Flexible PET/ITO/Ag SERS Platform for Label-Free Detection of Pesticides
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- They are easy to fabricate: easy to bend and cut to any shape (in contrast to substrates based on silicon, glass or quartz),
- (ii)
- They do not crumble and/or break at loads with bending and torsional moments,
- (iii)
- They offer high enhancement of the Raman signal, so they can be used in most analytical applications,
- (iv)
- The technological process is simple and finished or semi-finished products (e.g., films coated with conductive oxide, foils or fabrics) can be purchased commercially in large quantities,
- (v)
- Flexible SERS platforms can be attached to rough, irregular surfaces and can be used to take samples directly from the surface of a body or pesticides from the surface of fruit (“paste and peel off” approach),
- (vi)
- Due to their flexibility, they offer increased versatility of sampling, e.g., swabs or micro-extractions,
- (vii)
- They are easy to use in the field (no need to apply solution as in the case of colloids or nanoparticles).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
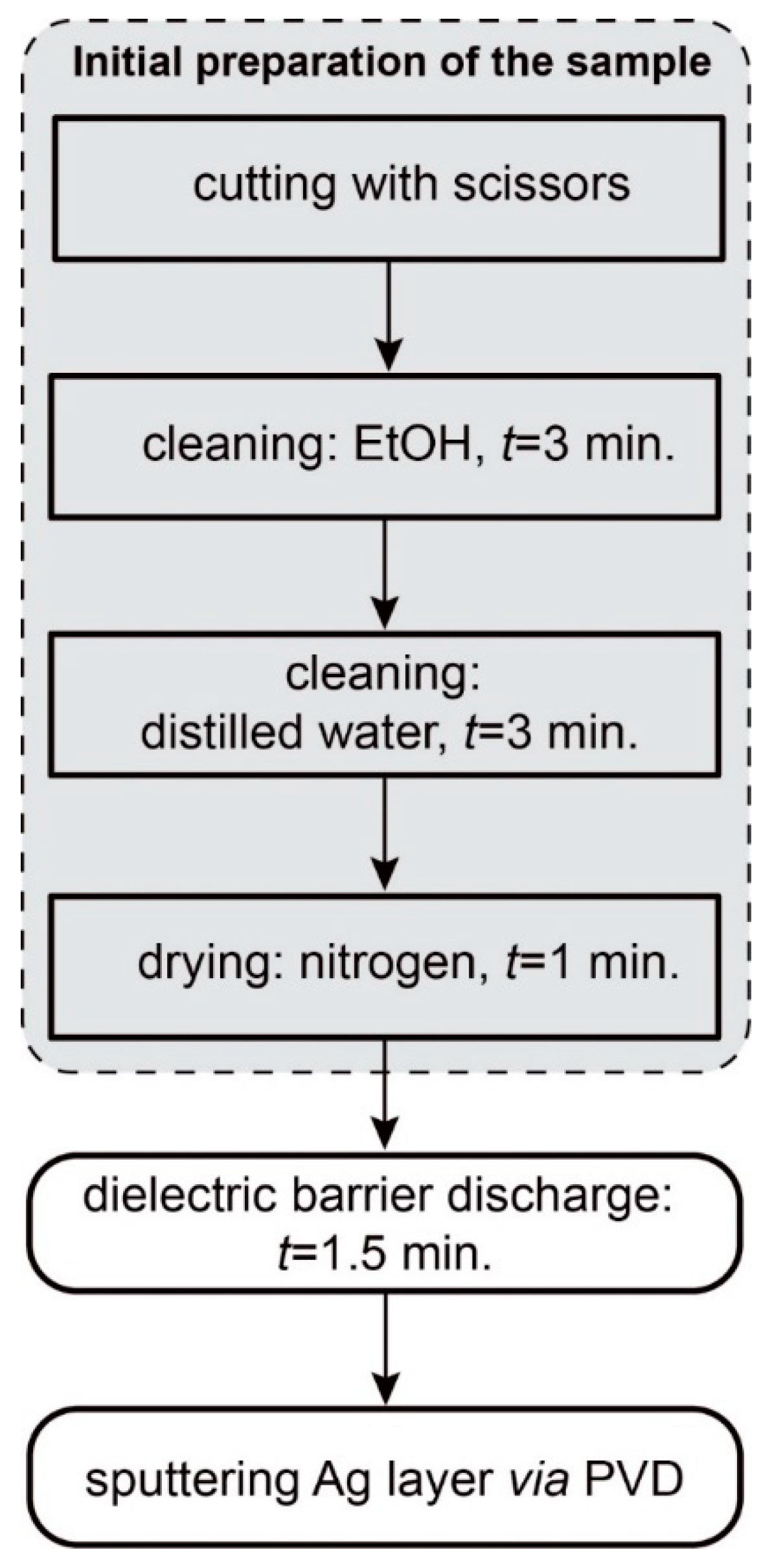
2.2. Preparation of the SERS Platform
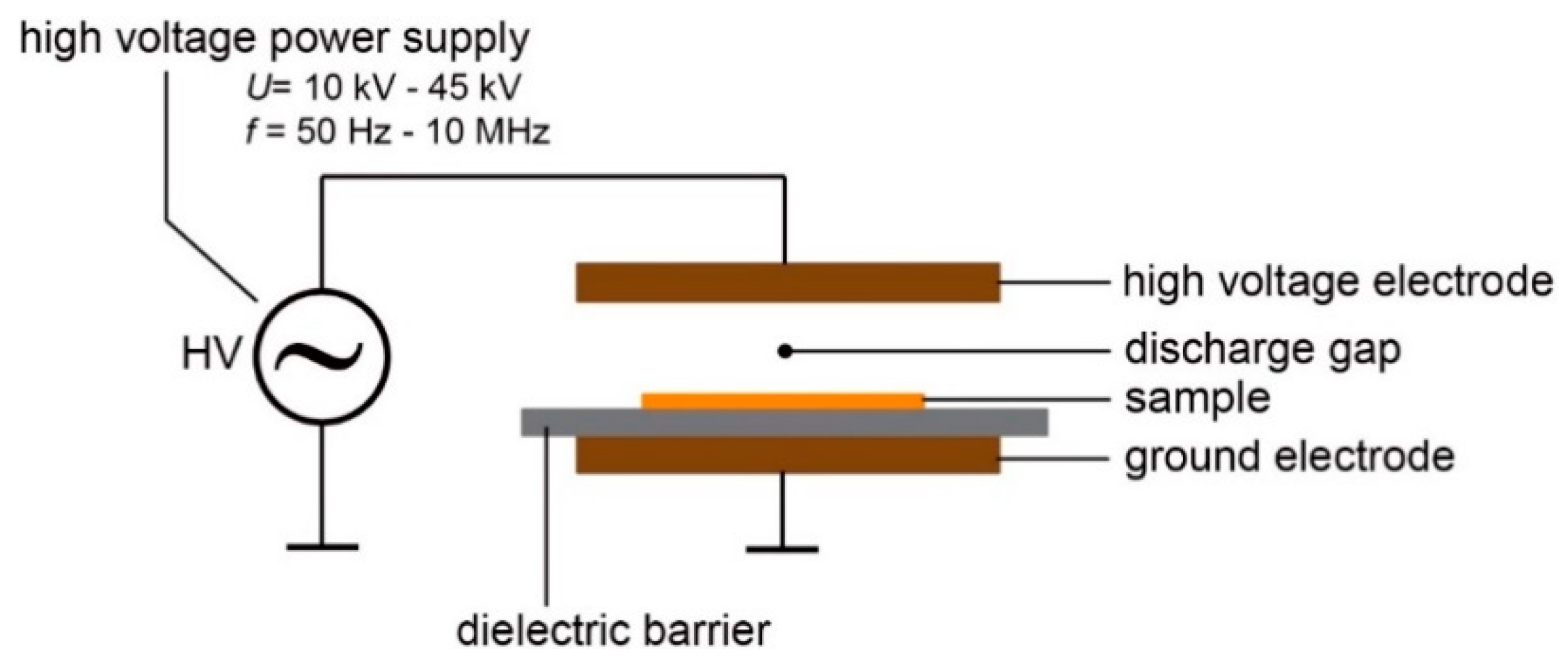
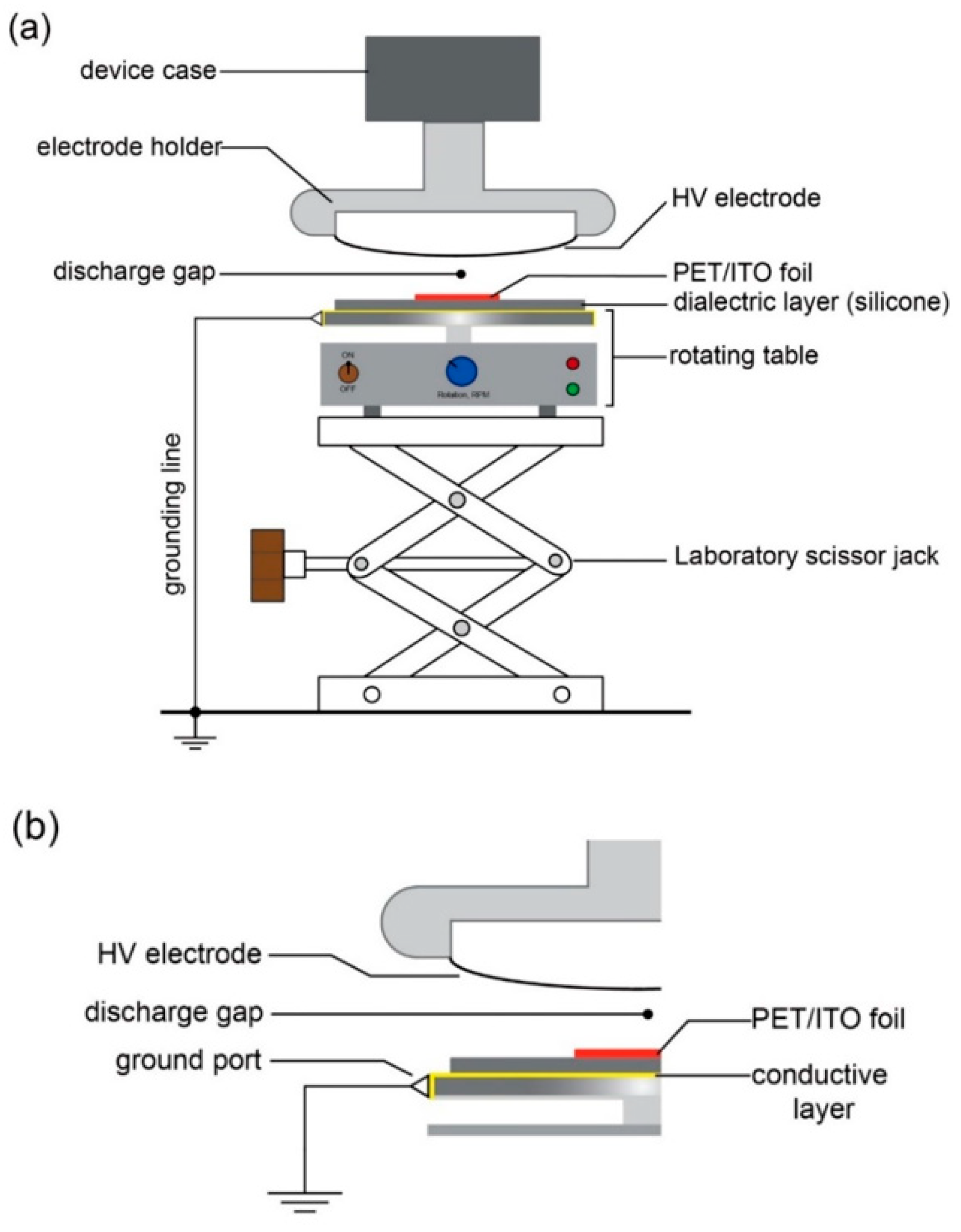
2.2.1. Modification of the Surface via Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD)
- (i)
- the distance d (mm) between the high voltage (HV) electrode and the PET/ITO foil,
- (ii)
- the voltage U (V) between the HV electrode and the ground,
- (iii)
- the time t (s) of the process.
2.2.2. Developing of SERS Platform via PVD
2.3. SERS Measurements
2.4. Microscopic Characterization
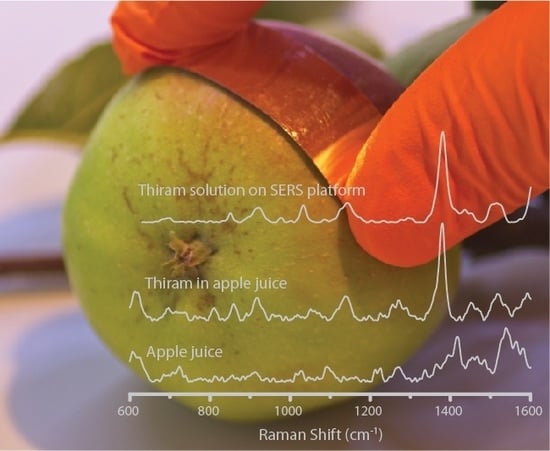
2.5. Preparation of the Samples for In Situ Detection of Pesticides
3. Results and Discussion
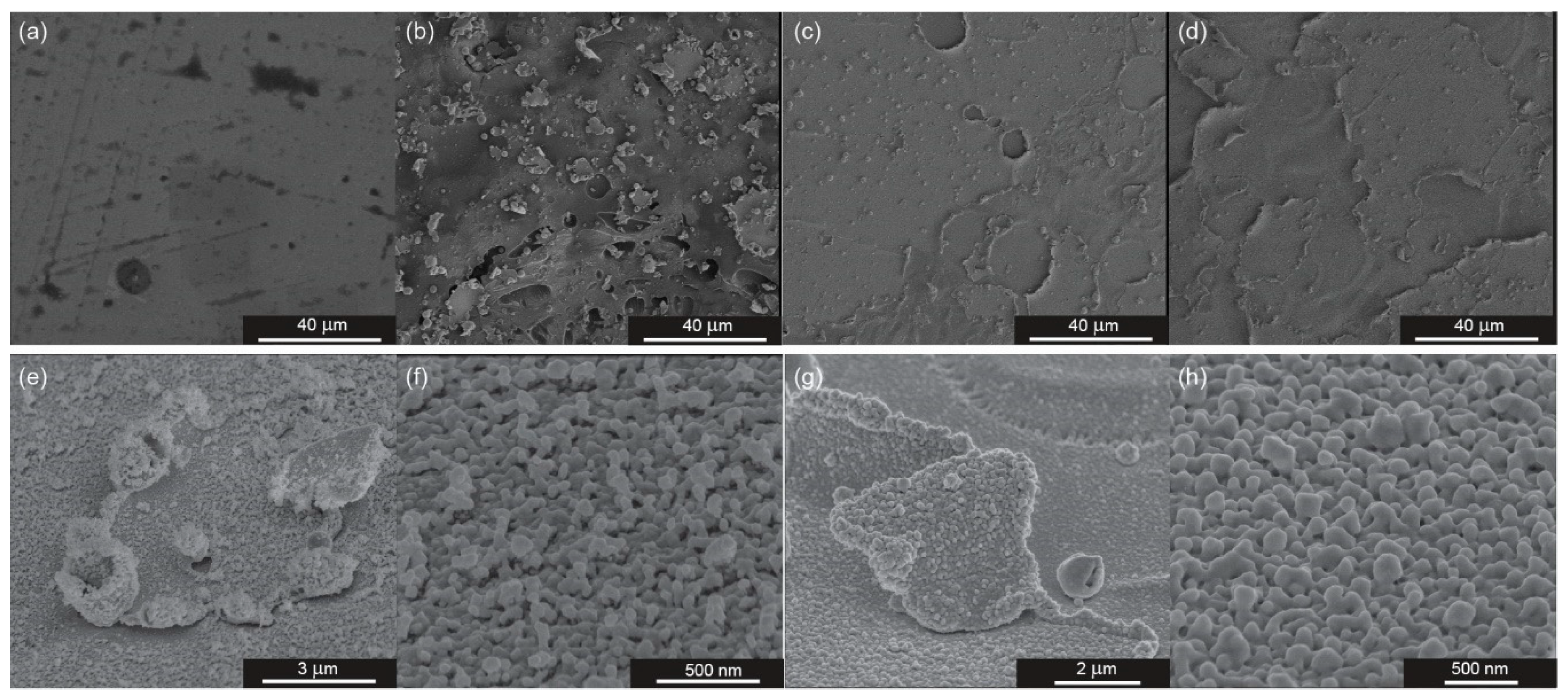
3.1. Morphology of the Platform
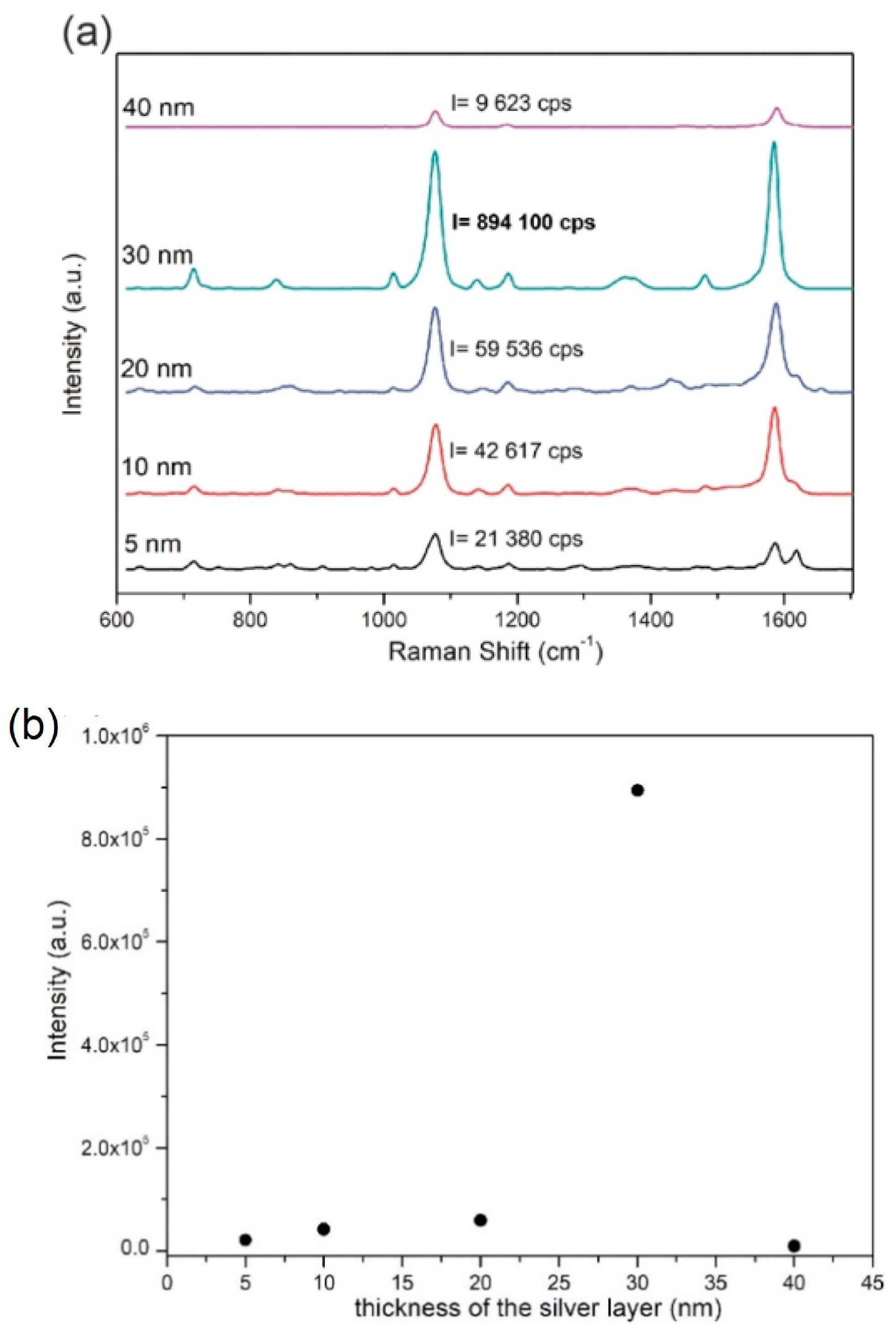
3.2. Enhancing Properties of Fabricated Platform
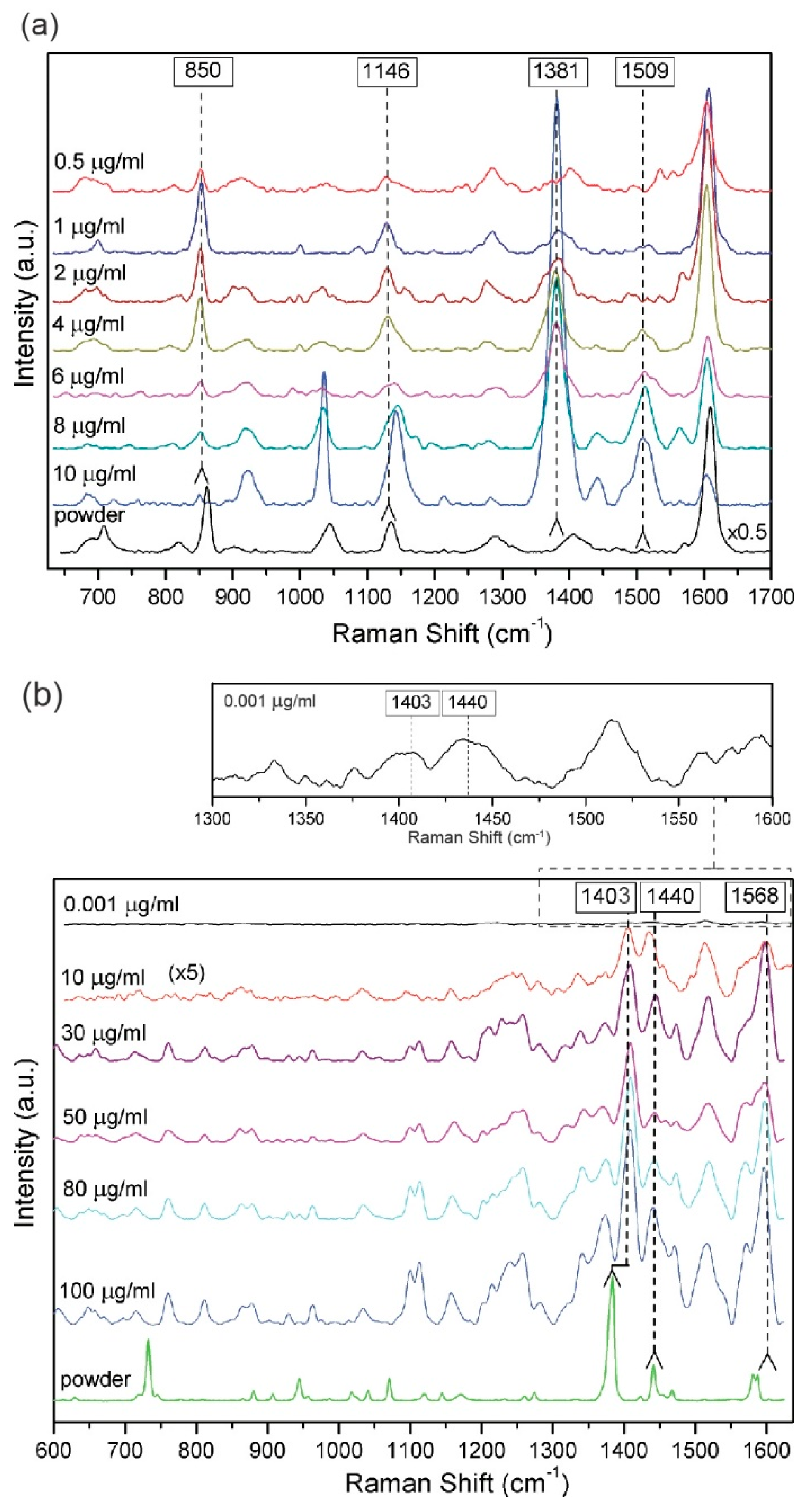
3.3. SERS Spectra of Pesticides
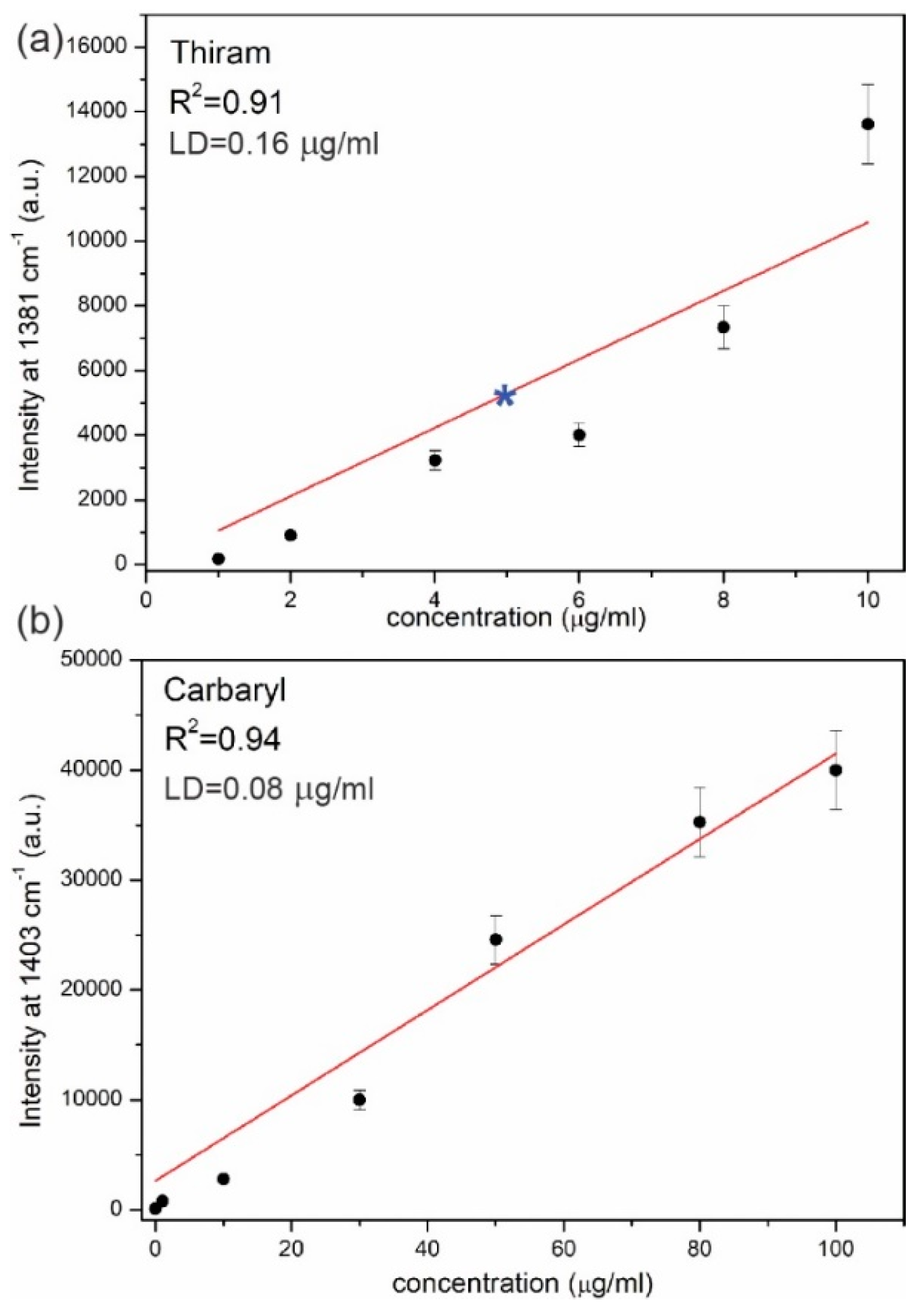
3.4. Reproducibility of SERS Signal and Calibration Curve of Pesticides
