Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment, Reagents, and Solutions
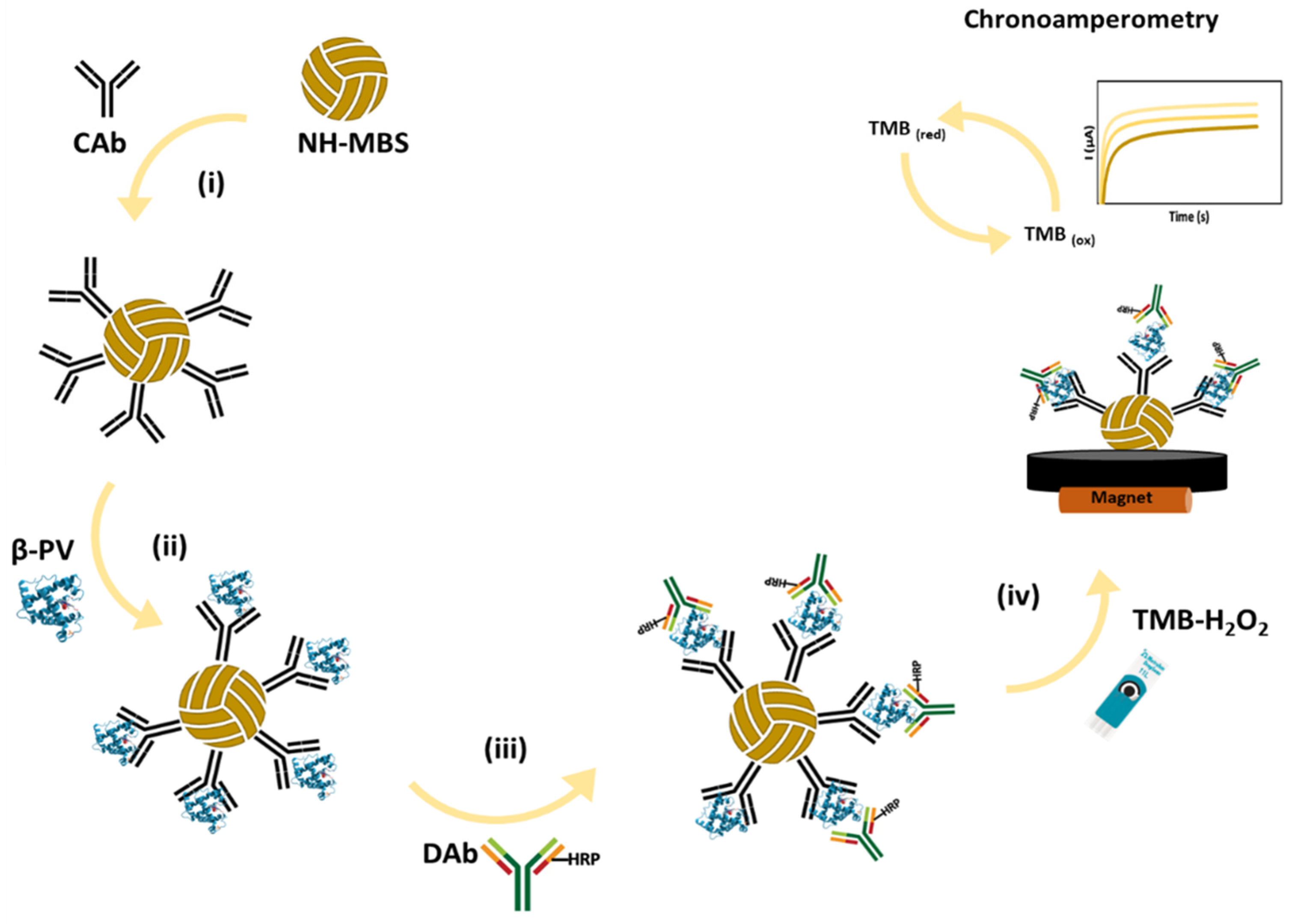
2.2. Electrochemical Assay
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. ELISA Procedure
3. Results
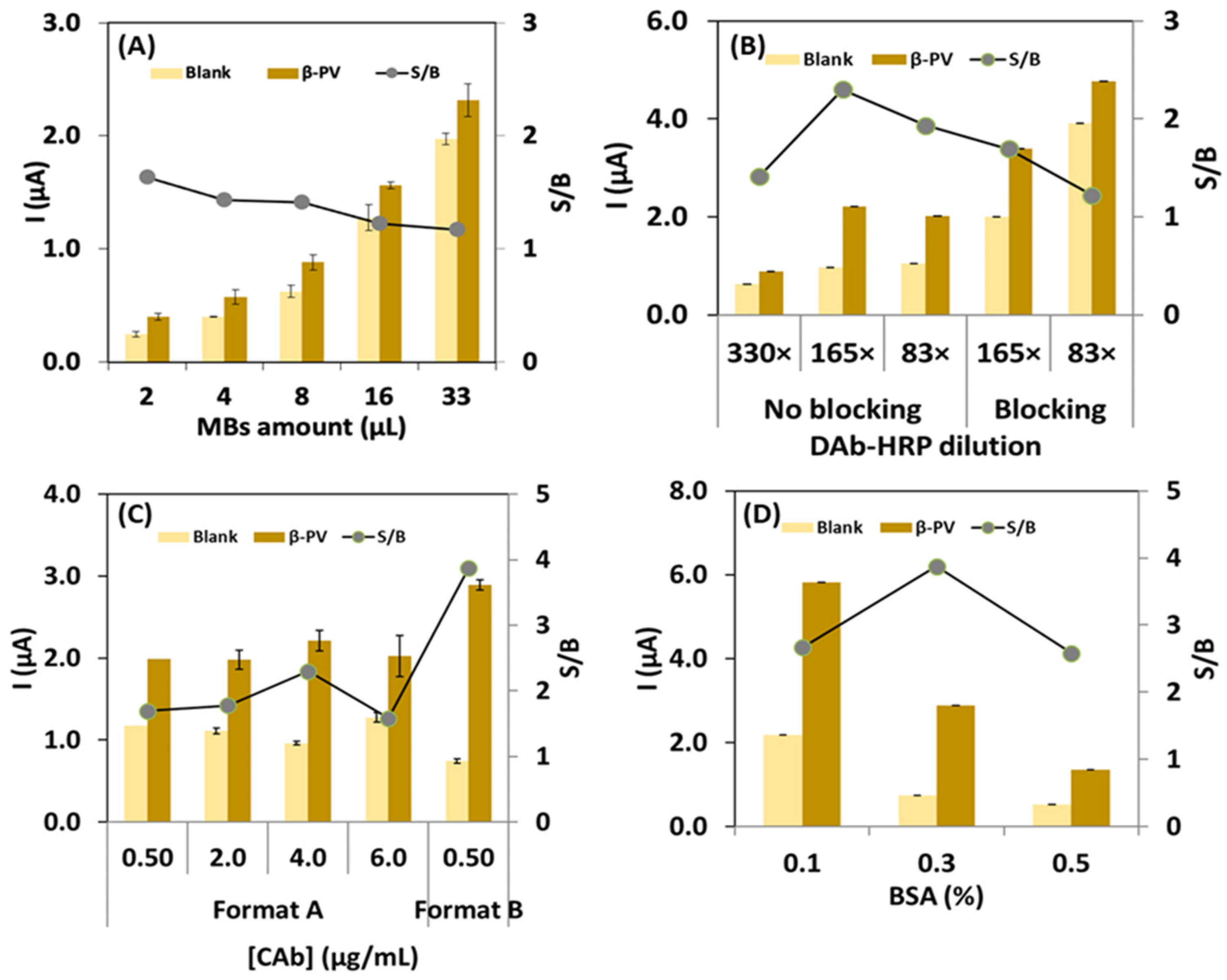
3.1. Immunoassay Optimization
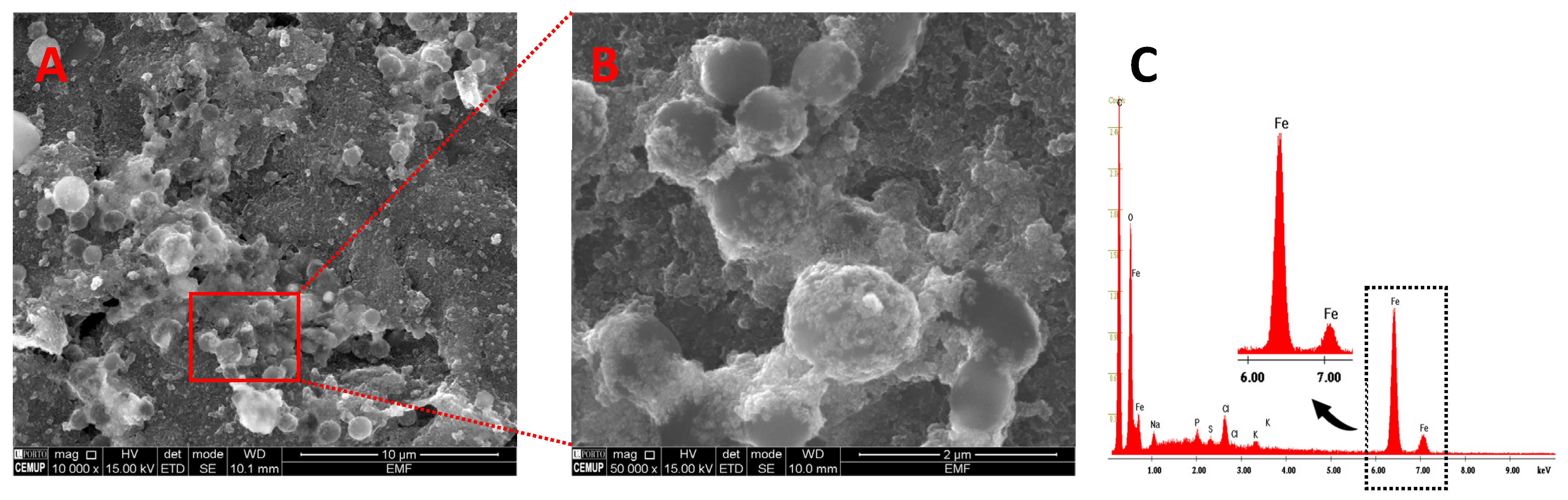
3.2. Transducer Surface Characterization
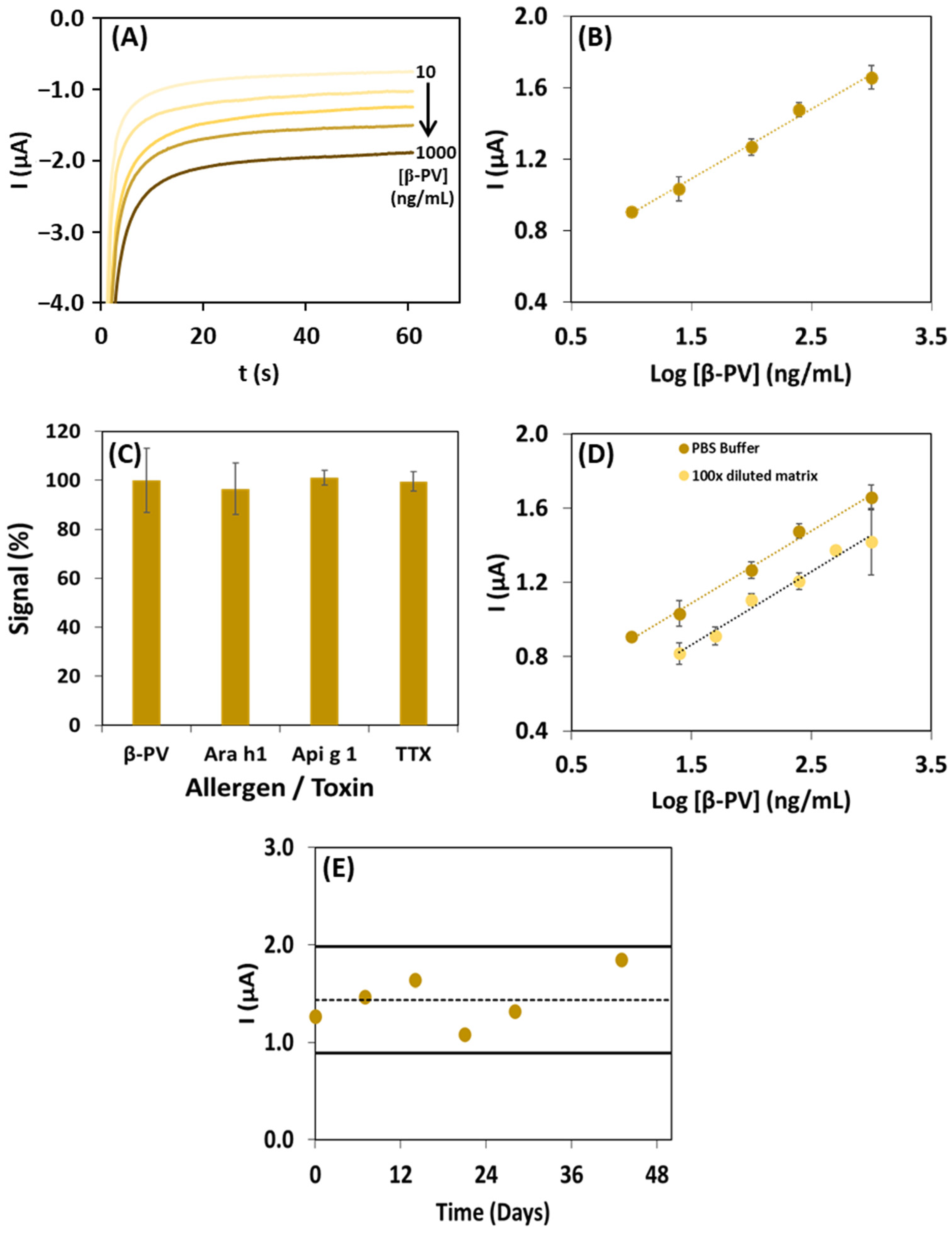
3.3. Analytical Characteristics and Assay Performance
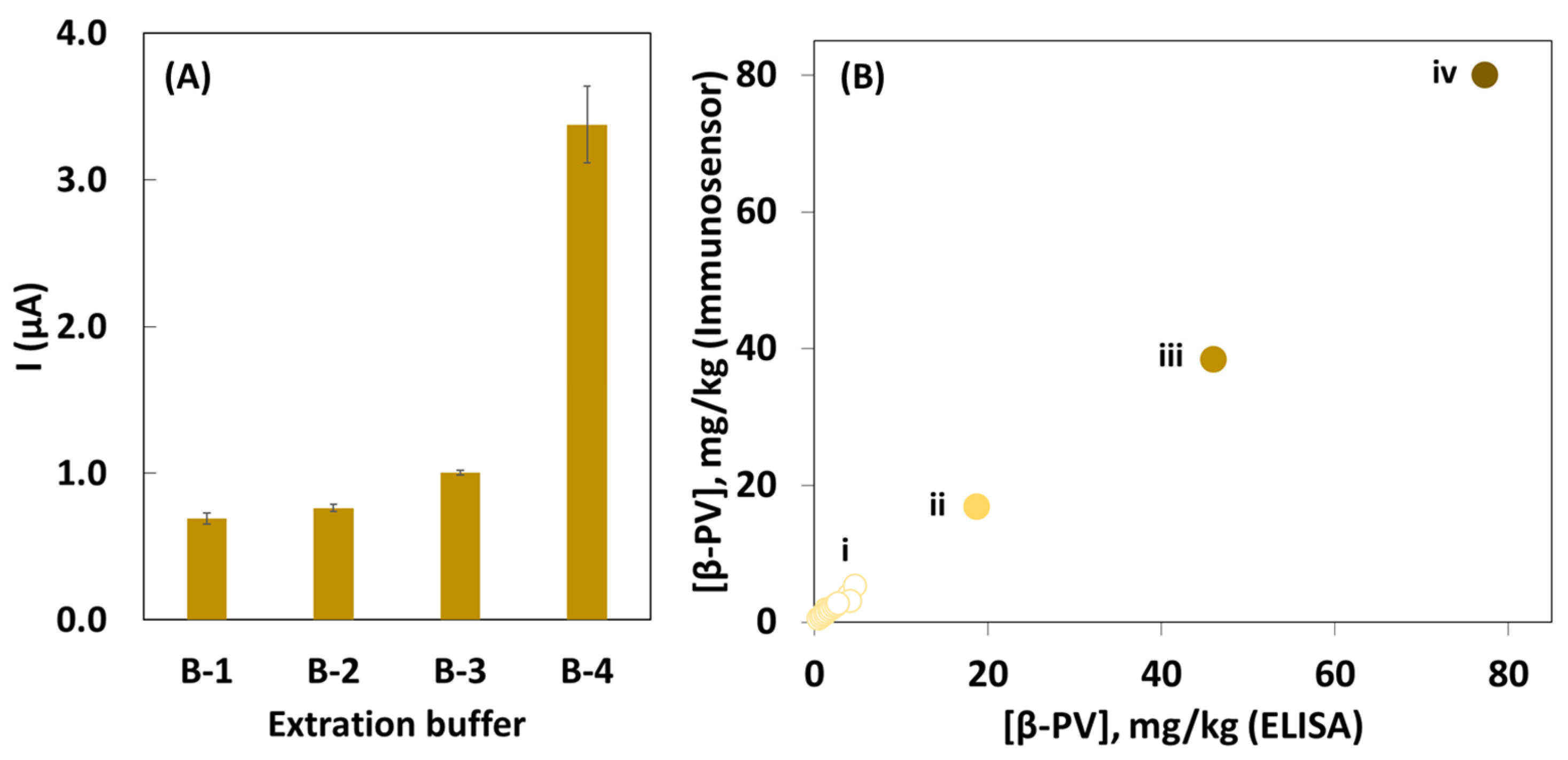
3.4. Application of the Magnetic Immunoassay to Food Analysis
3.5. Comparison with Other Immunosensors and Immunoassays for PV Analysis in Food Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Permyakov, E.A.; Uversky, V.N. What Is Parvalbumin for? Biomolecules 2022, 12, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.-W.; Nordlee, J.A.; Koppelman, S.J.; Baumert, J.L.; Taylor, S.L. Measuring parvalbumin levels in fish muscle tissue: Relevance of muscle locations and storage conditions. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, A.; Cavallo, C.; Del Giudice, T.; Vecchio, R.; Cicia, G. Consumer preferences for finfish: A systematic literature review. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 105, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Horka, P.; Zdenkova, K.; Cermakova, E. Parvalbumin: A Major Fish Allergen and a Forensically Relevant Marker. Genes 2023, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Xie, Y.; Chen, H. Fish Allergy: A Review of Clinical Characteristics, Mechanism, Allergens, Epitopes, and Cross-Reactivity. