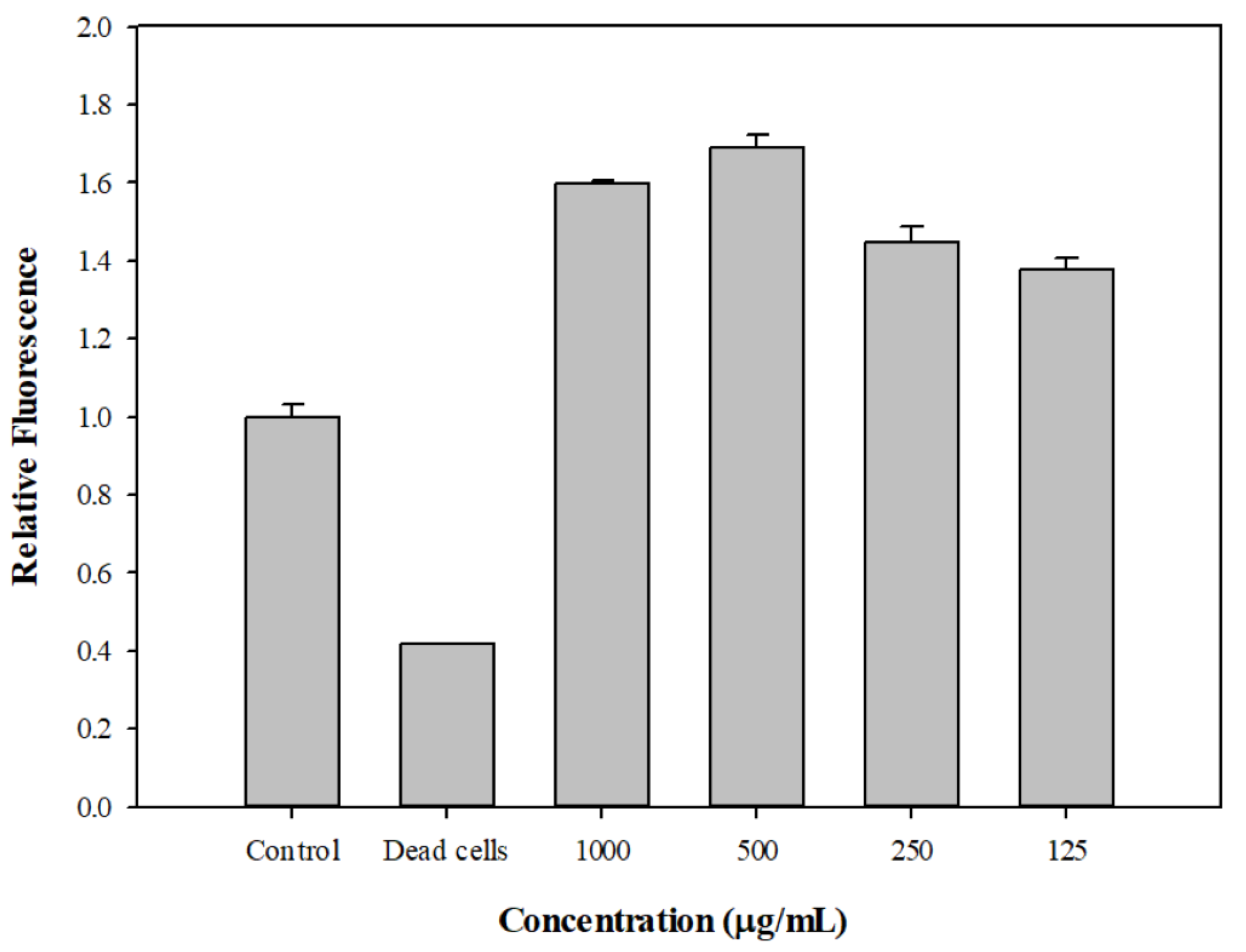
2.4. DPM Reduced Dye Efflux by E. coli Kam3-AcrB
2.5. Drug Efflux Interference by DPM Monitored Using MALDI-TOF
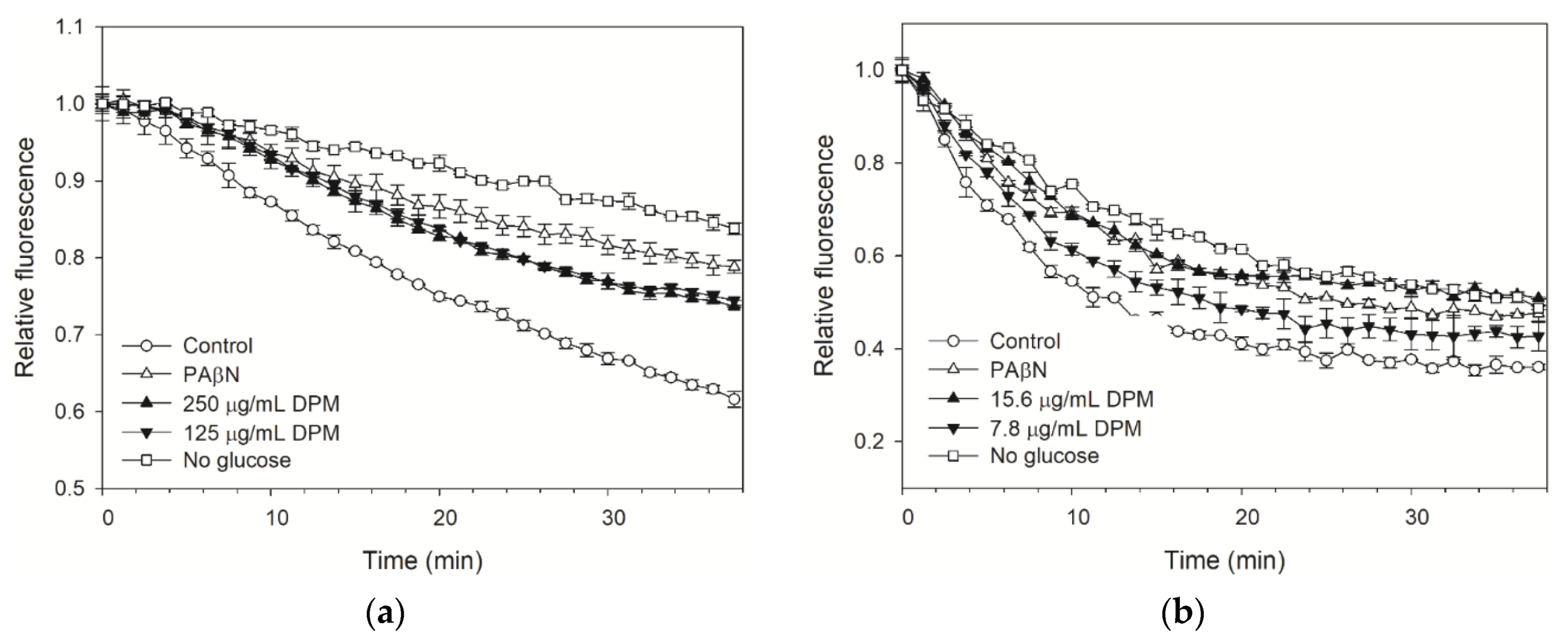
2.6. The Effect of DPM on Membrane Permeability and Post-Antibiotic Effect
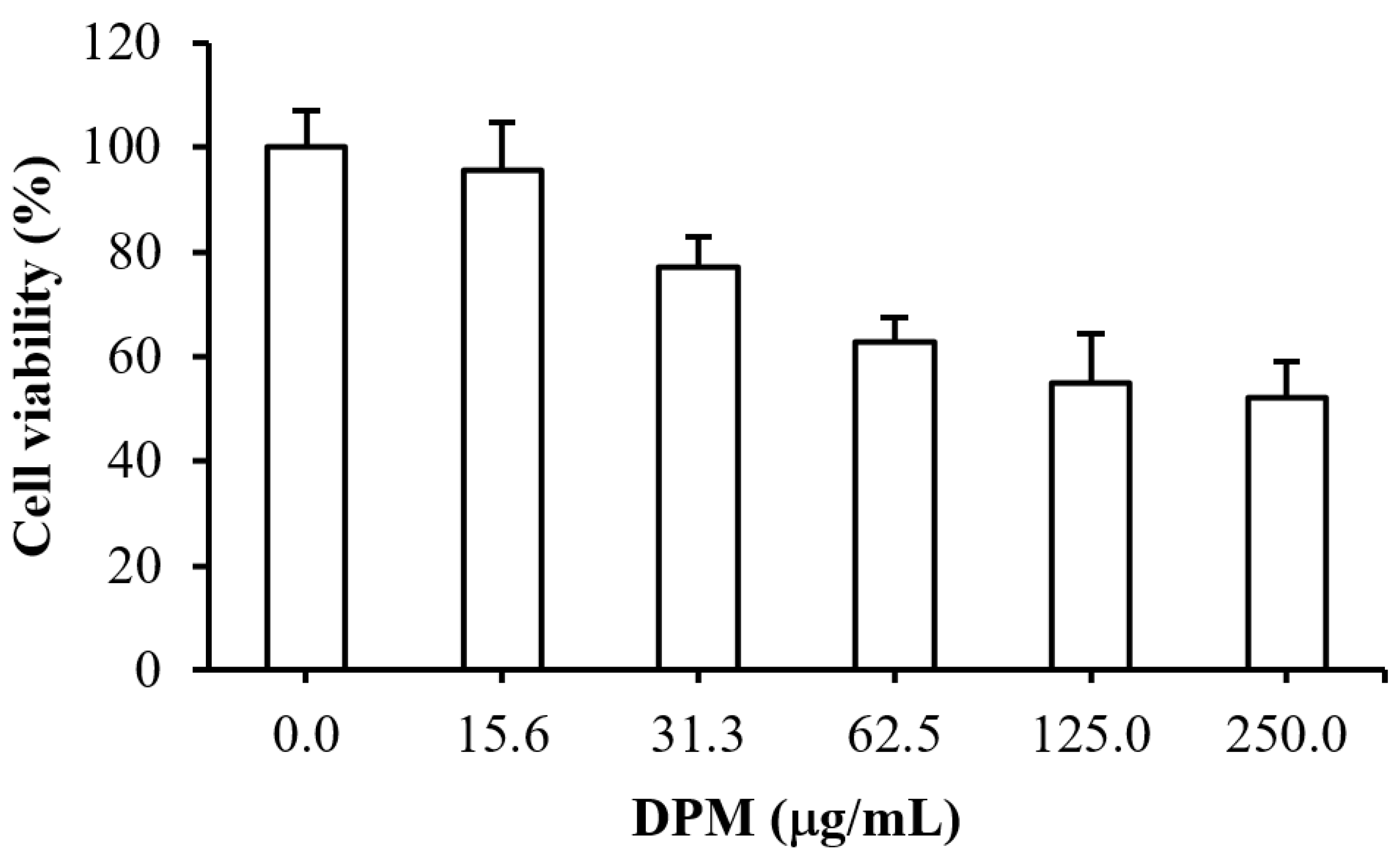
2.7. Cytotoxicity Test of DPM
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains, Constructs, Media, and Chemicals
3.2. Identification of the Seaweed Compounds by Using GC-MS
3.3. IC50 and Modulation Tests
3.4. Time-Kill Assays
3.5. Dye Accumulation Assay
3.6. Dye Efflux Assay
3.7. Monitoring Drug Efflux Using MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
3.8. Membrane Permeability Assay
3.9. Post-Antibiotic Effect Assay
3.10. Cell Toxicity Assays
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Interagency Coordination Group on Antimicrobial Resistance. No Time to Wait: Securing the Funture from Drug-Resistant Infections; 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/no-time-to-wait-securing-the-future-from-drug-resistant-infections (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Jasovsky, D.; Littmann, J.; Zorzet, A.; Cars, O. Antimicrobial resistance-a threat to the world’s sustainable development. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 121, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.J.; Lin, H.J.; Hsu, P.H.; Lin, H.T.V. Determination of drug efflux pump efficiency in drug-resistant bacteria using MALDI-TOF MS. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, R.; Chevalier, J.; Bryskier, A.; Pages, J.M. The AcrAB-TolC pump is involved in macrolide resistance but not in telithromycin efflux in Enterobacter aerogenes and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3621–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okusu, H.; Ma, D.; Nikaido, H. AcrAB efflux pump plays a major role in the antibiotic resistance phenotype of Escherichia coli multiple-antibiotic-resistance (Mar) mutants. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swick, M.C.; Morgan-Linnell, S.K.; Carlson, K.M.; Zechiedrich, L. Expression of multidrug efflux pump genes acrAB-tolC, mdfA, and norE in Escherichia coli clinical isolates as a function of fluoroquinolone and multidrug resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.P.; Nikaido, H. Kinetic parameters of efflux of penicillins