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alavanja, M.C. Introduction: Pesticides use and exposure extensive worldwide. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.L.; Gao, Y.; Han, X.X.; Zhao, B. Detection of Pesticide Residues in Food Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6719–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Yang, T.; He, L. Review of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) detection of synthetic chemical pesticides. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/airs/2018/environment-and-health/pesticides-sales (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Silva, V.; Mol, H.G.J.; Zomer, P.; Tienstra, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Pesticide residues in European agricultural soils—A hidden reality unfolded. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Lai, K.; Rasco, B.A.; Huang, Y. Analyses of phosmet residues in apples with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Food Control 2014, 37, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørling-Poulsen, M.; Andersen, H.R.; Grandjean, P. Potential developmental neurotoxicity of pesticides used in Europe. Environ. Health 2008, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, M.F.A.; Awadh, D.G.; Albaho, M.S.; Devi, V.Y.; Ahmad, N. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Commonly Used Fruits and Vegetables in Kuwait. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Q.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Yang, M.; Ouyang, Q.; Jiang, H. Highly sensitive and label-free determination of thiram residue using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) coupled with paper-based microfluidics. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6186–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Lin, M. Detection of Pesticides in Fruits by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Gold Nanostructures. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cortés, S.; Vasina, M.; Francioso, O.; García-Ramos, J.V. Raman and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of dithiocarbamate fungicides. Vib. Spectrosc. 1998, 17, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alak, A.M.; Vo-Dinh, T. Surface-enhanced Raman spectrometry of organo phosphorus chemical agents. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 2149–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.