Visible-Light Hyperspectral Reconstruction and PCA-Based Feature Extraction for Malignant Pleural Effusion Cytology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
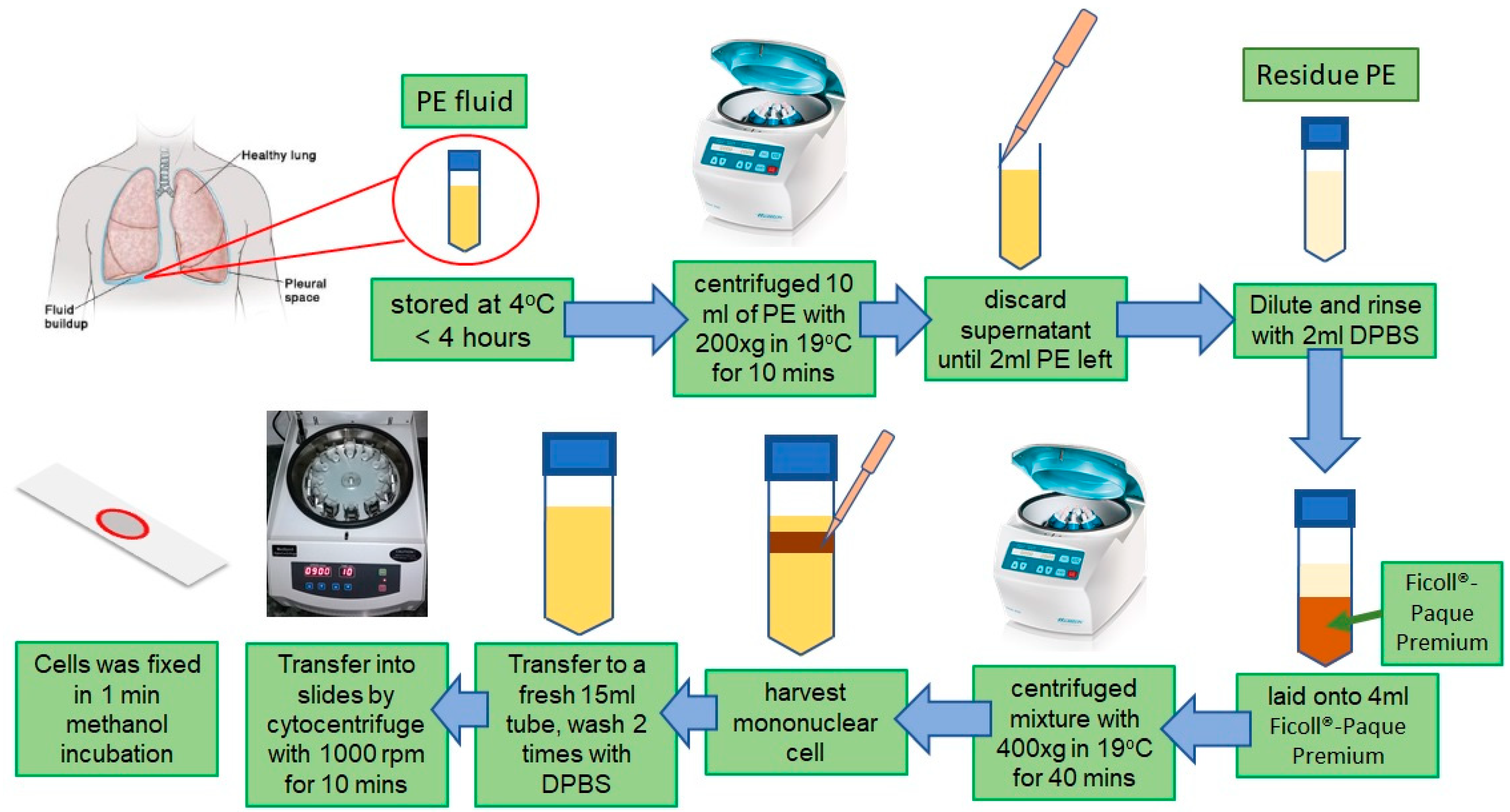
2.1. Sample Preparation
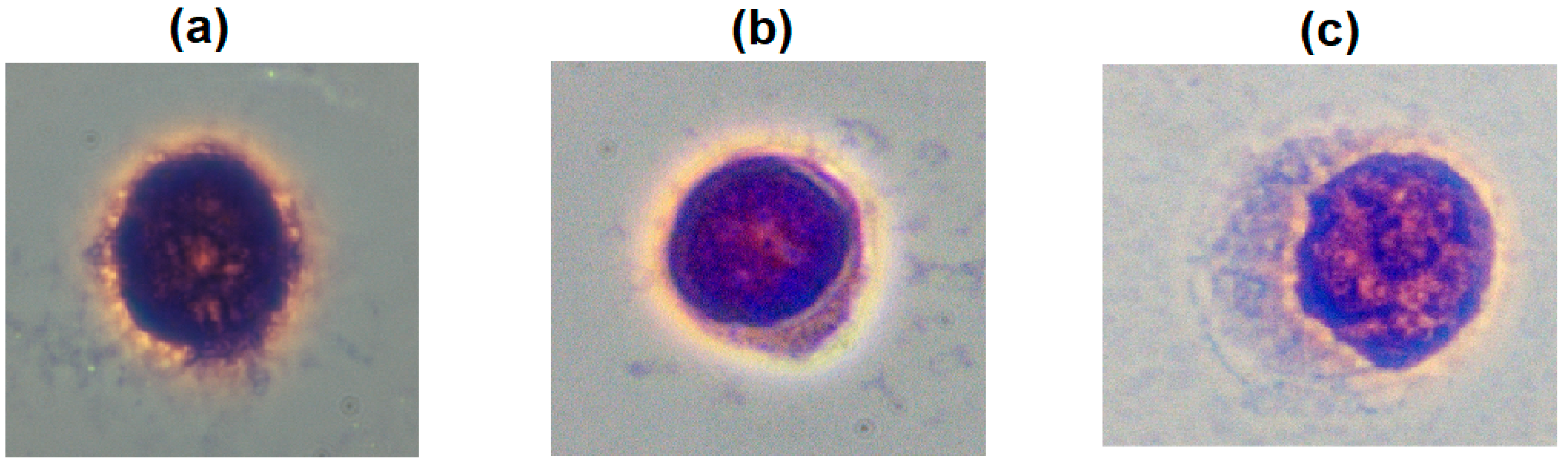
2.2. Cells Validation Under Microscopy
2.3. Visible-Light Spectrum Imaging Technology (VIS-HSI)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Discussion on the Intensity of the Average Spectra
3.2. Optimization of Filter Arrays in HSI Model’s Accuracy
3.3. Classification Types of Cells by PCA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shidham, V.B.; Atkinson, B.F. Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Serous Fluids; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; p. 269. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Xia, D. A technique based on wavelet and morphology transform to recognize the cancer cell in pleural effusion. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Medical Imaging and Augmented Reality, Hong Kong, China, 10–12 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, V.-T.; Lézoray, O.; Elmoataz, A.; Schüpp, S. Graph-based tools for microscopic cellular image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.Y.; Choomchuay, S. Automated segmentation of cell nuclei in cytology pleural fluid images using OTSU thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology (ICDAMT), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 1–4 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, B.; Liu, H. Optical and digital microscopic imaging techniques and applications in pathology. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2011, 34, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykal, E.; Dogan, H.; Ekinci, M.; Ercin, M.E.; Ersoz, S. Automated nuclei detection in serous effusion cytology based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, Turkey, 15–18 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baykal, E.; Dogan, H.; Ercin, M.E.; Ersoz, S.; Ekinci, M. Modern convolutional object detectors for nuclei detection on pleural effusion cytology images. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 15417–15436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, A.; Yamada, A.; Kiriyama, Y.; Tsukamoto, T.; Yan, K.; Zhang, L.; Imaizumi, K.; Saito, K.; Fujita, H. Automated classification of benign and malignant cells from lung cytological images using deep convolutional neural network. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2019, 16, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.E.; Wabuyele, M.B.; Chen, K.; Kasili, P.; Panjehpour, M.; Phan, M.; Overholt, B.; Cunningham, G.; Wilson, D.; DeNovo, R.C.; et al. Development of an advanced hyperspectral imaging (HSI) system with applications for cancer detection. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 34, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyotoki, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Okamoto, T.; Hamabe, K.; Saito, M.; Goto, A.; Fujita, Y.; Hamamoto, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Satori, S.; et al. New method for detection of gastric cancer by hyperspectral imaging: A pilot study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 026010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. Tumor tissue classification based on micro-hyperspectral technology and deep learning. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 6370–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.J. Diagnostic tools of pleural effusion. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2014, 76, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.; Chaudhuri, A.D.; Datta, S.B.S.; Dey, A.; Bhanja, P. Role of pleural biopsy in etiological diagnosis of pleural effusion. Lung India 2010, 27, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, B.; Sharma, S.K.; Negi, R.S.; Gupta, N.; Jaswal, V.M.S.; Niranjan, N. Pleural effusion: Role of pleural fluid cytology, adenosine deaminase level, and pleural biopsy in diagnosis. J. Cytol. 2016, 33, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffner, J.E.; Klein, J.S. Recent advances in the diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions. Mayo Clinic Proc. 2008, 83, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.E.; Bell, A.A.; Meyer-Ebrecht, D.; Böcking, A.; Aach, T. Computer-aided cytological cancer diagnosis: Cell type classification as a step towards fully automatic cancer diagnostics on cytopathological specimens of serous effusions. In Medical Imaging 2007: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 29 March 