Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Lidocaine Hydrochloride via Dissolvable Microneedles (LH-DMNs) for Rapid Local Anesthesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Blank Microneedle Patches and LH-DMNs
2.2.1. Selection of Microneedle Matrix Materials
2.2.2. Preparation of Blank and LH-Loaded Microneedle Patches
2.3. In Vitro Testing of Blank Microneedle Patches and LH-DMNs
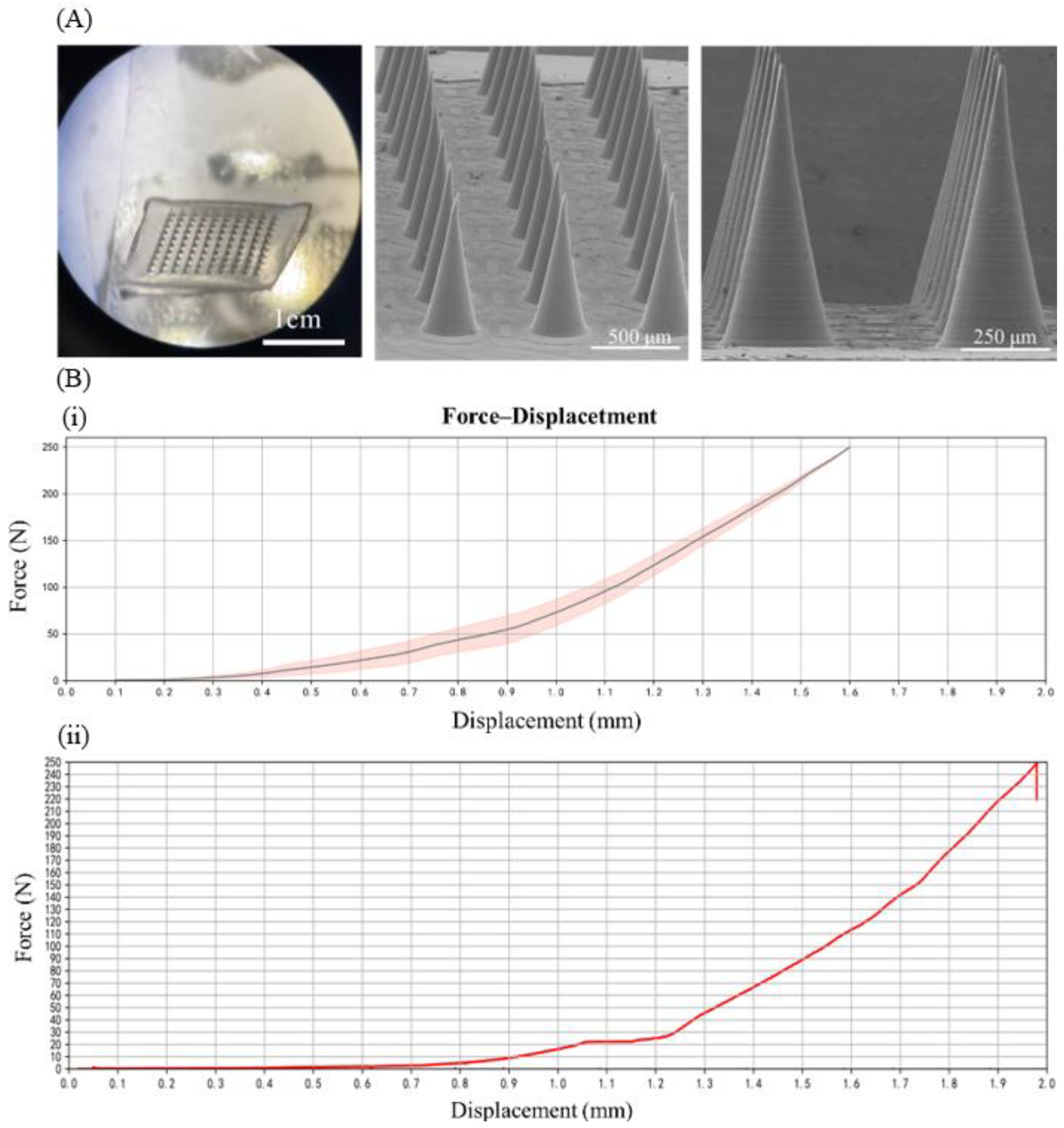
2.3.1. Morphological Characterization of LH-DMNs
2.3.2. Mechanical Performance Testing
2.3.3. HPLC Analysis of LH-DMNs
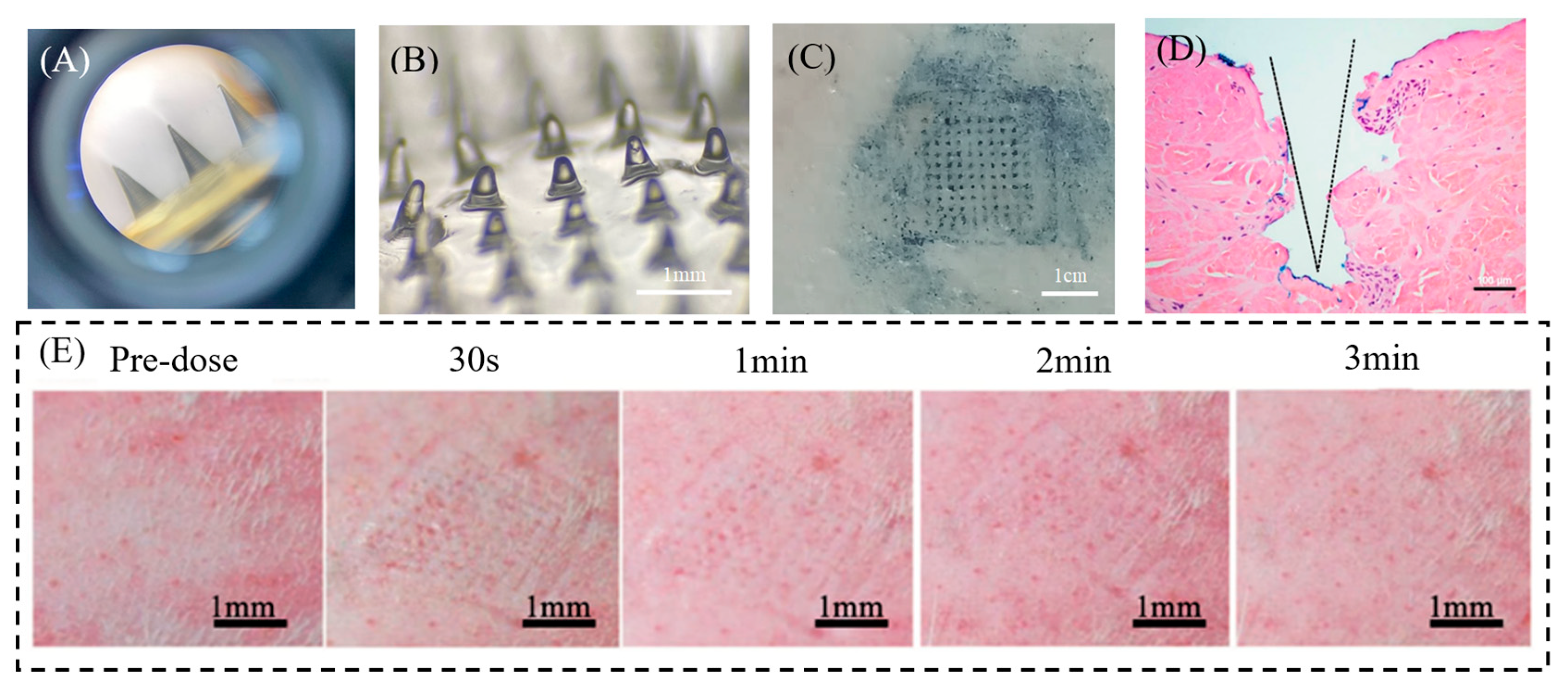
2.3.4. In Vitro Skin Penetration Test of LH-DMNs
2.4. In Vivo Testing of LH-DMNs
2.4.1. Skin Penetration Test
2.4.2. Skin Irritation Test in Rats
2.4.3. Analgesic Test (Hot Plate Method)
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Blank Microneedle Patches and LH-DMNs
3.2. Mechanical Performance Testing of Blank Microneedle Patches and LH-DMNs
3.3. HPLC Analysis of LH-DMNs
3.4. Evaluation of LH-DMN Penetration
3.5. In Vivo Anesthetic Evaluation of LH-DMNs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LH-DMNs | Lidocaine hydrochloride-loaded dissolvable microneedles |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| LH-GEL | Lidocaine hydrochloride gel |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
References
- Lancet, T. Malaysia’s Pain Free Programme. Lancet 2019, 393, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, E.; Okumura, Y.; Lindblad, M.; Nilsson, M.; Rouvelas, I.; Grip, J.; Klevebro, F. 72198—Pain Management after Minimally Invasive Gastrectomy: Do We Need Epidural Analgesia? BJS 2024, 111, znae175.008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Schindler, E. Regional Anesthesia as Part of Enhanced Recovery Strategies in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2023, 36, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.-K.; Wiesmann, T.; Dinges, H.-C. Measures to Prolong Duration of Sensory Block after Regional Anaesthesia. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2023, 36, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yu, X.; Yi, X.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Hao, Y.; Wang, W. Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.D.; Merry, S.P.; Boswell, C.L. Skin Biopsy Techniques. Prim. Care 2022, 49, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunyaratavej, S.; Rujitharanawong, C.; Kasemsarn, P.; Boonchai, W.; Muanprasert, C.; Matthapan, L.; Leeyaphan, C. Skin Scrapings versus Standardized Skin Surface Biopsy to Detect Demodex Mites in Patients with Facial Erythema of Uncertain Cause—A Comparative Study. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Maio, M. MD CodesTM: A Methodological Approach to Facial Aesthetic Treatment with Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Fillers. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 690–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdiales-Gálvez, F.; Martín-Sánchez, S.; Maíz-Jiménez, M.; Castellano-Miralla, A.; Lionetti-Leone, L. Concomitant Use of Hyaluronic Acid and Laser in Facial Rejuvenation. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votta-Velis, E.G.; Piegeler, T.; Minshall, R.D.; Aguirre, J.; Beck-Schimmer, B.; Schwartz, D.E.; Borgeat, A. Regional Anaesthesia and Cancer Metastases: The Implication of Local Anaesthetics. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2013, 57, 1211–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamaraux-Tran, T.-N.; Piegeler, T. The Amide Local Anesthetic Lidocaine in Cancer Surgery—Potential Antimetastatic Effects and Preservation of Immune Cell Function? A Narrative Review. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.J.; Jacob, S.E. Lidocaine. J. Dermatol. Nurses Assoc. 2016, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie, S.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Davaran, S.; Kouhsoltani, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Nanoethosomes for Dermal Delivery of Lidocaine. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yang, Y.; Yao, M.; Yang, L.; Ao, L.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Tan, Y.; Xing, W.; et al. Combination of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem (Stromal) Cell Transplantation with IFN-γ Treatment Synergistically Improves the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1298–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Kang, G.; Jang, M.; Um, D.J.; Shin, J.; Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Jung, H.; Ahn, H.; Gong, S.; et al. Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadon, D.; Permana, A.D.; Courtenay, A.J.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Tekko, I.A.; McAlister, E.; Anjani, Q.K.; Utomo, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Development, Evaluation, and Pharmacokinetic Assessment of Polymeric Microarray Patches for Transdermal Delivery of Vancomycin Hydrochloride. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3353–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchione, R.; Coppola, S.; Esposito, E.; Casale, C.; Vespini, V.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P.; Netti, P.A. Electro-Drawn Drug-Loaded Biodegradable Polymer Microneedles as a Viable Route to Hypodermic Injection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3515–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Chawla, R.; Goyal, M. Topical Anesthesia. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 31, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Nuki, T.; Tsunoda, T.; Ito, T.; Mori, R.; Akashi, T.; Oyama, Y.; Ikeda, M. Effectiveness of Intrabronchial Local Anesthesia with a Spray Catheter and Continuous Oral Suction in Reducing Cough during Bronchoscopy: A Prospective Study. Respir. Investig. 2025, 63, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wang, F. Effects of Dyclonine Mucilage and Compound Lidocaine Cream as Tracheal Catheter Lubricant on Postoperative Pharyngeal Complications After General Anesthesia. Int. J. Surg. 2025, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, F.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Kovács, A.; Ambrus, R.; Jójárt-Laczkovich, O.; Szalai, B.; Pavlić, B.; Simon, P.; Törteli, L.; Berkó, S. The Role of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents in a Hydrogel Formulation Containing Lidocaine. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-M.; Lee, C.; Lahiji, S.F.; Jung, U.-W.; Chung, G.; Jung, H. Dissolving Microneedles for Rapid and Painless Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzelanny, C.; Mess, C.; Schneider, S.W.; Huck, V.; Brandner, J.M. Skin Barriers in Dermal Drug Delivery: Which Barriers Have to Be Overcome and How Can We Measure Them? Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; Yu, K.; Yang, F.; Yu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y. Integrating Tacrolimus into Eutectic Oil-Based Microemulsion for Atopic Dermatitis: Simultaneously Enhancing Percutaneous Delivery and Treatment Efficacy with Relieving Side Effects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed Saeed AL-Japairai, K.; Mahmood, S.; Hamed Almurisi, S.; Reddy Venugopal, J.; Rebhi Hilles, A.; Azmana, M.; Raman, S. Current Trends in Polymer Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatale, V.; Vaiphei, K.K.; Jha, S.; Patil, D.; Agrawal, M.; Alexander, A. Overcoming Skin Barriers through Advanced Transdermal Drug Delivery Approaches. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu Li, Q.; Nan Zhang, J.; Zhi Chen, B.; Lei Wang, Q.; Dong Guo, X. A Solid Polymer Microneedle Patch Pretreatment Enhances the Permeation of Drug Molecules into the Skin. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15408–15415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omolu, A.; Bailly, M.; Day, R.M. Assessment of Solid Microneedle Rollers to Enhance Transmembrane Delivery of Doxycycline and Inhibition of MMP Activity. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Lim, Y.Y.; An, J.-H.; Kim, M.N.; Kim, B.J. Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Disk Microneedle Rollers in a Hairless Rat Model. Int. J. Dermatol. 2012, 51, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, X.; Yuan, X.; Wu, S.