Development of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Caffeine Quantification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
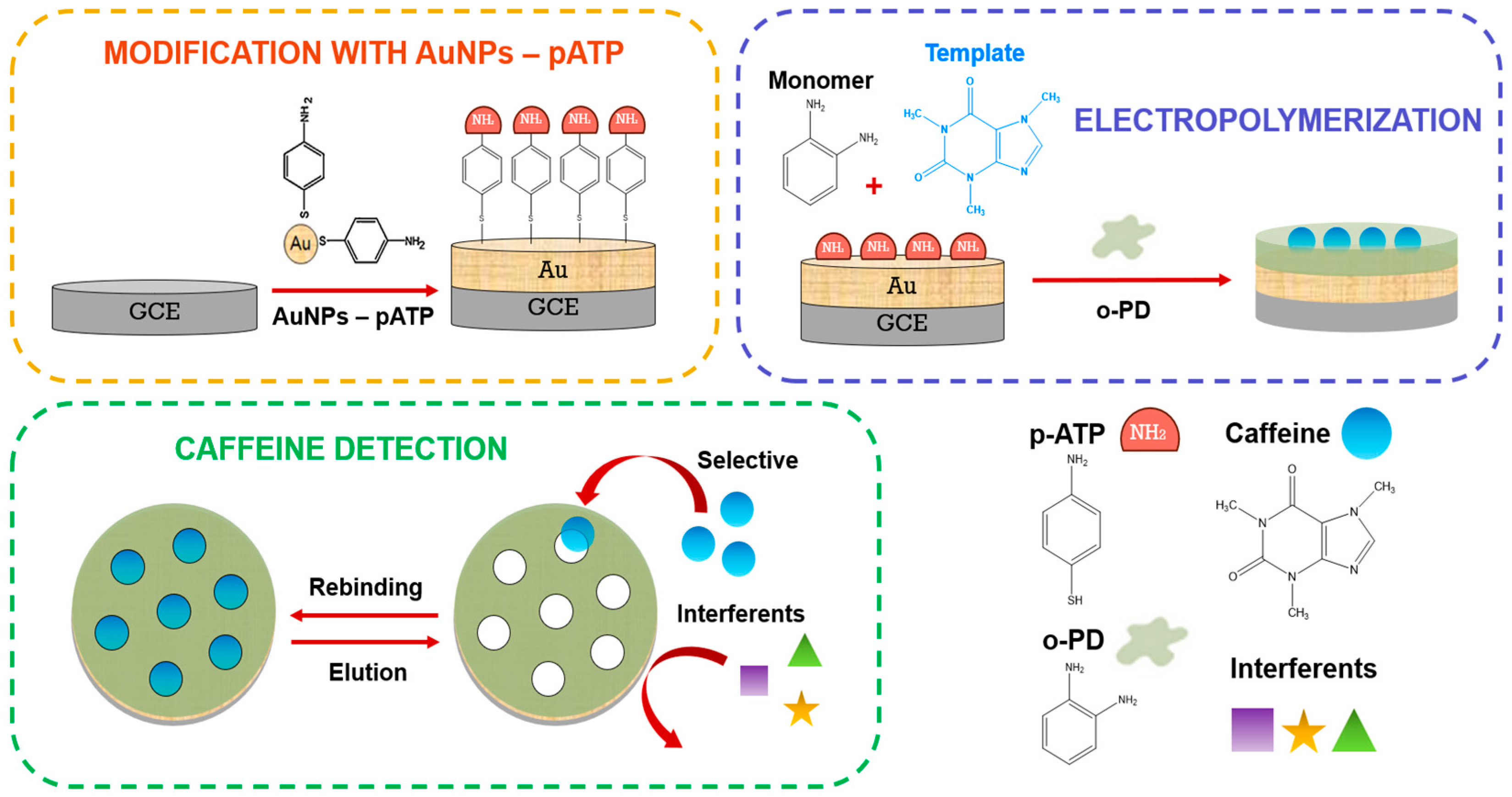
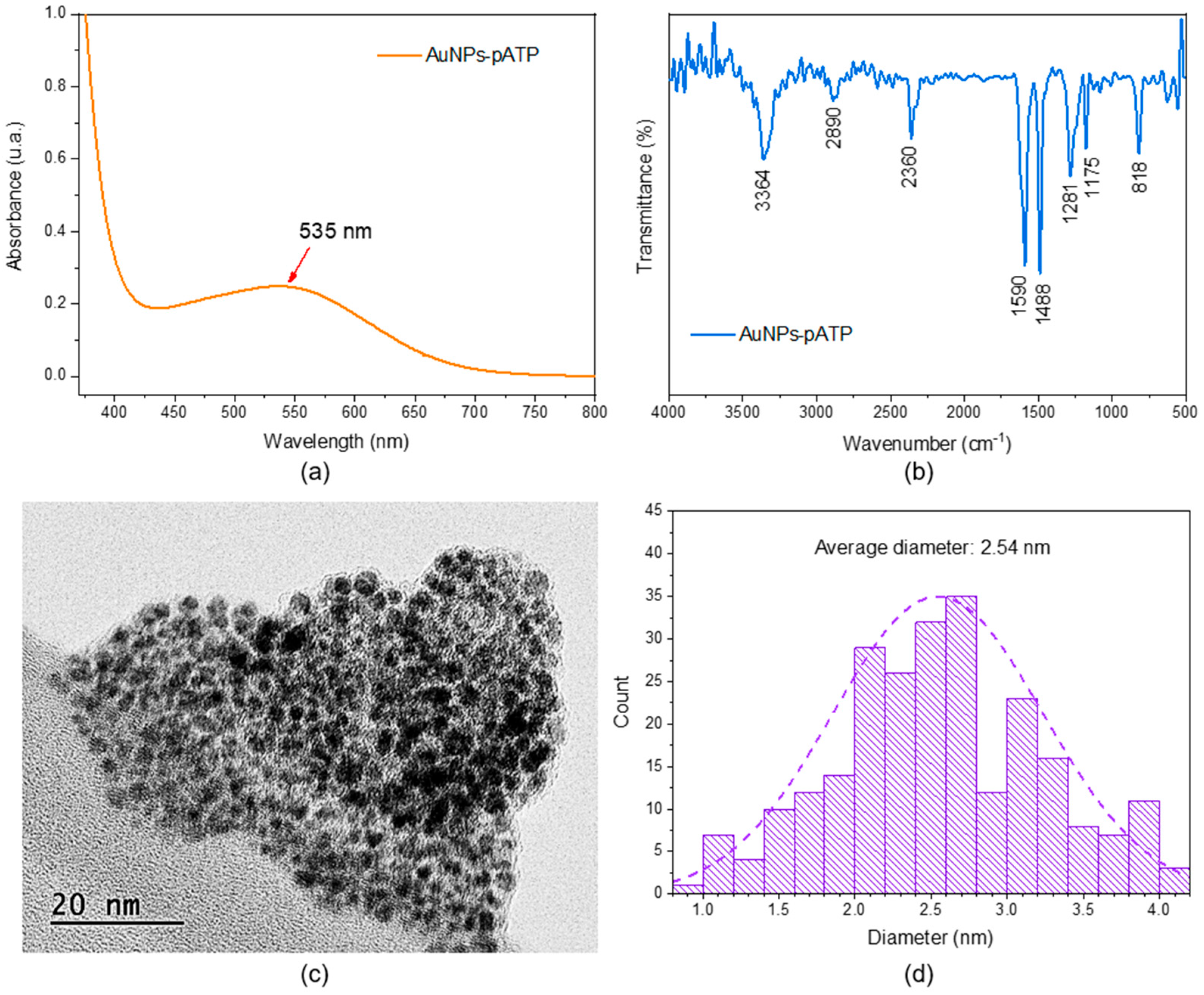
2.2. Synthesis of pATP-Functionalized AuNPs
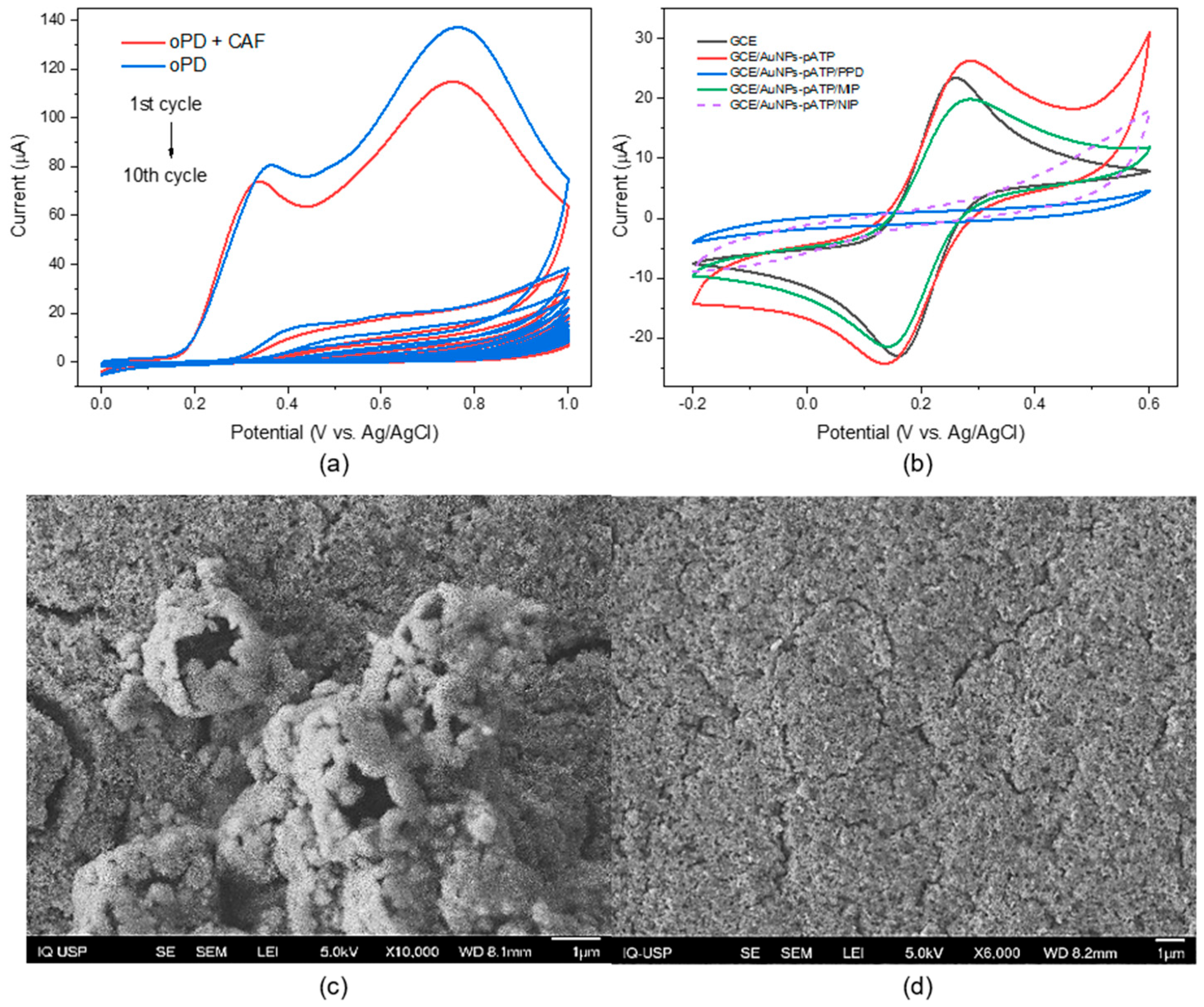
2.3. Caffeine–MIP Electrochemical Sensor Fabrication
2.4. Quantification of Caffeine Using the Caffeine–MIP Electrochemical Sensor
2.5. Quantification of Caffeine Using HPLC
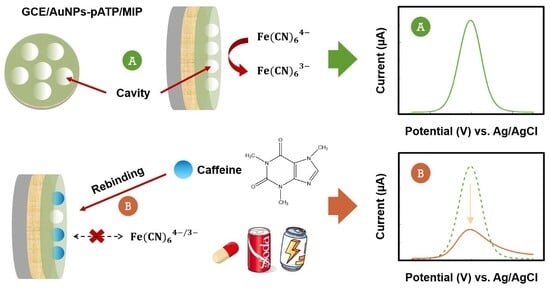
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization Experiments
3.2. Caffeine Sensor Modification
3.3. Optimization of Parameters
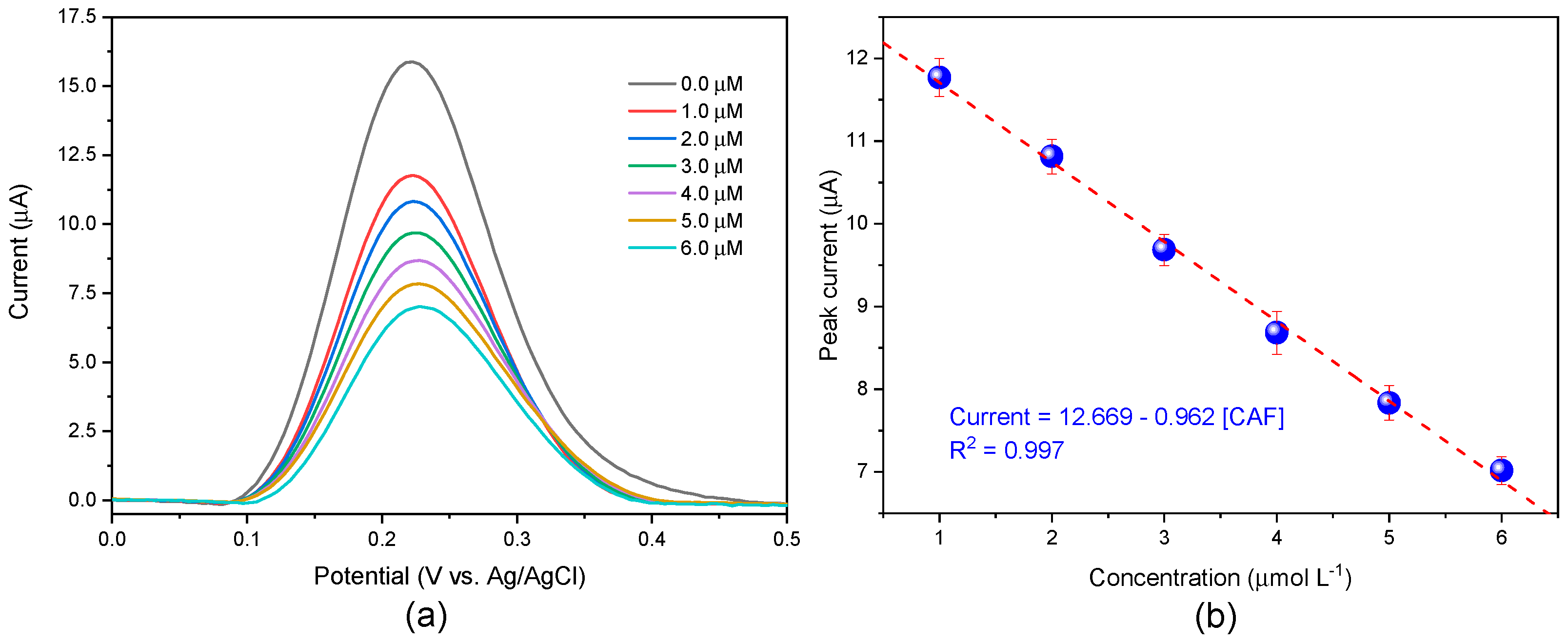
3.4. Detection of Caffeine (CAF)
3.5. Selectivity, Reuse, Reproducibility, and Stability
3.6. Detection of CAF in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAF | Caffeine |
| MIP | Molecularly Imprinted Polymer |
| NIP | Non Imprinted Polymer |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| oPD | o-Phenylendiamine |
| pATP | p-Aminothiophenol |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| SWV | Square Wave Voltammetry |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
References
- Urrialde, R. Caffeine. In Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition, 4th ed.; Caballero, B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 1–4, pp. 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Boroujeni, M.K.; Ensafi, A.A. Caffeine electrochemical sensor using imprinted film as recognition element based on polypyrrole, sol-gel, and gold nanoparticles hybrid nanocomposite modified pencil graphite electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, N.O.; Goldner, D.M.B.; Masini, J.C. Bentonite-modified glassy carbon electrode for the voltammetric determination of caffeine in beverages. Food Chem. 2025, 492, 145306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrych, M. Caffeine. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 4th ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; Volume 2, pp. 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.C.; Barsan, M.M.; Brett, C.M. Simple electrochemical sensor for caffeine based on carbon and Nafion-modified carbon electrodes. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G. Caffeine Electrochemical Sensor Constructed by Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Mini-review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2023, 19, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švorc, Ľ. Determination of Caffeine: A Comprehensive Review on Electrochemical Methods. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 5755–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.; Hu, Y.; Wen, L.; Ding, L.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Y.; Yao, L.; Xu, Z. Magnetic relaxation switching sensor based on self-generated porous Fe3O4 with controllable apparent diffusion coefficient for highly sensitive detection of caffeine. Talanta 2025, 294, 128230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckman, M.A.; Weil, J.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Caffeine (1, 3, 7-trimethylxanthine) in Foods: A Comprehensive Review on Consumption, Functionality, Safety, and Regulatory Matters. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R77–R87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; An, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q. Development of an electrochemical device based on aptasensors for the determination of caffeine in beverages. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.S.; Silva, C.F.; de Oliveira, H.L.; Dinali, L.A.F.; Nascimento, C.S.; Borges, K.B. Microextraction by packed molecularly imprinted polymer to selectively determine caffeine in soft and energy drinks. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wen, J.; He, B.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, J. Occurrence of caffeine in the freshwater environment: Implications for ecopharmacovigilance. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geravi, H.A.; Ghaemy, M. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for selective adsorption of caffeine using dual-functionalized Ag2S quantum dots. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 680, 132735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajeu, K.Y.; Ymele, E.; Jiokeng, S.L.Z.; Tonle, I.K. Electrochemical Sensor for Caffeine Based on a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with an Attapulgite/Nafion Film. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaidarova, L.G.; Chelnokova, I.A.; Koryakovtseva, D.A.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Budnikov, H.C. Voltammetric Determination of Caffeine in Energy Drinks Using an Electrode Modified with a Nafion Film and Mixed-Valence Iridium Oxides. J. Anal. Chem. 2024, 79, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkadesh, A.; Mathiyarasu, J.; Radhakrishnan, S. Voltammetric Sensing of Caffeine in Food Sample Using Cu-MOF and Graphene. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszczuk-Rotko, K.; Bęczkowska, I. Nafion covered lead film electrode for the voltammetric determination of caffeine in beverage samples and pharmaceutical formulations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsharara, H.; Asadian, E.; Mostafiz, B.; Banan, K.; Bigdeli, S.A.; Hatamabadi, D.; Keshavarz, A.; Hussain, C.M.; Keçili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorpeh, F. Molecularly imprinted