Insights into the Fabrication and Electrochemical Aspects of Paper Microfluidics-Based Biosensor Module
Abstract
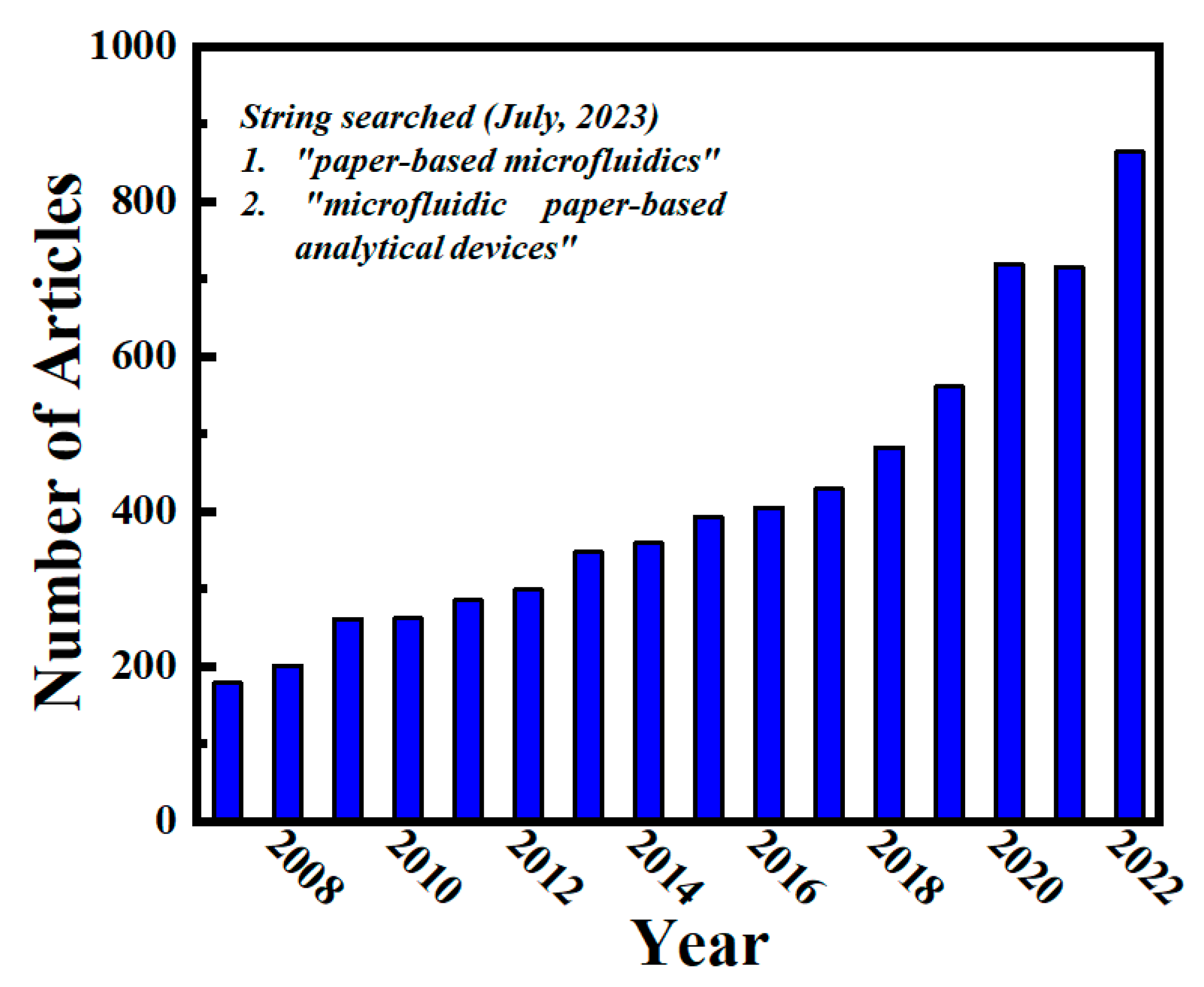
1. Introduction
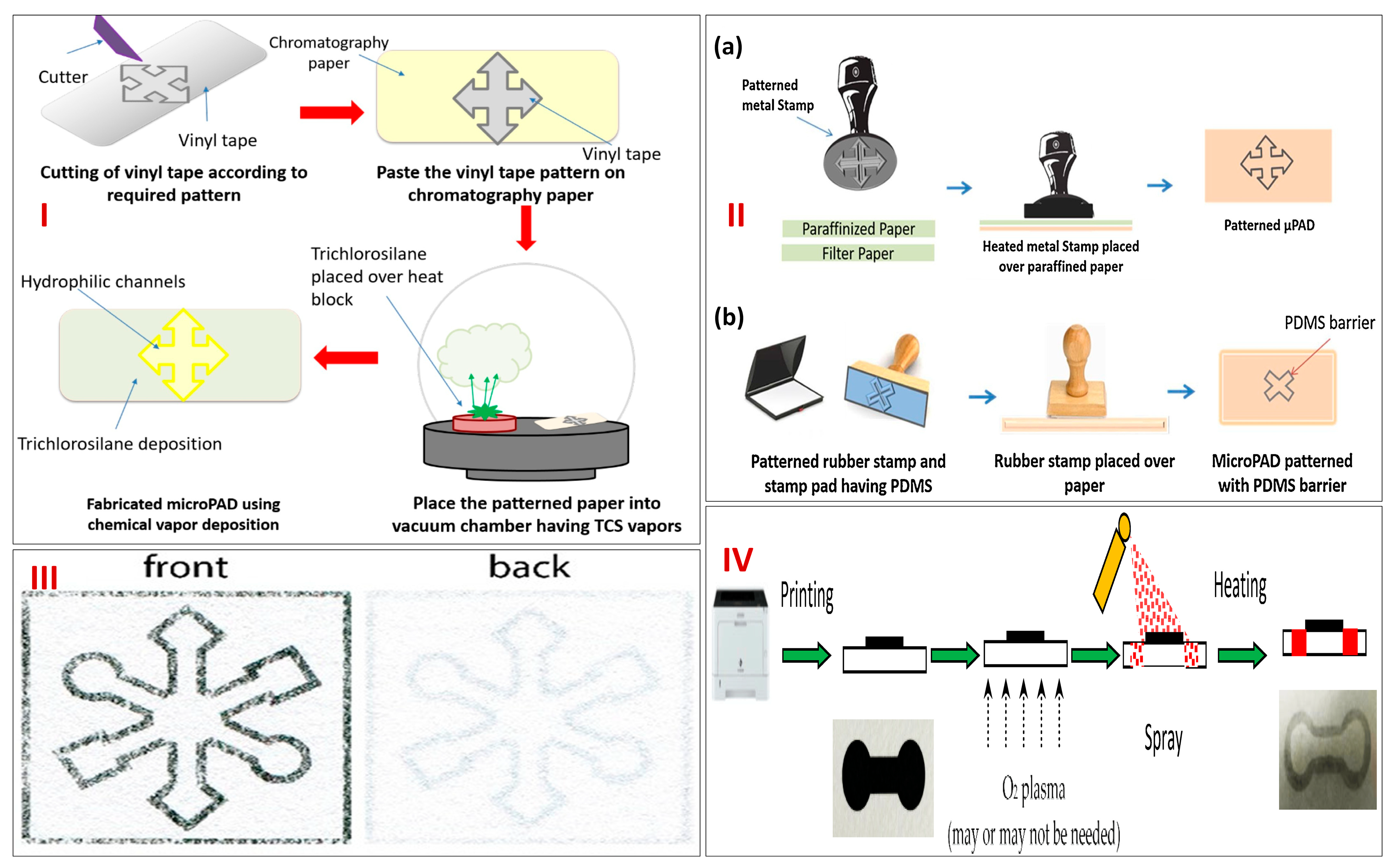
2. Designing and Fabrication of Paper Microfluidics-Based Biosensor Module

3. Applications
3.1. Paper-Based Microfluidics Platforms for Electrochemical Detection of Small Molecules
3.2. Paper-Based Microfluidics Platforms for Electrochemical Detection of Macromolecules

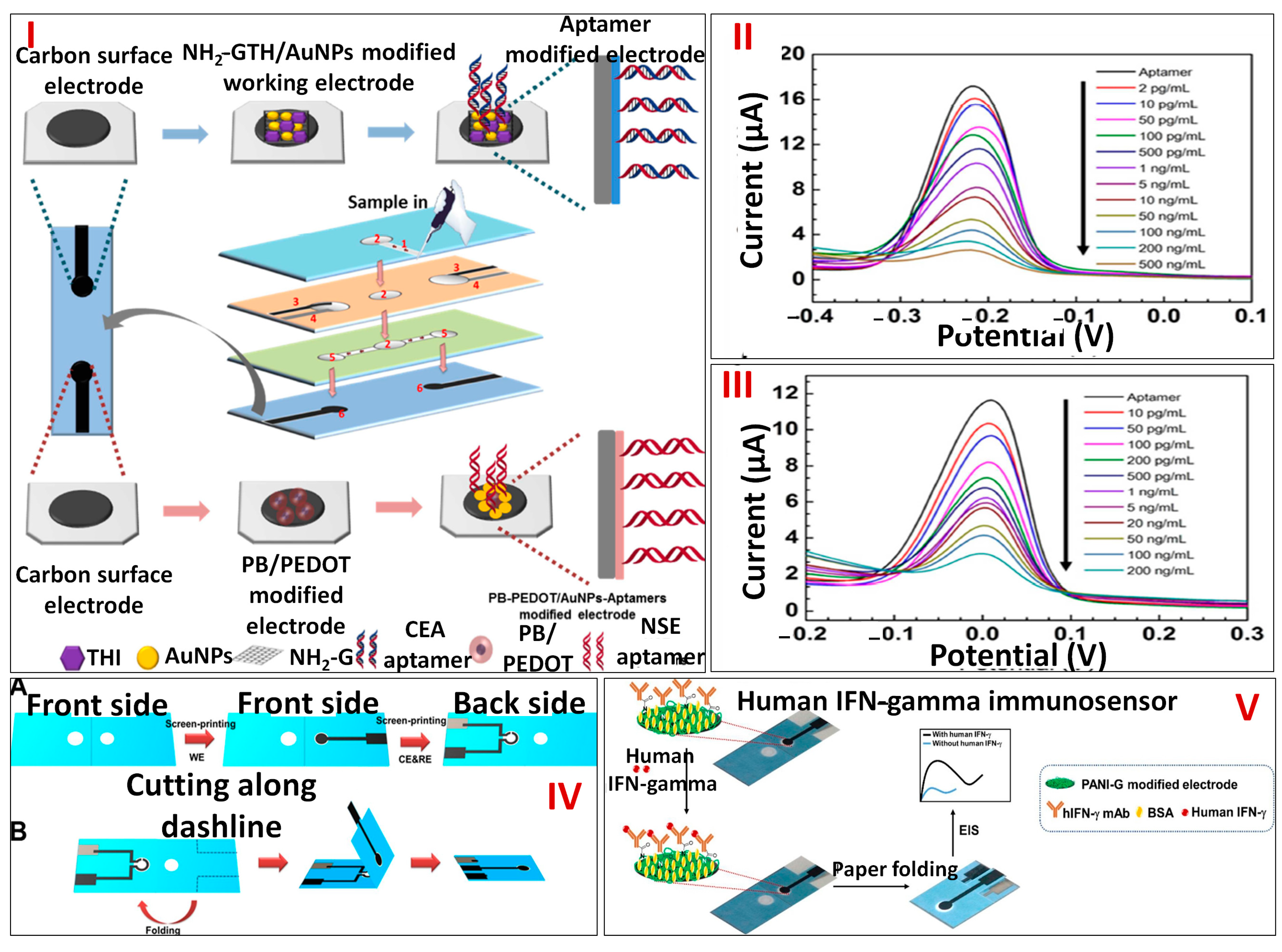
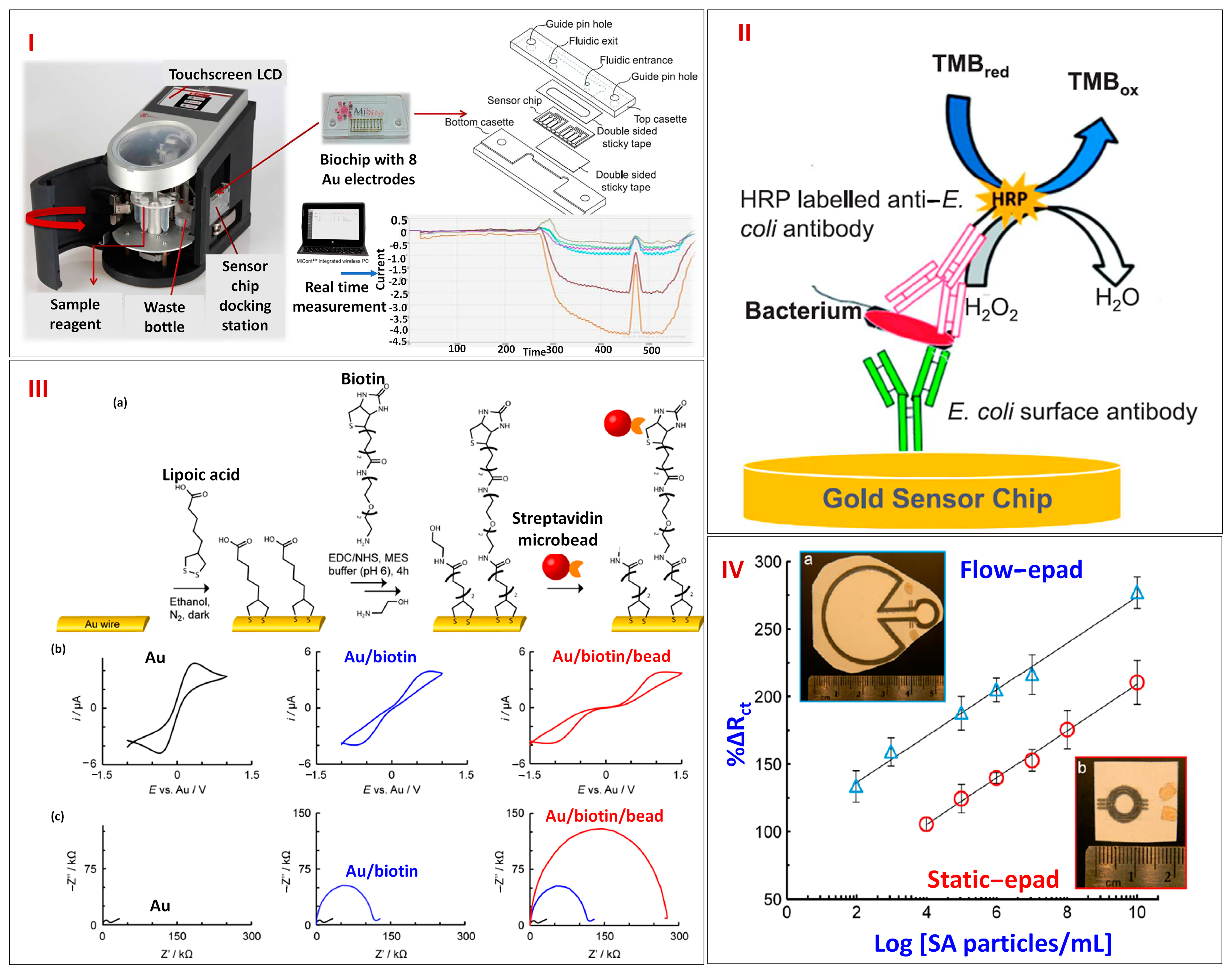
3.3. Paper-Based Microfluidics Platforms for Electrochemical Detection of Cells
4. Potential Applications of Micro-PADs in Various Domains
4.1. Healthcare Sector
4.2. Environmental Sector
4.3. Food Sector
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahato, K.; Srivastava, A.; Chandra, P. Paper Based Diagnostics for Personalized Health Care: Emerging Technologies and Commercial Aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Dkhar, D.S.; Mahapatra, S.; Divya; Kumar, R.; Chandra, P. Nano-Bioengineered Sensing Technologies for Real-Time Monitoring of Reactive Oxygen Species in in Vitro and in Vivo Models. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Glucose Biosensors: 40 Years of Advances and Challenges. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 383–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Trends in Miniaturized Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115701. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Zine, N.; Baraket, A.; Zabala, M.; Campabadal, F.; Caruso, R.; Trivella, M.G.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Errachid, A. A Novel Biosensor Based on Hafnium Oxide: Application for Early Stage Detection of Human Interleukin-10. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 175, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, K.; Kumar, A.; Maurya, P.K.; Chandra, P. Shifting Paradigm of Cancer Diagnoses in Clinically Relevant Samples Based on Miniaturized Electrochemical Nanobiosensors and Microfluidic Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 411–428. [Google Scholar]
- Nishat, S.; Jafry, A.T.; Martinez, A.W.; Awan, F.R. Paper-Based Microfluidics: Simplified Fabrication and Assay Methods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 336, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.B.; Chandra, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Shim, Y.B. A Simple Separation Method with a Microfluidic Channel Based on Alternating Current Potential Modulation. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9738–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrilho, E.; Martinez, A.W.; Whitesides, G.M. Understanding Wax Printing: A Simple Micropatterning Process for Paper-Based Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7091–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Kumachev, A.; Martinez, A.W.; Narovlyansky, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrochemical Sensing in Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviana, E.; Carrão, D.B.; Pratiwi, R.; Henry, C.S. Emerging Applications of Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Drug Analysis: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paschoalino, W.J.; Kogikoski, S.; Barragan, J.T.C.; Giarola, J.F.; Cantelli, L.; Rabelo, T.M.; Pessanha, T.M.; Kubota, L.T. Emerging Considerations for the Future Development of Electrochemical Paper-Based Analytical Devices. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 10–30. [Google Scholar]
- da Costa, T.H.; Song, E.; Tortorich, R.P.; Choi, J.-W. A Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor Using Inkjet-Printed Carbon Nanotube Electrodes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, S3044–S3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical Detection for Paper-Based Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, C.; Anderson, M.J.; Crooks, R.M. Electrochemistry in Hollow-Channel Paper Analytical Devices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4616–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, J.G.; Benavidez, T.E.; Duran, G.M.; Vinogradova, E.; Rios, A.; Garcia, C.D. Development and Characterization of Carbon Based Electrodes from Pyrolyzed Paper for Biosensing Applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 765, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tilli, M.; Paulasto-Kroâckel, M.; Petzold, M.; Theuss, H.; Motooka, T.; Lindroos, V. Handbook of Silicon Based MEMS Materials and Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128177860. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, M.B.; Ayachit, N.H.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Biosensors and Microfluidic Biosensors: From Fabrication to Application. Biosensors 2022, 12, 543. [Google Scholar]
