A Single-Use, In Vitro Biosensor for the Detection of T-Tau Protein, A Biomarker of Neuro-Degenerative Disorders, in PBS and Human Serum Using Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus and Reagents
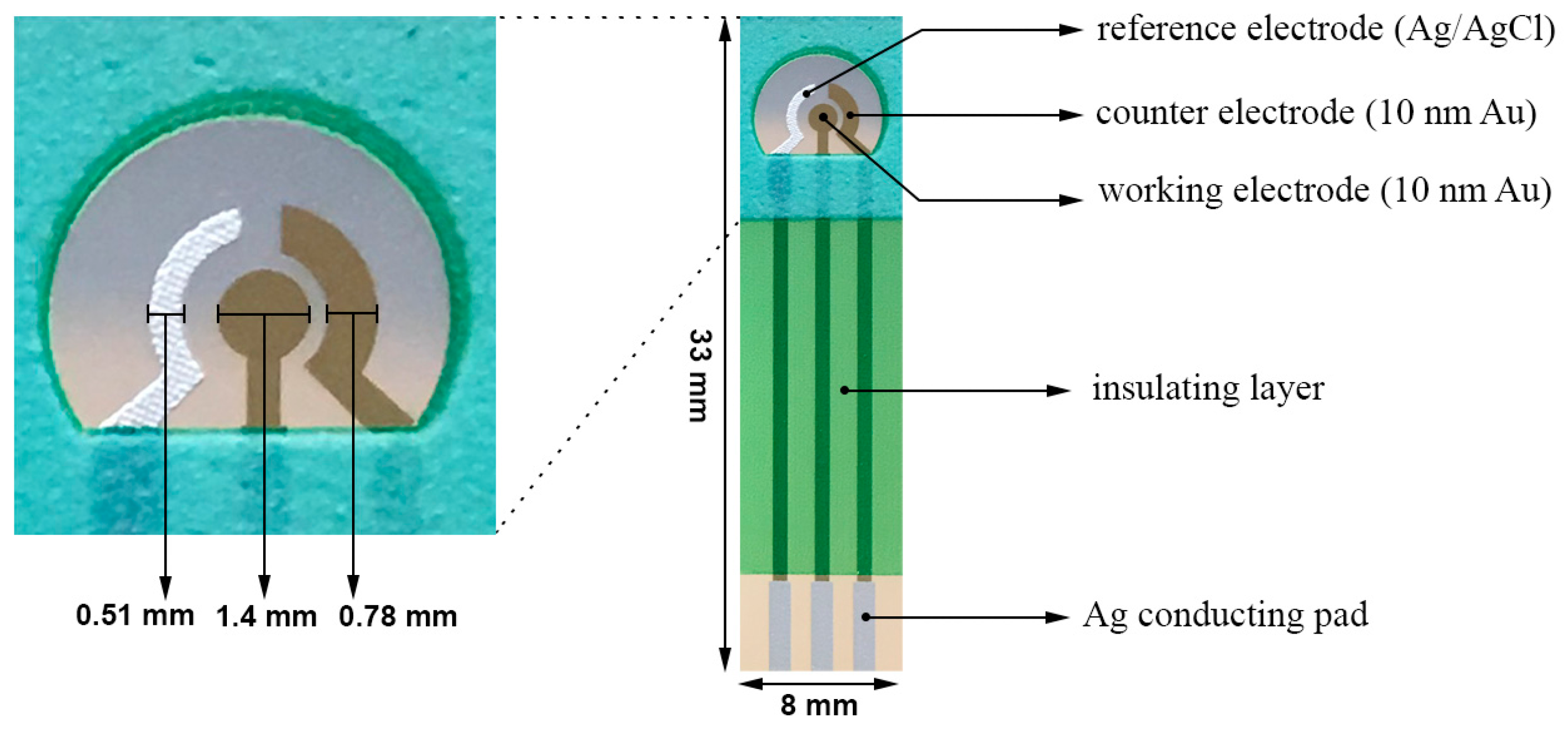
2.2. Design of the Biosensor
2.3. Pretreatment of the Biosensor
