Linking Single Domain Antibodies that Recognize Different Epitopes on the Same Target
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparing Linked Constructs
| Clone | Ricin KD (M) 1 | RCA120 KD (M) 1 | Putative Epitope |
|---|---|---|---|
| sdAb-B4 | 4 × 10−9 | No binding | Ricin B chain |
| sdAb-H1 | 3 × 10−10 | 5 × 10−9 | Ricin A/B interface |
| sdAb-C8 | 2 × 10−11 | 1.4 × 10−9 | Ricin A chain |
| sdAb-D1 | 5 × 10−10 | 6 × 10−9 | Ricin A chain |
| Linker length | Linker sequence |
|---|---|
| 11 | AAAGSGGASGS |
| 16 | AAAGSGSGGGSGASGS |
| 21 | AAAGSGSGGGSSGGGSGASGS |
| 26 | AAAGSGSGGGSSGGGSSGGGSGASGS |
| 31 | AAAGSGSGGGSSGGGSSGGGSSGGGSGASGS |
| 33 | AAAEPKIPQPQKPQPQPQPQPQQKPQQKPEPGS |
2.3. Preparation of Luminex Reagents and Assay Protocols
2.4. Circular Dichroism Measurements
2.5. SPR Kinetics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Linked Constructs
3.2. Determination of sdAb Function
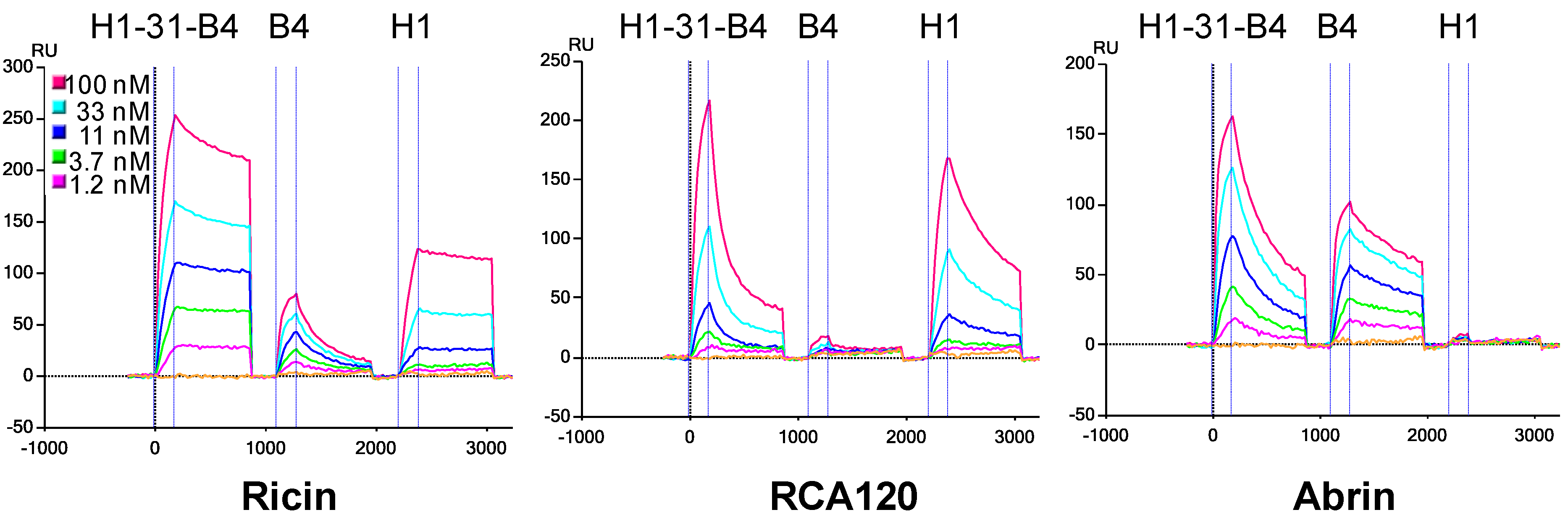
3.3. Determination of sdAb Binding Target Simultaneously

3.4. Effect of Linker Length and sdAb Order
| Affinity of linked constructs for ricin | Affinity of linked constructs for RCA 120 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clone | ka (1/Ms) 1 | kd (1/s) 1 | KD (M) 2 | ka (1/Ms) 1 | kd (1/s) 1 | KD (M) 2 |
| H1-11-B4 | 2.2 × 105 | 1.3 × 10−4 | 5.8 × 10−10 | 1.9 × 105 | 1.6 × 10−3 | 8.7 × 10−9 |
| H1-16-B4 | 2.4 × 105 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 5.0 × 10−10 | 2.2 × 105 | 1.8 × 10−3 | 7.9 × 10−9 |
| H1-21-B4 | 2.4 × 105 | 8.4 × 10−5 | 3.6 × 10−10 | 2.2 × 105 | 1.8 × 10−3 | 8.4 × 10−9 |
| H1-31-B4 | 2.1 × 105 | 1.8 × 10−4 | 8.9 × 10−10 | 2.4 × 105 | 3.7 × 10−3 | 1.6 × 10−8 |
| H1-33-B4 | 2.2 × 105 | 5.5 × 10−5 | 2.5 × 10−10 | 2.2 × 105 | 2.0 × 10−3 | 9.1 × 10−9 |
| C8-11-H1 | 5.3 × 105 | 1.9 × 10−5 | 3.6 × 10−11 | 1.5 × 105 | 3.3 × 10−4 | 2.1 × 10−9 |
| C8-26-H1 | 4.9 × 105 | 1.5 × 10−5 | 3.0 × 10−11 | 1.4 × 105 | 1.9 × 10−4 | 1.3 × 10−9 |
| B4-33-H1 | 2.0 × 105 | 8.9 × 10−4 | 4.6 × 10−9 | 1.6 × 105 | 3.0 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−8 |
| H1-16-C8 | 1.0 × 105 | 1.8 × 10−5 | 1.8 × 10−10 | 4.5 × 104 | 1.2 × 10−4 | 2.6 × 10−9 |
