Equivalent Circuit Modeling and Analysis for Microfluidic Electrical Impedance Monitoring of Single-Cell Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
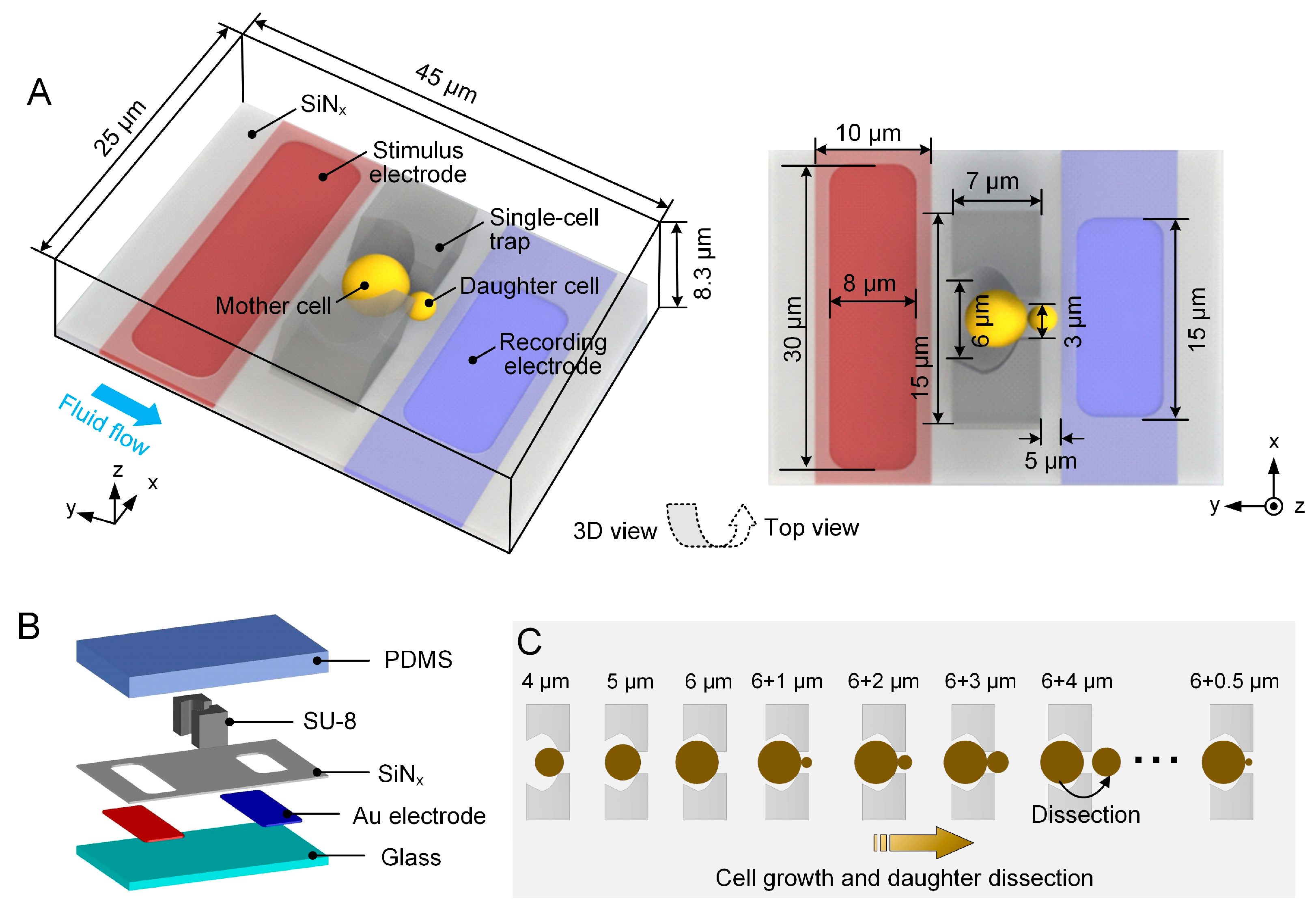
2.1. Design Concept of EIS Sensing Unit
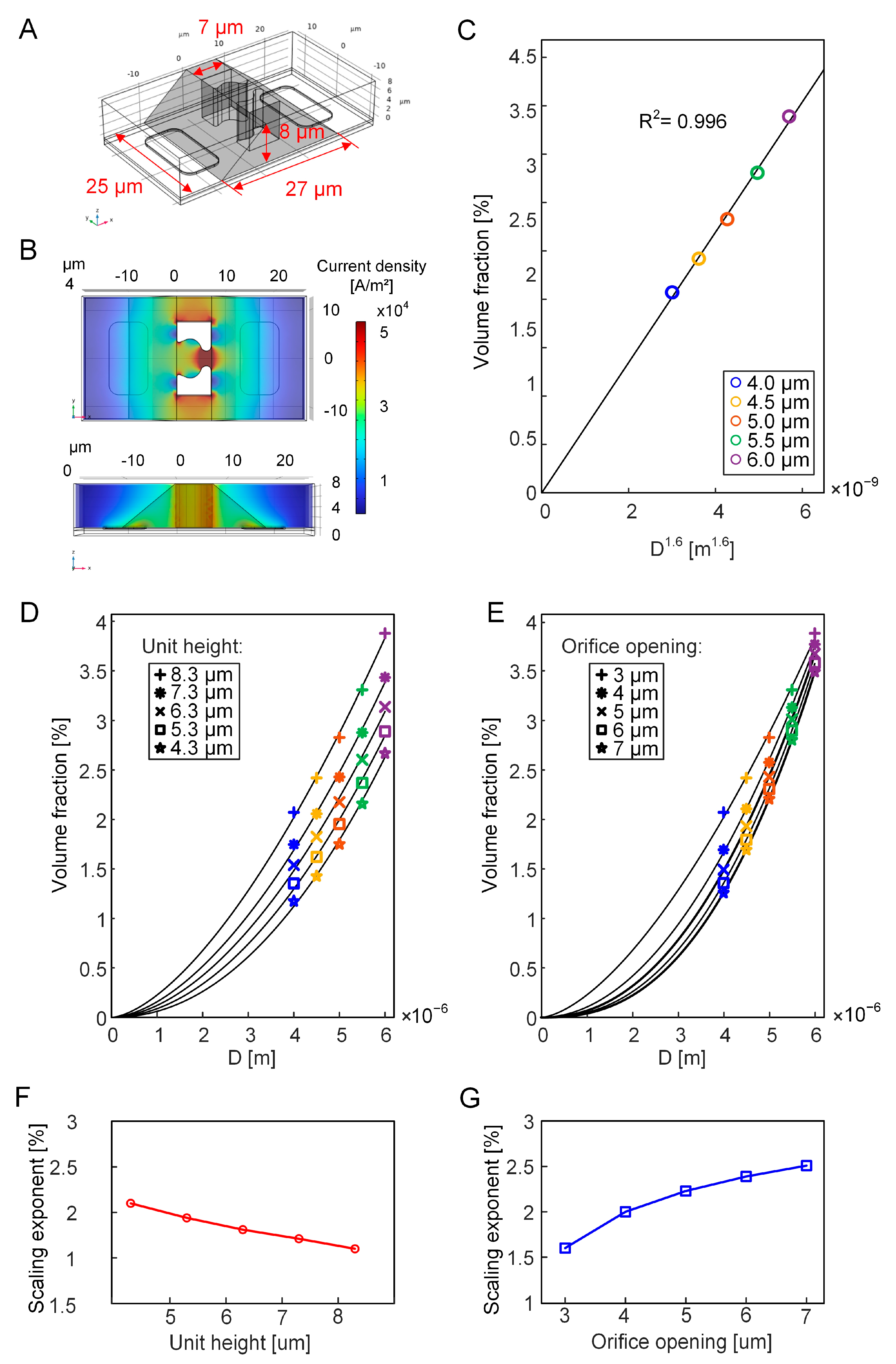
2.2. FEM of the EIS Sensing Unit
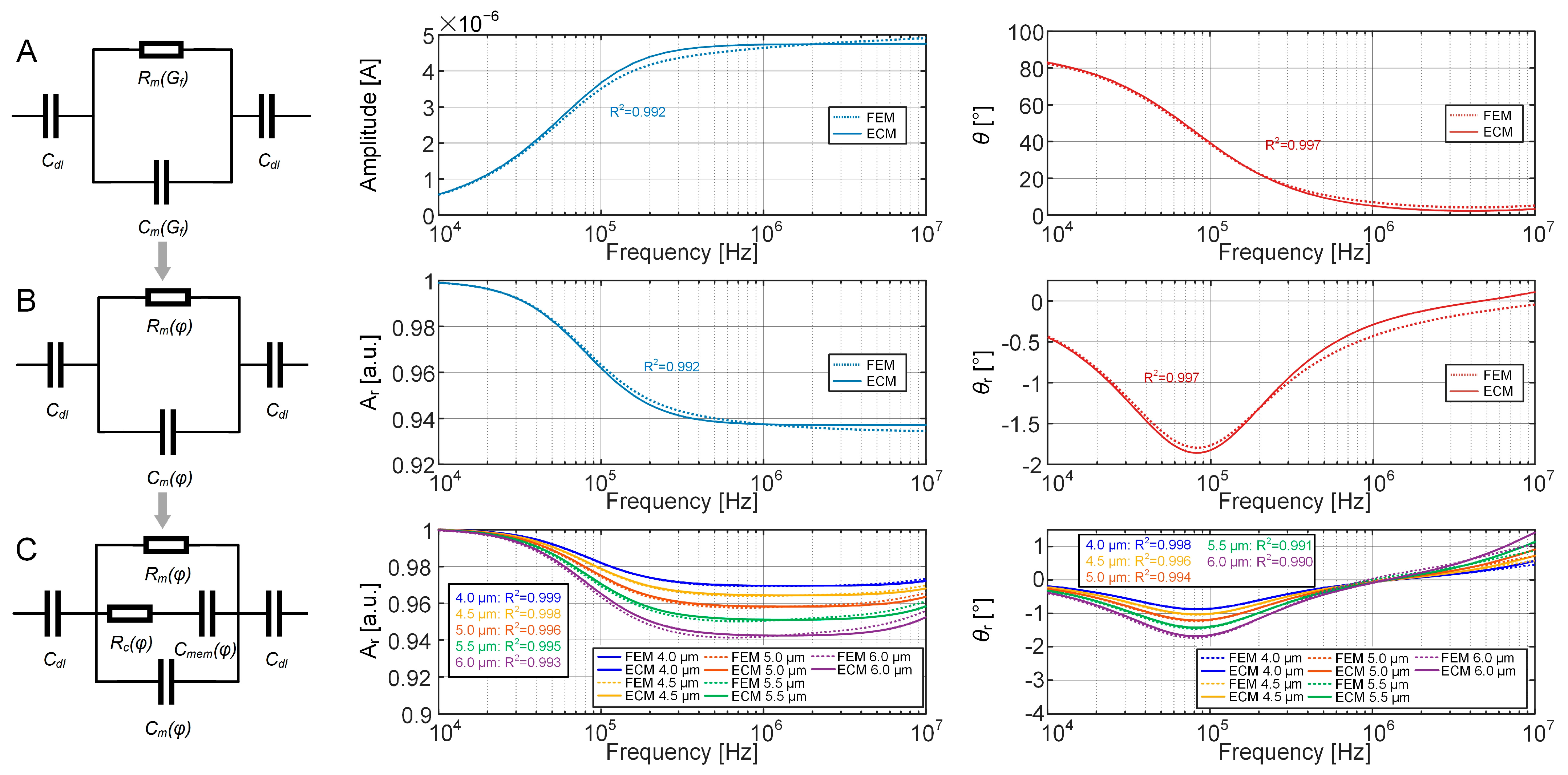
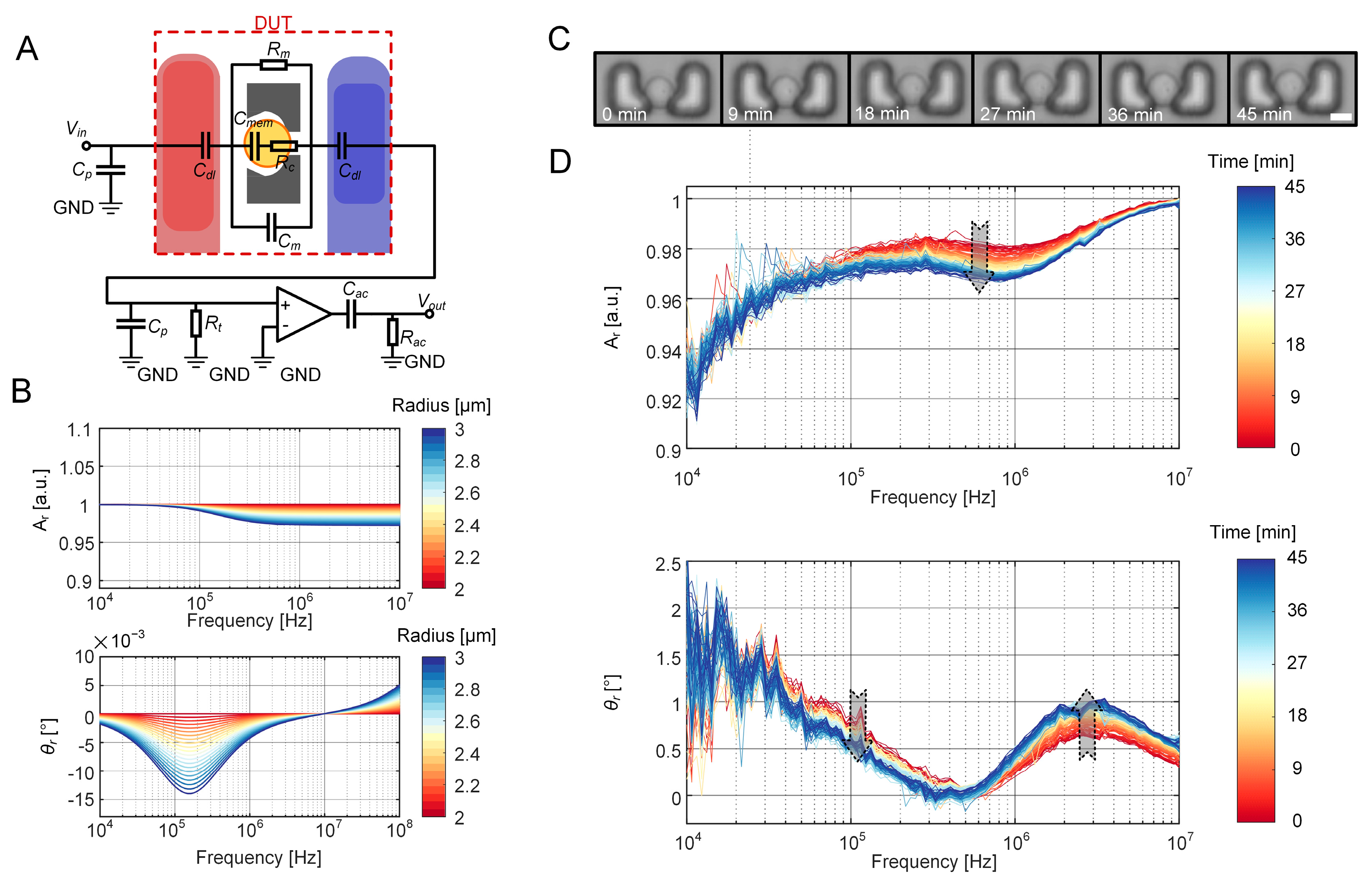
2.3. ECM of the EIS Sensing Unit with a Cell
2.4. Experimental Setup and Protocol for EIS Measurement
2.5. LPM of the Entire EIS Measurement System
3. Results
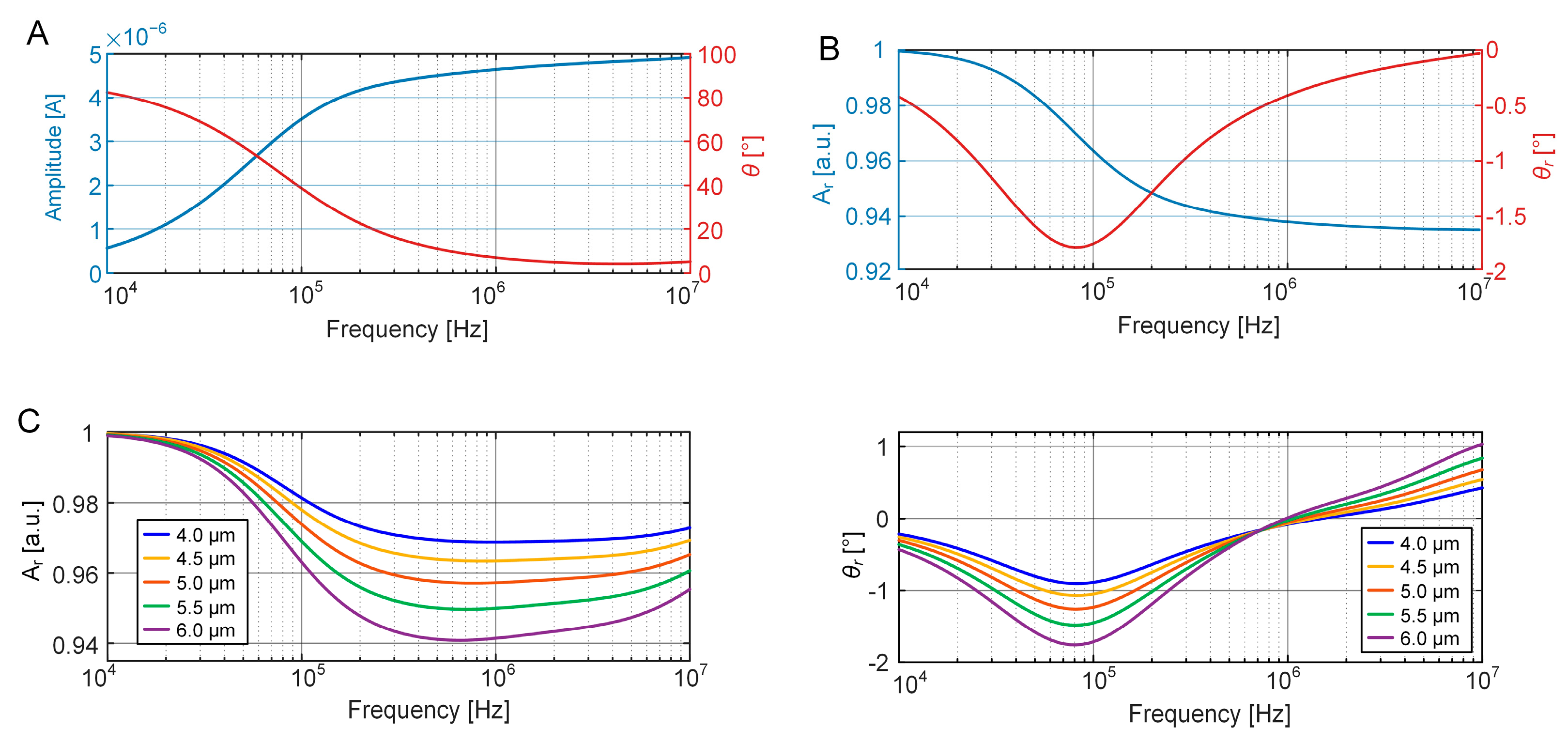
3.1. FEM Simulation of EIS Measurement of Cell Growth
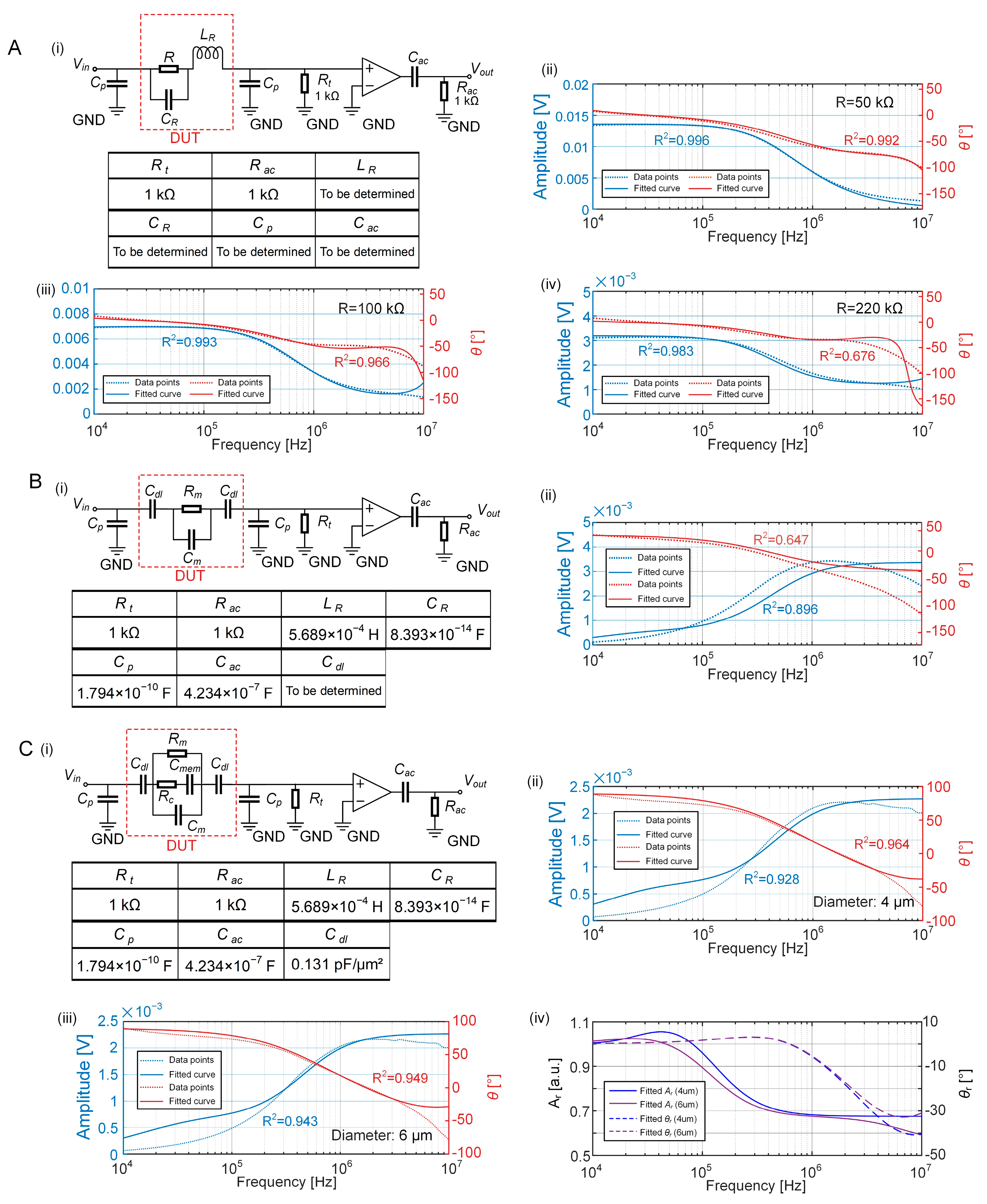
3.2. Establishment of the ECM of the EIS Sensing Unit
3.3. Equivalent Volume Fraction of the Growing Cell
3.4. LPM Fitting of the Entire EIS Measurement System
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarnoski, E.A.; Song, R.; Ertekin, E.; Koonce, N.; Acar, M. Fundamental characteristics of single-cell aging in diploid yeast. IScience 2018, 7, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, W.; Camellato, B.; Roney, I.J.; Kaern, M.; Godin, M. Measuring