A Portable Wireless Intelligent Nanosensor for 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin Analysis with A Black Phosphorene and Nano-Diamond Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents
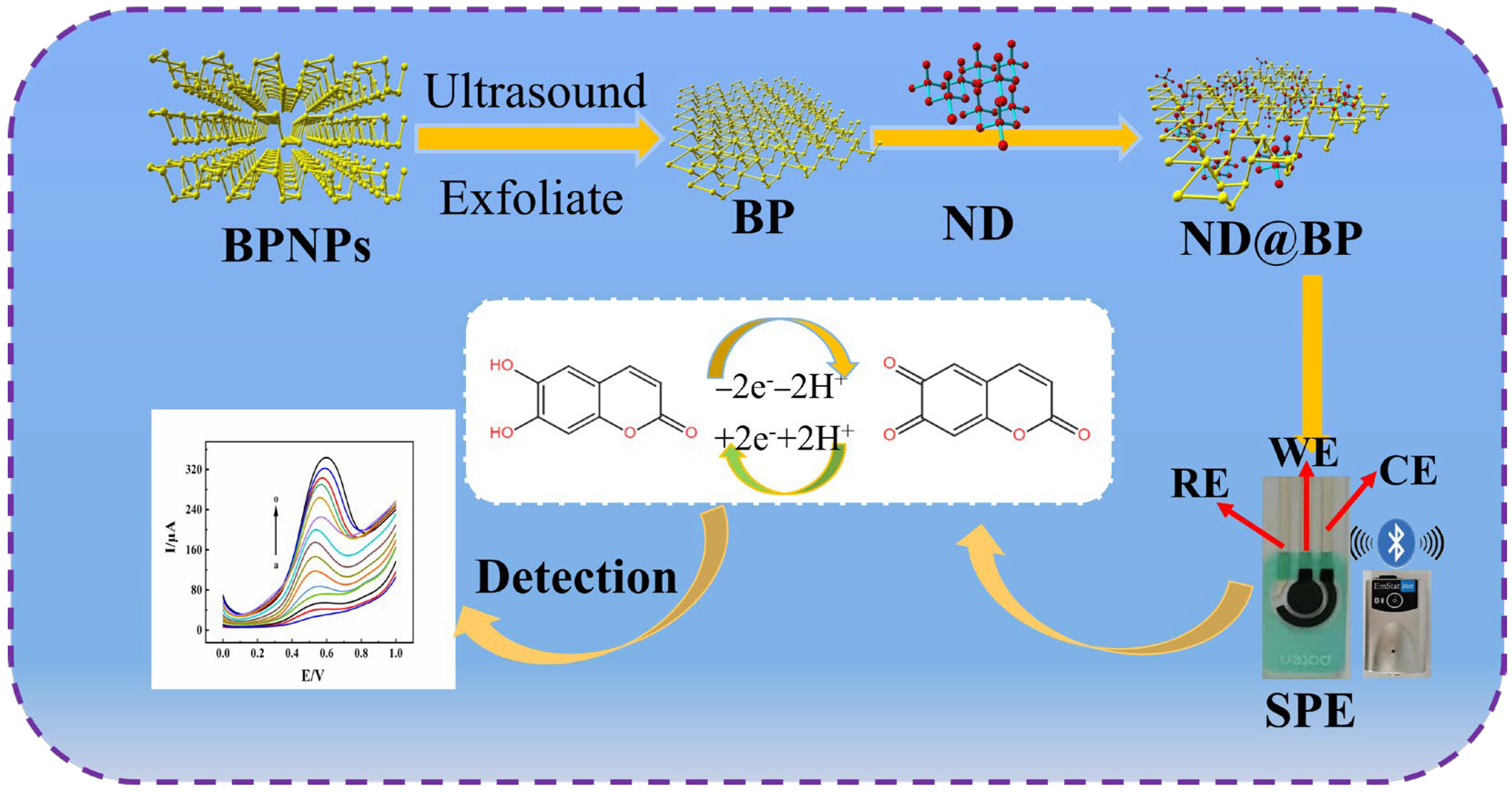
2.2. Synthesis of ND@BP
2.3. Materials Characterization
2.4. Construction of the Modified Electrodes
2.5. Electrochemical Investigations
3. Results and Discussions
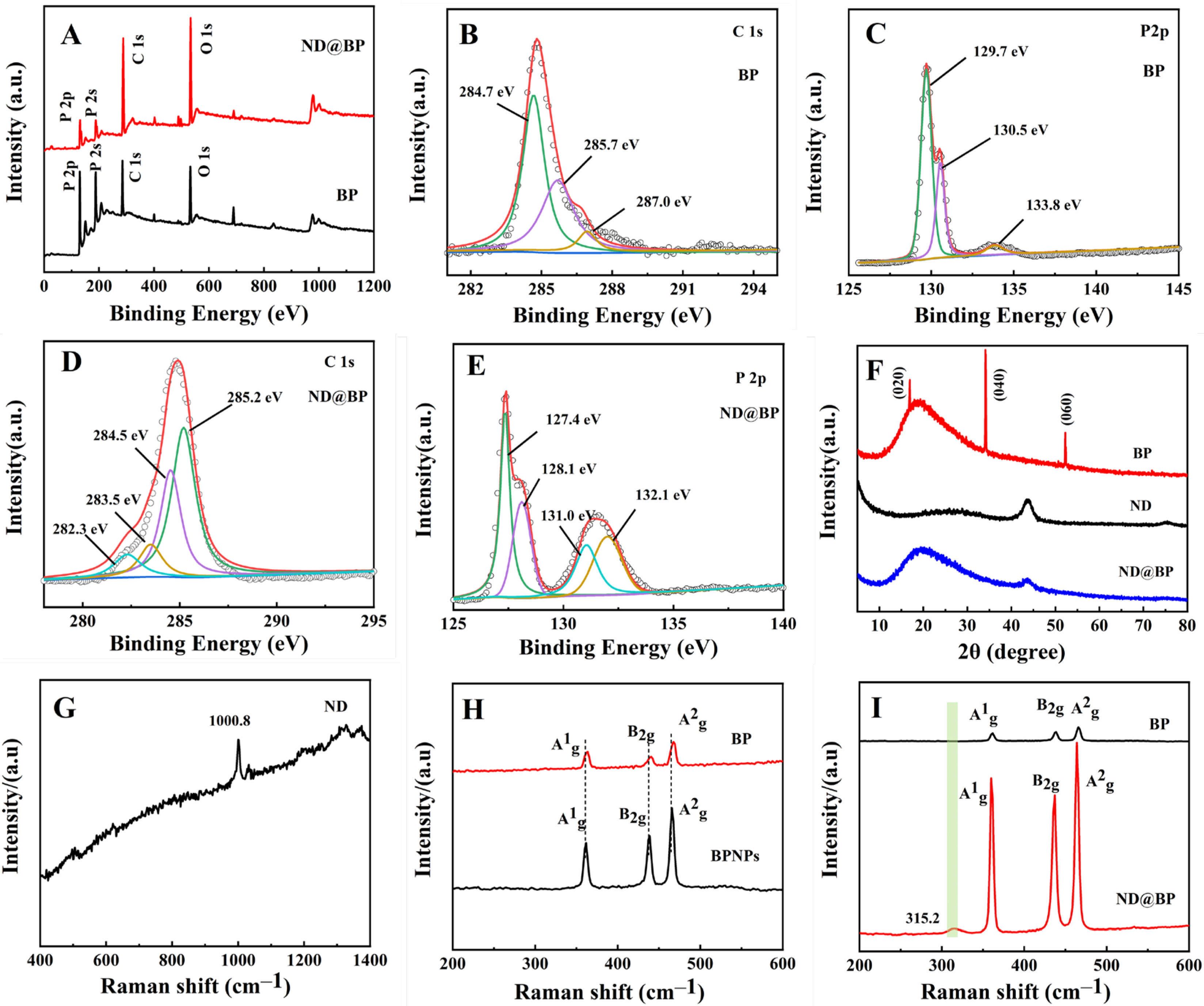
3.1. Characterization of ND@BP Nanocomposite
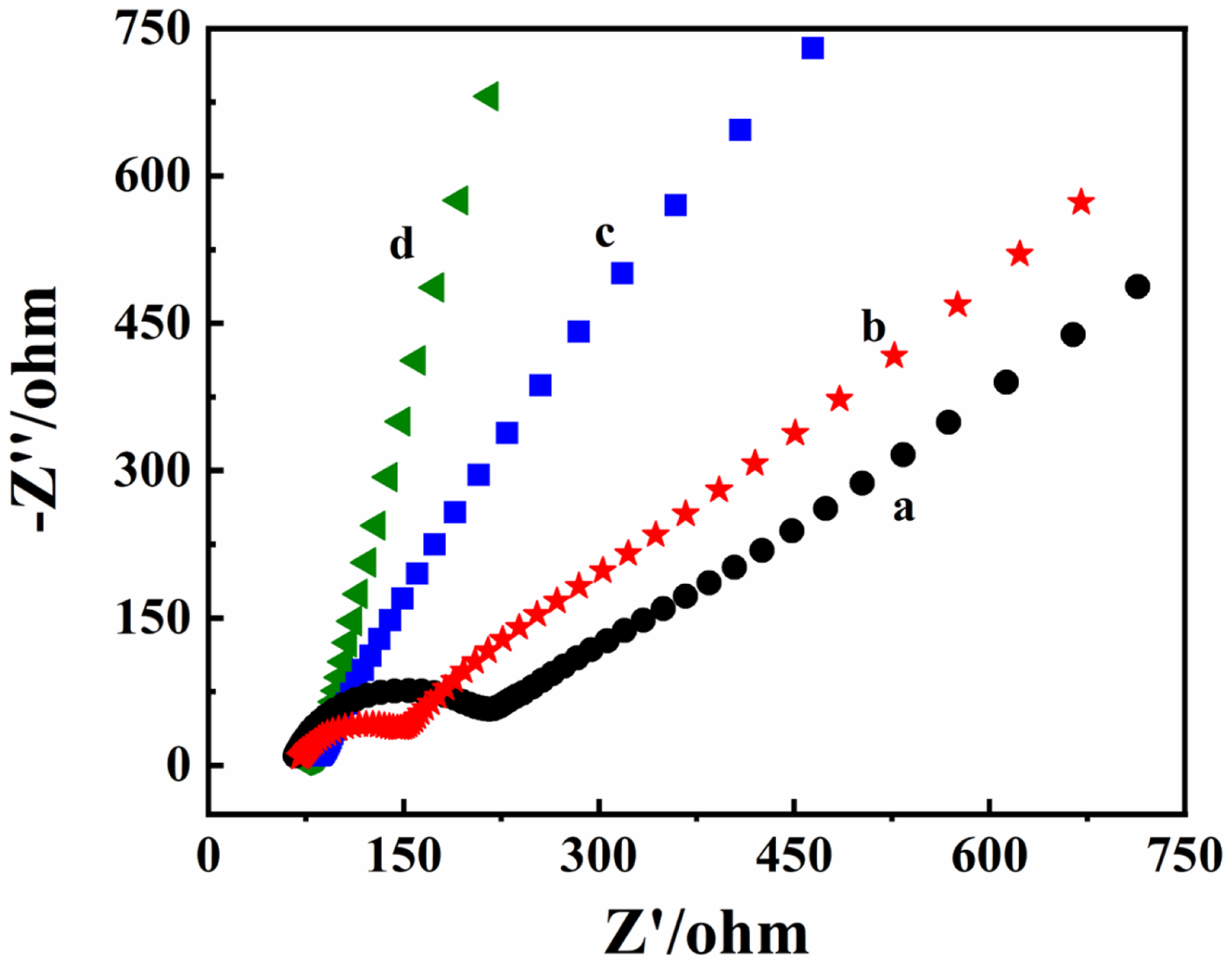
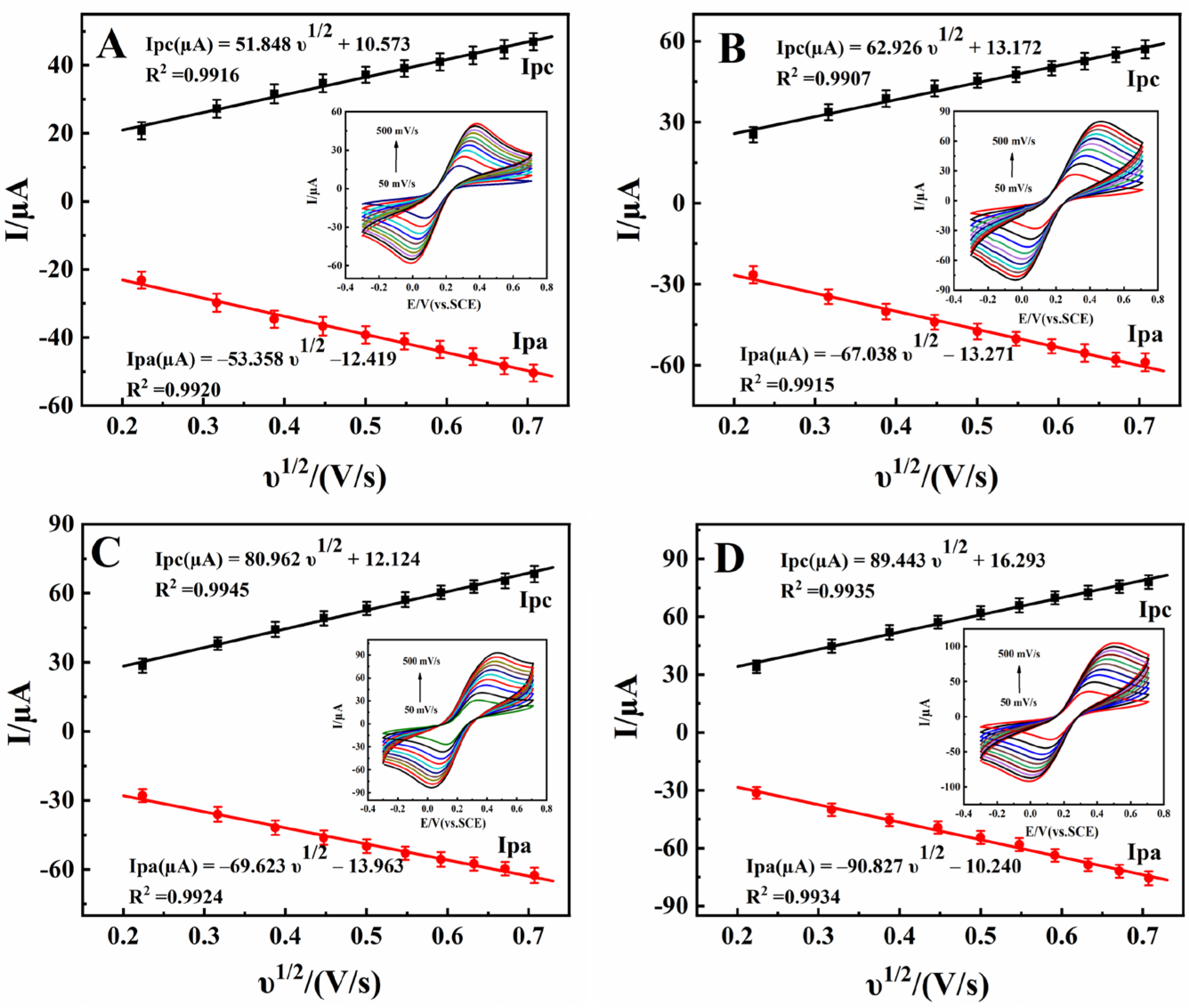
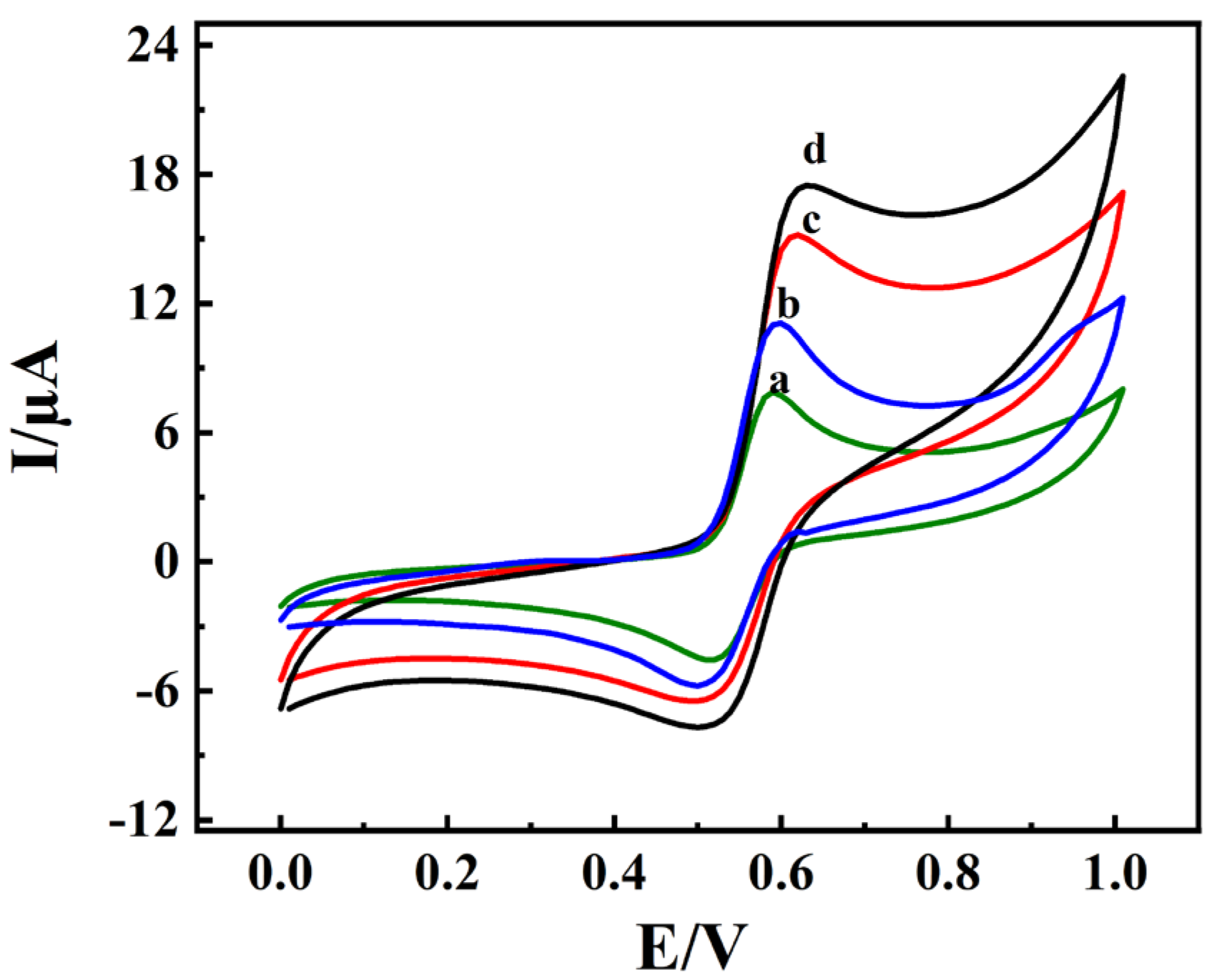
3.2. Electrochemical Characterizations
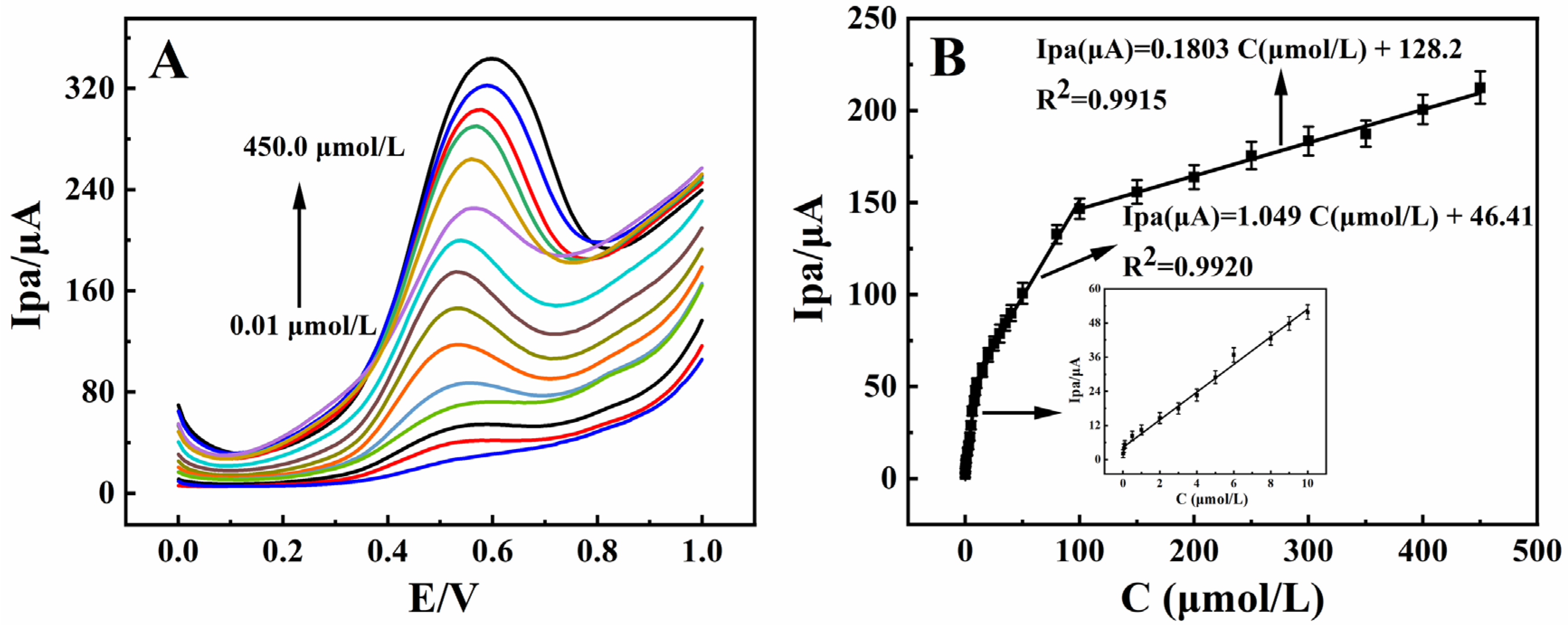
3.3. Calibration Curve
3.4. Samples Analysis
3.5. Interference
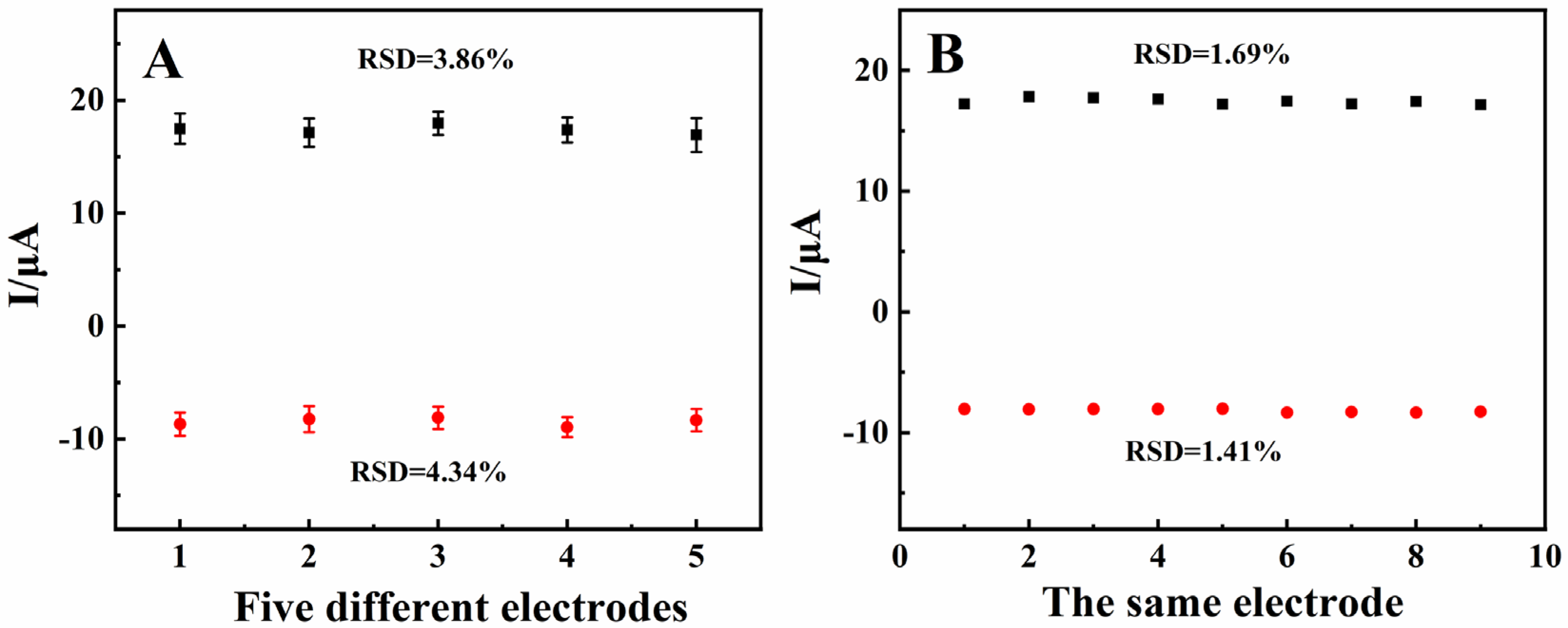
3.6. Stability, Repeatability, and Reproducibility
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madureira, J.; Botelho, M.L.; Cooper, W.J.; Leal, J.P.; Melo, R. Aqueous degradation of esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) using gamma radiation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 181, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.; Tomar, B.; Srivastava, A.; Narkhede, Y.B.; Gaikwad, A.N.; Lahiri, A.; Mulay, S.R. 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin ameliorates crystal-induced necroptosis during crystal nephropathies by inhibiting MLKL phosphorylation. Life Sci. 2021, 271, 119193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhang, F.Y.; Lu, D.B.; Du, Y.L.; Ye, W.C.; Wang, C.M. Fabrication of a CuS/graphene nanocomposite modified electrode and its application for electrochemical determination of esculetin. Anal. Methods. 2013, 5, 3992–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproll, C.; Ruge, W.; Andlauer, C.; Godelmann, R.; Lachenmeier, D.W. HPLC analysis and safety assessment of coumarin in foods. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Song, Y.Y.; Liu, C.H.; Huang, X.T.; Zheng, X.; Li, N.; Xu, M.L.; Mi, S.Q.; Wang, N.S. Simultaneous determination of esculin and its metabolite esculetin in rat plasma by LC–ESI-MS/MS and its application in pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 907, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Wan, C.J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.D. 2D material chemistry: Graphdiyne-based biochemical sensing, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2020, 36, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.L. A highly sensitive sensor based on electropolymerization for electrochemical detection of esculetin. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.C.; Wang, L.; Sheng, K.; Zoua, L.; Yea, B.X. Highly sensitive determination of esculetin on TiO2NPs-coated poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride)-functionalized graphene modified electrode. Talanta 2016, 161, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Yan, L.J.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L.; Shao, B.; Niu, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Yin, P.; Ge, Y.Q.; Sun, W.; et al. Recent applications of black phosphorus and its related composites in electrochemistry and bioelectrochemistry: A mini review. Electrochem. Commun. 2021, 129, 107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaim, W.; Mani, V.; Peramaiya, K.; Huang, K.W.; Salama, K.N. Ruthenium and nickel molybdate-decorated 2D porous graphitic carbon nitrides for highly sensitive cardiac troponin biosensor. Biosensors 2022, 12, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, R.M.; Zhu, Y.F.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Nie, P.C.; Liu, P.; Xu, L.L.; Wen, Y.P. Portable wireless intelligent sensing of ultra-trace phytoregulator α-naphthalene acetic acid using self-assembled phosphorene/Ti3C2-MXene nanohybrid with high ambient stability on laser induced porous graphene as nanozyme flexible electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zhu, X.B.; Yu, X.H.; Zeng, X.W.; Xiao, Q.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Ji, X.Y.; Wang, X.S.; Shi, J.J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Black phosphorus nanosheets as a robust delivery platform for cancer theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.B.; Xie, H.H.; Tang, S.Y.; Yu, X.F.; Guo, Z.N.; Shao, J.D.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.Y.; Chu, P.K. Ultrasmall black phosphorus quantum dots: Synthesis and use as photothermal agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2015, 54, 11526–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.U.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Choi, S.; Seo, S.; Kim, H.; Won, J.; Choi, K.; Kang, K.S.; Park, H.G. Black Phosphorus (BP) nanodots for potential biomedical applications. Small 2016, 12, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Brent, J.R.; Shorie, M.; Kaur, H.; Chadha, G.; Thomas, A.G.; Lewis, E.A.; Rooney, A.P.; Nguyen, L.; Zhong, X.L.; et al. Nanostructured aptamer-functionalized black phosphorus sensing platform for label-free detection of myoglobin, a cardiovascular disease biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 22860–22868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, Y.T.; Sofer, Z.