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Risk Assessment of Food Allergens: Part 2: Review and Establish Threshold Levels in Foods for the Priority Allergens: Meeting Report; FAO: Rome, Italy; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Ge, M.; Ahmed, I.; Pavase, T.R. Development of a method for the quantification of fish major allergen parvalbumin in food matrix via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with multiple reaction monitoring. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastián-González, E.; Morales-Reyes, Z.; Botella, F.; Naves-Alegre, L.; Pérez-García, J.M.; Mateo-Tomás, P.; Olea, P.P.; Moleón, M.; Barbosa, J.M.; Hiraldo, F.; et al. Network structure of vertebrate scavenger assemblages at the global scale: Drivers and ecosystem functioning implications. Ecography 2020, 43, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasanayaka, B.P.; Li, Z.; Ahmed, A.M.M.; Zhao, J.; Lin, H. Different Antibody Reactivity and Its Implications in Allergen Detection in Processed Fish. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Pramod, S.N.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. Development of an indirect competitive ELISA based on the common epitope of fish parvalbumin for its detection. Food Chem. 2024, 455, 139882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhruve, D.; Ratrey, V.P.; Lowanshi, A.; Chandravanshi, S.; Kashyap, N.; Pandey, S. Comprehensive Review of Seafood Allergens: Regulations, Detection Methods, and Implications for Public Health. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2024, 33, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y. Seafood allergy: Occurrence, mechanisms and measures. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ohshima, T.; Ushio, H. Rapid Detection of Fish Major Allergen Parvalbumin by Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, C652–C658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Reddy, Y.V.M.