Versatile Flexible Graphene Multielectrode Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
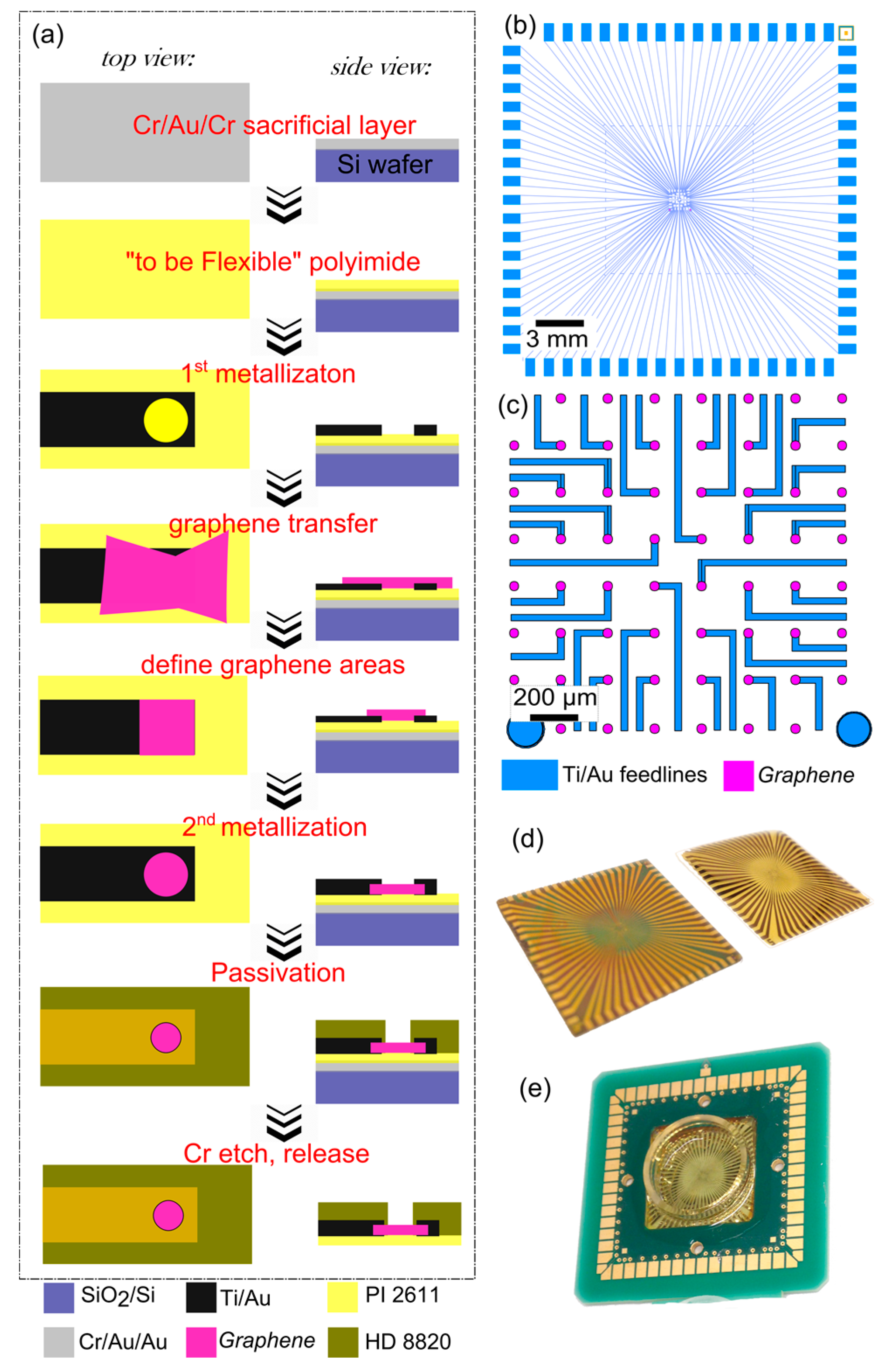
2.1. Fabrication
2.2. Soldering and Encapsulation
2.3. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
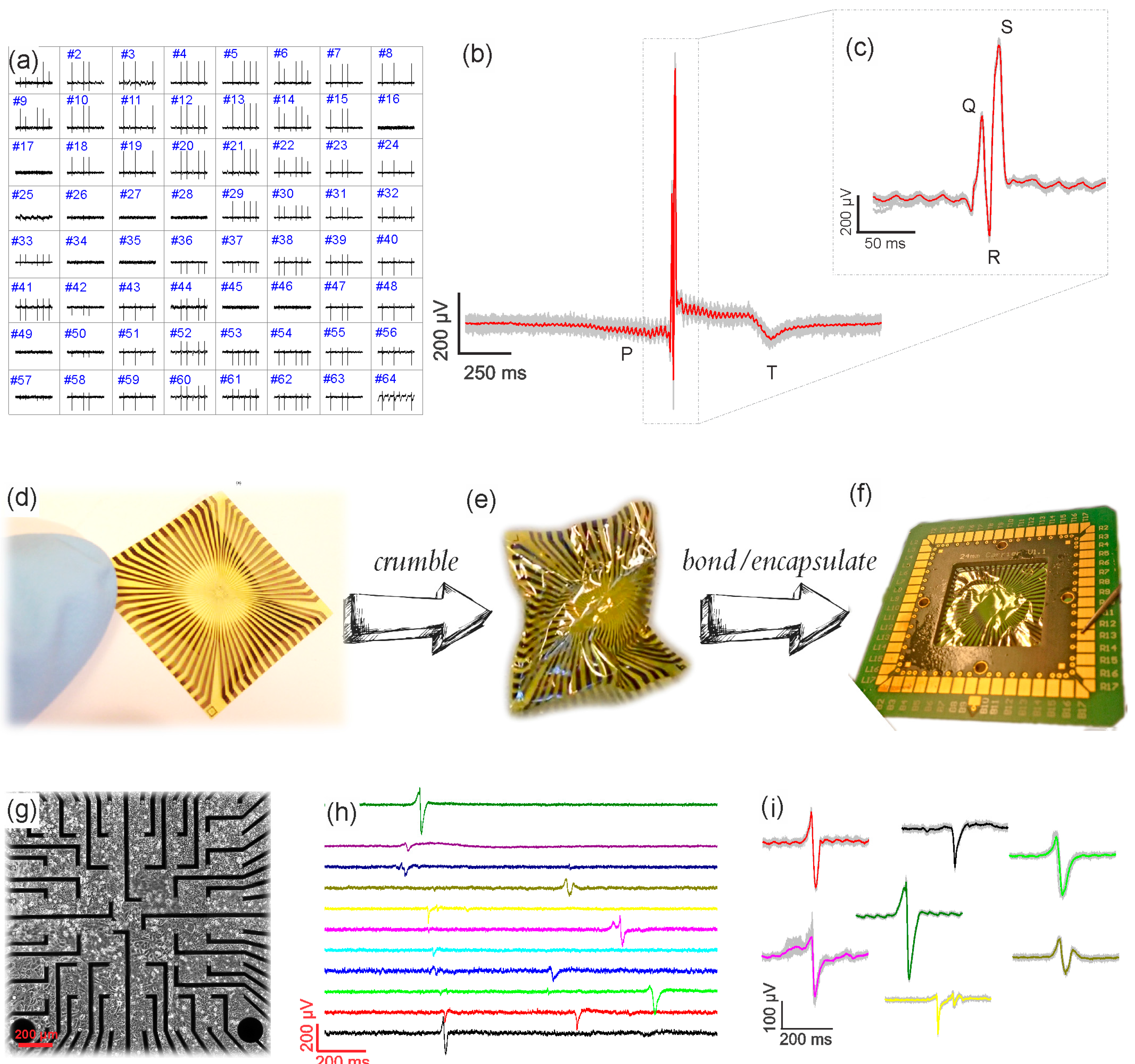
2.4. Multichannel Recordings
2.5. HL-1 Culture
2.6. Acute Heart Tissue Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, T.-M.; Hong, G.; Zhou, T.; Schuhmann, T.G.; Viveros, R.D.; Lieber, C.M. Stable Long-Term Chronic Brain Mapping at the Single-Neuron Level. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Ham, D.; Westervelt, R.M. CMOS Biotechnology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, U.; Egert, U.; Heer, F.; Hafizovic, S.; Hierlemann, A. Microelectronic system for high-resolution mapping of extracellular electric fields applied to brain slices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egert, U.; Heck, D.; Aertsen, A. Two-dimensional monitoring of spiking networks in acute brain slices. Exp. Brain Res. 2002, 142, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, M.E.; Hai, A. Multi-electrode array technologies for neuroscience and cardiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thormann, W.; Van den Bosch, P.; Bond, A.M. Voltammetry at Linear Gold and Platinum Microelectrode Arrays Produced by Lithographic Techniques. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 2764–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassum, K.M.; Tolosa, V.M.; Wang, J.; Walker, E.; Monbouquette, H.G.; Maidment, N.T. Silicon Wafer-Based Platinum Microelectrode Array Biosensor for Near Real-Time Measurement of Glutamate in Vivo. Sensors 2008, 8, 5023–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P.T.; Madangopal, R.; Otto, K.J.; Rao, M.P. Titanium-Based Multi-Channel, Micro-Electrode Array for Recording Neural Signals. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009.
