An Amperometric Acetylcholine Biosensor Based on Co-Immobilization of Enzyme Nanoparticles onto Nanocomposite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles (PtNPs)
2.4. Preparation of Porous Graphene Oxide Nanosheets (GONS)
2.5. Preparation of AChENPs/ChONPs
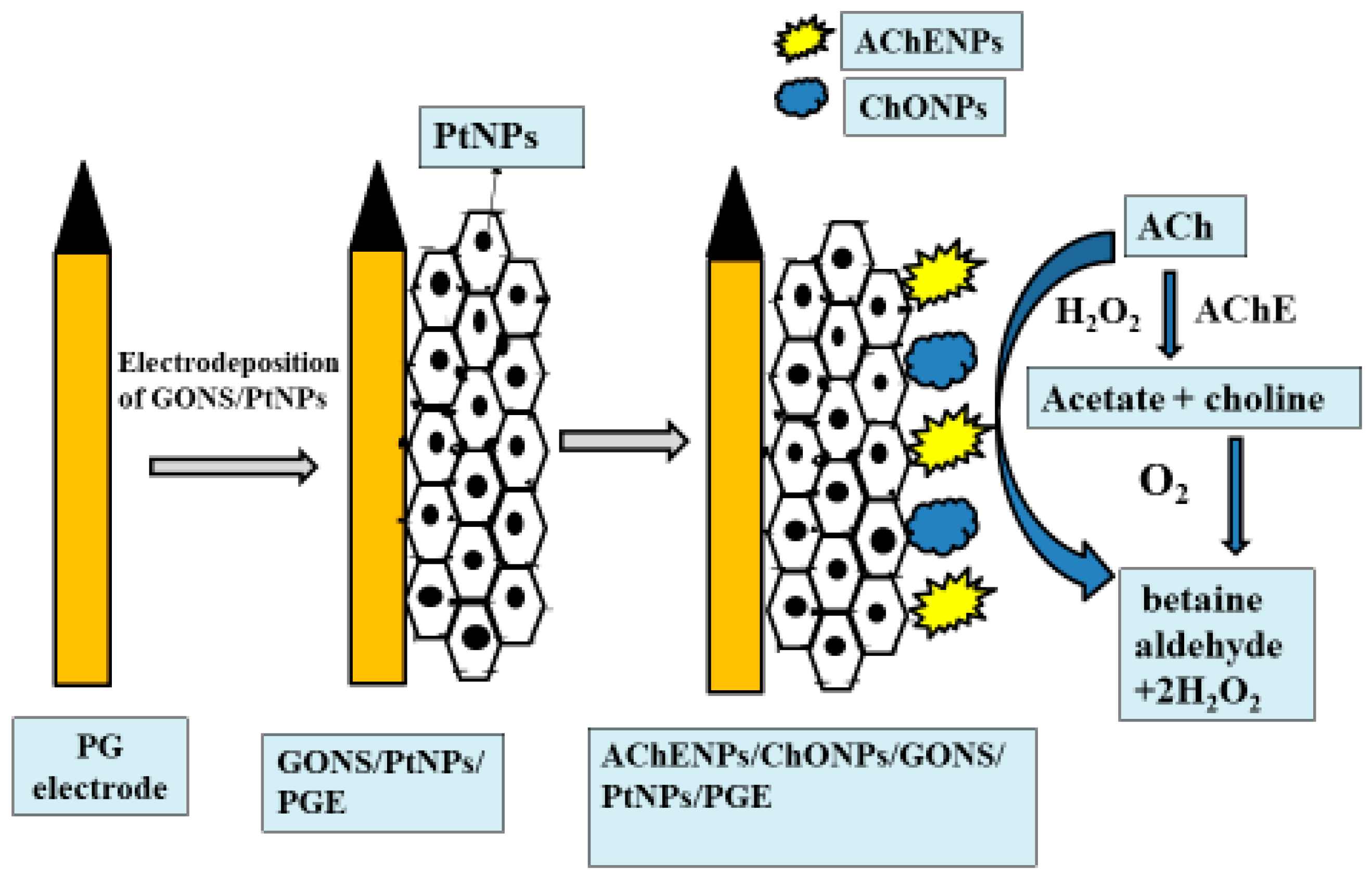
2.6. Preparation of GNs/PtNPs/PG Electrode
2.7. Co-Immobilization of AChENPs/ChONPs onto PtNPs/GONS-Modified PG Electrode
2.8. Construction of Amperometric Acetylcholine Biosensor



2.9. Optimization of Acetylcholine Biosensor
2.10. Evaluation of Acetylcholine Biosensor
3. Results and Discussion
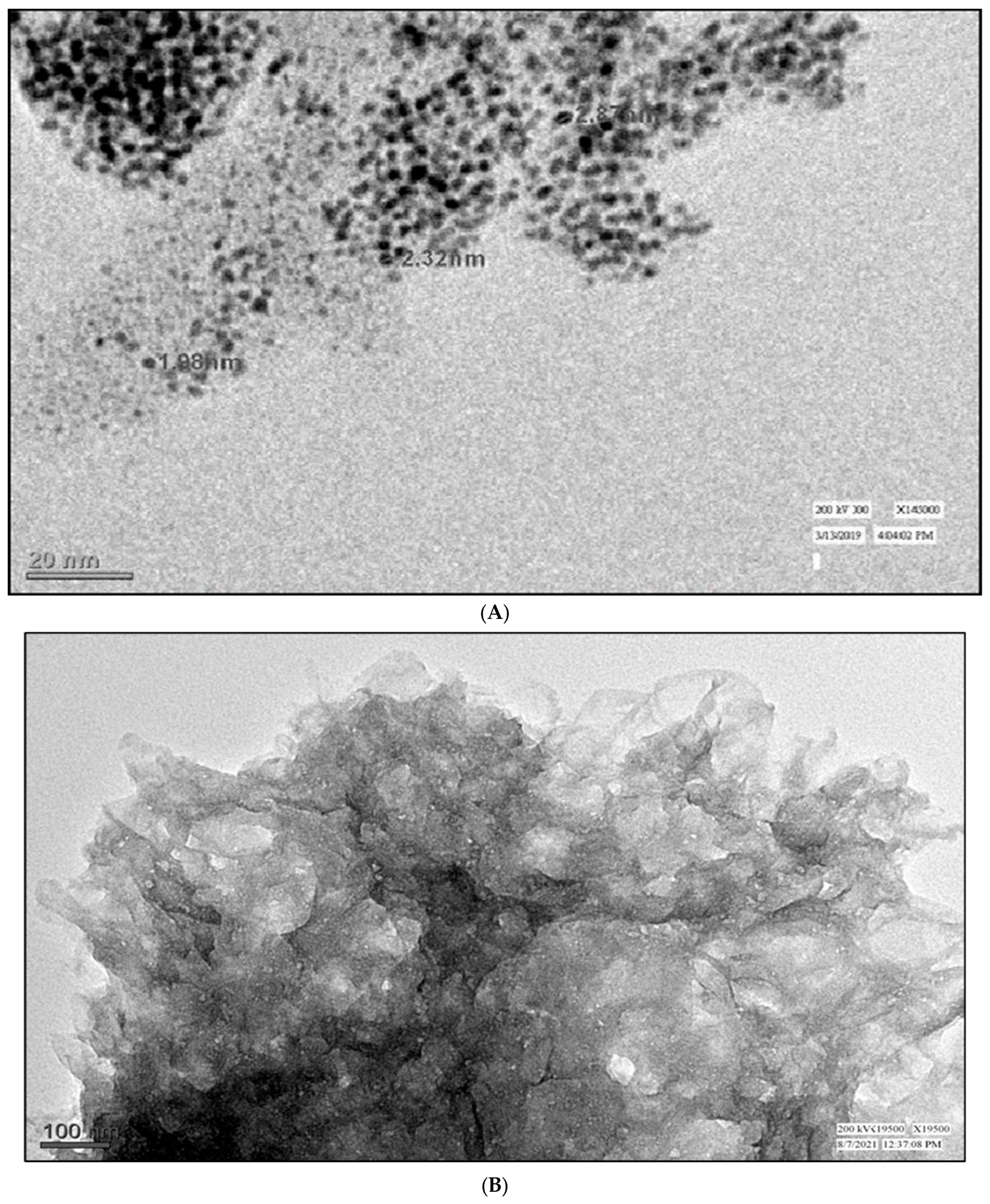
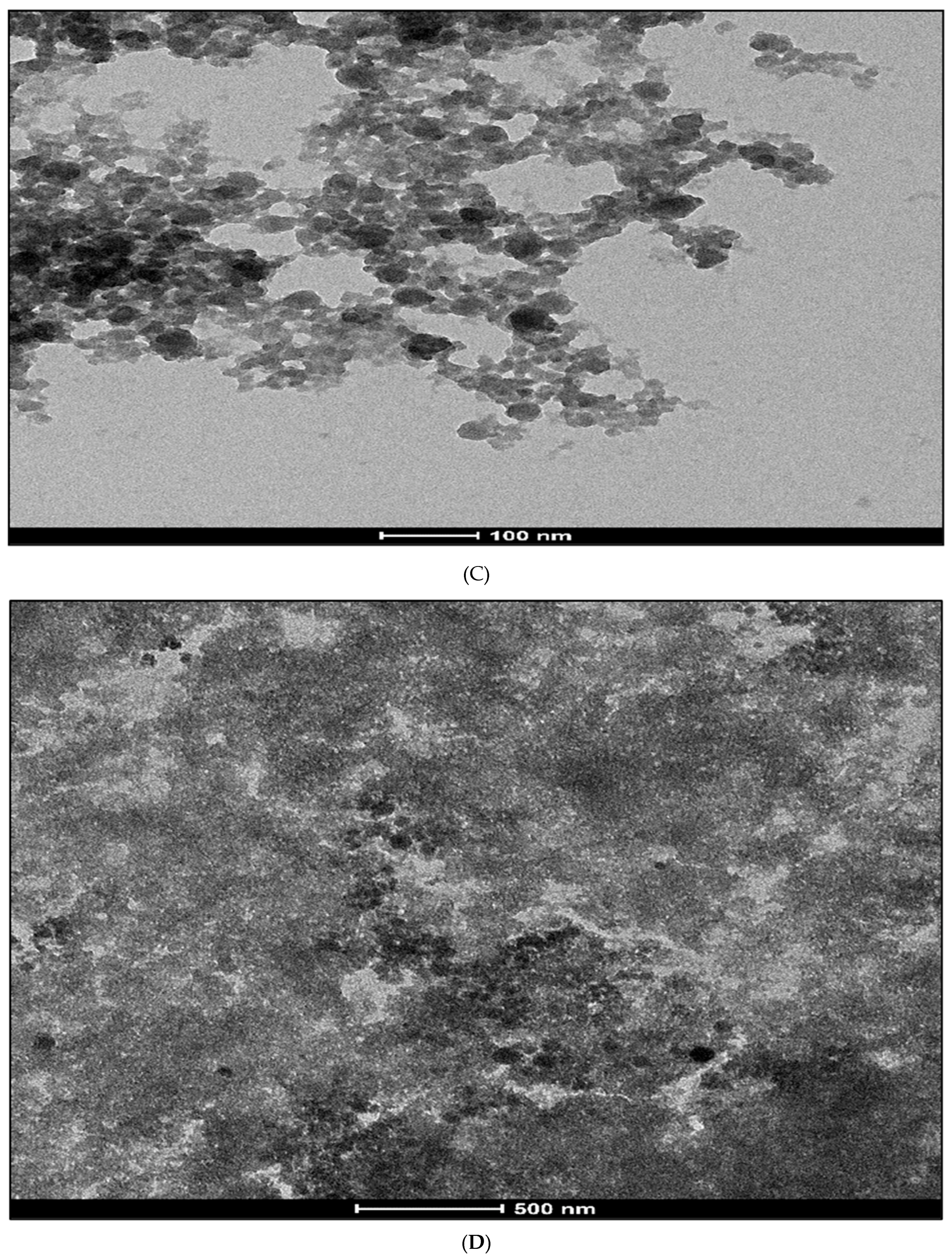
3.1. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Study
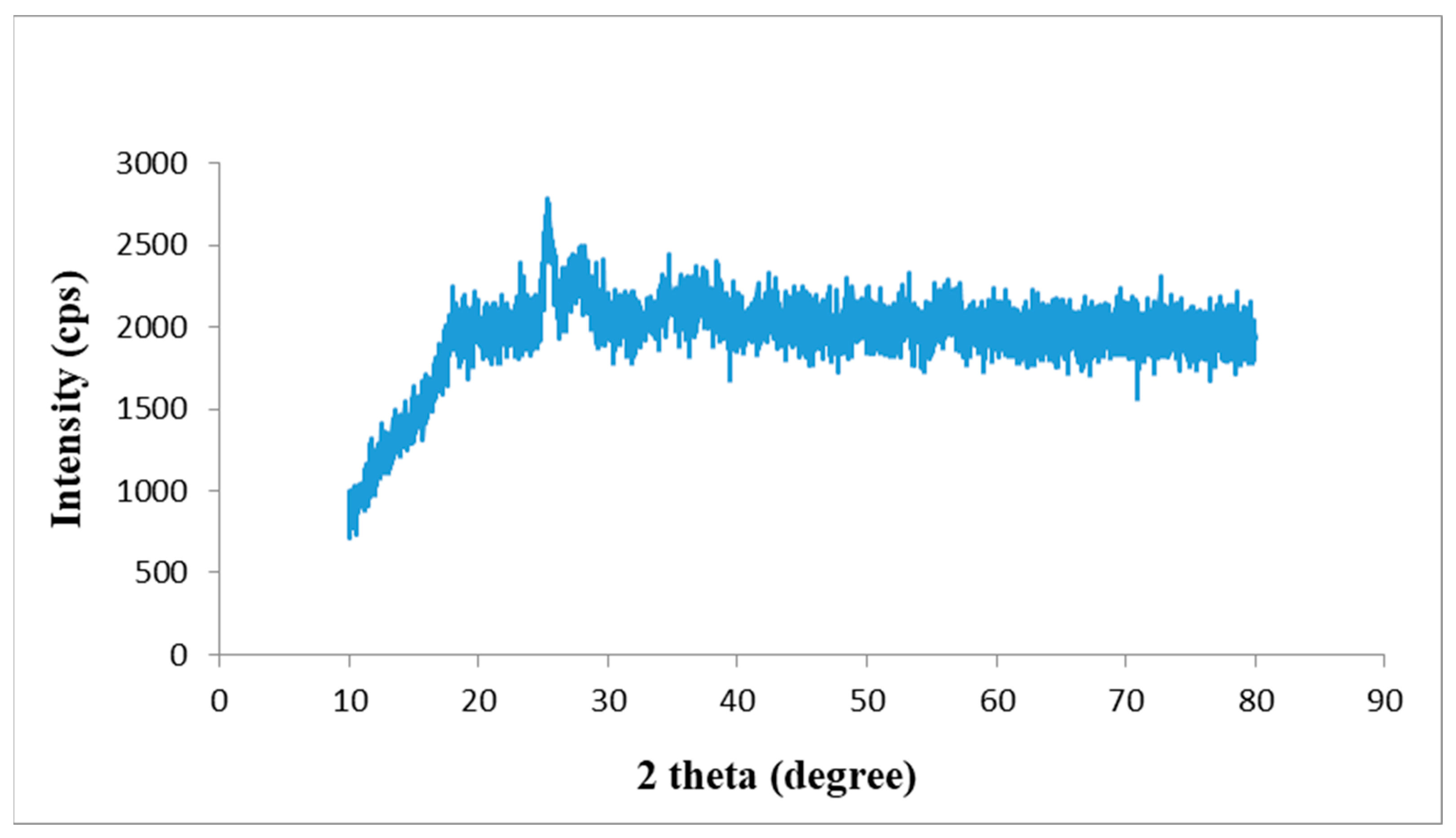
3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Study
3.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Study
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Study
3.5. Optimization of Acetylcholine Biosensor
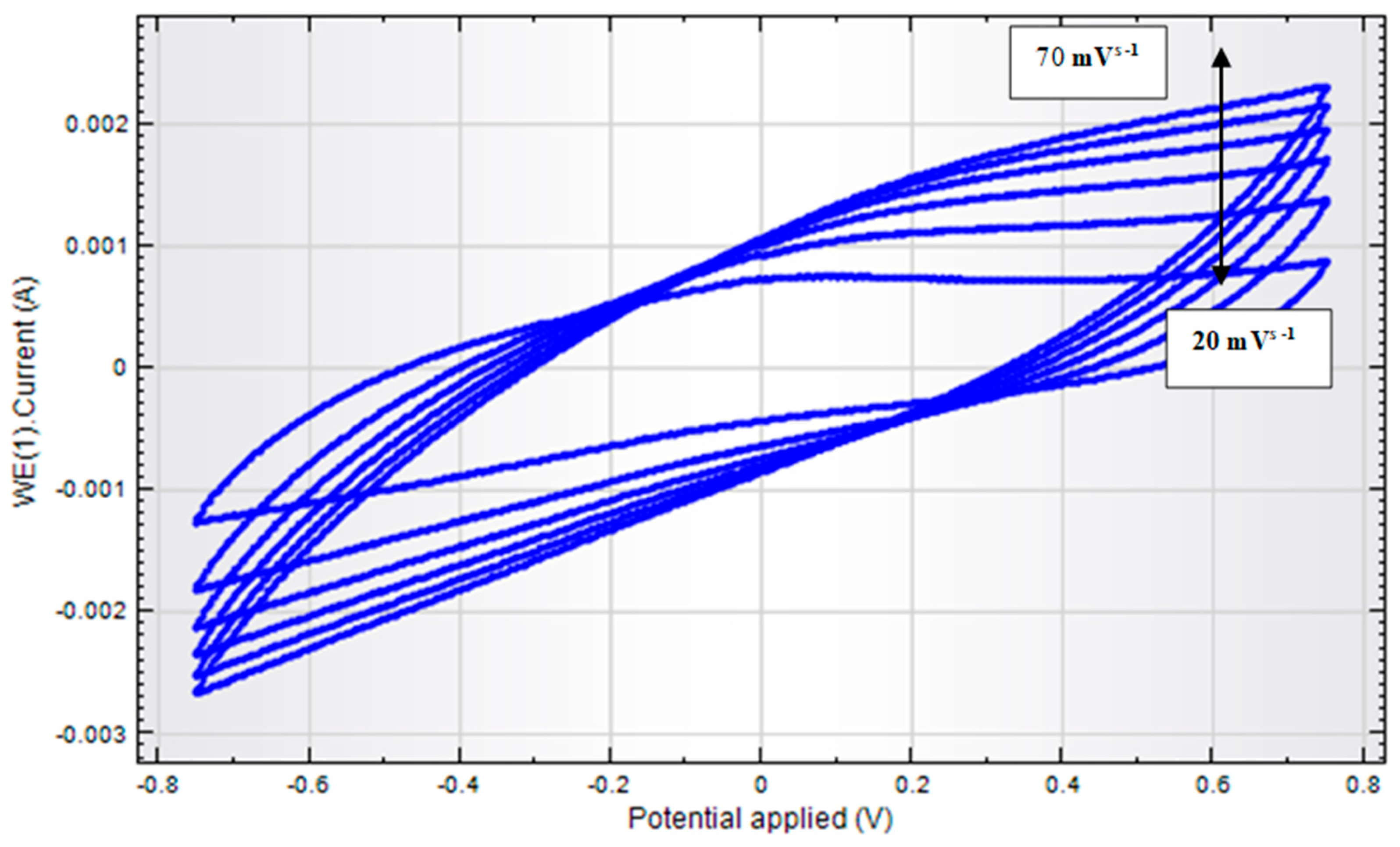
3.6. Study of Scan Rate
3.7. Evaluation of Acetylcholine Nanosensor
3.8. Analytical Recovery
3.9. Reproducibility
3.10. Application of Acetylcholine Biosensor
3.11. Correlation of Acetylcholine Biosensor
3.12. Interferents
3.13. Storage Stability and Reusability of AChENPs/ChONPs/GONS/PtNPs/PGE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tunç, A.T.; Koyuncu, E.A.; Arslan, F. Development of an acetylcholinesterase-choline oxidase based biosensor for acetylcholine determination. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kergoat, L.; Piro, B.; Simon, D.T.; Pham, M.C.; Noël, V.; Berggren, M. Detection of glutamate and acetylcholine with organic electrochemical transistors based on conducting polymer/platinum nanoparticle composites. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5658–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Yang, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, C.; Mao, H.; Wang, K. Facile preparation of Fe3O4 nanospheres/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with high peroxidase-like activity for sensitive and selective colorimetric detection of acetylcholine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, N.; Trenerry, V.C. The determination of choline in vitamin preparations, infant formula and selected foods by capillary zone electrophoresis with indirect ultraviolet detection. Electrophoresis 1996, 17, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, D.D.; Barkhimer, T.V.; Brault, P.A.; Kirchhoff, J.R.; Messer, W.S., Jr.; Hudson, R.A. Internal standard method for the measurement of choline and acetylcholine by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B-Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2002, 775, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Park, N.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, K.M.; Hong, J. Advances and challenges in neurochemical profiling of biological samples using mass spectrometry coupled with separation methods. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.S.; Yuan, Y.C.; Yin, Y.; Tang, Y.P.; Xu, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.D.; Yin, L.; Duan, J.L. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography combined with ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for determination of underivatized neurotransmitters in dementia patients’ urine samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1107, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albishri, H.M.; El-Hady, D.A. Hyphenation of enzyme/graphene oxide-ionic liquid/glassy carbon biosensors with anodic differential pulse stripping voltammetry for reliable determination of choline and acetylcholine in human serum. Talanta 2019, 200, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhong, X.