A Molecule of the Viridomycin Family Originating from a Streptomyces griseus-Related Strain Has the Ability to Solubilize Rock Phosphate and to Inhibit Microbial Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
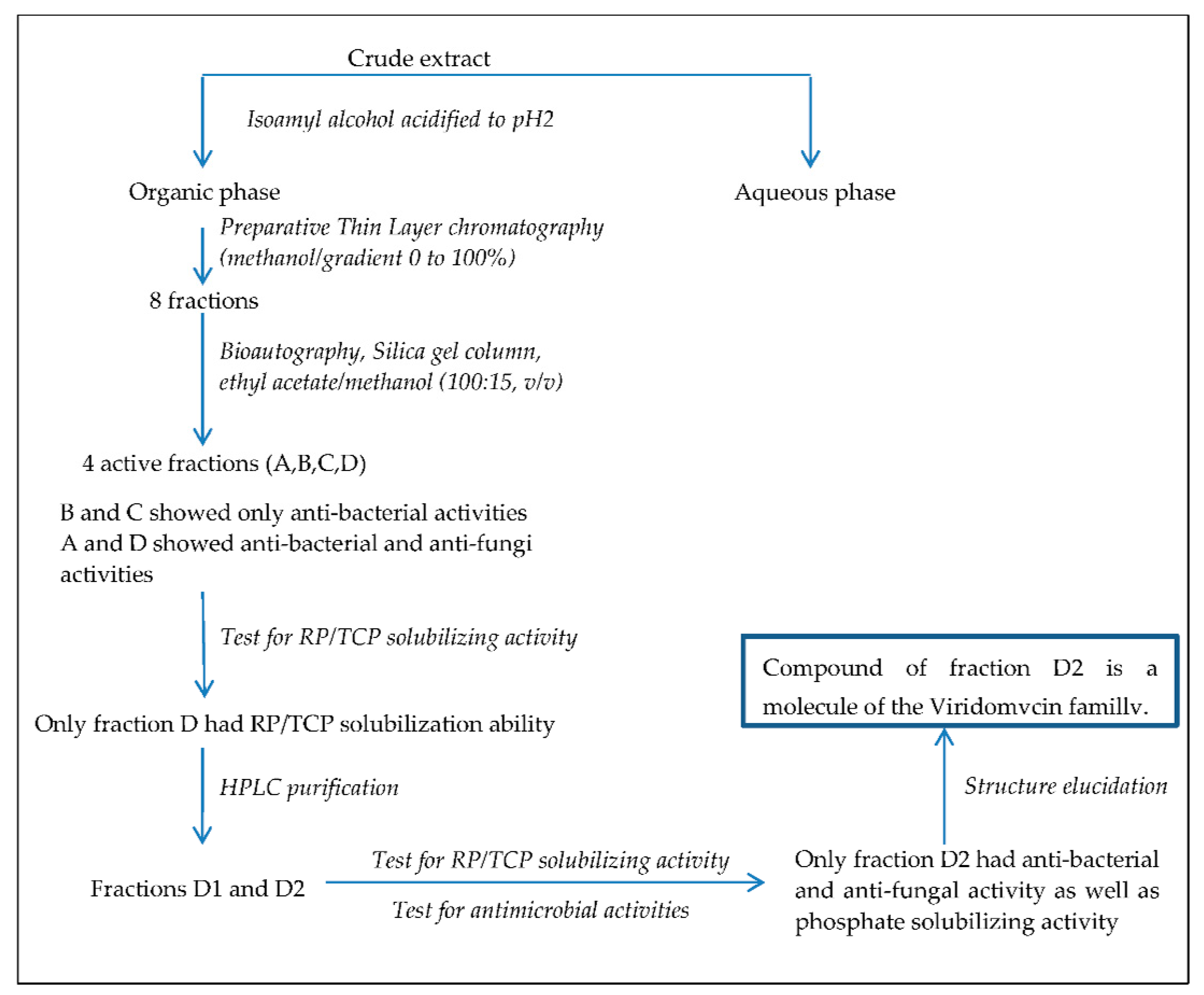
2.1. Detection and Purification of Bio-Active Fractions
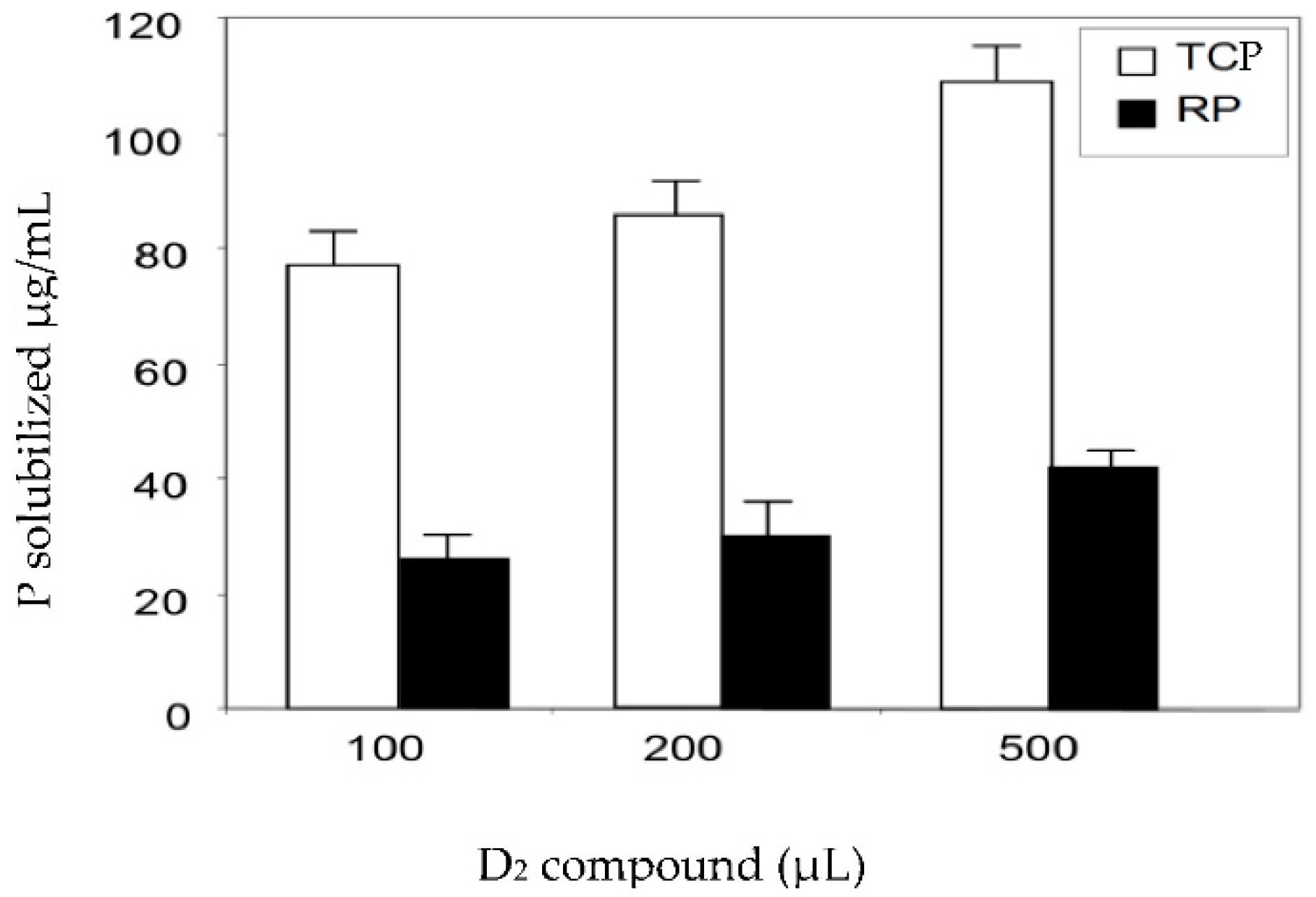
2.2. Determination of the Mineral Phosphate-Solubilizing Abilities of the Bio-Active Fractions
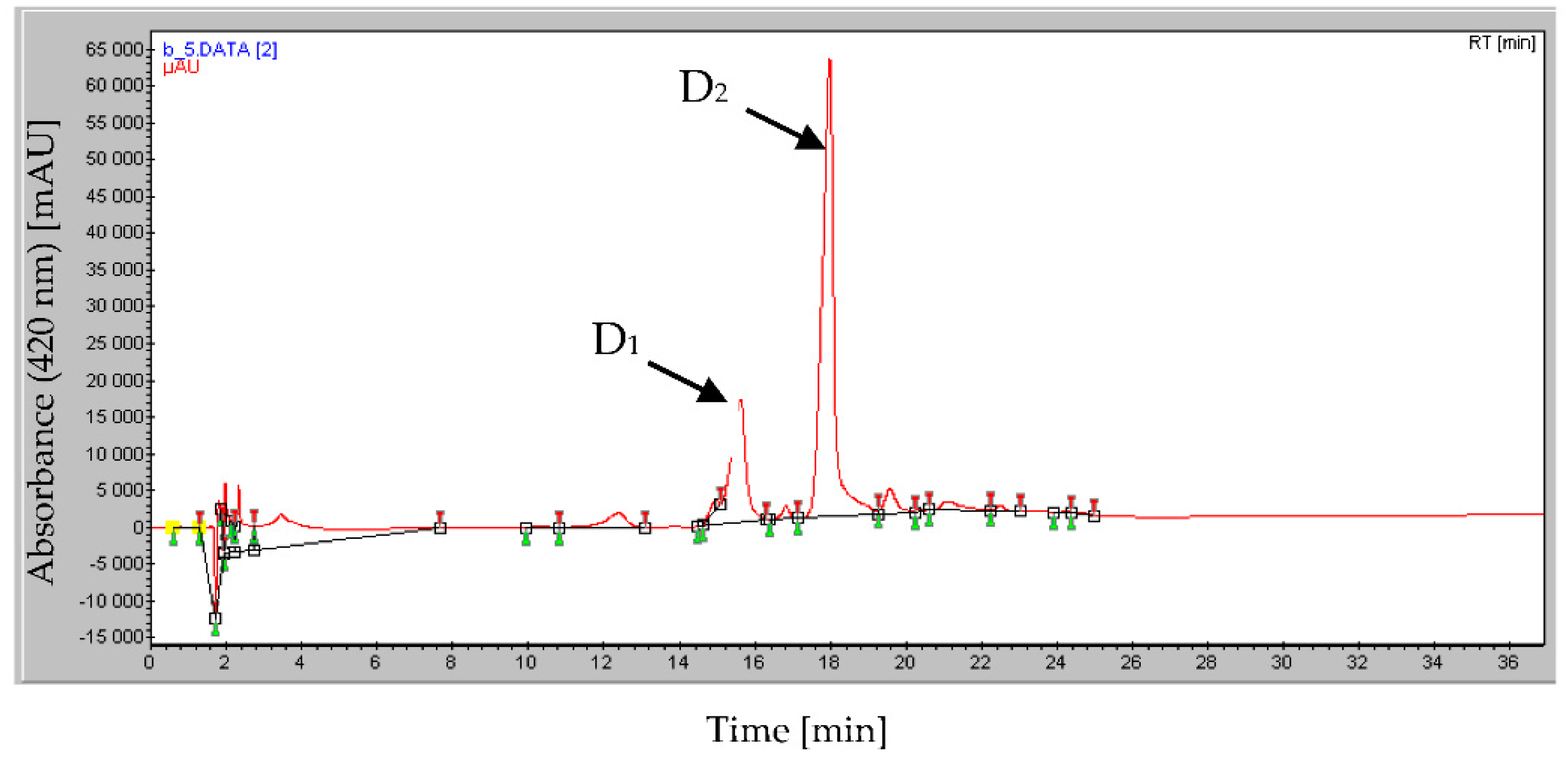
2.3. HPLC Analysis of the Bio-Active Fraction D that Also Bears Mineral Phosphate-Solubilizing Ability
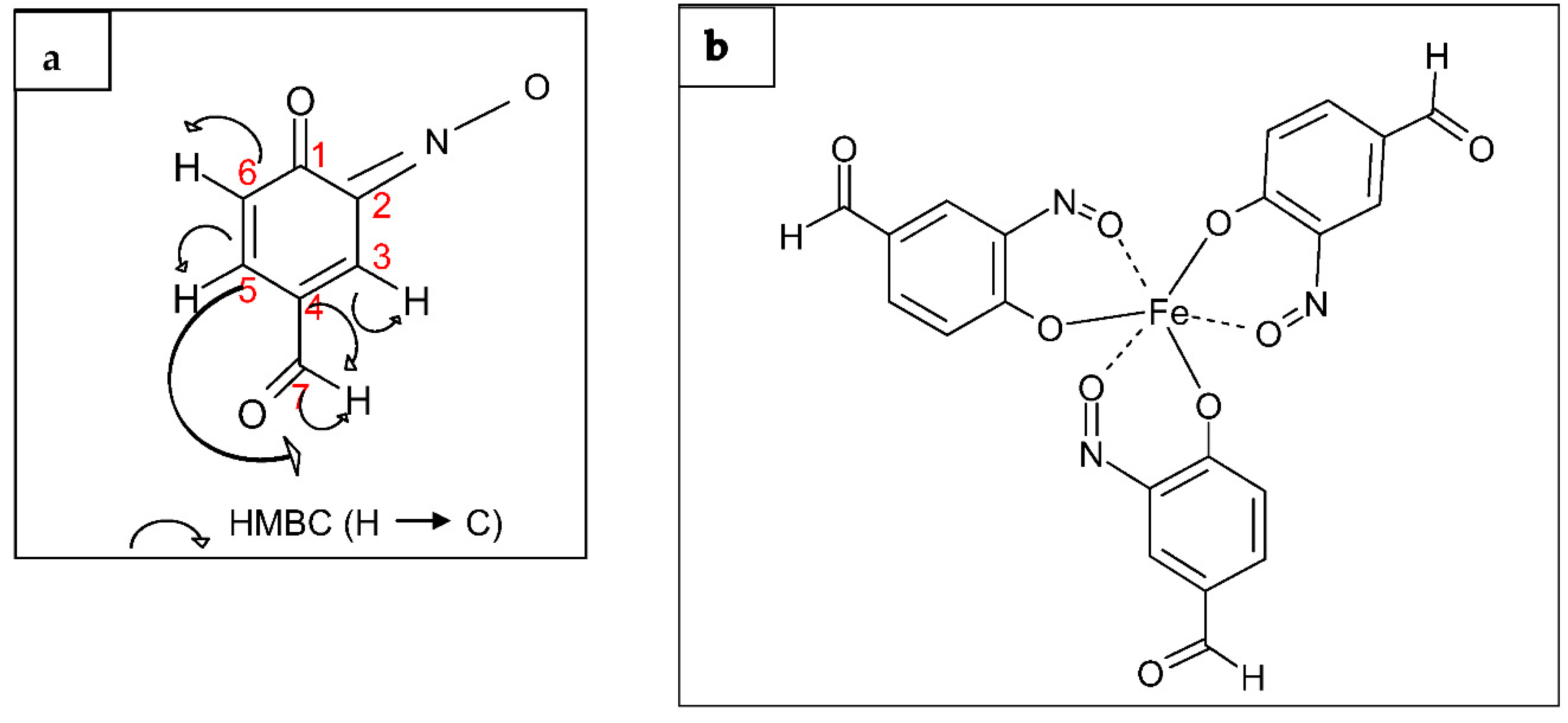
2.4. Structural Determination of the Bio-Active Compound of Fraction D2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain and Culture Conditions
4.2. Production and Extraction of Active Compounds
4.3. Detection and Purification of Active Fractions with Antimicrobial Activities
4.3.1. Antimicrobial Bioassay against Bacteria and Fungi
4.3.2. Determination of Phosphate-Solubilizing Abilities
4.4. Purification and Structure Elucidation of the Active Compound
4.5. Determination of the Iron Content of the Active Compound
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gyaneshwar, P.; Kumar, G.N.; Parekh, L.J.; Poole, P.S. Role of soil microorganisms in improving P nutrition of plants. Plant Soil 2002, 245, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, P.U.; Dahale, S. Mineral phosphate solubilization: Concepts and prospects in sustainable agriculture. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumare, A.; Boubekri, B.; Lyamlouli, K.; Hafidi, M.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Kouisni, L. From isolation of phosphate solubilizing microbes to their formulation and use as biofertilizers: Status and needs. