From Biomarkers to Biosensors: Modern Approaches for the Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
Molecular Mechanism of MMPs
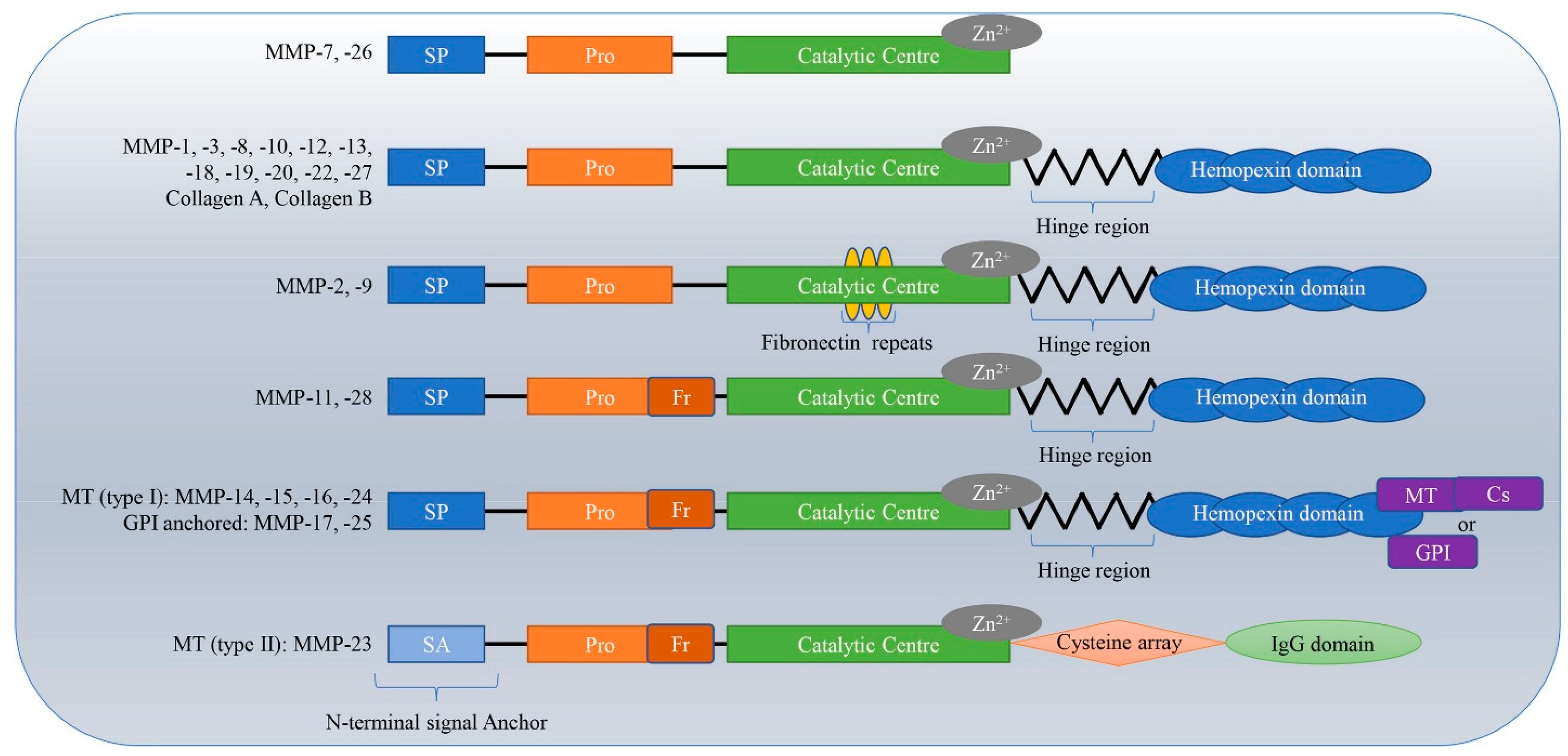
2. Types of MMP
2.1. Matrix Metalloproteinases-1 (MMP-1)
2.2. Matrix Metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2)
2.3. Matrix Metalloproteinases-3 (MMP-3)
2.4. Matrix Metalloproteinases-7 (MMP-7)
2.5. Matrix Metalloproteinases-8 (MMP-8)
2.6. Matrix Metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9)
2.7. Matrix Metalloproteinases-14 (MMP-14)
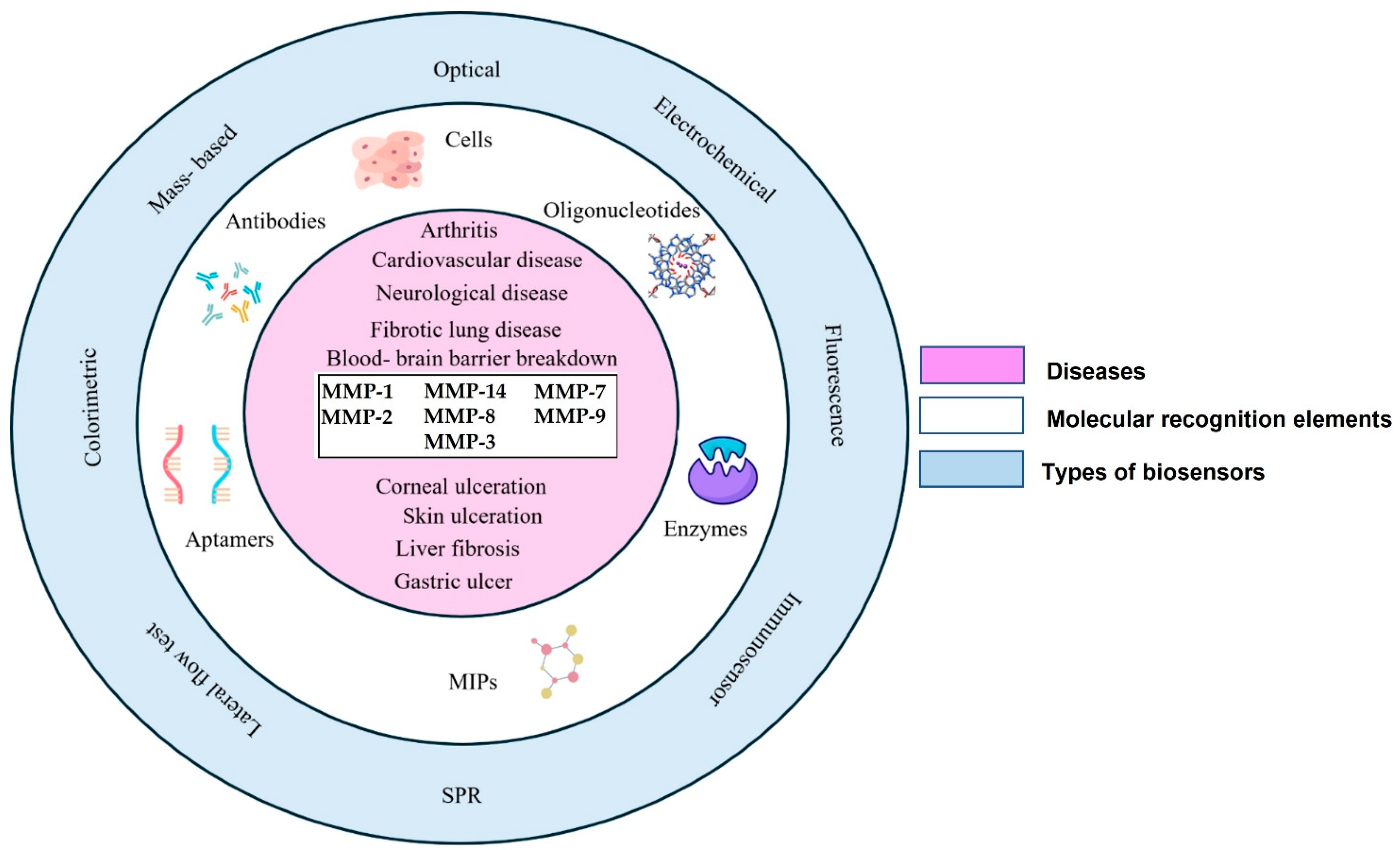
3. Detection of MMPs Using Various Biosensing Platforms
3.1. Biosensors for Matrix Metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2)
3.2. Biosensors for Matrix Metalloproteinases-3 (MMP-3)
3.3. Biosensors for Matrix Metalloproteinases-7 (MMP-7)
3.4. Biosensors for Matrix Metalloproteinases-8 (MMP-8)
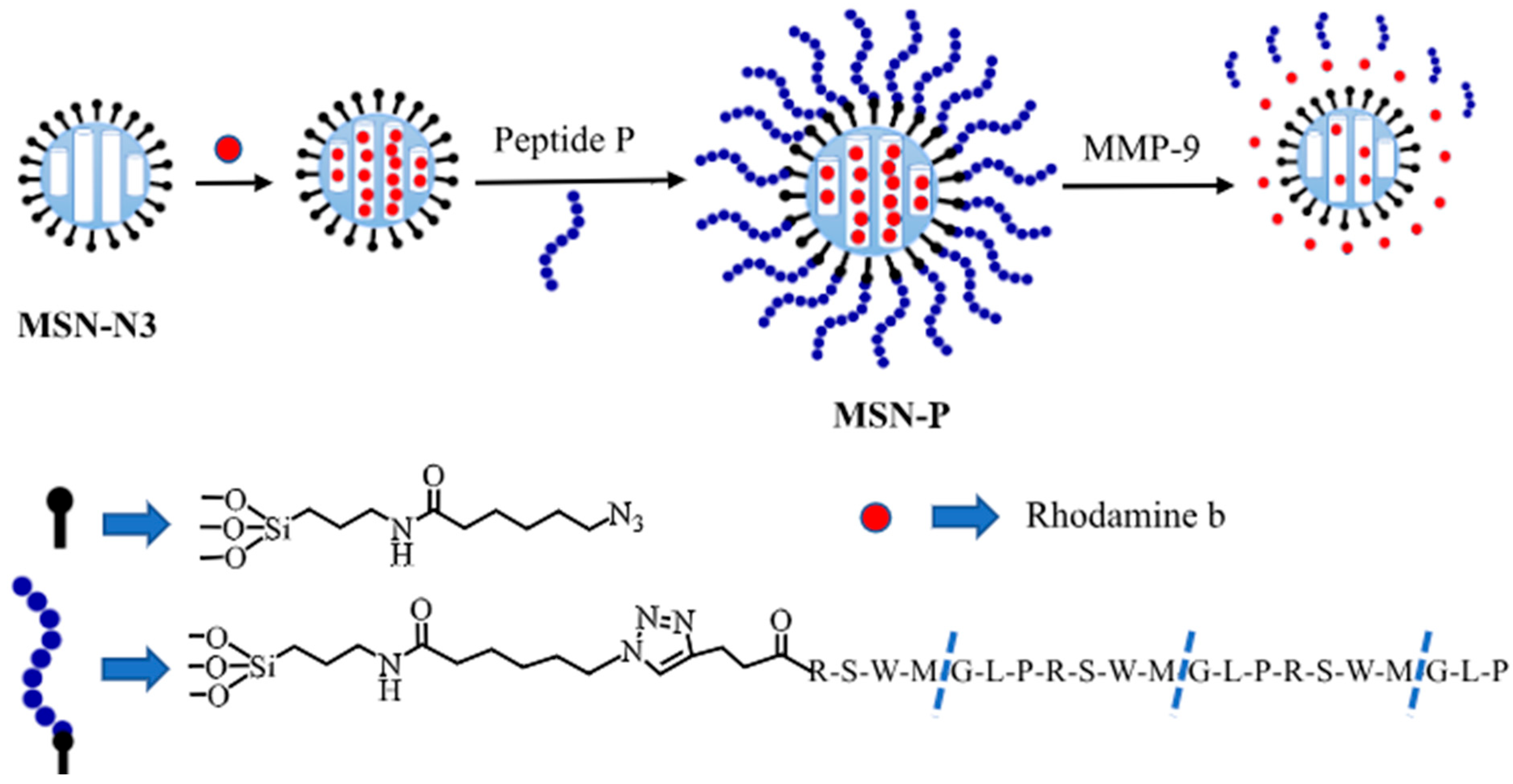
3.5. Biosensors for Matrix Metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9)
3.6. Biosensors for Matrix Metalloproteinases-14 (MMP-14)
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
5. Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amzat, J.; Razum, O. Medical Sociology in Africa; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, GX, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Napiórkowska-Baran, K.; Schmidt, O.; Szymczak, B.; Lubański, J.; Doligalska, A.; Bartuzi, Z. Molecular Linkage between Immune System Disorders and Atherosclerosis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 8780–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Biomarkers and Risk Assessment: Concepts and Principles; Environmental Health Criteria 155, International Programme on Chemical Safety; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993.
- Hatcher, H.; Stankeviciute, S.; Learn, C.; Qu, A.X. Regulatory, Translational, and Operational Considerations for the Incorporation of Biomarkers in Drug Development. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2025, 59, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H. Zinc Metalloproteinases in Health and Disease; Hooper, N.M., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nagase, H.; Visse, R.; Murphy, G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browner, M.F.; Smith, W.W.; Castelhano, A.L. Crystal structures of matrilysin-inhibitor complexes. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 6602–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Libert, C. Is there new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 904–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Bischoff, R. Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids 2010, 41, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Mustafa, A.; Yerzhan, A.; Merzhakupova, D.; Yerlan, P.; Orakov, A.N.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Miao, L. Nuclear matrix metalloproteinases: Functions resemble the evolution from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Moreau, C.S.; Cockrell, G.; Simpson, P.; Goel, R.; North, P.; Fowlkes, J.L.; Bunn, R.C. Physiological matrix metalloproteinase concentrations in serum during childhood and adolescence, using Luminex® Multiplex technology. cclm 2005, 43, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, L.; Kang, Q.; Chan, K.I.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Tan, W. The immunomodulatory role of matrix metalloproteinases in colitis-associated cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1093990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Sánchez, L.M.; Overall, C.M.; López-Otín, C. Human and mouse proteases: A comparative genomic approach. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Brick, P.; O’HAre, M.; Skarzynski, T.; Lloyd, L.; Curry, V.; Clark, I.; Bigg, H.; Hazleman, B.; Cawston, T.; et al. Structure of full-length porcine synovial collagenase reveals a C-terminal domain containing a calcium-linked, four-bladed β-propeller. Structure 1995, 3, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCawley, L.J.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases: They’re not just for matrix anymore! Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, M.P.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (MMP-1, MMP-13) genes in arthritis: Integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2002, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkola, J.; Vihinen, P.; Vuoristo, M.-S.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.; KähÄrI, V.