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. Recent advances in analytical strategies and microsystems for food allergen detection. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ye, Y.; Ji, J.; Sun, J.; Sun, X. Advances on the rapid and multiplex detection methods of food allergens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6887–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curulli, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensing Strategies for Food Allergen Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Carvalho, A.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Tracking Arachis hypogaea Allergen in Pre-Packaged Foodstuff: A Nanodiamond-Based Electrochemical Biosensing Approach. Biosensors 2022, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.; del Rio, M.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Tracking a Major Egg Allergen to Assess Commercial Food Label Compliance: Towards a Simple and Fast Immunosensing Device. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, K.; Jiang, H.; Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, D. Emerging electrochemical biosensing approaches for detection of allergen in food samples: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.S.; Freitas, M.; Oliveira, C.; Pereira, C.R.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Nouws, H.P.A. Voltammetric immunosensor based on oxidized carbon nanotubes/MnFe2O4 hybrid nanoplatform for amplified detection of celery (Apium graveolens). Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, R.; Freitas, M.; Costa-Rama, E.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Food allergen control: Tropomyosin analysis through electrochemical immunosensing. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.P.; Freitas, M.; Geraldo, D.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Nouws, H.P.A. Seafood product safety: A hybrid graphene/gold-based electrochemical immunosensor for fish allergen analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunati, S.; Giannetto, M.; Giliberti, C.; Mattarozzi, M.; Bertucci, A.; Careri, M. Magnetic Beads as Versatile Tools for Electrochemical Biosensing Platforms in Point-of-Care Testing. Anal. Sens. 2024, 4, e202300062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiani, G.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Campàs, M. Magnetic Beads in Marine Toxin Detection: A Review. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroozmand, F.; Mohammadipanah, F.; Faridbod, F. Emerging biosensors in detection of natural products. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2020, 5, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, S.; Tang, Z.; La, M. Overview on the design and application of magnetically-assisted electrochemiluminescence biosensors. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 221189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-P.; Yang, T.-H.; Wang, J.-C.; Chuang, H.-S. Recent Trends and Innovations in Bead-Based Biosensors for Cancer Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carinelli, S.; Luis-Sunga, M.; González-Mora, J.L.; Salazar-Carballo, P.A. Synthesis and Modification of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biosensing and Bioassay Applications: A Review. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, H.; Cao, H.; Xiang, X.; Wang, L. 3D bio-printing-based vascular-microtissue electrochemical biosensor for fish parvalbumin detection. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Qi, Q.; Fu, L. A colorimetric and fluorescent gold nanoparticle-based dual-mode aptasensor for parvalbumin detection. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhu, P.; Jiang, H.; Ji, J.; Sun, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, G. Fluorescent magnetic bead-based mast cell biosensor for electrochemical detection of allergens in foodstuffs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, H.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dasanayaka, B.P.; Ahmed, I.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z. Allergenicity determination of Turbot parvalbumin for safety of fish allergy via dendritic cells, RBL-2H3 cell and mouse model. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1959–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Protein Origin | Fish-Derived Species (%) | Food Processing /Conservation | Immunoassay | ELISA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [β-PV] (mg/kg) | CV (%) | [β-PV] (mg/kg) | CV (%) | ||||||
| β-PV-free | Allergen | Egg | Animal | n/a | Ground | <LOD | – | <LOD | – |
| Celery | Vegetable | ||||||||
| Peanut butter | Vegetable | ||||||||
| Other | Rice | Vegetable | n/a | Cooked | <LOD | – | <LOD | – | |
| Soy lecithin | Vegetable | Ground | |||||||
| Liquid protein yoghurt | Animal | Pasteurized | |||||||
| Vegetable soup | Vegetable | Lyophilized | |||||||
| Roast chicken | Animal | Grilled | |||||||
| Presence of β-PV | Contain | Salmon (fresh) | Animal | 100 | n/a | 38.6 | 15 | 46.0 | 24 |
