Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of PLA-HPG-Based Biodegradable Nanocarriers: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
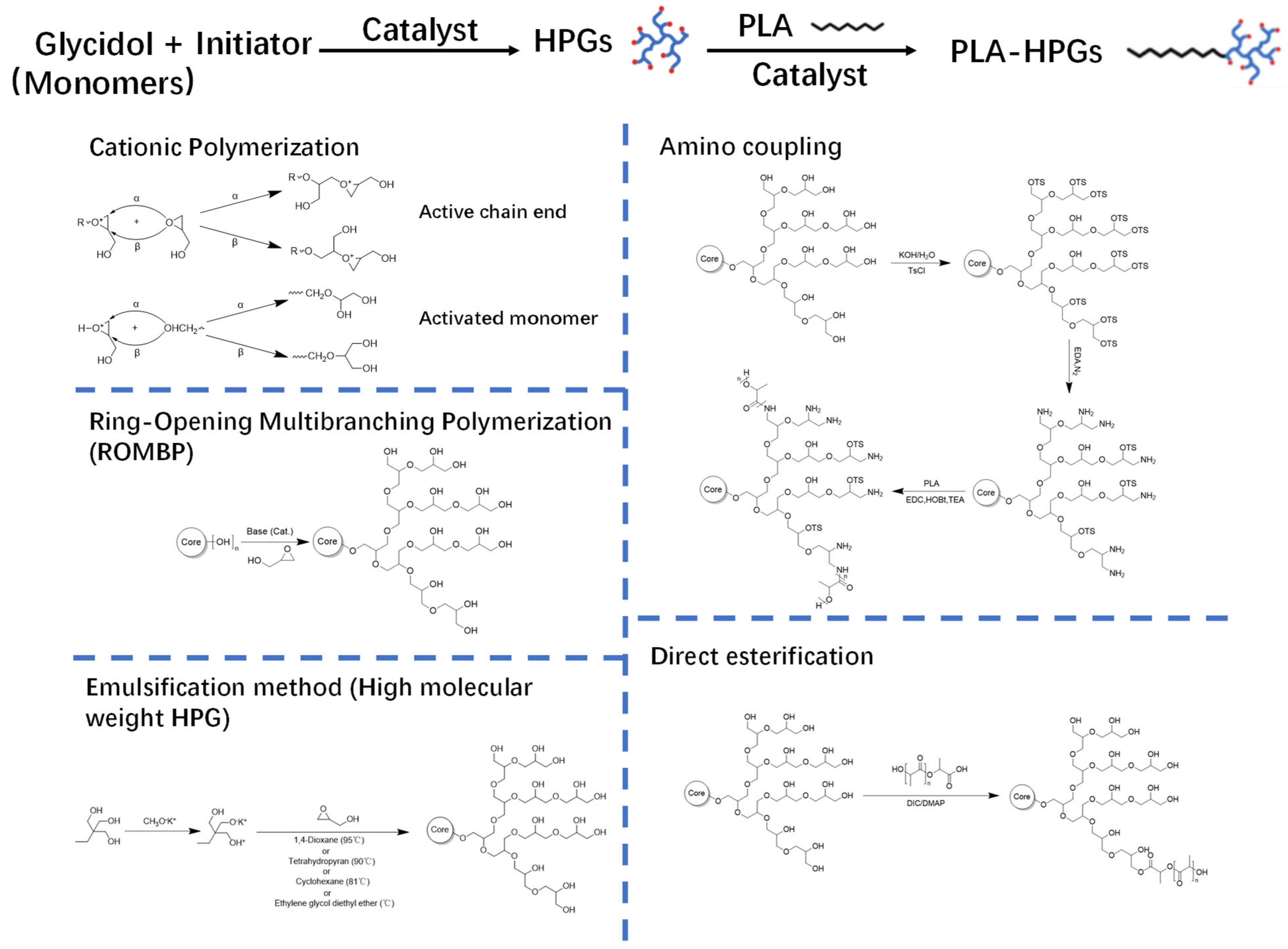
2. Synthesis of PLA-HPG
2.1. Synthesis of HPG
2.2. Synthesis of PLA-HPG Copolymers
2.3. Fabrication of PLA-HPG NPs
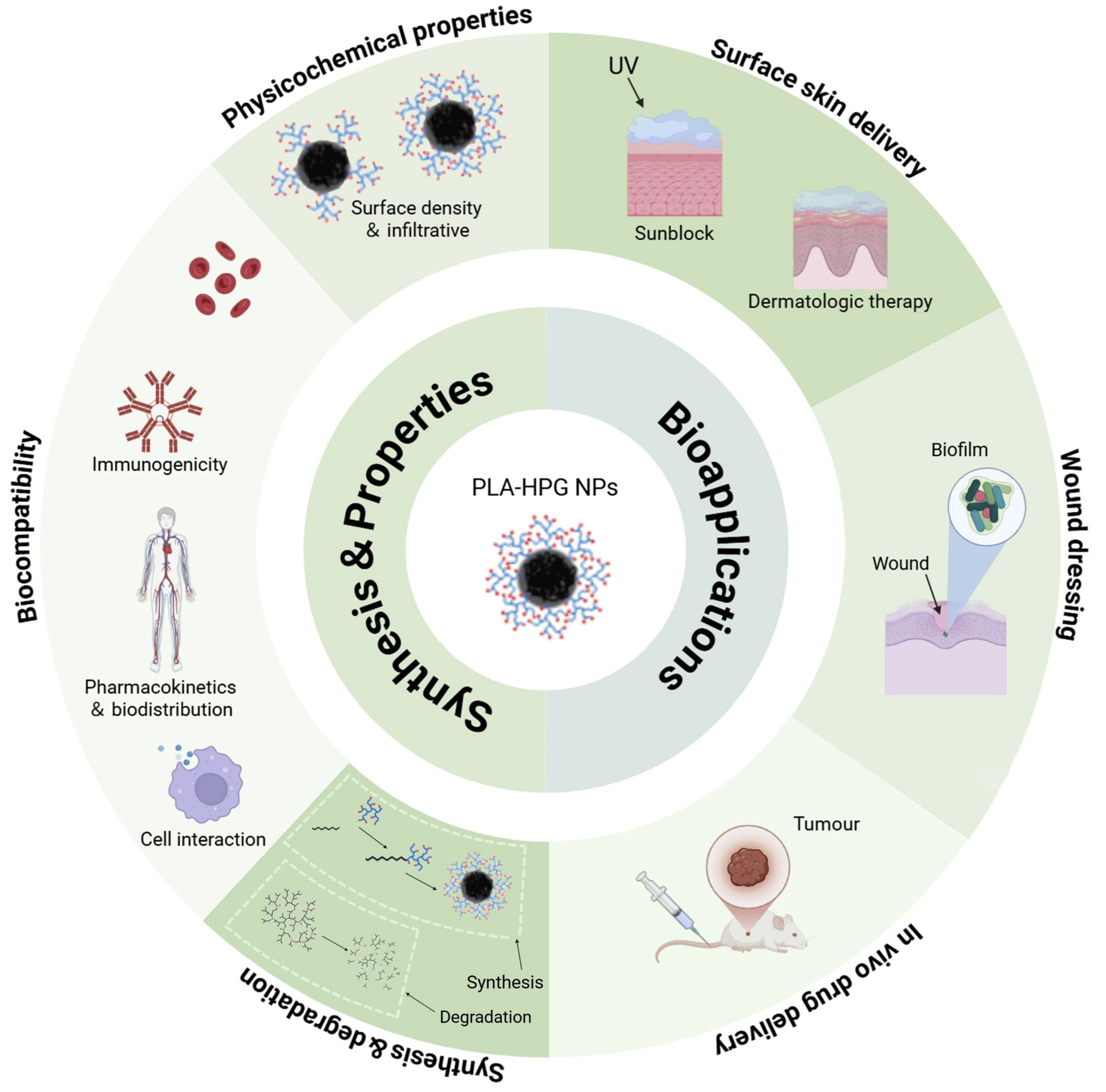
3. Properties of PLA-HPG
3.1. Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Biocompatibility
3.3. Degradation Properties
4. Biomedical Applications of PLA-HPG-Based Nanocarriers
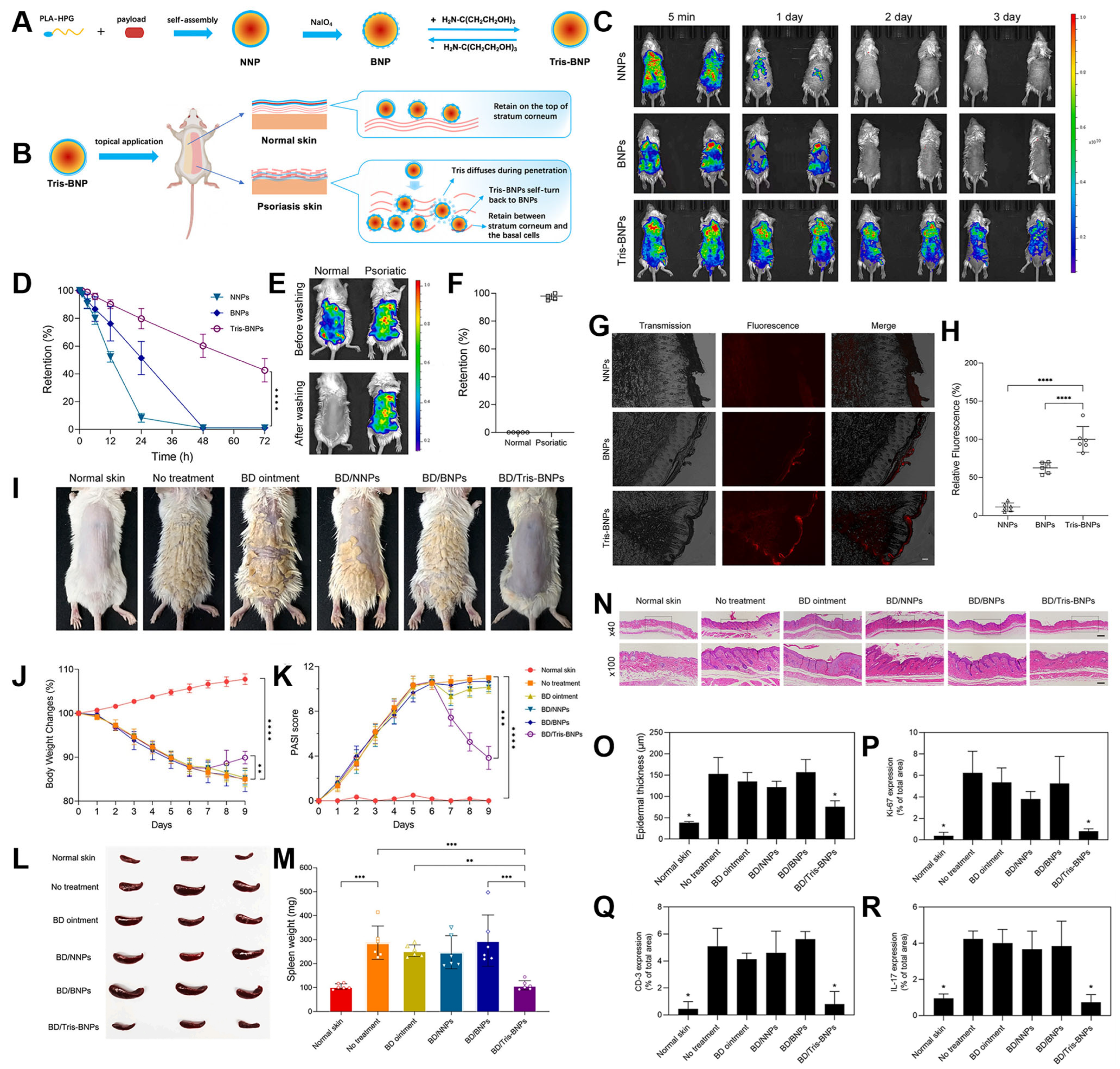
4.1. Surface Skin Delivery for Sunblock or Dermatologic Therapy
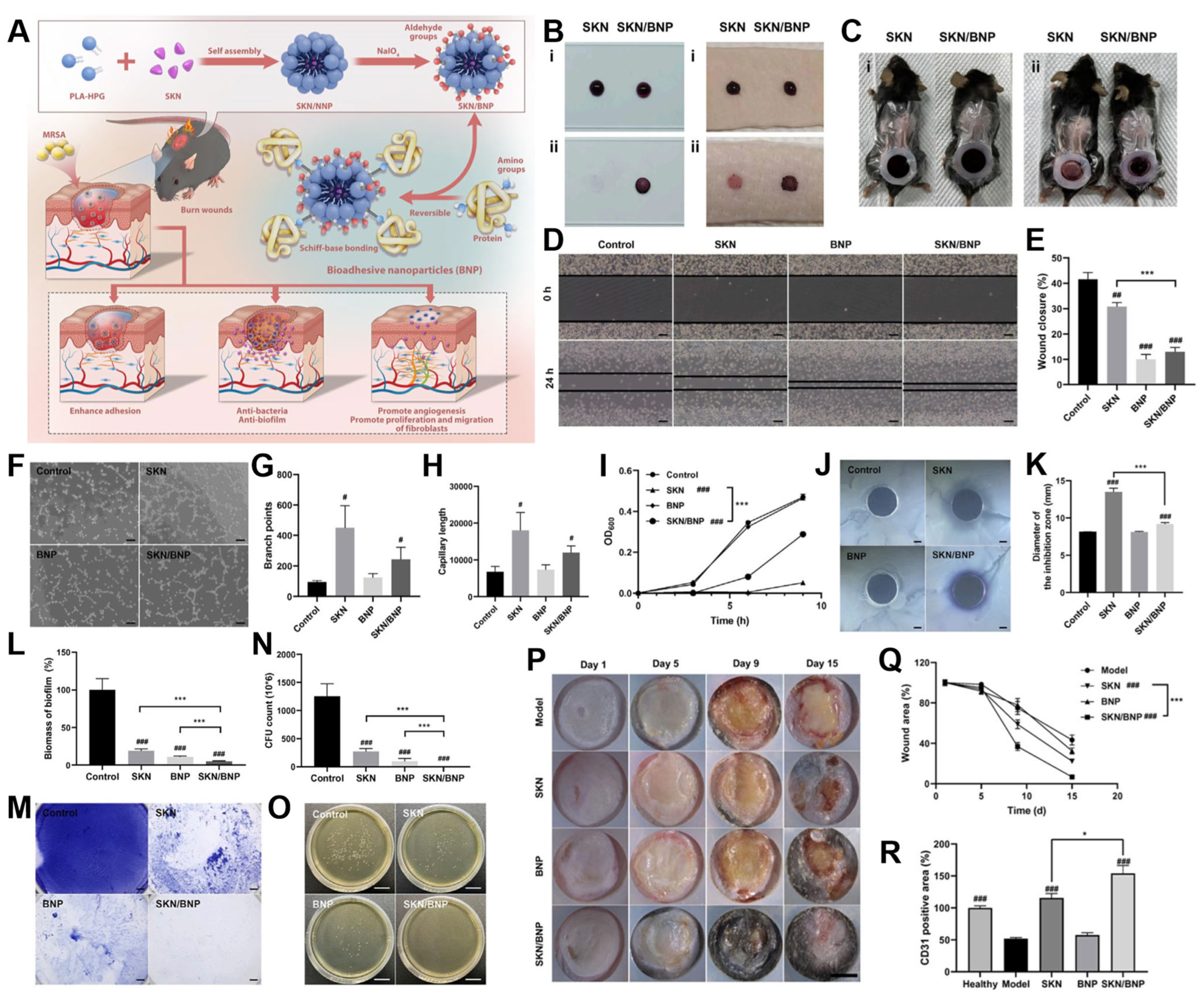
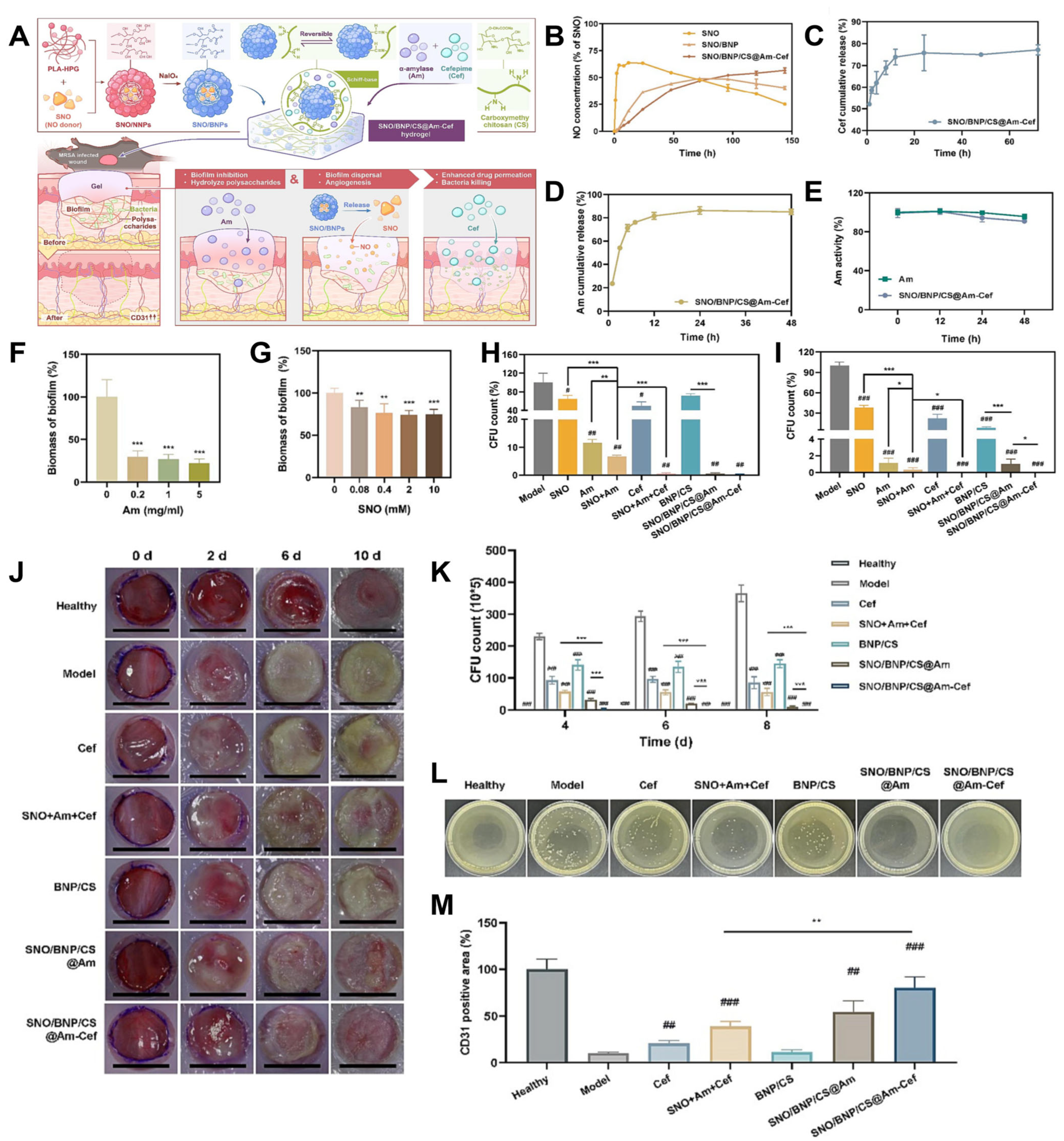
4.2. Wound Dressing
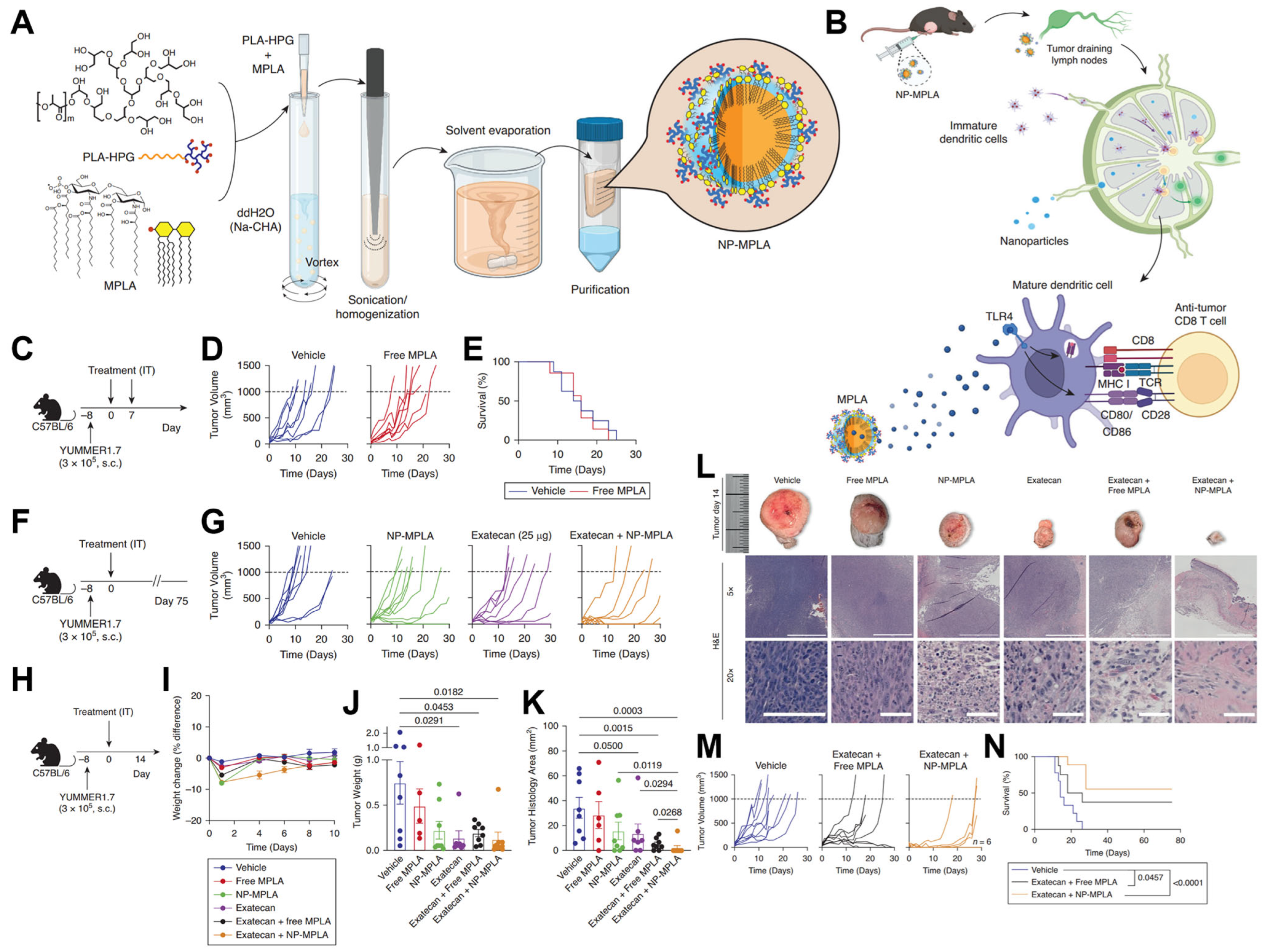
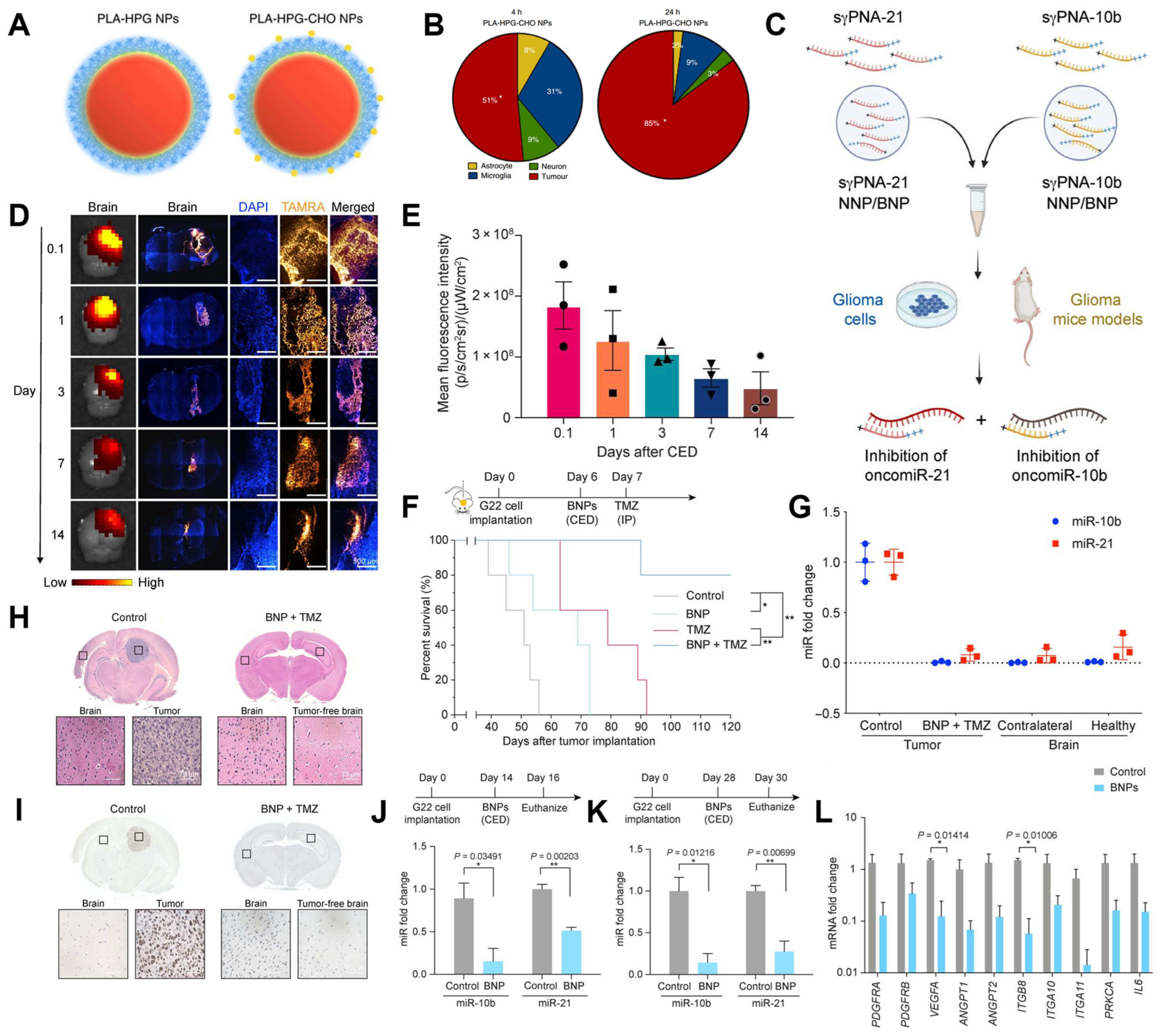
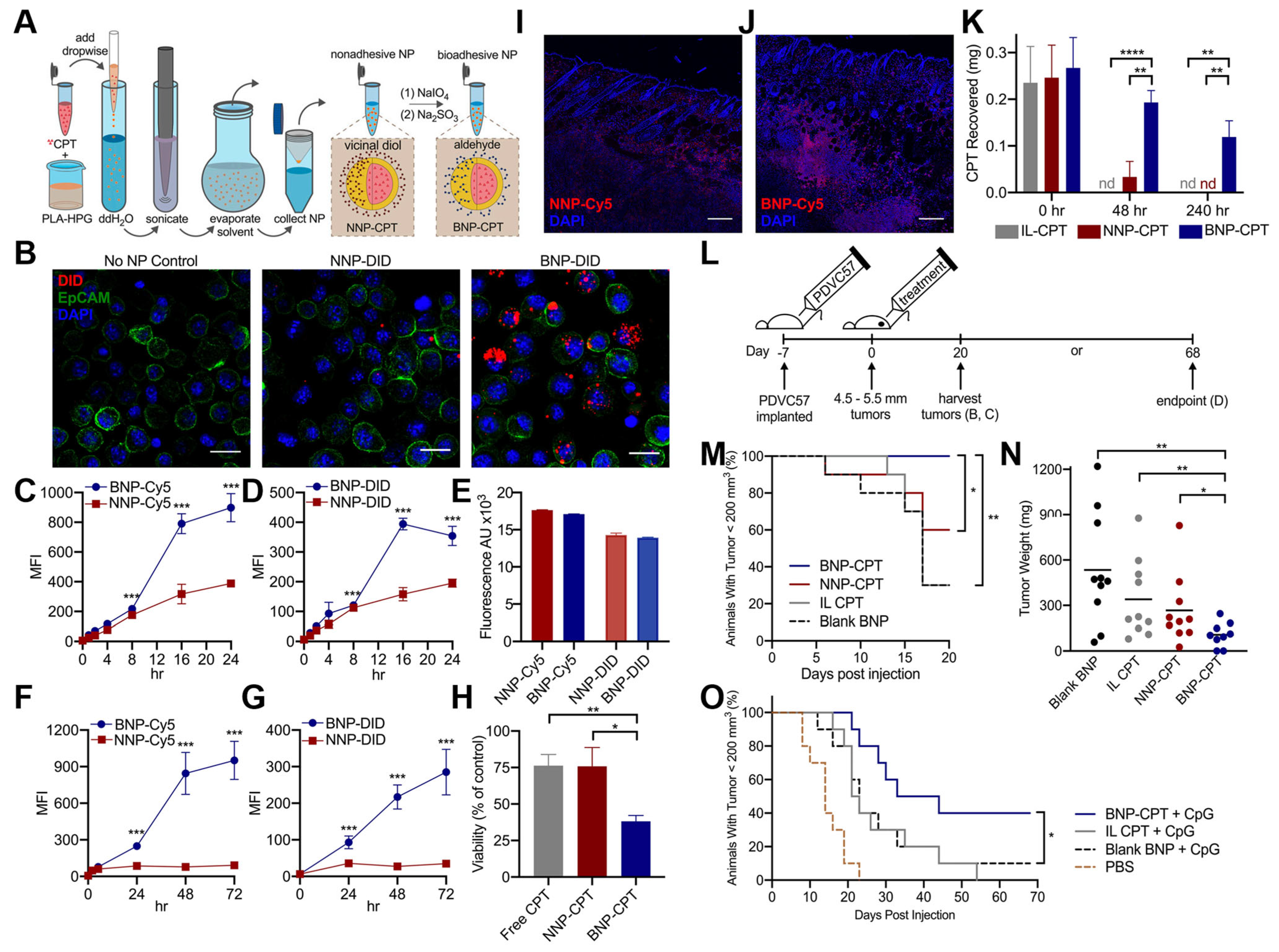
4.3. Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kashfia, H.; Rana, M.; Khan, M.S.S. Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Sustainable Drug Delivery. Biosens. Nanotheranostics 2023, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.; Müller, S.S.; Frey, H. Beyond Poly(ethylene glycol): Linear Polyglycerol as a Multifunctional Polyether for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1935–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T. Synthesis of Hyperbranched Polymer Using Slow Monomer Addition Method. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 2012, 816163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Saucier-Sawyer, J.K.; Hoimes, C.J.; Zhang, J.; Seo, Y.E.; Andrejecsk, J.W.; Saltzman, W.M. The effect of hyperbranched polyglycerol coatings on drug delivery using degradable polymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6595–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Wałach, W.; Bochenek, M.; Trzebicka, B.; Anioł, J.; Sieroń, A.L.; Kubacki, J.; Dworak, A. Branched polyglycidol and its derivatives grafted-from poly(ethylene terephthalate) and silica as surfaces that reduce protein fouling. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 105, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ramadan, E.; Elsadek, N.E.; Emam, S.E.; Shimizu, T.; Ando, H.; Ishima, Y.; Elgarhy, O.H.; Sarhan, H.A.; Hussein, A.K.; et al. Polyethylene glycol (PEG): The nature, immunogenicity, and role in the hypersensitivity of PEGylated products. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in Drug Delivery: Pros and Cons as Well as Potential Alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainthan, R.K.; J Yeh, P.Y.; Zou, Y.; Chiao, M.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Self-Assembled Monothiol-Terminated Hyperbranched Polyglycerols on a Gold Surface: A Comparative Study on the Structure, Morphology, and Protein Adsorption Characteristics with Linear Poly(ethylene glycol)s. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4907–4916. [Google Scholar]
- Imran ul-haq, M.; Lai, B.F.; Chapanian, R.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Influence of architecture of high molecular weight linear and branched polyglycerols on their biocompatibility and biodistribution. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9135–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haxton, K.J.; Burt, H.M. Hyperbranched polymers for controlled release of cisplatin. Dalton Trans. 2008, 43, 5872–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Schlesener, C.; Cromwell, O.; Hellmund, M.; Haag, H.; Guan, Z. Amino Acid-Functionalized Dendritic Polyglycerol for Safe and Effective siRNA Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3869–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, A.A.A.; Bressiani, J.C.; Bressiani, A.H.A.; Higa, O.Z.; Abraham, G.A. A Novel Bone Scaffolds Based on Hyperbranched Polyglycerol Fibers Filled with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: In Vitro Cell Response. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 396, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbina, S.; Vappala, S.; Kumar, P.; Siren, E.M.J.; La, C.C.; Abbasi, U.; Brooks, D.E.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Hyperbranched polyglycerols: Recent advances in synthesis, biocompatibility and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 9249–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Muhammad, F.; Akhtar, B. Biodegradable nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luten, J.; van Nostrum, C.F.; De Smedt, S.C.; Hennink, W.E. Biodegradable polymers as non-viral carriers for plasmid DNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, P.; Arora, M.; Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. Poly(lactic acid) blends in biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogina, A.; Pribolšan, L.; Hanžek, A.; Gόmez-Estrada, L.; Ferrer, G.G.; Marijanović, I.; Ivanković, M.; Ivanković, H. Macroporous poly(lactic acid) construct supporting the osteoinductive porous chitosan-based hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Polymer 2016, 98, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Munguia-Lopez, J.G.; Cho, Y.W.; Ma, X.; Song, V.; Zhu, Z.; Tran, S.D. Polymeric Scaffolds for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Regenerative Medicine. Molecules 2021, 26, 7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Laurencin, C.T.; Caterson, E.J.; Tuan, R.S.; Ko, F.K. Electrospun nanofibrous structure: A novel scaffold for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Suh, H.W.; Grundler, J.; Lynn, A.Y.; Pothupitiya, J.U.; Moscato, Z.M.; Reschke, M.; Bracaglia, L.G.; Piotrowski-Daspit, A.S.; Saltzman, W.M. Polyglycerol and Poly(ethylene glycol) exhibit different effects on pharmacokinetics and antibody generation when grafted to nanoparticle surfaces. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonhauser, C.; Schüll, C.; Dingels, C.; Frey, H. Branched Acid-Degradable, Biocompatible Polyether Copolymers via Anionic Ring-Opening Polymerization Using an Epoxide Inimer. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, P.J. Molecular Size Distribution in Three Dimensional Polymers. VI. Branched Polymers Containing A—R—Bf-1 Type Units. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 2718–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, S.R.; Berg, F.R. Room temperature polymerization of glycidol. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-1 Polym. Chem. 1966, 4, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworak, A.; Walach, W.; Trzebicka, B. Cationic polymerization of glycidol. Polymer structure and polymerization mechanism. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1995, 196, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunder, A.; Krämer, M.; Hanselmann, R.; Mülhaupt, R.; Frey, H. Molecular Nanocapsules Based on Amphiphilic Hyperbranched Polyglycerols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3552–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-haq, M.I.; Shenoi, R.A.; Brooks, D.E.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Solvent-assisted anionic ring opening polymerization of glycidol: Toward medium and high molecular weight hyperbranched polyglycerols. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy Royappa, A.; Vogt, M.L.; Sharma, V. Composition and long-term stability of polyglycidol prepared by cationic ring-opening polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, M.; Shamlooei, H.; Mohammadifar, E.; Adeli, M. Synthesis of hyperbranched polyglycerols using ascorbic acid as an activator. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, C. Encapsulation of BSA in polylactic acid–hyperbranched polyglycerol conjugate nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and release kinetics. Polym. Bull. 2010, 65, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, C. Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of a novel amphiphilic polylactic acid-hyperbranched polyglycerol conjugate for protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Rivas, C.J.; Tarhini, M.; Badri, W.; Miladi, K.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Nazari, Q.A.; Galindo Rodríguez, S.A.; Román, R.Á.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Nanoprecipitation process: From encapsulation to drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barichello, J.M.; Morishita, M.; Takayama, K.; Nagai, T. Encapsulation of Hydrophilic and Lipophilic Drugs in PLGA Nanoparticles by the Nanoprecipitation Method. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1999, 25, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Yu, M.; Qin, Y.; Girardi, M.; Saltzman, W.M.; Cocco, E.; Zhao, C.; Yu, L.; Jia, Y.; et al. Topical formulation based on disease-specific nanoparticles for single-dose cure of psoriasis. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Lila, A.S.; Kiwada, H.; Ishida, T. The accelerated blood clearance (ABC) phenomenon: Clinical challenge and approaches to manage. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ediriwickrema, A.; Yang, F.; Lewis, J.; Girardi, M.; Saltzman, W.M. A sunblock based on bioadhesive nanoparticles. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Chen, L.; Liang, S.; Lü, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, F.; Ge, L.; Xiao, L. PLA-HPG based coating enhanced anti-biofilm and wound healing of Shikonin in MRSA-infected burn wound. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1243525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xiao, L.; Fang, Y.; Chen, T.; Xie, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Nie, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. A nanocomposite hydrogel for co-delivery of multiple anti-biofilm therapeutics to enhance the treatment of bacterial biofilm-related infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 649, 123638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Shin, K.; Lewis, J.M.; Suh, H.W.; Lee, J.; Damsky, W.; Xu, S.; Bosenberg, M.; Saltzman, W.M.; Girardi, M. Enhanced Intratumoral Delivery of Immunomodulator Monophosphoryl Lipid A through Hyperbranched Polyglycerol–Coated Biodegradable Nanoparticles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Gaudin, A.; King, A.R.; Seo, Y.E.; Suh, H.W.; Deng, Y.; Cui, J.; Tietjen, G.T.; Huttner, A.; Saltzman, W.M. Surface chemistry governs cellular tropism of nanoparticles in the brain. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Malik, S.; Suh, H.W.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Fan, R.; Huttner, A.; Bindra, R.S.; Singh, V.; Saltzman, W.M.; et al. Anti-seed PNAs targeting multiple oncomiRs for brain tumor therapy. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eabq7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.K.; Suh, H.W.; Qureshi, M.; Lewis, J.M.; Yaqoob, S.; Moscato, Z.M.; Griff, S.; Lee, A.K.; Yin, E.S.; Saltzman, W.M.; et al. Nonsurgical treatment of skin cancer with local delivery of bioadhesive nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020575118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekmohammadi, S.; Jamshidi, R.; Sadowska, J.M.; Meng, C.; Abeykoon, C.; Akbari, M.; Gong, R.H. Stimuli-Responsive Codelivery System-Embedded Polymeric Nanofibers with Synergistic Effects of Growth Factors and Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound to Enhance Osteogenesis Properties. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 4293–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Song, J.; Malekmohammadi, S.; Meng, J.; Wei, W.; Li, R.; Feng, J.; Gong, R.H.; Li, J. Hierarchical porous poly (L-lactic acid) fibrous vascular graft with controllable architectures and stable structure. Mater. Des. 2024, 240, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Control Over MW | Polydispersity | Biocompatibility of Reagents | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anionic Polymerization | Excellent | ~1.2 | Moderate, requires basic initiators | Moderate, limited by initiator toxicity |
| Cationic Polymerization | Moderate | ~1.3–1.6 | Variable, dependent on catalysts | Not easily scalable due to catalyst |
| ROMBP | Excellent | <1.3 | High, uses non-toxic initiators | High, requires precise control of conditions |
| Ascorbic Acid Initiated | Moderate | ~1.5 | Excellent, biocompatible activator | High, no toxic solvents or reagents |
| Amino Coupling | Moderate | ~1.5 | Moderate, carbodiimide and amine activation | Moderate, efficient but sensitive to excess unreacted amines |
| Direct Esterification | Moderate | ~1.3 | High, uses simple coupling reagents | High, straightforward and efficient |
| Patent Number | Application Area | Key Features | Delivery Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN117679393 | Hypertrophic scar treatment | Vitepofen-loaded, local-adhesion, controlled-release | PLA-HPG sustained-release particles |