- Kakaei, K.; Esrafili, M.D.; Ehsani, A. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Supercapacitors. Interface Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 339–386. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, K.M.; Chakraborty, S. PDMS Microfluidics: A Mini Review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 137, 48958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.F.; Ju, W.J.; Wu, M.C.; Tai, C.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Fu, L.M. Rapid Prototyping of PMMA Microfluidic Chips Utilizing a CO2 Laser. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, N.K.; Chaurasia, P.; Chandra, P.; Mahto, S.K. Microfluidics Devices as Miniaturized Analytical Modules for Cancer Diagnosis. In Advanced Microfluidics-Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; ISBN 9781003033479. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zilberman, Y.; Mostafalu, P.; Sonkusale, S.R. Paper Based Platform for Colorimetric Sensing of Dissolved NH3 and CO2. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.I.; Gehlot, P.; Sidapra, K.; Edwards, A.D.; Reis, N.M. Portable Smartphone Quantitation of Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) in a Fluoropolymer Microfluidic Device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Jia, C.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Mao, H.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. A Microfluidic Chip Integrated with a High-Density PDMS-Based Microfiltration Membrane for Rapid Isolation and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafalu, P.; Akbari, M.; Alberti, K.A.; Xu, Q.; Khademhosseini, A.; Sonkusale, S.R. A Toolkit of Thread-Based Microfluidics, Sensors, and Electronics for 3D Tissue Embedding for Medical Diagnostics. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Huang, X.; Guo, J.; Ma, X. Automatic Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Biosensor System at the Point of Care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutse, S.W.; Yusof, N.A. Microfluidics-Based Lab-on-Chip Systems in DNA-Based Biosensing: An Overview. Sensors 2011, 11, 5754–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned Paper as a Platform for Inexpensive, Low-Volume, Portable Bioassays. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan Srivastava, V.; Kumari, R.; Chandra, P. Miniaturized Surface Engineered Technologies for Multiplex Biosensing Devices. Electroanalysis 2023, 35, e202200355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Advances in Paper-Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 585–597. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. Low-Cost Fabrication of Paper-Based Micro Fl Uidic Devices by One- Step Plotting. Anal Chem. 2012, 84, 6331–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Li, B.; Qi, J.; Ji, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, L. Low Cost Fabrication of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices with Water-Based Polyurethane Acrylate and Their Application for Bacterial Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 303, 127213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M. Three-Dimensional Microfluidic Devices Fabricated in Layered Paper and Tape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19606–19611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Wiley, B.J.; Gupta, M.; Whitesides, G.M. FLASH: A Rapid Method for Prototyping Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2146–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenda, K.; Ota, R.; Yamada, K.; Henares, T.G.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. High-Resolution Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Sub-Microliter Sample Analysis. Micromachines 2016, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Inkjet-Printed Microfluidic Multianalyte Chemical Sensing Paper. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6928–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xie, Z.; Wang, W.; Yuan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Gu, Z. Bio-Inspired Vapor-Responsive Colloidal Photonic Crystal Patterns by Inkjet Printing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11094–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkonen, J.; Lehtinen, K.; Erho, T. Flexographically Printed Fluidic Structures in Paper. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 10246–10250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. A Low-Cost, Simple, and Rapid Fabrication Method for Paper-Based Microfluidics Using Wax Screen-Printing. Analyst 2011, 136, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Savitha, R.; Renganathan, T.; Pushpavanam, S. Fabrication of Laser Printed Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices (LP-ΜPADs) for Point-of-Care Applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Paleja, B.; Larbi, K.; Kumar, P.; Tay, J.A.; Siew, J.Y.; Inci, F.; Wang, S.Q.; Chee, C.; Wang, Y.T.; et al. Microchip-Based Ultrafast Serodiagnostic Assay for Tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuo, M.M.; Martinez, R.V.; Lan, W.J.; Liu, X.; Barber, J.; Atkinson, M.B.J.; Bandarage, D.; Bloch, J.F.; Whitesides, G.M. Fabrication of Low-Cost Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by Embossing or Cut-and-Stack Methods. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4230–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, G.; Babur, E. Vapor-Phase Deposition of Polymers as a Simple and Versatile Technique to Generate Paper-Based Microfluidic Platforms for Bioassay Applications. Analyst 2014, 139, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, P.; Gupta, M. Vapor Phase Deposition of Functional Polymers onto Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices for Advanced Unit Operations. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10129–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, P.D.; Flowers, C.A.; Gupta, M. Three-Dimensional Patterning of Porous Materials Using Vapor Phase Polymerization. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2428–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Nguyen, T.; Shen, W. Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by Plasma Treatment. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9131–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.; Devadhasan, J.P.; Howse, R.; Kim, J. A Chemically Patterned Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device (C-ΜPAD) for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas, K.L.; Dossi, N.; Piccin, E. A Simple Method for Patterning Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) Barriers in Paper Using Contact-Printing with Low-Cost Rubber Stamps. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 858, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathaweesansurn, A.; Thongrod, S.; Khongkaew, P.; Phechkrajang, C.M.; Wilairat, P.; Choengchan, N. Simple and Fast Fabrication of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device by Contact Stamping for Multiple-Point Standard Addition Assay: Application to Direct Analysis of Urinary Creatinine. Talanta 2020, 210, 120675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Nie, J.; Le, S.; Qin, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Equipment-Free Quantitative Measurement for Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices Fabricated Using the Principles of Movable-Type Printing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, R.A.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Vazquez-Alvarado, M.; Martinez, N.W.; Martinez, A.W. Beyond Wax Printing: Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices Using a Thermal Transfer Printer. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8833–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.J.; Hsu, S.K. Fabrication of Paper-Based Microfluidics by Spray on Printed Paper. Polymers 2022, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anushka; Bandopadhyay, A.; Das, P.K. Paper Based Microfluidic Devices: A Review of Fabrication Techniques and Applications. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2023, 232, 781–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Dkhar, D.S.; Mahapatra, S.; Divya; Singh, S.P.; Chandra, P. Nano-Engineered Surface Comprising Metallic Dendrites for Biomolecular Analysis in Clinical Perspective. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, L.; Mazzaracchio, V.; Serani, A.; Fabiani, G.; Fabiani, L.; Volpe, G.; Moscone, D.; Bianco, G.M.; Occhiuzzi, C.; Marrocco, G.; et al. Microfluidic Paper-Based Wearable Electrochemical Biosensor for Reliable Cortisol Detection in Sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 379, 133258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor-Gutiérrez, O.