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.R. Computational Color Technology (SPIE Press Monograph Vol. PM159); SPIE-International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, M.; Anderson, M.; Chandrasekar, S.; Motta, R. A Standard Default Color Space for the Internet—sRGB. Available online: http://www.color.org/sRGB.xalter (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Đorđević, D.; Hladnik, A.; Javoršek, A. Performance of five chromatic adaptation transforms using large number of color patches. Acta Graph. Znan. časopis Tisk. Graf. Komun. 2009, 20, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.; Guild, J. The CIE colorimetric standards and their use. Trans. Opt. Soc. 1931, 33, 73–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, I.; Bildirici, I.O.; Yakar, M.; Yildiz, F. Color Calibration of Scanners Using Polynomial Transformation. In XXth ISPRS Congress Commission V; ISPRS Congress Commission V: Istanbul, Turkey, 2004; pp. 890–896. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, A. Regression and the Moore-Penrose Pseudoinverse; Department of Mathematics, Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, L.; Green, P. Colour Engineering: Achieving Device Independent Colour; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jen, C.-P.; Huang, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-S.; Kuo, C.-T.; Wang, H.-C. Diagnosis of human bladder cancer cells at different stages using multispectral imaging microscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, R.W.; Erozan, Y.S.; Ball, W.C. Cells in pleural fluid. Their value in differential diagnosis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1973, 132, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauers, J.; Aach, T. A color filter array based multispectral camera. In 12. Workshop Farbbildverarbeitung; Brauers and Aach: Ilmenau, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Monno, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Tanaka, M.; Okutomi, M. A practical one-shot multispectral imaging system using a single image sensor. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3048–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Q. spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. The generalization of Student’s ratio. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, J.J.; Xin, J.C.Y.; Zhang, S.; Olivo, M. Label-Free Pathology Imaging with Multimodal Hyperspectral Microscopy for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. In Biophotonics Congress: Biomedical Optics 2022 (Translational, Microscopy, OCT, OTS, BRAIN); Optica Publishing Group: Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, C.; Ran, T.; Pan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, T.; Zhang, B.; et al. A deep learning model using hyperspectral image for EUS-FNA cytology diagnosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 17005–17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



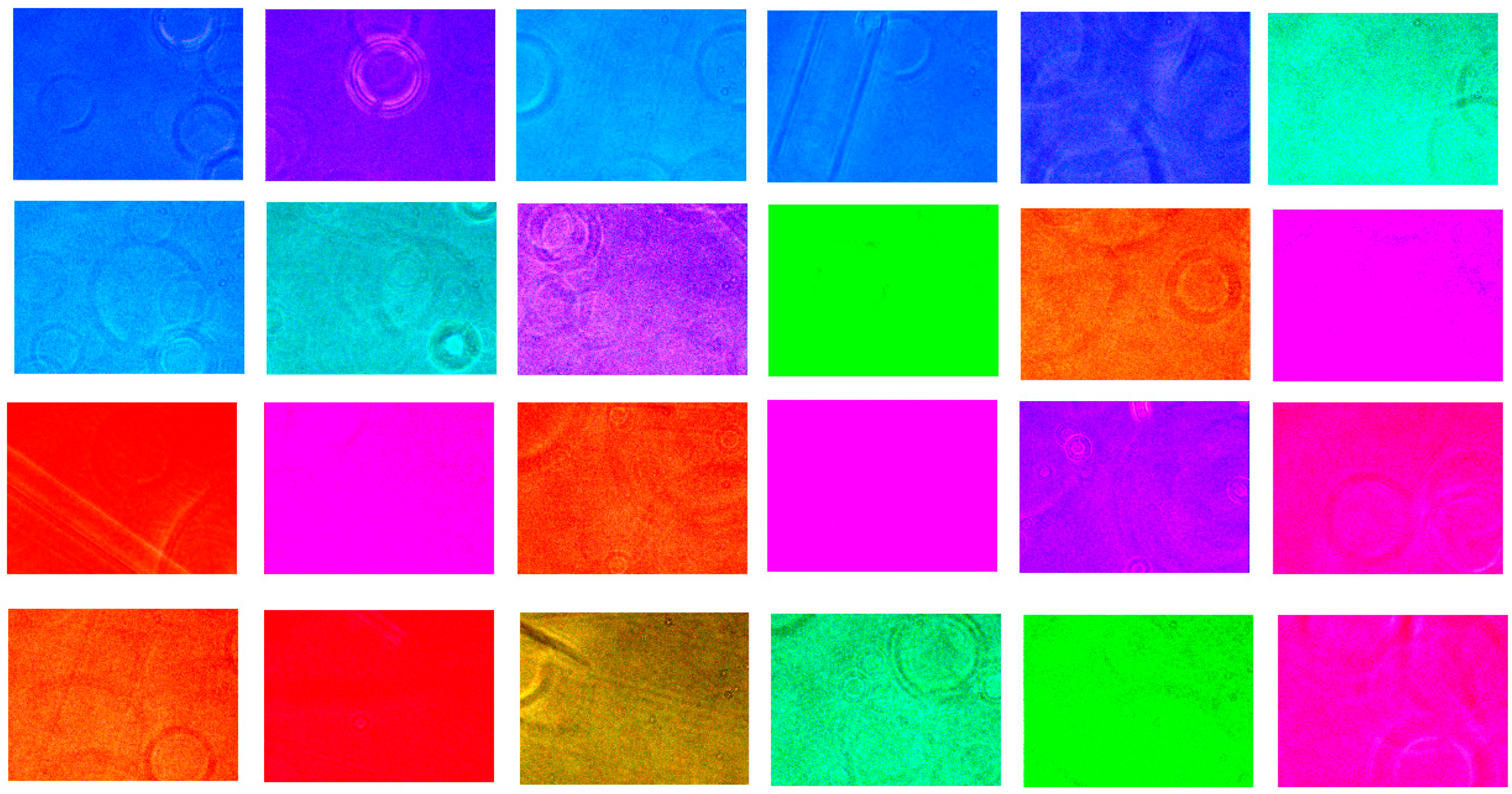

| Test Spectrum | RGB Filter | Braiers et al. [26] | Monno et al. [27] | Random 24 Color Filter | Magenta and Blue Tone 24 Color Filter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum 1 | 0.03626 | 0.03728 | 0.03729 | 0.03729 | 0.03730 |
| Spectrum 2 | 0.03602 | 0.03610 | 0.03610 | 0.03610 | 0.03610 |
| Spectrum 3 | 0.03780 | 0.03788 | 0.03789 | 0.03790 | 0.03791 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-L.; Lee, K.-H.; Nguyen, H.-T.; Mukundan, A.; Karmakar, R.; Chen, T.-H.; Lin, W.-S.; Wang, H.-C. Visible-Light Hyperspectral Reconstruction and PCA-Based Feature Extraction for Malignant Pleural Effusion Cytology. Biosensors 2025, 15, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110714
Lai C-L, Lee K-H, Nguyen H-T, Mukundan A, Karmakar R, Chen T-H, Lin W-S, Wang H-C. Visible-Light Hyperspectral Reconstruction and PCA-Based Feature Extraction for Malignant Pleural Effusion Cytology. Biosensors. 2025; 15(11):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Chun-Liang, Kun-Hua Lee, Hong-Thai Nguyen, Arvind Mukundan, Riya Karmakar, Tsung-Hsien Chen, Wen-Shou Lin, and Hsiang-Chen Wang. 2025. "Visible-Light Hyperspectral Reconstruction and PCA-Based Feature Extraction for Malignant Pleural Effusion Cytology" Biosensors 15, no. 11: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110714
APA StyleLai, C.-L., Lee, K.-H., Nguyen, H.-T., Mukundan, A., Karmakar, R., Chen, T.-H., Lin, W.-S., & Wang, H.-C. (2025). Visible-Light Hyperspectral Reconstruction and PCA-Based Feature Extraction for Malignant Pleural Effusion Cytology. Biosensors, 15(11), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15110714