single-cell phenotypic growth heterogeneity using a microfluidic cell volume sensor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestary, K.; Klemm, C.; Carling, B.; Marshall, J.; Savigny, J.; Storch, M.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. Phenotypic heterogeneity follows a growth-viability tradeoff in response to amino acid identity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botstein, D.; Fink, G.R. Yeast: An experimental organism for 21st century biology. Genetics 2011, 189, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasserre, J.P.; Dautant, A.; Aiyar, R.S.; Kucharczyk, R.; Glatigny, A.; Tribouillard-Tanvier, D.; Rytka, J.; Blondel, M.; Skoczen, N.; Reynier, P.; et al. Yeast as a system for modeling mitochondrial disease mechanisms and discovering therapies. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, E.M.; Pellegrini, M.; Ng, H.L.; Rice, D.W.; Yeates, T.O.; Eisenberg, D. Detecting protein function and protein-protein interactions from genome sequences. Science 1999, 285, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huberts, D.; Lee, S.; Gonzalez, J.; E Janssens, G.; Vizcarra, I.A.; Heinemann, M. Construction and use of a microfluidic dissection platform for long-term imaging of cellular processes in budding yeast. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eeckhoudt, R.; Christiaens, A.S.; Ceyssens, F.; Vangalis, V.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Boon, N.; Tavernier, F.; Kraft, M.; Taurino, I. Full-electric microfluidic platform to capture, analyze and selectively release single cells. Lab A Chip 2023, 23, 4276–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, X. Label-free mass cytometry for unveiling cellular metabolic heterogeneity. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9777–9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspert, T.; Hentsch, D.; Charvin, G. DetecDiv, a generalist deep-learning platform for automated cell division tracking and survival analysis. Elife 2022, 11, e79519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Basu, S.; Laue, E.D.; Seshia, A.A. Dynamic monitoring of single cell lysis in an impedance-based microfluidic device. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagoshtasbi, H.; Deng, P.; Lee, Y.K. A nonlinear size-dependent equivalent circuit model for single-cell electroporation on microfluidic chips. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, D.; Ebi, H.; Oku, N.; Matsuda, K.; Takao, H.; Ashiki, M.; Ishida, M. A sensor for blood cell counter using MEMS technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 83, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Xue, C.D.; Hu, S.Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Chen, X.-M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, K.-R. Long-Term Stable and Multifeature Microfluidic Impedance Flow Cytometry Based on a Constricted Channel for Single-Cell Mechanical Phenotyping. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 17754–17764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.R.; Schwan, H.P. Dielectrical properties of tissues and biological materials. a critical review. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1989, 17, 25–104. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Green, N.G.; Morgan, H. Analytical and numerical modeling methods for impedance analysis of single cells on-chip. Nano 2008, 3, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Green, N.G.; Gawad, S.; Morgan, H. Analytical electric field and sensitivity analysis for two microfluidic impedance cytometer designs. IET Nanobiotechnology 2007, 1, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.M.A.; Butt, N.Z. Design and analysis of microfluidic cell counter using spice simulation. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, P.; Liang, F.; Wang, W. A microfluidic device integrating impedance flow cytometry and electric impedance spectroscopy for high-efficiency single-cell electrical property measurement. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 15204–15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.L.; Tang, D.Z.; Ni, Z.H.; Xiang, N.; Yi, H. A portable single-cell analysis system integrating hydrodynamic trapping with broadband impedance spectroscopy. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, X.; Fang, L.; Pan, D.; Huang, Q.