High-Resolution Imaging of Morphological Changes Associated with Apoptosis and Necrosis Using Single-Cell Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apoptotic and Necrotic Cell Preparation
2.2. FF-OCT System Description
2.3. FF-OCT-Based 3D Topography
2.4. FF-OCT-Based Interference Reflection Microscopy (IRM) Imaging
3. Results
3.1. FF-OCT Imaging of a Single HeLa Cell Undergoing Apoptosis
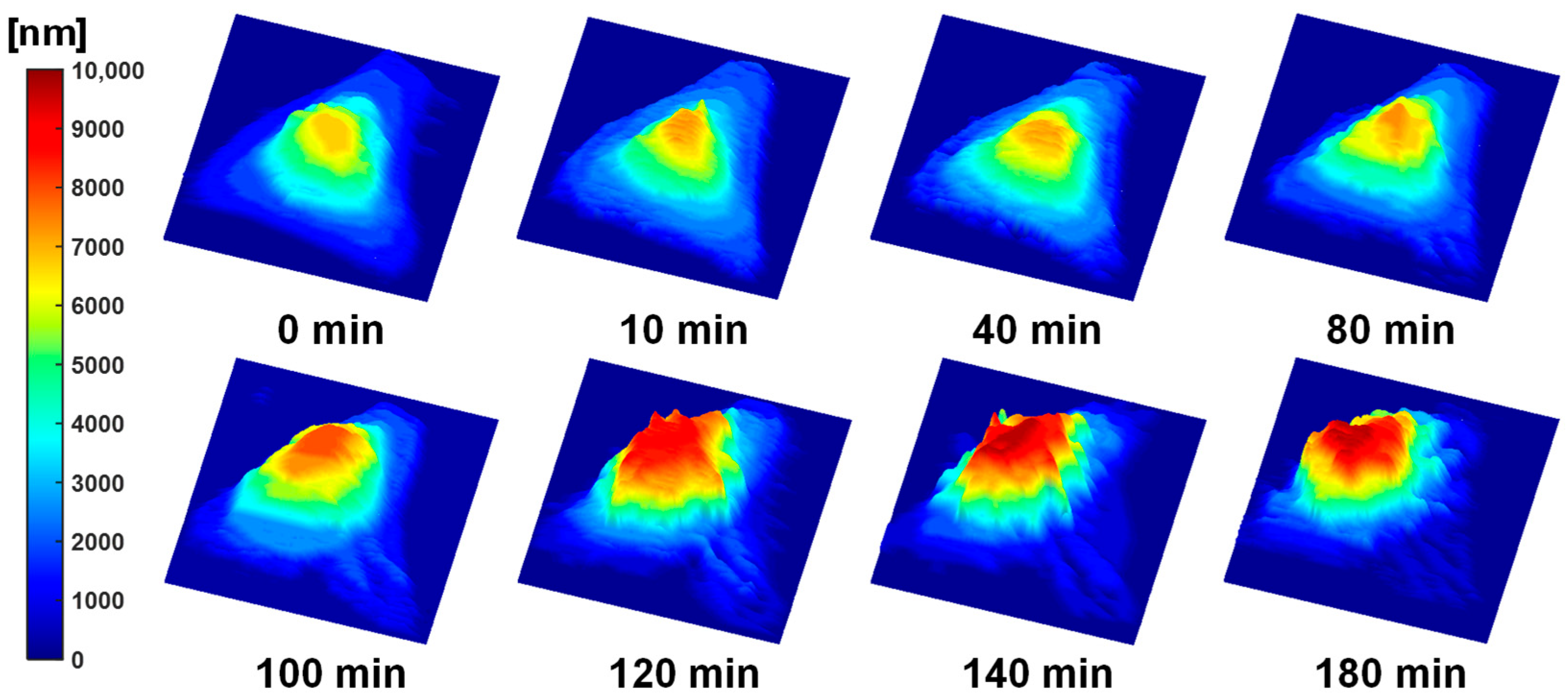
3.2. FF-OCT-Based Topographic Mapping of the Apoptotic HeLa Cell
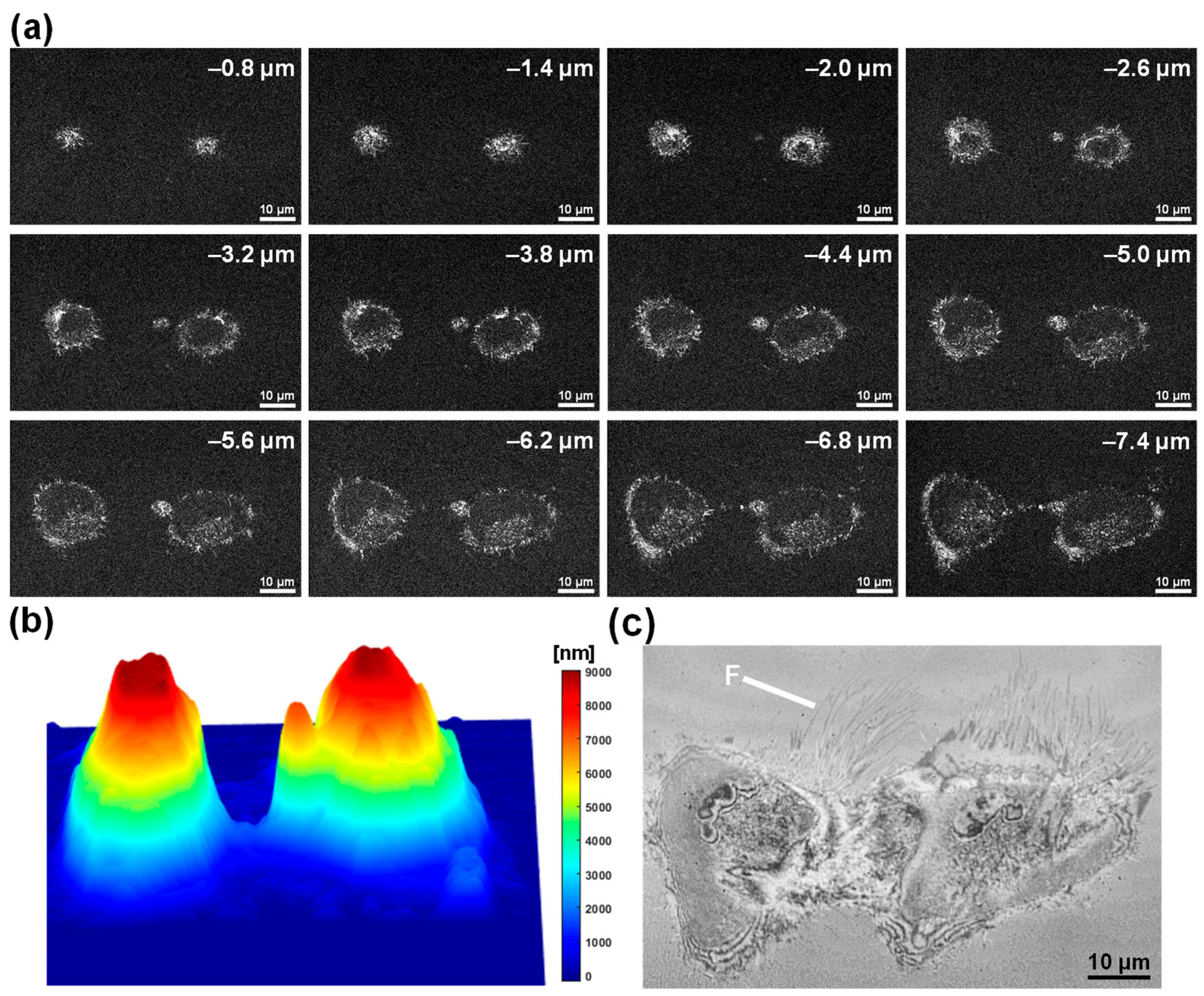
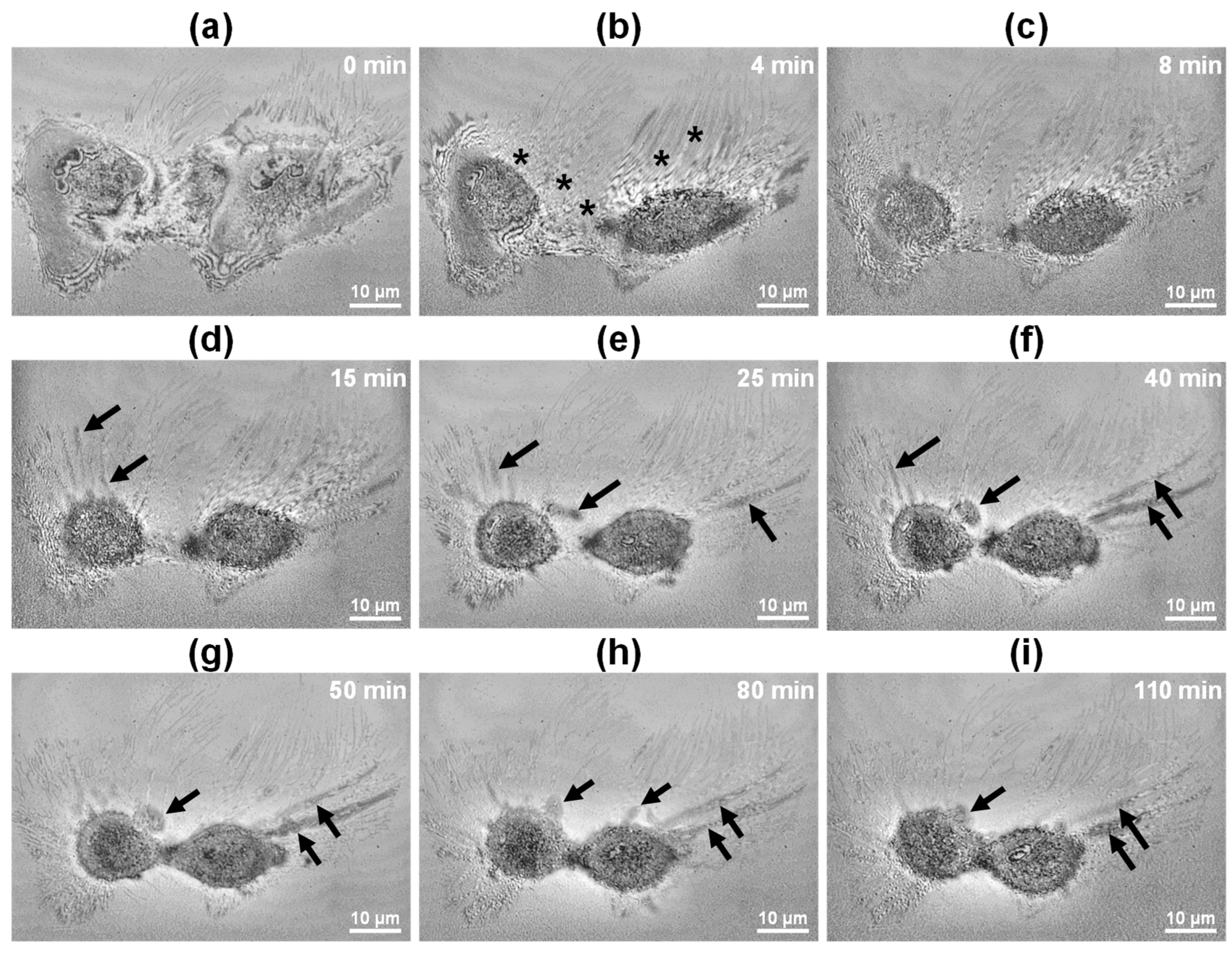
3.3. FF-OCT Imaging of Single HeLa Cells Undergoing Necrosis
3.4. FF-OCT-Based IRM-like Imaging of the Necrotic HeLa Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, K.; Strasser, A.; Kayagaki, N.; Dixit, V.M. Cell Death. Cell 2024, 187, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysko, D.V.; Vanden Berghe, T.; D’Herde, K.; Vandenabeele, P. Apoptosis and Necrosis: Detection, Discrimination and Phagocytosis. Methods 2008, 44, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.C. Mechanisms of Apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Moinuddin; Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S.; et al. Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golstein, P.; Kroemer, G. Cell Death by Necrosis: Towards a Molecular Definition. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermans, S.; Kestens, C.; Marques, P.E. Systemic Mechanisms of Necrotic Cell Debris Clearance. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekshmi, A.; Varadarajan, S.N.; Lupitha, S.S.; Indira, D.; Ann Mathew, K.; Nair, A.C.; Nair, M.; Prasad, T.; Sekar, H.; Gopalakrishnan, A.K.; et al. A Quantitative Real-Time Approach for Discriminating Apoptosis and Necrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 16101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, A.; Hollville, E.; Martin, S.J. Discriminating Between Apoptosis, Necrosis, Necroptosis, and Ferroptosis by Microscopy and Flow Cytometry. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rello, S.; Stockert, J.C.; Moreno, V.; Gámez, A.; Pacheco, M.; Juarranz, A.; Cañete, M.; Villanueva, A. Morphological Criteria to Distinguish Cell Death Induced by Apoptotic and Necrotic Treatments. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauchle, E.; Thude, S.; Brucker, S.Y.; Schenke-Layland, K. Cell Death Stages in Single Apoptotic and Necrotic Cells Monitored by Raman Microspectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Pradeep, S.; Judson-Torres, R.L.; Reed, J.; Teitell, M.A.; Zangle, T.A. Quantitative Phase Imaging: Recent Advances and Expanding Potential in Biomedicine. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11516–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.-C.; Lin, P.-T.; Sung, K.-B. Characterization and Identification of Cell Death Dynamics by Quantitative Phase Imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 046502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicar, T.; Raudenska, M.; Gumulec, J.; Balvan, J. The Quantitative-Phase Dynamics of Apoptosis and Lytic Cell Death. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, W.J.; Hoballah, J.; Wax, A. Molecular and Biophysical Analysis of Apoptosis Using a Combined Quantitative Phase Imaging and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Microscope. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201800126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, A.; Grieve, K.; Moneron, G.; Lecaque, R.; Vabre, L.; Boccara, C. Ultrahigh-Resolution Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 2874–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fu, R.; Xu, C.; Xu, M. Methods and Applications of Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography: A Review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 050901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June Choi, W.; In Jeon, D.; Ahn, S.-G.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Ha Lee, B.; Lekka, M.; Laidler, P.; Gil, D.; Lekki, J.; et al. Full-Field Optical Coherence Microscopy for Identifying Live Cancer Cells by Quantitative Measurement of Refractive Index Distribution. Opt. Express. 