| C8-11-D1 | 7.9 × 105 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 1.4 × 10−10 | 2.9 × 105 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 6.6 × 10−9 |
| D1-16-C8 | 8.4 × 105 | 3.6 × 10−5 | 4.3 × 10−11 | 2.5 × 105 | 2.5 × 10−4 | 9.9 × 10−10 |
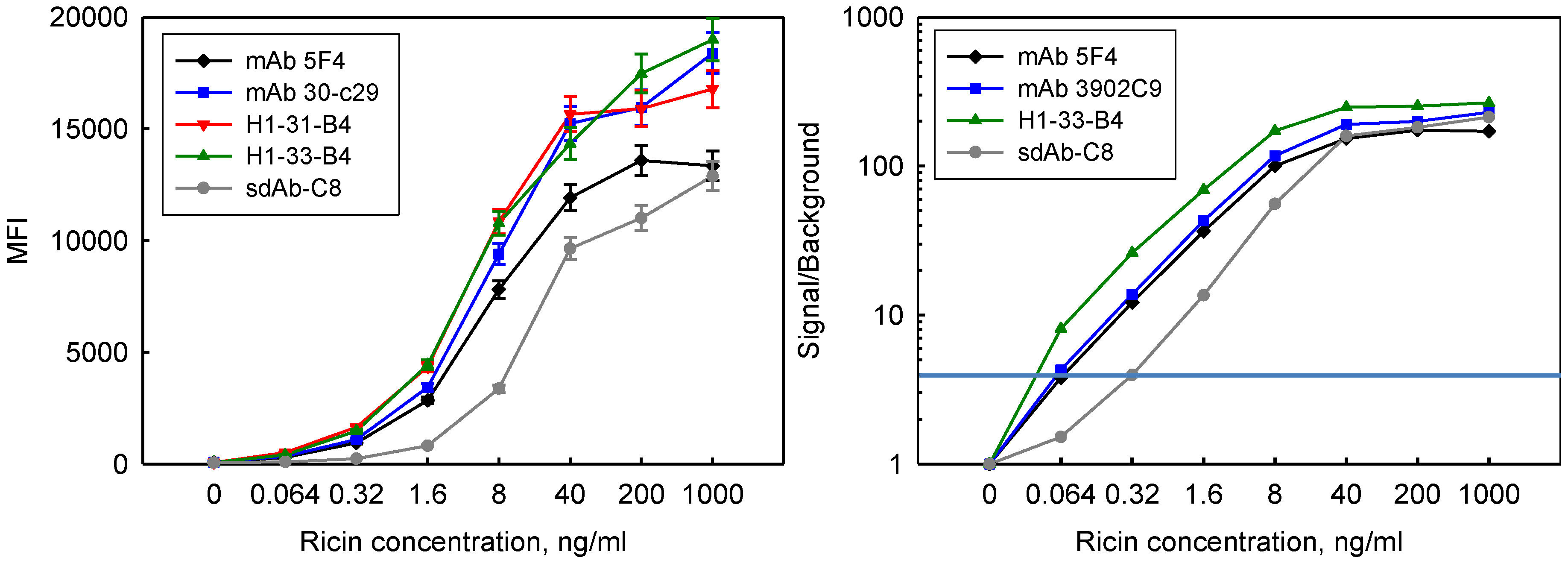
3.5. Incorporation in Sandwich Assays for Ricin Detection
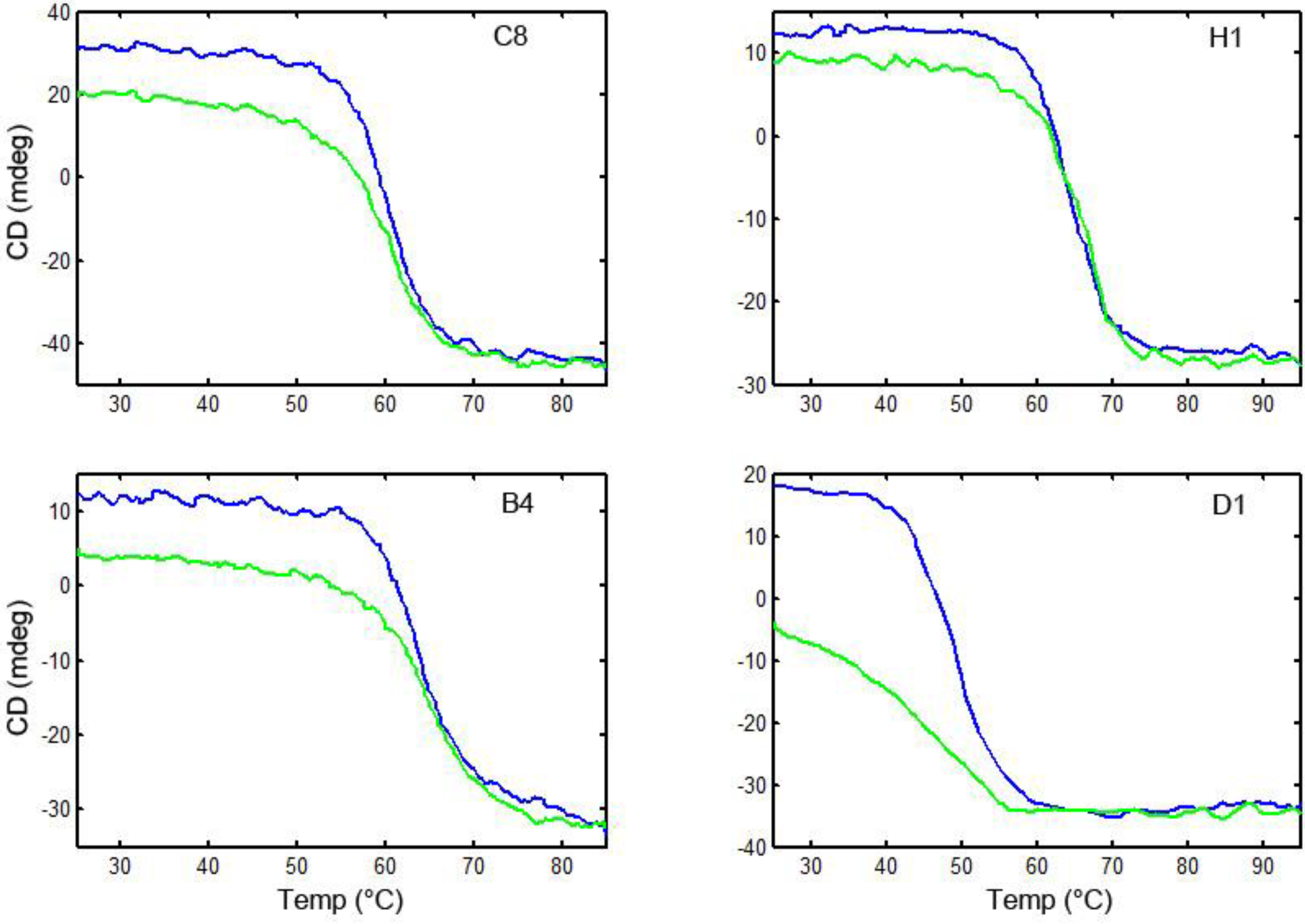
3.6. Thermal Stability and Ability to Refold after Heat Denaturation
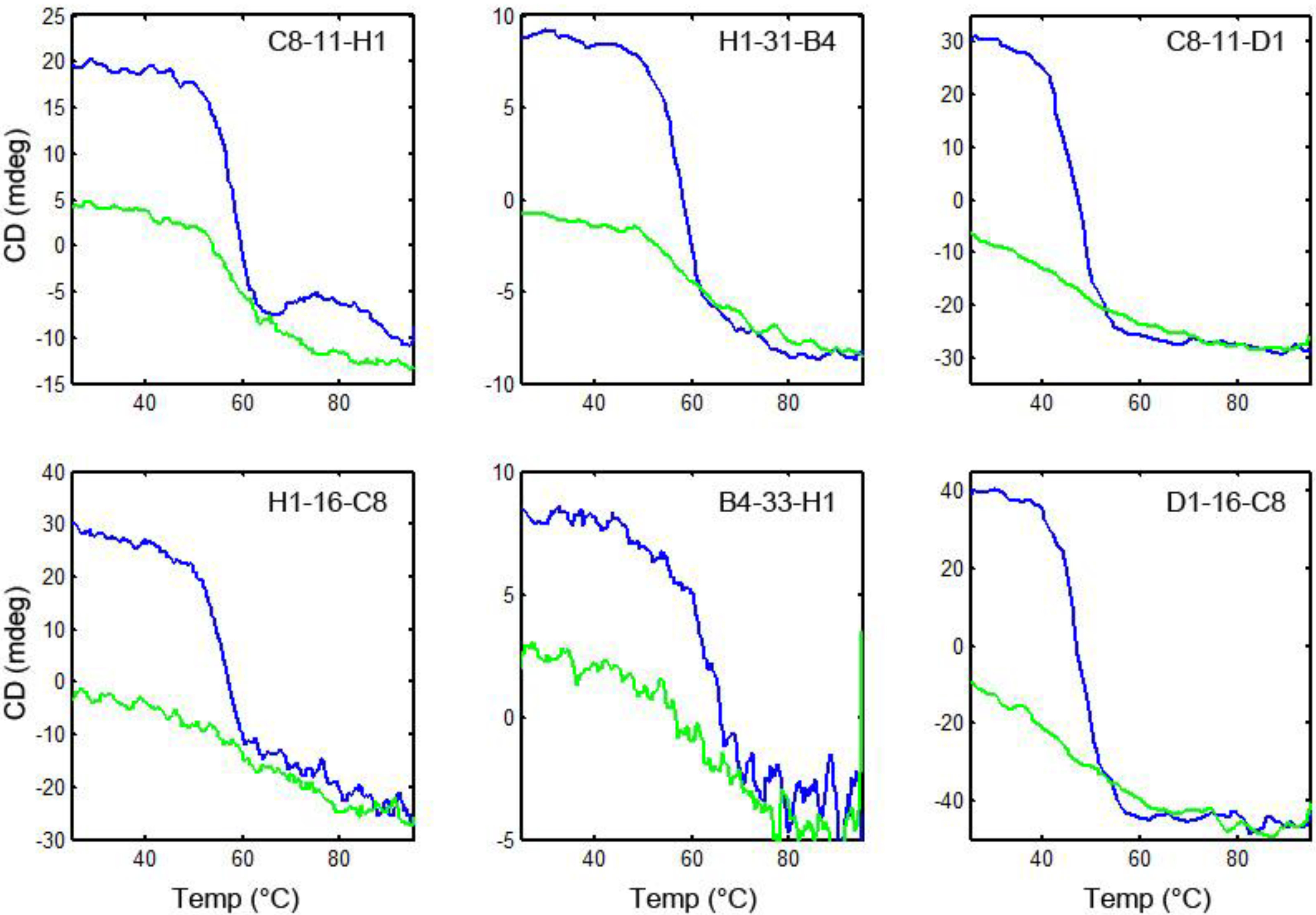
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ghahroudi, M.A.; Desmyter, A.; Wyns, L.; Hamers, R.; Muyldermans, S. Selection and identification of single domain antibody fragments from camel heavy-chain antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1997, 414, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, A.S.; Avila, D.; Hughes, M.; Hughes, A.; McKinney, E.C.; Flajnik, M.F. A new antigen receptor gene family that undergoes rearrangement and extensive somatic diversification in sharks. Nature 1995, 374, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hamerscasterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hamers, C.; Songa, E.B.; Bendahman, N.; Hamers, R. Naturally-occurring antibodies devoid of light-chains. Nature 1993, 363, 446–448. [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall, S.D.; Krishnan, U.V.; Hattarki, M.; de Gori, R.; Irving, R.A.; Hudson, P.J. Isolation of the new antigen receptor from wobbegong sharks, and use as a scaffold for the display of protein loop libraries. Mol. Immunol. 2001, 38, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowski, J.; Alzogaray, V.; Reyelt, J.; Unger, M.; Juarez, K.; Urrutia, M.; Cauerhff, A.; Danquah, W.; Rissiek, B.; Scheuplein, F.; Schwarz, N.; Adriouch, S.; Boyer, O.; Seman, M.; Licea, A.; Serreze, D.V.; Goldbaum, F.A.; Haag, F.; Koch-Nolte, F. Single domain antibodies: Promising experimental and therapeutic tools in infection and immunity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 198, 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- De Marco, A. Biotechnological