Electrochemical Tracking of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor: A Leap Toward Precision Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus, Instruments and Electrodes
2.2. Reagents and Solutions
2.3. Preparation of Magnetic Immunoconjugates
2.4. Amperometric Measurements
2.5. Protein Extracts from Paired Non-Tumoral and Tumoral CRC Tissues and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reliability and Fine-Tuning of the Methodology
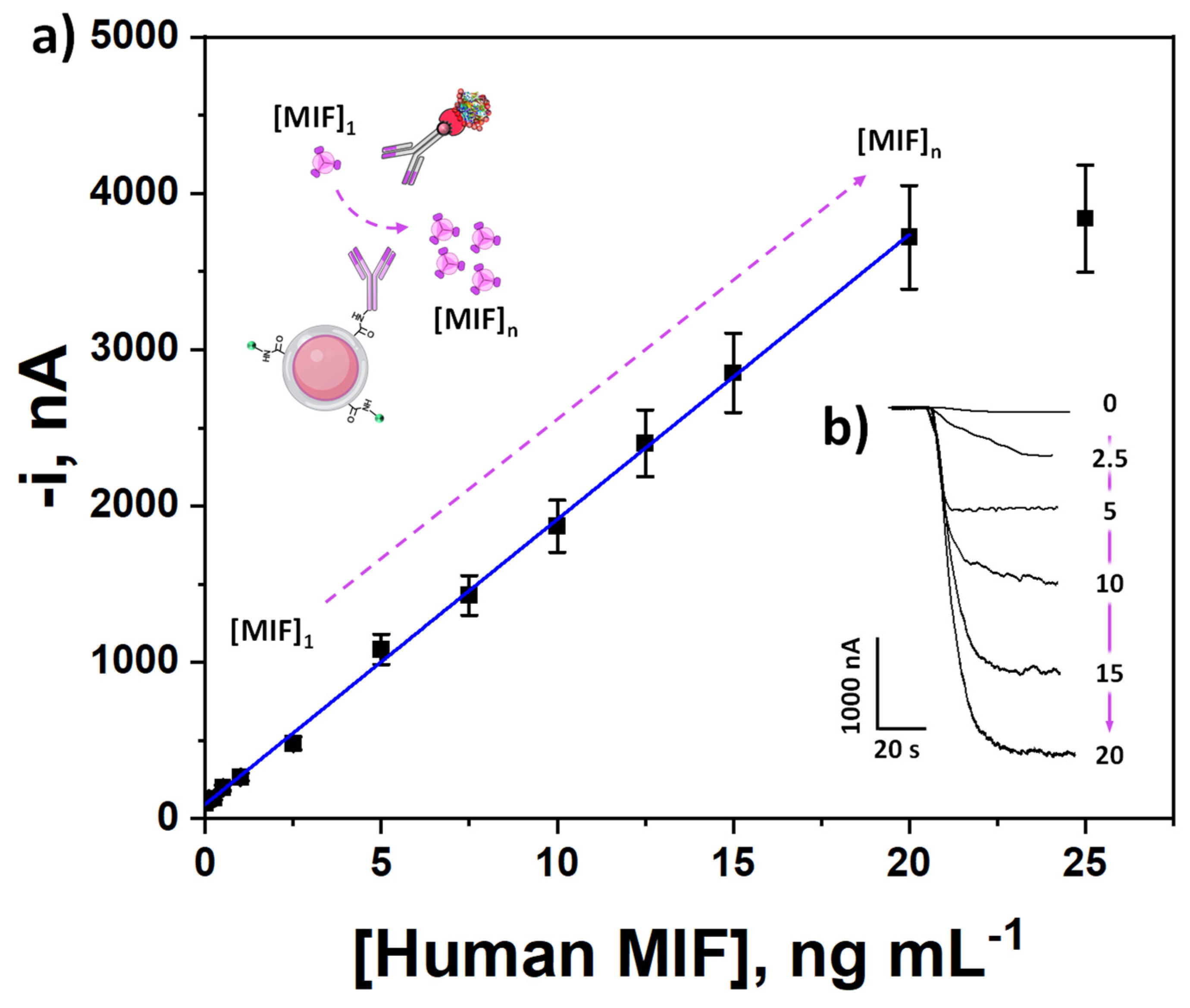
3.2. Analytical and Operational Performance
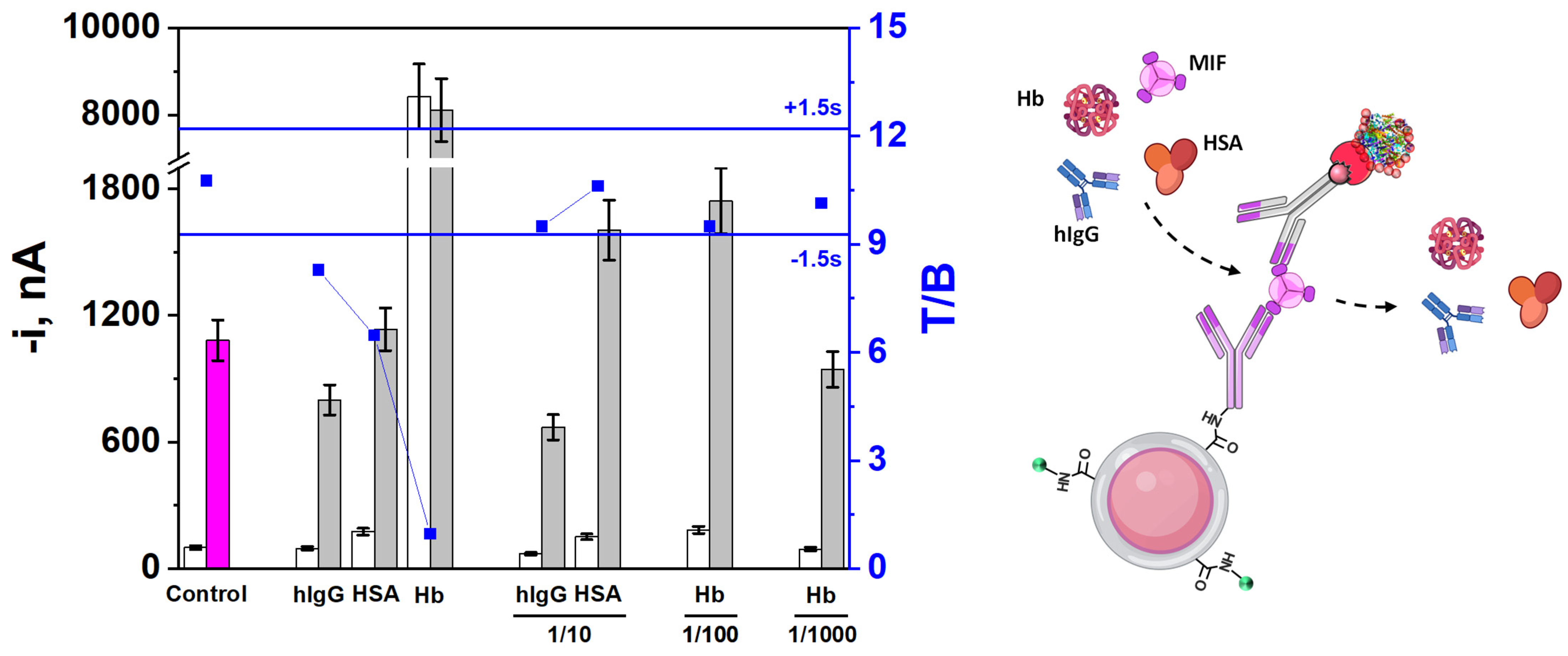
3.3. Selectivity
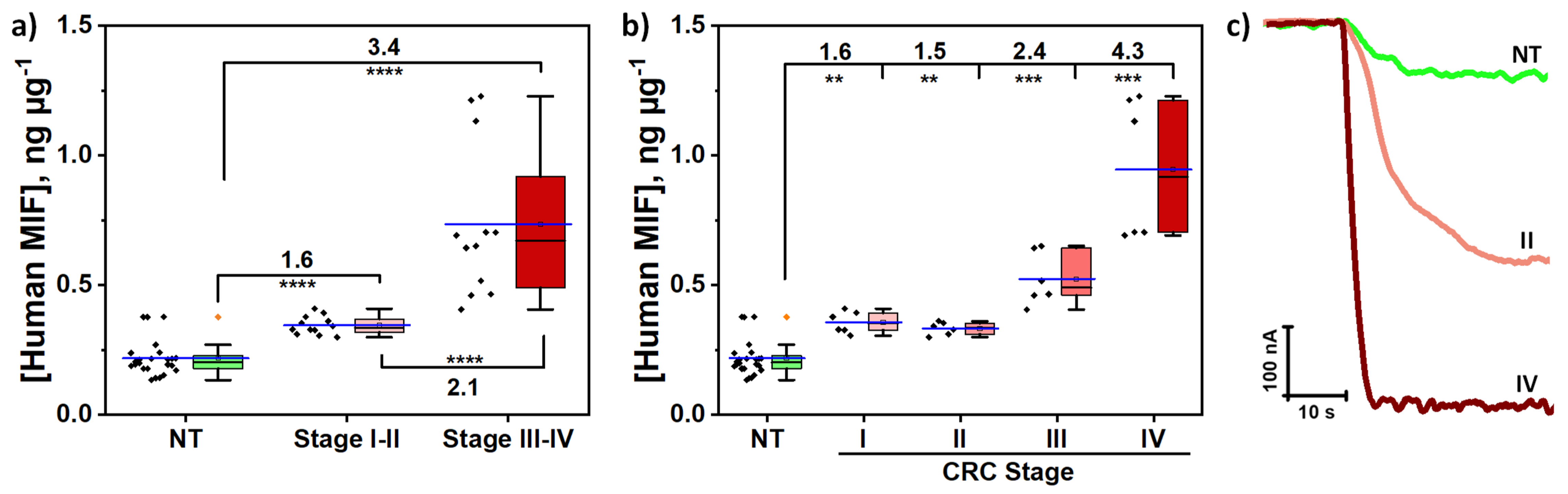
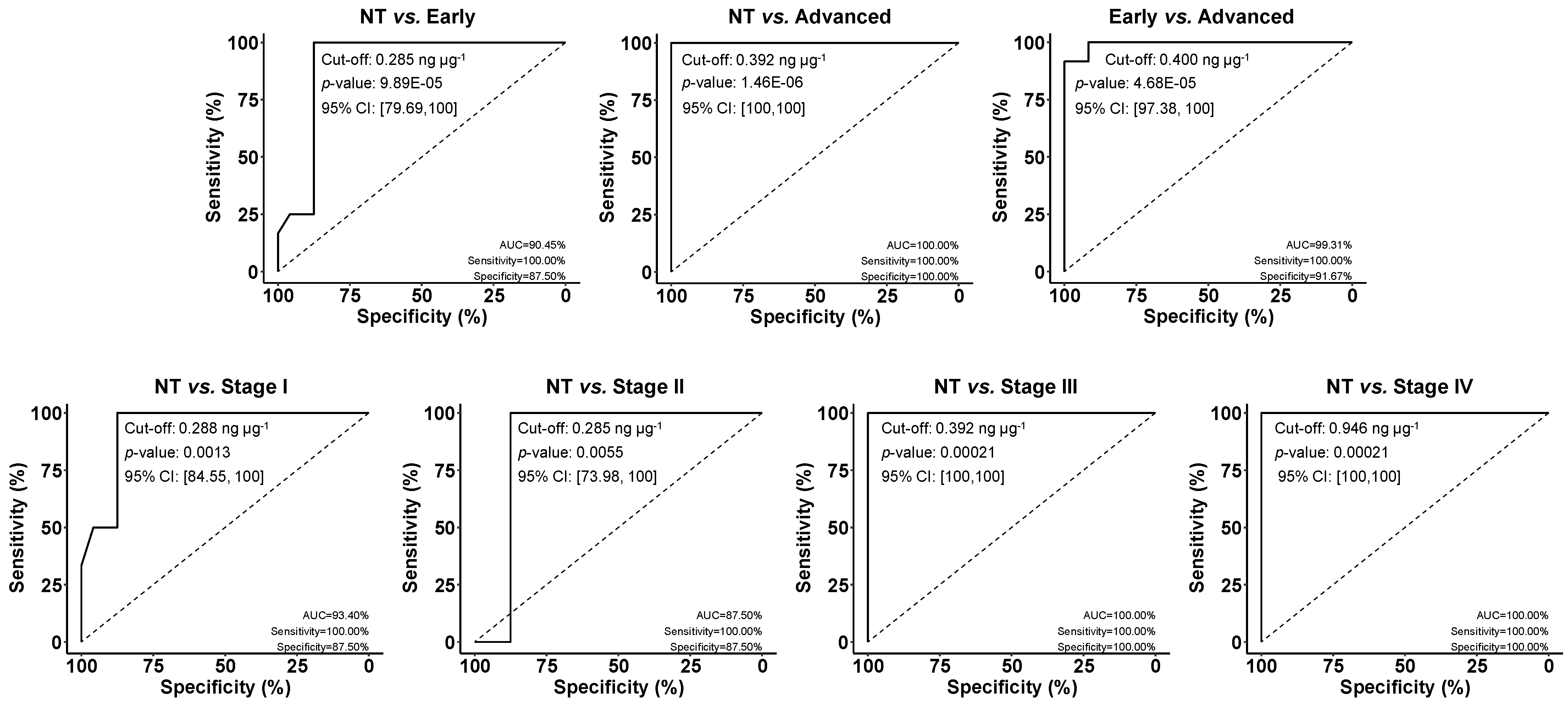
3.4. Analysis of Tissues of CRC Patients
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez-García, M.; Quinchia, J.; Ruíz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Serafín, V.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; García-Romero, A.; Orozco, J.; Barderas, R.; Pingarrón, J.M.; et al. Electroanalytical immunotool to determine matricellular protein periostin, a stromal biomarker of prognosis in colorectal cancer. ChemElectroChem 2024, 11, e202300641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlet, S.N.; Sanz-Pamplona, R.; Brix, S.; Leeming, D.J.; Karsdal, M.A.; Moreno, V. Excessive collagen turnover products are released during colorectal cancer progression and elevated in serum from metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. COL1A1: A potential therapeutic target for colorectal cancer expressing wild-type or mutant KRAS. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.-X.; Chen, K.; Yang, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Gan, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Coleman, T.R.; Al-Abed, Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes colorectal cancer. Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barjasteh, A.H.; AleKassar, R.J.M.; Al-Asady, A.M.; Latifi, H.; Avan, A.; Khazaei, M.; Ryzkikov, M.; Hassanian, S.M. Therapeutic potentials of miRNA for colorectal cancer liver metastasis treatment: A narrative review. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 50, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, R. COL1A1 promotes metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating the WNT/PCP pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5037–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Feng, J.; Fu, W.; Guo, Y. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) upregulates CXCR7 and contributes to chemotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 3437–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Zou, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Mechanisms of chemotherapeutic resistance and the application of targeted nanoparticles for enhanced chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Hou, H.; Liu, T.; Su, S.; Xi, X.; Liao, Y.; Xie, R.; Jin, G.