Recent Advances in Microfluidic Biofuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microfluidics for (Bio)fuel Cells
2.1. Applications and Examples of Microfluidics for Biofuel Cells
2.2. Selected Elemental Technology
2.2.1. Materials for Microfluidic Design
2.2.2. Immobilization of Biocatalysts
2.2.3. Biochemical or Biomedical Applications of Microfluidic Devices
2.2.4. Using Polymers, Photoimine Crosslinking, or Gels
3. Detailed Aspects of Biofuel Cells Used in Microfluidics
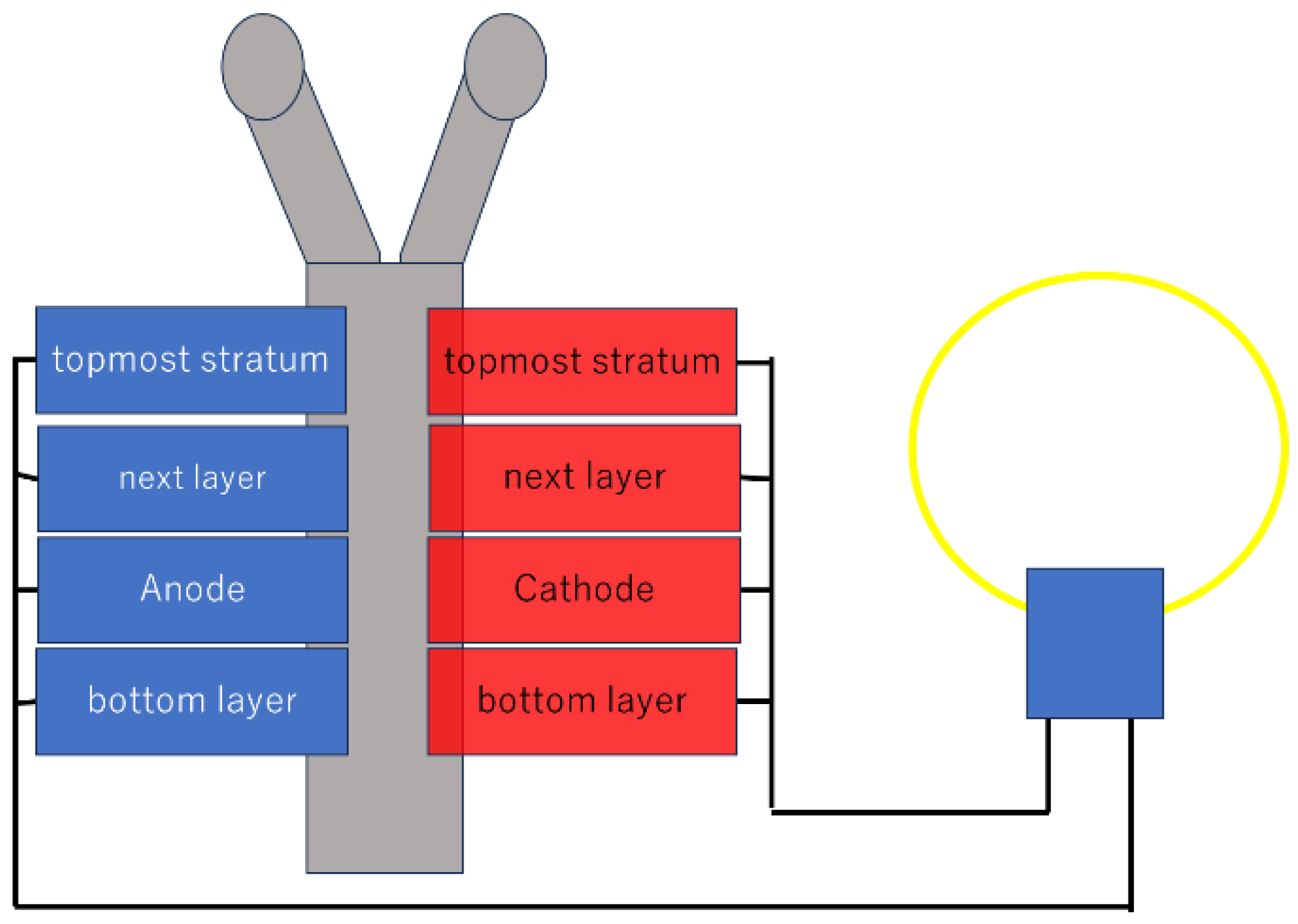
3.1. Types of Biofuel Cells and Basic Principles
3.2. Electrode Materials and Nanotechnology Applications
3.3. Direct or Mediated Electron Transfer
3.4. Operations Using Fuels in Biological Solutions
3.5. Evaluation of Performance of Cells
3.6. Towards Implantable and Wearable Devices
3.7. Issues to Be Overcome Regarding Battery Materials
3.8. Recent Research Related to Some Aspects
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEM | proton exchange membrane |
| MEMS | microelectromechanical systems |
| SAV | surface area-to-volume |
| BOD | bilirubin oxidase |
| GDH | glucose dehydrogenase |
| GOD | glucose oxidase |
| ADH | alcohol dehydrogenase |
| OKABTS | azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid |
| CLEA | cross-linked enzyme aggregates |
| PIC | photoinduced imine crosslinking |
| FRP | free radical polymerization |
| PEGDA | polyethylene glycol diacrylate |
| GelMA | methacrylated gelatin |
| MED | Mediator |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| SWCNT | Single-walled Carbon nanotube |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| Rgo | reduced graphene oxide |
| OCV | Open Circuit Voltage |