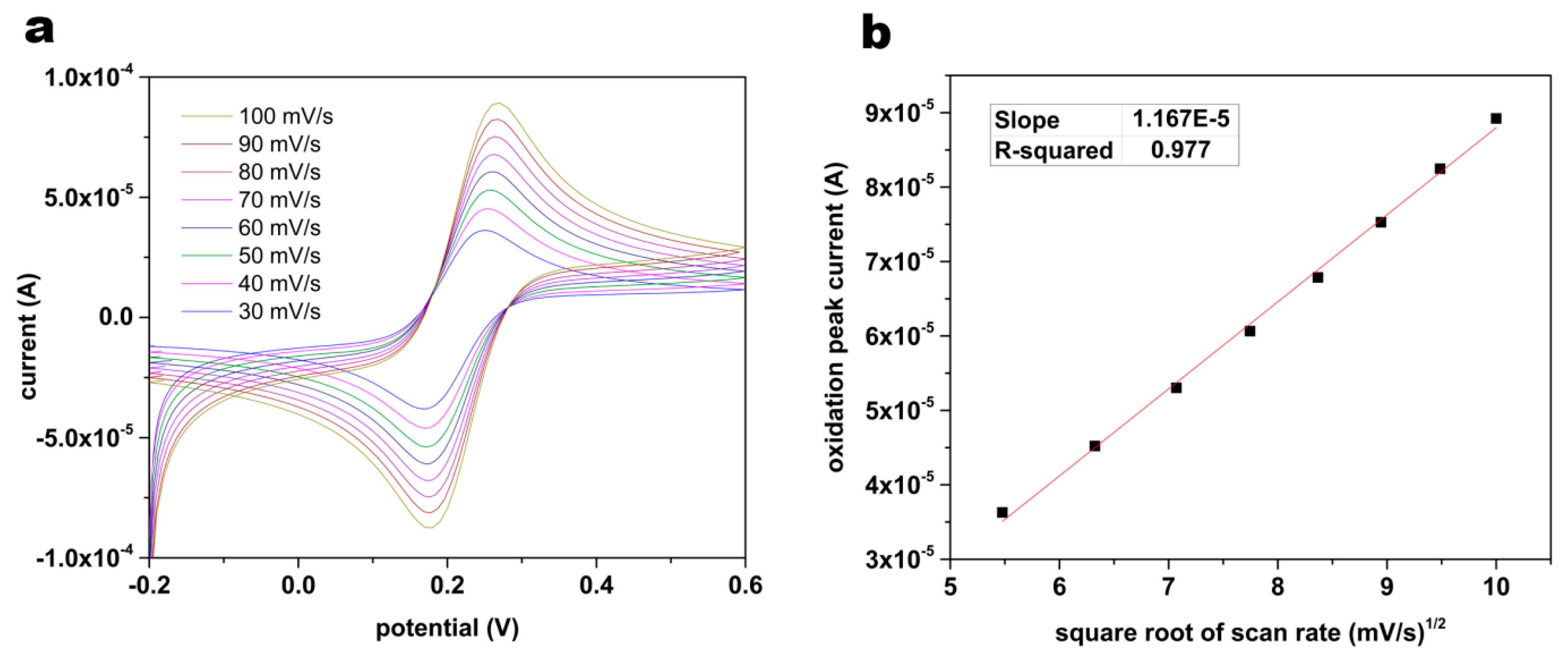
2.4 Characterization of the Surface Area
2.5. Immobilization of T-Tau Antibody onto the Gold Working Electrode of the Biosensor
2.6. Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV) Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