by the multidrug efflux transporter AcrAB-TolC of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.T.; Bavro, V.N.; Barrera, N.P.; Frankish, H.M.; Velamakanni, S.; van Veen, H.W.; Robinson, C.V.; Borges-Walmsley, M.I.; Walmsley, A.R. MacB ABC transporter is a dimer whose ATPase activity and macrolide-binding capacity are regulated by the membrane fusion protein MacA. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, D.; van Veen, H.W.; Luisi, B.F. Assembly and operation of bacterial tripartite multidrug efflux pumps. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pages, J.M.; Sandrine, A.F.; Mahamoud, A.; Bolla, J.M.; Davin-Regli, A.; Chevalier, J.; Garnotel, E. Efflux pumps of gram-negative bacteria, a new target for new molecules. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Bostian, K.A. Practical applications and feasibility of efflux pump inhibitors in the clinic—A vision for applied use. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, J.M.; Amaral, L. Mechanisms of drug efflux and strategies to combat them: Challenging the efflux pump of Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2009, 1794, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuruo, T.; Iida, H.; Tsukagoshi, S.; Sakurai, Y. Overcoming of vincristine resistance in P388 leukemia in vivo and in vitro through enhanced cytotoxicity of vincristine and vinblastine by verapamil. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pule, C.M.; Sampson, S.L.; Warren, R.M.; Black, P.A.; van Helden, P.D.; Victor, T.C.; Louw, G.E. Efflux pump inhibitors: Targeting mycobacterial efflux systems to enhance TB therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neyfakh, A.A.; Borsch, C.M.; Kaatz, G.W. Fluoroquinolone resistance protein NorA of Staphylococcus aureus is a multidrug efflux transporter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lomovskaya, O.; Warren, M.S.; Lee, A.; Galazzo, J.; Fronko, R.; Lee, M.; Blais, J.; Cho, D.; Chamberland, S.; Renau, T. Identification and characterization of inhibitors of multidrug resistance efflux pumps in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Novel agents for combination therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjuts, H.; Vargiu, A.V.; Kwasny, S.M.; Nguyen, S.T.; Kim, H.S.; Ding, X.; Ornik, A.R.; Ruggerone, P.; Bowlin, T.L.; Nikaido, H.; et al. Molecular basis for inhibition of AcrB multidrug efflux pump by novel and powerful pyranopyridine derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3509–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savoia, D. Plant-derived antimicrobial compounds: Alternatives to antibiotics. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.A.; Mirza, Z.M.; Kumar, A.; Verma, V.; Qazi, G.N. Piperine, a phytochemical potentiator of ciprofloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirza, Z.M.; Kumar, A.; Kalia, N.P.; Zargar, A.; Khan, I.A. Piperine as an inhibitor of the MdeA efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, S.; Nargotra, A.; Koul, S.; Khan, I.A. Piperine as an inhibitor of Rv1258c, a putative multidrug efflux pump of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine Algae Extracts: Processes, Products, and Applications; Kim, S.K.; Chojnacka, K. (Eds.) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; p. 784. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, Y.L.; Lim, Y.Y.; Omar, M.; Khoo, K.S. Antioxidant activity of three edible seaweeds from two areas in South East Asia. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmughapriya, S.; Manilal, A.; Sujith, S.; Selvin, J.; Kiran, G.S.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Antimicrobial activity of seaweeds extracts against multiresistant pathogens. Ann. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.T.V.; Lu, W.J.; Tsai, G.J.; Chou, C.T.; Hsiao, H.I.; Hwang, P.A. Enhanced anti-inflammatory activity of brown seaweed Laminaria japonica by fermentation using Bacillus subtilis. Process. Biochem. 2016, 51, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlowska, K.; Hsu, T.; Hou, C.C.; Yang, W.C.; Tsai, G.J. Anti-inflammatory properties of phenolic compounds and crude extract from Porphyra dentata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifuddin, Y.; Chin, Y.X.; Lim, P.E.; Phang, S.M. Potential bioactive compounds from seaweed for diabetes management. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5447–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.T.V.; Tsou, Y.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Lu, W.J.; Hwang, P.A. Effects of Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan and High Stability Fucoxanthin on Glucose Homeostasis, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Function in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moussavou, G.; Kwak, D.H.; Obiang-Obonou, B.W.; Maranguy, C.A.; Dinzouna-Boutamba, S.D.; Lee, D.H.; Pissibanganga, O.G.; Ko, K.; Seo, J.I.; Choo, Y.K. Anticancer effects of different seaweeds on human colon and breast cancers. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4898–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Lin, H.J.; Hsu, P.H.; Lai, M.; Chiu, J.Y.; Lin, H.T.V. Brown and red seaweeds serve as potential efflux pump inhibitors for drug-resistant Escherichia coli. Evid.-Based Complement Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1836982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poole, K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug efflux pumps of gram negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falcao-Silva, V.S.; Silva, D.A.; Souza Mde, F.; Siqueira-Junior, J.P. Modulation of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by a kaempferol glycoside from Herissantia tiubae (Malvaceae). Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Park, H.C.; Park, S.W.; Park, S.C.; Seo, M.G.; Her, M.; Kang, J. Synergism of the Combination of Traditional Antibiotics and Novel Phenolic Compounds against Escherichia coli. Pathogens 2020, 9, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belley, A.; Neesham-Grenon, E.; Arhin, F.F.; Mckay, G.A.; Parr, T.R.; Moeck, G. Assessment by time-kill methodology of the synergistic effects of oritavancin in combination with other antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3820–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opperman, T.J.; Kwasny, S.M.; Kim, H.-S.; Nguyen, S.T.; Houseweart, C.; D’Souza, S.; Walker, G.C.; Peet, N.P.; Nikaido, H.; Bowlin, T.L. Characterization of a novel pyranopyridine inhibitor of the AcrAB efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mouwakeh, A.; Kincses, A.; Nove, M.; Mosolygo, T.; Mohacsi-Farkas, C.; Kisko, G.; Spengler, G. Nigella sativa essential oil and its bioactive compounds as resistance modifiers against Staphylococcus aureus. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.; Piddock, L.J. How to measure export via bacterial multidrug resistance efflux pumps. MBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aron, Z.; Opperman, T.J. The hydrophobic trap-the Achilles heel of RND efflux pumps. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, E.; Vergalli, J.; Conraux, L.; Taillier, C.; Vassort, A.; Pajovic, J.; Refregiers, M.; Mourez, M.; Pages, J.M. Antibiotics and efflux: Combined spectrofluorimetry and mass spectrometry to evaluate the involvement of concentration and efflux activity in antibiotic intracellular accumulation. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.R.; Ettefagh, K.A.; Todd, D.; Cole, P.S.; Egan, J.M.; Foil, D.H.; Graf, T.N.; Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cech, N.B. A mass spectrometry-based assay for improved quantitative measurements of efflux pump inhibition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamut, A.; Peterlin Masic, L.; Kikelj, D.; Tomasic, T. Efflux pump inhibitors of clinically relevant multidrug resistant bacteria. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2460–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanberger, H.; Nilsson, L.E.; Kihlstrom, E.; Maller, R. Postantibiotic effect of beta-lactam antibiotics on Escherichia coli evaluated by bioluminescence assay of bacterial ATP. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1990, 34, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tambat, R.; Jangra, M.; Mahey, N.; Chandal, N.; Kaur, M.; Chaudhary, S.; Verma, D.K.; Thakur, K.G.; Raje, M.; Jachak, S.; et al. Microbe-derived indole metabolite demonstrates potent multidrug efflux pump inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Guo, N.; Feng, H.H.; Li, L.; Liang, J.C.; Sun, K.; Wu, X.P.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, M.Y.; et al. The plant alkaloid piperine as a potential inhibitor of ethidium bromide efflux in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Rais, J.; Ahmad, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Jafar, T.; Afzal, M.; Arshad, M. Induction of apoptosis by piperine in human cervical adenocarcinoma via ROS mediated mitochondrial pathway and caspase-3 activation. EXCLI J. 2019, 18, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, Y.; Kodama, K.; Shiota, S.; Mine, T.; Kataoka, A.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. NorM, a putative multidrug efflux protein, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its homolog in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soothill, J.S.; Ward, R.; Girling, A.J. The IC50: An exactly defined measure of antibiotic sensitivity. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1992, 29, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicetti, T.; Mangiaterra, G.; Cannalire, R.; Cedraro, N.; Pietrella, D.; Astolfi, A.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.J.; Lin, H.J.; Janganan, T.K.; Li, C.Y.; Chin, W.C.; Bavro, V.N.; Lin, H.V. ATP-binding cassette transporter VcaM from Vibrio cholerae is dependent on the outer membrane factor family for its function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, D.; Fernandes, L.; Costa, S.S.; Cannalire, R.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Couto, I.; Sabatini, S.; Viveiros, M. Mode of action of the 2-phenylquinoline efflux inhibitor PQQ4R against Escherichia coli. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Antibiotics | DPM Concentration(µg/mL) | IC50 (µg/mL) | Modulation Factor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alone | With DPM | |||
| Clarithromycin | 7.81 | 175 | 87.5 | 2 |
| Erythromycin | 125 | 125 | 62.5 | 2 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 7.81 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.-J.; Hsu, P.-H.; Chang, C.-J.; Su, C.-K.; Huang, Y.-J.; Lin, H.-J.; Lai, M.; Ooi, G.-X.; Dai, J.-Y.; Lin, H.-T.V. Identified Seaweed Compound Diphenylmethane Serves as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111378
Lu W-J, Hsu P-H, Chang C-J, Su C-K, Huang Y-J, Lin H-J, Lai M, Ooi G-X, Dai J-Y, Lin H-TV. Identified Seaweed Compound Diphenylmethane Serves as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(11):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111378
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wen-Jung, Pang-Hung Hsu, Chun-Ju Chang, Cheng-Kuan Su, Yan-Jyun Huang, Hsuan-Ju Lin, Margaret Lai, Gui-Xia Ooi, Jing-Yi Dai, and Hong-Ting Victor Lin. 2021. "Identified Seaweed Compound Diphenylmethane Serves as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli" Antibiotics 10, no. 11: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111378
APA StyleLu, W.-J., Hsu, P.-H., Chang, C.-J., Su, C.-K., Huang, Y.-J., Lin, H.-J., Lai, M., Ooi, G.-X., Dai, J.-Y., & Lin, H.-T. V. (2021). Identified Seaweed Compound Diphenylmethane Serves as an Efflux Pump Inhibitor in Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli. Antibiotics, 10(11), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10111378