2010, 18, 23285–23295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mazlin, V.; Fei, K.; Boccara, A.C.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, P. Time-Domain Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography (TD-FF-OCT) in Ophthalmic Imaging. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2023, 14, 20406223231170146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholler, J.; Groux, K.; Goureau, O.; Sahel, J.A.; Fink, M.; Reichman, S.; Boccara, C.; Grieve, K. Dynamic Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography: 3D Live-Imaging of Retinal Organoids. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, A.; Moneron, G.; Grieve, K.; Boccara, A.C. Three-Dimensional Cellular-Level Imaging Using Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bien, S.; Rimmbach, C.; Neumann, H.; Niessen, J.; Reimer, E.; Ritter, C.A.; Rosskopf, D.; Cinatl, J.; Michaelis, M.; Schroeder, H.W.S.; et al. Doxorubicin-Induced Cell Death Requires Cathepsin B in HeLa Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Konorev, E.A.; Kotamraju, S.; Joseph, J.; Kalivendi, S.; Kalyanaraman, B. Doxorubicin Induces Apoptosis in Normal and Tumor Cells via Distinctly Different Mechanisms: INTERMEDIACY OF H2O2- AND P53-DEPENDENT PATHWAYS. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25535–25543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamen, S.; Anel, A.; Lasierra, P.; Alava, M.A.; Martinez-Lorenzo, M.J.; Piñeiro, A.; Naval, J. Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis in Human T-Cell Leukemia Is Mediated by Caspase-3 Activation in a Fas-Independent Way. FEBS Lett. 1997, 417, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, Y.; Kalant, H.; Orrego, H.; Khanna, J.M.; Videla, L.; Phillips, J.M. Experimental Alcohol Induced Hepatic Necrosis: Suppression by Propylthiouracil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Fan, X. Ethanol Induces Necroptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells in Vitro. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, R.; González, R.; Fouad, D.; Fraga, E.; Muntané, J. Dual Effect of Ethanol on Cell Death in Primary Culture of Human and Rat Hepatocytes. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June Choi, W.; Pi, L.-Q.; Min, G.; Lee, W.-S.; Ha Lee, B. Qualitative Investigation of Fresh Human Scalp Hair with Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 036010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, V.A.; Bunnell, S.C. Interference Reflection Microscopy. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2009, 45, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limozin, L.; Sengupta, K. Quantitative Reflection Interference Contrast Microscopy (RICM) in Soft Matter and Cell Adhesion. ChemPhysChem 2009, 10, 2752–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraste, A.; Pulka, K. Morphologic and Biochemical Hallmarks of Apoptosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 45, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed Abdul Rahman, S.N.; Abdul Wahab, N.; Abd Malek, S.N. In Vitro Morphological Assessment of Apoptosis Induced by Antiproliferative Constituents from the Rhizomes of Curcuma Zedoaria. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 257108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willingham, M.C. Cytochemical Methods for the Detection of Apoptosis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1999, 47, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cruchten, S.; Van den Broeck, W. Morphological and Biochemical Aspects of Apoptosis, Oncosis and Necrosis. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2002, 31, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Farias, T.; Da, M.; Sales, C.; Julia, A.; Borges, C.; Gorbenko, D.A.; Belashov, A.V.; Belyaeva, T.N.; Kornilova, E.S.; Semenova, I.V.; et al. Quantification of Changes in Cellular Morphology during Cell Necrosis Obtained from 3D Refractive Index Distributions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1236, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghe, T.V.; Vanlangenakker, N.; Parthoens, E.; Deckers, W.; Devos, M.; Festjens, N.; Guerin, C.J.; Brunk, U.T.; Declercq, W.