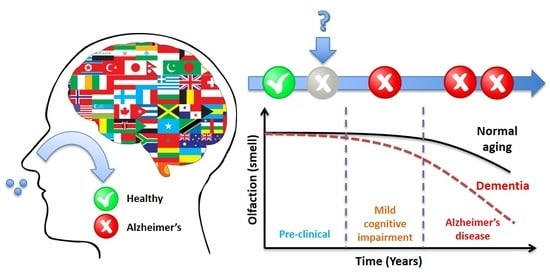
Olfactory Dysfunction as a Global Biomarker for Sniffing out Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
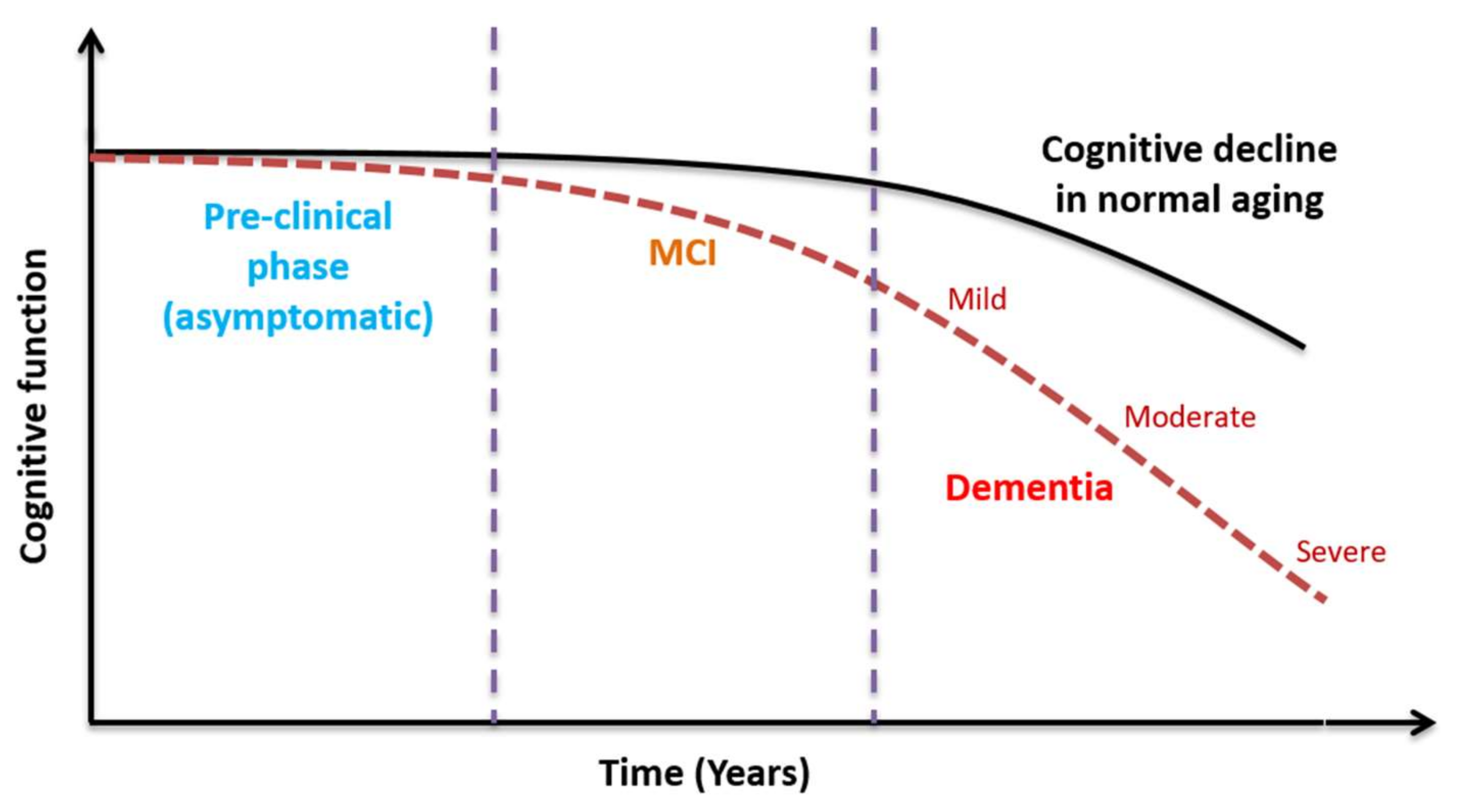
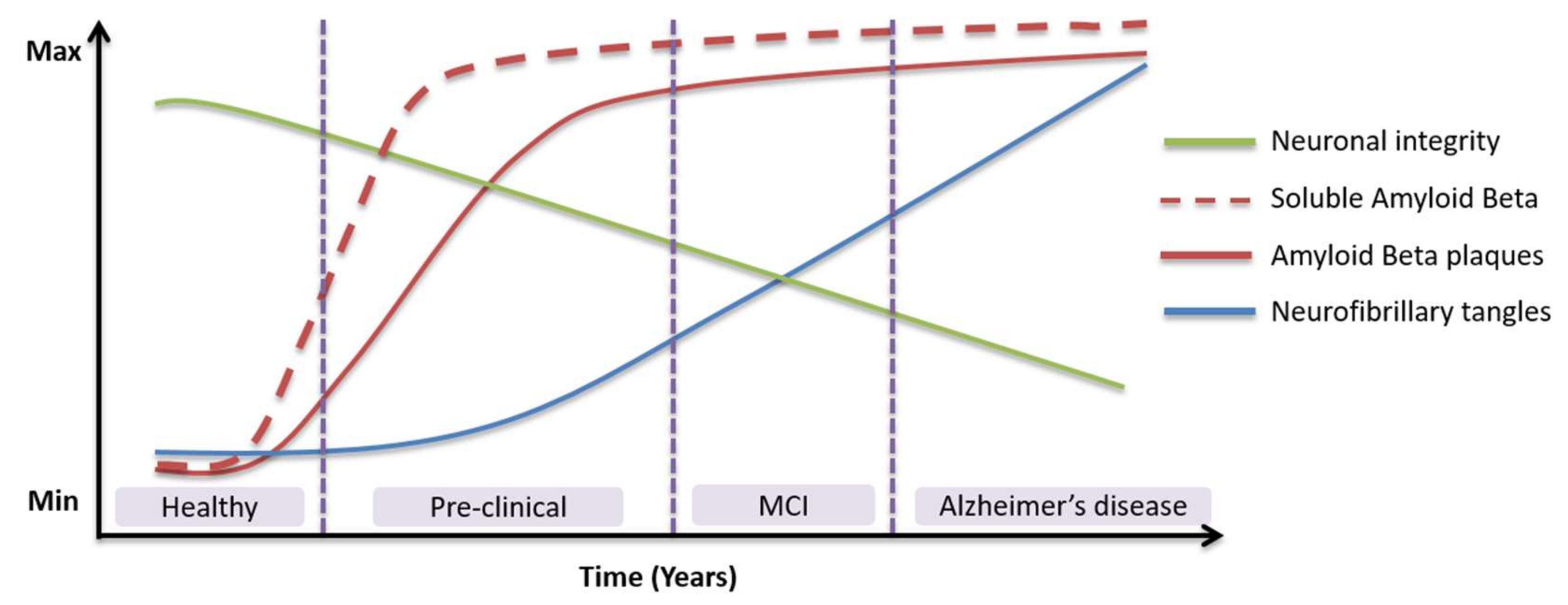
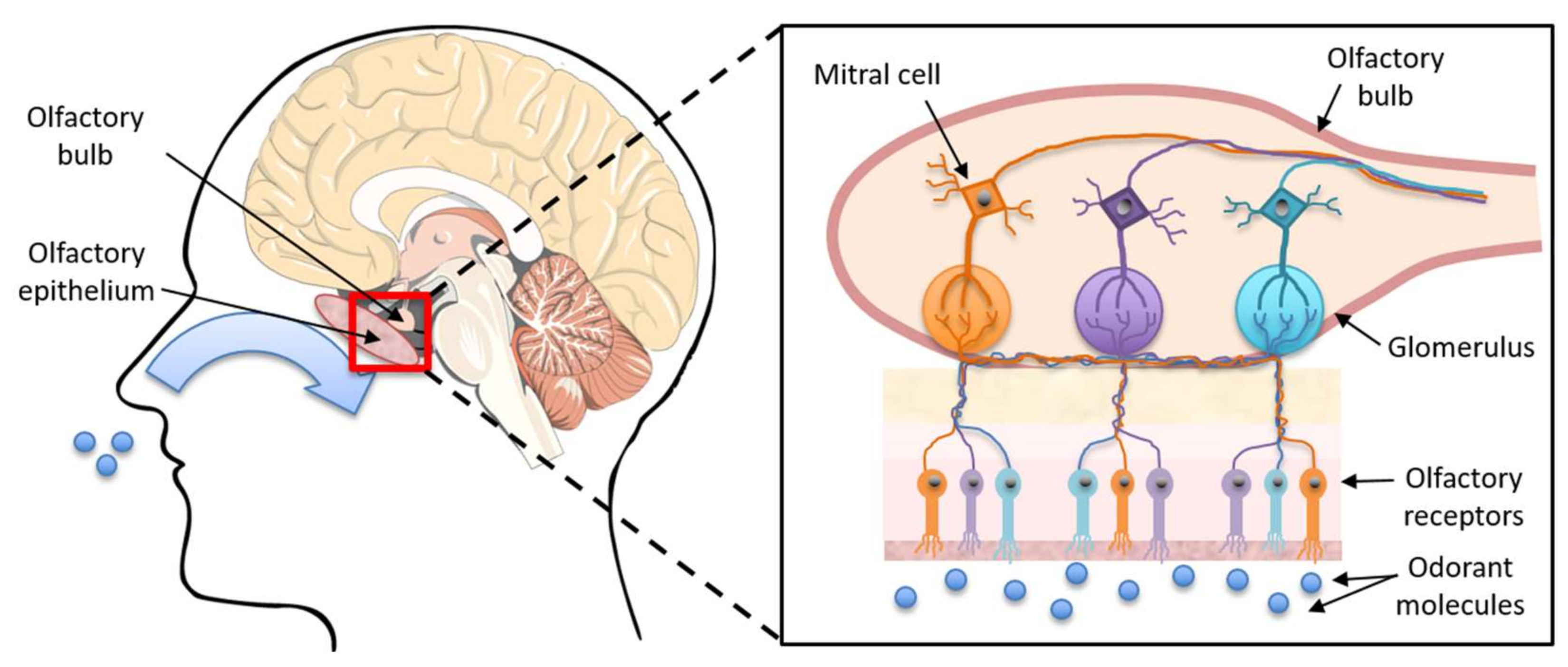
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
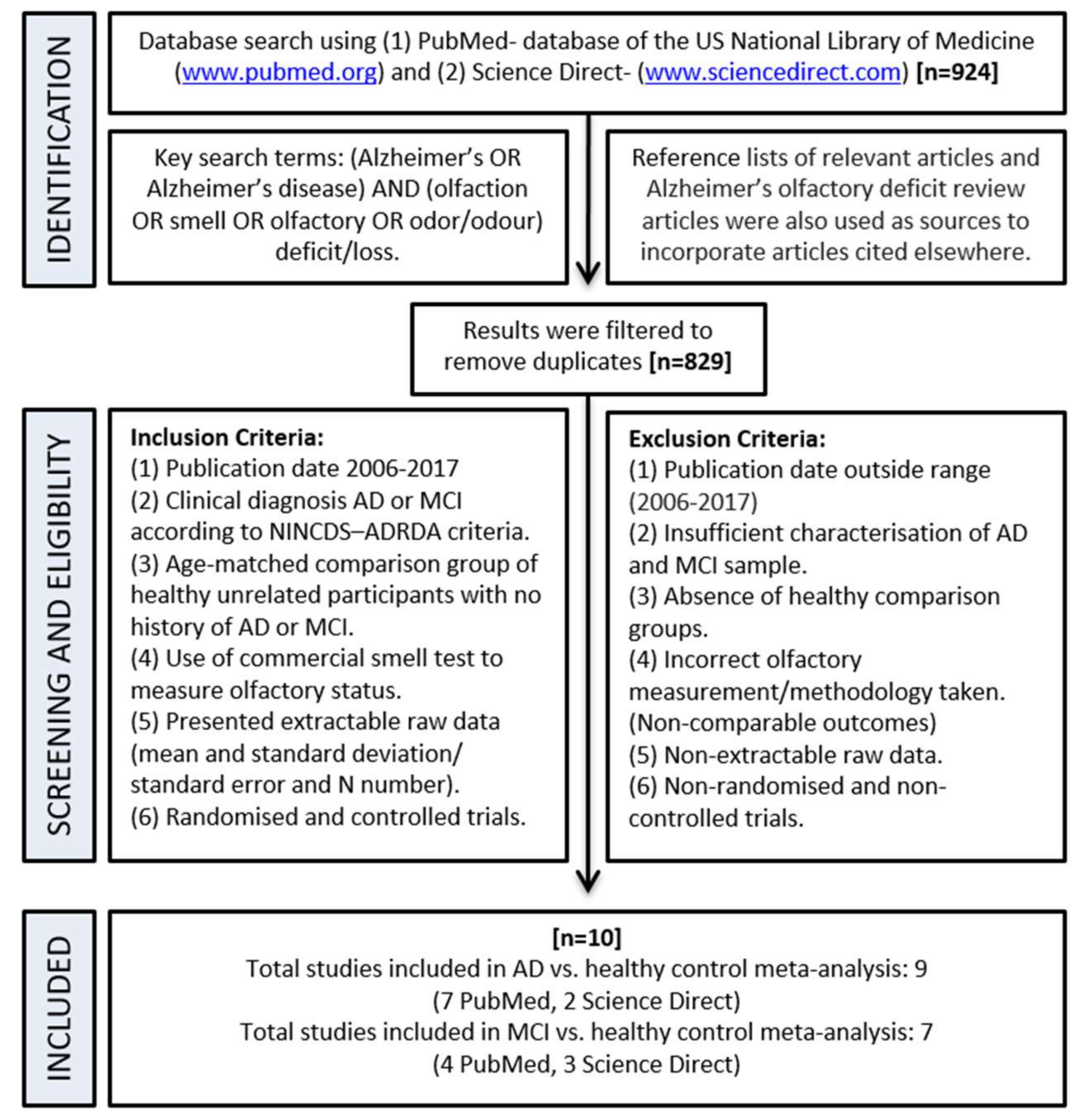
2.1. Identification of Studies to Include in the Meta-Analysis
2.2. Meta-Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
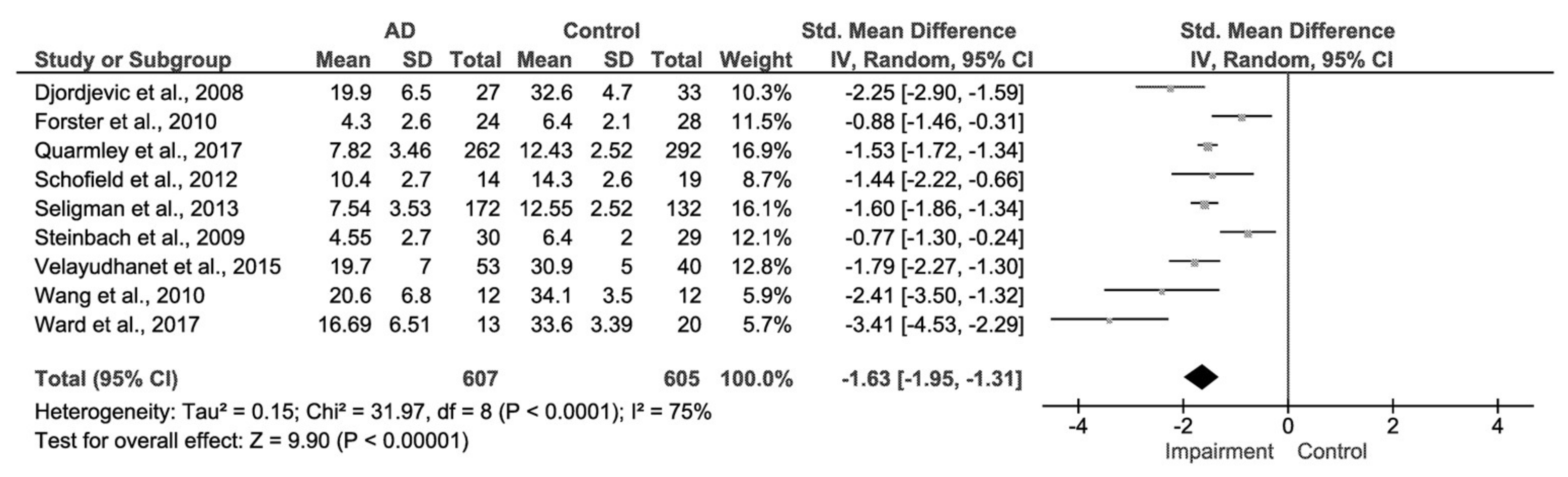
3.2. AD and Control Group
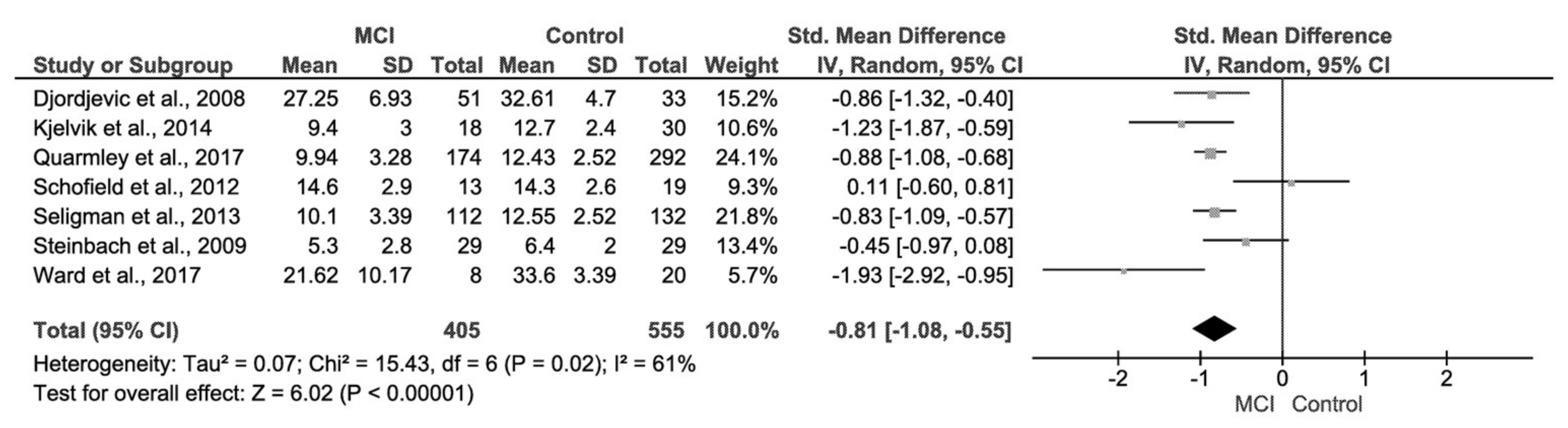
3.3. Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Control Group
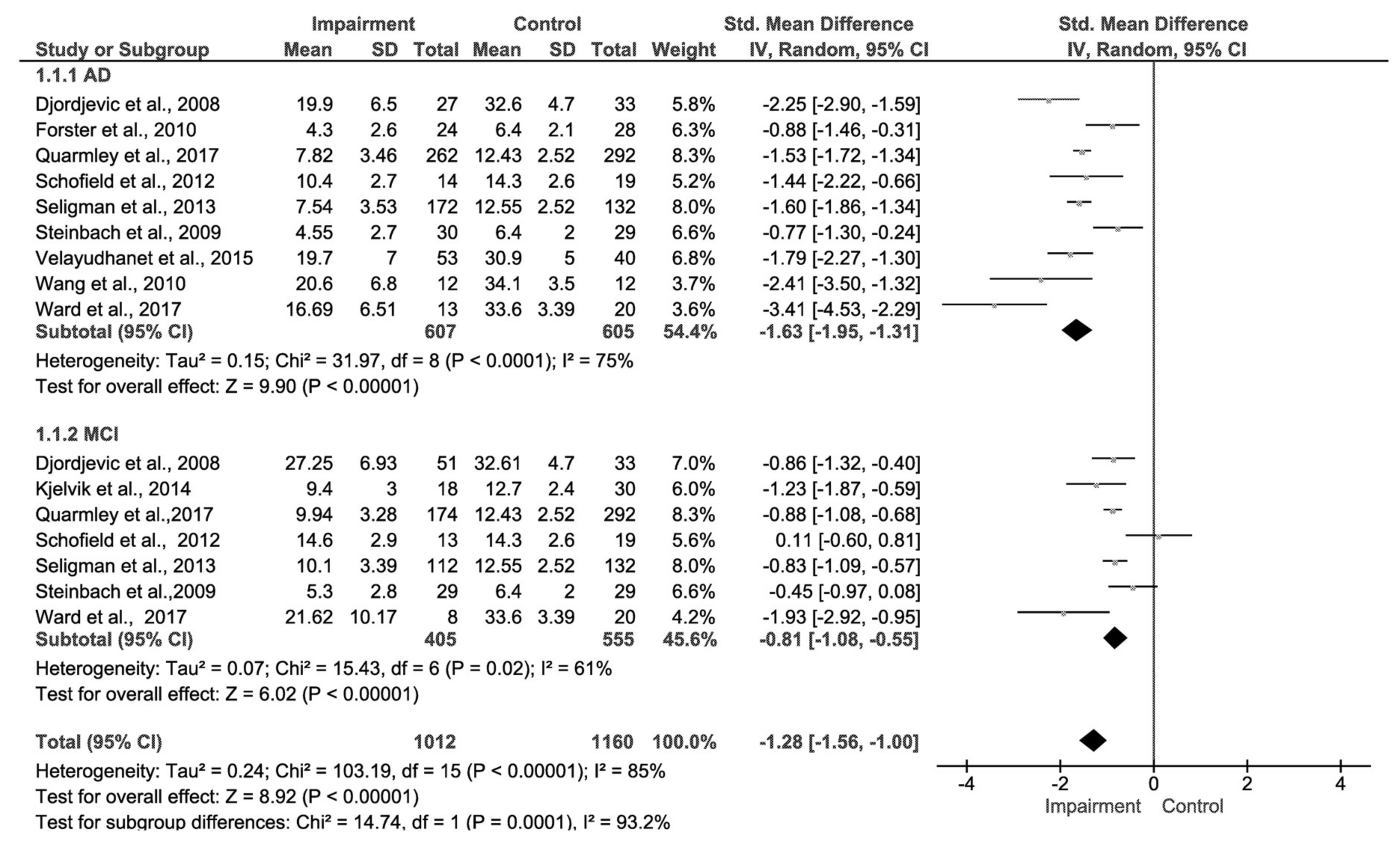
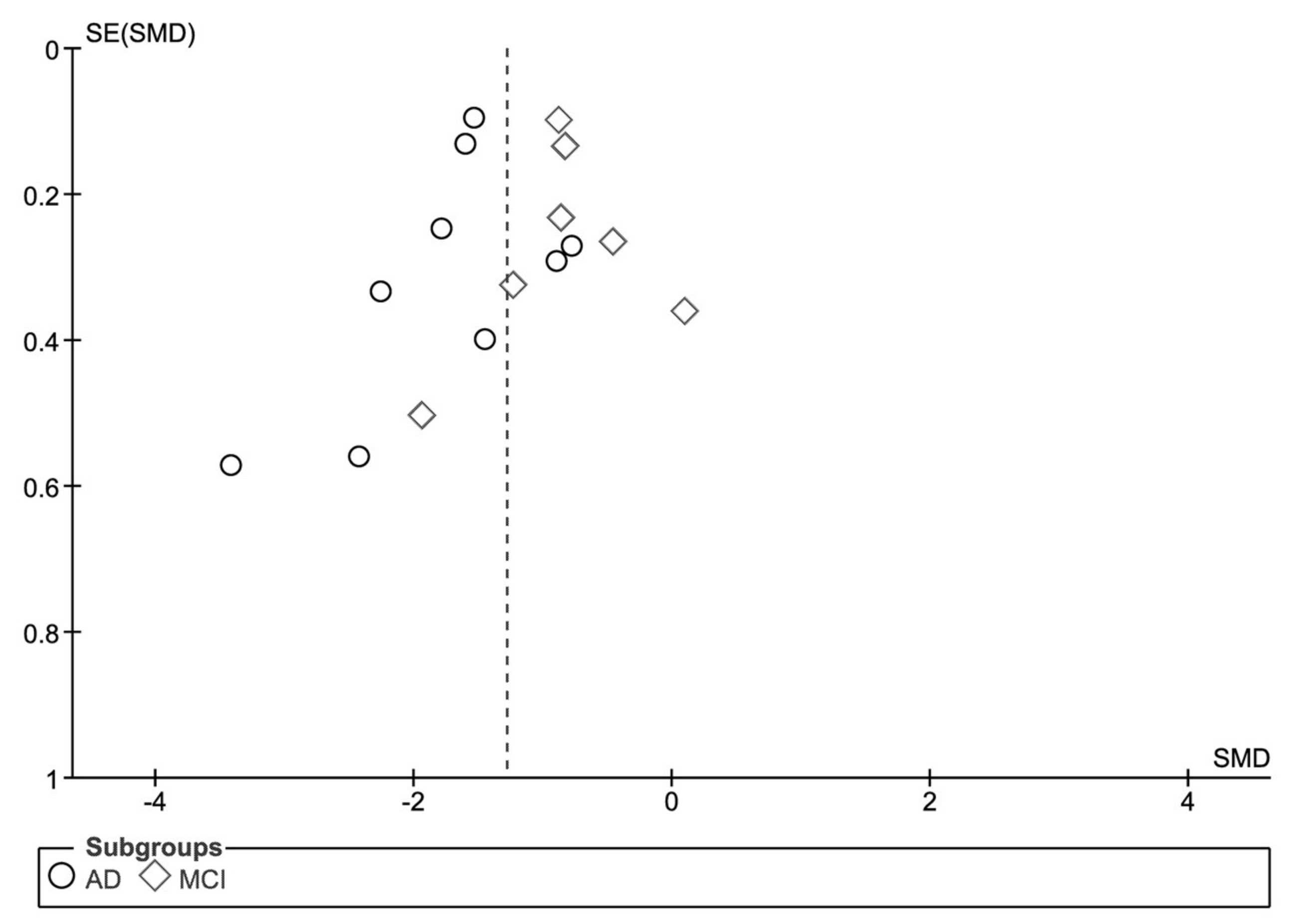
3.4. Comparison of Effect Sizes and Test of Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s Disease: Facts and Figures 2016; World Alzheimer Report; Alzheimer’s Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux, R.; Stern, Y. Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashta, O. Number of people in UK with dementia will more than double by 2050. Br. Med. J. 2007, 334, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiandaca, M.S.; Mapstone, M.E.; Cheema, A.K.; Federoff, H.J. The critical need for defining preclinical biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprott, R. Biomarkers of aging and disease: Introduction and definitions. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 45, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaria, R.N.; Maestre, G.E.; Arizaga, R.; Friedland, R.P.; Galasko, D.; Hall, K.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Ogunniyi, A.; Perry, E.K.; Potocnik, F.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in developing countries: Prevalence, management, and risk factors. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, I.O. Alzheimer’s disease: A clinical and basic science review. Med. Stud. Res. J. 2014, 4, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, N.; Tan, M.; Yu, J.; Tan, L. Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms in Alzheimer’s Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panza, F.; Seripa, D.; D’Onofrio, G.; Frisardi, V.; Solfrizzi, V.; Mecocci, P.; Pilotto, A. Neuropsychiatric Symptoms, Endophenotypes, and Syndromes in Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on APOE Gene. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the national institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, T.; Monsell, S.; Phillips, L.; Kukull, W. Accuracy of the Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease at National Institute on Aging Alzheimer Disease Centers, 2005–2010. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, R.C. Biomarkers for early detection of Alzheimer disease. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2010, 110, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Humpel, C. Identifying and validating biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, K. CSF biomarkers for mild cognitive impairment. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Persson, S.; Arai, H.; Batish, S.; Bernardini, S.; Bocchio-Chiavetto, L.; Blankenstein, M.; Carrillo, M.; Chalbot, S.; et al. The Alzheimer’s association external quality control program for cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. The amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.A. Has the amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease been proved? Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2006, 3, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushworth, J.V.; Hooper, N.M. Lipid Rafts: Linking Alzheimer’s Amyloid-β Production, Aggregation, and Toxicity at Neuronal Membranes. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushworth, J.V.; Griffiths, H.H.; Watt, N.T.; Hooper, N.M. Prion protein-mediated toxicity of amyloid-β oligomers requires lipid rafts and the transmembrane LRP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8935–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushworth, J.V.; Ahmed, A.; Griffiths, H.H.; Pollock, N.M.; Hooper, N.M.; Millner, P.A. A label-free electrical impedimetric biosensor for the specific detection of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta oligomers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 15, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomic, J.L.; Pensalfini, A.; Head, E.; Glabe, C.G. Soluble fibrillar oligomer levels are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease brain and correlate with cognitive dysfunction. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 35, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buée, L.; Bussière, T.; Buée-Scherrer, V.; Delacourte, A.; Hof, P. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res. 2000, 33, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; Avila, J. Tau aggregates and Tau pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2008, 14, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Sanchez, D.; Flores-Cuadrado, A.; Ubeda-Bañon, I.; De la Rosa Prieto, C.; Martinez-Marcos, A. Interneurons in the human olfactory system in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 279, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraen-Maschke, S.; Sergeant, N.; Dhaenens, C.; Bombois, S.; Deramecourt, V.; Caillet-Boudin, M.; Pasquier, F.; Maurage, C.; Sablonnière, B.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Tau as a biomarker of neurodegenerative diseases. Biomark. Med. 2008, 2, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghidoni, R.; Squitti, R.; Siotto, M.; Benussi, L. Innovative Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on the Hidden Disease Biomarkers. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagyinszky, E.; Youn, Y.; An, S.; Kim, S. Characterization of inflammatory biomarkers and candidates for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. BioChip J. 2014, 8, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L. Autoantibodies in Alzheimer’s disease: Potential biomarkers, pathogenic roles, and therapeutic implications. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 30, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.-X.; Gong, Y.; Moore, C.; Fu, M.; German, D.C.; Chang, L.-Y.; Rosenberg, R.; Diaz-Arrastia, R. Beta-Amyloid auto-antibodies are reduced in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 274, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Reddy, P.H. MicroRNA-455-3p as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N. Exploring Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, KE01–KE06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anoop, A.; Singh, P.; Jacob, R.; Maji, S. CSF Biomakers for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.; Petrosyan, A.; Magalhães, R. Olfactory dysfunction in dementia. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E. Olfactory system: Functional organization and involvement in neurodegenerative disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, T.; Sekinger, B.; Wolf, S.R.; Pauli, E.; Kobal, G. “Sniffin’ sticks”: Olfactory performance assessed by the combined testing of odor identification, odor discrimination and olfactory threshold. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katotomichelakis, M.; Balatsouras, D.; Tripsianis, G.; Tsaroucha, A.; Homsioglou, E.; Danielides, V. Normative values of olfactory function testing using the ‘Sniffin’ Sticks. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L. Olfactory dysfunction and its measurement in the clinic. World J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2015, 1, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L.; Shaman, P.; Kimmelman, C.P.; Dann, M.S. University of Pennsylvania smell identification test: A rapid quantitative olfactory function test for the clinic. Laryngoscope 1984, 94, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre; The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager, Version 5.3.5; The Nordic Cochrane Centre: Copenhagen, Denmark; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach, S.; Hundt, W.; Vaitl, A.; Heinrich, P.; Förster, S.; Bürger, K.; Zahnert, T. Taste in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. 2009, 257, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, P.; Ebrahimi, H.; Jones, A.; Bateman, G.; Murray, S. An olfactory ‘stress test’ may detect preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurol. 2012, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, J.; Jones-Gotman, M.; De Sousa, K.; Chertkow, H. Olfaction