Irregular Antibody Screening Using a Microdroplet Platform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chip Design and Fabrication
2.2. Experimental Principle and Design
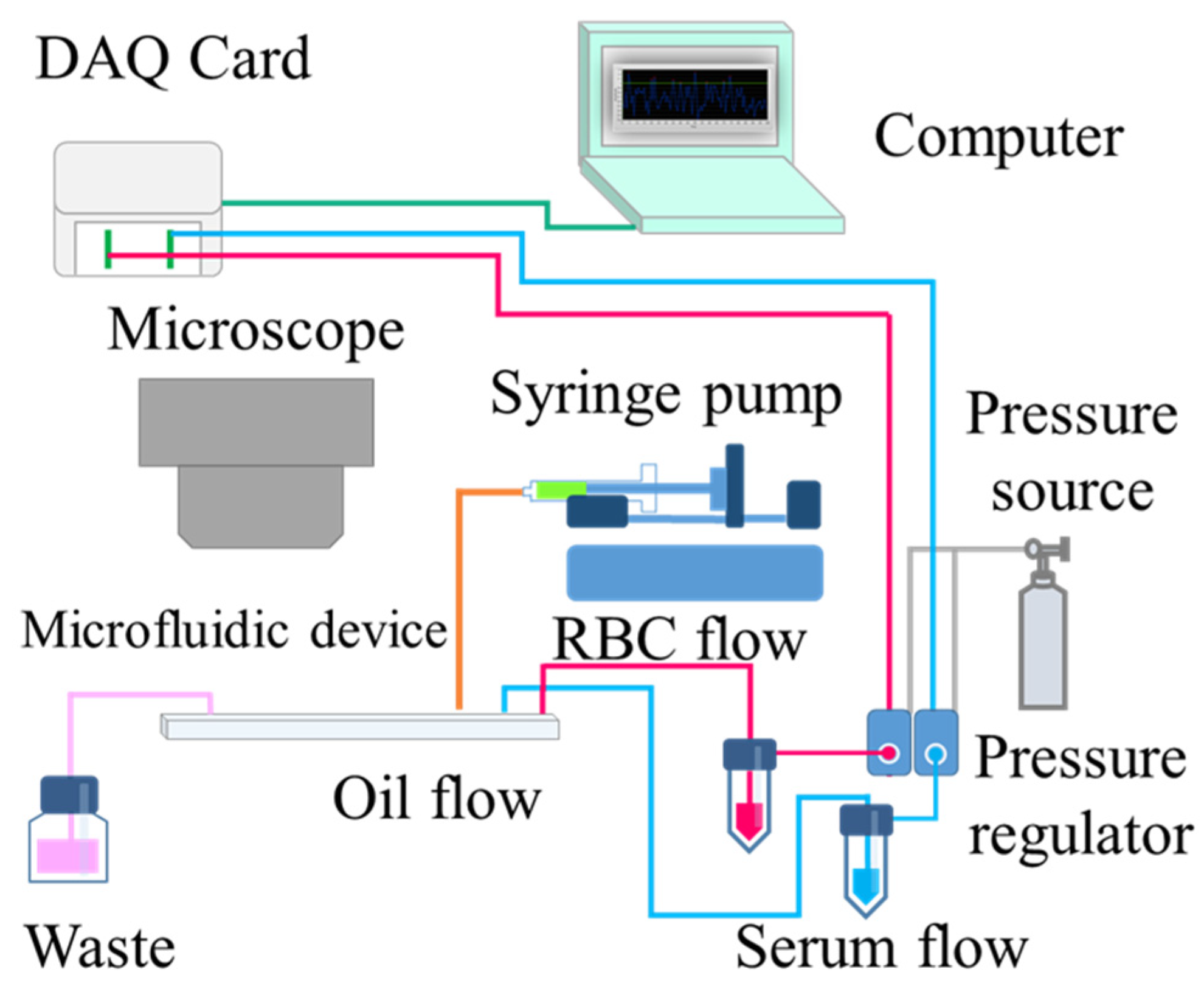
2.3. Experimental Setup and Reagent Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
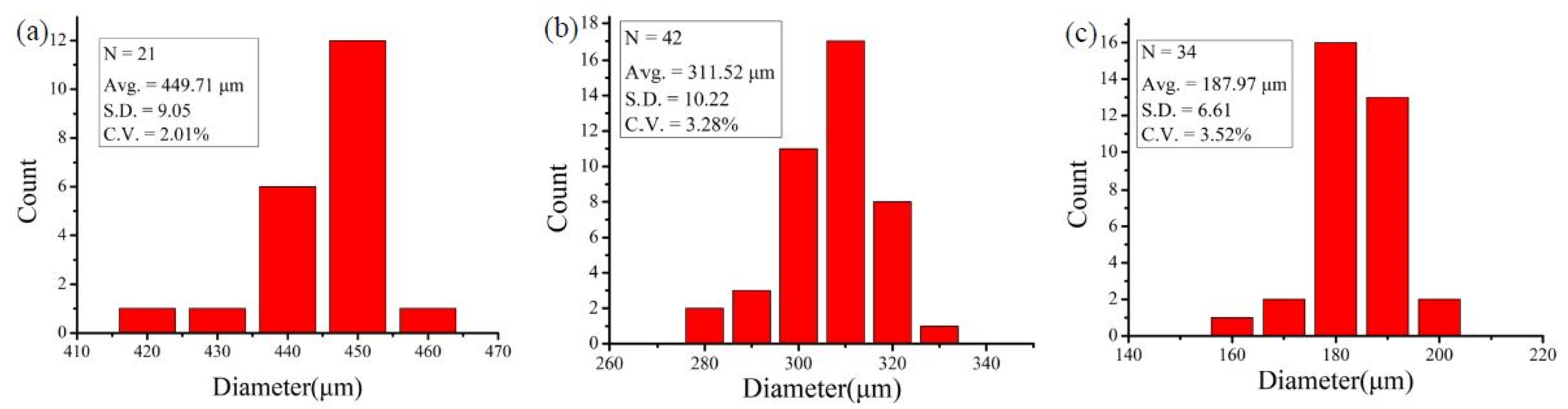
3.1. Control of Sample Volume Ratio and Droplet Size
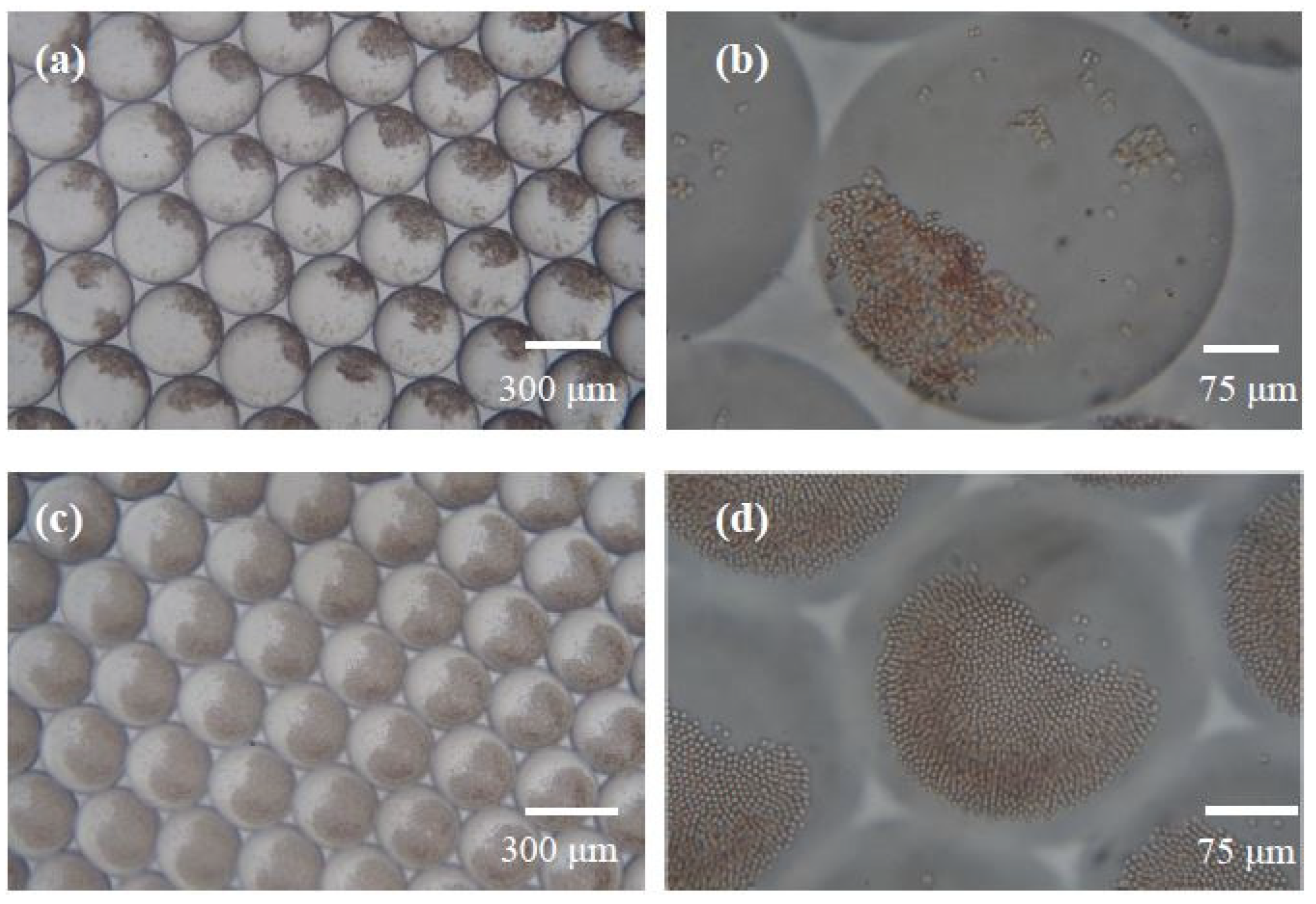
3.2. Eight Irregular Antibodies and Screening RBC Tests in Microdroplets
3.3. Agglutination Test for Diluted Anti-D Antibody and Microchannel Structure for Reaction Acceleration
4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, W.J.; Westhoff, C.M.; Gleadall, N.S.; Aguad, M.; Smeland-Wagman, R.; Vege, S.; Simmons, D.P.; Mah, H.H.; Lebo, M.S.; Walter, K.; et al. MedSeq Project automated typing of red blood cell and platelet antigens: A whole-genome sequencing study. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e241–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, R.; Mishra, N.; Rath, G.P. Blood groups systems. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 524–528. [Google Scholar]
- Quraishy, N.; Sapatnekar, S. Advances in blood typing. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Makowski, G.S., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016; pp. 221–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirani, R.; Tarafdar, S.; Mondy, P.; Powley, T.; Daly, J.; Irving, D.O. Understanding the demand for phenotyped red blood cell units and requests to perform molecular red blood cell typing for Australian patients. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2021, 60, 102968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songjaroen, T.; Primpray, V.; Manosarn, T.; Khumchanta, W.; Sakuldamrongpanich, T.; Kulkeratiyut, S.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. A simple and low-cost portable paper-based ABO blood typing device for point-of-care testing. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2018, 39, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathan, P.; Jain, A.; Marwaha, N. Frequency of irregular red cell antibodies in blood donor population. Glob. J. Transfus. Med. 2019, 4, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.H.; Chu, S.L.; Chang, J.G.; Shih, M.C.; Peng, C.T. Haemolytic disease of the newborn due to maternal