- Massobrio, P.; Massobrio, G.; Martinoia, S. Interfacing Cultured Neurons to Microtransducers Arrays: A Review of the Neuro-Electronic Junction Models. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacour, S.P.; Benmerah, S.; Tarte, E.; FitzGerald, J.; Serra, J.; McMahon, S.; Fawcett, J.; Graudejus, O.; Yu, Z.; Morrison, B. Flexible and Stretchable Micro-Electrodes for in Vitro and in Vivo Neural Interfaces. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, C.; Seo, J. A Review of Electrodes for the Electrical Brain Signal Recording. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2016, 6, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.; Pavinatto, F.J.; Lin, M.C.; Liao, A.; Swisher, S.L.; Mann, K.; Subramanian, V.; Maharbiz, M.M.; Arias, A.C. Inkjet-Printed Flexible Gold Electrode Arrays for Bioelectronic Interfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bareket-Keren, L.; Hanein, Y. Carbon Nanotube-Based Multi Electrode Arrays for Neuronal Interfacing: Progress and Prospects. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Chen, C.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Masurkar, N.; Cavanaugh, J.; Cheng, M.M.-C. A Flexible and Implantable Microelectrode Arrays Using High-Temperature Grown Vertical Carbon Nanotubes and a Biocompatible Polymer Substrate. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 125301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Park, J.; Sohn, J.; Cho, D.; Jeon, S. Bioinspired, Highly Stretchable, and Conductive Dry Adhesives Based on 1D-2D Hybrid Carbon Nanocomposites for All-in-One ECG Electrodes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4770–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbro, A.; Scaini, D.; León, V.; Vázquez, E.; Cellot, G.; Privitera, G.; Lombardi, L.; Torrosi, F.; Tomarchio, F.; Bonaccorso, F.; et al. Graphene-Based Interfaces Do Not Alter Target Nerve Cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veliev, F.; Briançon-Marjollet, A.; Bouchiat, V.; Delacour, C. Impact of Crystalline Quality on Neuronal Affinity of Pristine Graphene. Biomaterials 2016, 86, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avouris, P. Graphene: Electronic and Photonic Properties and Devices. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro Neto, A.H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.R.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The Electronic Properties of Graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 109–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Feng, L.; Mayer, D.; Panaitov, G.; Kireev, D.; Offenhäusser, A.; Krause, H.-J. Electrolyte-Gated Graphene Ambipolar Frequency Multipliers for Biochemical Sensing. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiaoui, R.; Tan, S.; Cong, L.; Singh, R.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W. Multispectral Terahertz Sensing with Highly Flexible Ultrathin Metamaterial Absorber. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 083103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, R.; Strikwerda, A.C.; Jepsen, P. Terahertz Plasmonic Structure with Enhanced Sensing Capabilities. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-W.; Schendel, A.A.; Mikael, S.; Brodnick, S.K.; Richner, T.J.; Ness, J.P.; Hayat, M.R.; Atry, F.; Frye, S.T.; Pashaie, R.; et al. Graphene-Based Carbon-Layered Electrode Array Technology for Neural Imaging and Optogenetic Applications. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzum, D.; Takano, H.; Shim, E.; Reed, J.C.; Juul, H.; Richardson, A.G.; de Vries, G.; Bink, H.; Dichter, M.A.; Lucas, T.H.; et al. Transparent and Flexible Low Noise Graphene Electrodes for Simultaneous Electrophysiology and Neuroimaging. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kireev, D.; Sarik, D.; Wu, T.; Xie, X.; Wolfrum, B.; Offenhäusser, A. High Throughput Transfer Technique: Save Your Graphene. Carbon 2016, 107, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeschik, A.; Rinklin, P.; Derra, U.; Ullmann, S.; Holik, P.; Steltenkamp, S.; Offenhäusser, A.; Wolfrum, B. Nanostructured Cavity Devices for Extracellular Stimulation of HL-1 Cells. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9275–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eick, S. Extracellular Stimulation of Individual Electrogenic Cells with Micro-Scaled Electrodes. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ecken, H.; Ingebrandt, S.; Krause, M.; Richter, D.; Hara, M.; Offenhäusser, A. 64-Channel Extended Gate Electrode Arrays for Extracellular Signal Recording. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 3355–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Ingebrandt, S.; Richter, D.; Denyer, M.; Scholl, M.; Sprössler, C.; Offenhäusser, A. Extended Gate Electrode Arrays for Extracellular Signal Recordings. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2000, 70, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claycomb, W.C.; Lanson, N.A.; Stallworth, B.S.; Egeland, D.B.; Delcarpio, J.B.; Bahinski, A.; Izzo, N.J. HL-1 cells: A cardiac muscle cell line that contracts and retains phenotypic characteristics of the adult cardiomyocyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2979–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wu, L.; Cheng, J.; Huang, S.; Cai, Q.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. Graphene Microelectrode Arrays for Neural Activity Detection. J. Biol. Phys. 2015, 41, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Guo, H.; Jin, Y.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. Electrochemistry Investigation on the Graphene/Electrolyte Interface. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2760–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Tao, N. Measurement of the Quantum Capacitance of Graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luryi, S. Quantum Capacitance Devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1988, 52, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromherz, P. Self-Gating of Ion Channels in Cell Adhesion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4131–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosser, M.S.; Brown, M.A.; McEuen, P.L.; Minot, E.D. Determination of the Thermal Noise Limit of Graphene Biotransistors. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5404–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werth, G.; Dadgar, P. Zum Elektrokardiogramm der Ratte mit und ohne Narkose, bei Beatmung mit Sauerstoffmangelgemischen sowie bei Intoxikation mit Malachitgrün, unter gleichzeitiger Bestimmung des effektiven Sauerstoffverbrauches. Arch. Kreislaufforsch. 