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Fully Integrated Sampler and Dilutor in an Electrochemical Paper-Based Device for Glucose Sensing. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoh, A.; Chaiyo, S.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. 3D Capillary-Driven Paper-Based Sequential Microfluidic Device for Electrochemical Sensing Applications. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Christensen, M.G.; Iles, A.; Sharma, A.L.; Singh, S.; Pamme, N. Microfluidic-Based Electrochemical Immunosensing of Ferritin. Biosensors 2020, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.L.; Zhang, G.R.; Li, W.; Biesalski, M.; Etzold, B.J.M. Modifier-Free Microfluidic Electrochemical Sensor for Heavy-Metal Detection. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4593–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Minotti, C.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. Fully Integrated Ready-to-Use Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensor to Detect Nerve Agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukird, J.; Soum, V.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. 3D Paper-Based Microfluidic Device: A Novel Dual-Detection Platform of Bisphenol A. Analyst 2020, 145, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núnez-Bajo, E.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Costa-García, A.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. In Situ Gold-Nanoparticle Electrogeneration on Gold Films Deposited on Paper for Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Determination of Glucose. Talanta 2018, 178, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pungjunun, K.; Yakoh, A.; Chaiyo, S.; Praphairaksit, N.; Siangproh, W.; Kalcher, K.; Chailapakul, O. Laser Engraved Microapillary Pump Paper-Based Microfluidic Device for Colorimetric and Electrochemical Detection of Salivary Thiocyanate. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Kadian, S.; Zareei, A.; Rivera, U.H.; Rahimi, R. Printed Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensor with Integrated Paper Microfluidics for Rapid Lidocaine Detection in Blood. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1229, 340332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, T.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, G.; Jin, H.; Cai, X. Folding Paper-Based Aptasensor Platform Coated with Novel Nanoassemblies for Instant and Highly Sensitive Detection of 17β-Estradiol. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3186–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobphahom, S.; Ruecha, N.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Remcho, V.T. A Copper Oxide-Ionic Liquid/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Sensor Enabled by Digital Dispensing: Non-Enzymatic Paper-Based Microfluidic Determination of Creatinine in Human Blood Serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1083, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Crooks, R.M. Aptamer-Based Origami Paper Analytical Device for Electrochemical Detection of Adenosine. Angew. Chemie 2012, 124, 7031–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroma, L.Y.; Santhiago, M.; Gobbi, A.L.; Kubota, L.T. Separation and Electrochemical Detection of Paracetamol and 4-Aminophenol in a Paper-Based Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 725, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossi, N.; Toniolo, R.; Pizzariello, A.; Impellizzieri, F.; Piccin, E.; Bontempelli, G. Pencil-Drawn Paper Supported Electrodes as Simple Electrochemical Detectors for Paper-Based Fluidic Devices. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Hu, J.; Wee, W.H.; Han, Y.L.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Direct Writing Electrodes Using a Ball Pen for Paper-Based Point-of-Care Testing. Analyst 2015, 140, 5526–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wang, P.; Ge, S.; Ge, L.; Yu, J.; Yan, M. Photoelectrochemical Sensor for Pentachlorophenol on Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device Based on the Molecular Imprinting Technique. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jian, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, S.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Film and Boronate Affinity Sandwich Assay for Glycoprotein Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 16198–16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Cui, K.; Liu, Y.; Hao, S.