A Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Aquatic Products Freshness Assessment in Cold Chain Logistics
Abstract
1. Introduction
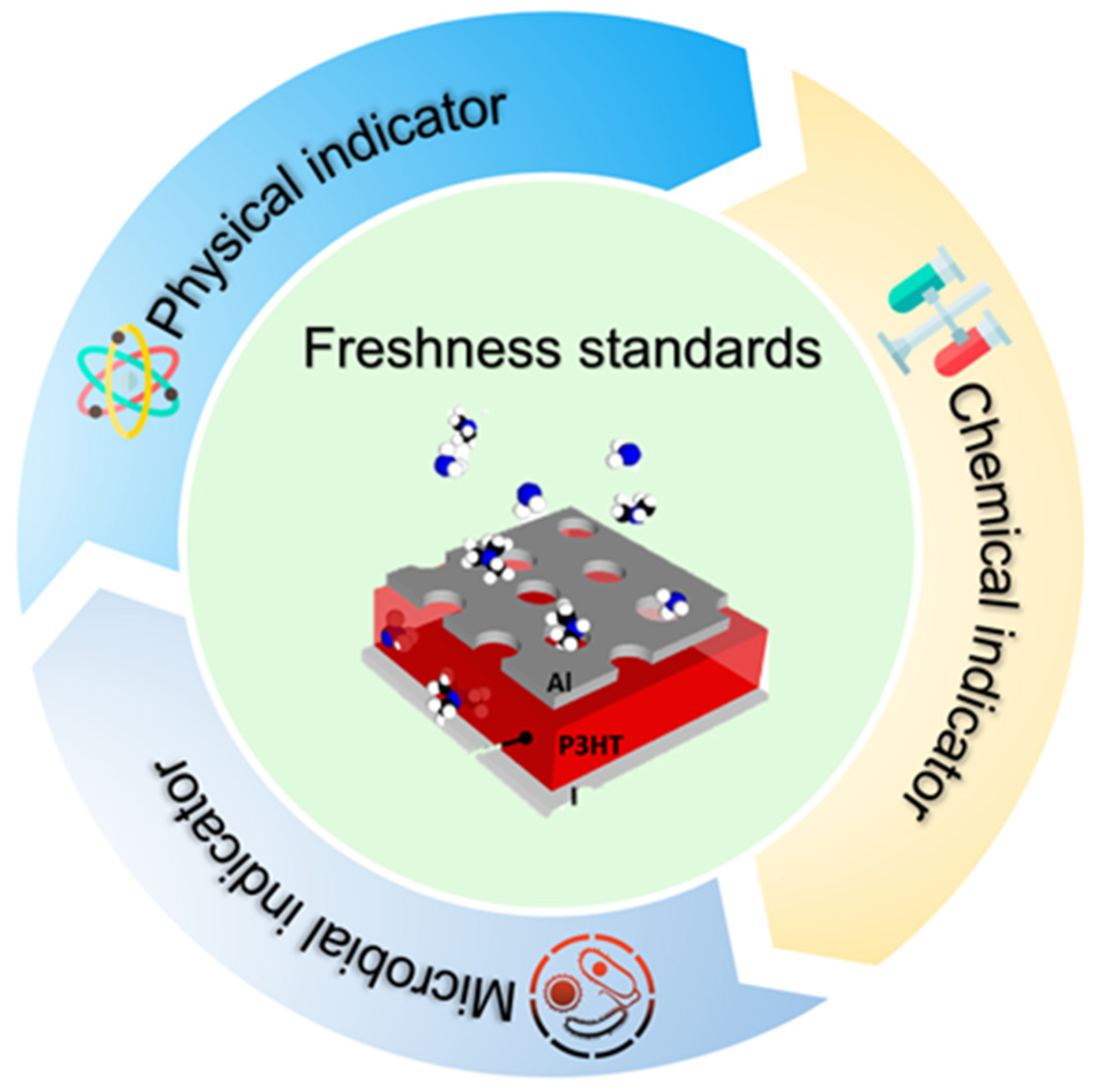
2. Traditional Indicators
2.1. Chemical Indicators
2.2. Physical Indicators
2.3. Microbial Indicators
3. Development of Advanced Sensor Technologies
3.1. Biomimetic Sensors
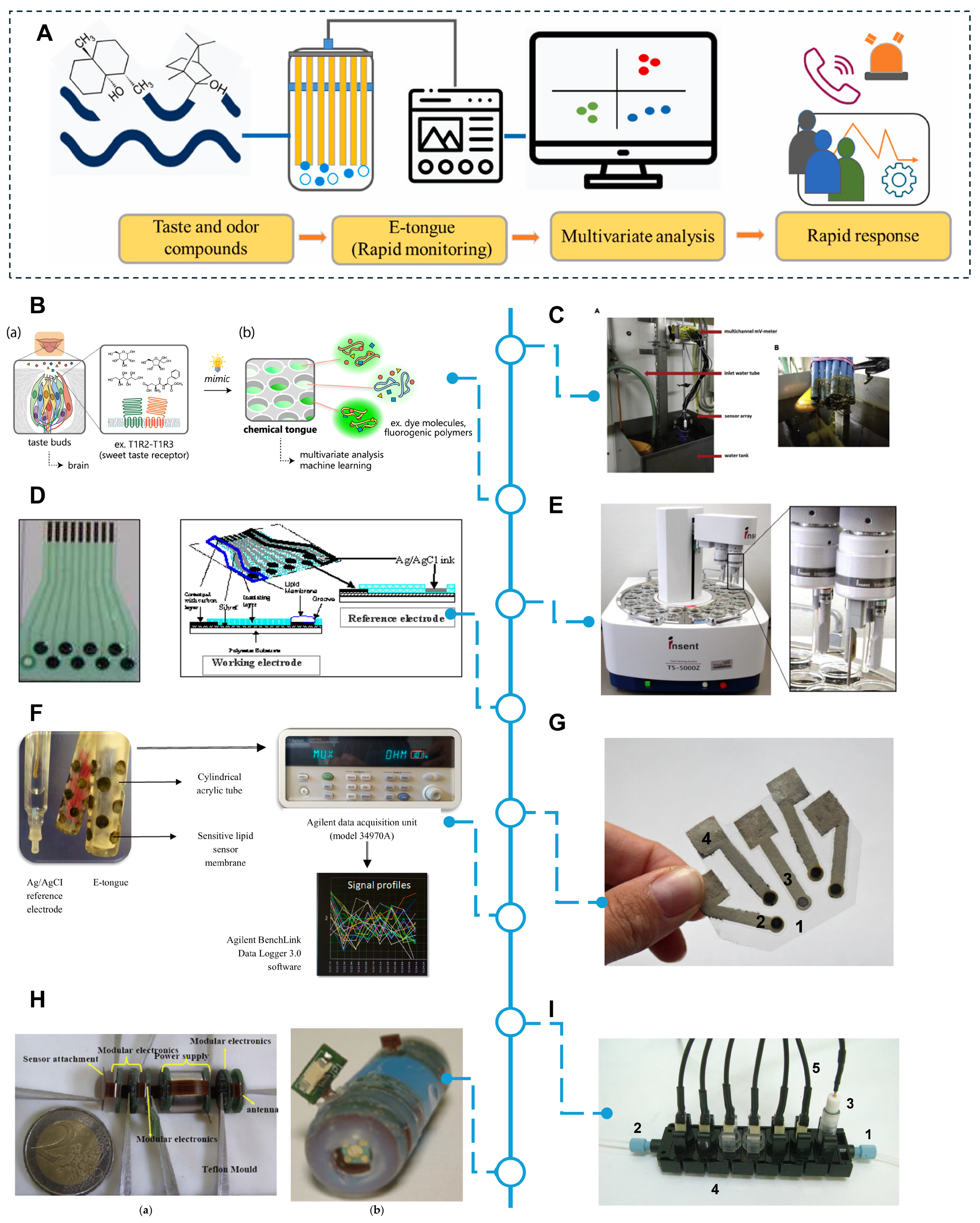
3.1.1. Electronic Nose (E-Nose)

3.1.2. Electronic Tongue (E-Tongue)
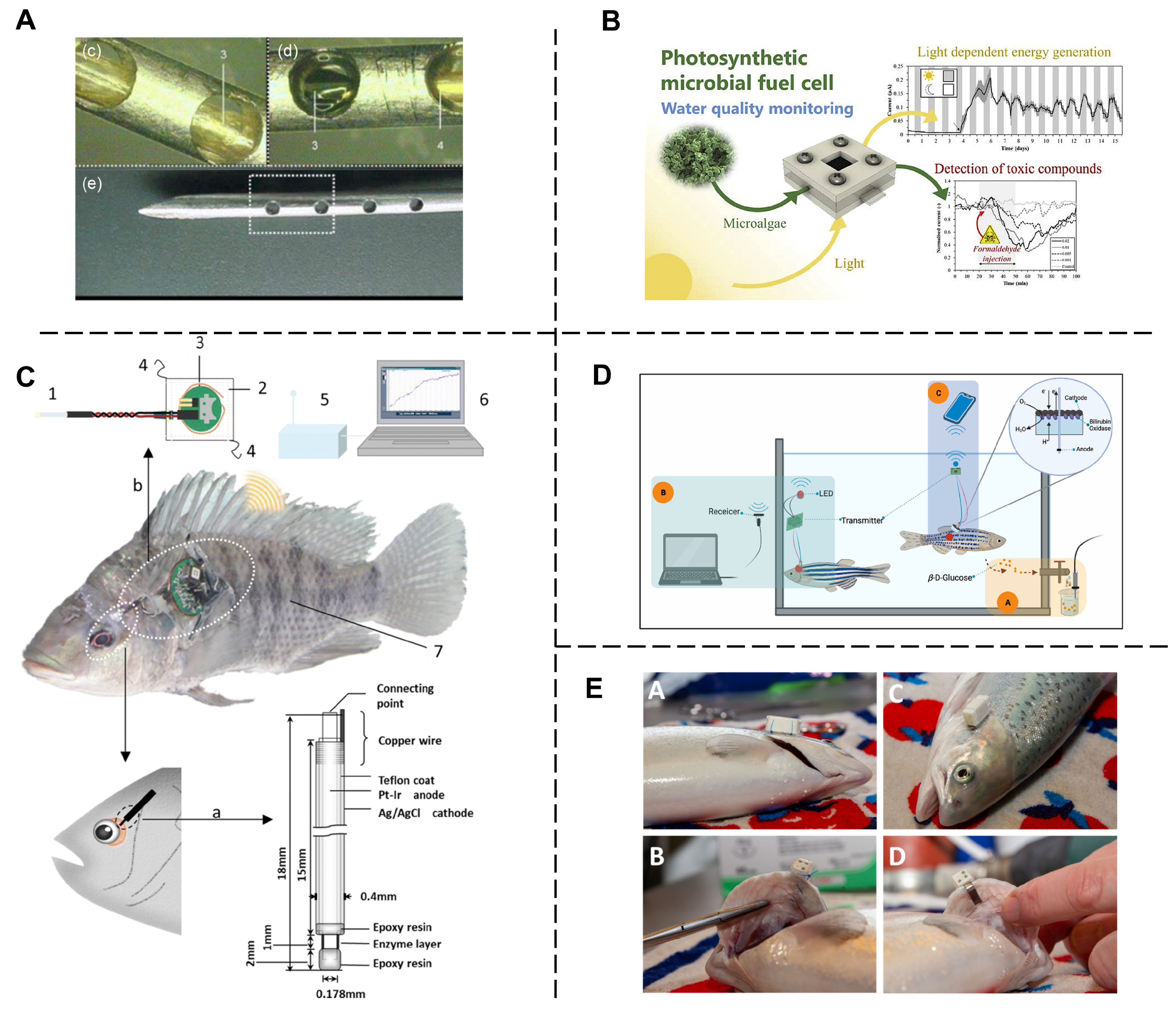
3.2. Biosensors
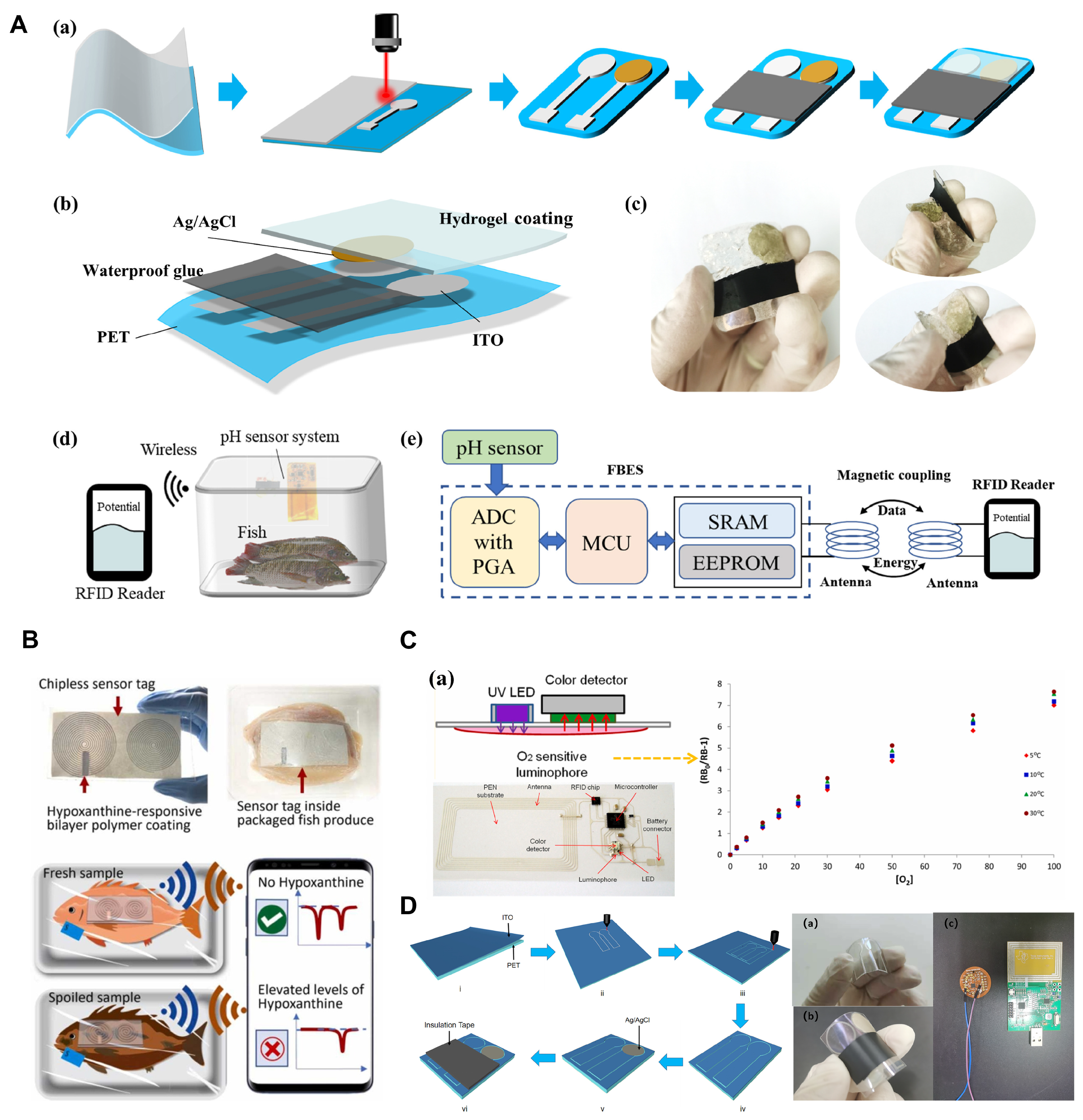
3.3. Flexible Sensors
4. Comparison and Application of Sensor Technologies
5. Discussion and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, F. The Development Model of Japanese Cold Chain Logistics: The Example of Seafood Transportation. Asian Bus. Res. 2022, 7, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Gao, W.; Cong, C. Oyster cold chain logistics monitoring system based on RFID and cloud platforms. SPIE 2023, 12, 3012115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H. Application of RFID Information Technology in Fresh Food Cold Chain Logistics Management. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 1881, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Chen, J.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y. Application of nondestructive evaluation (NDE) technologies throughout cold chain logistics of seafood: Classification, innovations and research trends. LWT 2022, 158, 113127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-Y.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X. Flexible Multimode Sensors Based on Hierarchical Microstructures Enable Non-Destructive Grading of Fruits in Cold Chain Logistics. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 25, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Q.-S.; Li, F.; Jin, C. Research on Green Technology Path of Cold-Chain Distribution of Fresh Products Based on Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guney, S.; Atasoy, A. Fish Freshness Assessment by Using Electronic Nose. In Proceedings of the 2013 36th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Rome, Italy, 2–4 July 2013; pp. 742–746. [Google Scholar]
- Apetrei, I.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Apetrei, C.; de Saja, J.A. Fish Freshness Monitoring Using an E-Tongue Based on Polypyrrole Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2548–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Huang, X.; Teye, E.; Gu, F.; Gu, H. Nondestructive detection of fish freshness during its preservation by combining electronic nose and electronic tongue techniques in conjunction with chemometric analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 5290–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, D.; Syarwan, N.F.; Nugraha, M.A.; Ananda, D.; Fahrudin, T.; Handayani, R. Seafood Quality Detection Using Electronic Nose and Machine Learning Algorithms With Hyperparameter Optimization. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 27935–27945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.; Finardi, S.; de Souza, C.K.; Meinert, C.; Pateiro, M.; Hoffmann, T.; Domínguez, R.; Bertoli, S.; Kumar, M.; Lorenzo, J. Applications of Electronic Nose, Electronic Eye and Electronic Tongue in Quality, Safety and Shelf Life of Meat and Meat Products: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Genua, M.; Batista, D.T.; Calemczuk, R.; Buhot, A.; Fornarelli, P.; Koubachi, J.; Bonnaffé, D.; Saesen, E.; Laguri, C.; et al. Continuous evolution profiles for electronic-tongue-based analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12200–12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhuang, L.; Zhen, Q.; Gao, K.; Gao, Z.B. Research Progress of Bioinspired Smell and Taste Sensors. J. Appl. Chem. 2021, 8, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, X.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Tian, L.-Y.; Hou, F.; Li, H.; Fan, X.-H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Shi, J.; et al. Authenticity and species identification of Fritillariae cirrhosae: A data fusion method combining electronic nose, electronic tongue, electronic eye and near infrared spectroscopy. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1179039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Wang, Y.-L.; Gui, X.; Fan, X.-H.; Dong, F.-Y.; Zhang, P.-P.; Li, X.; Liu, R. Identification of Bletilla striata and related decoction pieces: A data fusion method combining electronic nose, electronic tongue, electronic eye, and high-performance liquid chromatography data. Front. Chem. 2024, 11, 1342311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Fang, C.