polymer-modified carbon paste electrodes (MIP-CPE): A review on sensitive electrochemical sensors for pharmaceutical determinations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, D. Electrochemical detection of caffeine in sports drinks based on molecular imprinting technology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 3577–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Zare, M.; Norouzi, P. Development of a voltammetric sensor based on a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for caffeine measurement. Electrochimica Acta 2010, 55, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polyscopoletin for the Electrochemical Detection of the Chronic Disease Marker Lysozyme. Biosensors 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Florea, A.; Cristea, C.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Goutaland, F.; Zhang, A.; Săndulescu, R.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. 1,3,5-Trinitrotoluene detection by a molecularly imprinted polymer sensor based on electropolymerization of a microporous-metal-organic framework. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdőssy, J.; Horváth, V.; Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Vagin, M.; Zavar, M.H.A.; Chamsaz, M.; Turner, A.P.; Tiwari, A. An ultrasensitive molecularly-imprinted human cardiac troponin sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Pharmacopoeia 11.0: Supplement 11.2; Council of Europe, European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare: Strasbourg, France, 2023; pp. 4837–5029. Available online: https://pheur.edqm.eu/ (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Baia, M.; Toderas, F.; Baia, L.; Popp, J.; Astilean, S. Probing the enhancement mechanisms of SERS with p-aminothiophenol molecules adsorbed on self-assembled gold colloidal nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 422, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia, M.; Toderas, F.; Baia, L.; Maniu, D.; Astilean, S. Multilayer Structures of Self-Assembled Gold Nanoparticles as a Unique SERS and SEIRA Substrate. Chemphyschem 2009, 10, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toderas, F.; Baia, M.; Baia, L.; Astilean, S. Controlling gold nanoparticle assemblies for efficient surface-enhanced Raman scattering and localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 255702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.B.; Mehta, V.N.; Kumar, M.A.; Kailasa, S.K. 4-Aminothiophenol functionalized gold nanoparticles as colorimetric sensors for the detection of cobalt using UV–Visible spectrometry. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2012, 39, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Mahima, S.; Kakade, B.A.; Pasricha, R.; Mandale, A.B.; Vijayamohanan, K. Solvent-Assisted One-Pot Synthesis and Self-Assembly of 4-Aminothiophenol-Capped Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13280–13286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Braiek, M.; Florea, A.; Chrouda, A.; Farre, C.; Bonhomme, A.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Zhang, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Aflatoxin B1 Detection Using a Highly-Sensitive Molecularly-Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on an Electropolymerized Metal Organic Framework. Toxins 2015, 7, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, R. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted composite membrane of poly(o-aminothiophenol) with gold nanoparticles for sensitive determination of herbicide simazine in environmental samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Lu, L.; Fan, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhou, R.; Xia, Y.; Lyu, F.; Zhang, X.; Nicole, J.