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Gou, M. Fast Customization of Hollow Microneedle Patches for Insulin Delivery. Int. J. Bioprinting 2022, 8, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartawi, Z.; Blackshields, C.; Faisal, W. Dissolving Microneedles: Applications and Growing Therapeutic Potential. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 186–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo-Martínez, Á.; Mallon, B.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Vora, L.K.; Anjani, Q.K.; Donnelly, R.F. Hollow Microneedles: A Perspective in Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-Array Patches Loaded with Hypoxia-Sensitive Vesicles Provide Fast Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migdadi, E.M.; Courtenay, A.J.; Tekko, I.A.; McCrudden, M.T.; Kearney, M.-C.; McAlister, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Hydrogel-forming microneedles enhance transdermal delivery of metformin hydrochloride. J. Control. Release 2018, 285, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtenay, A.J.; McAlister, E.; McCrudden, M.T.; Vora, L.; Steiner, L.; Levin, G.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Shterman, N.; Kearney, M.-C.; McCarthy, H.O.; et al. Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays as a therapeutic option for transdermal esketamine delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansathien, K.; Suriyaamporn, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Opanasopit, P.; Rangsimawong, W. A Novel Approach for Skin Regeneration by a Potent Bioactive Placental-Loaded Microneedle Patch: Comparative Study of Deer, Goat, and Porcine Placentas. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ji, S.; Huang, Z.; Zang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z. Transdermal Delivery of Colchicine Using Dissolvable Microneedle Arrays for the Treatment of Acute Gout in a Rat Model. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2984–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, H.L.; Bonham, L.; Hughes, C.M.; Donnelly, R.F. Design of a Dissolving Microneedle Platform for Transdermal Delivery of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Cardiovascular Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirobe, S.; Azukizawa, H.; Hanafusa, T.; Matsuo, K.; Quan, Y.-S.; Kamiyama, F.; Katayama, I.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Clinical Study and Stability Assessment of a Novel Transcutaneous Influenza Vaccination Using a Dissolving Microneedle Patch. Biomaterials 2015, 57, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid Alkilani, A.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, W. Inhibit Diffusion of the Small Molecule Drug Lidocaine Hydrochloride in Dissolving Microneedles Based on a Phase Separation Approach. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 100, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhang, B.L.; Chu, H.Q.; Liang, L.; Chen, B.Z.; Zheng, H.; Guo, X.D. A High-Dosage Microneedle for Programmable Lidocaine Delivery and Enhanced Local Long-Lasting Analgesia. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhong, C.; Nie, L.; Shavandi, A.; Yunusov, K.E.; Jiang, G. Fabrication of Lidocaine-Loaded Polymer Dissolving Microneedles for Rapid and Prolonged Local Anesthesia. Biomed. Microdevices 2024, 26, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gan, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G. Recent Advances in Biodegradable and Biocompatible Synthetic Polymers Used in Skin Wound Healing. Materials 2023, 16, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basa, B.; Jakab, G.; Kállai-Szabó, N.; Borbás, B.; Fülöp, V.; Balogh, E.; Antal, I. Evaluation of Biodegradable PVA-Based 3D Printed Carriers during Dissolution. Materials 2021, 14, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.G. Production and Application of Biomaterials Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) as Wound Dressing. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G.S.N.K. Pharmaceutical Assessment of Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): As Excipient from Conventional to Controlled Delivery Systems with a Spotlight on COVID-19 Inhibition. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.R.S.; Tekko, I.A.; Al-Shammari, F.; Ali, A.A.; McCarthy, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Rapidly Dissolving Polymeric Microneedles for Minimally Invasive Intraocular Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 800–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Hong, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Shi, X.; et al. High-Performance Flexible Microneedle Array as a Low-Impedance Surface Biopotential Dry Electrode for Wearable Electrophysiological Recording and Polysomnography. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekizawa, J.; Yasuhara, K.; Suyama, Y.; Yamanaka, S.; Tobe, M.; Nishimura, M. A Simple Method for Screening Assessment of Skin and Eye Irritation. J. Toxicol. Sci. 1994, 19, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarango-Granda, P.; Espinoza, L.C.; Díaz-Garrido, N.; Alvarado, H.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Baldomá, L.; Calpena, A. Effect of Penetration Enhancers and Safety on the Transdermal Delivery of Apremilast in Skin. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzotti, E.M.; Santos, C.V.F.; Rodrigues, H.M.S.L.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Andrade, M.R.; Antoniolli, A.R. Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic Activity and Acute Toxicity of Sida Cordifolia L. (Malva-Branca). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 72, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qiao, L.