| AuNP | Gold nanoparticle |
| CDH | cellobiose dehydrogenase |
| NPG | nanoporous gold |
References
- Estrada-Osorio, D.V.; Escalona-Villalpando, R.A.; Gurrola, M.P.; Chaparro-Sánchez, R.; Rodríguez-Morales, J.A.; Arriaga, L.G.; Ledesma-García, J. Abiotic, Hybrid, and Biological Electrocatalytic Materials Applied in Microfluidic Fuel Cells: A Com-prehensive. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2024, 4, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarahim, O.A.; Navarro-Segarra, M.; Sadeghi, P.; Sabaté, N.; Esquivel, J.P.; Kjeang, E. Microfluidics for Electrochemical Energy Conversion. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 7236–7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, M.; Blum, Z.; Shleev, S. Direct electron transfer based enzymatic fuel cells. Electrochem. Acta 2012, 82, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, R.A.S.; Pereira, A.R.; de Souza, J.C.P.; Sales, F.C.P.F.; Crespilho, F.N. Enzyme Biofuel Cells: Thermodynamics, Kinetics and Challenges in Applicability. ChemElectroChem 2014, 1, 1751–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Ahmad, F.; Khan, M.I.; Shanableh, A.; Taj, A.B.; Rao, K.A.; Voskressensky, L.G.; Luque, R. A critical review of biofuel cell cathodes. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2025. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Kjeang, E. A perspective on microfluidic biofuel cells. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Tao, K.; Chang, H. Generating Electricity on Chips: Microfluidic Biofuel Cells in Perspective. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, B. Microfluidic microbial fuel cells: From membrane to membrane free. J. Power Sources 2016, 324, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiao, M.; Lam, K.B.; Lin, L. Micromachined microbial and photosynthetic fuel cells. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, C.-P.-B.; Chiao, M. A Microfabricated PDMS Microbial Fuel Cell. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.G.; Palmore, G.T.P. Microfluidic biofuel cells: The influence of electrode diffusion layer on performance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Minteer, S.D.; Martin, R.S. Microchip-based ethanol/oxygen biofuel cell. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, F.; Baum, M.; Gu, Q.; Morse, D.E. A 1.5 µL microbial fuel cell for on-chip bioelectricity generation. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3076–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEA®s): Stable and recyclable biocatalysts. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.G.; Park, K.J.; Seok, S.; Shin, S.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Heo, Y.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, T.J. 3D Printed Modules for Integrated Microfluidic Devices. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32876–32880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Wang, F.; McAlpine, M.C. 3D Printed Microfluidics: Advances in Strategies, Integration, and Applications. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 1279–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochol, R.D.; Sweet, E.; Glick, C.C.; Wu, S.-Y.; Yang, C.; Restaino, M.; Lin, L. 3D Printed Microfluidics and Microelectronics. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 189, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Bersano-Begey, T.; Park, J.Y.; Burns, M.A.; Takayama, S. Next-Generation Integrated Microfluidic Circuits. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2813–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlfeld, T.; Cidonio, G.; Kilian, D.; Duin, S.; Akkineni, A.R.; Dawson, J.I.; Yang, S.; Lode, A.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Gelinsky, M. Development of a Clay-Based Bioink for 3D Cell Printing for Skeletal Application. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 034103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Sasaki, M.; Nakasu, A.; Takayanagi, M.; Taguchi, T. An Antithrombogenic Citric Acid-Crosslinked Gelatin with Endothelialization Activity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pati, F.; Choi, Y.-J.; Rijal, G.; Shim, J.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Ray, A.R.; Cho, D.-W.; Ghosh, S. Bioprintable Cell-Laden Silk Fibroin–Gelatin Hydrogel Supporting Multilineage Differentiation of Stem Cells for Fabrication of Three-Dimensional Tissue Constructs. Acta Biomater. 2015, 1, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Z.; Li, C.; Li, P. One-Step Enzyme Kinetics Measurement in 3D Printed Microfluidics Devices Based on a High-Performance Single Vibrating Sharp-Tip Mixer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1172, 338677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mross, S.; Pierrat, S.; Zimmermann, T.; Kraft, M. Microfluidic Enzymatic Biosensing Systems: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncombe, T.A.; Tentori, A.M.; Herr, A.E. Microfluidics: Reframing Biological Enquiry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2015, 16, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Bao, B.; Sun, K.