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Pumera, M. Black phosphorus nanoparticles as a novel fluorescent sensing platform for nucleic acid detection. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.; Liu, Z.M.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.Q.; Fei, X.X.; Su, C.K.; Wang, C.M.; Zhuang, Z.F.; Guo, Z.Y. Facile synthesis of black phosphorus–Au nanocomposites for enhanced photothermal cancer therapy and surface-enhanced Raman scattering analysis. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Wang, D.; Liang, W.Y.; Liu, L.P.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Sang, D.K.; Xing, C.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Dong, B.Q.; et al. Novel concept of the smart NIR-light–controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qiao, J.; He, K.; Bliznakov, S.; Sutter, E.; Chen, X.J.; Luo, D.; Meng, F.K.; Su, D.; Decker, J.; et al. Interaction of black phosphorus with oxygen and water. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmao, R.; Sofer, Z.; Pumera, M. Black phosphorus rediscovered: From bulk to monolayer. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 8052–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, C.R.; Wood, J.D.; Wells, S.A.; Yang, Y.; Jariwala, D.; Marks, T.J.; Schatz, G.C.; Hersam, M.C. Covalent functionalization and passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus via aryl diazonium chemistry. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.X.; Qia, X.J.; Zhao, H.Y.; He, Y.P.; Sheng, Q.L.; Yue, T.L. Ultrasensitive and label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on carbon dots-black phosphorus nanohybrid for the detection of ochratoxins A. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Luo, J.J.; Jiang, X.X.; Li, X.Q.; Yang, M.H. Gold nanoparticle–modified black phosphorus nanosheets with improved stability for detection of circulating tumor cells. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Q.; Wang, L.S.; Wang, B.L.; Zhang, S.Y.; Jiang, M.; Fu, W.T.; Sun, W. Preparation and application of electrochemical horseradish peroxidase sensor based on a black phosphorene and single-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite. Molecules 2022, 27, 8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Rhee, K.Y.; Hui, D.; Park, S.J. A