Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay Implemented with Isothermal Gene Amplification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples, Nucleic Acids, and Chemical Reagents
2.2. AuNP–Reporter Probe Conjugation
2.3. Fabrication of the Lateral Flow Strip
2.4. Preparation of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp RNA
2.5. Reverse Transcription–RPA (RT-RPA)
2.6. LFA
2.7. Viral RNA Extraction from Clinical Samples
2.8. RT-qPCR
2.9. Automated Electrophoresis
2.10. Rapid Antigen Test Kit
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Principle of the RT-RPA-LFA Platform
3.2. Characterization of AuNP–Reporter Probe Conjugate
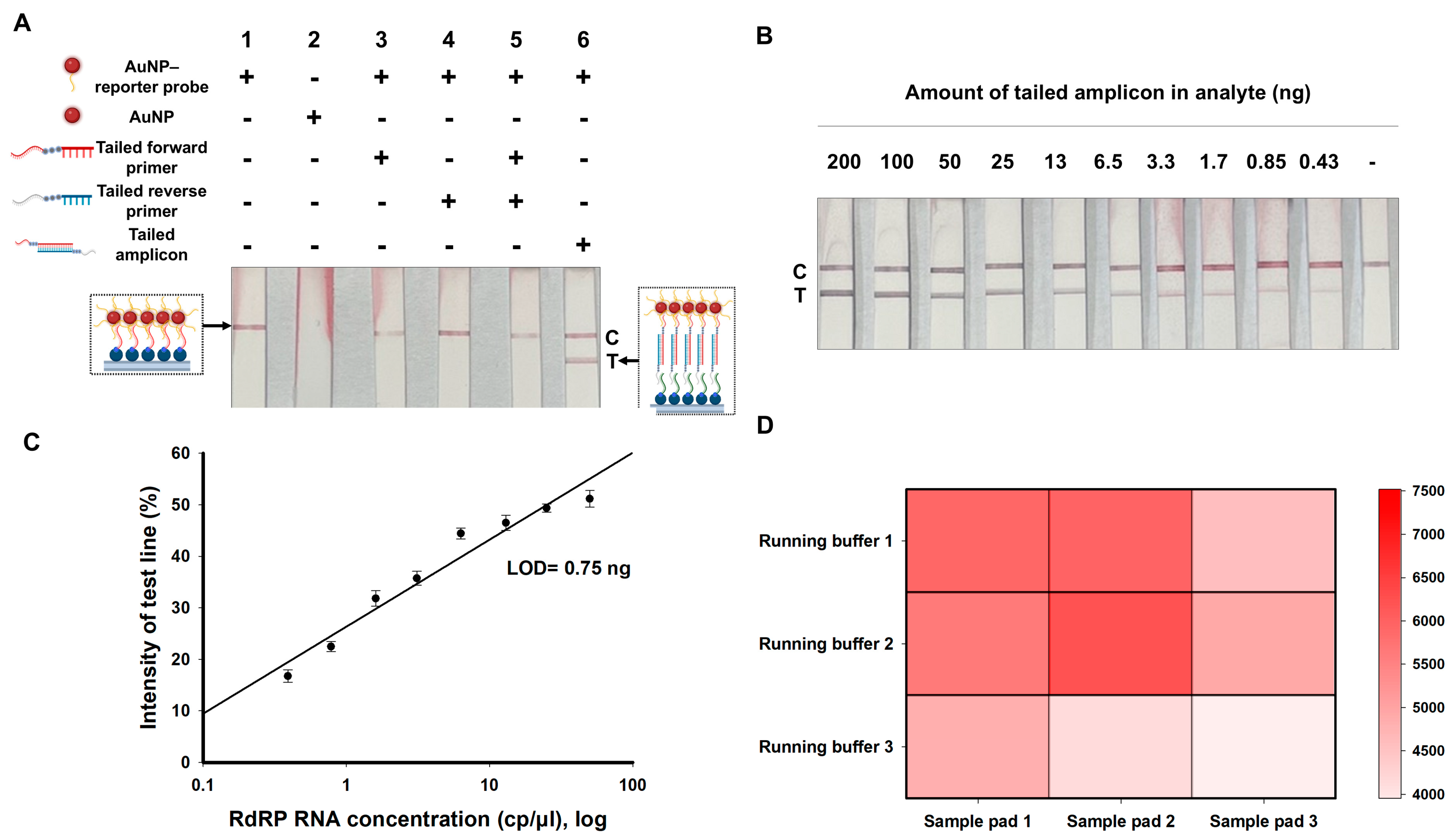
3.3. Validation of the NALFA Platform
3.4. Optimization of RT-RPA
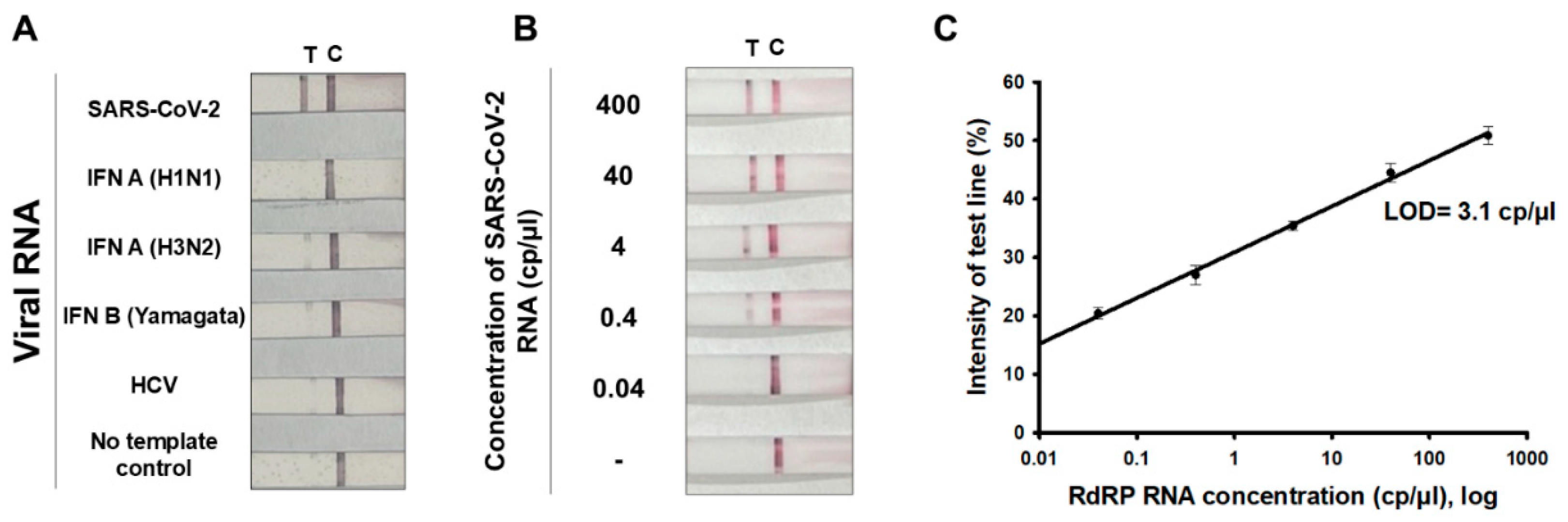
3.5. Specificity and Limit of Detection (LOD) of RT-RPA-LFA
3.6. Testing of SARS-CoV-2-Positive Clinical Samples via RT-RPA-LFA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, J.F.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.H.; To, K.K.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.; Poon, R.W.; et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, P.Y.; Coleman, K.K.; Tan, Y.K.; Ong, S.W.X.; Gum, M.; Lau, S.K.; Lim, X.F.; Lim, A.S.; Sutjipto, S.; Lee, P.H.; et al. Detection of air and surface contamination by SARS-CoV-2 in hospital rooms of infected patients. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holshue, M.L.; DeBolt, C.; Lindquist, S.; Lofy, K.H.; Wiesman, J.; Bruce, H.; Spitters, C.; Ericson, K.; Wilkerson, S.; Tural, A.; et al. First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfinrud, P.; Stadnytskyi, V.; Bax, C.E.; Bax, A. Visualizing Speech-Generated Oral Fluid Droplets with Laser Light Scattering. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2061–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, J.; Dai, H.; Gao, R.; Lin, H.; Zhang, D.; Ge, S. Development of amplification system for point-of-care test of nucleic acid. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 25, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogels, C.B.F.; Brito, A.F.; Wyllie, A.L.; Fauver, J.R.; Ott, I.M.; Kalinich, C.C.; Petrone, M.E.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Catherine Muenker, M.; Moore, A.J.; et al. Analytical sensitivity and efficiency comparisons of SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR primer-probe sets. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, S.M.; Martinez, I. Universal and rapid salt extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4692–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinnes, J.; Sharma, P.; Berhane, S.; van Wyk, S.S.; Nyaaba, N.; Domen, J.; Taylor, M.; Cunningham, J.; Davenport, C.; Dittrich, S.; et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 7, CD013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Point-of-care COVID-19 diagnostics powered by lateral flow assay. TrAc-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.N.; Lee, J.; Kang, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, S.; Chung, H.J. A Lateral Flow Assay for Nucleic Acid Detection Based on Rolling Circle Amplification Using Capture Ligand-Modified Oligonucleotides. BioChip J. 2022, 16, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.R.; Hu, J.; Gong, Y.; Feng, S.; Wan Abas, W.A.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Xu, F. An integrated lateral flow assay for effective DNA amplification and detection at the point of care. Analyst 2016, 141, 2930–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Boswell, S.A.; Chidley, C.; Lu, Z.X.; Pettit, M.E.; Gaudio, B.L.; Fajnzylber, J.M.; Ingram, R.T.; Ward, R.H.; Li, J.Z.; et al. An enhanced isothermal amplification assay for viral detection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Jiang, L.; Huang, G.; Pu, H.; Gong, B.; Lin, H.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Long, B.; Si, G.; et al. Comparison of different samples for 2019 novel coronavirus detection by nucleic acid amplification tests. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riffelmann, M.; Wirsing von Konig, C.H.; Caro, V.; Guiso, N. Nucleic Acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Bordetella infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4925–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, D.R. Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests for the Diagnosis of Pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obande, G.A.; Banga Singh, K.K. Current and Future Perspectives on Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technologies for Diagnosing Infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 455–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esbin, M.N.; Whitney, O.N.; Chong, S.; Maurer, A.; Darzacq, X.; Tjian, R. Overcoming the bottleneck to widespread testing a rapid review of nucleic acid testing approaches for COVID-19 detection. RNA 2020, 26, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-meidated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauset-Rubio, M.; Svobodova, M.; Mairal, T.; McNeil, C.; Keegan, N.; Saeed, A.; Abbas, M.N.