applications of recombinant single-domain antibody fragments. Microb. Cell Factories 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Linden, R.H.J.; Frenken, L.G.J.; de Geus, B.; Harmsen, M.M.; Ruuls, R.C.; Stok, W.; de Ron, L.; Wilson, S.; Davis, P.; Verrips, C.T. Comparison of physical chemical properties of llama V-HH antibody fragments and mouse monoclonal antibodies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1431, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J.M.J.; Renisio, J.G.; Prompers, J.J.; van Platerink, C.J.; Cambillau, C.; Darbon, H.; Frenken, L.G.J. Thermal unfolding of a llama antibody fragment: A two-state reversible process. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ewert, S.; Cambillau, C.; Conrath, K.; Pluckthun, A. Biophysical properties of camelid V-HH domains compared to those of human VH3 domains. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3628–3636. [Google Scholar]
- Pluckthun, A.; Pack, P. New protein engineering approaches to multivalent and bispecific antibody fragments. Immunotechnology 1997, 3, 83–105. [Google Scholar]
- Crothers, D.M.; Metzger, H. Influence of polyvalency on binding properties of antibodies. Immunochemistry 1972, 9, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.X. Quantitative account of the enhanced affinity of two linked scFvs specific for different epitopes on the same antigen. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 329, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Neri, D.; Momo, M.; Prospero, T.; Winter, G. High affinity antigen-ginding by chelating-recombinant-antibodies (CRABS). J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 246, 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Korn, T.; Nettelbeck, D.M.; Volkel, T.; Muller, R.; Kontermann, R.E. Recombinant bispecific antibodies for the targeting of adenoviruses to CEA-expressing tumour cells: A comparative analysis of bacterially expressed single-chain diabody and tandem scFv. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.J.; Deonarain, M.P. Phage display of chelating recombinant antibody libraries. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2860–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Conrath, K.E.; Lauwereys, M.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. Camel single-domain antibodies as modular building units in bispecific and bivalent antibody constructs. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7346–7350. [Google Scholar]
- Coppieters, K.; Dreier, T.; Silence, K.; de Haard, H.; Lauwereys, M.; Casteels, P.; Beirnaert, E.; Jonckheere, H.; de Wiele, C.V.; Staelens, L.; Hostens, J.; Revets, H.; Remaut, E.; Elewaut, D.; Rottiers, P. Formatted anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha VHH proteins derived from camelids show superior potency and targeting to inflamed joints in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar]
- Hmila, I.; Abdallah, B.A.B.; Saerens, D.; Benlasfar, Z.; Conrath, K.; El Ayeb, M.; Muyldermans, S.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B. VHH, bivalent domains and chimeric Heavy chain-only antibodies with high neutralizing efficacy for scorpion toxin AahI’. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, D.P.; Abregu, F.A.; Krishnan, U.V.; Proll, D.F.; Streltsov, V.A.; Doughty, L.; Hattarki, M.K.; Nuttall, S.D. Dimerisation strategies for shark IgNAR single domain antibody fragments. J. Immunol. Methods 2006, 315, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hultberg, A.; Temperton, N.J.; Rosseels, V.; Koenders, M.; Gonzalez-Pajuelo, M.; Schepens, B.; Ibanez, L. I.; Vanlandschoot, P.; Schillemans, J.; Saunders, M.; Weiss, R.A.; Saelens, X.; Melero, J.A.; Verrips, C.T.; Van Gucht, S.; de Haard, H.J. Llama-derived single domain antibodies to build multivalent, superpotent and broadened neutralizing anti-viral molecules. PLoS One 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Hale, M.L.; Bernstein, R.D.; Moore, M.; Swain, M.D.; Goldman, E.R. Development of antiricin single domain antibodies toward detection and therapeutic reagents. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9604–9611. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.P.; Bernstein, R.D.; Swain, M.D.; Zabetakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Binding kinetics of antiricin single domain antibodies and improved detection using a B chain specific binder. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7202–7207. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, E.R.; Anderson, G.P.; Liu, J.L.; Delehanty, J.B.; Sherwood, L.J.; Osborn, L.E.; Cummins, L.B.; Hayhurst, A. Facile generation of heat-stable antiviral and antitoxin single domain antibodies from a semisynthetic llama library. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8245–8255. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, J.O.; Sherwood, L.J.; Collazo, M.T.; Garza, J.A.; Hayhurst, A. Llama single domain antibodies specific for the 7 botulinum neurotoxin serotypes as heptaplex immunoreagents. PLoS One 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.P.; Zabetakis, D.; Bernstein, R.D.; Cai, S.W.; Singh, B.R.; Goldman, E.R. Evaluation of anti-hemagglutinin Hn-33 single domain antibodies: Kinetics, binding epitopes, and thermal stability. Botulinum J. 2011, 2, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.M.; Lamb, F.I.; Pappin, D.J.C.; Lord, J.M. The primary sequence of ricin-communis agglutinin—Comparison with ricin. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 5682–5686. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M.; Sumizawa, T.; Funatsu, G. The complete amino-acid sequences of the B-chains of abrin-A and abrin-G, toxic proteins from the seeds of Abrus-precatorius. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.A.; Lord, J.M.; Wawrzynczak, E.J.; Piatak, M. Preproabrin—Genomic cloning, characterization and the expressin of the A-chain in Escherichia-coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 198, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertus, J.D.; Monzingo, A.F. The structure of ribosome inactivating proteins. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 477–486. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.B.; Li, Q.