critical review of nanodiamond based nanocomposites: Synthesis, properties and applications. Compos. Part B 2018, 143, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanowicz, R.; Dettlaff, A.; Skiba, F.; Trzcinski, K.; Szkoda, M.; Sobaszek, M.; Ficek, M.; Dec, B.; Macewicz, L.; Wyrębski, K.; et al. Enhanced charge storage mechanism and long-term cycling stability in diamondized titania nanocomposite supercapacitors operating in aqueous electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 15698–15712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yence, M.; Cetinkaya, A.; Ozcelikay, G.; Kaya, S.I.; Ozkan, S.A. Boron-doped diamond electrodes: Recent developments and advances in view of electrochemical drug sensors. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 1122–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarakhman, O.; Švorc, L. A review on recent advances in the applications of boron-doped diamond electrochemical sensors in food analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 791–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecmarová, M.; Gulka, M.; Vandenryt, T.; Hrubý, J.; Fekete, L.; Hubík, P.; Taylor, A.; Mortet, V.; Thoelen, R.; Bourgeois, E.; et al. A label-free diamond microfluidic DNA sensor based on active nitrogen-vacancy center charge state control. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18500–18510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Zang, J.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Bian, L.Y. Electrochemical oxidation of nitrite on nanodiamond powder electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3442–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhian, S.; Ghalkhani, M. Glassy carbon electrodes modified with a film of nanodiamond–graphite/chitosan: Application to the highly sensitive electrochemical determination of Azathioprine. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3621–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simioni, N.B.; Oliveira, G.G.; Vicentini, F.C.; Lanza, M.; Janegitz, B.C.; FatibelloFilho, O. Nanodiamonds stabilized in dihexadecyl phosphate film for electrochemical study and quantification of codeine in biological and pharmaceutical samples. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 74, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, X.Y.; Luo, G.L.; Niu, Y.Y.; Zou, R.Y.; Yin, C.X.; Huang, S.M.; Sun, W.; Li, G.J. Nano-diamond modified electrode for the investigation on direct electrochemistry and electrocatalytic behavior of myoglobin. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 97, 107453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamu, V.N.; Poudyal, D.C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor system to detect and distinguish between glyphosate and glufosinate. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 057531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.J.; Hu, T.X.; Li, X.Q.; Ding, F.Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.L.; Zhang, B.X.; Shi, F.; Sun, W. Graphdiyne and ionic liquid composite modified gold electrode for sensitive voltammetric analysis of rutin. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Erdem, O.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. An alternative medical diagnosis method: Biosensors for virus detection. Biosensors 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, M.; Wang, S.F.; Huang, C.H.; Alshgari, R.A.; Ouladsmane, M. Colloidal synthesis of perovskite-type lanthanum aluminate incorporated graphene oxide composites: Electrochemical detection of nitrite in meat extract and drinking water. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Wang, B.L.; Yan, L.J.; Wang, B.; Niu, Y.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Sun, W. In-site growth of nitrogen-doped carbonized polymer dots on black phosphorus for electrochemical DNA biosensor of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 148, 108226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; Henry, C.S. Review-recent advances in sensor arrays for the simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple analytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 057507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Sun, Y.X.; Niu, Y.Y.; Wang, B.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zeng, L.N.; Li, L.; Sun, W. Portable electrochemical sensing of indole-3-acetic acid based on self-assembled Mxene and carbon nanotube composite modified screen-printed electrode. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoilett, O.S.; Walker, J.F.; Balash, B.M.; Jaras, N.J.; Boppana, S.; Linnes, J.C. KickStat: A coin-sized potentiostat for high-resolution electrochemical analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, P.; Xu, L.J.; Qu, M.G.; Hao, W.X.; Liang, H.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Wen, Y.P. A portable wireless intelligent electrochemical sensor based on layer-by-layer sandwiched nanohybrid for terbutaline in meat products. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.F.; Wen, L.K.; Tian, J.; Wu, Y.H.; Liu, F.; Lin, Y.J.; Hua, W.; Wu, G. A portable electrochemical immunosensor for highly sensitive point-of-care testing of genetically modified crops. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnapaiyan, S.; Rajaji, U.; Chen, S.M.; Liu, T.Y.; Filho, J.I.O.; Chang, Y.S. Fabrication of thulium metal-organic frameworks based smartphone sensor towards arsenical feed additive drug detection: Applicable in food safety analysis. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 401, 139487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Bo, X.J. Laser-enabled flexible electrochemical sensor on finger for fast food security detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Ai, Y.J.; Yan, L.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, Y.H.; Zou, Q.W.; Fu, H.Y.; Niu, X.L.; Sun, W. Wireless electrochemical sensor for the detection of phytoregulator indole-3-acetic acid using gold-nanoparticles and three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide modified screen printed carbon electrode. Talanta 2023, 253, 124030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Ai, Y.J.; Wang, B.L.; Yao, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.H.; Sun, W. Portable wireless intelligent electrochemical sensor for the ultrasensitive detection of rutin using functionalized black phosphorene nanocomposite. Molecules 2022, 27, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Liu, S.H.; Yang, Z.B.; Li, Y.Y.; Ng, W.T.; Xu, Z.Q.; Bao, Q.L.; Hao, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Surya, C.; et al. Solution-processable ultrathin black phosphorus as an effective electron transport layer in organic photovoltaics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pan, Z.H.; Zhong, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.Y. Electrostatic self-assembly of heterostructured black phosphorus-Mxene nanocomposites for flexible microsupercapacitors with high rate performance. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 36, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machabaphala, M.K.; Hlekelele, L.; Dlamini, L.N. A heterostructure of black phosphorus and zirconium-based MOF as a photocatalyst for photocatalytic applications. Mater. Lett. 2020, 281, 128660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.C.; Cai, Y.Q.; Ng, R.J.; Huang, L.; Fang, X.W.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.W.; Nijhuia, C.A.; Liu, X.K.; Ang, K.W. Few-layer black phosphorus carbide field-effect transistor via carbon doping. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700503–1700509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.A.; Kim, E.H.; Gopannagari, M.; Kim, Y.; Kumar, D.P.; Kim, T.K. Few layered black phosphorus/MoS2 nanohybrid: A promising co-catalyst for solar driven hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 241, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favron, A.; Gaufrès, E.; Fossard, F.; Phaneuf-L’Heureux, A.L.; Tang, N.Y.W.; Lévesque, P.L.; Loiseau, A.; Leonelli, R.; Francoeur, S.; Martel, R. Photooxidation and quantum confinement effects in exfoliated black phosphorus. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.D.; Lu, Q.J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Mei, Y. Facile synthesis of holey phosphorene via low temperature electrochemical exfoliation for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 5021–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cui, X.M.; Gao, X.; Liu, S.Z.; Sun, Q.; Lian, H.Q.; Zu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.D.; Cui, X.G. Electrochemically prepared black phosphorene micro-powder as flame retardant for epoxy resin. Compos. Interface 2020, 28, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.J.; Fortunato, G.V.; Kronka, M.S.; Vernasqui, L.G.; Ferreira, N.G.; Lanza, M.R.V. Electrochemical oxidation of ciprofloxacin in different aqueous matrices using synthesized boron-doped micro and nano-diamond anodes. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Hu, Y.Y.; Qi, F.; Ding, L.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, Q.W.; Liu, L.Z.; Sun, H.Z.; Qu, P. Anchoring black phosphorus nanoparticles onto ZnS porous nanosheets: Efficient photocatalyst design and charge carrier dynamics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8157–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.C.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Zahed, M.A.; Park, C.; Yoon, S.H.; Zhang, S.P.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.Y. A highly selective and stable cationic polyelectrolyte encapsulated black phosphorene based impedimetric immunosensor for interleukin-6 biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.; Abrantes, J. Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to monitor the corrosion of reinforced concrete: A new approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.L.; Wen, Z.R.; Li, X.B.; Zhao, W.S.; Li, X.Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, Q.T.; Li, G.J.; Sun, W. Fabrication of graphene and gold nanoparticle modified acupuncture needle electrode and its application in rutin analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviron, E. General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1979, 101, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviron, E. Adsorption, autoinhibition and autocatalysis in polarography in linear potential sweep voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1974, 52, 355–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.S.; Shain, I. Theory of stationary electrode polarography for a chemical reaction coupled between two charge transfers. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Detected (μmol/L) | Added (μmol/L) | Total (μmol/L) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (Z20026310) | 1.96 | 5.00 | 6.71 | 3.28 | 95.0 |
| 10.00 | 12.11 | 3.11 | 101.5 | ||
| 15.00 | 16.24 | 2.07 | 95.2 | ||
| Sample 2 (Z54020022) | 2.60 | 5.00 | 7.82 | 3.10 | 104.4 |
| 10.00 | 12.58 | 1.41 | 99.8 | ||
| 15.00 | 16.81 | 2.55 | 94.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, L.; Yan, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W. A Portable Wireless Intelligent Nanosensor for 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin Analysis with A Black Phosphorene and Nano-Diamond Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode. Biosensors 2023, 13, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020153
Li X, Wang L, Yan L, Han X, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Sun W. A Portable Wireless Intelligent Nanosensor for 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin Analysis with A Black Phosphorene and Nano-Diamond Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020153
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoqing, Lisi Wang, Lijun Yan, Xiao Han, Zejun Zhang, Xiaoping Zhang, and Wei Sun. 2023. "A Portable Wireless Intelligent Nanosensor for 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin Analysis with A Black Phosphorene and Nano-Diamond Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020153
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, L., Yan, L., Han, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., & Sun, W. (2023). A Portable Wireless Intelligent Nanosensor for 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin Analysis with A Black Phosphorene and Nano-Diamond Nanocomposite-Modified Electrode. Biosensors, 13(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020153