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemical/Visual Analytical Device via Signal Amplification of Pd@Hollow Zn/Co Core-Shell ZIF67/ZIF8 Nanoparticles for Prostate-Specific Antigen Detection. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5459–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Cai, X. Label-Free Microfluidic Paper-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor for Ultrasensitive and Simultaneous Multiplexed Detection of Cancer Biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 136, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. Label-Free Paper-Based Electrochemical Impedance Immunosensor for Human Interferon Gamma Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teengam, P.; Siangproh, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Henry, C.S.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Electrochemical Paper-Based Peptide Nucleic Acid Biosensor for Detecting Human Papillomavirus. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 952, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Ge, L.; Sun, X.; Li, F. A Universal Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Zero-Background Assay of Diverse Biomarkers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15381–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Luo, J.; Xiong, Y.; Ming, T.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Low Sample Volume Origami-Paper-Based Graphene-Modified Aptasensors for Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of Cancer Biomarker-EGFR. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, M.; Muruganand, S.; Parthiban, C. Development of Novel Paper Based Electrochemical Immunosensor with Self-Made Gold Nanoparticle Ink and Quinone Derivate for Highly Sensitive Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fang, C.; Zeng, R.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z. Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices for Electrochemical Immunofiltration Analysis of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksin, E.; Torul, H.; Yarali, E.; Tamer, U.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Erdem, A. Paper-Based Electrode Assemble for Impedimetric Detection of MiRNA. Talanta 2021, 225, 122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasetsirikul, S.; Tran, K.T.; Clack, K.; Soda, N.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Nguyen, N.T. Low-Cost Electrochemical Paper-Based Device for Exosome Detection. Analyst 2022, 147, 3732–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Mao, K.; Liu, N.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z. Graphene Nanocomposites Modified Electrochemical Aptamer Sensor for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Prostate Specific Antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkaew, S.; Yakoh, A.; Chuaypen, N.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Rengpipat, S.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. An Automated Fast-Flow/Delayed Paper-Based Platform for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.G.; Regiart, M.D.; Rodríguez-Martínez, A.; De Miguel-Pérez, D.; Serrano, M.J.; Lorente, J.A.; Tortella, G.; Rubilar, O.; Sapag, K.; Bertotti, M.; et al. Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Paper-Based Immunosensor for Claudin 7 and CD81 Dual Determination on Extracellular Vesicles from Breast Cancer Patients. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.S.; Cao, X.; Gao, N.; Jin, Q.; Sanjay, S.T.; Henao-Pabon, G.; Li, X.J. A Low-Cost Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor on Paper for High-Sensitivity Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, W.; Yang, H.; Ma, C.; Yu, J.; Yan, M.; Song, X. Sensitive Origami Dual-Analyte Electrochemical Immunodevice Based on Polyaniline/Au-Paper Electrode and Multi-Labeled 3D Graphene Sheets. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 120, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ge, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M.; Yuan, L.; Ge, Q.; Fang, W.; Ju, X. A Novel Electrochemical Mast Cell-Based Paper Biosensor for the Rapid Detection of Milk Allergen Casein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xue, P.; Hui, K.M.; Kang, Y. A Paper-Based Microfluidic Electrochemical Immunodevice Integrated with Amplification-by-Polymerization for the Ultrasensitive Multiplexed Detection of Cancer Biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Akgun, M.; Kokturk, G.; Uludag, Y. A Fully Automated Microfluidic-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Real-Time Bacteria Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya; Dkhar, D.S.; Kumari, R.; Mahapatra, S.; Kumar, R.; Chandra, P. Ultrasensitive Aptasensors for the Detection of Viruses Based on Opto-Electrochemical Readout Systems. Biosensors 2022, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channon, R.B.; Yang, Y.; Feibelman, K.M.