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Electrochemiluminescence acetylcholine biosensor based on biofunctional AMs-AChE-ChO biocomposite and electrodeposited Graphene-Au-chitosan nanocomposite. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 147, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Lei, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, H. Amplified electrochemiluminescence of quantum dots by electrochemically reduced graphene oxide for nanobiosensing of acetylcholine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4552–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Qu, S.; Liu, Y. Study on the Highly Sensitive AChE Electrode Based on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynaci, E.; Yasar, A.; Arslan, F. An amperometric biosensor for acetylcholine determination prepared from acetylcholinesterase-choline oxidase immobilized in polypyrrole-polyvinylsulpfonate film. Sensor. Actuator. B Chem. 2014, 202, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Balayan, S.; Jain, U. Sensitive biosensing of neurotransmitter: 2D material wrapped nanotubes and MnO2 composites for the detection of acetylcholine. Synth. Met. 2020, 263, 116354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Tiwari, S.; Narayan, T.; Jain, U. Bienzymatic assembly formed @ Pt nano sensing framework detecting acetylcholine in aqueous phase. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 474, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, C.; Chauhan, N.; Tripathi, A.; Jain, U.; Avasthi, D.K. Voltammetric measurements of neurotransmitter-acetylcholine through metallic nanoparticles embedded 2-D material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Narang, J.; Jain, U. Highly sensitive and rapid detection of acetylcholine using an ITO plate modified with platinum-graphene nanoparticles. Analyst 2015, 140, 1988–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Chawla, S.; Pundir, C.S.; Jain, U. An electrochemical sensor for detection of neurotransmitter-acetylcholine using metal nanoparticles, 2D material and conducting polymer modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.H.; Hussain, K.K.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Shim, Y.B. Detection of Ca2+-induced acetylcholine released from leukemic T-cells using an amperometric microfluidic sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodur, O.C.; Dinc, S.; Ozmen, M.; Arslan, F. A sensitive amperometric detection of neurotransmitter acetylcholine using carbon dot-modified carbon paste electrode. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2020, 68, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Qi, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q. Ultrasensitive, label-free voltammetric determination of norfloxacin based on molecularly imprinted polymers and Au nanoparticle-functionalized black phosphorus nanosheet nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, J.; Wan, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole film-coated poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):polystyrene sulfonate-functionalized black phosphorene for the selective and robust detection of norfloxacin. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Sheikhshoaie, M.; Sheikhshoaie, I.; Ranjbar, M.; Alizadeh, J.; Maxakato, N.W.; Abbaspourrad, A. A novel electrochemical epinine sensor using amplified CuO nanoparticles and a n-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate electrode. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S. Enzyme Nanoparticles; Elsevier Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Malik, J.; Prashant, A.; Jaiwal, P.K.; Pundir, C.S. Amperometric determination of serum total cholesterol with nanoparticles of cholesterol esterase and cholesterol oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 500, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, J.; Aggarwal, V.; Jaiwal, R.; Pundir, C.S. An Improved Amperometric Lactose Biosensor Based on Enzyme Nanoparticles. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotech. 2022, 10, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.; Kawde, A.N. Nanomolaramperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide using a graphite pencil electrode modified with palladium nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Moldovan, Z.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Badea, I.A. Cheap pencil graphite electrodes for rapid voltammetric determination of chlorogenic acid in dietary supplements. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6537–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; He, D.; Luo, S.; Cai, Q. An amperometric glucose biosensor fabricated with Pt nanoparticle-decorated carbon nanotubes/TiO2 nanotube arrays composite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Yang, H.J.; Shen, G.X.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Guo, S.W. Reduction of graphene oxide via L-ascorbic acid. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1112–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, T.T.; Aravind, S.S.J.; Arockiadoss, T.; Rakhi, R.B. Metal decorated graphene nanosheets as immobilization matrix for amperometric glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrinha, Á.; Tavares, M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Moaris, S. A self-powered biosensor for glucose detection using modified pencil graphite electrodes as transducers. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurugan, A.; Aswitha, P.; Kiruthika, C.; Nagarajan, S.; Christy, A.N. Greensynthesis of platinum nanoparticles using Azadirachtaindica—An eco-friendlyapproach. Mater. Lett. 2016, 170, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, B.; Bulin, C.; Li, R.; Xing, R. High-efficient Synthesis of Graphene Oxide Based on Improved Hummers Method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohwal, B.; Kumar, P.; Pundir, C.S. Fabrication and application of an amperometric lysine biosensor based on covalently immobilized lysine oxidase nanoparticles onto Au electrode. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narwal, V.; Pundir, C.S. Development of glycerol biosensor based on co-immobilization of enzyme nanoparticles decorated pencil graphite electrode. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinne, J.O.; Kaasinen, V.; Järvenpaa, T.; Någren, K.; Roivainen, A.; Yu, M.; Oikonen, V.; Kurki, T. Brain acetylcholinesterase activity in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| S.No. | Sex | Age (Year) | Apparently Healthy Persons (nM) | Sex | Age (Year) | Alzheimer’s Patients (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 50 | 10.0 ± 0.7 | M | 61 | 4.0 ± 0.8 |
| 2 | M | 56 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | M | 65 | 4.4 ± 0.5 |
| 3 | M | 48 | 10.7 ± 0.2 | M | 82 | 3.0 ± 0.4 |
| 4 | M | 52 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | F | 63 | 3.5 ± 0.7 |
| 5 | F | 60 | 9.2 ± 0.5 | M | 60 | 4.8 ± 0.6 |
| 6 | M | 40 | 11.1 ± 0.2 | M | 47 | 5.4 ± 0.8 |
| 7 | F | 65 | 9.0 ± 0.8 | M | 38 | 5.7 ± 0.9 |