-M.; PyrhönEn, S. High serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 are associated with rapid progression in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5158–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mandal, M.; Chakraborti, T.; Mandal, A.; Chakraborti, S. Isolation of MMP-2 from MMP-2/TIMP-2 complex: Characterization of the complex and the free enzyme in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle plasma membrane. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2004, 1674, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.; Trudgill, P.W. Purification and Properties of Cyclopentanone Oxygenase of Pseudomonas NCIB 9872. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 63, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Hayashi, M.; Tamita, T.; Nomura, Y.; Kojima, N.; Mitani, A.; Takeda, T.; Hitaka, K.; Kato, Y.; Kamitani, M.; et al. Discovery of Aryloxyphenyl–Heptapeptide Hybrids as Potent and Selective Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8493–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, J.L.; Akers, K.T.; Weingarten, H.; Grant, G.A.; McCourt, D.W.; Eisen, A.Z. Cleavage specificity of human skin type IV collagenase (gelatinase). Identification of cleavage sites in type I gelatin, with confirmation using synthetic peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 20409–20413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.M.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. The role of matrix metalloproteases and their inhibitors in tumour invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtala, P.; Chow, L.T.; Tryggvason, K. Structure of the human type IV collagenase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 11077–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, T.; Sasaki, T.; Takeda, T.; Okamoto, T.; Mori, C.; Furukawa, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kasuga, A.; Matsuyama, M.; Ozaka, M.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Serial Pancreatic Juice Aspiration Cytologic Examination with Brush Cytology for Pancreatic Ductal Stenosis. Pancreas 2022, 51, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenskiöld, M.; Holmdahl, L.; Falk, P.; Ivarsson, M.-L. Increased plasma MMP-2 protein expression in lymph node-positive patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2004, 20, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, R.E.; Yamamoto, M.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Wang, S.W.; Mohanam, S.; Fuller, G.N.; McCutcheon, I.E.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Nicolson, G.L.; Rao, J.S. Expression and localization of 72 kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-2) in human malignant gliomas in vivo. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1996, 14, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudel, D.; Fradet, Y.; Meyer, F.; Harel, F.; Têtu, B. Membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase, matrix metalloproteinase 2, and tissue inhibitor of matrix proteinase 2 in prostate cancer: Identification of patients with poor prognosis by immunohistochemistry. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périgny, M.; Bairati, I.; Harvey, I.; Beauchemin, M.; Harel, F.; Plante, M.; Têtu, B. Role of Immunohistochemical Overexpression of Matrix Metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-11 in the Prognosis of Death by Ovarian Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 129, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Lotan, D.; Baig, M.; Carralero, R.; Wood, W.; Hendrix, M.; Lotan, R. Inhibition by retinoic acid of type-IV collagenolysis and invasion through reconstituted basement-membrane by metastatic rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, M.; Welch, D.; Belloni, P.; Nicolson, G. Degradation of basement-membrane type-IV collagen and lung subendothelial matrix by rat mammary adenocarcinoma cell clones of differing metastatic potentials. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar]