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Henry, C.S. Development of an Electrochemical Paper-Based Analytical Device for Trace Detection of Virus Particles. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7777–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, L.; Liu, H.; Yan, M.; Huang, J.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Cancer Cells Sensor Based on Trimetallic Dendritic Au@PtPd Nanoparticles for Signal Amplification on Lab-on-Paper Device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, J.; Devarakonda, S.; Kumar, S.; Jang, J. Development of a Paper-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor Using an Antibody-Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes Bio-Conjugate Modified Electrode for Label-Free Detection of Foodborne Pathogens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. An Innovative Blood Plasma Separation Method for a Paper-Based Analytical Device Using Chitosan Functionalization. Analyst 2020, 145, 5491–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomean, S.; Attapong, J.; Jitsuvantaya, S.; Poomsaard, K.; Dongwilai, C.; Bunnun, P.; Kaset, C. Development of Mia Phenotyping Using Paper-Based Device. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonhorn, J.E.; Fernandes, S.C.; Rajaratnam, A.; Deraney, R.N.; Rollanda, J.P.; Mace, C.R. A Device Architecture for Three-Dimensional, Patterned Paper Immunoassays. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4653–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerabhadrappa, B.; Delaby, C.; Hirtz, C.; Vialaret, J.; Alcolea, D.; Lleó, A.; Fortea, J.; Santosh, M.S.; Choubey, S.; Lehmann, S. Detection of Amyloid Beta Peptides in Body Fluids for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Where Do We Stand? Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, A.; Mancini, M.; Gioia, V.; Cinti, S. Office Paper-Based Electrochemical Strips for Organophosphorus Pesticide Monitoring in Agricultural Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8859–8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Rama, E.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Preconcentration and Sensitive Determination of the Anti-Inflammatory Drug Diclofenac on a Paper-Based Electroanalytical Platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1074, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, K.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ge, S.; Yu, J. A Self-Powered Origami Paper Analytical Device with a Pop-up Structure for Dual-Mode Electrochemical Sensing of ATP Assisted by Glucose Oxidase-Triggered Reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, T.M.G.; Garcia, P.T.; Coltro, W.K.T. Colorimetric Determination of Nitrite in Clinical, Food and Environmental Samples Using Microfluidic Devices Stamped in Paper Platforms. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7311–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimchuk, E.; Hu, Y.; Nilghaz, A.; Hua, M.Z.; Sun, S.; Lu, X. Development of Paper-Based Microfluidic Device for the Determination of Nitrite in Meat. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Lu, L.; Fang, C.; Duan, B.; Zhu, Z. Determination of Apparent Amylose Content in Rice by Using Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9863–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
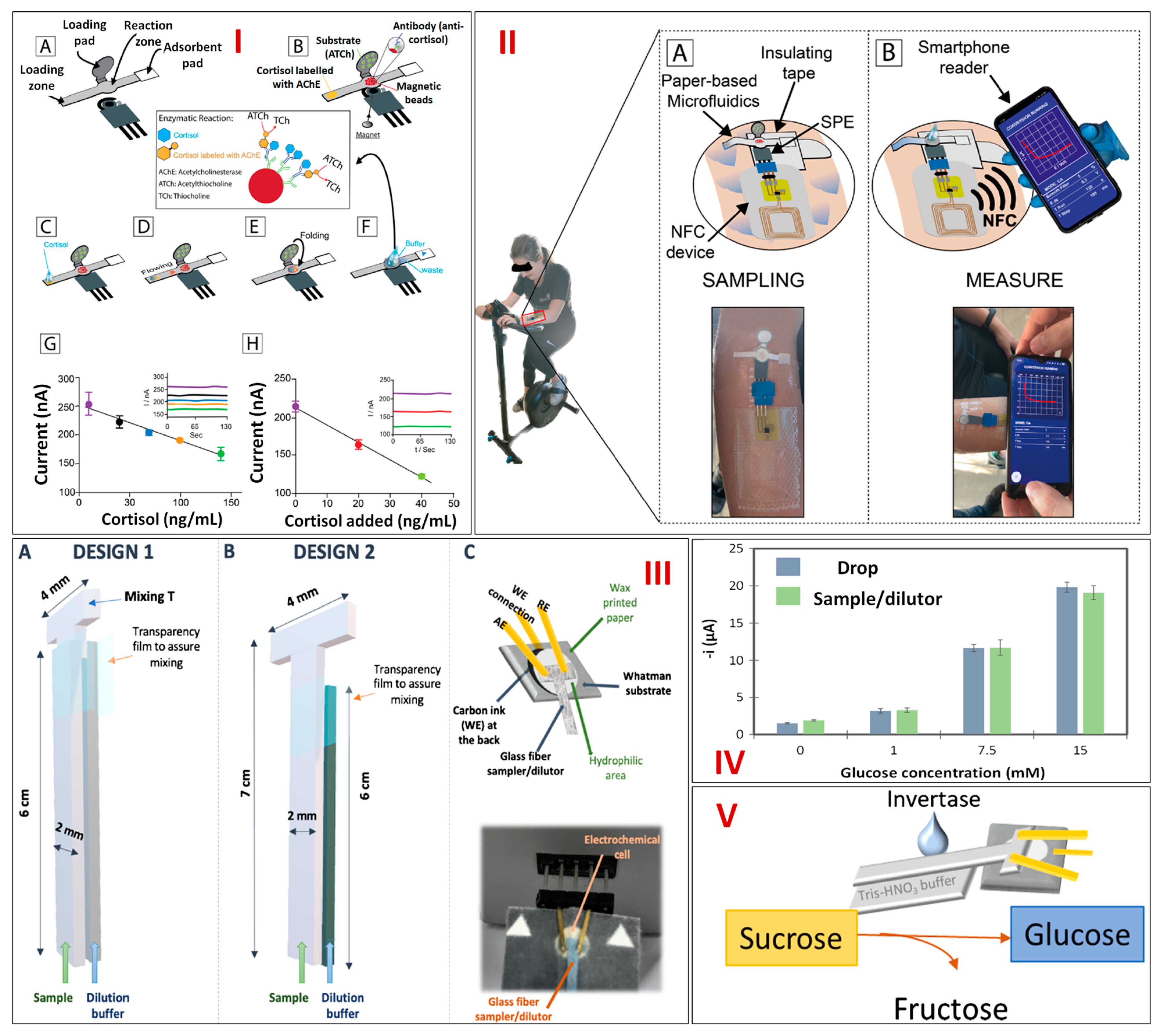
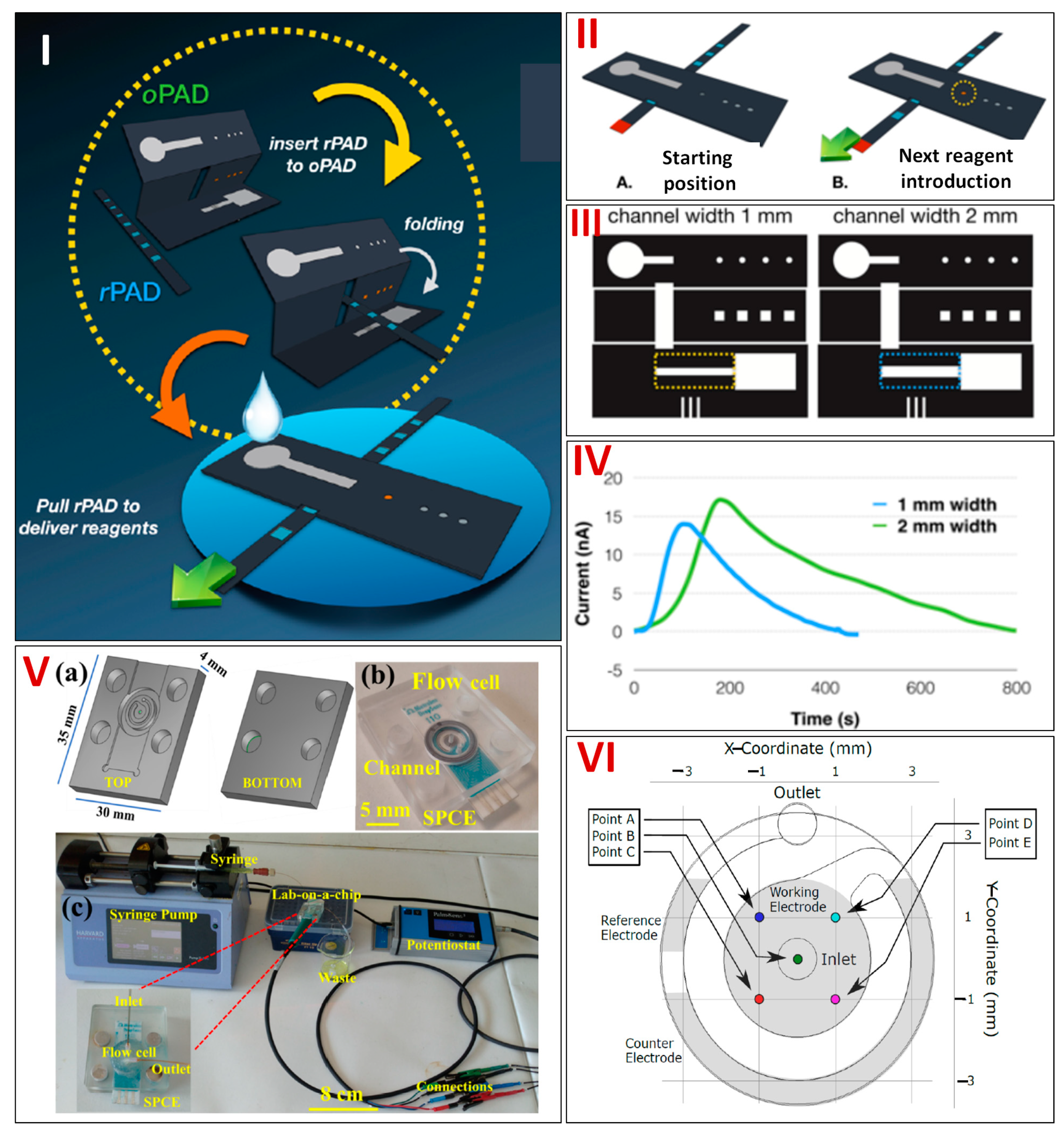
| Sensing Molecule | Electrochemical Technique Used | Fabrication Strategy | Fabrication Steps | Paper Type | LDR | LOD | Real Sample | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cd2+, Pb2+ | SWASV | 3D microfluidic paper and graphite foil used to fabricate sensor. Modified working electrode prepared using Bi2O3. | 3 | Filter paper (pore size: 12−15 μm; thickness: 305 μm) | 5–500 μg/L for Cd2+ and 5–100 μg/L for Pb2+ | 1.2 μg/L for Cd2+, 1.8 μg/L for Pb2+ | Commercial mineral water | [60] |
| 2 | Paraoxon (Nerve agent stimulant) | CV and CA | Working electrode modified with Carbon Black/Prussian Blue nanocomposite powder. Paper-based test area was integrated with nitrocellulose membrane holding SPCE and BChe. | 3 | Filter paper (density: 67 g/m2) | 5–100 μg/L | 3 μg/L | NR | [61] |
