The Assessment of Methyl Methanesulfonate Absorption by Amphipods from the Environment Using Lux-Biosensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
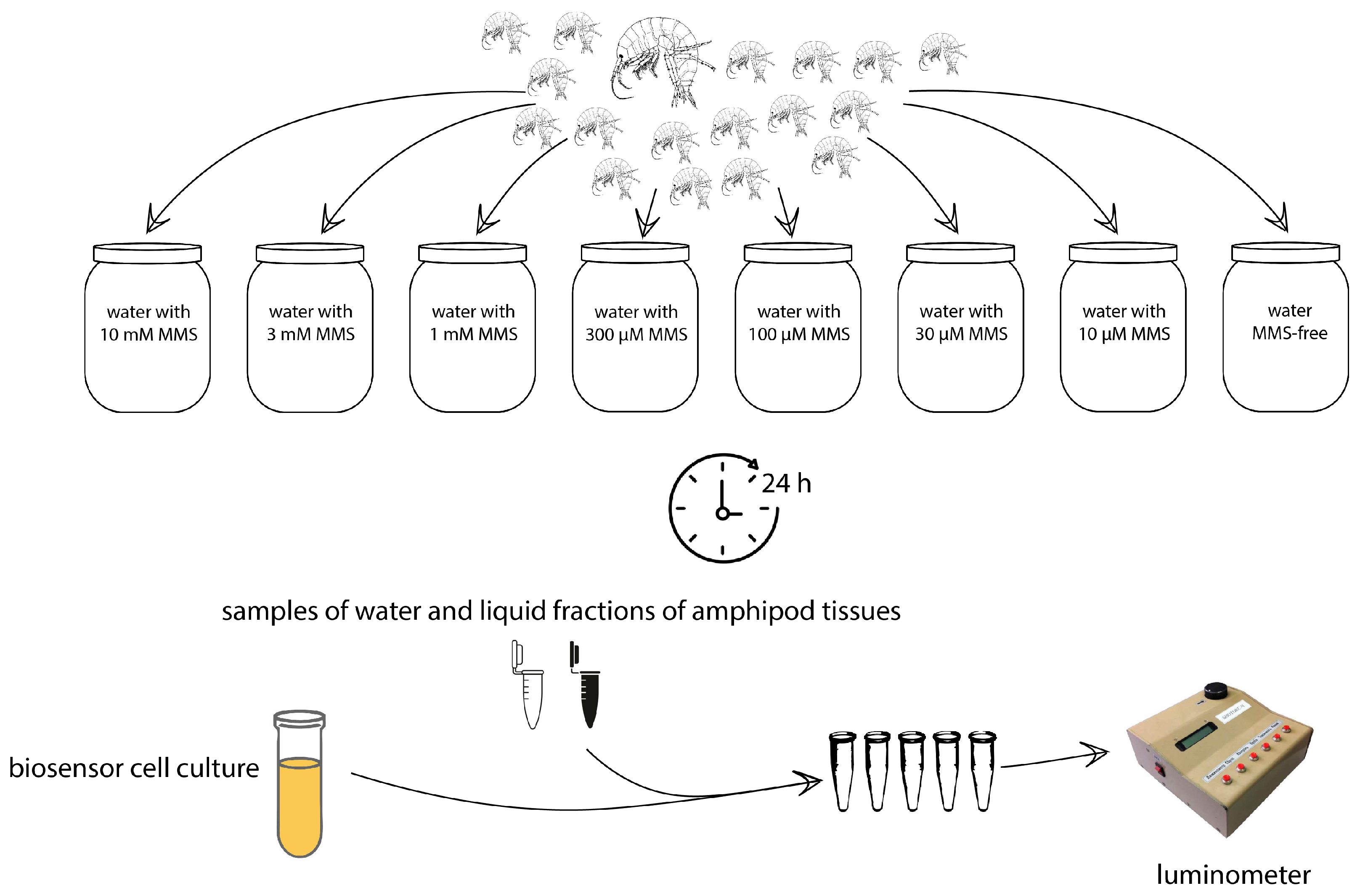
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Organisms
2.2. Bacterial Strains
2.3. Culture Medium and Growth Conditions
2.4. Measurement of Bioluminescence
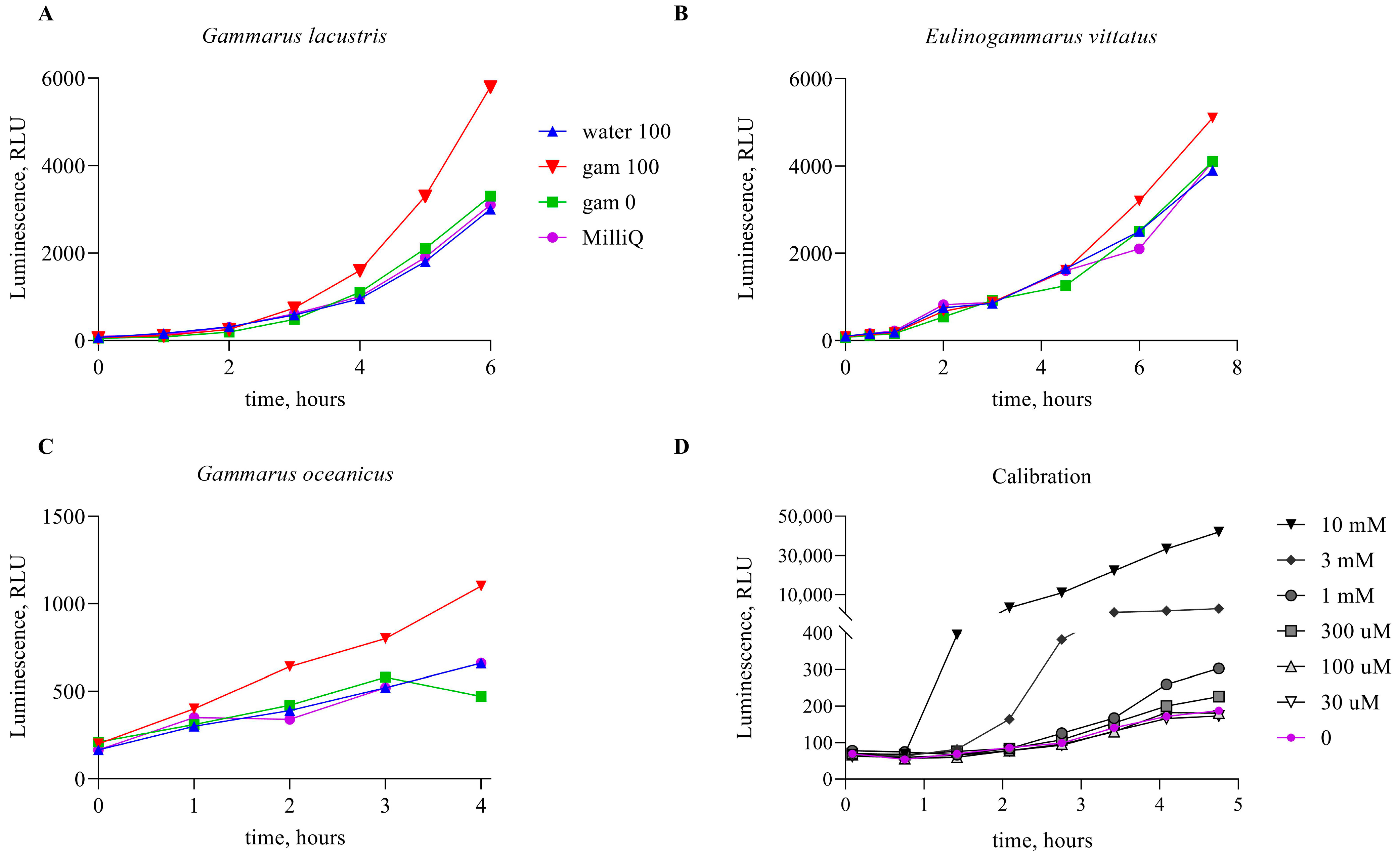
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burridge, T.R.; Lavery, T.; Lam PK, S. Acute toxicity tests using Phyllopsora comosa (Labillardieri) C. Agardh (Phaeophyta: Fucales) and Allorchestes compressa Dana (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1995, 55, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCahon, C.P.; Pascoe, D. Use of Gammarus pulex (L.) in safety evaluation tests: Culture and selection of a sensitive life stage. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1988, 15, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildish, D.J. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in sea water and their effect on reproduction of Gammarus oceanicus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1972, 7, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Roessink, I.; van den Brink, N.W.; van den Brink, P.J. Size- and sex-related sensitivity differences of aquatic crustaceans to imidacloprid. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gestin, O.; Lopes, C.; Delorme, N.; Garnero, L.; Geffard, O.; Lacoue-Labarthe, T. Organ-specific accumulation of cadmium and zinc in Gammarus fossarum exposed to environmentally relevant metal concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijošek, T.; Filipović Marijić, V.; Dragun, Z.; Ivanković, D.; Krasnići, N.; Erk, M. Efficiency of metal bioaccumulation in acanthocephalans, gammarids and fish in relation to metal exposure conditions in a karst freshwater ecosystem. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 73, 127037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosio, C.; Degli-Esposti, D.; Almunia, C.; Gaillet, V.; Sartelet, H.; Armengaud, J.; Chaumot, A.; Geffard, O.; Geffard, A. Subcellular Distribution of Dietary Methyl-Mercury in Gammarus fossarum and Its Impact on the Amphipod Proteome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10514–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reish, D.J. Effects of metals and organic compounds on survival and bioaccumulation in two species of marine gammaridean amphipod, together with a summary of toxicological research on this group. J. Nat. Hist. 1993, 27, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Hooda, P.S.; Swinden, J.; Barker, J.; Barton, S. Spatial (bio)accumulation of pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs, plasticisers, perfluorinated compounds and metabolites in river sediment, aquatic plants and benthic organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashauer, R.; Caravatti, I.; Hintermeister, A.; Escher, B.I. Bioaccumulation kinetics of organic xenobiotic pollutants in the freshwater invertebrate Gammarus pulex modeled with prediction intervals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC—International Agency for Research on Cancer. Some Anti-thyroid and Related Substances, Nitrofurans and Industrial Chemicals. In IARC Monograhs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogeic Risk of Chemicals to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1974; Volume 7, pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, M.D.; Pittman, D.L. Methylating Agents and DNA Repair Responses: Methylated Bases and Sources of Strand Breaks. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1580–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapp, N.K.; Craig, A.W.; Toya, R.E. Oncogenicity by Methyl Methanesulfonate in Male RF Mice. Science 1968, 161, 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC—International Agency for Research on Cancer. Re-evaluation of Some Organic Chemicals, Hydrazine, and Hydrogen Peroxide. In ARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1999; Volume 71, pp. 1059–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, B.N.; Lee, F.D.; Durston, W.E. An Improved Bacterial Test System for the Detection and Classification of Mutagens and Carcinogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, D.M.; Ames, B.N. Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat. Res. Environ. Mutagen. Relat. Subj. 1983, 113, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillardet, P.; Huisman, O.; D’Ari, R.; Hofnung, M. SOS chromotest, a direct assay of induction of an SOS function in Escherichia coli K-12 to measure genotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 5971–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazhenov, S.V.; Novoyatlova, U.S.; Scheglova, E.S.; Prazdnova, E.V.; Mazanko, M.S.; Kessenikh, A.G.; Kononchuk, O.V.; Gnuchikh, E.Y.; Liu, Y.; Al Ebrahim, R.; et al. Bacterial lux-biosensors: Constructing, applications, and prospects. In Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, V.S.; Ismailov, A.D. Bacterial luciferase as a biosensor of biologically active compounds. Biotechnology 1989, 11, 39–78. Available online: http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/2650767 (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- Nazarov, P.A.; Khrulnova, S.A.; Kessenikh, A.G.; Novoyatlova, U.S.; Kuznetsova, S.B.; Bazhenov, S.V.; Sorochkina, A.I.; Karakozova, M.V.; Manukhov, I.V. Observation of Cytotoxicity of Phosphonium Derivatives Is Explained: Metabolism Inhibition and Adhesion Alteration. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechor, O.; Smulski, D.R.; Van Dyk, T.K.; LaRossa, R.A.; Belkin, S. Recombinant microorganisms as environmental biosensors: Pollutants detection by Escherichia coli bearing fabA′::lux fusions. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 94, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotova, V.Y.; Manukhov, I.V.; Zavilgelskii, G.B. Lux-biosensors for detection of SOS-response, heat shock, and oxidative stress. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2010, 46, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igonina, E.V.; Marsova, M.V.; Abilev, S.K. Lux Biosensors: Screening Biologically Active Compounds for Genotoxicity. Russ. J. Genet. Appl. Res. 2018, 8, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryanin, I.; Kotova, V.; Krasnopeeva, E.; Manukhov, I.; Chubukov, P.; Balabanov, V.; Chalkin, S.; Shatrov, T.; Zavilgelsky, G. Genotoxic action of the 1, 1-dimethylhydrazine determined by alkylating compounds appearing in the result of oxidation and hydrogen peroxide. Tr. MIPT 2013, 5, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk, T.K.; Rosson, R.A. Photorhabdus luminescens LuxCDABE Promoter Probe Vectors. In Bioluminescence Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 102, p. 8595. [Google Scholar]
- Fomin, V.V.; Bazhenov, S.V.; Kononchuk, O.V.; Matveeva, V.O.; Zarubina, A.P.; Spiridonov, S.E.; Manukhov, I.V. Photorhabdus lux-operon heat shock-like regulation. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenikh, A.G.; Novoyatlova, U.S.; Bazhenov, S.V.; Stepanova, E.A.; Khrulnova, S.A.; Gnuchikh, E.Y.; Kotova, V.Y.; Kudryavtseva, A.A.; Bermeshev, M.V.; Manukhov, I.V. Constructing of Bacillus subtilis-based lux-biosensors with the use of stress-inducible promoters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTP (National Toxicology Program). Report on Carcinogens, Fifteenth Edition; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/go/roc15 (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Pedrazzani, R.; Ceretti, E.; Zerbini, I.; Casale, R.; Gozio, E.; Bertanza, G.; Gelatti, U.; Donato, F.; Feretti, D. Biodegradability, toxicity and mutagenicity of detergents: Integrated experimental evaluations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cann, H.M.; Verhulst, H.L. Toxicity of Household Soap and Detergent Products and Treatment of Their Ingestion. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1960, 100, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahaya, T.; Okpuzor, J.; Oladele, E.O. Investigation of Toxicity of Detergents. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Feng, X. Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine and related compounds in the environment: Recent updates on pretreatment, analysis, and removal techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, T.V.; Semenkov, I.N.; Lednev, S.A.; Soldatova, O.S. Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) and Its Transformation Products in Soils: A Review of the Sources, Detection, Behavior, Toxicity, and Remediation of Polluted Territories. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechaykina, O.V.; Laptev, D.S.; Petunov, S.G.; Bobkov, D.V. Effect of Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine on Isolated Heart and Lymphatic Vessels. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 172, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavilgelsky, G.B.; Kotova, V.Y.; Manukhov, I.V. Action of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine on bacterial cells is determined by hydrogen peroxide. Mutat. Res. 2007, 634, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, D.; Gupta, N. Nitrate pollution of groundwater and associated human health disorders. Indian J. Environ. Health 2000, 42, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.; Bakuła, T.; Matusiak, K.; Gałęcki, R.; Borowski, S.; Gutarowska, B. Odorous compounds from poultry manure induce DNA damage, nuclear changes, and decrease cell membrane integrity in chicken liver hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Description | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|
| strain | E. coli MG1655 | F- ilvG rfb-50 rph 1 | (VKPM, Russia) |
| plasmids | pAlkA-lux | pDEW201 [25] vector-based plasmid pAlkA-lux, where PalkA promoter from E. coli is transcriptionally fused with luxCDABE genes from P. luminescens. Ampicillin resistance (Apr) | [24] |
| pDlac | Plasmid based on pDEW201 with the insertion of a Plac promoter | [26] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novoyatlova, U.S.; Kudryavtseva, A.A.; Bazhenov, S.V.; Utkina, A.A.; Fomin, V.V.; Nevmyanov, S.A.; Zhoshibekova, B.S.; Fedyaeva, M.A.; Kolobov, M.Y.; Manukhov, I.V. The Assessment of Methyl Methanesulfonate Absorption by Amphipods from the Environment Using Lux-Biosensors. Biosensors 2024, 14, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14090427
Novoyatlova US, Kudryavtseva AA, Bazhenov SV, Utkina AA, Fomin VV, Nevmyanov SA, Zhoshibekova BS, Fedyaeva MA, Kolobov MY, Manukhov IV. The Assessment of Methyl Methanesulfonate Absorption by Amphipods from the Environment Using Lux-Biosensors. Biosensors. 2024; 14(9):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14090427
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovoyatlova, Uliana S., Anna A. Kudryavtseva, Sergey V. Bazhenov, Anna A. Utkina, Vadim V. Fomin, Shamil A. Nevmyanov, Bagila S. Zhoshibekova, Maria A. Fedyaeva, Mikhail Y. Kolobov, and Ilya V. Manukhov. 2024. "The Assessment of Methyl Methanesulfonate Absorption by Amphipods from the Environment Using Lux-Biosensors" Biosensors 14, no. 9: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14090427
APA StyleNovoyatlova, U. S., Kudryavtseva, A. A., Bazhenov, S. V., Utkina, A. A., Fomin, V. V., Nevmyanov, S. A., Zhoshibekova, B. S., Fedyaeva, M. A., Kolobov, M. Y., & Manukhov, I. V. (2024). The Assessment of Methyl Methanesulfonate Absorption by Amphipods from the Environment Using Lux-Biosensors. Biosensors, 14(9), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14090427