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by interacting with transgelin in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8790–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Stein, R.M.; Aalbers, A.G.J.; Sonke, G.S.; van Driel, W.J. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for ovarian and colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, D.; Oki, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Yukami, H.; Mishima, S.; Bando, H.; Shirasu, H.; Yamazaki, K.; Watanabe, J.; Kotaka, M.; et al. Molecular residual disease and efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, B.E.; Willer, S.S.; Zundel, W.; Mitchell, R.A. Mechanisms of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF)-dependent tumor microenvironmental adaptation. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, J.T.; Mitchell, R.A. MIF-Dependent control of tumor immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 609948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaiya, K.; Langford, D.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Shanmughapriya, S. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): A multifaceted cytokine regulated by genetic and physiological strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, N.; Journe, F.; Laurent, G.; Saussez, S. Involvement of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cancer and novel therapeutic targets (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putha, L.; Kok, L.K.; Fellner, M.; Rutledge, M.T.; Gamble, A.B.; Wilbanks, S.M.; Vernall, A.J.; Tyndall, J.D.A. Covalent Isothiocyanate Inhibitors of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor as Potential Colorectal Cancer Treatments. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindt, N.; Preillon, J.; Kaltner, H.; Gabius, H.J.; Chevalier, D.; Rodriguez, A.; Johnson, B.D.; Megalizzi, V.; Decaestecker, C.; Laurent, G.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Clinical and experimental studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelmess, R.M.; Stijlemans, B.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Hallmarks of cancer affected by the MIF cytokine family. Cancers 2023, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, H.; Decaestecker, C.; Nagy, N.; Hendlisz, A.; Schüring, M.P.; Salmon, I.; Gabius, H.J.; Pector, J.C.; Kiss, R. Prognostic values of galectin-3 and the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human colorectal cancers. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemke, L.; De Oliveira, T.; Witt, D.; Winkler, N.; Bohnenberger, H.; Bucala, R.; Conradi, L.-C.; Schulz-Heddergott, R. Hsp90-stabilized MIF supports tumor progression via macrophage recruitment and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoori, A.; Gopalan, V.; Lu, C.-T.; Chua, T.C.; Morris, D.L.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K.-Y. Expression pattern of miR-451 and its target MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor) in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasasever, V.; Camlica, H.; Duranyildiz, D.; Oguz, H.; Tas, F.; Dalay, N. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cancer. Cancer Investig. 2007, 25, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Rhee, H.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Min, B.S.; Kim, N.K.; Kim, H. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor May Be Used as an Early Diagnostic Marker in Colorectal Carcinomas. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 129, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieb, G.; Merk, M.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): A promising biomarker. Drug News Perspect. 2010, 23, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzad, F.; Yaghoubi, N.; Avval, F.Z.; Khadem-Rezaiyan, M.; Azad, F.J.; Youssefi, M. Increasing levels of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in COVID-19 infection and its pathophysiological role; cut-off value determination might be clinically misleading. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 18, e133714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, F.; Zeng, M.; Wang, B.; Huang, S.; Chen, S.; Tao, Z. Targeted knockdown of macrophage migration inhibitory factor enhances UVB irradiation-induced apoptosis via increasing ROS generation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231163436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos-Navarro, G.; Del Toro-Arreola, A.; Daneri-Navarro, A.; Quintero-Ramos, A.; Bautista-Herrera, L.A.; Franco Topete, R.A.; Anaya-Macias, B.U.; Javalera-Castro, D.I.; de Jesús Morán-Mendoza, A.; Oceguera-Villanueva, A.; et al. Association of the genetic variants (-794 CATT5-8 and -173 G > C) of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) with higher soluble levels of MIF and TNFα in women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, A.; Sandin, S.I.; Knittel, J.; Franz, A.H.; Ren, J.; de Alba, E.; Pantouris, G. Underrepresented impurities in 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate affect the catalytic activity of multiple enzymes. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 4957–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, D.; Deng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, L. The Applications of electrochemical immunosensors in the detection of disease biomarkers: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, S.; Giannetto, M.; Giliberti, C.; Mattarozzi, M.; Bertucci, A.; Careri, M. Magnetic beads as versatile tools for electrochemical biosensing platforms in point-of-care testing. Anal. Sens. 2024, 4, e202300062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, C.; Cancelliere, R.; Ceccarelli, A.; Moscone, D.; Cozzi, L.; La Rosa, G.; Suffredini, E.; Micheli, L. Evaluation of an Enzyme-Linked Magnetic Electrochemical Assay for Hepatitis a Virus Detection in Drinking and Vegetable Processing Water. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Su, S.; Zhao, L.; Hu, C. Development of a novel method to measure macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis by combined electrochemical immunosensor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Z.; Hou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Shen, R.; et al. Development of MIF/IL-1β biosensors for discovery of critical quality attributes and potential allergic rhinitis targets from clinical real-world data by intelligent algorithm coupled with in vitro and vivo mechanism validation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Calle, A.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Poves, C.; Sanz, R.; Dziakova, J.; Peláez-García, A.; de los Ríos, V.; Martinez-Useros, J.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J.; Barderas, R. In-depth proteomic analysis of paraffin-embedded tissue samples from colorectal cancer patients revealed TXNDC17 and SLC8A1 as key proteins associated with the disease. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 4802–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Gaugaz, F.Z. Fast and sensitive total protein and peptide assays for proteomic analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4110–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, E.; Miglione, A.; Montero-Calle, A.; Cinti, S.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S. Electrochemical immunosensing of the neo-antigen collagen type I α 1 to assist in the personalized management of advanced colorectal cancer. Electroanalysis 2025, 37, e12052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, E.; Rejas-González, R.; Montero-Calle, A.; Arévalo, B.; Valverde, A.; Pastora-Salvador, N.; Crespo-Carballés, M.J.; Sánchez-Naves, J.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Barderas, R.; et al. Electrochemical immunosensing for rapid glaucoma disease diagnosis through simultaneous determination of SPP1 and GAS6 proteins in ocular fluids. Talanta 2026, 296, 128438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguílaz, M.; Moreno-Guzmán, M.; Campuzano, S.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. An electrochemical immunosensor for testosterone using functionalized magnetic beads and screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzuelo, F.; Gamella, M.; Campuzano, S.; Pinacho, D.G.; Reviejo, A.J.; Marco, M.P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable and integrated amperometric immunosensor for direct determination of sulfonamide antibiotics in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamella, M.; Campuzano, S.; Conzuelo, F.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Amperometric magnetoimmunosensors for direct determination of D-dimer in human serum. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Escamilla-Gómez, V.; Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Salvador, J.P.; Marco, M.P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Ultrasensitive amperometric magnetoimmunosensor for human C-reactive protein quantification in serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Valverde, A.