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Tremblay, T.L.; Stone, E.; To, R.; Kelly, J.; MacKenzie, C.R. A pentavalent single-domain antibody approach to tumor antigen discovery and the development of novel proteomics reagents. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, L.J.; Osborn, L.E.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Patterson, J.L.; Hayhurst, A. Rapid assembly of sensitive antigen-capture assays for Marburg virus, using in vitro selection of llama single-domain antibodies, at biosafety level 4. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, S213–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, M.D.; Anderson, G.P.; Serrano-González, J.; Liu, J.L.; Zabatakis, D.; Goldman, E.R. Immunodiagnostic reagents using llama single domn antibody-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, E.; Hirama, T.; Tanha, J.; Tong-Sevinc, H.; Li, S.H.; MacKenzie, C.R.; Zhang, J.B. The assembly of single domain antibodies into bispecific decavalent molecules. J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 318, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Glaven, R.H.; Anderson, G.P.; Zabetakis, D.; Liu, J.L.; Long, N.C.; Goldman, E.R. Linking Single Domain Antibodies that Recognize Different Epitopes on the Same Target. Biosensors 2012, 2, 43-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010043
Glaven RH, Anderson GP, Zabetakis D, Liu JL, Long NC, Goldman ER. Linking Single Domain Antibodies that Recognize Different Epitopes on the Same Target. Biosensors. 2012; 2(1):43-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010043
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlaven, Richard H., George P. Anderson, Dan Zabetakis, Jinny L. Liu, Nina C. Long, and Ellen R. Goldman. 2012. "Linking Single Domain Antibodies that Recognize Different Epitopes on the Same Target" Biosensors 2, no. 1: 43-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010043
APA StyleGlaven, R. H., Anderson, G. P., Zabetakis, D., Liu, J. L., Long, N. C., & Goldman, E. R. (2012). Linking Single Domain Antibodies that Recognize Different Epitopes on the Same Target. Biosensors, 2(1), 43-56. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010043