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, H. The Effect of Heat Stress on Sensory Properties of Fresh Oysters: A Comprehensive Study Using E-Nose, E-Tongue, Sensory Evaluation, HS–SPME–GC–MS, LC–MS, and Transcriptomics. Foods 2024, 13, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura-Aguilar, R.; Lucas-Bautista, J.A.; Árevalo-Galarza, M.L.; Bosquez-Molina, E. Volatile Organic Compounds as a Diagnostic Tool for Detecting Microbial Contamination in Fresh Agricultural Products: Mechanism of Action and Analytical Techniques. Processes 2024, 12, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.; Upadhyay, J.B.; Koshta, V. Application of biosensors in dairy-food industry. J. Food Qual. 2015, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Sun, J.; Chen, M.; Ge, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Pang, J.; Yan, Z. Effect of oxidized chitin nanocrystals and curcumin into chitosan films for seafood freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shen, J.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y. Ultra-efficient trimethylamine gas sensor based on Au nanoparticles sensitized WO3 nanosheets for rapid assessment of seafood freshness. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 133318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöning, M.; Poghossian, A. Recent advances in biologically sensitive field-effect transistors (BioFETs). Anal. Chem. 2022, 24, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Research progress in several types of fish freshness rapid detection methods. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 28, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, T. Research on the Safety of Sea Crab Based on Machine Olfactory. In Proceedings of the 2020 13th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design (ISCID), Hangzhou, China, 12–13 December 2020; Volume 5122, pp. 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Zhou, T.; Xia, H.; Zhang, T. Flexible Room-Temperature Ammonia Gas Sensors Based on PANI-MWCNTs/PDMS Film for Breathing Analysis and Food Safety. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, C.; Wan, B. Semiconductor-Type Triethylamine Sensor for Food Detection Based on WO3 Nanomaterials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.-Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Yi, S.-Y.; Sun, A.Y.; Gao, D.-Y.; Wan, D. Food Quality Monitor: Paper-Based Plasmonic Sensors Prepared Through Reversal Nanoimprinting for Rapid Detection of Biogenic Amine Odorants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xu, S.; Zhao, C.; Qiao, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhu, Y. Bimetallic Au@Pt Nanocrystal Sensitization Mesoporous α-Fe2O3; Hollow Nanocubes for Highly Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Fish Freshness at Low Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 25032–25040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Tian, W.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Amine-responsive cellulose-based ratiometric fluorescent materials for real-time and visual detection of shrimp and crab freshness. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Jiang, B.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Su, X. Flexible-fabricated sensor module with programmable magnetic actuators coupled to L-cysteine functionalized Ag@Fe3O4 complexes for Cu2+ detection in fish tissues. Biomed. Microdevices 2023, 25, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, R.S.; Schneider, R.; DeLima, G.R.; Fugikawa-Santos, L.; Corrêa, D. Wireless Sensor for Meat Freshness Assessment Based on Radio Frequency Communication. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 3c01657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Sang, S.; Jia, L.; Ou, C. Emerging Approach for Fish Freshness Evaluation: Principle, Application and Challenges. Foods 2022, 11, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Liu, Z. Recent advances in preservation and freshness monitoring methods for fish: A review on the quality and structural changes of fish after slaughter. Adv. Fish Technol. 2024, 5, 123129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, J.R. Evaluation of Seafood Freshness Quality; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Zeng, X.; Liu, D. Recent Advances in Methods and Techniques for Freshness Quality Determination and Evaluation of Fish and Fish Fillets: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1012–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shamery GE, M. Studies on Microbial, Physical and Chemical Quality of Fresh Yemeni Rabbit Meats During Storage in Taiz City. Taiz Univ. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2023, 3, 1278. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Pu, H.; Zhu, Z. Development of hyperspectral imaging coupled with chemometric analysis to monitor K value for evaluation of chemical spoilage in fish fillets. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, H.; Xu, L. Novel ammonia-responsive carboxymethyl cellulose/Co-MOF multifunctional films for real-time visual monitoring of seafood freshness. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, S.K.; Ambrose, B.; Sudalaimani, S.; Pandiaraj, M.; Giribabu, K.; Kathiresan, M. A review on chemical and electrochemical methodologies for the sensing of biogenic amines. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1693–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaut, A.; Duthen, S.; Grard, T.; Krzewinski, F.; N’Guessan, A.; Brisabois, A.; Duflos, G. Development of an SPME-GC-MS method for the specific quantification of dimethylamine and trimethylamine: Use of a new ratio for the freshness monitoring of cod fillets. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2597–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacquit, A.; Lau, K.; Diamond, D. Development of a colorimetric sensor for monitoring of fish spoilage amines in packaging headspace. IEEE Sens. 2004, 1, 365–367. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, D.-W.; Ma, J.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.; Lin, X.-R.; Cao, S.-L. Assembly-Induced Emission of Copper Nanoclusters: Revealing the Sensing Mechanism for Detection of Volatile Basic Nitrogen in Seafood Freshness On-Site Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Karoui, R. Quality evaluation of fish and other seafood by traditional and nondestructive instrumental methods: Advantages and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr 2015, 57, 1976–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsfall Jnr, M.; Gentleman, P.C.; Adowei, P.; Dikio, E.D. Evaluation of total volatile bases and trimethylamine in hake (Merluccius capensis) fish preserved at low temperature in Vanderbijlpark, South Africa. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 19, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliadourou, D.; Papadopoulos, V.D.; Domvridou, E.; Savvaidis, I.; Kontominas, M. Microbiological, chemical and sensory changes of whole and filleted Mediterranean aquacultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) stored in ice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschelli, L.; Berardinelli, A.; Dabbou, S.; Ragni, L.; Tartagni, M. Sensing Technology for Fish Freshness and Safety: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkaya, P.; Dağbağlı, S. Usage of Natural Colour Indicators in Packaging Materials for Monitorization of Meat Freshness. Turk. J. Agric.—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 9, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athauda, T.; Karmakar, N.C. Review of RFID-based sensing in monitoring physical stimuli in smart packaging for food-freshness applications. Wirel. Power Transf. 2019, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Xu, W.; Teng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Gong, C.; Wang, Q. An Integrated Food Freshness Sensor Array System Augmented by a Metal-Organic Framework Mixed-Matrix Membrane and Deep Learning. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Xia, F.; Wu, L.; Jin, Y.; Saldaña, M.A.; Sun, W. Poly-L-lactic acid/lead(II) acetate basic colour indicator membrane for visual monitoring in shrimp freshness. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2023, 36, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Qiu, L.; Tian, Y. Super Anti-Wetting Colorimetric Starch-Based Film Modified with Poly(dimethylsiloxane) and Micro-/Nano-Starch for Aquatic-Product Freshness Monitoring. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3243–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zaitoon, A.; Lim, L. A review on colorimetric indicators for monitoring product freshness in intelligent food packaging: Indicator dyes, preparation methods, and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-M.; Li, B.-H.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Xiong, X.-B.; Han, W.-D.; Liu, B.; Yang, S. Intelligent biogenic pH-sensitive and amine-responsive color-changing label for real-time monitoring of shrimp freshness. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarayan, K.; Palanisamy, Y.; Mohan, G.; Theivasigamani, A.; Kandasamy, S.; Sekar, V.; John, E.U.S.; Sukumaran, M.; Marimuthu, R.; Anjappan, H. Non-invasive measurement of spoilage of packed fish using halochromic sensor. Pigment Resin Technol. 2024, 53, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozzi, K.; Nakbi, A.; Challouf, R.; Dhiab, R. A review on microbial contamination cases in Tunisian coastal marine areas. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Khoshnoudi-Nia, S. Combining Knowledge- and Data-driven Fuzzy Approach to Evaluate Shelf-life of Various Seafood Products. Food Qual. Saf. 2021, 5, fyab022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelin, V.G.; Shogah, Z.A.; Bolshakov, D.; Tretyakov, A.V.; Nesterenko, I.S.; Kish, L. Determination of seafood spoilage by digital colorimetry of indicator test systems. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 89, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Bhandari, B. Freshness monitoring technology of fish products in intelligent packaging. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liao, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Enhancement of Colorimetric pH-Sensitive Film Incorporating Amomum tsao-ko Essential Oil as Antibacterial for Mantis Shrimp Spoilage Tracking and Fresh-Keeping. Foods 2024, 13, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, D.S.; Abramov, A.A.; Gaidarzhi, V.P.; Kaplun, D.S.; Agina, E.V.; Ponomarenko, S.A. Food Freshness Measurements and Product Distinguishing by a Portable Electronic Nose Based on Organic Field-Effect Transistors. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 4649–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meléndez, F.; Arroyo, P.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Palomeque-Mangut, S.; Suárez, J.; Lozano, J. Portable Electronic Nose Based on Digital and Analog Chemical Sensors for 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole Discrimination. Sensors 2022, 22, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, R.; Wahyudi, E.; Adhityamurti, M.D.; Putro JP, L.Y.; Barokah, B.; Rohmah, D.N. Freshness assessment of tilapia fish in traditional market based on an electronic nose. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2021, 10, 3111–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.; Alejo, M.; Escribano, P.; Arroyo, P.; Meléndez, F.; Lozano, J. Classification of Fish Freshness and Prediction of Mesophilic Aerobic Microbial Count with an Electronic Nose. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, S.; Benedetti, S.; Opizzio, M.; Nardo, E.D.; Buratti, S. Meat and Fish Freshness Assessment by a Portable and Simplified Electronic Nose System (Mastersense). Sensors 2019, 19, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, F.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. Real-time assessment of food freshness in refrigerators based on a miniaturized electronic nose. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5404–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloyarova, Y. Application of the “electronic nose” for evaluating volatile compounds of semi-finished small fish. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2023, 26, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhubhashini, M.N.; Liyanage, C.P.; Alahakoon, A.; Liyanage, R. Development of a comprehensive classification model for determining the storage day of frigate tuna (Auxis thazard) for freshness evaluation using a portable electronic nose. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 4672–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhosseini, H.; Luo, D.; Liu, H.; Xu, G. Intelligent Processing of E-nose Information for Fish Freshness Assessment. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.-Y.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.-M. Rapid Classification of Hairtail Fish and Pork Freshness Using an Electronic Nose Based on the PCA Method. Sensors 2011, 12, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X. Tilapia freshness prediction utilizing gas sensor array system combined with convolutional neural network pattern recognition model. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 25, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Chen, C.-S.; Xu, B.; Lu, M. Research on Freshness Detection for Chinese Mitten Crab Based on Machine Olfaction. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2016, 9758, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, X.; Luan, X.; Kong, C.; Chang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Al-Majeed, S.; Xiao, Y. A Comprehensive Method for Assessing Meat Freshness Using Fusing Electronic Nose, Computer Vision, and Artificial Tactile Technologies. J. Sens. 2020, 14, 8838535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohareb, F.; Papadopoulou, O.S.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.E.; Bessant, C. Ensemble-based support vector machine classifiers as an efficient tool for quality assessment of beef fillets from electronic nose data. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2025–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgués, J.; Esclapez, M.; Doñate, S.; Marco, S. RHINOS: A lightweight portable electronic nose for real-time odor quantification in wastewater treatment plants. iScience 2021, 24, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, K.; Huang, M.; Mujumdar, A.; Yang, C. Intelligent detection and control of quality deterioration of fresh aquatic products in the supply chain: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Xu, L.; Wu, F. Electronic Nose System implemented on ZYNQ Platform for Fruits Freshness Classification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 6th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, ITNEC, Chongqing, China, 24–26 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gu, J.; Zhang, R.; Mao, Y.; Tian, S. Freshness Evaluation of Three Kinds of Meats Based on the Electronic Nose. Sensors 2019, 19, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, S.; Yong, C.