-I.; Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R.P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Faulds, K. Quantitative SERRS for DNA sequence analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peron, O.; Rinnert, E.; Toury, T.; Lamy de la Chapelle, M.; Compere, C. Quantitative SERS sensors for environmental analysis of naphthalene. Analyst 2011, 136, 1018–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulds, K.; Smith, W.E.; Graham, D.; Lacey, R.J. Assessment of silver and gold substrates for the detection of amphetamine sulfate by surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Analyst 2002, 127, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.P.; Franca, A.S.; Irudayaraj, J. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Applied to Food Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungroo, N.A.; Oliveira, G.; Neethirajan, S. SERS based point-of-care detection of food-borne pathogens. Microchim. Acta 2015, 183, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppmann, E.P.; Yu, W.W.; White, I.M. Highly sensitive and flexible inkjet printed SERS sensors on paper. Methods 2013, 63, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Mou, T.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Wang, B.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Paper-based SERS analysis with smartphones as Raman spectral analyzers. Analyst 2018, 144, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Huang, M.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Kong, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Lin, M. A “drop-wipe-test” SERS method for rapid detection of pesticide residues in fruits. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Bai, X.; He, M.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Ran, J.; Cai, G.; Wang, X. Polydopamine-assisted immobilization of Ag@AuNPs on cotton fabrics for sensitive and responsive SERS detection. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4191–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; He, M.; Ran, J.; Cai, G.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Depositing a flexible substrate of triangular silver nanoplates onto cotton fabrics for sensitive SERS detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 270, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, A.; Guang, S.; Cai, Z. Flexible and recyclable SERS substrate fabricated by decorated TiO2 film with Ag NPs on the cotton fabric. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuni, B.; Fujita, Y.; Ricci, M.; Inose, T.; Aubert, R.; Lu, G.; Hutchison, J.A.; Hofkens, J.; Latterini, L.; Uji, I.H. A novel method for in situ synthesis of SERS-active gold nanostars on polydimethylsiloxane film. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5121–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Jiang, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M. Controlled depositing of silver nanoparticles on flexible film and its application in ultrasensitive detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 42358–42363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiohara, A.; Langer, J.; Polavarapu, L.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Solution processed polydimethylsiloxane/gold nanostar flexible substrates for plasmonic sensing. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9817–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Meng, G.; Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q. Ag-nanoparticle-decorated porous ZnO-nanosheets grafted on a carbon fiber cloth as effective SERS substrates. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 15280–15285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaja, K.; Bhuvaneswari, S.; Ganiga, M.; Divyamol, R.; Anup, S.; Cyriac, J.; George, B.K. Effective SERS detection using a flexible wiping substrate based on electrospun polystyrene nanofibers. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3998–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, C.; Ge, M.; Pan, H.; Wang, J.; Nie, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y. In situ synthesis of low-cost and large-scale flexible metal nanoparticle–polymer composite films as highly sensitive SERS substrates for surface trace analysis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-X.; Wang, Y.-T.; You, T.-T.; Zhai, J.; Yin, P.-G. Stable and Recyclable SERS Substrates Based on Au-Loaded PET Nanocomposite Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Nano 2018, 13, 1850053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Meng, G.; Huang, Q.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. CNTs-anchored egg shell membrane decorated with Ag-NPs as cheap but effective SERS substrates. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Kannan, P.