Development of Chemiluminescent Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of Nucleic Acids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
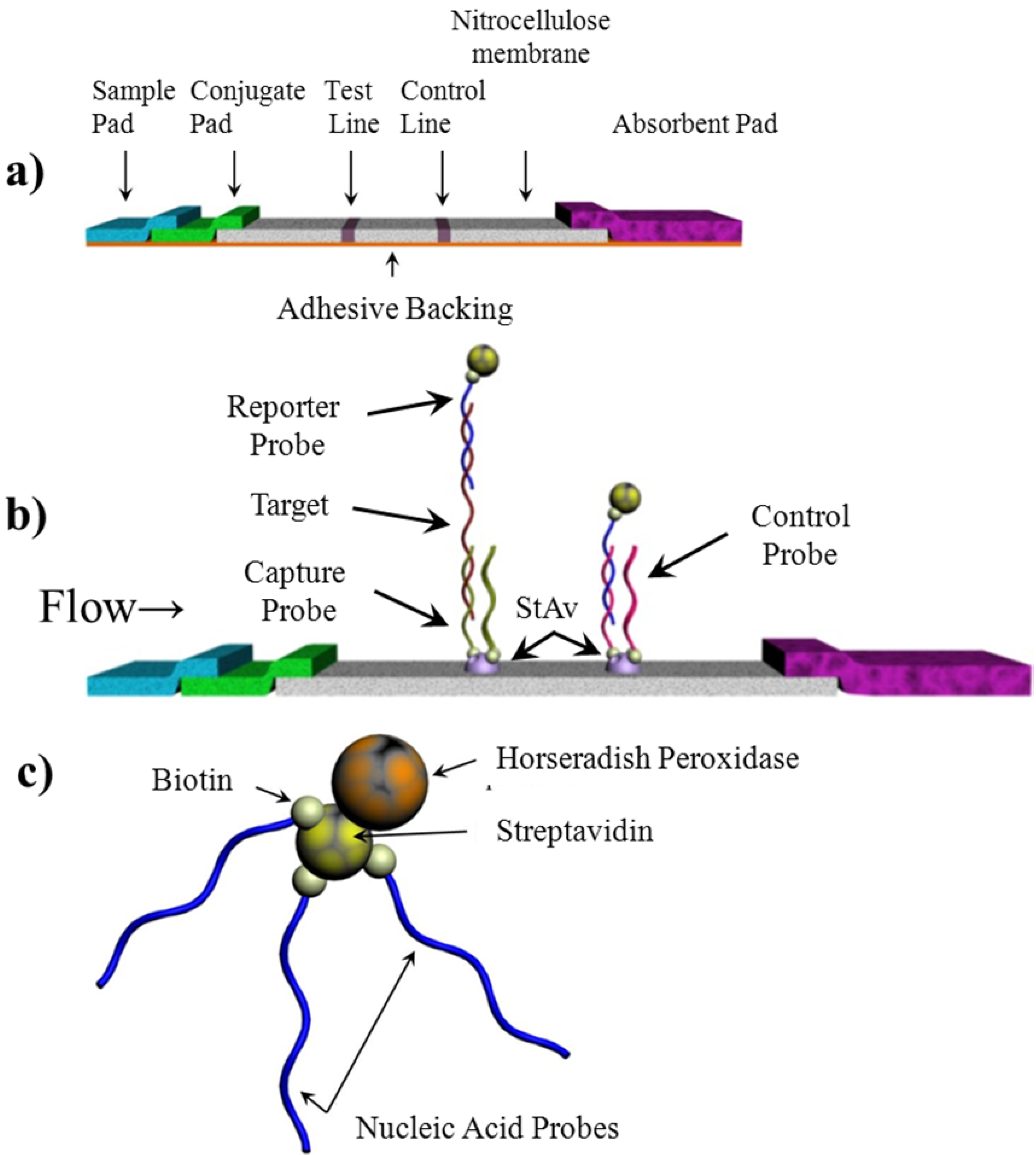
2.1. Capture and Reporter Probe Design
| Target Sequence | AAC GCT ATT ATT AGA ACA GTT TCT GTA CTA TAT TGA ACA TCA AGC AAA GAA AAT AAA TGC AGT TTT CAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AA |
| Leader Sequence | AAC GCT ATT ATT AGA ACA GTT TCT GTA CTA TAT TG-biotin |
| Reporter Probe: Leader Sequence Complement | CAA TAT AGT ACA GAA ACT GTT CTA ATA ATA GCG TT-biotin |
| Capture Probe: Poly (A)25 | biotin-AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA AAA A |
| Control Probe: Oligo d(T)25 | biotin-TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT T |
2.2. Lateral Flow Assay Fabrication
2.2.1. Sample Pad
2.2.2. Conjugate Pad
2.2.3. Nitrocellulose Membrane
2.2.4. Absorbent Pad
2.3. Lateral Flow Assay Assembly
2.4. Assay Procedure

2.5. Assay Optimization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemiluminescence Optimization
3.2. Limit of Detection of the Test Strip
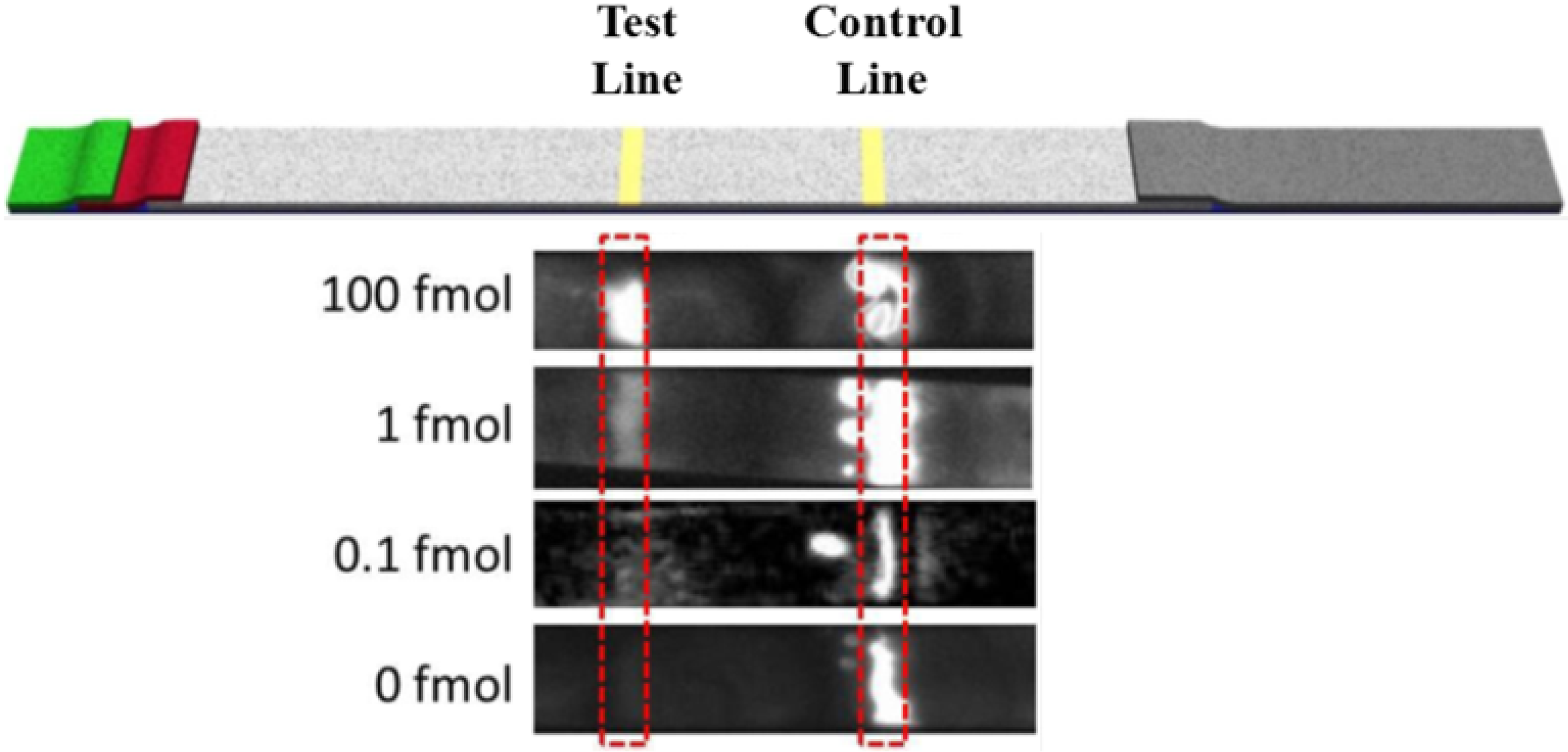

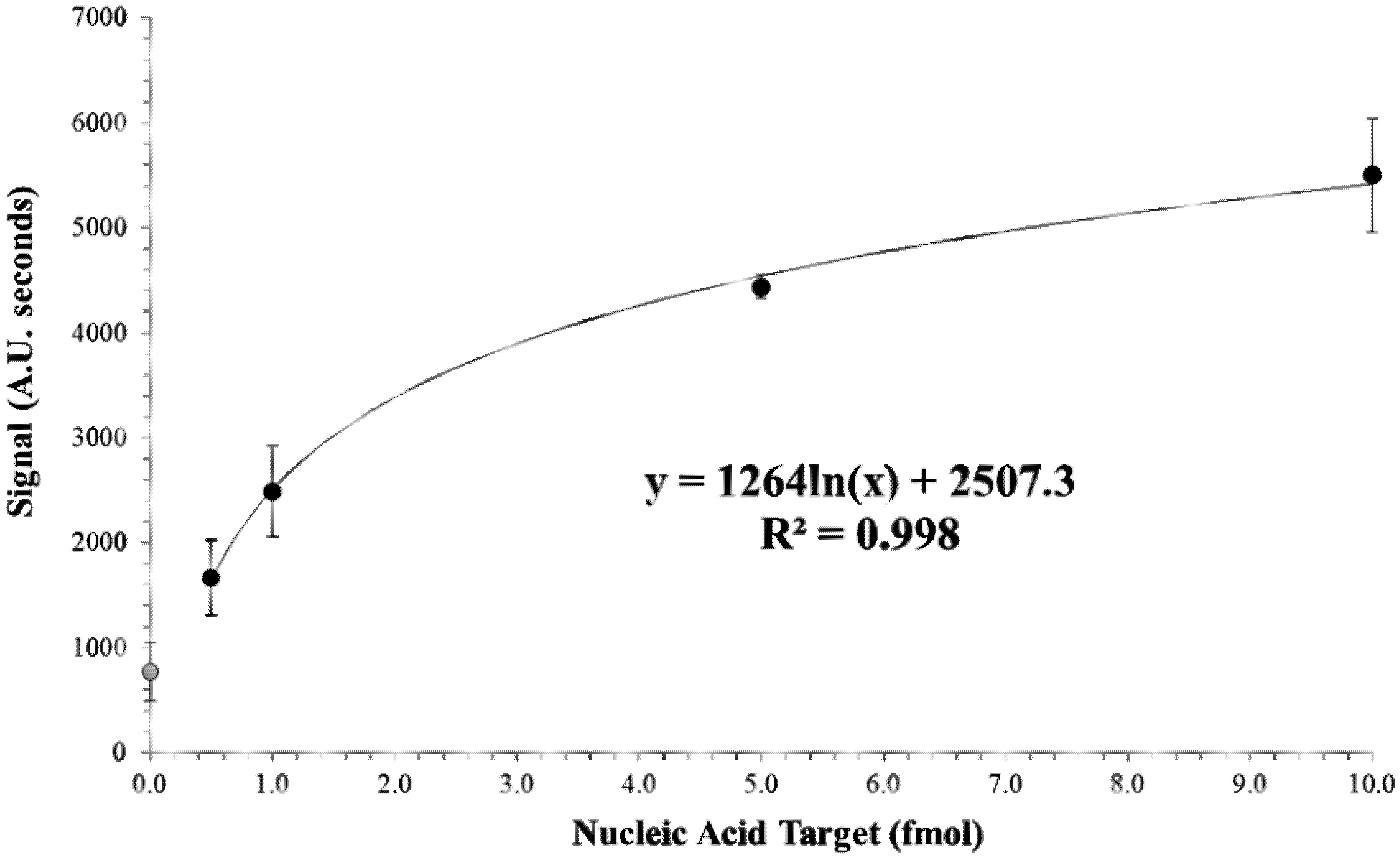
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
References
- Reithinger, R.; Grijalva, M.J.; Chiriboga, R.F.; Alarcon de Noya, B.; Torres, J.R.; Pavia-Ruz, N.; Manrique-Saide, P.; Cardinal, M.V.; Guertler, R.E. Rapid detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in human serum by use of an immunochromatographic dipstick test. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3003–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, J.E.; Olivares Villagomez, D.; Vnencak Jones, C.L.; McCurley, T.L.; Carter, C.E. Detection of Trypanosoma cruzi with the polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization in infected murine cardiac tissue. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Larrouy, G.; Brochier, B.; Dossantos, L.G.; Queiroz, S.F.; Magnaval, J.F. The ELISA methods for the screening of Trypanosoma cruzi carriers—comparative-study. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1983, 76, 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, H.A.; Pereira, J.B.; Thiemann, O.; Depaiva, E.; Degrave, W.; Morel, C.M.; Simpson, L. Detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in blood specimens of chronic chagasic patients by polymerase chain-reaction amplification of kinetoplast minicircle dna—comparison with serology and xenodiagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 2421–2426. [Google Scholar]
- Lejon, V.; Buscher, P.; Magnus, E.; Moons, A.; Wouters, I.; van Meirvenne, N. A semi-quantitative ELISA for detection of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense specific antibodies in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of sleeping sickness patients. Acta Trop. 1998, 69, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiby, D.A.; Wendel, S.; Takaoka, D.T.; Fachini, R.M.; Oliveira, L.C.; Tibbals, M.A. Serologic testing for Trypanosoma cruzi: Comparison of radioimmunoprecipitation assay with commercially available indirect immunofluorescence assay, indirect hemagglutination assay, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 639–642. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, P.D.; Boughton, R.; Dorn, P.L.; Steurer, F.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Esfandiari, J.; Goncalves, E.; Diaz, J.; Malone, J.B. Comparison of two immunochromatographic assays and the indirect immunofluorscence antibody test for diagnosis of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in dogs in south central Louisiana. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, M.; Salas, J.; Tavares, L.; Fontes, C. Validation of a particle gel immunoassay for Trypanosoma cruzi antibody detection using plasma samples collected with capillary tubes. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2010, 4, 590–592. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinal, M.V.; Reithinger, R.; Guertler, R.E. Use of an immunochromatographic dipstick test for rapid detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in sera from animal reservoir hosts. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3005–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Nantulya, V.M. Molecular diagnosis of parasites. Experientia 1991, 47, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, A.; Fernandes, E.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2005, 65, 45–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dorn, P.L.; Engelke, D.; Rodas, A.; Rosales, R.; Melgar, S.; Brahney, B.; Flores, J.; Monroy, C. Utility of the polymerase chain reaction in detection of Trypanosoma cruzi in Guatemalan Chagas’ disease vectors. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 60, 740–745. [Google Scholar]
- Chiurillo, M.A.; Crisante, G.; Rojas, A.; Peralta, A.; Dias, M.; Guevara, P.; Anez, N.; Ramirez, J.L. Detection of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli infection by duplex PCR assay based on telomeric sequences. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Schapachnik, E.; Perez Riera, A.R.; Dubner, S.; Ferreira Filho, C.; Hiroshi Uchida, A.; Ferreira, C. Dr. Carlos Justiniano Ribeiro Das Chagas (1879–1934): A giant of the Third World. Cardiol. J. 2009, 16, 592–593. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandari, A.; Kim, W.; Hohn, K. Luminol-based enhanced chemiluminescence assay for quantification of peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solutions: Effect of reagent pH and ionic strength. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 136, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Mugasa, C.M.; Laurent, T.; Schoone, G.J.; Kager, P.A.; Lubega, G.W.; Schallig, H.D.F.H. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification with oligochromatography for detection of Trypanosoma brucei in clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 630–635. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, Y.O.; Mohamed-Ahmed, M.M.; Lubna, T.K.; El Rayah, I.E. Detection of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense and T.b. rhodesiense in Glossina fuscipes fuscipes (Diptera: Glossinidae) and Stomoxys flies using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique in southern Sudan. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6408–6412. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, N.; Galindo, I.; Guevara, P.; Novak, E.; Scorza, J.V.; Anez, N.; Dasilveira, J.F.; Ramirez, J.L. Identification and detection of Trypanosoma cruzi by using a DNA amplification fingerprint obtained from the ribosomal intergenic spacer. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threat. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, P.; Domingo, G.J.; Gerdes, J. Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 107–144. [Google Scholar]
- Connelly, J.T.; Nugen, S.R.; Borejsza-Wysocki, W.; Durst, R.A.; Montagna, R.A.; Baeumner, A.J. Human pathogenic Cryptosporidium species bioanalytical detection method with single oocyst detection capability. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Nugen, S.R.; Leonard, B.; Baeumner, A.J. Application of a unique server-based oligonucleotide probe selection tool toward a novel biosensor for the detection of Streptococcus pyogenes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumanan, V.; Nugen, S.R.; Baeumner, A.J.; Chang, Y. A biosensor assay for the detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis in fecal samples. J. Vet. Sci. 2009, 10, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Ko, H.; Kang, M.; Pyun, J. Highly sensitive rapid test with chemiluminescent signal bands. Biochip J. 2010, 4, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, G. Disposable nucleic acid biosensors based on gold nanoparticle probes and lateral flow strip. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Walder, J.; Eder, P.; Engman, D.; Brentano, S.; Walder, R.; Knutzon, D.; Dorfman, D.; Donelson, J. The 35-nucleotide spliced leader sequence is common to all trypanosome messenger RNA’s. Science 1986, 233, 569–571. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.; Nelson, R.G.; Watkins, K.P.; Agabian, N. Trypanosome mRNAs share a common 52 spliced leader sequence. Cell 1984, 38, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missler, U.; Wiesmann, M.; Friedrich, C.; Kaps, M. S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase concentrations in blood as indicators of infarction volume and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 1997, 28, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Manfred, A.K. Determination of copper at ng mL−1-levels based on quenching of the europium chelate luminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 364, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjems, L.; Roder, M.; Dinesen, B.; Hartling, S.; Jorgensen, P.; Binder, C. Highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay of proinsulin immunoreactivity with use of two monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 2146–2150. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Fill, C.; Nugen, S.R. Development of Chemiluminescent Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of Nucleic Acids. Biosensors 2012, 2, 32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010032
Wang Y, Fill C, Nugen SR. Development of Chemiluminescent Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of Nucleic Acids. Biosensors. 2012; 2(1):32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuhong, Catherine Fill, and Sam R. Nugen. 2012. "Development of Chemiluminescent Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of Nucleic Acids" Biosensors 2, no. 1: 32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010032
APA StyleWang, Y., Fill, C., & Nugen, S. R. (2012). Development of Chemiluminescent Lateral Flow Assay for the Detection of Nucleic Acids. Biosensors, 2(1), 32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios2010032