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Microfluidic-templated cell-laden microgels fabricated using phototriggered imine-crosslinking as injectable and adaptable granular gels for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2023, 157, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Tang, N.; Lei, C. Research Progresses and Application of Biofuel Cells Based on Immobilized Enzymes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, A.; Slaughter, G. Nanomaterial-Enabled Enhancements in Thykoid Bsed Biofuel Cells. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, Y.; Tadesse, S. Advancements in Bioelectricity Generation Through Nanamaterial-Modified Anode Electrodes in Microbioal Fuel Cells. Front. Nanotechnol. 2022, 4, 876014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltysheva, D.; Shchurska, K.; Kuzminskyi, Y. Microalgae and cyanobacteria as biological agents of biocathodes in biofuel cells. BioTechnologia 2021, 102, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, S.; Zhang, S. Current development of stretchable self- powered technology based on nanomaterials toward wearable biosensors in biomedical applications. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1164805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Yeo, W.-H. Advances in Energy Harvesting Technologies for Wearable Devices. Micromachines 2024, 15, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Khang, D.Y. Stretchable Enzymatic Biofuel Cells Based on Microfluidic Structured Elastomeric Polydimethylsiloxane with Wrinkled Gold Electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2309386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cui, L.; Shi, X.; Wu, S. Emerging