- Turpeenniemi-Hujanen, T.; Thorgeirsson, U.P.; Hart, I.R.; Grant, S.S.; Liotta, L.A. Expression of collagenase IV (basement membrane collagenase) activity in murine tumor cell hybrids that differ in metastatic potential. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1985, 75, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcova, M.; Šimko, F. Multiplex biomarker approach to cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijnen, H.R. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Cellular Fibrinolytic Activity. Biochemistry 2002, 67, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-M.; Hwang, O. Role of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2010, 116, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingleton, B. Chapter 159—Matrix Metallopeptidase-10/Stromelysin 2. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Rawlings, N.D., Salvesen, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Kuchiiwa, S.; Oiso, S.; Futagawa, T.; Masuda, S.; Takeda, Y.; Yamada, K. Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-3 in the dorsal root ganglion of rats with paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Ye, Y.; Yin, Y.; Sang, P.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Wan, W.; Li, R.; Bai, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Association of matrix metalloprotease 1, 3, and 12 polymorphisms with rheumatic heart disease in a Chinese Han population. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Han, L.-Y.; Huang, X.-D.; Guan, C.-H.; Mao, X.-L.; Ye, Z.-S. Impact of 5A/6A polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase-3 on recurrent atherosclerotic ischemic stroke in Chinese. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Proteinases and Matrix Degradation. In Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology: Volume 1–2, 9th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.L.; Ouellette, A.J.; Satchell, D.P.; Ayabe, T.; LópEz-Boado, Y.S.; Stratman, J.L.; Hultgren, S.J.; Matrisian, L.M.; Parks, W.C. Regulation of intestinal alpha-defensin activation by the metalloproteinase matrilysin in innate host defense. Science 1999, 286, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, K.F.; van Till, J.O.; Boermeester, M.A.; de Reuver, P.R.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Kate, F.J.T.; Busch, O.R.; van Gulik, T.M.; Gouma, D.J.; et al. Evaluation of Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 in Plasma and Pancreatic Juice as a Biomarker for Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Nakano, J.; Ishikawa, S.; Yokomise, H.; Ueno, M.; Kadota, K.; Urushihara, M.; Huang, C.-L. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) correlates with tumor proliferation, and a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2007, 58, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, J.; Nadal, C.; Garcia-Albeniz, X.; Gallego, R.; Carcereny, E.; Almendro, V.; Mármol, M.; Gallardo, E.; Augé, J.M.; Longarón, R.; et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels identifies poor prognosis advanced colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, J.J. Interstitial Collagenases. In Matrix Metalloproteinases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Yan, H.; Huang, L. Salivary matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8 as a biomarker for periodontitis: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, A.; Hagström, J.; Mustonen, H.; Kokkola, A.; Tervahartiala, T.; Sorsa, T.; Böckelman, C.; Haglund, C. Serum MMP-8 and TIMP-1 as prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 2018, 40, 1010428318799266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckelman, C.; Beilmann-Lehtonen, I.; Kaprio, T.; Koskensalo, S.; Tervahartiala, T.; Mustonen, H.; Stenman, U.-H.; Sorsa, T.; Haglund, C. Serum MMP-8 and TIMP-1 predict prognosis in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandooren, J.; van den Steen, P.E.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 222–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Gong, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. High matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression induces angiogenesis and basement membrane degradation in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats after cerebral infarction. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, A.R.; Mackay, A.R. Gelatinase B/MMP-9 in Tumour Pathogenesis and Progression. Cancers 2014, 6, 240–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamenkovic, I. Extracellular matrix remodelling: The role of matrix metalloproteinases. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 448–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhard, S.M.; Razak, K.; Ethell, I.M. A delicate balance: Role of MMP-9 in brain development and pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backstrom, J.R.; Lim, G.P.; Cullen, M.J.; Tökés, Z.