in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjelvik, G.; Saltvedt, I.; White, L.R.; Stenumgård, P.; Sletvold, O.; Engedal, K.; Skåtun, K.; Lyngvær, A.K.; Steffenach, H.A.; Håberg, A.K. The brain structural and cognitive basis of odor identification deficits in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Eslinger, P.J.; Doty, R.L.; Zimmerman, E.K.; Grunfeld, R.; Sun, X.; Meadowcroft, M.D.; Connor, J.R.; Price, J.L.; Smith, M.B.; et al. Olfactory deficit detected by fMRI in early Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2010, 1357, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarmley, M.; Moberg, P.J.; Mechanic-Hamilton, D.; Kabadi, S.; Arnold, S.E.; Wolk, D.A.; Roalf, D.R. Odor identification screening improves diagnostic classification in incipient Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 55, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seligman, S.C.; Kamath, V.; Giovannetti, T.; Arnold, S.E.; Moberg, P.J. Olfaction and apathy in Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, and healthy older adults. Aging Ment. Health 2013, 17, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayudhan, L.; Gasper, A.; Pritchard, M.; Baillon, S.; Messer, C.; Proitsi, P. Pattern of smell identification impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 46, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, S.; Vaitl, A.; Teipel, S.; Yakushev, I.; Mustafa, M.; la Fougère, C.; Rominger, A.; Cumming, P.; Bartenstein, P.; Hampel, H.; et al. Functional representation of olfactory impairment in early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 22, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.; Calamia, M.; Thiemann, E.; Dunlap, J.; Tranel, D. Association between olfaction and higher cortical functions in Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, and healthy older adults. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2017, 39, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahayel, S.; Frasnelli, J.; Joubert, S. The effect of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease on olfaction: A meta-analysis. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 231, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Raji, C.; MacEachern, M.; Burke, J. Olfactory identification testing as a predictor of the development of Alzheimer’s dementia: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roalf, D.R.; Moberg, M.; Turetsky, B.; Brennan, L.; Kabadi, S.; Wolk, D.; Moberg, P. A quantitative meta-analysis of olfactory dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafaille-Magnan, M.E.; Poirier, J.; Etienne, P.; Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Frenette, J.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Breitner, J.C.S.; PREVENT-AD Research Group. Odor identification as a biomarker of preclinical AS in older adults at risk. Neurology 2017, 89, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.; Christianson, T.; Kremers, W.; Mielke, M.; Machulda, M.; Vassilaki, M.; Alhurani, R.; Geda, Y.; Knopman, D.; Petersen, R. Association Between Olfactory Dysfunction and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease Dementia. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macknin, J.; Higuchi, M.; Lee, V.; Trojanowski, J.; Doty, R. Olfactory dysfunction occurs in transgenic mice overexpressing human τ protein. Brain Res. 2004, 100, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesson, D.W.; Levy, E.; Nixon, R.A.; Wilson, D.A. Olfactory dysfunction Correlates with Amyloid-β burden in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Pichon, C.E.; Firestein, S. Expression and localization of the prion protein PrP(C) in the olfactory system of the mouse. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2008, 508, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, N.L.; Wesson, D.W.; Brundin, P. The olfactory bulb as the entry site for prion-like propagation in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 109, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullard, M.E.; Morley, J.F.; Duda, J.E. Olfactory Dysfunction as an Early Biomarker in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, F.A.; Gonzalez, L.; Favila, R.; Alonso, M.E.; Salgado, P.M.; Diaz, R.