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Peláez-García, A.; Mendiola, M.; et al. Versatile Electroanalytical bioplatforms for simultaneous determination of cancer-related DNA 5-methyl- and 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosines at global and gene-specific levels in human serum and tissues. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.H.-X.; Yang, Y.; Chu, K.-M.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; He, H.; Wong, M.W.; Leung, S.-Y.; Yuen, S.-T.; Yuen, M.-F.; et al. Serum macrophage migration-inhibitory factor as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer. Cancer 2009, 115, 5441–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, F.; Cao, Y.; Qin, J. Construction of “Coral” SERS sensor for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of harmful component macrophage migration inhibitory factor in Platelet-rich Plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 242, 115718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-D.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.-P.; Ye, X.; Wang, H.; Deng, A.-M.; Kong, J.-L. An ultrasensitive polydopamine bi-functionalized SERS immunoassay for exosome-based diagnosis and classification of pancreatic cancer. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 5372–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.rndsystems.com/products/human-mif-quantikine-elisa-kit_dmf00b#product-datasheets (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.rndsystems.com/products/human-mif-duoset-elisa_dy289#product-details (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.raybiotech.com/human-mif-elisa-elh-mif (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.biolegend.com/en-gb/products/legend-max-human-active-mif-elisa-kit-with-pre-coated-plates-7510?GroupID=GROUP21 (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Available online: https://www.fishersci.es/shop/products/mif-human-elisa-kit-4/p-7231032 (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Melanson, S.E.F.; Tanasijevic, M.J.; Jarolim, P. Cardiac troponin assays. Circulation 2007, 116, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshida, S.; Asanuma, K.; Kuribayashi, K.; Goto, M.; Tsuji, N.; Kobayashi, D.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, N. Prevalence of human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMAs) in routine examinations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, A.; Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical immunosensor for IL-13 receptor α2 determination and discrimination of metastatic colon cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, B.; Blázquez, M.; Serafín, V.; Montero-Calle, A.; Calero, M.; Valverde, A.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Unraveling autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases by amperometric serological detection of antibodies against aquaporin-4. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 144, 108041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejerina-Miranda, S.; Pérez-Ginés, V.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S. Magneto-controlled electrochemical immunosensing platform to assess the senescence-associated GDF-15 marker in colorectal cancer. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Kuribayashi, K.; Umemori, Y.; Ohe, Y.; Asanuma, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Watanabe, N. High prevalence of human anti-mouse antibodies in the serum of colorectal cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4353–4356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grigorieva, D.V.; Gorudko, I.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Kosmachevskaya, O.V.; Topunov, A.F.; Buko, I.V.; Konstantinova, E.E.; Cherenkevich, S.N.; Panasenko, O.M. Measurement of plasma hemoglobin peroxidase activity. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 155, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.-N.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Jia, L.-P.; Ma, R.-N.; Zhang, W.; Shang, L.; Xue, Q.-W.; Wang, H.-S. A sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for Mucin 1 detection based on catalytic hairpin assembly coupled with PtPdNPs peroxidase-like activity. Talanta 2019, 200, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Pérez-Ginés, V.; Camps, J.; Arenas, M.; Barderas, R.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Campuzano, S. Anticipating metastasis through electrochemical immunosensing of tumor hypoxia biomarkers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.M.; Estévez-Pérez, M.G. Statistical comparison of the slopes of two regression lines: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 838, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.T.L.; Chang, S.C.; Ke, T.W.; Chiang, H.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Lo, W.Y. Identification of biomarkers to improve diagnostic sensitivity of sporadic colorectal cancer in patients with low preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen by clinical proteomic analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, B.E.; Roger, T.; Teneng, I.; Zhao, M.; AlAbed, Y.; Calandra, T.; Mitchell, R.A. Regulation of human lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and invasion by macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29910–29918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans, E.; Noetzel, E.; Bektas, N.; Schütz, A.K.; Lue, H.; Lennartz, B.; Hartmann, A.; Dahl, E.; Bernhagen, J. Dual role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, V.; Kindt, N.; Decaestecker, C.; Gabius, H.J.; Laurent, G.; Noël, J.C.; Saussez, S. Involvement of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptor (CD74) in human breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Li, W.; He, M. Macrophage immigration