Trends in Microfluidic Biomaterials: From Functional Design to Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanjani, E.; Fergola, A.; Antoni, J.; Martínez, L.; Nazarnezhad, S.; Terre, J.C.; Marasso, S.L.; Aghajanloo, B. Capillary microfluidics for diagnostic applications: Fundamentals, mechanisms, and capillarics. Front. Lab Chip Technol. 2025, 4, 1502127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Warden, A.R.; Ding, X. Recent advances in microfluidics for drug screening. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 061503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
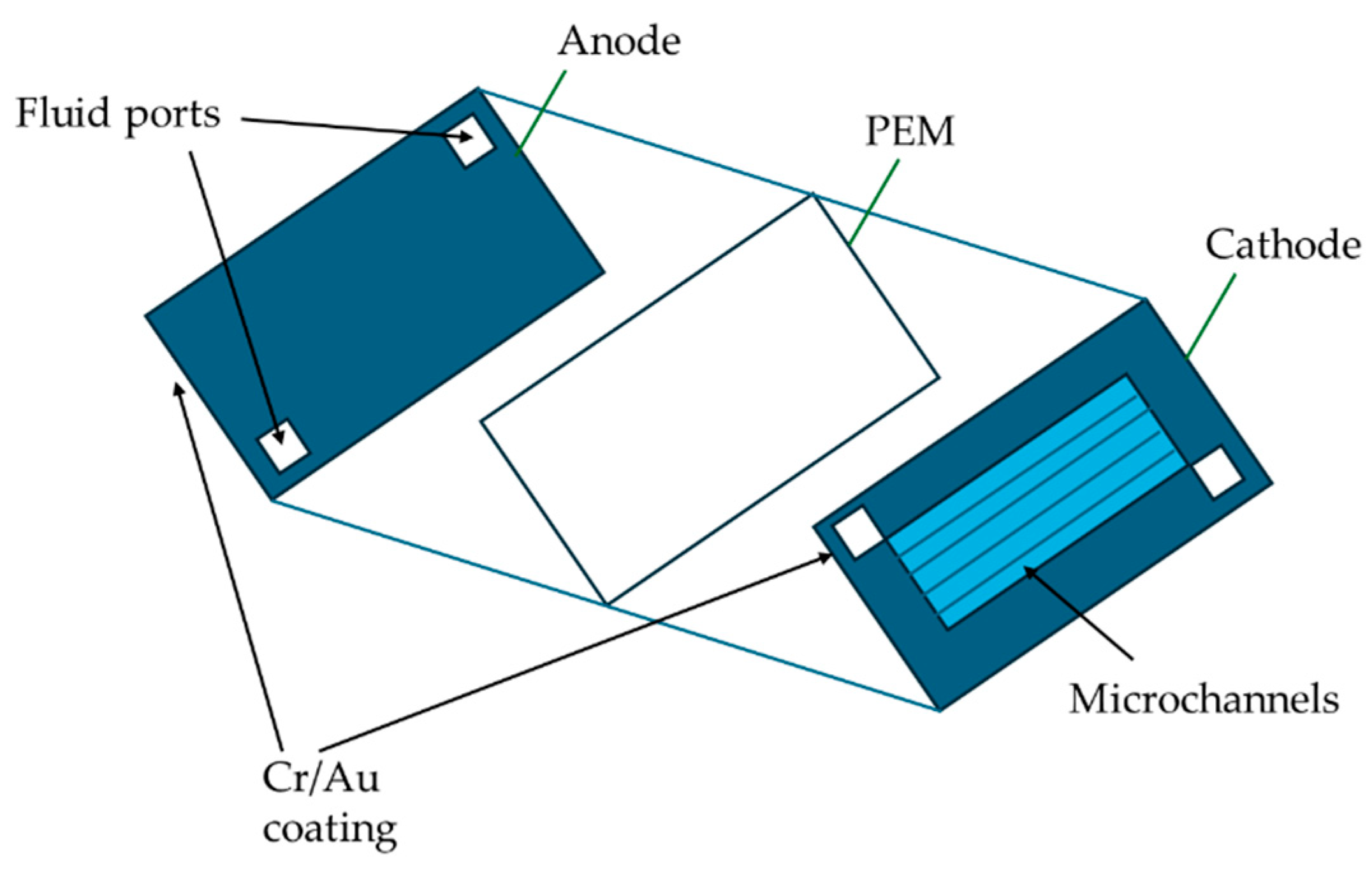

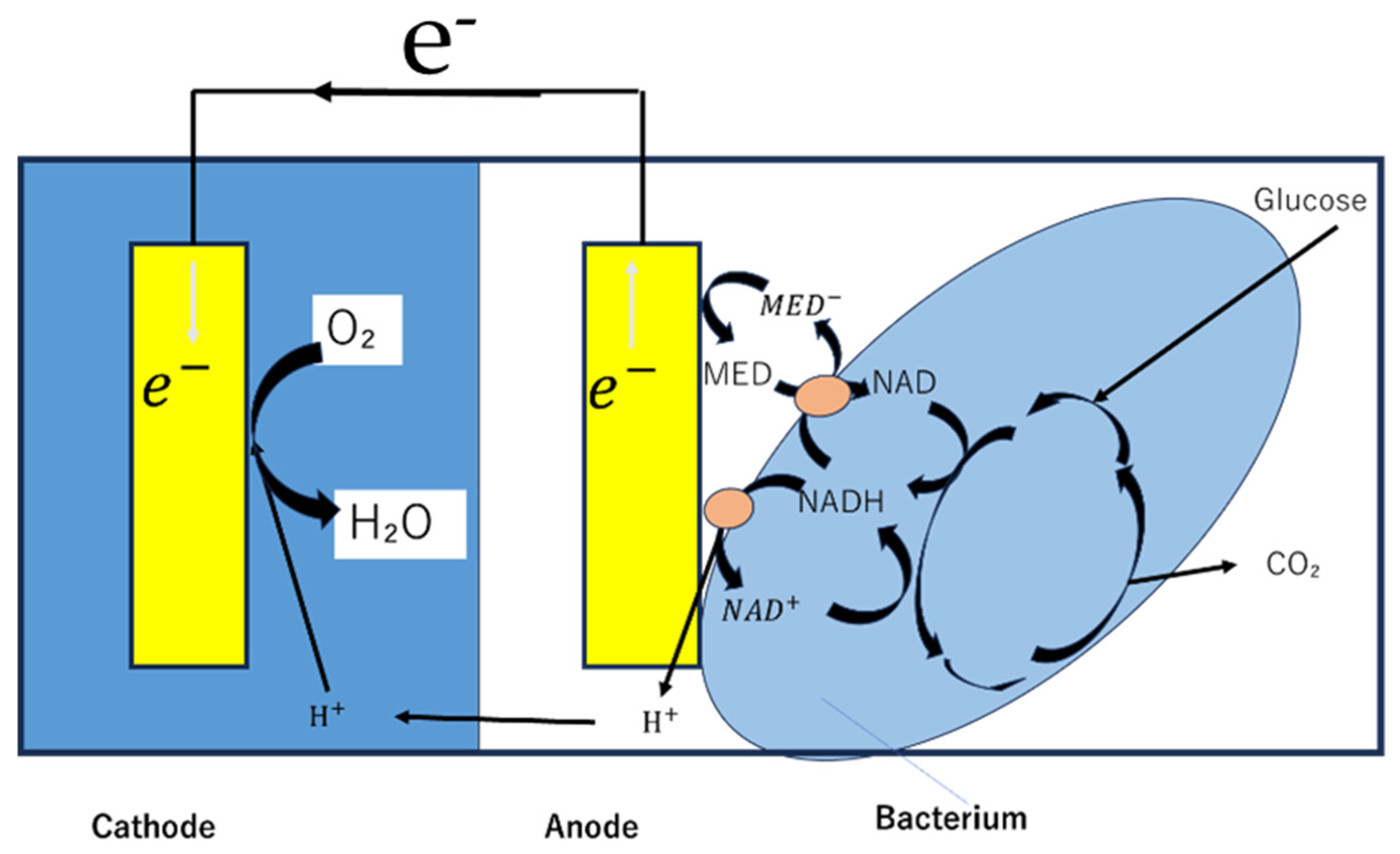
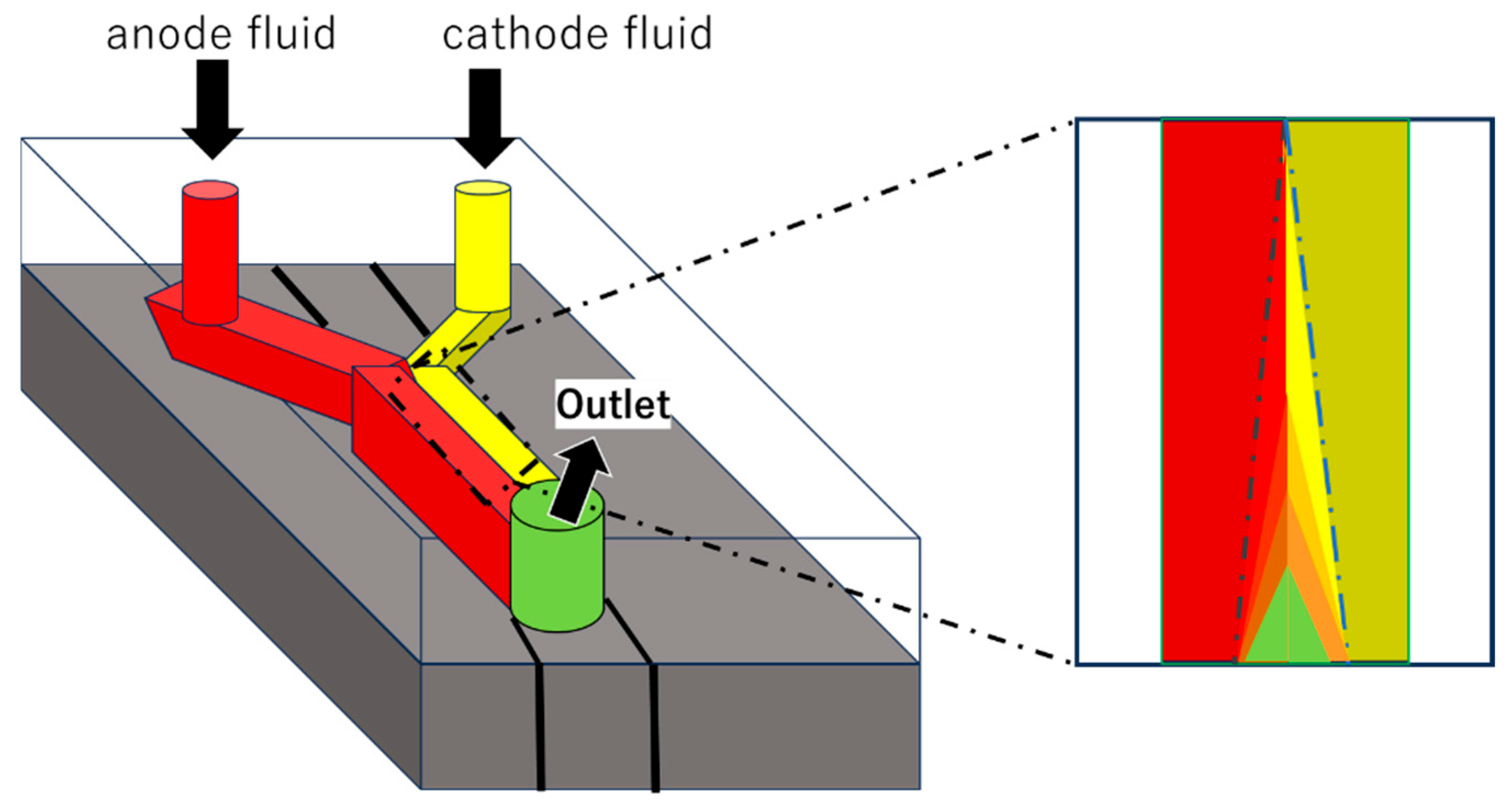
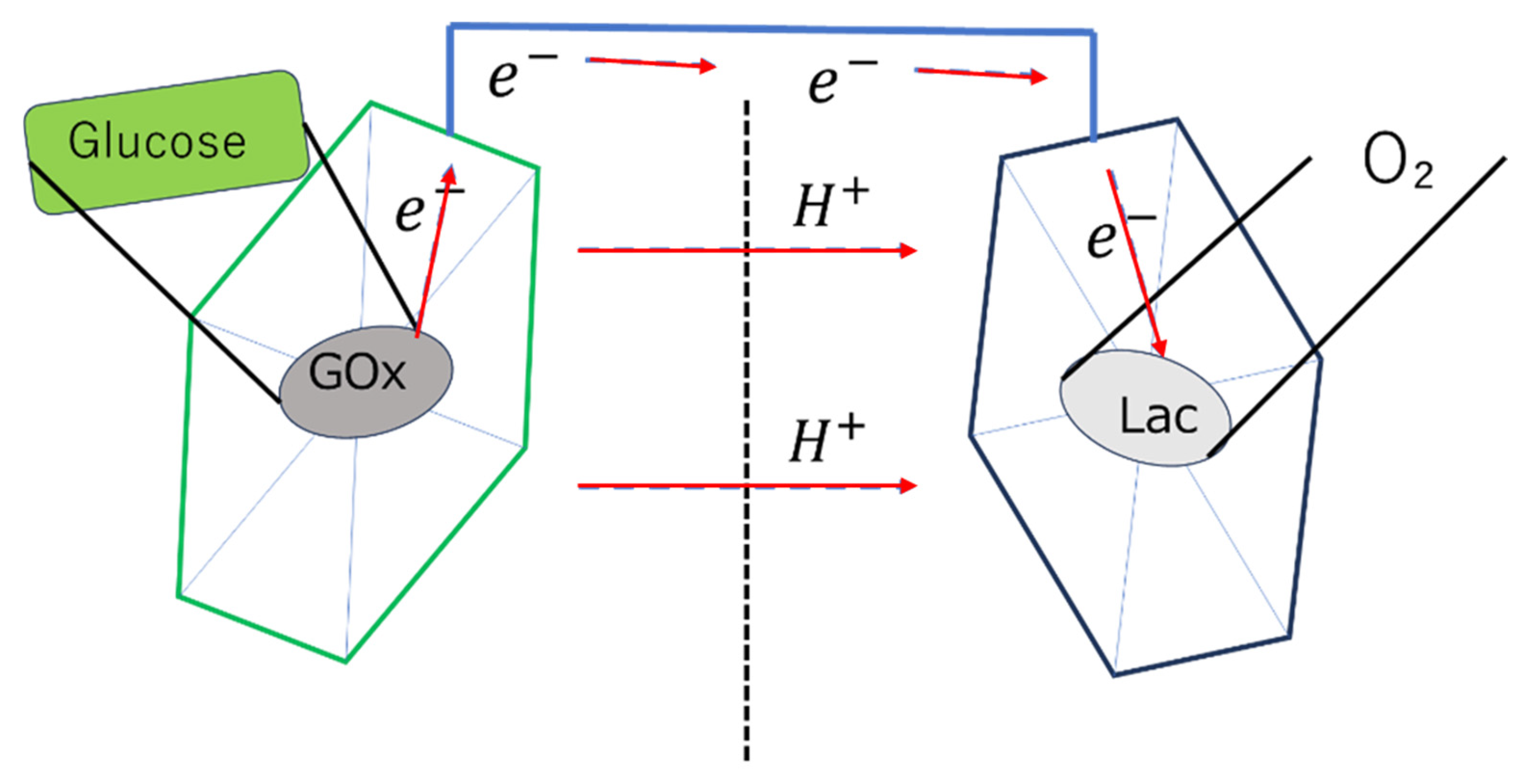

| Fuel Cell Types | Fuel | Oxidant | Cell Voltage (V) | Maximum Current Density (mA/cm2) | Maximum Power Density (μW/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial | Glucose | Air | 0.52 | - | 0.0494 |
| Enzymatic | Methanol | Air | 0.65 | 50 | 8.5 |
| Enzymatic | Glucose | Oxygen | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.021 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Glucose | [Fe(CN)6]3− | 0.45 | 0.016 | 2.3 × 10−6 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Glucose | [Fe(CN)6]3− | 0.488 | 0.03 | 4.01 × 10−4 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Lactate | [Fe(CN)6]3− | - | 0.013 | 1.5 × 10−4 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Acetate | Oxygen | 0.619 | 0.14 | 0.012 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Ethanol | Air | 0.34 | 0.053 | 5.0 × 10−3 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Acetate | Air | 0.4 | 0.45 | 25 × 10−3 |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Glucose | Oxygen | 0.55 | 0.065 | - |