| Sardine pâté | 58 | Pâté | <LOQ | - | <LOQ | – | |||
| Canned fish Surimi | 100 | Canned in oil | <LOQ | - | <LOQ | – | |||
| Fish surimi | 100 | Packed in vacuum | 16.9 | 22 | 18.7 | 27 | |||
| Squid (fresh) | 100 | n/a | <LOQ | - | <LOQ | – | |||
| Canned tuna | 100 | Canned | <LOQ | - | <LOQ | – | |||
| Tuna pâté | 45 | Pâté | 80.0 | 30 | 77.3 | 22 | |||
| Tuna burger | 52 | Packed in vacuum | <LOQ | - | <LOQ | – | |||
| Pasta with tuna | 40 | Packed in vacuum | 664 | 9 | <LOQ | – | |||
| May contain | Quinoa salad | Vegetable | n/a | Packed in vacuum | <LOD | – | <LOQ | – | |
| Seafood shrimp patty | Animal | 30 | Fried | ||||||
| Sensing Surface/Platform | Stability (Days) | Technique | Probe/Label | LOD (ng/mL) | Food Samples | Interferents Tested | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPCE/NH-MBs | 43 | CA | HRP/TMB | 1.8 | Egg, ground celery, peanut butter, rice, soy lecithin, liquid protein yoghurt, vegetable soup, roast chicken, salmon (fresh), sardine pâté, canned fish surimi, fish surimi, squid (fresh), canned tuna, tuna pâté, tuna burger, pasta with tuna, quinoa salad, seafood shrimp patty | TPM Ara h 1 Api g 1 TTX | This work |
| SPCE/rGO-AuNP | 15 | CA | HRP/TMB | 9.9 | Salmon (fresh, grilled, canned, smoked, pâté), cod (smoked, canned), tuna (canned), sardines (canned), needlefish (canned), mackerel (canned), broth (fish, seafood, and stew), vegetable soup, lettuce, and egg | TPM Ara h 1 Gal d 3 Cyp c 1 TTX | [22] |
| MGCE/CMFNPs | – | EIS | [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- | 0.16 | Crucian carp and brown shrimp | Pen a 1 β-conglycinin Ara h 1 | [31] |
| Microtiter plate/MB-GO | – | ELISA | HRP-Ab-AuNP | 4.29 | Fish (Ctenopharyngodon idellus, Aristichthys nobilis, Oreochroms mossambcus, and Gadus macrocephalus) | BSA OVA, TPM, AK, COL | [30] |