inhibitory factor promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of cervical adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5095–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Vecchio, M.T.; Tripodi, S.A.; Arcuri, F.; Pergola, L.; Hako, L.; Vatti, R.; Cintorino, M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in prostatic adenocarcinoma: Correlation with tumor grading and combination endocrine treatment-related changes. Prostate 2000, 45, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MeyerSiegler, K.L.; Iczkowski, K.A.; Leng, L.; Bucala, R.; Vera, P.L. Inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor or its receptor (CD74) attenuates growth and invasion of DU-145 prostate cancer cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8730–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.J.; Xie, D.; Hu, P.J.; Liao, Y.J.; Deng, H.X.; Kung, H.F.; Zhu, S.L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a potential prognostic factor in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 9916–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


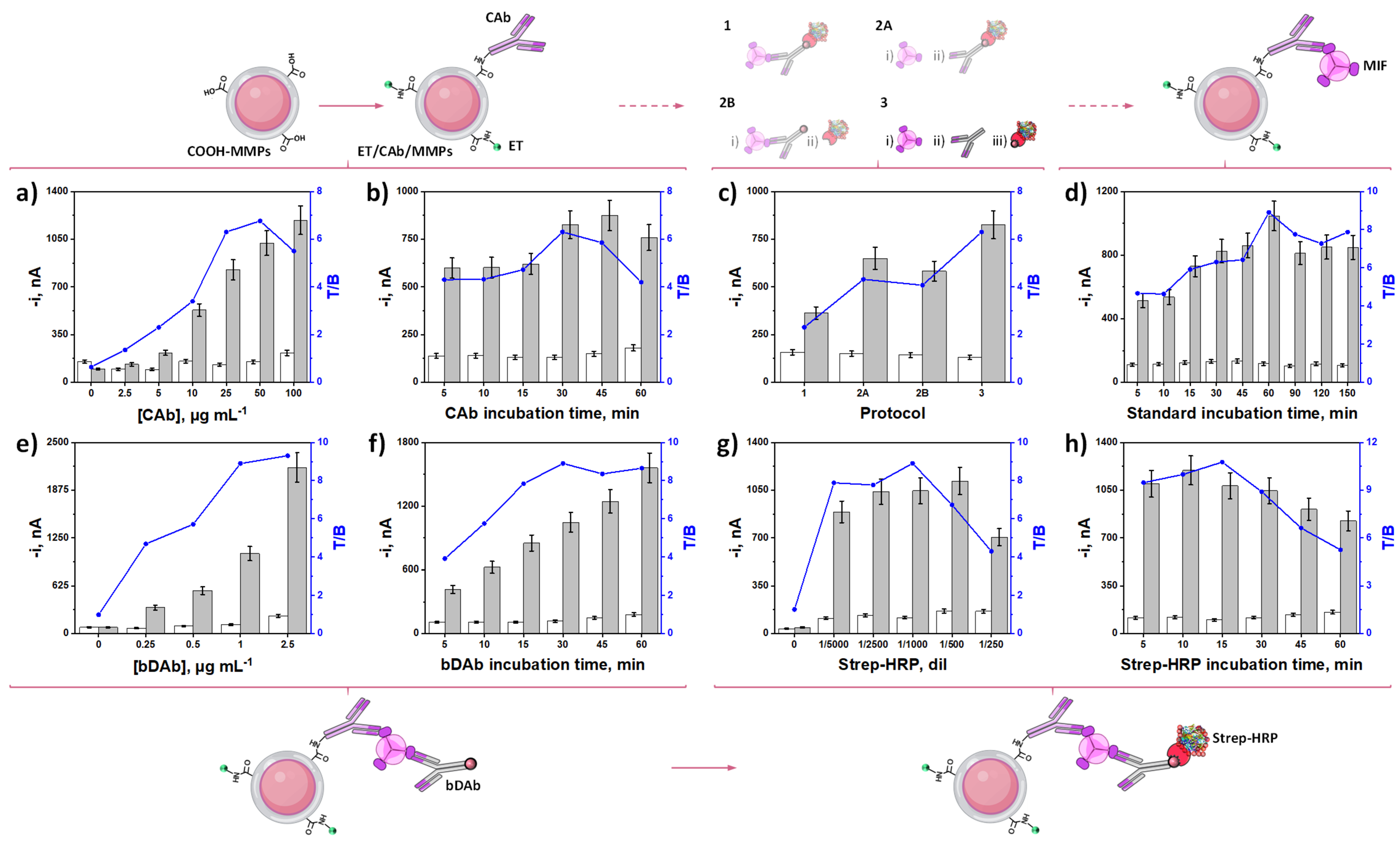
| Protocol | Steps 1 | Total Assay Time, min 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | i: MIF + bDAb + Strep-HRP | 30 |
| 2A | i: MIF; ii: bDAb + Strep-HRP | 60 |
| 2B | i: MIF + bDAb; ii: Strep-HRP | 60 |
| 3 | i: MIF; ii: bDAb; iii: Strep-HRP | 90 |
| Variable | Evaluated Range | Selected Value |
|---|---|---|
| [CAb], µg mL−1 | 0.0–100.0 | 25.0 |
| CAbi-t 1, min | 5–60 | 30 |
| Protocol | 1–3 | 3 |
| MIFi-t 1, min | 5–150 | 60 |
| [bDAb], µg mL−1 | 0.0–2.5 | 1.0 |
| bDAbi-t 1, min | 5–60 | 30 |
| Strep-HRP, dil | 0–1/250 | 1/1000 |
| Strep-HRPi-t 1, min | 5–60 | 15 |
| Detection Strategy | Technique | Lineal Range (ng mL−1)/ LOD (ng mL−1) | Assay Preparation Time | Storage Stability, Days | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au electrode modified with AuNPs/TiO2 NPs/thionine/IgM monoclonal antibodies | Differential pulse voltammetry | 0.03–230/ 0.02 | 12 h 10 min | 30 | Serum samples of rheumatoid arthritis patients | [33] |
| HEMT | Change in drain–source current upon analyte binding due to surface charge variation | 0.018–180/ 0.018 | 2 h + chip preparation | -- | Allergic rhinitis samples | [34] |
| Dopamine-coated Ab-Au (core)-Ag (shell)-SERS sensor | SERS | 1–5000/ 0.09 | 6 h 30 min | 7 | Platelet-rich plasma of osteoarthritis | [45] |
| Polydopamine-immunocapture substrate and polydopamine-encapsulated Ab-Ag(shell)/Au(core) multilayer SERS tags | SERS | 5.44 × 102–2.72 × 104 particles mL−1/ 1 exosome in 2 mL of sample solution (~9 × 10−19 mol L−1) | 9 h | 182 | Pancreatic cancer serum samples | [46] |
| Sandwich immunoassay based on magnetic microparticles | Amperometry | 0.24–20/ 0.07 | 1 h 45 min | 38 | Tissue extracts of CRC patients | This work |
| Slope, nA mL ng−1 | texp 1 | ttab 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | 182 ± 4 | -- | -- | |