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapata, F.; Zaharah, A.R. Phosphorus availability from phosphate rock and sewage sludge as influenced by the addition of water-soluble phosphate fertilizer. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Knight, J.D. Enhanced solubilization of rock phosphate by Penicillium bilaiae in pH-buffered solution culture. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, H.; Fraga, R. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, N.; Vassileva, M.; Nikolaeva, I. Simultaneous P-solubilizing and biocontrol activity of microorganisms: Potentials and future trends. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, P.A.; Khan, M.S.; Zaidi, A. Chromium reduction, plant growth-promoting potentials and metal solubilization by Bacillus sp. isolated from alluvial soil. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 54, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te-Hsiu, M. The international program on plant bioassays and the report of the follow-up study after the hands-on workshop in China. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 1999, 426, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdali, H.; Bouizgarne, B.; Hafidi, M.; Lebrihi, A.; Virolle, M.J.; Ouhdouch, Y. Screening for rock phosphate solubilizing Actinomycetes from Moroccan phosphate mines. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 38, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdali, H.; Hafidi, M.; Virolle, M.J.; Ouhdouch, Y. Rock phosphate solubilizing Actinomycetes: Screening for plant growth promoting activities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdali, H.; Hafidi, M.; Virolle, M.J.; Ouhdouch, Y. Growth promotion and protection against damping–off of wheat by two rock phosphate solubilizing Actinomycetes in a P-deficient soil under greenhouse conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdali, H.; Smirnov, A.; Esnault, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Virolle, M.J. Comparative physiological studies of Actinomycetes originating from Moroccan phosphate mines and Streptomyces lividans. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 44, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mba, C.C. Rock phosphate solubilizing Streptosporangium isolates from casts of tropical earthworms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T. Pharmacological effects of ivermectin, an antiparasitic agent for intestinal strongyloidiasis: Its mode of action and clinical efficacy. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi 2003, 122, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Jain, P.C. Isolation, characterization and antifungal activity of Streptomyces sampsonii GS 1322. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 45, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, S.; Enomoto, Y.; Shinose, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Iwai, Y.; Shiomi, K. Isolation and structure of a new antibiotic Viridomycin F produced by Streptomyces sp. K96-01 88. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chain, E.B.; Tonolo, A.; Carilli, A. Ferroverdin, green pigment containing iron produced by a Streptomycete. Nature 1955, 176, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, I.N.; Egorova, S.A.; Marchenko, I.V.; Saulina, L.I.; Blinov, N.O.; Khokhlov, A.S. New iron-containing antibiotics: Extraction and properties of Viridomycin A, B, and C. Khimiya Prir. Soedin. 1975, 11, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- Kurobane, I.; Dale, P.L.; Vining, L.C. Characterization of new viridomycins and requirements for production in cultures of Streptomyces griseus. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, I.V.; Egorova, S.A.; Blinov, N.O.; Krasilnikov, N.A. Proviridomycin-a precursor of the green pigment of Actinomycetes. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1968, 180, 978–980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Leong, J. Mode of antibiotic action of 4-hydroxy-3-nitrosobenzaldehyde from Streptomyces viridians. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 20, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, H.P.; Krastel, P.; Müller, J.; Gebhardt, K.; Zeeck, A. Enterobactin: The characteristic catecholate siderophore of Enterobacteriaceae is produced by Streptomyces species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 196, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liermann, L.J.; Kalinowski, B.E.; Brantley, S.L.; Ferry, J.G. Role of bacterial siderophores in dissolution of hornblende. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, B.; Gerlitz, M.; Paululat, T.; Rasser, H.F.; Grün-Wollny, I.; Hansske, F.G. Oxachelin, a Novel Iron Chelator and Antifungal Agent from Streptomyces sp. GW9/1258. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; Yuan, H. Mechanisms for solubilization of various insoluble phosphates and activation of immobilized phosphates in different soils by an efficient and salinity-tolerant Aspergillus niger strain An2. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 2755–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, N.; Mendes, G.; Costa, M.; Vassileva, M. Biotechnological tools for enhancing microbial solubilization of insoluble inorganic phosphates. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, I.; Bernier, L.; Simard, R.R.; Tanguay, P.; Antoun, H. Characteristics of phosphate solubilization by an isolate of a tropical Penicillium rugulosum and two UV-induced mutants. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 28, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narsian, V.; Patel, H.H. Aspergillus aculeatus as a rock phosphate solubilizer. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, S.A.; Taunton, A.E.; Banfield, J.F. Effect of microorganisms and microbial metabolites on apatite dissolution. Geomicrobiol. J. 2002, 19, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallaiah, K.V.; Sridevi, M. Production of hydroxamate-type of siderophores by Rhizobium strains from Sesbania sesban (L.). Merr. Int. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 3, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frei, A.; Zuegg, J.; Elliott, A.G.; Baker, M.; Braese, S.; Brown, C.; Chen, F.; Dowson, C.G.; Dujardin, G.; Jung, N.; et al. Metal complexes as a promising source for new antibiotics. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, L.; Dyson, P.; Ratcliffe, N.; Castro, H.C.; Vicente, A.C.P. Biotechnological Potential of Streptomyces Siderophores as New Antibiotics. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 2627–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betina, V. Bioautography in paper and thin layer chromatography and its scope in the antibiotic field. J. Chromatogr. A 1973, 78, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeny, D.R., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Rauret, G.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauvillier, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monitor. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antimicrobial Activity a against | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram Positive Bacteria | Fungi | |||
| Bacillus subtilis ATCC 9524 | Micrococcus luteus ATCC 381 | Pythium ultimum BCCM 16164 | Mucor ramannianus NRRL 1829 | |