| WO2022165403/US20240423972 | Cancer therapy | CPT delivery with immune adjuvants | Bioadhesive PLA-HPG NPs |
| CN115531349 | Bacterial conjunctivitis | PEG network system enhances ocular retention | PPHNP-AL-PEG adhesive NP system |
| CN115737598 | Brain disease treatment | Intranasal BNP-PAMAM cluster targets CNS | Excellent, biocompatible activator |
| WO2023060716/CN113975249 | Psoriasis | Tris neutralization reversibly masks adhesiveness | Al-PHNPs-PAMAM nano cluster |
| CN116327965 | Skin drug delivery | Schiff-base hydrogel network enhances dual drug | Variable, dependent on catalysts |
| CN113876716 | Gastrointestinal diseases | GI adhesion prolongs local effect | High, uses non-toxic initiators |
| CN116832011 | Scald wound | SKN-loaded BNP prolongs local effect | Excellent, biocompatible activator |
| WO2023220067/US20230355801 | Cancer immunotherapy | MPLA-loaded BNPs improve dendritic cell response and lymphatic targeting | Excellent, biocompatible activator |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of PLA-HPG-Based Biodegradable Nanocarriers: A Review. Biosensors 2025, 15, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080502
Shen Y, He X, Chen L. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of PLA-HPG-Based Biodegradable Nanocarriers: A Review. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080502
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yijun, Xuehan He, and Lei Chen. 2025. "Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of PLA-HPG-Based Biodegradable Nanocarriers: A Review" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080502
APA StyleShen, Y., He, X., & Chen, L. (2025). Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of PLA-HPG-Based Biodegradable Nanocarriers: A Review. Biosensors, 15(8), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080502