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Guo, L. Flexible and Adhesive Surface Enhance Raman Scattering Active Tape for Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues in Fruits and Vegetables. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Zou, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, S.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Z. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection of Pesticide Residues Using Transparent Adhesive Tapes and Coated Silver Nanorods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9129–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Cheng, F.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; Lin, J.; Brolo, A.G.; Zhan, H. Ag decorated sandpaper as flexible SERS substrate for direct swabbing sampling. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodjo, E.K.; Riaz, S.; Li, D.-W.; Qu, L.-L.; Marius, N.P.; Albert, T.; Long, Y.-T. Cu@Ag/β-AgVO3 as a SERS substrate for the trace level detection of carbamate pesticides. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.; Caro, C.; Mendes, M.J.; Nunes, D.; Fortunato, E.; Franco, R.; Águas, H.; Martins, R. Highly efficient nanoplasmonic SAB. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 415202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.C.; Wang, M.L.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Shen, L.; Ma, W.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, R.F. Dragonfly wing decorated by gold nanoislands as flexible and stable substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. Au-Decorated Dragonfly Wing Bioscaffold Arrays as Flexible Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrate for Simultaneous Determination of Pesticide Residues. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. Synthesis of flexible and stable SERS substrate based on Au nanofilms/cicada wing array for rapid detection of pesticide residues. Opt. Commun. 2018, 425, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, X.; Shi, G.; Ma, W.; Ren, L. Rapid, simple and quantitative detection of metolcarb residues in apples by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, A.; Szymborski, T.; Jaroch, T.; Zmysłowski, A.; Szterk, A. Gold-capped silicon for ultrasensitive SERS-biosensing: Towards human biofluids analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 84, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Tian, S.; Zhou, Q.; Adkins, J.; Gu, Z.; Li, X.; Zheng, J. SERS detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on a bowl-shaped silver cavity substrate. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25989–25996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, A.; Szymborski, T.; Witkowska, E.; Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Świeszkowski, W.; Niciński, K.; Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J.; Girstun, A. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Membrane-Based SERS Platform: A New Diagnostic Approach for ‘Liquid Biopsy’. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowska, E.; Szymborski, T.; Kamińska, A.; Waluk, J. Polymer mat prepared via Forcespinning™ as a SERS platform for immobilization and detection of bacteria from blood plasma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, M.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Pedireddy, S.; Phang, I.Y.; Tjiu, W.W.; Tan, J.M.R.; Ling, X.Y. A Chemical Route to Increase Hot Spots on Silver Nanowires for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Application. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14441–14449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-J.; Roy, P.K.; Chattopadhyay, S. An ink-jet printed, surface enhanced Raman scattering paper for food screening. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40487–40493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Marta, S.; Novara, C.; Giorgis, F.; Bonifacio, A.; Sergo, V. Optimization and Characterization of Paper-Made Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrates with Au and Ag NPs for Quantitative Analysis. Materials 2017, 10, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier-Boss, P.A. Review of SERS Substrates for Chemical Sensing. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.M.; Narayanan, N.; Nair, J.B.; Karunakaran, V.; Ramya, A.N.; Sujai, P.T.; Saranya, G.; Arya, J.S.; Vijayan, V.M.; Maiti, K.K. Exploring the margins of SERS in practical domain: An emerging diagnostic modality for modern biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2018, 181, 140–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-T.; Hsu, I.L.; Cheng, T.-Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Lee, C.-W.; Li, T.-J.; Cheung, C.I.; Chin, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-C.; Chiu, Y.