| Tissue extract | NT (IV) | 206 ± 41 | 1.8 | 2.8 |
| T (IV) | 190 ± 20 | 0.9 | 2.8 | |
| NT 1 | T 1 | T/NT Ratio | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | CRC Stage | 2 [MIF], ng µg−1 | RSD(n=3), % | 2 [MIF], ng µg−1 | RSD(n=3), % | Patient | CRC Stage | EarlyI–II/AdvancedIII–IV Stages vs. NT |
| 1 | I | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 11.1 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 4.0 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| 2 | 0.377 ± 0.001 | 0.1 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 4.0 | 1.0 | |||
| 3 | II | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 3.5 | 0.34 ± 0.07 | 8.0 | 2.4 | 2.2 | |
| 4 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 8.6 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 6.8 | 1.9 | |||
| 5 | III | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 5.4 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 12.5 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 3.4 |
| 6 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 4.1 | 0.44 ± 0.08 | 7.4 | 2.1 | |||
| 7 | IV | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 6.5 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 4.4 | 6.3 | 4.8 | |
| 8 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 11.7 | 0.70 ± 0.02 | 1.0 | 3.3 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Povedano, E.; Carbonaro, A.-B.; Serafín, V.; Gamella, M.; Giuffrida, A.; Montero-Calle, A.; Pingarrón, J.M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S. Electrochemical Tracking of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor: A Leap Toward Precision Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Biosensors 2025, 15, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110739
Povedano E, Carbonaro A-B, Serafín V, Gamella M, Giuffrida A, Montero-Calle A, Pingarrón JM, Barderas R, Campuzano S. Electrochemical Tracking of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor: A Leap Toward Precision Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Biosensors. 2025; 15(11):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110739
Chicago/Turabian StylePovedano, Eloy, Antonino-Biagio Carbonaro, Verónica Serafín, María Gamella, Alessandro Giuffrida, Ana Montero-Calle, José Manuel Pingarrón, Rodrigo Barderas, and Susana Campuzano. 2025. "Electrochemical Tracking of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor: A Leap Toward Precision Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis" Biosensors 15, no. 11: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110739
APA StylePovedano, E., Carbonaro, A.-B., Serafín, V., Gamella, M., Giuffrida, A., Montero-Calle, A., Pingarrón, J. M., Barderas, R., & Campuzano, S. (2025). Electrochemical Tracking of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor: A Leap Toward Precision Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Biosensors, 15(11), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110739