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) Is Synthesized in Neurons of the Human Hippocampus and Is Capable of Degrading the Amyloid-β Peptide (1–40). J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 7910–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FernánDez, C.A.; Yan, L.; Louis, G.; Yang, J.; Kutok, J.L.; Moses, M.A. The Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Complex Plays a Role in Breast Tumor Growth and Is Present in the Urine of Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5390–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranuncolo, S.M.; Armanasco, E.; Cresta, C.; Joffe, E.B.d.K.; Puricelli, L. Plasma MMP-9 (92 kDa-MMP) activity is useful in the follow-up and in the assessment of prognosis in breast cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Cui, Y.-Z.; Song, G.-H.; Zong, M.-J.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, J.-X. Proteomic analysis identifies MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG as overexpressed proteins in pancreatic juice from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Ediger, D.; Budak, F.; Karadağ, M.; Oral, H.B.; Uzaslan, E.; Ege, E.; Gözü, R.O. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) Elevated in Serum but not in Bronchial Lavage Fluid in Patients with Lung Cancer. Tumori J. 2006, 92, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, C.; Cobos, E.; Lox, C. Determination of the serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in patients with either advanced small-cell lung cancer or non-small-cell lung cancer prior to treatment. Respir. Med. 2004, 98, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, E.; Wasowicz, W.; Gromadzinska, J.; Reszka, E. Functional polymorphisms in the matrix metalloproteinase genes and their association with bladder cancer risk and recurrence: A mini-review. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.B.; Lee, W.Y.; Song, S.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Yun, S.H.; Chun, H.-K. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity is associated with poor prognosis in T3-T4 node-negative colorectal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengyel, E.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Konik, E.; Späthe, K.; Härting, K.; Fenn, A.; Berger, U.; Fridman, R.; Schmitt, M.; Prechtel, D.; et al. Expression of Latent Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) Predicts Survival in Advanced Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2001, 82, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Louis, G.; Loughlin, K.R.; Wiederschain, D.; Kilroy, S.M.; Lamb, C.C.; Zurakowski, D.; Moses, M.A. Tumor-Specific Urinary Matrix Metalloproteinase Fingerprinting: Identification of High Molecular Weight Urinary Matrix Metalloproteinase Species. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6610–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.S.; Yamamoto, M.; Mohaman, S.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Fuller, G.N.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Rao, V.H.; Liotta, L.A.; Nicolson, G.L.; Sawaya, R.E. Expression and localization of 92 kDa type IV collagenase/gelatinase B (MMP-9) in human gliomas. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1996, 14, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, S.; Gilmer, J.F.; Medina, C.; Oral, H.B. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Update. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 964131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wei, S.; Zhai, Z.; Wu, Y.; Sun, F.; et al. Rapid and quantitative detection of tear MMP-9 for dry eye patients using a novel silicon nanowire-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 214, 114498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Takino, T.; Okada, Y.; Cao, J.; Shinagawa, A.; Yamamoto, E.; Seiki, M. A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature 1994, 370, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekita, T.; Itoh, Y.; Yana, I.; Ohno, H.; Seiki, M. Cytoplasmic tail–dependent internalization of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is important for its invasion-promoting activity. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez, B.G.; Matías-Román, S.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Arroyo, A.G. Caveolae Are a Novel Pathway for Membrane-Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase Traffic in Human Endothelial Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; Peng, Z.; Yin, J.; Yang, Z.; Shang, J. Expression of MMP-14 and prognosis in digestive system carcinoma: A meta-analysis and databases validation. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
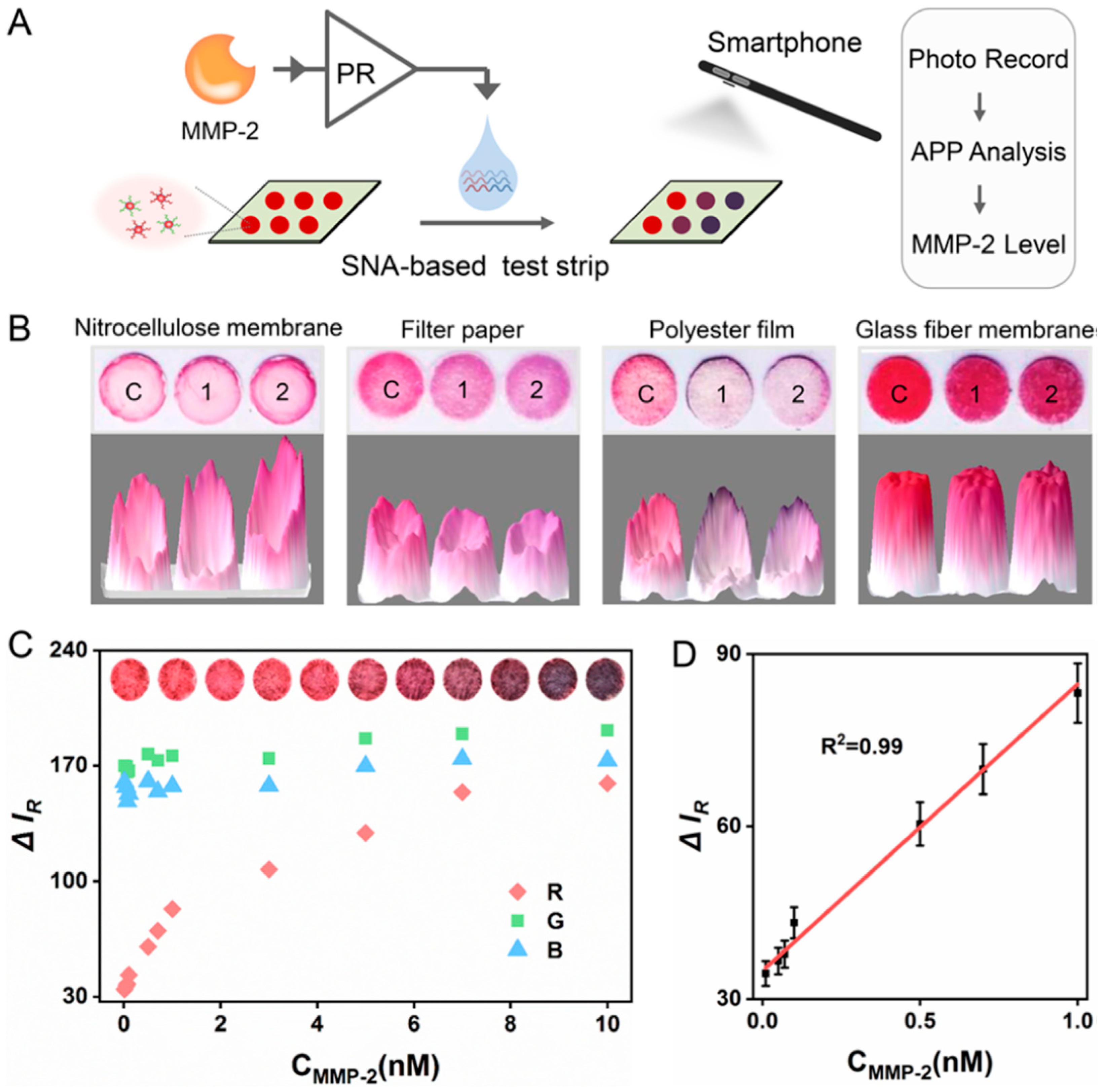
- Liu, F.; Chen, R.; Song, W.; Li, L.; Lei, C.; Nie, Z. Modular Combination of Proteolysis-Responsive Transcription and Spherical Nucleic Acids for Smartphone-Based Colorimetric Detection of Protease Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