-C.; et al. Off-Resonance SERS Nanoprobe-Targeted Screen of Biomarkers for Antigens Recognition of Bladder Normal and Aggressive Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8213–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.-S.; Sun, I.W.; Huang, C.-C. Promotion of SERS and catalytic activities with bimetallic and ternary concave nanolayers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13041–13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, C.; Gamez, F.; Zaderenko, A.P. Preparation of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates Based on Immobilized Silver-Capped Nanoparticles. J. Spectrosc. 2018, 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Ko, H.; Chang, S.-H.G.; Huang, C.-C. Invisible-ink-assisted pattern and written surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates for versatile chem/biosensing platforms. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 5318–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Z.; Tan, C.F.; Kang, N.; Chen, L.; Ren, L.; Thian, E.S.; Ho, G.W.; Ji, R.; Hong, M. Uniaxially Stretched Flexible Surface Plasmon Resonance Film for Versatile Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Diagnostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26341–26349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro, C.; Sayagues, M.J.; Franco, V.; Conde, A.; Zaderenko, P.; Gámez, F. A hybrid silver-magnetite detector based on surface enhanced Raman scattering for differentiating organic compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, R. Dielectric barrier discharges: Progress on plasma sources and on the understanding of regimes and single filaments. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2017, 26, 053001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelschatz, U. Dielectric-Barrier Discharges: Their History, Discharge Physics, and Industrial Applications. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2003, 23, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, B.; Kogelschatz, U. Nonequilibrium volume plasma chemical processing. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1991, 19, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laboratory Corona Treater. Operating Manual, 1st ed.; Electro-Technic Product Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Horticulture Innovation Australia Limited, Strategic Agrichemical Review Process. Available online: https://www.horticulture.com.au/contentassets/804e6c98ef15453dbc9707cb92640c96/apple--pear-2017-sarp---24-may-2017.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2019).