-R.; Guo, Z. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensor Based on the Electropolymerization of p-Aminothiophenol-Functionalized Au Nanoparticles Electrode for the Detection of Nonylphenol. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.; Guo, Z.; Cristea, C.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Goutaland, F.; Dzyadevych, S.; Săndulescu, R.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Anticancer drug detection using a highly sensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on an electropolymerized microporous metal organic framework. Talanta 2015, 138, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Turner, A.P.; Tiwari, A. Electrochemical evaluation of troponin T imprinted polymer receptor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, G. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on Au nanoparticles-poly(o-phenylenediamine) for diethylstilbestrol detection. Synth. Met. 2024, 311, 117814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Fu, L.; Breadmore, M.C.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Challenges of molecularly imprinted polymers in impacting environmental monitoring and remediation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 193, 118434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Cornejo, E.; Khan, S.; Vega-Chacón, J.; Wong, A.; Neres, L.C.d.S.; Picasso, G.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Biomimetic Material for Quantification of Methotrexate Using Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole Film and MWCNT/GCE. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

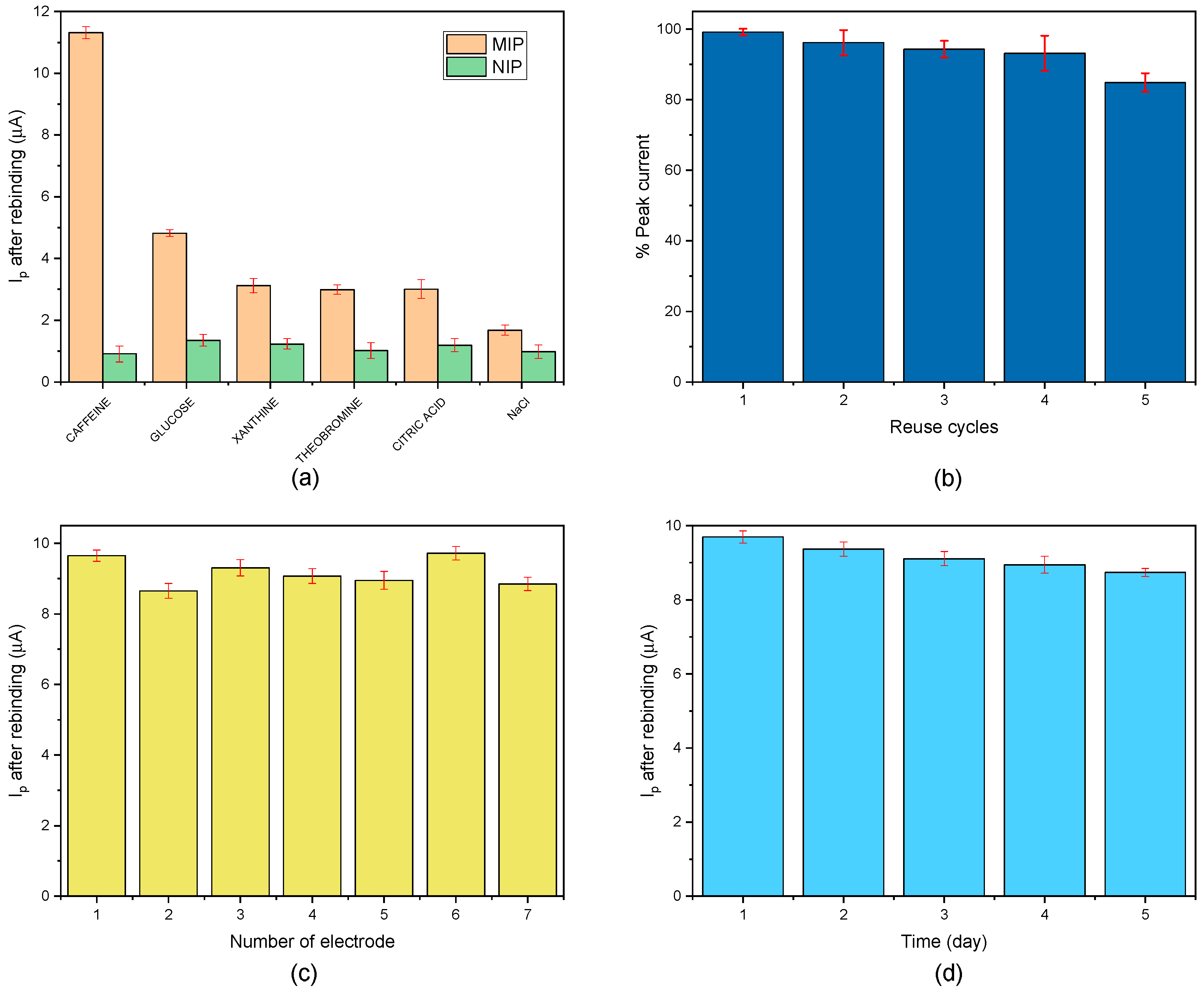
| Molecule | ΔIMIP (µA) | ΔINIP (µA) | IF (1) | β (2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 11.31 | 0.91 | 12.43 | 1.00 |