| Microtiter plate | – | ELISA | HRP/TMB | 0.20 | Aquatic products, cereal products, baby food, snacks, dips and sauces, beverages, and other edible products | – | [32] |
| Graphite rod electrode/Au-Cu-MOF-PDA-MWCNT | – | DPV | Endothelial cells/NO | 65.0 | Carp | BSA, OVA, Soybean Globulin COL | [29] |
| Microtiter plate | – | ELISA | HRP/TMB | 10.15 | Seafood-flavored puffed potato, cod stick, crab-flavored fish stick, Antarctic krill ball, grilled fish fillet, seafood noodle, bear-shaped biscuit, hand-torn bread, ice cream, chocolate, crab-flavored broad bean, and cheese sticks | – | [10] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocha, J.P.; Freitas, M.; Geraldo, D.; Bento, F.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Nouws, H.P.A. Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin. Biosensors 2024, 14, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120639
Rocha JP, Freitas M, Geraldo D, Bento F, Delerue-Matos C, Nouws HPA. Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin. Biosensors. 2024; 14(12):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120639
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocha, José Pedro, Maria Freitas, Dulce Geraldo, Fátima Bento, Cristina Delerue-Matos, and Henri P. A. Nouws. 2024. "Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin" Biosensors 14, no. 12: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120639
APA StyleRocha, J. P., Freitas, M., Geraldo, D., Bento, F., Delerue-Matos, C., & Nouws, H. P. A. (2024). Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin. Biosensors, 14(12), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120639