-A. Investigation of geometry-dependent sensing characteristics of microfluidic electrical impedance spectroscopy through modeling and simulation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, F.; Marchisio, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Pan, D.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Q.-A. Design and 3D modeling investigation of a microfluidic electrode array for electrical impedance measurement of single yeast cells. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, K.; Xiao, Q.; Geng, Y.; Xu, F.; Ouyang, S.; Zheng, K.; Fan, Y.; Jin, N.; et al. High-throughput microfluidic diploid yeast long-term culturing (DYLC) chip capable of bud reorientation and concerted daughter dissection for replicative lifespan determination. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Nguyen, D.; Greve, D.W.; Domach, M. Simulation of microelectrode impedance changes due to cell growth. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| D [μm] | 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 |
| φ [%] | 0.0207 | 0.0242 | 0.0283 | 0.0331 | 0.0388 |
| Diameter [μm] | Cm | Rm | Rc | Cmem |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 997 kΩ | 0.98 pF | 1.75 MΩ | 0.13 pF |
| 6 | 991 kΩ | 0.78 pF | 1.09 MΩ | 0.20 pF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Ouyang, J.; Zhu, Z. Equivalent Circuit Modeling and Analysis for Microfluidic Electrical Impedance Monitoring of Single-Cell Growth. Biosensors 2025, 15, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15020113
Wang Y, Wu H, Geng Y, Zhang Z, Fu J, Ouyang J, Zhu Z. Equivalent Circuit Modeling and Analysis for Microfluidic Electrical Impedance Monitoring of Single-Cell Growth. Biosensors. 2025; 15(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yingying, Haoran Wu, Yulu Geng, Zhao Zhang, Jiaming Fu, Jia Ouyang, and Zhen Zhu. 2025. "Equivalent Circuit Modeling and Analysis for Microfluidic Electrical Impedance Monitoring of Single-Cell Growth" Biosensors 15, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15020113
APA StyleWang, Y., Wu, H., Geng, Y., Zhang, Z., Fu, J., Ouyang, J., & Zhu, Z. (2025). Equivalent Circuit Modeling and Analysis for Microfluidic Electrical Impedance Monitoring of Single-Cell Growth. Biosensors, 15(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15020113