| Microfluidic/ microbial | Glucose | Oxygen | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.11 |
| Battery Type | Type of Catalysts | OCV (V) | Power Density (μW/cm2) | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBFC | GDH, Dp, VK3 | 0.8 | 530 | NA |
| EBFC | GDH, Dp, VK3 | 0.55 | 32 | >18 h |
| Microbial BFC | ADH, PMG | 0.34 | 53 ± 9.1 | NA |
| Microbial BFC | S, cerevisiae, MB | 0.488 | 401.2 | >60 m |
| EBFC | S, cerevisiae, MB | 0.475 | 364.1 | >60 m |
| EBFC | ADH | 0.61–0.82 | 1000–2040 | >450 days |
| Microbial BFC | S, oneidensis MR-1 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 160 h |
| Microbial BFC | S, cerevisiae, MB | 0.3–0.5 | 2.3 | 40 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawaguchi, T.; Ito, S.; Nakane, D.; Akitsu, T. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Biofuel Cells. Biosensors 2025, 15, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090627
Kawaguchi T, Ito S, Nakane D, Akitsu T. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Biofuel Cells. Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090627
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawaguchi, Takahiro, Shota Ito, Daisuke Nakane, and Takashiro Akitsu. 2025. "Recent Advances in Microfluidic Biofuel Cells" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090627
APA StyleKawaguchi, T., Ito, S., Nakane, D., & Akitsu, T. (2025). Recent Advances in Microfluidic Biofuel Cells. Biosensors, 15(9), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090627