| 8 | M | 43 | 9.7 ± 0.1 | M | 77 | 1.6 ± 0.5 |
| 9 | M | 48 | 9.6 ± 0.5 | M | 81 | 3.4 ± 0.2 |
| 10 | F | 68 | 9.3 ± 0.9 | M | 85 | 3.1 ± 0.3 |
| 11 | M | 38 | 11.1 ± 0.5 | F | 61 | 3.7 ± 0.5 |
| 12 | M | 36 | 11.7 ± 0.8 | M | 79 | 3.2 ± 0.3 |
| 13 | M | 25 | 12.2 ± 0.4 | F | 71 | 1.0 ± 0.5 |
| 14 | M | 44 | 9.9 ± 0.6 | M | 70 | 3.6 ± 0.4 |
| 15 | M | 39 | 9.2 ± 0.3 | M | 66 | 4.8 ± 0.7 |
| 16 | M | 27 | 12.0 ± 0.4 | M | 37 | 6.2 ± 0.9 |
| 17 | M | 30 | 11.7 ± 0.8 | M | 80 | 3.2 ± 0.5 |
| 18 | M | 37 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | F | 62 | 2.9 ± 0.8 |
| 19 | M | 29 | 12.1 ± 0.7 | M | 61 | 4.2 ± 0.7 |
| 20 | F | 55 | 10.3 ± 0.9 | M | 54 | 6.5 ± 0.6 |
| Sr. No. | Composition of Electrode | Detection Method | Method of Immobilization | LOD (µM) | Linear Range (µM) | Optimum pH | Optimum Temperature (°C) | Response Time (Second) | Storage Life (Days) | Samples | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AChE-ChO/GO-IL/GCE | ADPSV | Adsorption | 8.85 × 10−4, 1.352 × 10−3 | 5 × 10−3–1 × 10−6 | 7.4 | NR | NR | 90 | Serum | [7] |
| 2 | AChE-ChO/GO-AuNPs-CS/Fe3O4–TiO2@NH2/GCE | ECL | Cross-linking | 0.002.2 | 6.7 × 10−3 –0.92 × 103 | 8 | NR | NR | 15 | Serum | [8] |
| 3 | AChE-ChO/QDs/rGO/GCE | ECL, CV | Cross-linking | 8.8, 4.7 | 10–210, 10–250 | 9.0 | NR | NR | 7 | Serum | [9] |
| 4 | AChE-ChO/a PDDA/ZnO/MWCNTs/PGE | CV | Adsorption | 0.3 | 1.0–0.8 × 103, 1.0–103 | NR | 50 | 60 | 90 | Serum | [10] |
| 5 | AChE-ChO/c PPy-PVS/Pt | CV | Cross-linking | 5.0 × 10−3 | 10−5–10−3 | 9.0 | 65 | 200 | NR | Artificial blood | [11] |
| 6 | AChE-ChO/MWCNT-MnO2/rGO/Au | CV | Cross-linking | 0.1 | 0.1–1.00 | 7.4 | 35 | NR | 90 | Serum | [12] |
| 7 | AChE-ChO/MOF/PtNPs/Au | DPV | Covalent attachment | 0.01 | 0.01–500 | 7.4 | 30 | NR | 120 | Serum | [13] |