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis, Necrosis and Secondary Necrosis Converge on Similar Cellular Disintegration Features. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apelian, C.; Harms, F.; Thouvenin, O.; Boccara, A.C. Dynamic Full-field Optical Coherence Tomography: Subcellular Metabolic Contrast Revealed in Tissues by Interferometric Signals Temporal Analysis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, A.; Moon, S.; Choi, Y.-W.; Choi, W.J. Single-shot Full-field Optical Coherence Tomography with A Single Polarization Camera. Biomed. Opt. Express 2025, 16, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanfar, S.; Kenny, K.B.; Tasimi, K.; Corwin, A.D.; Dixon, E.L.; Filkins, R.J. Simple and Robust Image-based Autofocusing for Digital Microscopy. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 8670–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.; Kim, K.R.; Cho, M.; Hwang, J.; Yang, J.-M.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, W.J. High-Resolution Imaging of Morphological Changes Associated with Apoptosis and Necrosis Using Single-Cell Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. Biosensors 2025, 15, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080522
Kang S, Kim KR, Cho M, Hwang J, Yang J-M, Kim JK, Choi WJ. High-Resolution Imaging of Morphological Changes Associated with Apoptosis and Necrosis Using Single-Cell Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080522
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Suyeon, Kyeong Ryeol Kim, Minju Cho, Joonseup Hwang, Joon-Mo Yang, Jun Ki Kim, and Woo June Choi. 2025. "High-Resolution Imaging of Morphological Changes Associated with Apoptosis and Necrosis Using Single-Cell Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080522
APA StyleKang, S., Kim, K. R., Cho, M., Hwang, J., Yang, J.-M., Kim, J. K., & Choi, W. J. (2025). High-Resolution Imaging of Morphological Changes Associated with Apoptosis and Necrosis Using Single-Cell Full-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. Biosensors, 15(8), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080522