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; et al. Ultrasensitive, rapid and inexpensive detection of DNA using paper based lateral flow assay. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taton, T.A. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticle–DNA Conjugates. Curr. Protoc. Nucleic Acid Chem. 2002, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S. A rapid water bath PCR combined with lateral flow assay for the simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza B virus. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongkhao, K.; Tungphatthong, C.; Sukrong, S. A PCR-lateral flow immunochromatographic assay (PCR-LFA) for detecting Aristolochia species, the plants responsible for aristolochic acid nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veigas, B.; Fernandes, A.R.; Baptista, P.V. AuNPs for identification of molecular signatures of resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storhoff, J.J.; Elghanian, R.; Mucic, R.C.; Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L. One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.; Hwang, S.H.; Jeong, W.; Kim, D.E. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA through tandem isothermal gene amplification without reverse transcription. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1212, 339909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyung, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, D.-E. Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay Implemented with Isothermal Gene Amplification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Biosensors 2024, 14, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120585
Kyung K, Lee H, Kim S-K, Kim D-E. Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay Implemented with Isothermal Gene Amplification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Biosensors. 2024; 14(12):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120585
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyung, Kangwuk, Hyojin Lee, Soo-Kyung Kim, and Dong-Eun Kim. 2024. "Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay Implemented with Isothermal Gene Amplification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA" Biosensors 14, no. 12: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120585
APA StyleKyung, K., Lee, H., Kim, S.-K., & Kim, D.-E. (2024). Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay Implemented with Isothermal Gene Amplification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Biosensors, 14(12), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14120585