| 3 | Bisphenol A | CV, DPV | MWCNT electrode modified by ZnO. | 3 | NR | 0–5 mM | 0.35 μM | NR | [62] |
| 4 | Glucose | LSV | SPCE were paired with paper-based gold working electrodes to produce gold nanoparticles electrochemically in a repeatable manner. | 8 | Whatman chromatographic papers grade 1 (180-μm thick) and grade 3MM (260-μm thick) | 0.01–5 mM | 6 μM | Orange juice, energetic beverage and cola beverage | [63] |
| 5 | Salivary thiocyanate | SWASV | A micropump made from a capillary channel that was created via laser-engraved micropatterning on paper. CuPc/SPGE, a graphene electrode modified with copper (II) phthalocyanine, was used. | 3 | Filter paper (Whatman No. 1) | 0.025–100 mmol/L | 6 μmol/L | Real human saliva | [64] |
| 6 | Lidocaine | SWV | Integrated graphene-based paper microfluidic electrode. Laser printing and NIR drying utilized for fabrication. | 6 | Filter paper (Whatman, φ = 55 mm with particle retention of 20–25 μm) | 1–100 μM | 0.8 μM | Serum and blood | [65] |
| 7 | 17β-estradiol | CV and DPV | Modified electrode fabricated using amine-functionalized SWCNT/new methylene blue/ (AuNPs). | 4 | Chromatography paper (Whatman No. 1) | 10 pg/mL–500 ng/mL | 5 pg/mL | Clinical serum samples | [66] |
| 8 | Creatinine | CV and amperometry | Electrochemically reduced graphene modified SPCE (CuO/IL/ERGO/SPCE) on a PAD. | 5 | Filter paper (Whatman no. 1, Camlab, UK) | 0.01–2.0 mM | 0.22 mM | Human serum sample | [67] |
| 9 | Glucose, lactate, and uric acid | CA | Microfluidic channels designed using photolithography and electrodes made using screen printing. | 3 | Filter paper (Whatman grade-1) | 0–100 nM (Glucose), 0–50 nM (Lactate) and 0–35 nM (Uric acid) | 0.21 mM (glucose), 0.36 mM (lactate), 1.38 mM (uric acid) | Human serum sample | [14] |
| 10 | Adenosine | CC | Origami paper analytical device with microfluidic channel made using wax printing and electrode fabricated using screen printing with glucose oxidase labeled DNA aptamer. | 4 | Chromatography paper (Whatman grade-1) | NR | 11.8 μM | NR | [68] |
| 11 | Paracetamol and 4-amino phenol | CA | Wax printing used to create microfluidic channel and electrochemical detection system made using sputtering at the end of channel. | 4 | Chromatographic papers n1 and p81 (Whatman) | NR | Paracetamol: 25 μmol/L(paracetamol) and 10 μmol/L (4-amino phenol) | Pharmaceutical tablets | [69] |
| 12 | Ascorbic acid and sunset yellow | CA | Wax printing is used to fabricate microfluidic channel and pencil drawing used to create electrode. | 3 | Filter paper foil type 1 (Whatman) | 50–1000 μM | 30 μM (ascorbic acid) and 90 μM (sunset yellow) | NR | [70] |
| 13 | Melamine | DPV | Electrodes fabricated using ink writing using ball-pen device. | 4 | A4 paper of 70 mg | 0–100.0 μΜ | 1.0 μM | Artificial urine sample | [71] |
| 14 | Pentachlorophenol | PEC | Combination of micro-PADs and molecular imprinting technique. AuNP-decorated working electrode with polypyrrole-functionalized Zno NP. | 6 | Chromatography paper No. 1 (Whatman) | 0.01–100 ng/mL | 4 pg/mL | Spiked samples with river water and pure drinking water | [72] |
| 15 | Pb2+ | ASV | Micro-PADs fabricated by photolithography/wax printing and electrode fabricated using screen-printing. | 3 | Chromatography paper (Whatman No. 1) | NR | 1.0 ppb | NR | [10] |
| Sensing Molecule | Electrochemical Technique Used | Fabrication Strategy | Fabrication Steps | Paper Type | LDR | LOD | Real Sample | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PD-L1 | DPV | Paper microfluidic device aptasensor created. Amine-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube, new methylene blue and gold nanoparticles nanocomposites synthesized for binding aptamer. | 3 | Chromatography paper (Whatman No. 1) | 10 pg/mL– 2.5 ng/mL | 10 pg/mL | Serum sample | [77] |
| 2 | ALP, miRNA | DPV | Paper modified with signal molecule labeled DNA along with target recognition solutions and screen-printed electrodes. | 3 | Cellulose chromatography paper (Whatman) | NR | NR | Human serum sample | [78] |
| 3 | EGFR | CV and DPV | The working electrode was altered using amino-functionalized graphene (NH2-GO), thionine (THI), and gold particle (AuNP) nanocomposites. | 3 | Chromatography paper (Whatman No. 1) | 0.05–200 ng/mL | 5 pg/mL | Serum | [79] |
| 4 | CEA | DPV | The reference electrode was created using commercial silver ink, the working and counter electrodes were printed using a gold nanoparticle ink. | 3 | Grade 1 chromatography paper (Whatman®) | 1.0–100.0 ng/mL | 0.33 ng/mL | Serum | [80] |