| Diameter of the inhibition zone (mm) | 29 ± 1.2 | 45 ± 1.4 | 27 ± 1.1 | 38 ± 1.0 |
| Position | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | HMBC a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 182.0 | ||
| 2 | 159.3 | ||
| 3 | 115.7 | 7.56 s | Observed |
| 4 | 123.9 | Observed | |
| 5 | 134.5 | 7.96 d (9) | Observed |
| 6 | 122.5 | 7.16 d (9) | |
| 7 | 190.5 | 9.78 s | Observed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamdali, H.; Lebrihi, A.; Monje, M.C.; Benharref, A.; Hafidi, M.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Virolle, M.J. A Molecule of the Viridomycin Family Originating from a Streptomyces griseus-Related Strain Has the Ability to Solubilize Rock Phosphate and to Inhibit Microbial Growth. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010072
Hamdali H, Lebrihi A, Monje MC, Benharref A, Hafidi M, Ouhdouch Y, Virolle MJ. A Molecule of the Viridomycin Family Originating from a Streptomyces griseus-Related Strain Has the Ability to Solubilize Rock Phosphate and to Inhibit Microbial Growth. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamdali, Hanane, Ahmed Lebrihi, Marie Carmen Monje, Ahmed Benharref, Mohamed Hafidi, Yedir Ouhdouch, and Marie Joëlle Virolle. 2021. "A Molecule of the Viridomycin Family Originating from a Streptomyces griseus-Related Strain Has the Ability to Solubilize Rock Phosphate and to Inhibit Microbial Growth" Antibiotics 10, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010072
APA StyleHamdali, H., Lebrihi, A., Monje, M. C., Benharref, A., Hafidi, M., Ouhdouch, Y., & Virolle, M. J. (2021). A Molecule of the Viridomycin Family Originating from a Streptomyces griseus-Related Strain Has the Ability to Solubilize Rock Phosphate and to Inhibit Microbial Growth. Antibiotics, 10(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010072