| 8 | AChE-ChO/CS/Fe@AuNPs/Au | SWV | Cross-linking | 5 × 10−2 | 5.0 × 10−3–400 | 7.0 | 30 | 3 | 90 | Serum | [14] |
| 9 | AChE-ChO/rGO/PtNP/ITO | CV | Cross-linking | 5 × 10−3 | 5.0 × 10−3−700 | 7.0 | 35 | 4 | 120 | Serum | [15] |
| 11 | AChE-ChO/Fe2O3/rGO/PEDOT/FTO | EIS | Cross-linking | 4.0 × 10−3 | 0.004–800 | 7.0 | 30 | 3 | 90 | Serum | [16] |
| 12 | AChE-ChO/AuNPs/pTTB/SPCE | CA | Covalent attachment | 0.0026 | 0.7 × 10−3 −1.5 × 103 | NR | NR | NR | NR | Serum | [17] |
| 13 | AChE-ChO/CDs-APTES/CPE | CV | Cross-linking | 5.0 × 10−3 | 10−5−10−2 | 7.0 | 60 | 200 | NR | Artificial blood | [18] |
| 14 | AChE/PANI-Nano-ZSM−5/GCE | SWV | Entrapment | 0.1 | 1.0–103 | 7.4 | NR | NR | 15 | - | [33] |
| 15 | AChENPs/ChONPs/GONS/PtNPs/PGE | CV | Adsorption | 0.001 | 0.001–200 | 7.5 | 35 | 3 | 180 | Serum | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahlawat, J.; Sharma, M.; Pundir, C.S. An Amperometric Acetylcholine Biosensor Based on Co-Immobilization of Enzyme Nanoparticles onto Nanocomposite. Biosensors 2023, 13, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030386
Ahlawat J, Sharma M, Pundir CS. An Amperometric Acetylcholine Biosensor Based on Co-Immobilization of Enzyme Nanoparticles onto Nanocomposite. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030386
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhlawat, Jyoti, Minakshi Sharma, and Chandra Shekhar Pundir. 2023. "An Amperometric Acetylcholine Biosensor Based on Co-Immobilization of Enzyme Nanoparticles onto Nanocomposite" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030386
APA StyleAhlawat, J., Sharma, M., & Pundir, C. S. (2023). An Amperometric Acetylcholine Biosensor Based on Co-Immobilization of Enzyme Nanoparticles onto Nanocomposite. Biosensors, 13(3), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030386