1965, 48, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timko, B.P.; Cohen-Karni, T.; Yu, G.; Qing, Q.; Tian, B.; Lieber, C.M. Electrical Recording from Hearts with Flexible Nanowire Device Arrays. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbach, M.; Egert, U.; Hescheler, J.; Banach, K. Estimation of Action Potential Changes from Field Potential Recordings in Multicellular Mouse Cardiac Myocyte Cultures. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 13, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, B.; Kätelhön, E.; Schottdorf, M.; Offenhäusser, A.; Wolfrum, B. Nanocavity Electrode Array for Recording from Electrogenic Cells. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrenbach, J.P.; Mejia-Alvarez, R.; Banach, K. The Relevance of Non-Excitable Cells for Cardiac Pacemaker Function. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottdorf, M.; Hofmann, B.; Kätelhön, E.; Offenhäusser, A.; Wolfrum, B. Frequency-dependent signal transfer at the interface between electrogenic cells and nanocavity electrodes. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 031917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, B.M.; Lottner, M.; Drieschner, S.; Calia, A.B.; Stoiber, K.; Rousseau, L.; Lissourges, G.; Garrido, J.A. Flexible Graphene Transistors for Recording Cell Action Potentials. 2D Mater. 2016, 3, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.C.; Nam, Y. In Vitro Microelectrode Array Technology and Neural Recordings. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maybeck, V.; Edgington, R.; Bongrain, A.; Welch, J.O.; Scorsone, E.; Bergonzo, P.; Jackman, R.B.; Offenhäusser, A. Boron-Doped Nanocrystalline Diamond Microelectrode Arrays Monitor Cardiac Action Potentials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
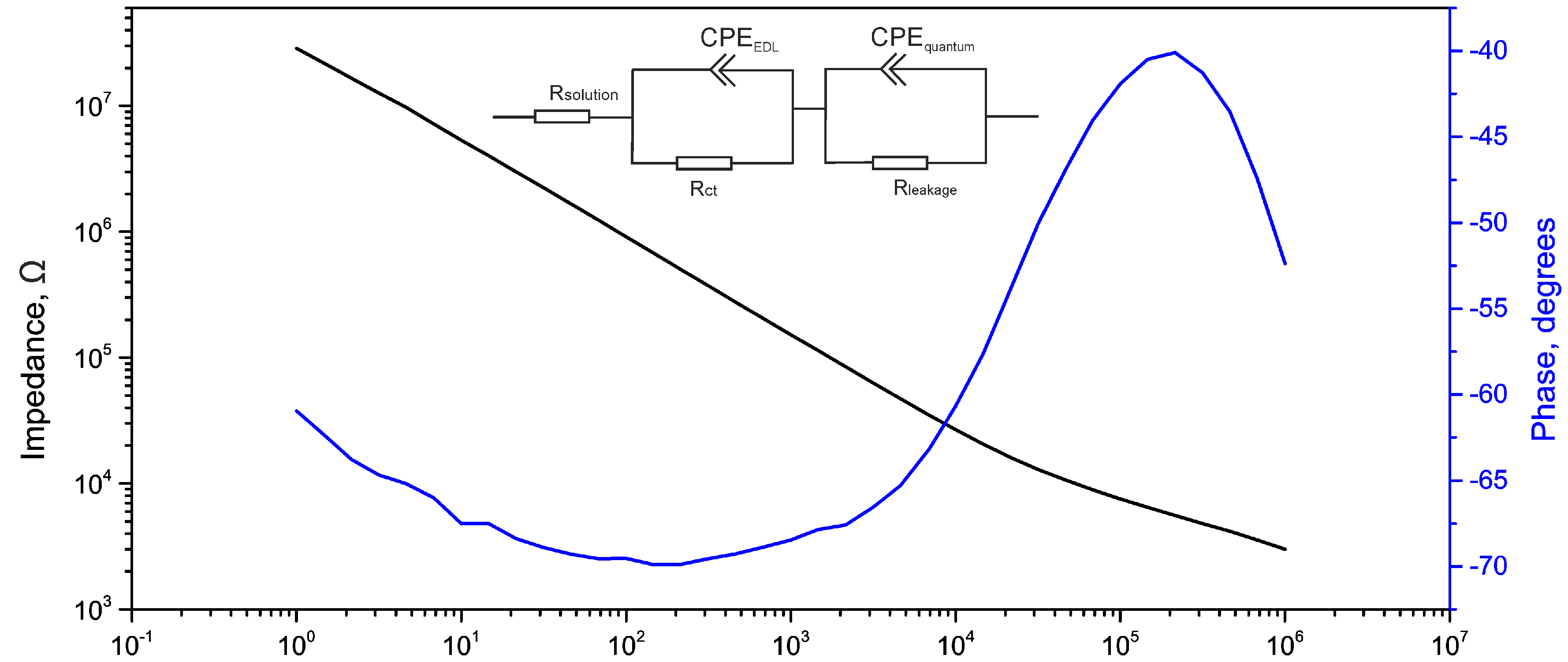
| Used Model | RS (kΩ) | CPE1 (S·sn) | RCT (Ω) | ZW (S·s1/2) | CPE2 (S·sn) | RL (Ω) | Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | n | Q | n | |||||||
| This work | RS + Q2/R2 + Q3/R3 | 0.8 | 5.0 × 10−9 | 0.68 | 5.8k | – | 7.36 × 10−9 | 0.78 | 140M | 314 µm2 |
| Kuzum et al. [24] | RS + Q2/(R2 + W2) | – | 5.6 × 10−9 | 0.67 | 85M | 17.36 × 10−9 | – | – | – | 2500 µm2 |
| Du et al. [31] | RS + Q2/(R2 + W2) + Q3/R3 | 0.17 | 5.75 × 10−7 | 0.67 | 3k | 8.12 × 10−6 | 5.55 × 10−7 | 0.9 | 23.4M | 7000 µm2 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kireev, D.; Seyock, S.; Ernst, M.; Maybeck, V.; Wolfrum, B.; Offenhäusser, A. Versatile Flexible Graphene Multielectrode Arrays. Biosensors 2017, 7, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010001
Kireev D, Seyock S, Ernst M, Maybeck V, Wolfrum B, Offenhäusser A. Versatile Flexible Graphene Multielectrode Arrays. Biosensors. 2017; 7(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKireev, Dmitry, Silke Seyock, Mathis Ernst, Vanessa Maybeck, Bernhard Wolfrum, and Andreas Offenhäusser. 2017. "Versatile Flexible Graphene Multielectrode Arrays" Biosensors 7, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010001
APA StyleKireev, D., Seyock, S., Ernst, M., Maybeck, V., Wolfrum, B., & Offenhäusser, A. (2017). Versatile Flexible Graphene Multielectrode Arrays. Biosensors, 7(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7010001