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J. Olfaction and neurodegeneration in HD. Neuroreport 2007, 18, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batur Caglayan, H.Z.; Irkec, C.; Nazliel, B.; Akyol Gurses, A.; Capraz, I. Olfactory functioning in early multiple sclerosis: Sniffin’ Sticks Test study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 2143–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Rossi, F.; Rinaldi, F.; Compostella, S.; Cosseddu, M.; Borroni, B.; Filosto, M.; Padovani, A. Exploring Olfactory Function and Its Relation with Behavioral and Cognitive Impairment in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Neurodegener. Dis. 2016, 16, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesholam, R.I.; Moberg, P.J.; Mahr, R.N.; Doty, R.L. Olfaction in neurodegenerative disease: A meta-analysis of olfactory functioning in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.F.; Cohen, A.; Silveira-Moriyama, L.; Lees, A.J.; Williams, D.R.; Katzenschlager, R.; Hawkes, C.; Shtraks, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Doty, R.L.; et al. Optimizing olfactory testing for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: Item analysis of the university of Pennsylvania smell identification test. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2018, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, T.; Whitcroft, K.L.; Andrews, P.; Altundag, A.; Cinghi, C.; Costanzo, R.M.; Damm, M.; Frasnelli, J.; Gudziol, H.; Gupta, N.; et al. Position paper on olfactory dysfunction. Rhinology 2017, 54, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Citation | Smell Test | Mean Age (±SD/Range) | Sample Size | Mean Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD | MCI | CTRL | AD | MCI | CTRL | AD | MCI | CTRL | ||
| Steinbach et al., 2010 [40] | SSIT | 73.3 ± 7.8 | 71.7± 7.7 | 68.2 ± 3.9 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 4.55 ± 2.7 | 5.3 ± 2.8 | 6.4 ± 2.0 |
| Schofield et al., 2012 [41] | UPSIT-20 | 75.3 ± 4.6 | 77.1 ± 5.6 | 74 ± 6.6 | 14 | 13 | 19 | 10.4 ± 2.7 | 14.6 ± 2.9 | 14.3 ± 2.6 |
| Djordjevic et al., 2008 [42] | UPSIT-40 | 77.0 (55–88) | 75.4 (59–86) | 73.7 (63–87) | 27 | 51 | 33 | 19.89 ± 6.5 | 27.25 ± 6.93 | 32.61 ± 4.7 |