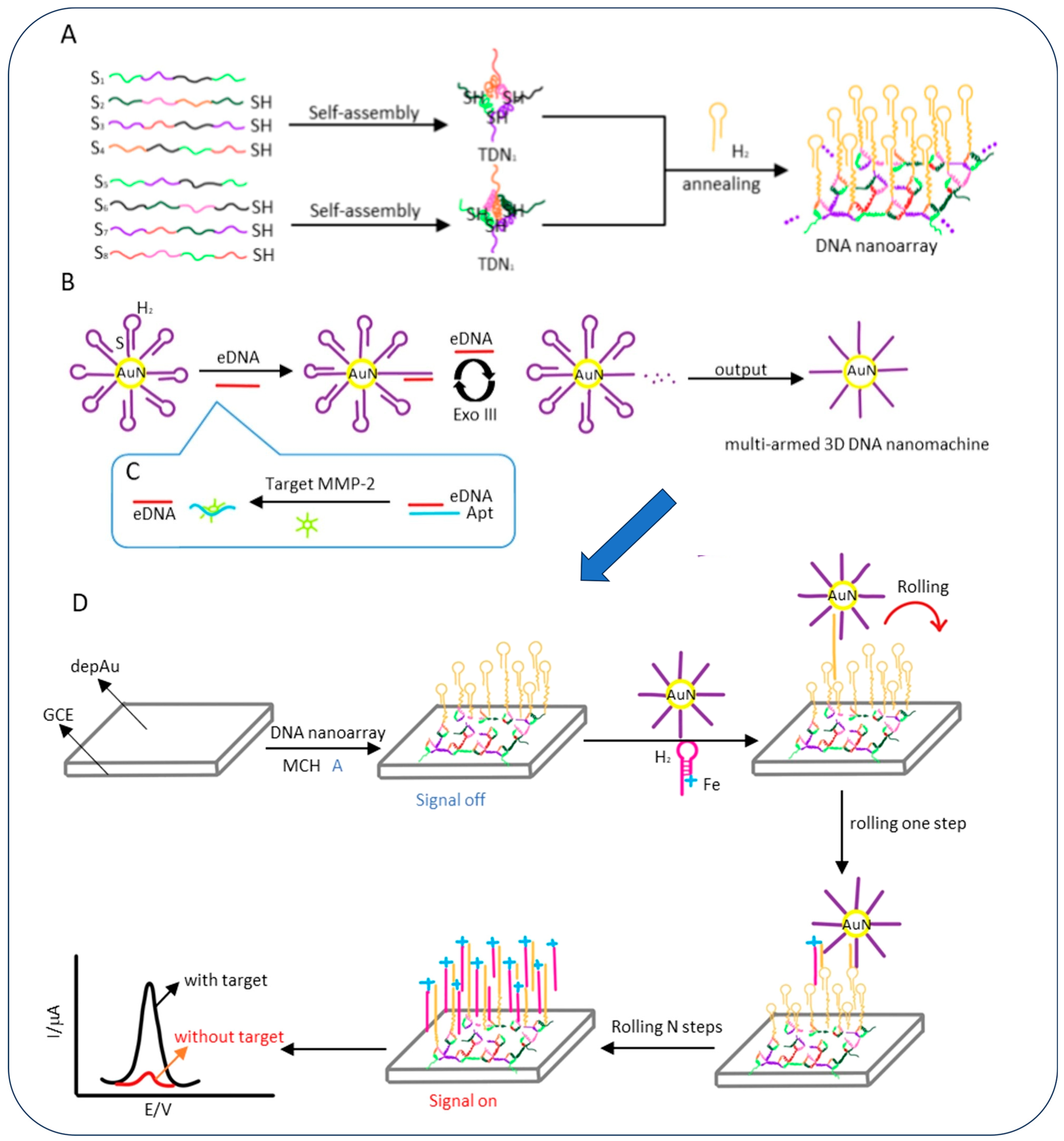
- Yao, T.; Chen, J.; Kong, L.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. Efficient Three-Dimensional DNA Nanomachine Guided by a Robust Tetrahedral DNA Nanoarray Structure for the Rapid and Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinase 2. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13211–13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.-J.; Lou, X.; Xia, F.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Tunning Intermolecular Interaction of Peptide-Conjugated AIEgen in Nano-Confined Space for Quantitative Detection of Tumor Marker Secreted from Cells. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16257–16263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; He, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ju, H. In Situ Protease Secretion Visualization and Metastatic Lymph Nodes Imaging via a Cell Membrane-Anchored Upconversion Nanoprobe. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7258–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Copper nanoclusters electrochemiluminescence with tunable near-infrared emission wavelength for ultrasensitive detection of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 238, 115580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarić, S.; Schobesberger, S.; Velicki, L.; Milovančev, A.; Nikolić, S.; Ertl, P.; Bobrinetskiy, I.; Knežević, N.Ž. Direct electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide thin film for aptamer-based selective and highly sensitive detection of matrix metalloproteinase 2. Talanta 2024, 274, 126079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; An, Z.; Li, X.; Shan, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based photoelectrochemical biosensing system with graphitic carbon nitride/gold nanoparticles modified electrodes for matrix metalloproteinase-2 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Huang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yang, F.; Hao, N. A novel isothermal amplification strategy for rapid and sensitive detection of Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 using a bipedal DNA walker in anti-aging research. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 397, 134650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Guo, L.; Che, X.; Yuan, Z.; Sang, S. A Novel Magnetoelastic Biosensor With Flexible TbDyFe Film as Sensing Materials for Osteoarthritis Marker MMP-3 Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19129–19135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Feng, J.; Xiong, Q.; Han, H.; Ma, Z. A novel electrochemical sensor based on HER overpotential of Ag-Cu bimetallic catalyst. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
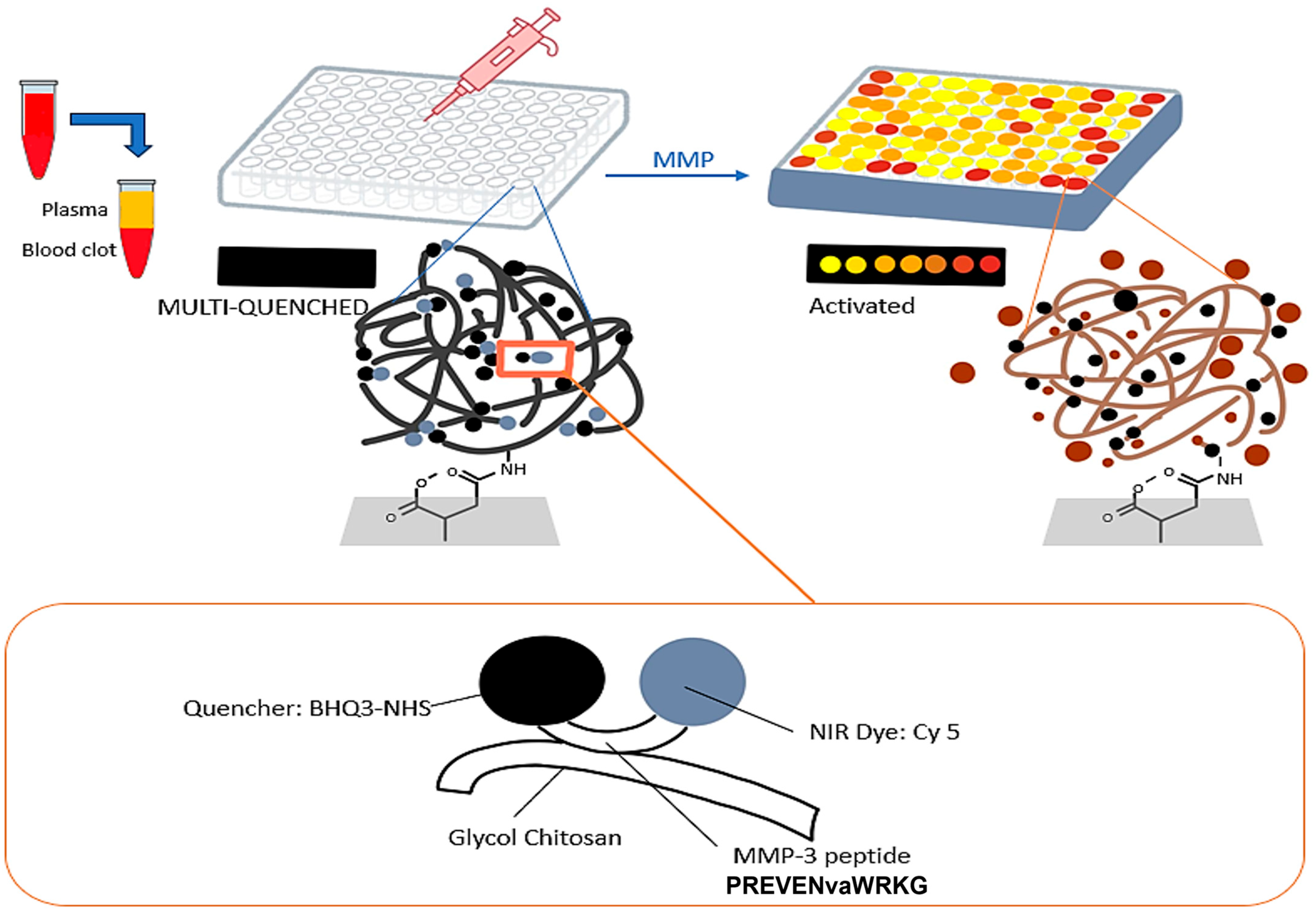
- Lee, R.; Choi, S.-J.; Moon, K.C.; Park, J.W.; Kim, K.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Youn, I. Fluorogenic Probe for Detecting Active Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) in Plasma and Peripheral Blood Neutrophils to Indicate the Severity of Rheumatoid Arthritis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on peptide modified MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for matrix metalloproteinase-7 activity detection in vitro and in vivo. Analyst 2022, 147, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
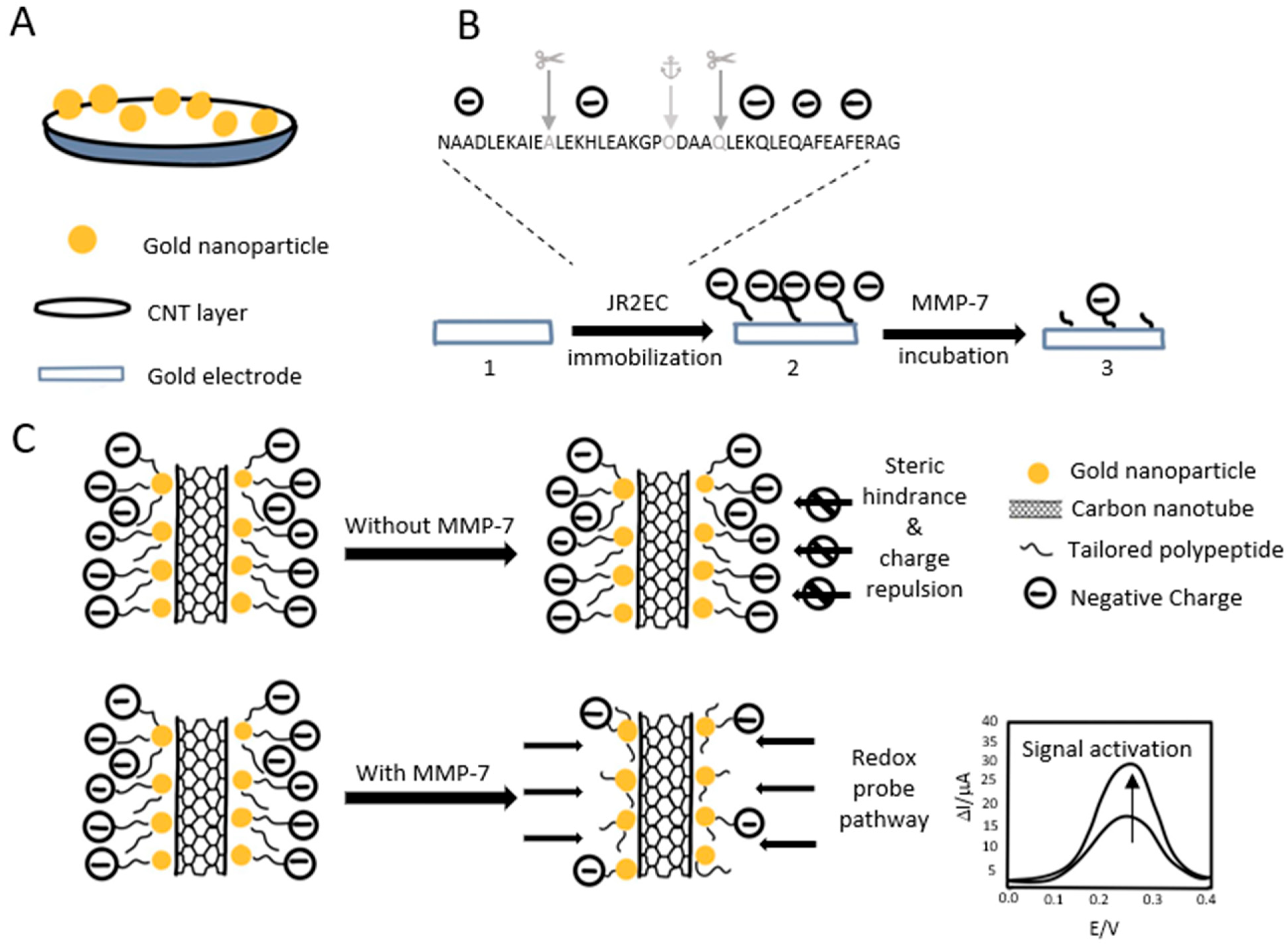
- Palomar, Q.; Xu, X.; Selegård, R.; Aili, D.; Zhang, Z. Peptide decorated gold nanoparticle/carbon nanotube electrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive detection of matrix metalloproteinase-7. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piloto, A.M.L.; Ribeiro, D.S.M.; Santos, J.L.M.; Sales, G. Development of a Sensitive Ratiometric Imprinted Hydrogel for the Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7) Biomarker. ACS Appl. Opt. Mater. 2023, 2, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C.-Y. Construction of a sensitive protease sensor with DNA-peptide conjugates for single-molecule detection of multiple matrix metalloproteinases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, B.; Ma, Z.; Han, H. Antifouling and sensitive biosensor based on multifunctional peptide and urease@ZIFs for metal matrix protease-7. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 364, 131844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
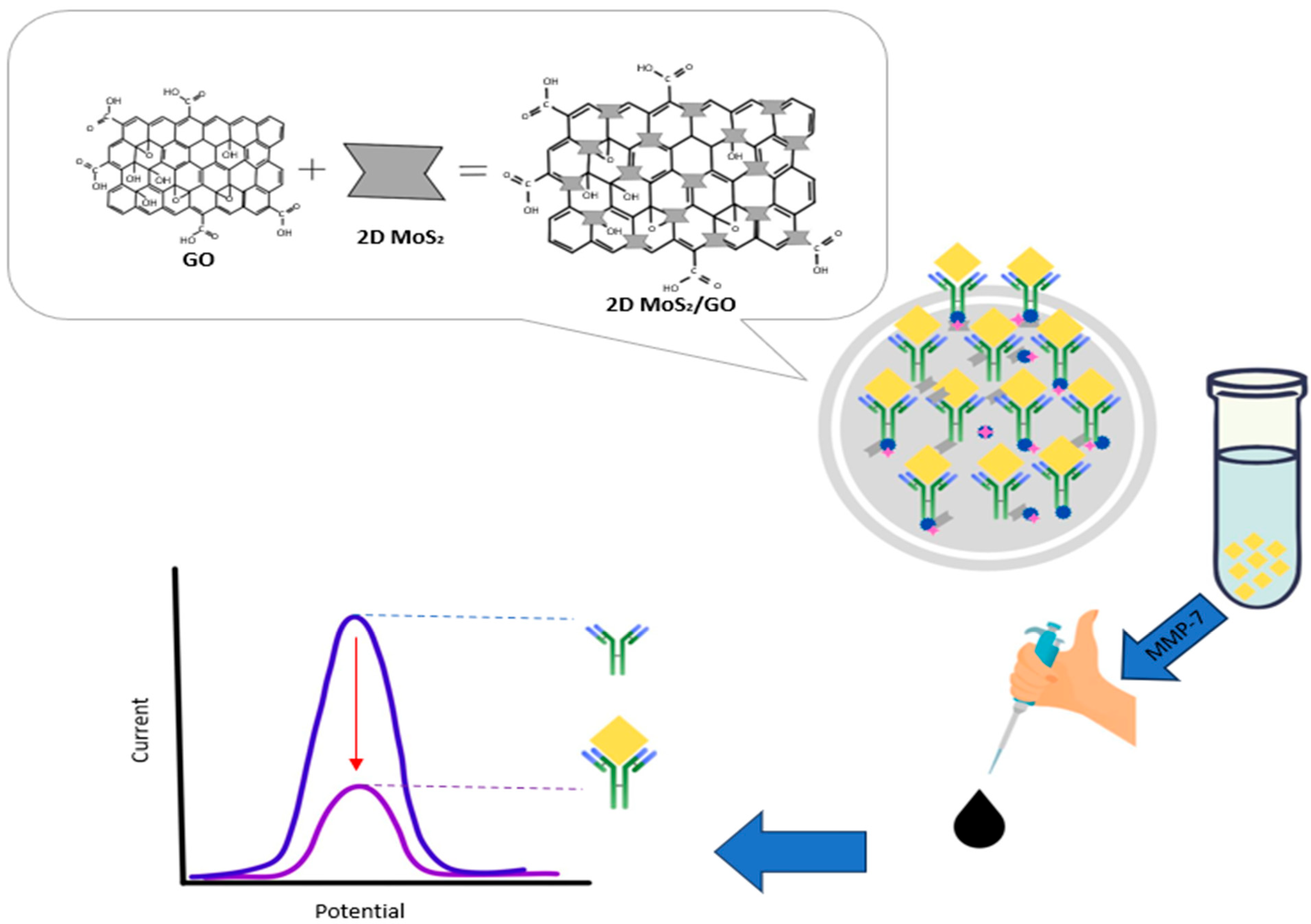
