Multiplex PCR-Lateral Flow Dipstick Method for Detection of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin (TDH) Producing V. parahaemolyticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Culture Medium, and Spiked Sample Preparation
2.2. DNA Extraction
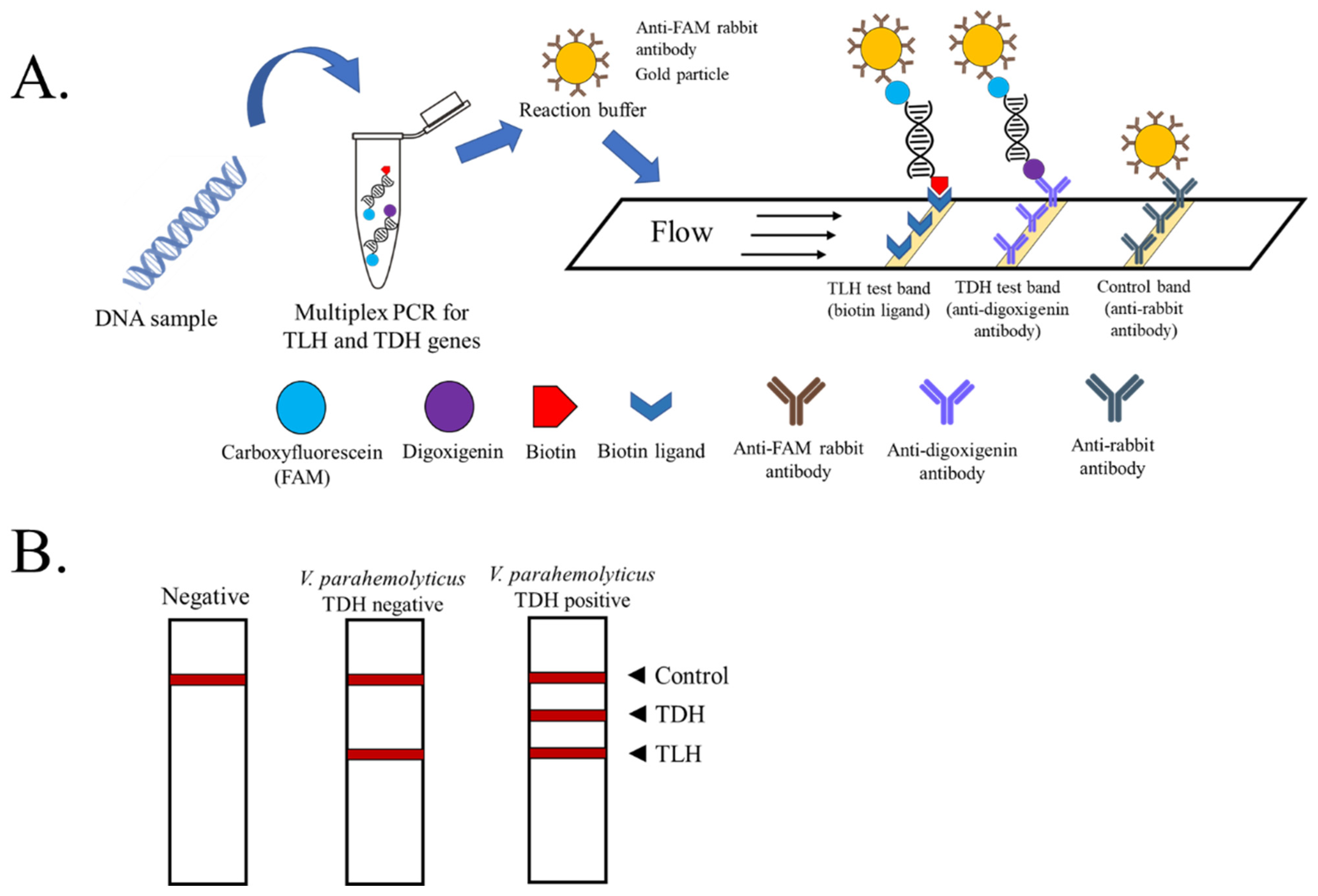
2.3. PCR and PCR-LFD Assay
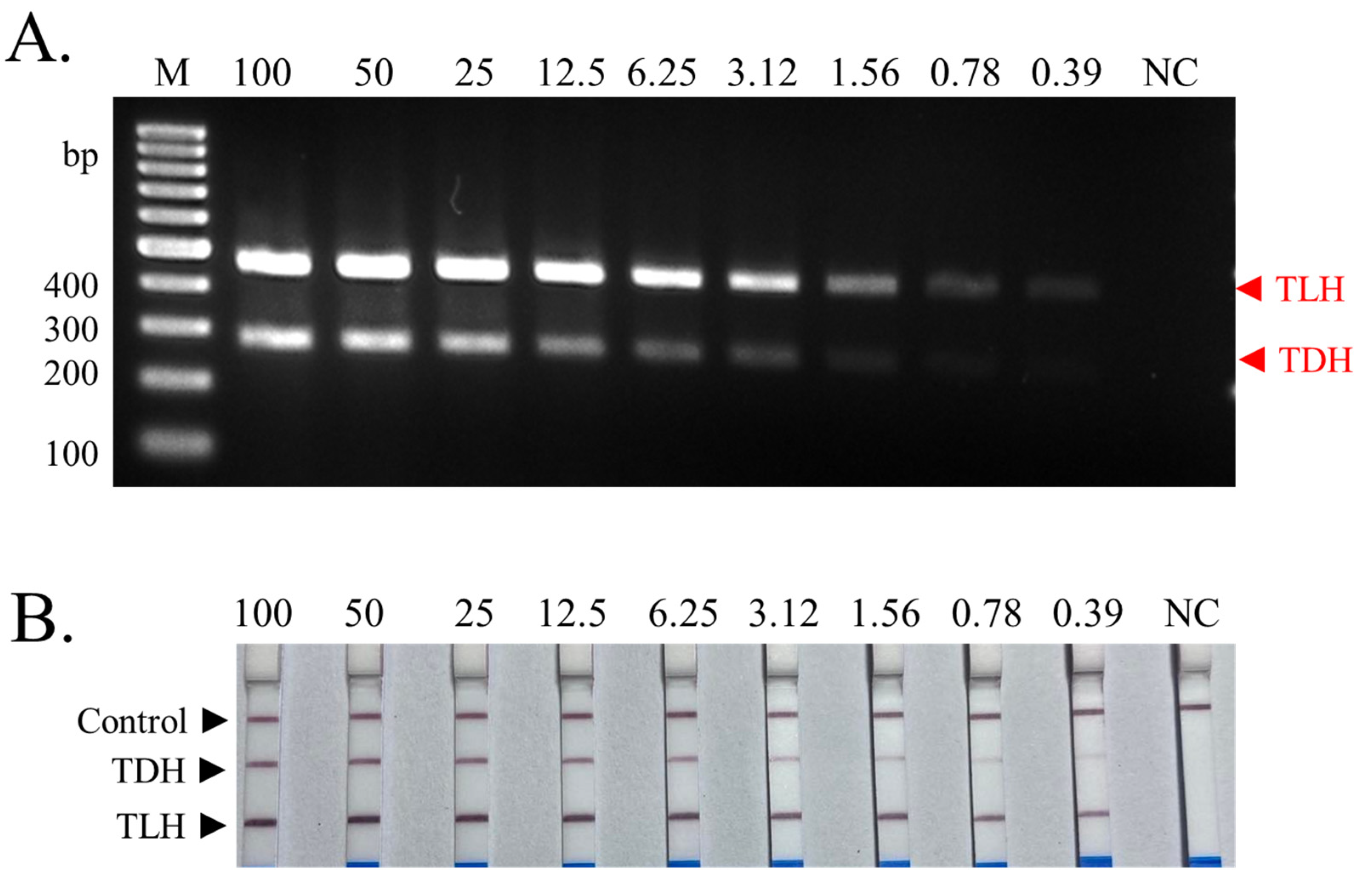
2.4. Specificity and Sensitivity Testing
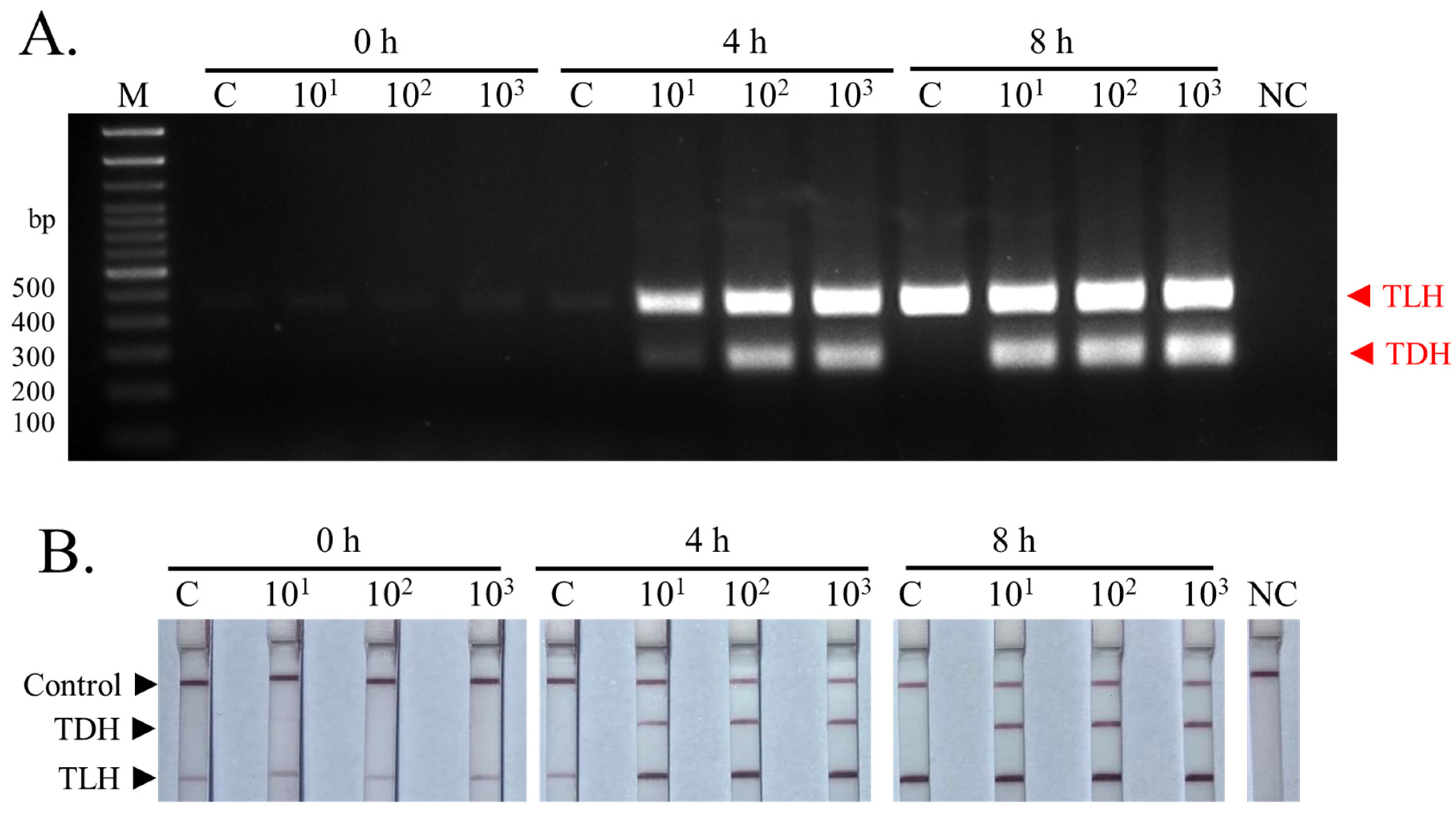
2.5. Artificial Spiking Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Multiplex PCR-LFD Assay
3.2. Specificity Evaluation of Multiplex PCR-LFD Assay
3.3. Sensitivity Determination of Multiplex PCR-LFD Assay
3.4. Detection of Pathogenic TDH+ V. parahaemolyticus-Contaminated Samples Using Multiplex PCR-LFD Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broberg, C.A.; Calder, T.J.; Orth, K.V. parahaemolyticus Cell Biology and Pathogenicity Determinants. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, P.S.M.; Boor, K.J. Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Prevention of Foodborne V. parahaemolyticus Infections. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2004, 1, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellett, A.N.; Rosales, D.; Jacobs, J.M.; Paranjpye, R.; Parveen, S. Growth Rates of V. parahaemolyticus Sequence Type 36 Strains in Live Oysters and in Culture Medium. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02112-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Non-Cholera Vibrios: The Microbial Barometer of Climate Change. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, X.; Yuan, J.; Saeed, A.F.; Wang, S. The Pathogenesis, Detection, and Prevention of V. parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, D.; Li, Y.; Jia, M. Molecular Mechanisms of V. parahaemolyticus Pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 222, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theethakaew, C.; Feil, E.J.; Castillo-Ramírez, S.; Aanensen, D.M.; Suthienkul, O.; Neil, D.M.; Davies, R.L. Genetic Relationships of V. parahaemolyticus Isolates from Clinical, Human Carrier, and Environmental Sources in Thailand, Determined by Multilocus Sequence Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2358–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yingkajorn, M.; Mitraparp-arthorn, P.; Nuanualsuwan, S.; Poomwised, R.; Kongchuay, N.; Khamhaeng, N.; Vuddhakul, V. Prevalence and Quantification of Pathogenic V. parahaemolyticus during Shrimp Culture in Thailand. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 112, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongjun, J.; Mittraparp-arthorn, P.; Yingkajorn, M.; Kongreung, J.; Nishibuchi, M.; Vuddhakul, V. The Trend of V. parahaemolyticus Infections in Southern Thailand from 2006 to 2010. Trop. Med. Health 2013, 41, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.H.T.; Yanagawa, H.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hara-Kudo, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Hayashidani, H. Prevalence of V. parahaemolyticus in Seafood and Water Environment in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, P. Roles of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin (TDH) and TDH-Related Hemolysin (TRH) in V. parahaemolyticus. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.B.; Ayachit, N.H.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent Advances in Microfluidics-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Biosensors 2023, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik-Karpinska, E.; Ceremuga, M.; Niemcewicz, M.; Podogrocki, M.; Stela, M.; Cichon, N.; Bijak, M. Immunosensors—The Future of Pathogen Real-Time Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, S.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Campana, R.; Ciandrini, E.; Baffone, W.; Gianotti, A. Development of a Rapid PCR Protocol to Detect V. parahaemolyticus in Clams. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Jeon, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, M.; Kim, S. Multiplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays for Simultaneous Detection of V. cholerae, V. parahaemolyticus, and V. vulnificus. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2013, 4, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xing, J.; Zhan, X.; Yang, Z.; Qi, J.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y. Improvement of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Combined with Chromatographic Flow Dipstick Assay for Salmonella in Food Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgöwer, S.M.; Hartmann, C.A.; Holzhauser, T. The Development of Highly Specific and Sensitive Primers for the Detection of Potentially Allergenic Soybean (Glycine Max) Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipstick (LAMP-LFD). Foods 2020, 9, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Yang, X.; Hu, T.; Jiao, B.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shen, D. Comparative Evaluation of a Novel Recombinase Polymerase Amplification-Lateral Flow Dipstick (RPA-LFD) Assay, LAMP, Conventional PCR, and Leaf-Disc Baiting Methods for Detection of Phytophthora sojae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bej, A.K.; Patterson, D.P.; Brasher, C.W.; Vickery, M.C.; Jones, D.D.; Kaysner, C.A. Detection of Total and Hemolysin-Producing V. parahaemolyticus in Shellfish Using Multiplex PCR Amplification of Tl, TDH and TRH. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 36, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Risk Assessment of V. parahaemolyticus in Seafood: Interpretative Summary and Technical Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Wang, P.; Liao, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Yi, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, H.; Gao, S.; Lu, Q. Duplex On-Site Detection of V. cholerae and V. vulnificus by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Three-Segment Lateral Flow Strips. Biosensors 2021, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamae, S.; Mittal, A.; Yingkajorn, M.; Saetang, J.; Buatong, J.; Tyagi, A.; Singh, P.; Benjakul, S.V. parahaemolyticus Isolates from Asian Green Mussel: Molecular Characteristics, Virulence and Their Inhibition by Chitooligosaccharide-Tea Polyphenol Conjugates. Foods 2022, 11, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaysner, C.A.; DePaola, A., Jr.; Jones, J. BAM Chapter 9: Vibrio; FDA: Rome, Italy, 2020.