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X. Non-Destructive Detection of Chicken Freshness Based on Electronic Nose Technology and Transfer Learning. Agriculture 2023, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Evaluation of IoT-Enabled Monitoring and Electronic Nose Spoilage Detection for Salmon Freshness During Cold Storage. Foods 2020, 9, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, Z.; Koca, I. Electronic Tongue Applications in Food Engineering. Turk. J. Agric.—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.; Moazzem, M. Recent Applications of Potentiometric Electronic Tongue and Electronic Nose in Sensory Evaluation. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 27, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lei, J.; Liang, D. Identification of Fake Green Tea by Sensory Assessment and Electronic Tongue. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2021, 21, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinin, A.C.V.; Coatrini-Soares, A.; Franco, G.T.; Bondancia, T.J.; Coatrini-Soares, J.; Oliveira, O.N.; Mattoso, L.H. Electronic tongue made of gelatin self-supporting films on printed electrodes to detect lactose. Front. Sens. 2024, 3, 1401077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, K. Engineered nanomaterials-based sensing systems for assessing the freshness of meat and aquatic products: A state-of-the-art review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowshad, F.; Khan, M. Electronic Tongue for Food Safety and Quality Assessment. In Nondestructive Testing of Food Quality; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 207–231. [Google Scholar]
- Waimin, J.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Heredia-Rivera, U.; Kerr, N.A.; Nejati, S.; Gallina, N.L.; Bhunia, A.; Rahimi, R. Low-Cost Nonreversible Electronic-Free Wireless pH Sensor for Spoilage Detection in Packaged Meat Products. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 45752–45764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Ding, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Smartphone-assisted multicolor hypoxanthine sensing for on-site freshness assessment of aquatic products. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 369, 133246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.-J.; Koo, J.; Shin, Y.; Hwang, T. Electronic tongue for the simple and rapid determination of taste and odor compounds in water. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 139511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S. Chemical Tongues: Biomimetic Recognition Using Arrays of Synthetic Polymers. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. Electronic tongue applications for wastewater and soil analysis. iScience 2022, 25, 104304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-C.; Saad, B.; Surif, M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Shakaff, A.Y.M. Disposable E-Tongue for the Assessment of Water Quality in Fish Tanks. Sensors 2008, 8, 3665–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podrażka, M.; Baczynska, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Witkowska Nery, E. Electronic Tongue—A Tool for All Tastes? Biosensors 2018, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrissi, H.; Veloso, A.C.; Marx, I.M.G.; Dias, T.; Peres, A.M. A Potentiometric Electronic Tongue as a Discrimination Tool of Water-Food Indicator/Contamination Bacteria. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Pandey, C.M.; Kumar, D. Highly Sensitive Enzymatic Biosensor Based on Polyaniline-Wrapped Titanium Dioxide Nanohybrid for Fish Freshness Detection. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 195, 3052–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X. Colorimetric Biosensor Based on Magnetic Enzyme and Gold Nanorods for Visual Detection of Fish Freshness. Biosensors 2022, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.-M. RhB@MOF-5 Composite Film as a Fluorescence Sensor for Detection of Chilled Pork Freshness. Biosensors 2022, 12, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi-Moayed, S.; Orouji, A.; Hormozi-Nezhad, M. Multiplex Detection of Biogenic Amines for Meat Freshness Monitoring Using Nanoplasmonic Colorimetric Sensor Array. Biosensors 2023, 13, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriramulu, G.; Verma, R.; Singh, K.R.B.; Singh, P.; Chakra, C.; Mallick, S.; Singh, R.P.; Sadhana, K.; Singh, J. Self-assembled Copper Oxide Nanoflakes for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Xanthine Detection in Fish-Freshness Biosensors. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 138, 137640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuş, S.; Baytemir, G.; Taşaltın, N. Digital Colorimetric and Non-Enzymatic Biosensor with Nanoarchitectonics of Lepidium Meyenii-Silver Nanoparticles and Cotton Fabric: Real-Time Monitoring of Milk Freshness. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Sutarlie, L.; Loh, X. Sensors, Biosensors, and Analytical Technologies for Aquaculture Water Quality. Biosensors 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forinová, M.; Seidlová, A.; Pilipenco, A.; Lynn, N.S., Jr.; Obořilová, R.; Farka, Z.; Skládal, P.; Saláková, A.; Spasovová, M.; Houska, M.; et al. A Comparative Assessment of a Piezoelectric Biosensor Based on a New Antifouling Nanolayer and Cultivation Methods: Enhancing S. aureus Detection in Fresh Dairy Products. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2023, 6, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, B.; Shen, C.; Lai, O.; Tan, C.; Cheong, L. Electrochemical Biosensing of Chilled Seafood Freshness by Xanthine Oxidase Immobilized on Copper-Based Metal–Organic Framework Nanofiber Film. J. Food Sci. 2019, 12, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gurr, P.; Qiao, G. An irreversible spoilage sensor for protein-based food. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2903–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lim, L. An Inkjet-Printed Sulfonephthalein Dye Indicator Array for Volatile Amine Detection. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milintha Mary, T.P.; Kumaravel, B.; Nagamaniammai, G.; Karishma, S.; Essa, M.M.; Qoronfleh, M.W.; Chacko, L. Biosensors as Freshness Indicator for Packed Animal and Marine Products: A Review. Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, A.; Lewis, B.; Raducanu, M.; Kim, J. An Array-Based Sensor for Seafood Freshness Assessment. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 3084–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Majer-Baranyi, K.; Székács, A.; Adányi, N. Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Food Spoilage. Biosensors 2023, 13, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Hubbe, M.; Liu, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Rojas, O. Recent Developments in Colorimetric and Optical Indicators Stimulated by Volatile Base Nitrogen to Monitor Seafood Freshness. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Sun, C.; Fang, G.-z.; Wu, X.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Development of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Detection of Tyramine as an Index of Freshness in Meat and Seafood. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9279–9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, X.; Pei, X.; Huang, F.; Li, X.; Chen, A. Development of Halochromic Labels Based on Binary Systems of Cationic Guar Gum and κ-Carrageenan Loaded with Alizarin Red S for Monitoring Milk and Seafood Freshness. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 133, 108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, S.K.; Koshy, R.R.; Daniel, J.; Koshy, J.; Pothen, L.; Thomas, S. Development of Starch Based Intelligent Films by Incorporating Anthocyanins of Butterfly Pea Flower and TiO2 and Their Applicability as Freshness Sensors for Prawns During Storage. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37657–37666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Wu, H. Biosensors for the Assessment of Fish Health: A Review. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouler, J.; Monti, M.D.; Morgan, W.J.; Cameron, P.J.; Di Lorenzo, M. A Photosynthetic Toxicity Biosensor for Water. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 309, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Tan, Y.; Mubango, E.; Shi, C.; Regenstein, J.M.; Yang, Q.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Rapid Freshness and Survival Monitoring Biosensors of Fish: Progress, Challenge, and Future Perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarevic, J.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Espmark, Å.M.; Evensen, T.; Sosa, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. A Novel Miniaturized Biosensor for Monitoring Atlantic Salmon Swimming Activity and Respiratory Frequency. Animals 2021, 11, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Xia, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X. Improvement of Non-Destructive Detection of Lamb Freshness Based on Dual-Parameter Flexible Temperature-Impedance Sensor. Food Control 2023, 153, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, L.; Ni, A.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Gao, H.; Lin, P.; Zhang, K.; Chu, X.; Wang, S. Tough and Antifreezing MXene@Au Hydrogel for Low-Temperature Trimethylamine Gas Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 30633–30641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, W.; Shi, J.; Luo, H.; Fan, C.; Lv, W.; Chen, X.; Zeng, M.; Yang, J.; Hu, N.; Su, Y.; et al. Fully Flexible MXene-Based Gas Sensor on Paper for Highly Sensitive Room-Temperature Nitrogen Dioxide Detection. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Gao, Y.; Wu, R.; Ju, K.; Tan, J.; Xuan, F. Laser Direct Writing of Flexible Sensor Arrays Based on Carbonized Carboxymethylcellulose and Its Composites for Simultaneous Mechanical and Thermal Stimuli Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12374–12383. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Chu, Z.; Nie, X.; Wang, R.; He, X. SnS2 Quantum Dots Based Optoelectronic Flexible Sensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of NO2 Down to One-ppb. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25894–25902. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Xu, Y.; Zou, X. Easy-to-Use Visual Sensing System for Milk Freshness, Sensitized with Acidity-Responsive N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots. Foods 2022, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, P.; Luca, A.; Edelenbos, M. Development of a Small and Flexible Sensor-Based Respirometer for Real-Time Determination of Respiration Rate, Respiratory Quotient and Low O2 Limit of Fresh Produce. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmazoğlu, E. Digital Image Colorimetric Detection of H2O2 Utilizing PEG/Ag/AgO Nanoparticles Derived from Tangerine Leaf Extract. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2024, 11, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestry, S.; Satalkar, V.; Mhaske, S.T. Development of Imine-Azo-Dyes Derived from Vanillin and Salicylaldehyde for pH-Sensing in Smart Packaging. Pigment Resin Technol. 2023, 52, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnyk, I.; Janeček, E.-R.; Vaucher-Joset, J.; Stellacci, F. Edible Sensors for Meat and Seafood Freshness. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Xing, D.; Li, F.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, W. Design of Seafood Freshness Detector Based on Trimethylamine Gas Measurement. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2477, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplev, G.; Sünter, A.; Kuznetsov, A.; Frorip, A.; Korsakov, V.; Stepanova, O.; Lyalin, D.; Stepanova, O.V. Assessment of the Freshness of Fish and Poultry Meat by Fast Protein and Metabolite Liquid Chromatography Using a New Optical Sensor. Proc. Int. Electron. Conf. Biosens. 2023, 3, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Zhuo, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, X. Flexible Ammonia Sensor Based on PEDOT Silver Nanowire Composite Film for Meat Freshness Monitoring. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, D.; Mi, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xi, G. Highly Sensitive Trimethylamine QCM Sensor Based on Porous Functionalized Tungsten Disulfide/Polyacrylic Acid Composite for Seafood Freshness Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 392, 12345–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Javeed, A.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Chen, B.; Han, B. Preparation and Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan-Based Hydrogel with Dual pH/NH3 Sensor for Naked-Eye Monitoring of Seafood Freshness. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 233, 130440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Visagie, I.; Chen, Y.; Abbel, R.; Parker, K. NFC-Enabled Dual-Channel Flexible Printed Sensor Tag. Sensors 2023, 23, 6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoo, H.; Pham Ba, V.A.; Shin, N.; Hong, S. Dye-Functionalized Sol-Gel Matrix on Carbon Nanotubes for Refreshable and Flexible Gas Sensors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Dong, Y.; Qian, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Nikitina, M.A.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X. Hydrogel Coating Flexible pH Sensor System for Fish Spoilage Monitoring. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 24, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Nejati, S.; Sedaghat, S.; Gupta, K.; Mishra, R.; Rahimi, R. Electronic-Free Low-Cost Wireless Sensor Tag for Monitoring Fish Freshness. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 381, 133398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Fu, Y.; Huang, S.; Glamuzina, B.; Zhang, X. Novel Flexible Sensing Technology for Nondestructive Detection on Live Fish Health/Quality During Waterless and Low-Temperature Transportation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 228, 115211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damdam, A.; Ozay, L.; Ozcan, C.; Alzahrani, A.; Helabi, R.; Salama, K. IoT-Enabled Electronic Nose System for Beef Quality Monitoring and Spoilage Detection. Foods 2023, 12, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicia, W.X.L.; Rovina, K.; Nur’ Aqilah, N.M.; Vonnie, J.; Yin, K.W.; Huda, N. Assessing Meat Freshness via Nanotechnology Biosensors: Is the World Prepared for Lightning-Fast Pace Methods? Biosensors 2023, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.; Lin, Y.; Haenen, S.R.R.; Marschall, J.; Hummel, A.; Wouters, S.F.A.; Raats, J.; de Jong, A.D.; Yan, J.; Prins, M. Real-Time Immunosensor for Small-Molecule Monitoring in Industrial Food Processes. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 7950–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, F.; Liang, Z.; Deng, J.; Lin, Q.; Li, W.; Peng, Q.; Fang, Y. Toward Intelligent Food Packaging of Biosensor and Film Substrate for Monitoring Foodborne Microorganisms: A Review of Recent Advancements. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3290–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R.; Duan, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Z. Fiber-Optic-Based Biosensor as an Innovative Technology for Point-of-Care Testing Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria To Defend Food and Agricultural Product Safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10982–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Si, Y.; Liu, R.; Guo, X. Flexible Organic Polymer Gas Sensor and System Integration for Smart Packaging. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Huang, W.-Y.; Majer-Baranyi, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X. Conformal Temperature/Impedance Sensing Patch Based on Graphene Materials for Nondestructive Detection of Fish Freshness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 45095–45105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Mechanism | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principal Component Analysis (PCA) | Statistical technique for dimensionality reduction and data pattern recognition | 91% | 90.9% | Simple data processing, good correlation | Sensitive to noise, requires large sample data | [67] |
| Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) | Deep learning model for hierarchical pattern recognition | 92.31% | 91.5% | Highly nonlinear modeling, high prediction accuracy | Computationally complex, long training time | [69] |
| Laplacian Eigenmap (LE) | Nonlinear dimensionality reduction method using graph-based techniques | 85% | 84.1% | Can handle nonlinear data | High algorithmic complexity | [70] |
| Ensemble-based Support Vector Machine (SVM) | Combines multiple SVM classifiers for robust decision-making | 84.1% | 72.7% | Effective for high-dimensional data | Sensitive to parameter selection, computationally expensive | [72] |
| Ultra-Fast Gas Chromatography (UFGC) | Separates and analyzes volatile compounds using high-speed gas chromatography | 89% | 88% | Fast speed, high resolution | Expensive equipment, complex operation | [71] |
| Advanced Sensor Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic Nose | Short response time, fast monitoring, simple pre-processing, wide evaluation range, good repeatability | Susceptible to environmental interference, high equipment cost | Rapid detection of odor in food products |
| Electronic Tongue | Responds to some low concentrations of substances generated in the early stages | Susceptible to environmental interference, high equipment cost | Rapid detection of taste in food |
| Biosensors | High sensitivity and specificity | Poor stability, not suitable for precise biochemical analysis | Sensitive biochemical analysis in controlled conditions |
| Flexible Sensors | Flexibility, multi-functional integration, suitable for real-time and continuous monitoring | Currently facing challenges in stability and long-term use in complex environments | Real-time freshness detection and continuous monitoring in aquatic products |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Liu, K.; Wei, G.; He, A.; Kong, W.; Zhang, X. A Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Aquatic Products Freshness Assessment in Cold Chain Logistics. Biosensors 2024, 14, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100468
Wang B, Liu K, Wei G, He A, Kong W, Zhang X. A Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Aquatic Products Freshness Assessment in Cold Chain Logistics. Biosensors. 2024; 14(10):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100468
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Baichuan, Kang Liu, Guangfen Wei, Aixiang He, Weifu Kong, and Xiaoshuan Zhang. 2024. "A Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Aquatic Products Freshness Assessment in Cold Chain Logistics" Biosensors 14, no. 10: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100468
APA StyleWang, B., Liu, K., Wei, G., He, A., Kong, W., & Zhang, X. (2024). A Review of Advanced Sensor Technologies for Aquatic Products Freshness Assessment in Cold Chain Logistics. Biosensors, 14(10), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14100468