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoin, P.G. Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Enhancement Factors: A Comprehensive Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, C.; Quaresma, P.; Pereira, E.; Franco, J.; Pernia Leal, M.; García-Martín, M.L.; Royo, J.L.; Oliva-Montero, J.M.; Merkling, P.J.; Zaderenko, A.P.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Elongated-Shaped Silver Nanoparticles as a Biocompatible Anisotropic SERS Probe for Intracellular Imaging: Theoretical Modeling and Experimental Verification. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, M.S. SERS of Dithiocarbamate Pesticides Adsorbed on Silver Surface; Thiram. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, 23, 1604. [Google Scholar]

| Pesticide | SERS Raman Shift (cm−1) | Band Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| Thiram | 860 | υ(CH3N) |
| 921 | υ(CH3N), υ(C=S) | |
| 1142 | ρ(CH3), υ(CN) | |
| 1381 | δs(CH3), υ(CN) | |
| 1444 | δas(CH3), υ(CN) | |
| 1508 | υ(CN), δ(CH3), δas(CH3) | |
| Carbaryl | 1403 | symmetric ring vibration naphthalene |
| 1440 | unspecified ring vibration of mono-substituted naphthalene | |
| 1568 | υ(C=C) in naphthalene ring |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowicka, A.B.; Czaplicka, M.; Kowalska, A.A.; Szymborski, T.; Kamińska, A. Flexible PET/ITO/Ag SERS Platform for Label-Free Detection of Pesticides. Biosensors 2019, 9, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030111
Nowicka AB, Czaplicka M, Kowalska AA, Szymborski T, Kamińska A. Flexible PET/ITO/Ag SERS Platform for Label-Free Detection of Pesticides. Biosensors. 2019; 9(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowicka, Ariadna B., Marta Czaplicka, Aneta A. Kowalska, Tomasz Szymborski, and Agnieszka Kamińska. 2019. "Flexible PET/ITO/Ag SERS Platform for Label-Free Detection of Pesticides" Biosensors 9, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030111
APA StyleNowicka, A. B., Czaplicka, M., Kowalska, A. A., Szymborski, T., & Kamińska, A. (2019). Flexible PET/ITO/Ag SERS Platform for Label-Free Detection of Pesticides. Biosensors, 9(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030111