- Kang, C.-H.; Shin, Y.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.; Song, K.; Oh, E.-G.; Kim, S.; Yu, H.; So, J.-S. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of V. parahaemolyticus Isolated from Oysters in Korea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.W.-F.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Rapid Methods for the Detection of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens: Principles, Applications, Advantages and Limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilan, R.G.; Caro-Castro, J.; Blondel, C.J.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Vibrio parahaemolyticus Epidemiology and Pathogenesis: Novel Insights on an Emerging Foodborne Pathogen. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1404, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, S. Detection of Escherichia coli in Food Samples Using Culture and Polymerase Chain Reaction Methods. Cureus 2022, 14, e32808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, M.S.; Bustami, Y.; Hamzah, H.H.; Zambry, N.S.; Najib, M.A.; Khalid, M.F.; Aziah, I.; Abd Manaf, A. Advancement in Salmonella Detection Methods: From Conventional to Electrochemical-Based Sensing Detection. Biosensors 2021, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brengi, S.P.; Sun, Q.; Bolaños, H.; Duarte, F.; Jenkins, C.; Pichel, M.; Shahnaij, M.; Sowers, E.G.; Strockbine, N.; Talukder, K.A.; et al. PCR-Based Method for Shigella flexneri Serotyping: International Multicenter Validation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01592-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, F.; López-Acedo, E.; Tabla, R.; Roa, I.; Gómez, A.; Rebollo, J.E. Improved Detection of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria by Multiplex PCR. BMC Biotechnol. 2015, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.H.; Sun, Y.; Høgberg, J.; Quyen, T.L.; Engelsmann, P.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D. Direct PCR—A Rapid Method for Multiplexed Detection of Different Serotypes of Salmonella in Enriched Pork Meat Samples. Mol. Cell. Probes 2017, 32, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Cao, A.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Molecular Methods for Identification and Quantification of Foodborne Pathogens. Molecules 2022, 27, 8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Mukhopadhyay, U.K. Novel Multiplex PCR Approaches for the Simultaneous Detection of Human Pathogens: Escherichia coli 0157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 68, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuakrod, A.; Sripumkhai, W.; Jeamsaksiri, W.; Pattamang, P.; Loymek, S.; Brindley, P.J.; Sarasombath, P.T.; Wongkamchai, S. A MiniPCR-Duplex Lateral Flow Dipstick Platform for Rapid and Visual Diagnosis of Lymphatic Filariae Infection. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Feng, N.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M. Development of a PCR-Based Lateral Flow Strip Assay for the Simple, Rapid, and Accurate Detection of Pork in Meat and Meat Products. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taboada, L.; Sánchez, A.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Sotelo, C.G. A New Method for the Rapid Detection of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua), Pacific Cod (Gadus macrocephalus), Alaska Pollock (Gadus chalcogrammus) and Ling (Molva molva) Using a Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwawukume, S.; Velez, F.J.; Williams, D.; Cui, L.; Singh, P. Rapid PCR-Lateral Flow Assay for the Onsite Detection of Atlantic White Shrimp. Food Chem. 2023, 6, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y. Improvement and Evaluation of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Combined with Chromatographic Flow Dipstick Assays for V. parahaemolyticus. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 171, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, J.L.; Vickery, M.C.L.; Blackstone, G.M.; Murray, S.L.; DePaola, A. Development of a Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay with an Internal Amplification Control for the Detection of Total and Pathogenic V. parahaemolyticus Bacteria in Oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5840–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. V. parahaemolyticus: A Review on the Pathogenesis, Prevalence, and Advance Molecular Identification Techniques. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, X.; Guo, L.; Shen, Z.; LV, L.; Li, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, D. Rapid and Visual Detection of V. parahaemolyticus in Aquatic Foods Using BlaCARB-17 Gene-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with Lateral Flow Dipstick (LAMP-LFD). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, L.; Chen, Y. Pathogenic Characteristics of and Variation in V. parahaemolyticus Isolated from Acute Diarrhoeal Patients in Southeastern China from 2013 to 2017. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, F.; Wu, M.; Wang, R.; Zheng, S.; Han, D.; Yang, Q.; Kong, H.; Zhou, F.; et al. Serology, Virulence, Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Molecular Characteristics of Clinical V. parahaemolyticus Strains Circulating in Southeastern China from 2009 to 2013. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 258.e9-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Hong, B.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, L.; Malakar, P.K.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Novel QPCR Method for Simultaneous Detection and Quantification of Viable Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic V. parahaemolyticus (Tlh+, TDH+, and UreR+). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.T.; Kim, Y.-O.; Kong, I.-S. Multiplex PCR for the Detection and Differentiation of V. parahaemolyticus Strains Using the GroEL, TDH and TRH Genes. Mol. Cell. Probes 2013, 27, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.N.; Bej, A.K. Detection of V. parahaemolyticus in Shellfish by Use of Multiplexed Real-Time PCR with TaqMan Fluorescent Probes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W. Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection of Pathogenic V. parahaemolyticus Strains. Mol. Cell. Probes 2014, 28, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhao, H.; Xian, Y.; Hussain, M.A.; Wu, X. Multiplex PCR Assays for the Detection of V. alginolyticus, V. parahaemolyticus, V. vulnificus, and V. cholerae with an Internal Amplification Control. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sea-liang, N.; Sereemaspun, A.; Patarakul, K.; Gaywee, J.; Rodkvamtook, W.; Srisawat, N.; Wacharaplusadee, S.; Hemachudha, T. Development of Multiplex PCR for Neglected Infectious Diseases. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, T.C. Polymerase Chain Reaction: Basic Protocol Plus Troubleshooting and Optimization Strategies. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, G.; Rose, P.; Hickey, W.J.; Harkin, J.M. Selective and Sensitive Method for PCR Amplification of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA Genes in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ji, L.; Wu, X.; Yan, W.; Chen, L. Detection and Differentiation of V. parahaemolyticus by Multiplexed Real-Time PCR. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saetang, J.; Sukkapat, P.; Palamae, S.; Singh, P.; Senathipathi, D.N.; Buatong, J.; Benjakul, S. Multiplex PCR-Lateral Flow Dipstick Method for Detection of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin (TDH) Producing V. parahaemolyticus. Biosensors 2023, 13, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070698
Saetang J, Sukkapat P, Palamae S, Singh P, Senathipathi DN, Buatong J, Benjakul S. Multiplex PCR-Lateral Flow Dipstick Method for Detection of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin (TDH) Producing V. parahaemolyticus. Biosensors. 2023; 13(7):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070698
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaetang, Jirakrit, Phutthipong Sukkapat, Suriya Palamae, Prashant Singh, Deep Nithun Senathipathi, Jirayu Buatong, and Soottawat Benjakul. 2023. "Multiplex PCR-Lateral Flow Dipstick Method for Detection of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin (TDH) Producing V. parahaemolyticus" Biosensors 13, no. 7: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070698
APA StyleSaetang, J., Sukkapat, P., Palamae, S., Singh, P., Senathipathi, D. N., Buatong, J., & Benjakul, S. (2023). Multiplex PCR-Lateral Flow Dipstick Method for Detection of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin (TDH) Producing V. parahaemolyticus. Biosensors, 13(7), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13070698