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; Piccinni-Ash, T.J.; Chen, Z.-F. Molecular and Neural Basis of Pleasant Touch Sensation. Science 2022, 376, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Soto, F.; Wang, C.; Rueda, R.; Shukla, S.; Silva-Lopez, C.; Kupor, D.; McBride, D.A.; Pokorski, J.K.; Nourhani, A.; et al. Built-In Active Microneedle Patch with Enhanced Autonomous Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1905740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzbelger Feldman, D.; Laun, B.B.; Patel, C.; Pande, S.V.; Boddu, S.H.S. A Buffered Local Anesthetic Without Epinephrine: Development, Characterization, and In Vivo Efficacy and Toxicity Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, E.; Tibbits, D.L.; Reilley, T.E.; McSweeney, T.D. Comparison of Effects of Lidocaine Hydrochloride, Buffered Lidocaine, Diphenhydramine, and Normal Saline after Intradermal Injection. J. Clin. Anesth. 2002, 14, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
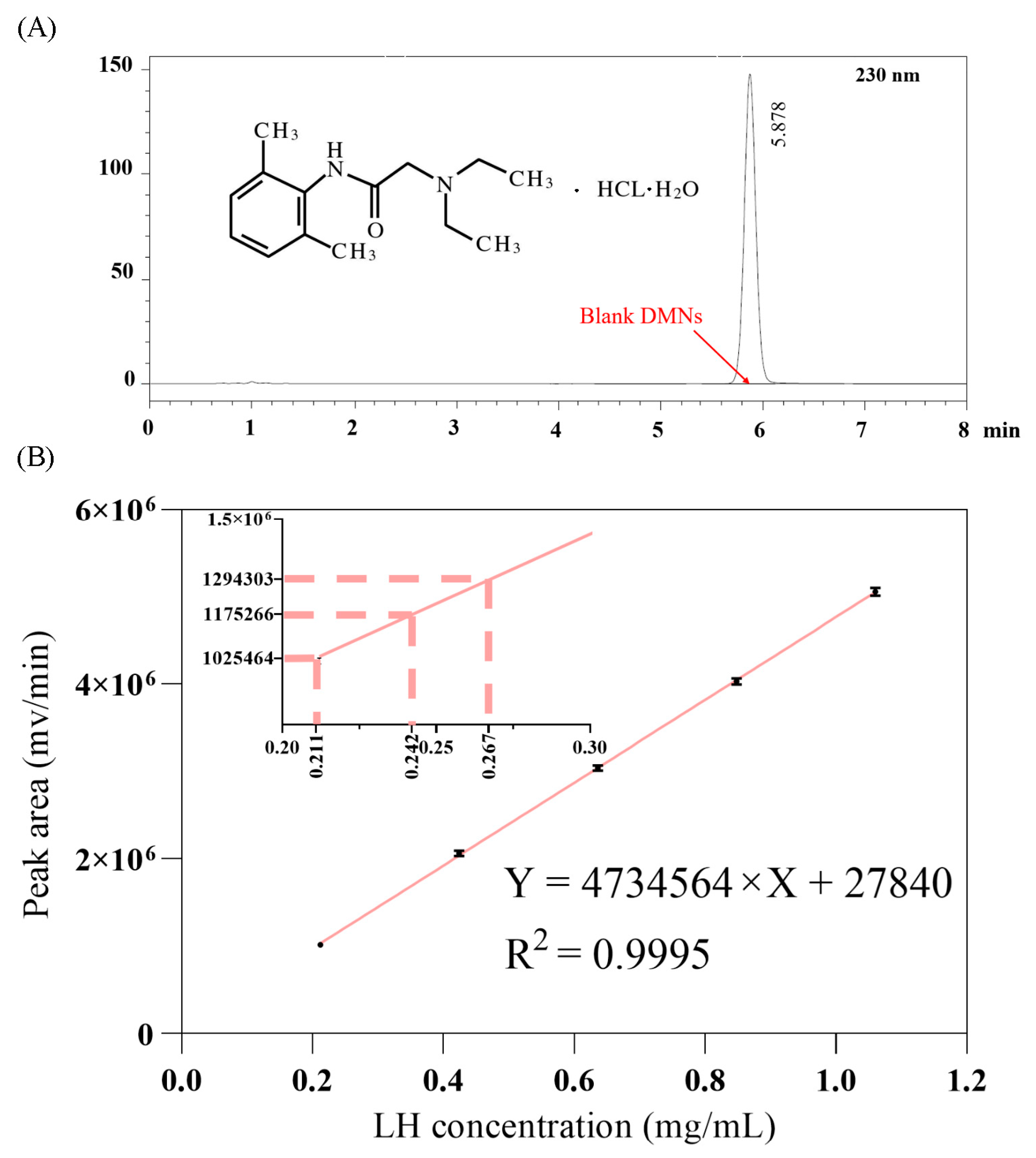

| Sample | Sample Solution Peak Area (mV/min) | Sample Solution Concentration (mg/mL) | Dilution Volume (mL) | Content per Sample (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1,175,266 | 0.24235 | 100 | 24.235 |
| 2 | 1,025,464 | 0.21071 | 100 | 21.071 |
| 3 | 1,294,303 | 0.26749 | 100 | 26.749 |
| Group | Pre-Dose | 5 min | 10 min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 19.78 ± 0.97 | 20 ± 1.58 | 20.56 ± 1.13 |
| LH-DMNs | 20 ± 1.22 | 36.11 ± 1.62 ** | 32 ± 1.41 * |
| LH-GEL | 20 ± 0.5 | 19.89 ± 0.6 | 20.22 ± 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, R.; Feng, S.; Ming, Z. Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Lidocaine Hydrochloride via Dissolvable Microneedles (LH-DMNs) for Rapid Local Anesthesia. Biosensors 2025, 15, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080552
Bian S, Chen J, Chen R, Feng S, Ming Z. Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Lidocaine Hydrochloride via Dissolvable Microneedles (LH-DMNs) for Rapid Local Anesthesia. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080552
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Shengtai, Jie Chen, Ran Chen, Shilun Feng, and Zizhen Ming. 2025. "Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Lidocaine Hydrochloride via Dissolvable Microneedles (LH-DMNs) for Rapid Local Anesthesia" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080552
APA StyleBian, S., Chen, J., Chen, R., Feng, S., & Ming, Z. (2025). Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Lidocaine Hydrochloride via Dissolvable Microneedles (LH-DMNs) for Rapid Local Anesthesia. Biosensors, 15(8), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080552