irregular antibodies in the Chinese population in Taiwan. Transfus. Med. 2003, 13, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromilow, I.M.; Adams, K.E.; Hope, J.; Eggington, J.A.; Duguid, J.K.M. Evaluation of the ID-gel test for antibody screening and identification. Transfus. Med. 1991, 1, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostendorp, M.; Lammerts van Bueren, J.J.; Doshi, P.; Khan, I.; Ahmadi, T.; Parren, P.W.H.I.; van Solinge, W.W.; De Vooght, K.M.K. When blood transfusion medicine becomes complicated due to interference by monoclonal antibody therapy. Transfusion 2015, 55, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, R.R.; Mourant, A.E.; Race, R.R. A new test for the detection of weak and incomplete Rh agglutinins. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1945, 26, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Orlando, N.; Bianchi, M.; Valentini, C.G.; Maresca, M.; Massini, G.; Putzulu, R.; Zini, G.; Teofili, L. Red cell alloantibody screening: Comparative analysis of three different technologies. Transfus. Med. Hemother 2018, 45, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre, Y.; Rigal, D.; Adam, J.; Josef, D.; Meyer, F.; Greber, S.; Drot, C. The gel test: A new way to detect red cell antigen-antibody reactions. Transfusion 1990, 30, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, K.J.; Chachowski, R.; Cupido, A.; Davies, D.; Jakway, J.; Setcavage, T.M. Column agglutination technology: The antiglobulin test. Transfusion 1993, 33, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawierucha, J.; Posset, M.; Hähnel, V.; Johnson, C.L.; Hutchinson, J.A.; Ahrens, N. Comparison of two column agglutination tests for red blood cell antibody testing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0210099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomme, S.; De Maertelaere, E.; Verhoye, E. A comparison of three column agglutination tests for red blood cell alloantibody identification. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, E. Solid phase red cell adherence assay: A tubeless method for pretransfusion testing and other applications in transfusion science. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2012, 46, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalezari, P.; Jiang, A.F. The manual polybrene test: A simple and rapid procedure for detection of red cell antibodies. Transfusion 1980, 20, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.K.; Chakraborty, S. PDMS microfluidics: A mini review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Hanson, R.L.; Almughamsi, H.M.; Pang, C.; Fish, T.R.; Woolley, A.T. Microfluidics: Innovations in materials and their fabrication and functionalization. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Feng, S.; Lin, L.; Mao, S.; Lin, J.M. Emerging open microfluidics for cell manipulation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5333–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Tsai, T.T.; Zeng, Q.; Chang, C.Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, C.F. A multifunctional microfluidic device for blood typing and primary screening of blood diseases. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiba, H.; Fujimaki, M.; Awazu, K.; Tanaka, T.; Makishima, M. Microfluidic chips for forward blood typing performed with a multichannel waveguide-mode sensor. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2016, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Mehrdel, P.; Farré-Lladós, J.; Casals-Terré, J. A passive portable microfluidic blood–plasma separator for simultaneous determination of direct and indirect ABO/Rh blood typing. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3249–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, F.; Shojaeifard, Z.; Hemmateenejad, B. Point-of-need determination of blood typing using a three-dimensional origami microfluidic paper based analytical device. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Li, W.T.; Chang, Y.; Lee, R.H.; Hsiue, G.H. Blood-typing and irregular antibody screening through multi-channel microfluidic discs with surface antifouling modification. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 034107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Ho, C.Y.; Zhou, X.M.; Yen, H.R. Determination of degree of RBC agglutination for blood typing using a small quantity of blood sample in a microfluidic system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Fan, Y.H.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lou, L.Y. An automatic lab-on-disc system for blood typing. SLAS Technol. 