| Glucose | 4.82 | 1.35 | 3.57 | 3.48 |
| Xanthine | 3.12 | 1.23 | 2.54 | 4.90 |
| Theobromine | 2.99 | 1.02 | 2.93 | 4.24 |
| Citric acid | 3.01 | 1.19 | 2.53 | 4.91 |
| NaCl | 1.68 | 0.98 | 1.71 | 7.25 |
| Sample | Caffeine Expected | Caffeine Measured by HPLC | Caffeine Measured by Sensor | % Recovery of Sensor (HPLC *) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coca-Cola | <150 mg L−1 (1) | 93.04 mg L−1 | 72.57 mg L−1 | - | (77.99 *) |
| Red Bull | 320 mg L−1 | 305.99 mg L−1 | 298.24 mg L−1 | 93.2 | (97.47 *) |
| Caffeine capsules | 200 mg | 163.62 mg | 142.40 mg | 71.2 | (87.03 *) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinoza-Torres, S.; Choquehuanca-Azaña, A.; Rufino, M.; da Silva, E.; Angnes, L. Development of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Caffeine Quantification. Biosensors 2025, 15, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100704
Espinoza-Torres S, Choquehuanca-Azaña A, Rufino M, da Silva E, Angnes L. Development of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Caffeine Quantification. Biosensors. 2025; 15(10):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100704
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinoza-Torres, Sergio, Astrid Choquehuanca-Azaña, Marcos Rufino, Eleilton da Silva, and Lucio Angnes. 2025. "Development of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Caffeine Quantification" Biosensors 15, no. 10: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100704
APA StyleEspinoza-Torres, S., Choquehuanca-Azaña, A., Rufino, M., da Silva, E., & Angnes, L. (2025). Development of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Using Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Caffeine Quantification. Biosensors, 15(10), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15100704