- Yaiwong, P.; Semakul, N.; Bamrungsap, S.; Jakmunee, J.; Ounnunkad, K. Electrochemical detection of matrix metalloproteinase-7 using an immunoassay on a methylene blue/2D MoS2/graphene oxide electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 142, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, L.; Bencivenga, D.; Annunziata, M.; Arcadio, F.; Borriello, A.; Della Ragione, F.; Formisano, A.; Piccirillo, A.; Zeni, L.; Cennamo, N. An optical fiber-based point-of-care test for periodontal MMP-8 detection: A proof of concept. J. Dent. 2023, 134, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; You, M.; Li, Z.; Cao, L.; Xu, F.; Li, F.; Li, A. Upconversion nanoparticles-based lateral flow immunoassay for point-of-care diagnosis of periodontitis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, V.Ö.; Emingil, G.; Umeizudike, K.; Tervahartiala, T.; Gieselmann, D.-R.; Maier, K.; Köse, T.; Sorsa, T.; Alassiri, S. Evaluation of active matrix metalloproteinase-8 (aMMP-8) chair-side test as a diagnostic biomarker in the staging of periodontal diseases. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 124, 104955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
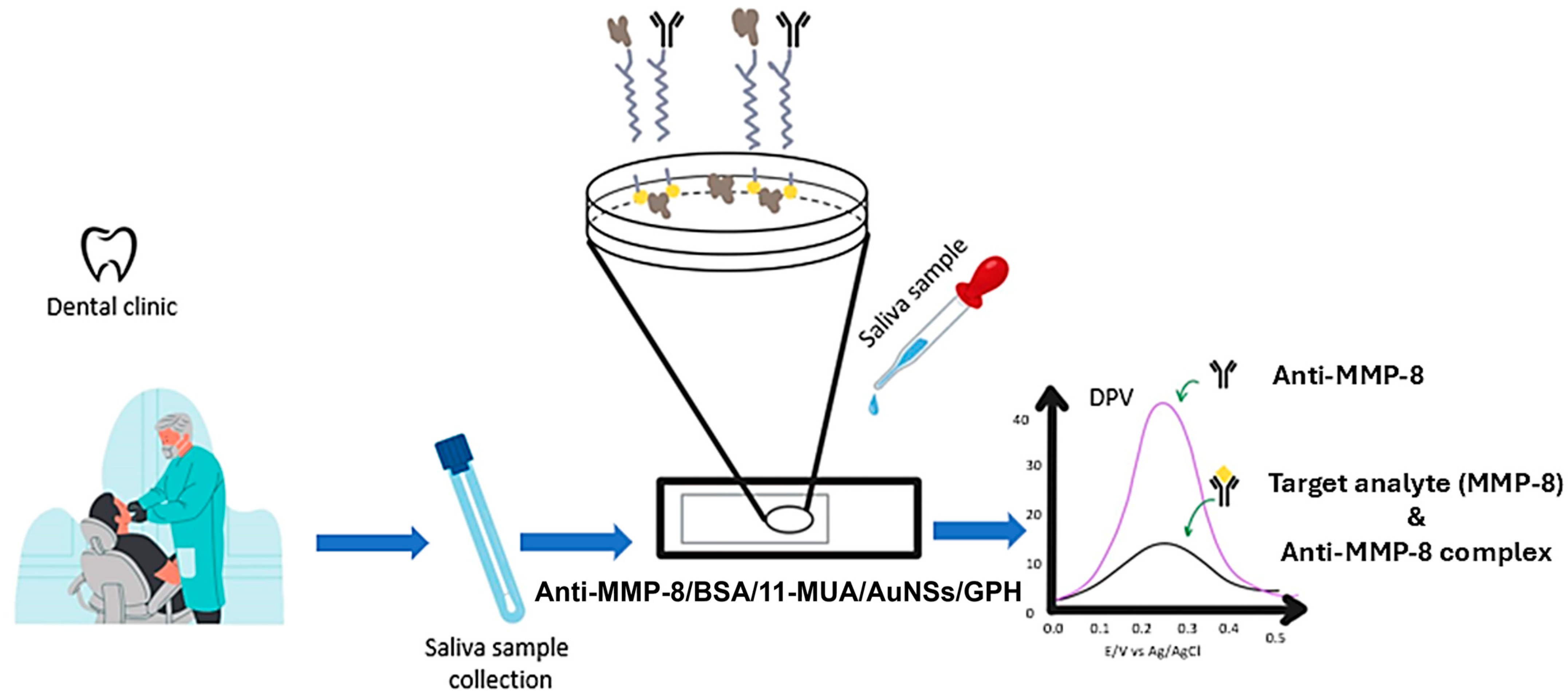
- Tortolini, C.; Gigli, V.; Angeloni, A.; Tasca, F.; Thanh, N.T.; Antiochia, R. A disposable immunosensor for the detection of salivary MMP-8 as biomarker of periodontitis. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 156, 108590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, M.; Arcadio, F.; Borriello, A.; Bencivenga, D.; Piccirillo, A.; Stampone, E.; Zeni, L.; Cennamo, N.; Della Ragione, F.; Guida, L. A novel surface plasmon resonance-based optical biosensor for point-of-care detection of periodontal biomarkers. In Proceedings of the 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences, Virtual, 27 October–10 November 2023; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, B.; Karpíšek, M.; Baumgartner, D.; Klein, V.; Bostanci, N.; Paust, N.; Früh, S.M.; Zengerle, R.; Mitsakakis, K. One-step, wash-free, bead-based immunoassay employing bound-free phase detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1153, 338280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-D.; Lee, C.-S.; Cho, H.-J.; Jeon, S.; Choi, Y.-N.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, H.J.; Vu, H.; Jeong, H.-J.; et al. Diagnostic ability of salivary matrix metalloproteinase-9 lateral flow test point-of-care test for periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Viennois, E.; Fang, J.; Merlin, D.; Iyer, S.S. Toward Point-of-Care Diagnostics to Monitor MMP-9 and TNF-α Levels in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 6582–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, E.; Abdekhodaie, M.J.; Mousavi, S.A.; Taghipour, F. ZnO nanoparticle/nanorod-based label-free electrochemical immunoassay for rapid detection of MMP-9 biomarker. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 164, 107772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.N.; Rotake, D.; Kumar, S.; Kaur, I.; Singh, S.G. Tear-based MMP-9 detection: A rapid antigen test for ocular inflammatory disorders using vanadium disulfide nanowires assisted chemi-resistive biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1263, 341281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, J.; Lim, H.Q.; Attia, A.B.E.; Raziq, R.; Leavesley, D.I.; Upton, Z.; Dinish, U.; Olivo, M. Novel cellulose fibre-based flexible plasmonic membrane for point-of-care sers biomarker detection in chronic wound healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5869–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainu, S.; Parameswaran, S.; Krishnakumar, S.; Singh, N. Dual-sensitive fluorescent nanoprobes for detection of matrix metalloproteinases and low pH in a 3D tumor microenvironment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 5388–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, B.; ben Hassine, A.; Valverde, A.; Serafín, V.; Montero-Calle, A.; Raouafi, N.; Camps, J.; Arenas, M.; Barderas, R.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; et al. Electrochemical immunoplatform to assist in the diagnosis and classification of breast cancer through the determination of matrix-metalloproteinase-9. Talanta 2021, 225, 122054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yu, A.M.; Kubelick, K.P.; Emelianov, S.Y. Gold nanoparticles conjugated with DNA aptamer for photoacoustic detection of human matrix metalloproteinase-9. Photoacoustics 2021, 25, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Qiao, X.; Xu, L.; Sun, L.; Ma, F. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor for assay of matrix metalloproteinase-14 and protein-expressing cancer cells via inhibitory peptides-based sandwich assay. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.H.; Zulfiqar, S.; Abbas, M.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Han, W.; He, D.D.; Liu, N.; Hayat, A.; Akhtar, M.H.; et al. Copper-pyridine-2,4,6-tricarboxylate metal organic framework nanoparticles based opto-electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 679, 132618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.; Chande, C.; Kulkarni, S.; Morel, J.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Shimizu, E.; Cugini, C.; Basuray, S.; Kumar, V. Point-of-care diagnostic devices for periodontitis—Current trends and urgent need. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asumadu, P.; Guo, Z.; Qi, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Kong, D.; Ye, H.; Fu, C.; Wang, Z. Programmable DNA aptamer logic gates: From structural design to integrated systems for intelligent nanoscale biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, Y.M.; Mohamed, A.S.; El-Sayed, W.M. Recent developments and future directions in point-of-care next-generation CRISPR-based rapid diagnosis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Rios, P.; Hernández, M.; Garrido, M.; Tervahartiala, T.; Leppilahti, J.; Kuula, H.; Heikkinen, A.M.; Mäntylä, P.; Rathnayake, N.; Nwhator, S.; et al. Oral fluid matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8 as a diagnostic tool in chronic periodontitis. Met. Med. 2016, 3, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabed, S.; Belal, A.; Shamayleh, A. Sustainability of Medical Equipment in the Healthcare Industry: An Overview. In Proceedings of the 2019 Fifth International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), Tripoli, Lebanon, 17–19 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Patel, K.D. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) And MMP-9 in Pulmonary Pathology. Exp. Lung Res. 2005, 31, 599–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Biomarkers | Materials Used for Sensing Application | Method of Detection | LOD | Detection Range | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-2 | Gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) | Colorimetric | 3.3 pM | 0.01–10 nM |
|
| [71] |
| Cu- pyridine-2,4,6-tricarboxylate (PTC) metal–organic framework (MOF) | Electrochemical Detection | 0.8 ng/mL | 1 ng/mL to 175 ng/mL |
|
| [103] | |
| Multi-armed three-dimensional (3D) DNA nanomachine | Electrochemical Detection | 11.4 fg/mL | - |
| Instrumentation required reducing portability | [72] | |
| Intensified aggregation-induced emission (AIE) by slippery lubricant-infused porous substrates (SLIPS) | Fluorescence | 3.7 ng/mL | 1.6 μg/mL–50 ng/mL | Potential for high-throughput | Fluorescence signal prone to photobleaching | [73] | |
| Cell membrane-anchored radiometric up conversion nanoprobe (UCNPs-Cy3/Pep-QSY7/Ab) | Fluorescence | 0.51 ng/mL | 1 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | Provides a universal platform for the study of proteases and contributes for tumor assessment | Potential damage to cells due to exposure to short-wavelength (high energy) excitation light | [74] | |
| Methionine (Met)/N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) templated copper nanoclusters (Met/NAC-Cu NCs) | Electrochemiluminescence | 1.65 fg/mL | - |
| Limited structural clarity due to smaller size of copper nanoclusters. | [75] | |
| Electrochemically reduced graphene oxide (ERGO) thin film-modified gold electrodes | Aptasensor | 3.32 pg/mL | 10 pg/mL–10 ng/mL |
|
| [76] | |
| Graphitic carbon nitride/gold nanoparticles loaded on indium tin oxide electrodes | Photoelectrochemical | 0.48 pg/mL | 1 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL |
| Limited excitation performance with blue and green LEDs; system works best only with purple (400 nm) meaning limited compatibility with other photoactive materials that don’t absorb well at 400 nm. | [77] | |
| PEI@Ru(bpy)32+-Ti3C2 @AuNPs-modified electrode | Electrochemiluminescence | 80.6 fM | - | Highly sensitive and specific | Potential high cost associated with modified electrodes | [78] | |
| MMP-3 | TbDyFe/polystyrene-poly (ethylene-butylene)-polystyrene block copolymer (SEBS) film | Magnetoelastic Biosensor | 0.76 ng/mL | 0.76 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL | Wide range of detection and highly sensitive | Higher doping led to an adverse effect of mechanical | [79] |