| 5 | HCG | DPV | Antibodies conjugated covalently on hydrophilic detection zone of SPCE. Electrochemical immunofiltration designed and constructed. | 4 | Chromatography paper (Whatman No. 1) | 1.0 mIU/mL–100.0 IU/mL | 0.36 mIU/mL | Serum | [81] |
| 6 | miRNA-155 | EIS | Modified paper-based electrode using gold nanoparticles (AuNP-PE) | 5 | Nitrocellulose membrane | 0–1.5 μg/mL | 93.4 nM | Fetal bovine serum | [82] |
| 7 | Exosomes | DPV | Paper-based three electrode devices made with parafilm hot film, which was later cut by laser for making patterns. | 5 | Chromatography filter paper (CHR, Whatman, UK) | 108–1010 exosomes/mL | 9.3 × 107 exosomes/mL | Human serum and plasma | [83] |
| 8 | PSA | DPV | Wax-printed and screen-printed electrode modified with AuNPs/rGO/THI nanocomposites for immobilization of DNA aptamer probe. | 5 | Chromatography paper No. 1 (Whatman) pure cellulose paper | 0.05–200 ng/mL | 10 pg/mL | Serum | [84] |
| 9 | HPV B sAg and HPV C cAg | Chronoamperometry | Wax printing was completed on paper followed by electrode fabrication using carbon-based ink using in-house screening method. | 8 | Filter paper | 0.1–250 ng/mL for HBsAg and 0.001–250 ng/mL for HCVcAg | 18.2 pg/mL for HBsAg and 1.19 pg/mL for HCVcAg | Clinical serum samples | [85] |
| 10 | Claudin 7 and CD81 | Amperometry | Dual electrochemical immunosensor with paper designed by wax printing while electrodes printed using GO and silver ink. | 4 | Filter paper (Whatman No.1) | 2–1000 pg/mL for Claudin 7 and 0.01–10 ng/mL | 0. pg/mL for Claudin 7 and 3 pg/mL for CD81 | 60 breast cancer patients and 20 healthy volunteers | [86] |
| 11 | PEAK 1 | DPV | Paper-based electrodes immobilized with GO for the incorporation of antibodies. | 3 | Chromatography paper (Whatman No.1) | 10–106 pg/mL | 10 pg/mL | NR | [87] |
| 12 | miR-21 | SWV | Paper modified with signal molecule labelled DNA and electrode made using screen-printing electrode. | 3 | Cellulose chromatographic paper (Whatman) | 1 fM–1 μM | 0.1 fM | Serum sample | [78] |
| 13 | AFP | DPV | Origami-based electrochemical immunodevice-based PANI-AuNP-modified PWE. | NR | NR | 0.001–100 ng/mL | 0.80 pg/mL | Human serum | [88] |
| 14 | Milk allergen casein | DPV | Electrode made of GN/CN/GelMA composite material and paper microfluidic channels fabricated using wax printing. | 5 | Pure cellulose paper | 1 × 10−7–1 × 10−6 g/mL | 0.032 μg/mL | Rat basophilic leukemia mast cells | [89] |
| 15 | CA-125 | DPV | Graphene used to modify immunosurface device. AGET ATRP used. | 3 | Chromatography paper no.1 (Whatman) | 0.05–100 ng/mL | 0.05 ng/mL | Human CA-125 | [90] |
| Sensing Molecule | Electrochemical Technique Used | Fabrication Strategy | Fabrication Steps | Paper Type | LDR | LOD | Real Sample | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HPV | SWV | Combining G-PANI modified electrode with an AQ-labeled acpcPNA probe to create DNA biosensor. | 5 | Filter paper (Whatman No. 1) | 10–200 nM | 2.3 nM | NR | [77] |
| 2 | K-562 cell | DPV | Fabrication of folic acid-functionalized Au-paper working electrode on origami electrochemical device. | 4 | Cellulose paper | 1.0 × 102–1.0 × 106 cells/mL | 31 cells/mL | Human serum | [94] |
| 3 | Staphylococcus aureus | DPV | Ab-SWCNT bioconjugates immobilized on working electrode. | 5 | Chromatography paper (Whatman) | 0–107 CFU/mL | 13 CFU/mL | Food samples | [95] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumari, R.; Singh, A.; Azad, U.P.; Chandra, P. Insights into the Fabrication and Electrochemical Aspects of Paper Microfluidics-Based Biosensor Module. Biosensors 2023, 13, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090891
Kumari R, Singh A, Azad UP, Chandra P. Insights into the Fabrication and Electrochemical Aspects of Paper Microfluidics-Based Biosensor Module. Biosensors. 2023; 13(9):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090891
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumari, Rohini, Akanksha Singh, Uday Pratap Azad, and Pranjal Chandra. 2023. "Insights into the Fabrication and Electrochemical Aspects of Paper Microfluidics-Based Biosensor Module" Biosensors 13, no. 9: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090891
APA StyleKumari, R., Singh, A., Azad, U. P., & Chandra, P. (2023). Insights into the Fabrication and Electrochemical Aspects of Paper Microfluidics-Based Biosensor Module. Biosensors, 13(9), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090891