| Kjelvik et al., 2014 [43] | B-SIT-12 | - | 67.4 ± 7.6 | 74.6 ± 6.3 | - | 18 | 30 | - | 6.6 ± 2.6 | 9.6 ± 2.0 |
| SSIT-16 | 9.4 ± 3.0 | 12.7 ± 2.4 | ||||||||
| SSDT-16 | 7.5 ± 3.0 | 9.2 ± 3.3 | ||||||||
| Wang et al., 2010 [44] | UPSIT-40 | 74.5 ± 7.5 | - | 67.8 ± 9.8 | 12 | - | 12 | 20.6 ± 6.8 | - | 34.1 ± 3.5 |
| Quarmley et al., 2017 [45] | SSIT-16 | 75.18 ± 8.22 | 72.46 ± 8.57 | 70.96 ± 8.74 | 262 | 174 | 292 | 7.82 ± 3.46 | 9.94 ± 3.28 | 12.43 ± 2.52 |
| Seligman et al., 2013 [46] | SSIT-16 | 75.98 ± 7.53 | 72.63 ± 8.19 | 72.57 ± 9.52 | 172 | 112 | 132 | 7.54 ± 3.53 | 10.10 ± 3 .39 | 12.55 ± 2.52 |
| Velayudhan et al., 2015 [47] | UPSIT-40 | 73.5 ± 11 | - | 70.5 ± 9 | 54 | - | 40 | 19.7 ± 7 | - | 30.9 ± 5 |
| UPSIT-12 | 5.4 ± 3 | 10.4 ± 2 | ||||||||
| Förster et al., 2010 [48] | SSIT-12 | 71.4 ± 7.9 | - | 68.2 ± 3.9 | 24 | - | 28 | 4.3 ± 2.6 | - | 6.4 ± 2.1 |
| Ward et al., 2017 [49] | UPSIT-40 | 76.77 ± 6.95 | 76.13 ± 6.29 | 76.65 ± 6.48 | 13 | 8 | 20 | 16.69 ± 6.51 | 21.62 ± 10.2 | 33.60 ± 3.34 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotecha, A.M.; Corrêa, A.D.C.; Fisher, K.M.; Rushworth, J.V. Olfactory Dysfunction as a Global Biomarker for Sniffing out Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Biosensors 2018, 8, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020041
Kotecha AM, Corrêa ADC, Fisher KM, Rushworth JV. Olfactory Dysfunction as a Global Biomarker for Sniffing out Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Biosensors. 2018; 8(2):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotecha, Alisha M., Angelo D. C. Corrêa, Kim M. Fisher, and Jo V. Rushworth. 2018. "Olfactory Dysfunction as a Global Biomarker for Sniffing out Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis" Biosensors 8, no. 2: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020041
APA StyleKotecha, A. M., Corrêa, A. D. C., Fisher, K. M., & Rushworth, J. V. (2018). Olfactory Dysfunction as a Global Biomarker for Sniffing out Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Biosensors, 8(2), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020041