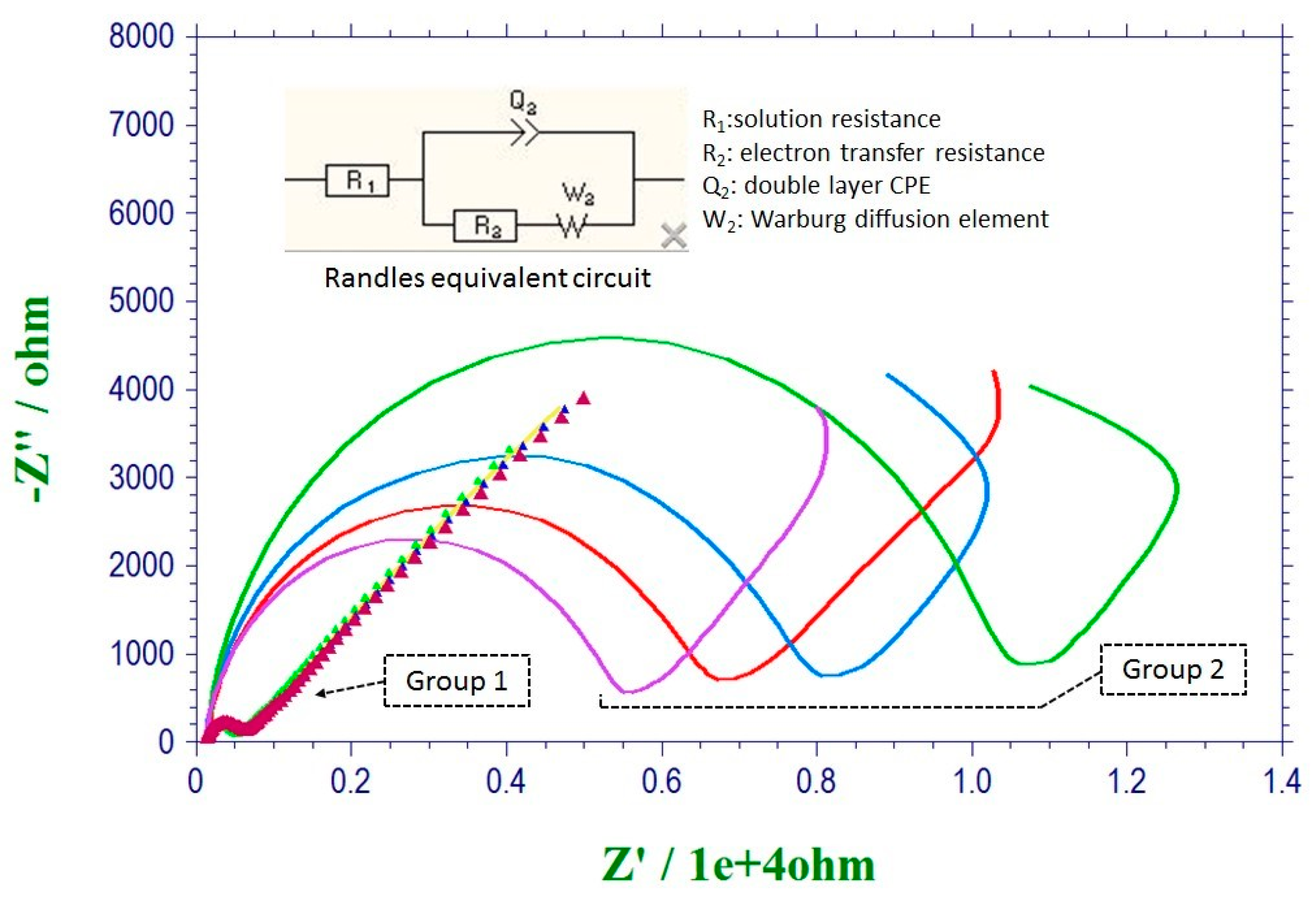
3.1. Evaluation of the Pretreatment Procedure by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
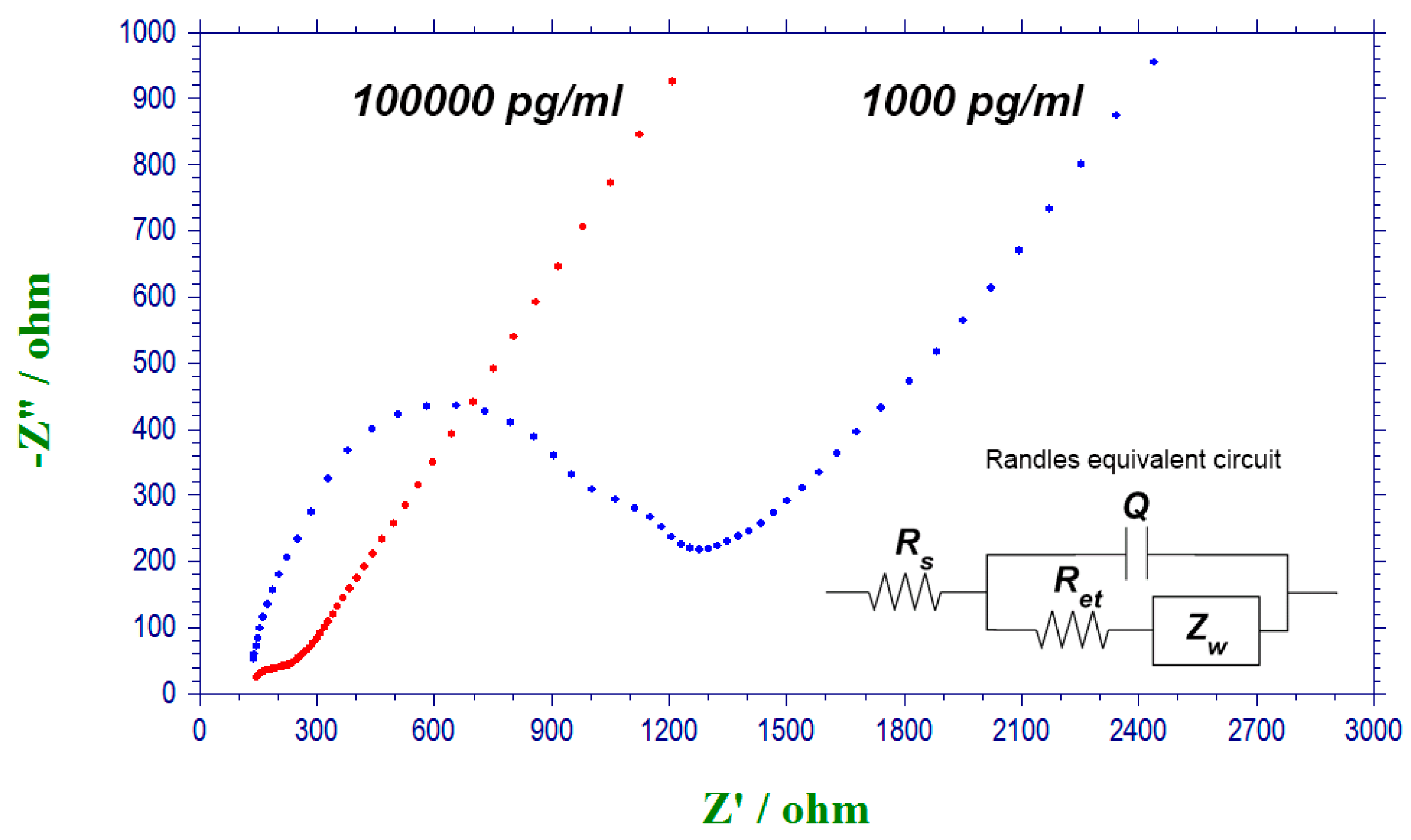
3.2. Measurement of T-Tau Proteins in PBS Solution
3.3. Measurement of T-Tau Proteins in Undiluted Human Serum
3.4. Interference Study of T-Tau Proteins Measurement of This Biosensor
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Available online: http://www.alz.org/facts/overview.asp (accessed on 18 January 2017).
- Swiezewski, S. Health Communities Com. Available online: http://www.neurologychannel.com/tbi/ (accessed on 18 January 2017).