| Ag-Cu bimetallic hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) catalyst | Electrochemical detection | 2.02 fg/mL | 0.001 ng/mL to 100 ng/mL | Exceptional consistency and dependable performance. | Requires precise optimization of multiple parameters | [79] | |
| Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-activated plasma | Fluorescence | 1.9 nM | 0.07–30 nM | Ease of use and highly sensitive | Cross reactivity and low natural levels | [81] | |
| Magnetoelastic (ME) chip immobilized with MMP-3 antibody and an electromagnetic coil | Magnetoelastic | 30.7 ng/mL | 30.7 ng/mL to 2000 ng/mL | Wide linear range and verified consistent performance. | Possible magnetic field interference due to reliance on magnetostrictive materials | [79] | |
| MMP-7 | MnFe2O4 nanoparticles (NPs) modified fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) labelled MMP-7 substrate | Fluorescence | 0.1 nM | 0.1 nM to 15 nM | Low sustained toxicity | Fluorescence signal prone to photobleaching | [82] |
| Nanocomposite of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and electrogenerated gold nanoparticles (GNPs) electrode | Electrochemical detection | 6 pg/mL | 0.01 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL | User-friendly and cost-effective | Limited long-term stability | [83] | |
| Imprinted ratiometric hydrogels: (generated from blue emitting carbon dots (CDs), molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and assembled around red emitting quantum dots (QDs) | Fluorescence | 4.11 pg/mL | 14.9 pg/mL to 1.92 ng/mL | Increased selectivity and higher sensitivity |
| [84] | |
| Fluorophore-quencher labelled DNA-peptide conjugates with specific protease cleavage sites | Fluorescence | 1.71 pM | Simultaneous monitoring of several MMP targets in complex samples | Complexity of method | [85] | ||
| Multifunctional peptide with urease@zeolite imidazole frameworks (urease@ZIFs) using sodium alginate-graphene oxide-Pb2+ (SA-GO-Pb2+) gel | Electrochemical detection | 24.32 fg/mL | 0.1 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL | Excellent stability and successful clinical application | Poor conductivity of biocomponents | [86] | |
| 2D MoS2/GO nanocomposite deposited screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) | Immunosensor | 0.007 ng/mL | 0.010 ng/mL to 75 ng/mL | High specificity and stability | Preparation of materials is complex involving complex surface chemistry | [87] | |
| MMP-8 | Anti-MMP-y antibody functionalized surface plasmon resonance (SPR) plastic optical fiber (POF) | SPR | 9.9 ng/mL | 22.9 ng/mL to 489.9 ng/mL |
| Clinical validation needed | [88] |
| Disk-like lateral flow immunoassay strip (LFIS) using green core-shell upconversion nanoparticles (G-UCNPs) as luminescent probe | Immunosensor | 5.455 ng/mL | - | Multiplexing capability and simplified operating procedure | Larger sample size is needed | [89] | |
| DipStick/Antibody | Immunosensor | 83.9%(specificity) | - |
|
| [90] | |
| Anti-MMP-8 functionalized graphene (GPH) screen-printed electrode (SPE) functionalized by gold-nanospheres (AuNSs | Voltametric immunosensor | 1 ng/mL | 2.5 ng/mL to 300 ng/mL |
|
| [91] | |
| Immunosensor | 0.24 ng/mL | 0.47 ng/mL to 30 ng/mL |
|
| [93] | ||
| MMP-9 | Capturing magnetic beads and fluorescent detection beads agents | Immunosensor | 0.38 ng/mL | 0.47 ng/mLto 30 ng/mL |
|
| [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chinnappan, R.; Ramachandran, L.; Uttam, I.; Citartan, M.; Ballal, N.V.; Mani, N.K. From Biomarkers to Biosensors: Modern Approaches for the Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs). Biosensors 2025, 15, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090603
Chinnappan R, Ramachandran L, Uttam I, Citartan M, Ballal NV, Mani NK. From Biomarkers to Biosensors: Modern Approaches for the Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs). Biosensors. 2025; 15(9):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090603
Chicago/Turabian StyleChinnappan, Raja, Lohit Ramachandran, Isha Uttam, Marimuthu Citartan, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal, and Naresh Kumar Mani. 2025. "From Biomarkers to Biosensors: Modern Approaches for the Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs)" Biosensors 15, no. 9: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090603
APA StyleChinnappan, R., Ramachandran, L., Uttam, I., Citartan, M., Ballal, N. V., & Mani, N. K. (2025). From Biomarkers to Biosensors: Modern Approaches for the Detection of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs). Biosensors, 15(9), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15090603