2018, 23, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Howes, P.D.; deMello, A.J. Recent advances in droplet microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Emerging droplet microfluidics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7964–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, E.M.; Holland-Moritz, D.A.; Sun, S.; Kennedy, R.T. High-throughput screening by droplet microfluidics: Perspective into key challenges and future prospects. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Zheng, M.; Li, C.; Shen, F.; Liu, M.; Luo, H.; Song, X.; Lan, Y.; Pan, J.Z.; Du, W. Assembled step emulsification device for multiplex droplet digital polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Manz, A.; Wu, W. Fully automatic integrated continuous-flow digital PCR device for absolute DNA quantification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1125, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongersun, A.; Smeenk, I.; Pratx, G.; Asuri, P.; Abbyad, P. Droplet microfluidic platform for the determination of single-cell lactate release. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, W.; Cui, S.; Sun, Q.; Si, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, K.; Li, L.; Tang, B. Dynamic fluorescent imaging analysis of mitochondrial redox in single cells with a microfluidic device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 129, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazutis, L.; Gilbert, J.; Ung, W.L.; Weitz, D.A.; Griffiths, A.D.; Heyman, J.A. Single-cell analysis and sorting using droplet-based microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 870–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcali, M.; Elbuken, C. Impedimetric detection and lumped element modelling of a hemagglutination assay in microdroplets. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2494–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklavounos, A.A.; Lamanna, J.; Modi, D.; Gupta, S.; Mariakakis, A.; Callum, J.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidic hemagglutination assays for blood typing, donor compatibility testing, and hematocrit analysis. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.P.; Chen, C.; Wu, P.