- More, S.S.; Beach, J.M.; Vince, R. Early detection of amyloidpathy in Alzheimer’s mice by hyperspectral endoscopy. Invest. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 3231–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderland, T.; Linker, G.; Mirza, N.; Putnam, K.T.; Friedman, D.L.; Kimmel, L.H.; Bergeson, J.; Manetti, G.J.; Zimmermann, M.; Tang, B.; et al. Decreased beta-amyloid-42 and increased tau levels in cerebrospinal; fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA 2003, 289, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, K.; Hampel, H.; Weiner, M.; Zetterberg, H. Cerebrospinal fluid and biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, S.S.; Vince, R. Hyperspectral, imaging signatures detect amyloidopathy in Alzheimer’s mouse retina well before onset of cognitive decline. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, G.; Martinelli, P.; Manners, D.; Scaglione, C.; Tonon, C.; Cortelli, P.; Malucelli, E.; Capellari, S.; Testa, C.; Parchi, P.; et al. Diffusion-weighted brain imaging study of patients with clinical diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson's disease. Brain 2008, 131, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.X.; Grundke-Igbal, I. Tau in Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R. Tauopathies: Classification and clinical update on neurodegenerative diseases associated with microtubule-associated protein tau. Intern. Med. J. 2006, 36, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoglinger, G.U.; Melhem, N.M.; Dickson, D.W.; Sleiman, P.M.A.; Wang, L.S.; Klei, L.; Rademakers, R.; Silva, R.; Litvan, I.; Riley, D.E.; et al. Identification of common variants influencing risk of the tauopathy progressive supranuclear palsy. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.E.; Kouri, N.; Lin, W.L.; Jack, C.R.; Dickson, D.W.; Vemuri, P. Clinicopathologic assessment and imaging of tauopathies in neurodegenerative dementias. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohran-Maschke, S.; Sergeant, N.; Dhaenens, C.M.; Bombois, S.; Deramecourt, V. Tau as a biomarker of neurodegenerative diseases. Biomark. Med. 2008, 2, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, R.; Chang, B.; Peterson, R.; Chiu, A.; Davis, P. T-tau and P-tau in brain and blood from natural and experimental prion diseases. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0143103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inekci, D.; Jonesco, D.S.; Kennard, S.; Karsdal, M.A.; Henriksen, K. The potential of pathological protein fragmentation in blood-based biomarker development for dementia-with emphasis on Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatson, J.; Diaz-Arrastia, R. Tau as a biomarker of concussion. JAMA Neurol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahim, P.; Yelveton, T.; Wilson, D.H.; Randall, J.; Skillbäck, T.; Pazooki, D.; Kallberg, B.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Blood biomarkers for brain injury in concussed professional ice hockey players. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 7, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- .Skillback, T.; Rosen, C.; Aszlely, F.; Mattsson, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Diagnostic performance of cerebrospinal fluid total tau and phosphate tau in Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease: Results from the Swedish Mortality Registry. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 7, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janyasupab, M.; Lee, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.W.; Cai, J.; Popa, A.; Samia, A.C.; Wang, K.W.; Xu, J.Q.; Hu, C.C.; et al. Detection of lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2), a biomarker of metastasis from breast cancers using human blood samples. Recent Pat. Biomark. 2015, 2, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molazemhosseini, A.; Magagnin, L.; Vena, P.; Liu, C.C. Single-use disposable electrochemical label-free immunosensor for detection of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Sensors 2016, 16, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willner, I.; Riklin, A.I. Electrical communication between electrodes and NAD(P)+-dependent enzymes using pyrroloquinolinequinone-enzyme electrodes in a self-assembled monolayer configuration: Design of a new class of amperometric biosensors. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Glávez, R.; Pedrero, M.; De Villena, F.J.M.; Pingarrón, J.M. Preparation, characterization and application of alkanethiol self-assembled monolayers modified with tetrathiafulvalene and glucose oxidase at a gold disk electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 626, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Rawat, S.; Bhalla, V.; Suri, C.R. Point-of-care amperometric testing of diabetic marker (HbA1c) using specific electroactive antibodies. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Chang, B.Y.; Nam, H.; Park, S.M. Selective electrochemical sensing of glycated hemoglobin (HbA(1c)) on thiophene-3-boronic acid self-assembled monolayer covered gold electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 20, 8035–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscovici, M.; Bhimj, A.; Kelley, S.O. Rapid and specific electrochemical detection of prostate cancer cells using an aperture sensor array. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Glidle, A.; Griffith, A.; McNeil, C.J.; Cooper, J.M. Characterising the formation of a bioelectrochemical interface at a self-assembled monolayer using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Bioelectrochemistry Bioenerg. 1997, 42, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, L.R.; Chen, W.; Yang, X.J.; Jin, B.; Zheng, L.M.; Xia, X.H. 3-Mercaptopropylphosphonic acid modified gold electrode for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 75, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourg, M.C.; Badia, A.; Lennox, R.B. Gold-sulfur bonding in 2D and 3D self-assembled monolayers: XPS characterization. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000, 104, 6562–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhlin, Y.; Likhatski, M.; Tomashevich, Y.; Romanchenko, A.; Erenburg, S.; Trubina, S. XAS and XPS examination of the Au-S nanostructures produced via the reduction of aqueous gold(III) by sulfide ions. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena. 2010, 177, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J.; Perez, M.; Hernandez, P. Role of tau protein in both physiological and pathological conditions. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buee, L.; Bussiere, T.; Buee-Scherrer, V.; Delacourte, A.; Hof, P.R. Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves-Villanueva, J.O.; Trzeciakiewicza, H.; Martic, S. A protein-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of tau protein, a neurodegenerative disease biomarker. Analyst 2014, 139, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
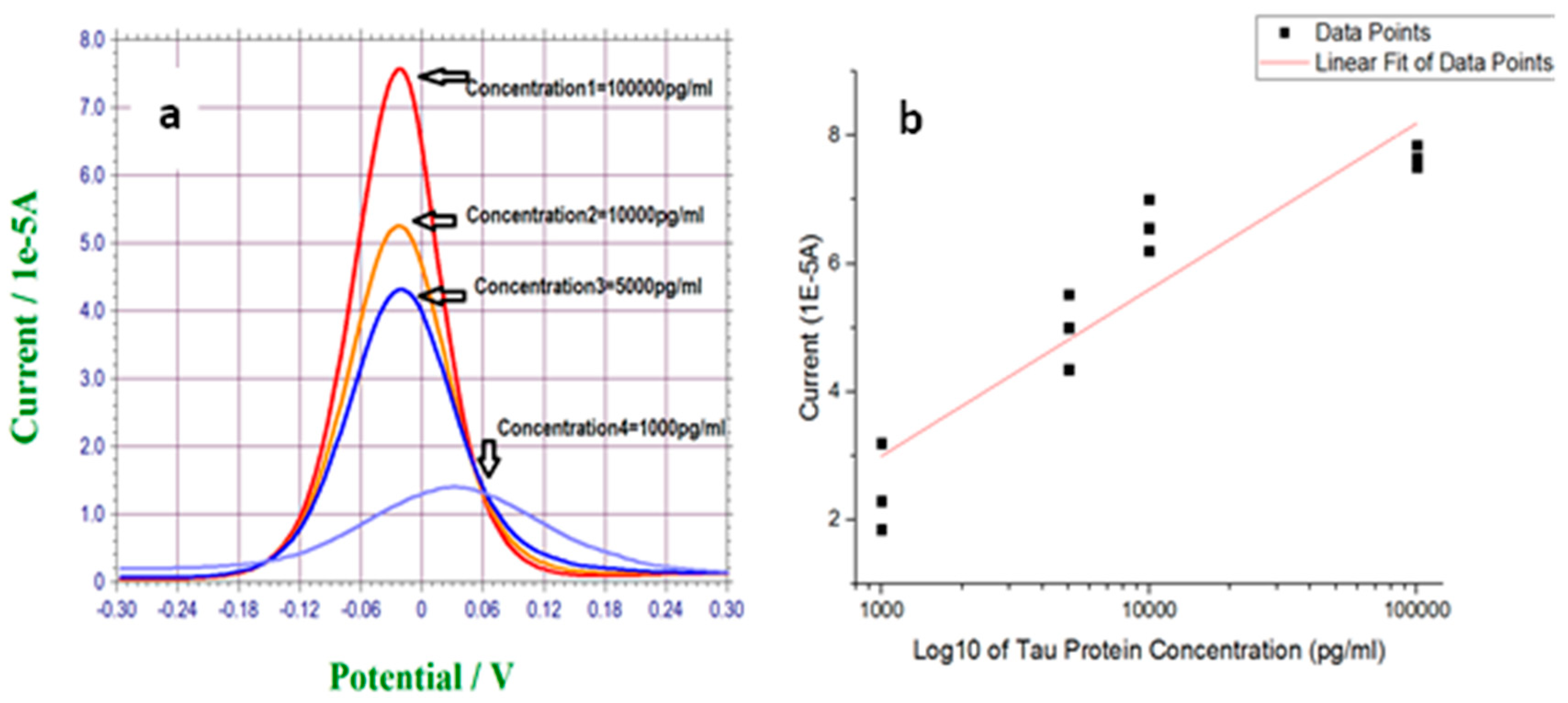
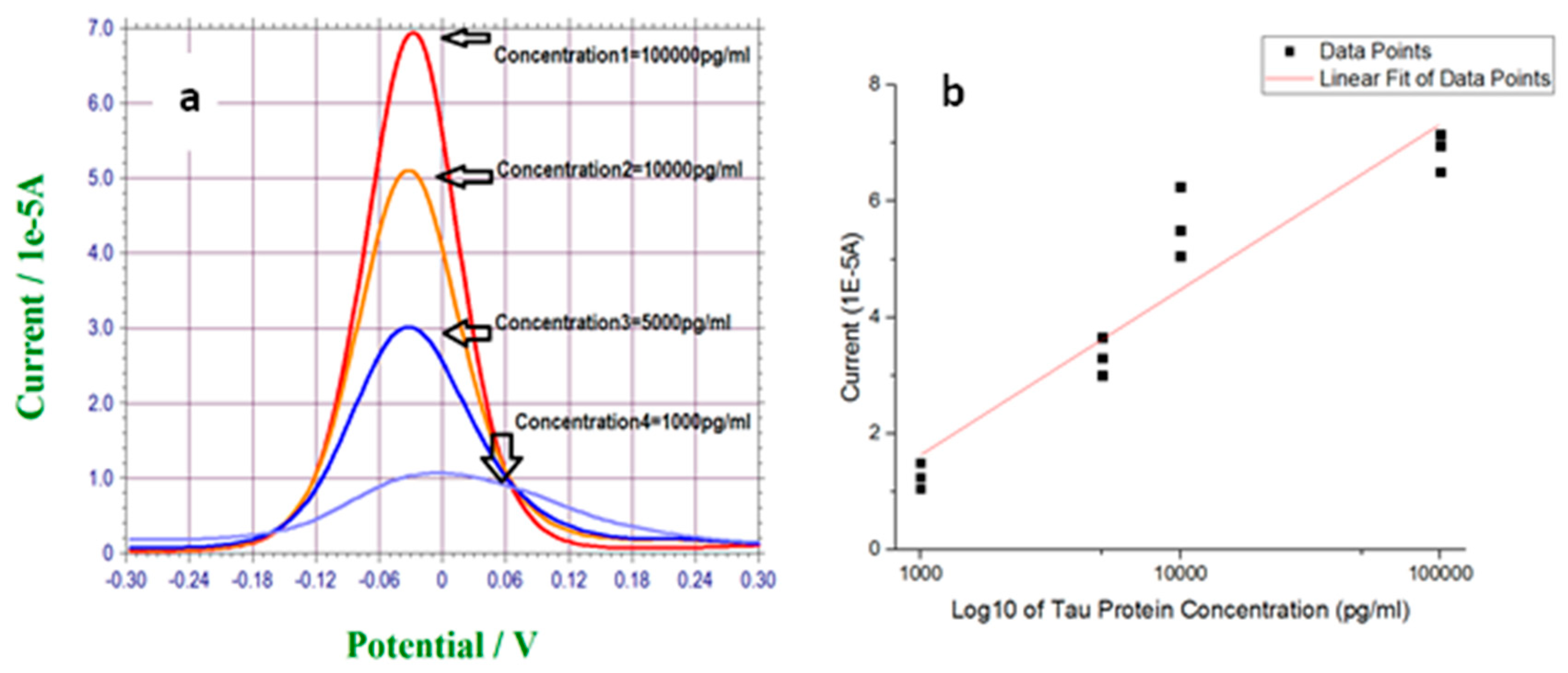
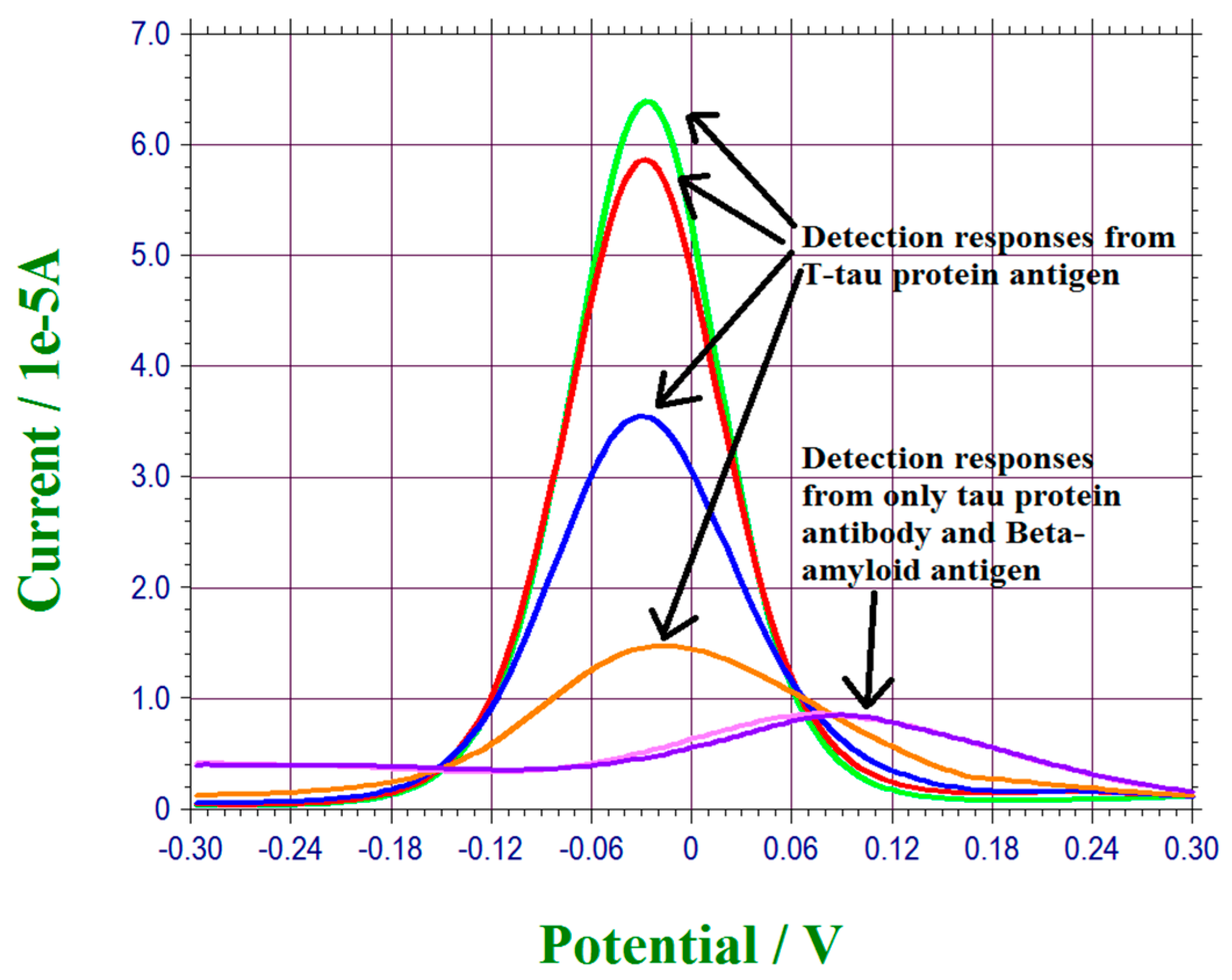
| Sensor #1 | Sensor #2 | Sensor #3 | Sensor #4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 198 Ω | 200 Ω | 201 Ω | 204 Ω |
| Group 2 | 6150 Ω | 6913 Ω | 7941 Ω | 11346 Ω |
| T-Tau (pg/mL) | Q(μF) | Ret(Ω) | Rs(Ω) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 1.33 | 1480 | 1154 | 125 |
| 100,000 | 120.8 | 1865 | 201.2 | 68.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Y.; Molazemhosseini, A.; Liu, C.C. A Single-Use, In Vitro Biosensor for the Detection of T-Tau Protein, A Biomarker of Neuro-Degenerative Disorders, in PBS and Human Serum Using Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV). Biosensors 2017, 7, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010010
Dai Y, Molazemhosseini A, Liu CC. A Single-Use, In Vitro Biosensor for the Detection of T-Tau Protein, A Biomarker of Neuro-Degenerative Disorders, in PBS and Human Serum Using Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV). Biosensors. 2017; 7(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Yifan, Alireza Molazemhosseini, and Chung Chiun Liu. 2017. "A Single-Use, In Vitro Biosensor for the Detection of T-Tau Protein, A Biomarker of Neuro-Degenerative Disorders, in PBS and Human Serum Using Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV)" Biosensors 7, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010010
APA StyleDai, Y., Molazemhosseini, A., & Liu, C. C. (2017). A Single-Use, In Vitro Biosensor for the Detection of T-Tau Protein, A Biomarker of Neuro-Degenerative Disorders, in PBS and Human Serum Using Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV). Biosensors, 7(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010010