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, W.T.; Yan, Y.L. Micro-droplet platform for exploring the mechanism of mixed field agglutination in B3 subtype. Biosensors 2021, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Caen, O.; Vrignon, J.; Zonta, E.; El Harrak, Z.; Nizard, P.; Baret, J.C.; Taly, V. High throughput single cell counting in droplet-based microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ab | Anti-D (Figure S1) | Anti-C (Figure S2) | Anti-E (Figure S3) | Anti-c (Figure S4) | Anti-e (Figure S5) | Anti-Lea (Figure S6) | Anti-S (Figure S7) | Anti-M (Figure S8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC Agglutination | |||||||||
| SI | Y (3 min) | N | Y (6 min) | Y (6 min) | N | Y (6 min) | N | Y (6 min) | |
| SII | Y (3 min) | Y (6 min) | N | N | Y (6 min) | N | Y (6 min) | Y (6 min) | |
| SIII | Y (3 min) | Y (6 min) | N | N | Y (6 min) | N | N | Y (6 min) | |
| Microdroplet Platform | MP Test in Tube | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Droplet Generation | Incubation | Sample Preparation | Promote Reaction | Form Nonspecific Binding | Resuspend RBC | |
| Reagent or sample | Serum + RBC | Oil | × | Serum + RBC | LIM | Polybrene | Sodium citrate |
| Volume (μL) | 10 + 5 | 100 | × | 100 + 50 | 600 | 100 | 100 |
| Time | 2 min | 3–6 min | 0.5 min | 1 min | 0.5 min (Centrifuge) | 1 min | |
| Total time | 5–8 min | 3–5 min | |||||
| Ab-D Dilution | 4 Times (Figure S9) | 16 Times (Figure S10) | 64 Times (Figure S11) | 128 Times (Figure S12) | 256 Times (Figure S13) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time for Agglutination | ||||||
| SI | 3 min | 4 min | 4 min | 10 min | 15 min | |
| SII | 3 min | 4 min | 4 min | 10 min | 15 min | |
| SIII | 3 min | 4 min | 4 min | 10 min | 15 min | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.-P.; Wu, P.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H. Irregular Antibody Screening Using a Microdroplet Platform. Biosensors 2023, 13, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090869
Chen D-P, Wu P-Y, Lin Y-H. Irregular Antibody Screening Using a Microdroplet Platform. Biosensors. 2023; 13(9):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090869
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ding-Ping, Pei-Yu Wu, and Yen-Heng Lin. 2023. "Irregular Antibody Screening Using a Microdroplet Platform" Biosensors 13, no. 9: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090869
APA StyleChen, D.-P., Wu, P.-Y., & Lin, Y.-H. (2023). Irregular Antibody Screening Using a Microdroplet Platform. Biosensors, 13(9), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13090869





